- Skip to navigation
- Skip to main content

- ImmiAccount
- Visa Entitlement Verification Online (VEVO)
- Select language Language Unavailable English

COVID-19 and the border
Updates to Australia's immigration and border arrangements during the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) pandemic.
Latest updates
From 12:01am on Saturday 11 March 2023, people travelling to Australia from China, including Hong Kong and Macau, will not be required to show evidence of a negative pre-departure test for COVID-19. For more information see Entering and leaving Australia .
Need a hand?
Popular searches, your previous searches.
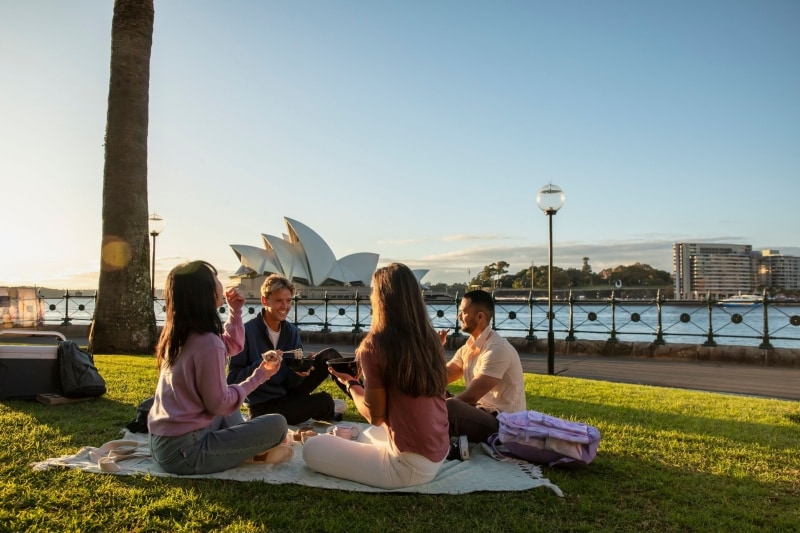
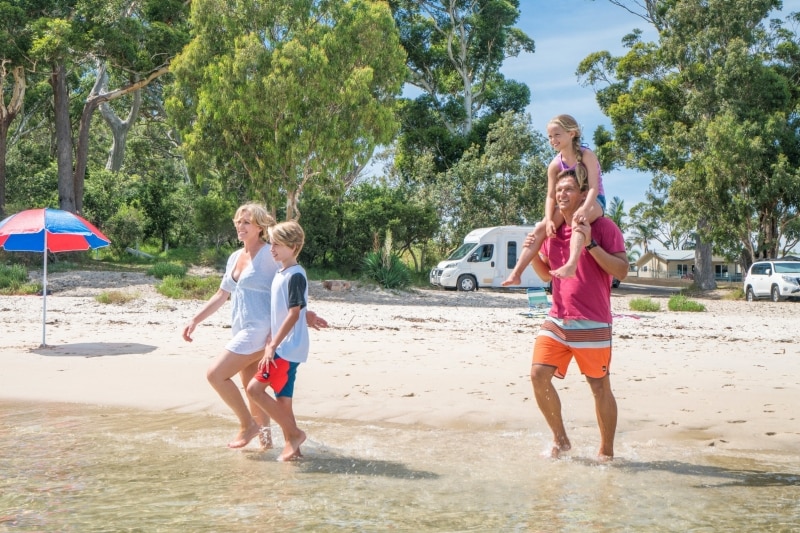
Australia's borders are open for tourism. Here's who can travel, and when
Australia's tourism industry is rejoicing at the news that tourists will soon be allowed into the country after almost two years of border restrictions.
The changes will also allow people to reunite with loved ones who were unable to get a visa under previous entry requirements.
However, strict COVID-19 rules will still apply.
Click on a link below to jump to the question:
When can tourists come to Australia?
- Is Western Australia open to tourists?
Do tourists need a COVID-19 vaccine to travel to Australia?
Can unvaccinated people travel to australia.
- What COVID-19 vaccines do Australia recognise?
Can unvaccinated children enter Australia?
Do tourists need to prove a negative covid test, are cruise ships allowed.
All fully vaccinated visa holders, including tourists, will be allowed to travel to Australia without an exemption from February 21 .
International arrivals will be subject to arrival caps and the quarantine requirements of each state or territory.
Australian citizens, permanent residents, their family members and some vaccinated visa holders are already allowed to travel to Australia.
Is Western Australia open to tourists?
WA is open to travellers who arrive from overseas, however, from February 9, the state's limit on international arrivals will be capped at 530 people per week.
International arrivals to WA must complete a G2G Pass declaration, undergo quarantine and COVID testing.
All international arrivals to Australia — including tourists — are required to be fully vaccinated unless they have proof of medical exemption.
The federal government defines fully vaccinated as two doses, for most vaccine brands , and does not require international arrivals to have a booster shot.
However, the Victorian government has flagged it may require international arrivals to have had two doses and a booster.
Other states and territories may follow suit if the government's vaccine advisory body ATAGI changes the definition of "fully vaccinated" to mean three doses.
In announcing the border reopening, Prime Minister Scott Morrison said people would not need three doses of a COVID vaccine to be considered fully vaccinated.
"It will be two [doses]. There are various arguments around the world for three doses. Two doses is what the Chief Medical Officer says is sufficient," Mr Morrison said on February 7.
Unvaccinated travellers will need to provide proof that there is a medical reason that they cannot be vaccinated in order to travel to Australia.
They must also apply for a travel exemption to come to Australia.
If they are granted permission to travel, they must undergo mandatory hotel quarantine upon arrival.
What COVID-19 vaccines does Australia recognise?
International travellers to Australia are considered fully vaccinated if they have received COVID-19 vaccines recognised by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
That includes receiving two doses ( mixed doses are accepted ) of:
- AstraZeneca Vaxzevria
- AstraZeneca Covishield
- Pfizer/Biontech Comirnaty
- Moderna Spikevax or Takeda
- Sinovac Coronavac
- Bharat Biotech Covaxin
- Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV (for people under 60 years of age on arrival in Australia)
- Gamaleya Research Institute Sputnik V
- Novavax/Biocelect Nuvaxovid
Or one dose of:
- Johnson & Johnson/Janssen-Cilag
The final dose required to be fully vaccinated must have been received at least seven days before travelling to Australia.
Travellers must show airline staff their International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate (ICVC) or a foreign vaccination certificate.
Children under 12 do not need to be vaccinated to travel to Australia.
However, if the child is travelling with an unvaccinated adult family member, the entire family group will be subject to arrival caps and have to undergo mandatory hotel quarantine.
Some state and territories allow for unvaccinated or partially vaccinated children aged 12 to 17 to travel with a fully vaccinated adult.
When checking in for their flight to Australia, international travellers must present either:
- A negative PCR test taken within three days of departure
- A negative Nucleic Acid Amplification Test taken within three days of departure
- A medical certificate as evidence of a negative RAT taken under medical supervision within 24 hours of departure
There is currently a ban on international cruise ships in Australia.
The ban came into effect in March 2020 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It has been extended until mid-February 2022 due to the fast-spreading Omicron variant.
The cruise industry says ships may not return to Australian waters until April or May this year.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Vaccinated tourists welcomed back as international border to reopen in two weeks.
International tourists will soon be touching down in Australia. Here's where they'll come from
Sunshine at last for tourism industry with international border set to reopen
- Epidemics and Pandemics
- Travel Health and Safety
Entering or leaving Australia
Australia welcomes millions of overseas visitors each year. Anyone who is not an Australian citizen needs a valid visa to enter the country.
International passenger caps have been removed for all international passenger arrivals into Australia.
All travellers should be aware that: People entering Australia do not need to provide evidence of vaccination status People entering Australia do not need to complete the Digital Passenger Declaration or Maritime Travel Declaration People leaving Australia will not be asked to provide evidence of their vaccination status Unvaccinated visa holders do not need a travel exemption to travel to Australia Mask wearing on international flights to Australia is no longer mandatory . It is important to remember that airlines, vessel operators and other countries may have specific requirements that travellers need to comply with.
Australian Citizens
All Australian citizens must enter and exit Australia on an Australian passport. Your Australian passport must be valid (not expired) on the day of your arrival in Australia. It does not need to have six months remaining validity to enter Australia unless you are passing through a third country that requires it. Citizens are not entitled to a visa, even if you are also a citizen of another country. Please see the Department of Home Affairs website for more information.
Immigration and Visas
All foreign travellers, except New Zealand citizens, must obtain a visa or travel authority before travelling to Australia.
» Immigration and visas
If you have a specific question, please contact the Department of Home Affairs .
You will also need to know what you can and cannot bring into Australia, knowing the duty-free concession limits and what to experience when travelling through Australian airports and seaports.
Please visit the Department of Home Affairs website for more information.
Plan your trip with australia.com , the official Tourism Australia website, offering a wide range of travel information and planning tools including over 2000 images, a currency converter, daily weather updates, interactive maps, suggested holiday itineraries, holiday deals, specialist travel agents and more. Available in nine languages.
Tourist Refund Scheme
The Tourist Refund Scheme enables you to claim a refund, subject to certain conditions, of the goods and services tax (GST) and wine equalisation tax (WET) that you pay on goods you buy in Australia.
Healthdirect Free Australian health advice you can count on.
Medical problem? Call 1800 022 222. If you need urgent medical help, call triple zero immediately
healthdirect Australia is a free service where you can talk to a nurse or doctor who can help you know what to do.
Travel and COVID-19
3-minute read
Share via email
There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
- Please enter your name
- Please enter your email
- Your email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Please enter recipient's email
- Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Agree to Terms required
Error: This is required
Error: Not a valid value
If you develop symptoms such as severe shortness of breath or chest pain, call triple zero (000) immediately. Tell the phone operator and the paramedics on arrival if you have COVID-19.
How to avoid catching COVID-19 including getting vaccinated, wearing masks and physical distancing.
Does Australia have COVID-19 travel restrictions?
Travelling to australia.
People travelling to Australia no longer need to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination or a negative COVID-19 test result.
Some countries, airlines and ships may have their own testing, vaccination and face-mask rules. You should check with them before travelling.
During your travel to Australia, you’re encouraged to wear a face mask to reduce your risk of getting and spreading COVID-19.
For more information, visit the Department of Home Affairs website.
Travelling interstate
You can freely travel within and between Australia’s states and territories. However, some remote communities may restrict who can enter and leave them.
Learn more about travelling in Australia:
- Australian Capital Territory
- New South Wales
- Northern Territory
- South Australia
- Western Australia
Do other countries have COVID-19 travel restrictions?
Some countries may have COVID-19 entry and exit rules. You may need to:
- show proof of COVID-19 vaccination
- show proof of a negative COVID-19 test result
- show proof of COVID-19 travel insurance
- quarantine for a certain time on arrival
Related topics

COVID-19 testing
Learn about COVID-19 testing, including when to get tested, what test you should use and what to do if you test positive to COVID-19.

- COVID-19 vaccination
Find out who can get the COVID-19 vaccine, including whether it's safe during pregnancy or for older people, and when and where you can get vaccinated.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content .
Last reviewed: December 2023
Search our site for
Coronavirus (covid-19), need more information.
These trusted information partners have more on this topic.
Top results
COVID-19 information for travellers - Better Health Channel
Find out about travelling to and from Victoria, including both interstate and international advice.
Read more on Better Health Channel website

COVID-19: health department information | Raising Children Network
Australian health department websites have the latest and most reliable health advice about coronavirus (COVID-19). This page lists these websites for you.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website

Immunisation for travel | Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
It’s important to protect your health when travelling overseas. You can avoid diseases and other health conditions by planning ahead for any vaccinations you may need.
Read more on Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care website

How to cope when things outside of your control happen overseas | Cultural Identity | ReachOut Australia
It can be hard being away when something bad happens back home, especially when there is an overseas travel ban. Here are our top tips for coping when you don’t know what to do.
Read more on ReachOut.com website

COVID-19 vaccination program | SA Health
About COVID-19 vaccines and vaccination programs to protect yourself and others and help stop the spread of coronavirus in South Australia.
Read more on SA Health website

COVID-19 - Coronavirus in-language resources — MHCS
Feeling unwell? If you develop a fever, a cough, sore throat or shortness of breath within 14 days of overseas travel, seek medical attention
Read more on Multicultural Health Communication Service website

COVID-19 | SA Health
Health information about coronavirus disease (COVID-19) for South Australians. Find COVID-19 testing clinics and read the latest health updates and advice on COVID-19.
Cancer and COVID-19 | Cancer Council
We understand that those affected by cancer may be feeling heightened concern about COVID-19. Find out answers to your COVID-19 questions here
Read more on Cancer Council Australia website

COVID-19 is a new coronavirus that was first identified in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China in December 2019. It is a new strain of coronaviruses that hasn’t previously been identified in humans.
Read more on WA Health website

COVID-19 - Resources
COVID 19 has been identified as a key issue for health and aged care. Information for being prepared in aged care, services and organisations, workforces, older people and their families on ELDAC website.
Read more on End of Life Directions for Aged Care ELDAC website

COVID-19 vaccines in 2023 - Australian Prescriber
As SARS‑CoV‑2 continues to evolve, vaccines are being updated, and policymakers are reviewing the optimal timing of future booster doses to maintain adequate protection against severe illness, particularly for older adults.
Read more on Australian Prescriber website

Resource library | Lifeblood
Our resources can be freely downloaded, and printed copies of selected resources can also be ordered at no cost.
Read more on Australian Red Cross Lifeblood website

Clinical indications | Lifeblood
Some types of anaemia, thrombocytopenia and platelet function disorders, bleeding disorders and massive transfusion are common clinical indications for blood components.
Emergency provision of red cells | Lifeblood
In emergency situations, it’s important for individuals requesting a transfusion to clearly inform the laboratory staff of the urgency of transfusion.
Adverse events | Lifeblood
Adverse transfusion reactions are when patients experience an undesirable response associated with transfusion of blood or blood products.
Red cell reference | Lifeblood
Our Red Cell Reference Service provides an internationally recognised scientific and diagnostic service to support transfusion practice and clinical need. Their primary role is to determine red cell phenotypes and antibodies to help find the most suitable specialised blood component for each patient.
Transplantation and immunogenetics services | Lifeblood
This expert team delivers agile and efficient transplantation and immunogenetics diagnostic testing services and scientific expertise for solid organ and stem cell transplants and platelet and neutrophil immunobiology diagnostics across the country.
Learn | Lifeblood
We provide an innovative range of education events and resources for health professionals to support safe transfusion practice at any stage of their career.
Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) | NCIRS
Mpox vaccines: Frequently asked questions NCIRS fact sheets.
Read more on National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance (NCIRS) website

Management of mammalian bites
Reproduced with permission from The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners
Read more on RACGP - The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners website

Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Healthdirect 24hr 7 days a week hotline
24 hour health advice you can count on
1800 022 222
Government Accredited with over 140 information partners
We are a government-funded service, providing quality, approved health information and advice

Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
© 2024 Healthdirect Australia Limited
Support for this browser is being discontinued
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
- Skip to navigation
- Skip to main content

Popular searches
Your previous searches.
All COVID-19 border restrictions to be lifted
People travelling to Australia will no longer have to complete a Digital Passenger Declaration (DPD) to declare their COVID-19 vaccination status, following changes to the Biosecurity Act, which come into effect from midnight AEST on Wednesday 6 July 2022.
“This is great news for families coming home from school holidays who now don’t need to use the DPD,” Minister for Home Affairs, Clare O’Neil, said.
The Biosecurity Act changes, which were made following health advice from the Chief Medical Officer, also mean that all visa holders can travel to Australia without needing a travel exemption.
“As more and more of us travel internationally and we get more confident in managing our risk of COVID, our airports are getting busier,” Minister O’Neil said.
“Removing these requirements will not only reduce delays in our airports but will encourage more visitors and skilled workers to choose Australia as a destination.
“And for Australian citizens, with the removal of these requirements, returning home will be much easier.
“I know anyone who has travelled internationally since the borders have opened will find this as one less thing to worry about – especially as more Australians get back to travelling overseas.
“We’ve also listened to feedback about the DPD. While in time it will replace the paper based incoming passenger card, it needs a lot more work to make it user friendly”
Those arriving by sea will also benefit, and no longer need to complete a Maritime Travel Declaration. Airlines, cruise ship operators and other countries may still have specific requirements that travellers need to comply with.
Australians planning to travel overseas are encouraged to check current travel advice by visiting Smartraveller .
For more information on the changes to international travel requirements visit: www.homeaffairs.gov.au/covid19 .
Need a hand?
Australia is ready to be explored as the last state reopens its border

Mar 3, 2022 • 3 min read

Western Australia reopened its borders today © Shutterstock
After nearly 700 days, Western Australia has lifted its hard border and is now permitting travelers to visit.
While Australia reopened its borders to international tourists last week, Western Australia lagged behind. Labeled the "hermit kingdom" due to its hard border rules, Australia's most remote state largely disconnected from the outside world and kept both domestic and international travelers out in order to keep the virus at bay.
That situation has changed today (March 3) as Western Australia emerges from isolation, becoming the last state to drop its travel entry ban.
“Australia is now finally back together,” Qantas Airways chief executive Alan Joyce said. “This day has been a long time coming.”
Travelers are free to visit without quarantine, but they'll need to abide by slightly different entry rules. While Australia generally requires travelers to be at least double vaccinated to visit, Western Australia wants proof of three doses.
If you're planning a visit to Australia, here's what you need to know about its entry rules.
When can I travel to New Zealand? Opening dates announced for 2022

What vaccines are accepted for travel to Australia?
To be considered fully vaccinated, arrivals must have received at least two doses (including mixed doses) of an approved vaccine which includes AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Moderna, Covax, Coronavac, Sputnik, Sinopharm, or Novavax, or one dose of a Johnson & Johnson vaccine. At least seven days must have passed since the final dose.
The rules are stricter for travel to Western Australia. The state requires that travelers are triple-vaccinated, complete a G2G pass before travel and take a COVID-19 test within 12 hours of arrival.
The latest Australia health and safety information
Do children have to be vaccinated to travel to Australia?
Children over the age of 12 are expected to show proof of full vaccination to travel to Australia. Though arrangements are in place in some states and territories to allow unvaccinated or partially vaccinated children aged 12-17 years to travel with a fully vaccinated adult. Children aged under 12 years are exempt.

How to present proof of vaccination to travel to Australia
People who were vaccinated in Australia can present their International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate (ICVC) to airline staff before boarding their flight. Overseas travelers can present their own official vaccination certificates.
Are COVID-19 tests required?
Yes, everyone over the age of five must present a negative PCR test result before flying to Australia. The results can be uploaded online, or presented to airline staff, during the check-in process. The test must be taken no later than 72 hours "before the scheduled departure of your first international flight", according to the Australian Embassy .
Travelers visiting Western Australia must take a test within 12 hours of arrival if entering by air (or 24 hours if not entering by air).
Do arrivals need to quarantine?
Quarantine has been scrapped for fully vaccinated arrivals, though unvaccinated arrivals have to quarantine (except in Western Australia where unvaccinated travelers are banned). Some states and territories have at-home quarantine measures in place for children aged between 12 and 17 who are not fully vaccinated.
To check requirements, see State and Territory Information for travelers .

What airlines are flying to Australia?
Major airlines such as Hawaiian Airlines, Etihad, Emirates and Air New Zealand have been ramping up operations since Australia started to reopen in November. Qantas Airways, Australia's national carrier, is operating three weekly return flights between Sydney and London and three weekly return flights between Sydney and Los Angeles to meet "pent up demand". Expect more to announce new schedules .
You might also like: Thailand changes its entry rules again - allowing more tourists to visit without quarantine These Southeast Asian tourist spots are open - here's how to get there Australia's newest national park will protect endangered species
This article was first published Oct 25, 2021 and updated Mar 3, 2022.
Explore related stories

Nov 30, 2021 • 6 min read
Countries around the world are imposing travel restrictions following the detection of a new fast-spreading COVID-19 variant.

Apr 4, 2024 • 5 min read

Mar 30, 2024 • 4 min read

Mar 22, 2024 • 9 min read

Mar 21, 2024 • 10 min read

Mar 17, 2024 • 10 min read

Mar 12, 2024 • 11 min read

Mar 11, 2024 • 5 min read

Mar 10, 2024 • 7 min read

Mar 2, 2024 • 7 min read
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

How have Australia’s international travel rules changed in response to Omicron?
We explain what border restrictions have changed and what the new Covid variant means for visa holders planning to travel to Australia
- Follow our live blog for the latest Covid developments
- Where has Omicron spread, and why are scientists so concerned?
- Download the free Guardian app ; get our morning email briefing
The Omicron variant of Covid-19 has prompted governments around the globe to take rapid action and reintroduce border restrictions in an attempt to stop it spreading from southern Africa.
But the evidence from the two years since the coronavirus emerged suggest those efforts may not be entirely effective. Already, cases of the new variant have been found in the UK, Europe, Hong Kong and Australia .
All of the cases were in people who had recently travelled from countries in southern Africa where the Omicron variant was reported last week.
So how has Australia responded so far and what does it mean for international students and other visa holders planning to return from December?
What has changed?
On Saturday, the federal government reintroduced border restrictions on some countries in southern Africa where the Omicron variant has been detected.
The countries are: South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, Malawi and Mozambique.
Anyone who has been in these countries and is not an Australian citizen, permanent resident, or their immediate family will not be able to enter Australia.
Australian citizens, permanent residents and their immediate family members arriving from these countries would need to go into “immediate supervised quarantine for 14 days subject to jurisdictional arrangements”.
That also applies to anyone who had already arrived in Australia and has been in any of the nine African countries within the previous 14 days.
The federal government announced on Monday night “these measures will be continued until 15 December” at least.
In New South Wales, the government said returnees from those nine countries “must enter hotel quarantine for 14 days” whether they are vaccinated or not.
What about arrivals from other countries?
All other international arrivals to Victoria, NSW and the ACT must isolate for 72 hours and get tested as a precaution. This can be done at their place of residence or accommodation, rather than hotel quarantine.
Victoria is also reportedly considering reintroducing 14-day quarantine for all international arrivals, although no announcements have been made.
South Australia has reimposed some border restrictions. All international travellers and people arriving in SA from high-risk Australian locations will again be required to quarantine for 14 days. People arriving from lower-risk locations interstate must also have a coronavirus test within the 72 hours prior to arrival and must show proof of a negative result.
Queensland, which still requires international arrivals to complete 14 days in hotel quarantine, said they will monitor news about the new variant, but have no plans to change reopening dates at this stage.
Are further border restrictions being considered?
The prime minister, Scott Morrison, has ruled out closing the international borders to citizens and has called for calm.
Any further action taken is set to be discussed at a national cabinet in the next 48 hours.
Health experts have also suggested that border closures would be unnecessary, while the NSW premier, Dominic Perrottet, warned against any “kneejerk” reactions.
“Ultimately we need to open up to the world (and) we need to do so safely,” he told reporters on Monday.
“We don’t need to have a kneejerk reaction, we need to have a proportionate and balanced response to the situation that’s in front of us. The responses should not be ‘let’s shut down’.”
What does it means for international students and skilled migrants?
From 1 December, fully vaccinated eligible visa holders were due to be able to enter Australia without needing to apply for a travel exemption. But that’s now been delayed until at least 15 December.
The eligible visa holders included skilled migrants and international students. Fully vaccinated international visitors from Japan and the South Korea were also set to return at the start of December.
But on Monday, Morrison announced the national security committee would meet to discuss whether those changes would be delayed after the discovery of the Omicron variant.
“On the basis of medical advice provided by the chief medical officer, Prof Paul Kelly, the national security committee has taken the necessary and temporary decision to pause the next step to safely reopen Australia to international skilled and student cohorts, as well as humanitarian, working holidaymaker and provisional family visa holders from 1 December until 15 December,” the prime minister said in a statement on Monday night.
“The reopening to travellers from Japan and the Republic of Korea will also be paused until 15 December.
“The temporary pause will ensure Australia can gather the information we need to better understand the Omicron variant, including the efficacy of the vaccine, the range of illness, including if it may generate more mild symptoms and the level of transmission.”
- Australia news
- Australian immigration and asylum
- Coronavirus
- Omicron variant
Most viewed

Search Smartraveller
What to do if you test positive to covid-19 when travelling overseas.
Last updated: 11 January 2022
Falling sick while travelling is never ideal but when it’s COVID-19 it can seriously disrupt travel plans.
If you’re thinking of travelling overseas, it’s important you understand the risks of contracting COVID-19 in your destination and what to do if you test positive while travelling. You’ll also need to understand the requirements for returning to Australia.
Arming yourself with the latest travel advice and information is essential. Read our travel advice for your destination so you’re aware of the risk of COVID-19 in that location and standards of medical care, in case you get sick. And subscribe for updates so you’re informed if anything changes.
Before you travel, arrange suitable travel insurance and check what the policy covers for COVID-19. And make sure you have sufficient funds to cover an extended stay if you need to quarantine or isolate.
What happens if I test positive to COVID-19 while I’m travelling
If you or someone in your immediate travelling party tests positive for COVID-19, you should isolate immediately and contact the local health authority for advice on what to do. You should also contact your airline or travel provider to reschedule your travel plans and seek advice from your travel insurer.
For information on managing COVID-19, including what to do in isolation and when to seek medical advice, see Health Direct.
If you need medical care, there’s a list of ‘local emergency contacts’ in our travel advice for your location . There’s also information on seeking medical assistance overseas as well as mental health and wellbeing resources on our website.
Will I have to quarantine?
If you test positive to COVID-19, you may be required to quarantine or self-isolate depending on what country or city you’re in. Many countries have penalties for breaking isolation rules, so it’s important you check with local authorities what the requirements are.
Some countries have government managed quarantine facilities or you’ll need to find suitable accommodation. You’re responsible for covering any costs involved with quarantine, which can be significant.
Be prepared for the possibility you may be in your destination longer than planned.
What can the Australian Government do for me?
If you have serious concerns about your welfare or that of another Australian overseas, the Australian Government can provide assistance in accordance with the Consular Services Charter .
Will I be able to return to Australia?
If you or a primary close contact of your travelling group tests positive, you won't be allowed to travel to Australia until you have recovered.
If you have isolated and recovered but your test results continue to be positive, you may be eligible for an exemption if you have a certificate from a medical practitioner. It’s important to note, the certificate must meet certain requirements outlined on the Department of Health website.
Local authorities, airlines and transit locations may have more rules in place for departures. We recommend you check these before arriving at the airport. If you're transiting during your trip, check the local requirements at each transit destination. Confirm any specific rules for onward travel with your airline.
See our re-entry and quarantine measures for more detail on returning to Australia.
Will I be able to travel to another country?
If you’re planning to travel to another overseas destination you will need to check the entry requirements for that country. Read our travel advice for your destination. If you have any queries about entry or exit requirements, check with the relevant embassy or consulate of the destinations you’re transiting and travelling to. You should also confirm rules for departure with your airline, noting these rules may vary between airlines.
I’m a close contact of someone who has tested positive what can I do?
If you’ve been exposed to someone in your travel group who has tested positive to COVID-19, you’ll need to follow the requirements for isolation and testing in the city you are located.
Where can I get a COVID-19 test?
For information on where to get tested, contact the local health authority in your location. Always use an accredited testing facility. Scammers are taking advantage of travellers by charging for fake tests.
If you’re in a country where COVID-19 testing is not reasonably available, you may be eligible for an extension or exemption when returning to Australia. For the list of countries see the Department of Health website.
Will I be covered by travel insurance?
Some travel insurers now offer limited cover for COVID-19. It will likely only cover medical, quarantine and cancellation costs if you test positive to COVID-19.
See our CHOICE travel insurance buying guide: COVID-19 edition for more information and carefully check the details of your travel insurance policy before you leave.
Want to know more?
See our Global COVID-19 health advisory and step-by-step guide to travel during COVID-19 .
- Azerbaijani
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Haitian Creole
- Kinyarwanda
- Kurdish (Kurmanji)
- Kurdish (Soranî)
- Odia (Oriya)
- Scots Gaelic
COVID-19 coronavirus: Information for travellers
International travellers, interstate travellers, cruise ship passengers, visiting remote aboriginal communities.
Frequently asked questions about travel to WA
Travellers are no longer required to provide a G2G Pass or proof of COVID-19 vaccination to enter WA.
People travelling to Australia no longer need to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination or a negative COVID-19 test result.
The Australian Government controls Australia’s international border. Visit the Department of Home Affairs for the latest advice on entering and leaving Australia.
You can enter WA from interstate without any requirements.
Interstate travellers and returning WA residents:
- do not need to show proof of COVID-19 vaccinations to enter WA
- do not need to undertake any pre-departure or arrival COVID-19 testing
If you are entering WA via cruise ship, guidelines are in place to keep you and our community safe from COVID-19.
WA has adopted the Eastern Seaboard and Western Australia protocols, which provide cruise ships with policy guidelines about how to manage COVID-19 restrictions and outbreaks on board.
Please follow all guidelines put in place by your cruise ship and continue to engage in COVID-19 safe behaviour, both onboard and during shore excursions.
WA encourages all visitors on cruise ships to take a RAT prior to shore excursions and follow recommendations on mask wearing in WA to help protect local communities.
There are more than 200 remote Aboriginal communities in Western Australia across the Midwest, Gascoyne, Pilbara, Goldfields and Kimberley regions. Restrictions on entering remote Aboriginal communities have now lifted, however, communities may continue to enforce their own restrictions for entry.
If you plan on visiting a remote Aboriginal community, you need to check with the community before leaving, to learn if there’s any restrictions on entry and make sure you have necessary approval before travelling. This is important if you are wanting to use amenities or to access food or fuel.
Contact the visitor centre for the region for the latest travel information.
Check ahead for any restrictions at your destination location before you leave WA. Visit the Smartraveller website for the latest travel advice.
Do I need a G2G Pass to enter WA?
No, a G2G Pass is no longer a requirement to enter WA.
Can I travel to WA unvaccinated?
Yes, proof of COVID-19 vaccination is no longer required to enter WA.
Do I need to take a RAT before travelling to or on arrival to WA?
No, you do not need to undertake any pre-departure or arrival COVID-19 testing to enter WA. However, it is recommended that you take a test to help protect others around you.
What travel restrictions are in place for WA?
There are no travel restrictions in place to enter WA. If you intend to travel to a remote Aboriginal community, some communities may have restrictions in place. Check before you travel.
Can I travel to WA from overseas?
Yes, eligible international travellers and visa holders may enter WA.
Visit the Department of Home Affairs for the latest information on entering and leaving Australia.
Can I travel to WA from another Australian state or territory?
Yes, interstate travellers can enter WA.
Are WA border restrictions still in place?
No, WA no longer has border restrictions in place.
Can I enter WA by road?
Yes, travellers driving to WA may enter by road.
Visit the WA COVID-19 information home page
Provided by
- Facebook share (Opens in a new tab/window)
- Twitter (Opens in a new tab/window)
- LinkedIn (Opens in a new tab/window)
Acknowledgement of Country
The Government of Western Australia acknowledges the traditional custodians throughout Western Australia and their continuing connection to the land, waters and community. We pay our respects to all members of the Aboriginal communities and their cultures; and to Elders both past and present.
Australia Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Australia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to australia, find stays in australia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Australia from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Australia.
Can I travel to Australia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Australia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Australia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Australia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Australia?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Australia.
Can I travel to Australia without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Australia?
Mask usage in Australia is not required in public spaces.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Australia?
Restaurants in Australia are open. Bars in Australia are .
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Find information on COVID-19, how to protect yourself and those around you, and the current situation in Australia.
Testing positive
Learn what to do if you test positive.
Oral treatments
Find out about the COVID-19 oral antiviral treatments, eligibility, and how to access them.
Find steps you can take to stay safe while travelling.
Protecting yourself and others
Learn how to keep yourself and those around you safe.

COVID-19 vaccines
Find out more about COVID-19 vaccines
Current national COVID-19 spread, vaccination and treatment metrics.
See the latest numbers

ATAGI recommendations on use of the Moderna and Pfizer monovalent Omicron XBB.1.5 COVID-19 vaccines

Update from CMO Professor Paul Kelly


AHPPC statement – End of COVID-19 emergency response

COVID-19 vaccination – COVID-19 booster – Easy Read

COVID-19 vaccination – Local Government Area (LGA) – 12 April 2024

COVID-19 vaccine rollout update – 12 April 2024

Australia Recommends 2024

Come and Say G'day

G'day, the short film

Discover your Australia

Travel videos

Deals and offers

Australian Capital Territory

New South Wales

Northern Territory

South Australia

Western Australia

External Territories

The Whitsundays

Mornington Peninsula

Port Douglas

Ningaloo Reef

Airlie Beach
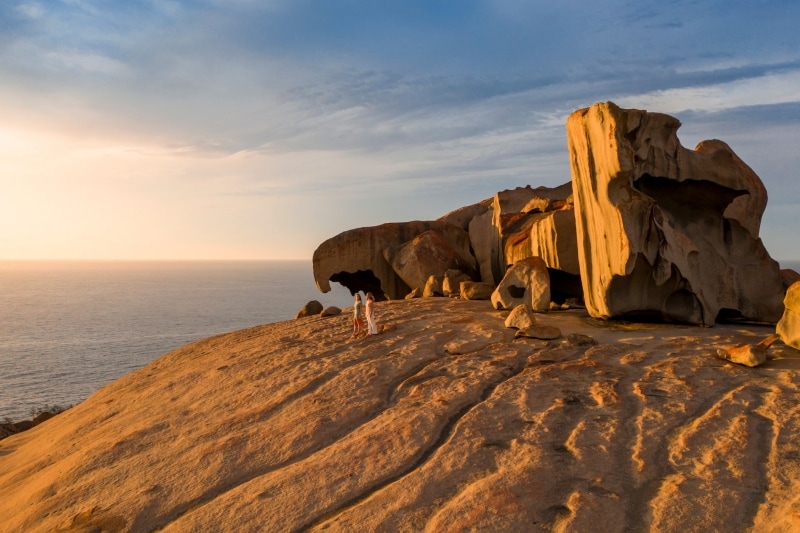

Kangaroo Island
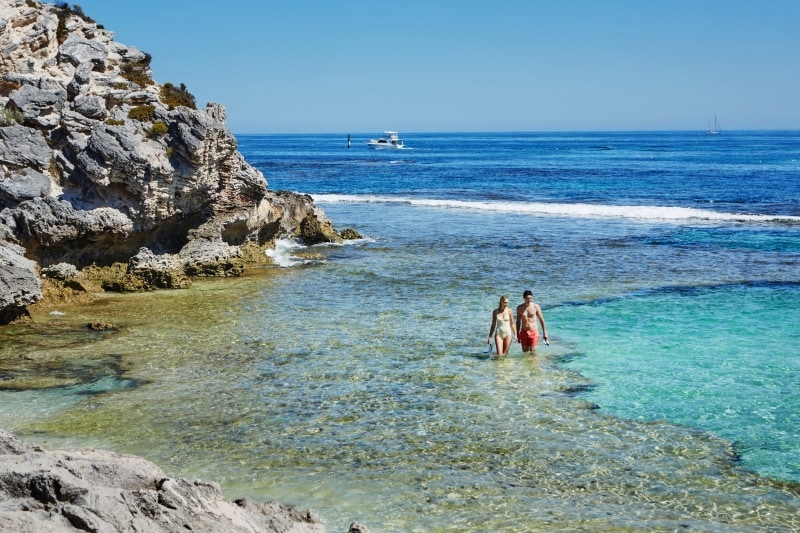

Rottnest Island
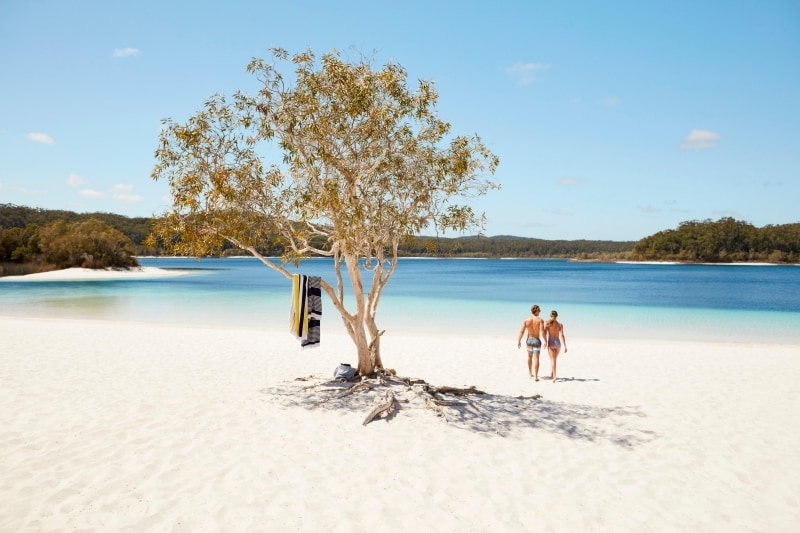

Hamilton Island
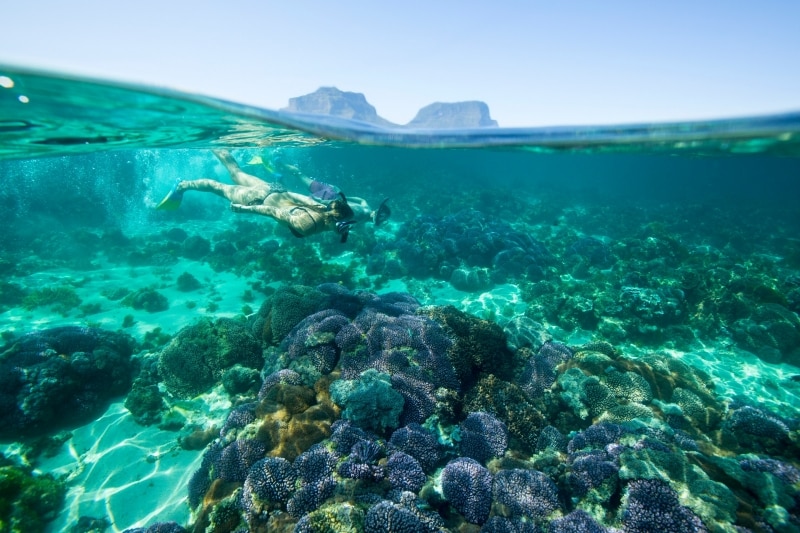

Lord Howe Island
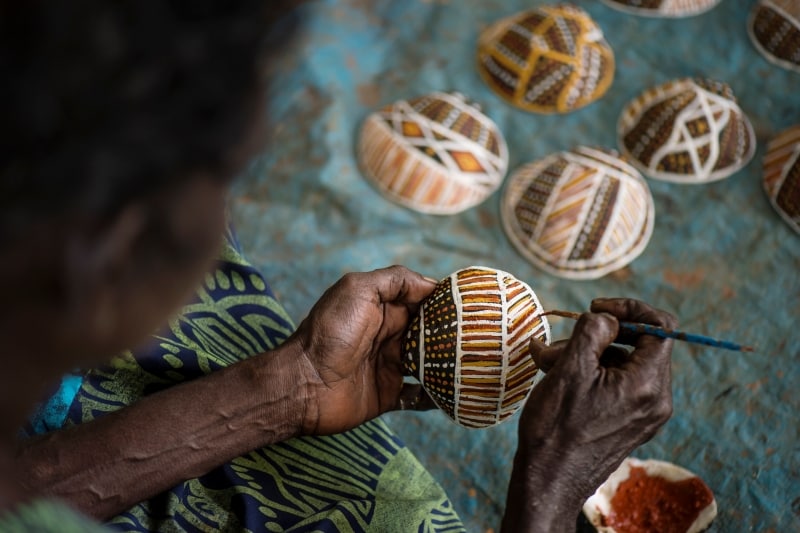

Tiwi Islands
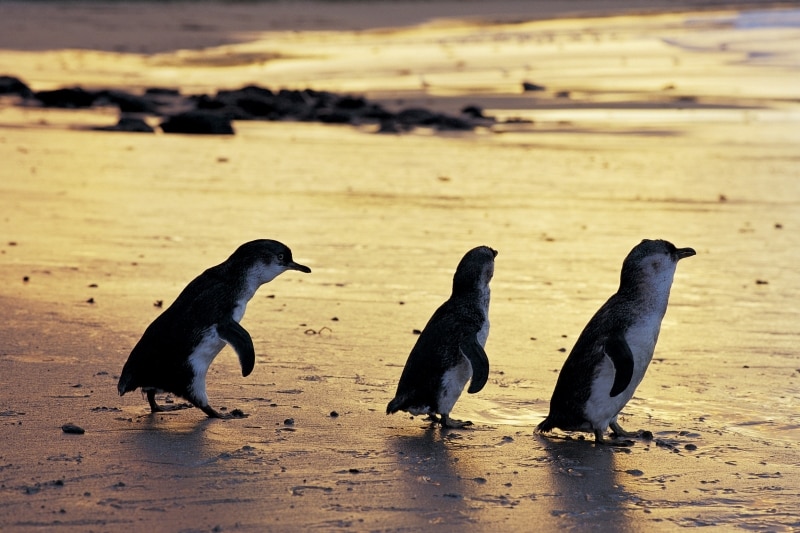

Phillip Island
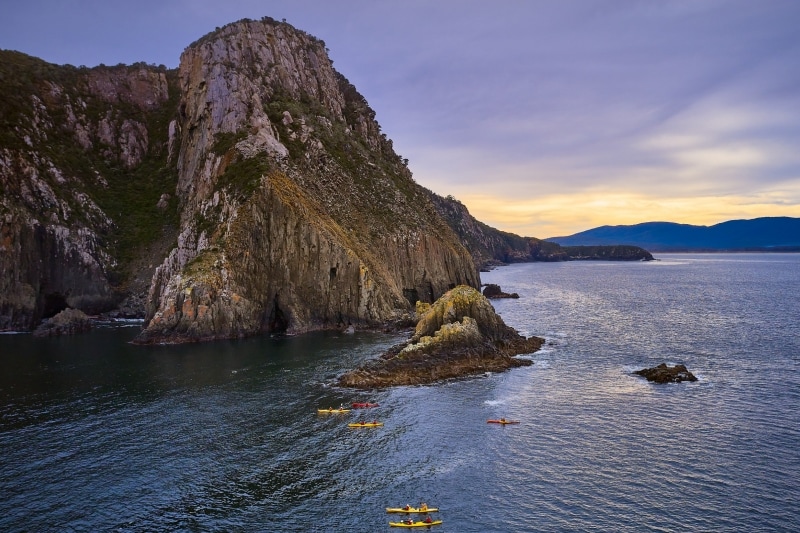

Bruny Island
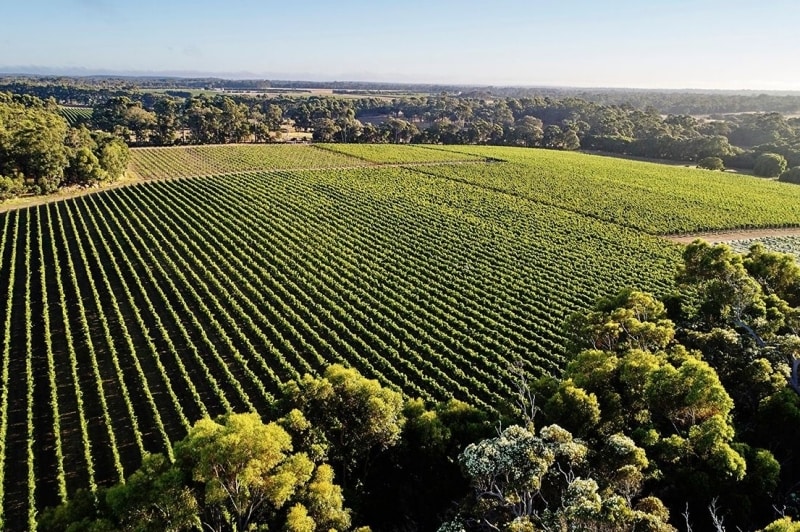

Margaret River

Barossa Valley

The Grampians

Hunter Valley

Yarra Valley

McLaren Vale

Glass House Mountains

Alice Springs

Uluru and Kata Tjuta

The Kimberley

Flinders Ranges

Kakadu National Park

Eyre Peninsula

Karijini National Park

Great Barrier Reef

Blue Mountains

Daintree Rainforest

Great Ocean Road

Purnululu National Park

Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park

Litchfield National Park

Aboriginal experiences

Arts and culture
Festivals and events

Food and drink

Adventure and sports

Walks and hikes

Road trips and drives

Beaches and islands

Nature and national parks

Eco-friendly travel

Health and wellness

Family travel

Family destinations

Family road trips
Backpacking

Work and holiday

Beginner's guide

Accessible travel

Planning tips

Trip planner

Australian budget guide

Itinerary planner

Find a travel agent

Find accommodation

Find transport

Visitor information centres
Deals and travel packages

Visa and entry requirements FAQ

Customs and biosecurity

Working Holiday Maker visas

Facts about Australia

Experiences that will make you feel like an Aussie

People and culture

Health and safety FAQ

Cities, states & territories

Iconic places and attractions

When is the best time to visit Australia?

Seasonal travel

Events and festivals

School holidays

Public holidays
How to get to Australia's most iconic cities

How long do I need for my trip to Australia?

How to travel around Australia

Guide to driving in Australia

How to hire a car or campervan

How to plan a family road trip

How to plan an outback road trip

General safety
Emergencies and natural disasters.
- Nature and wildlife
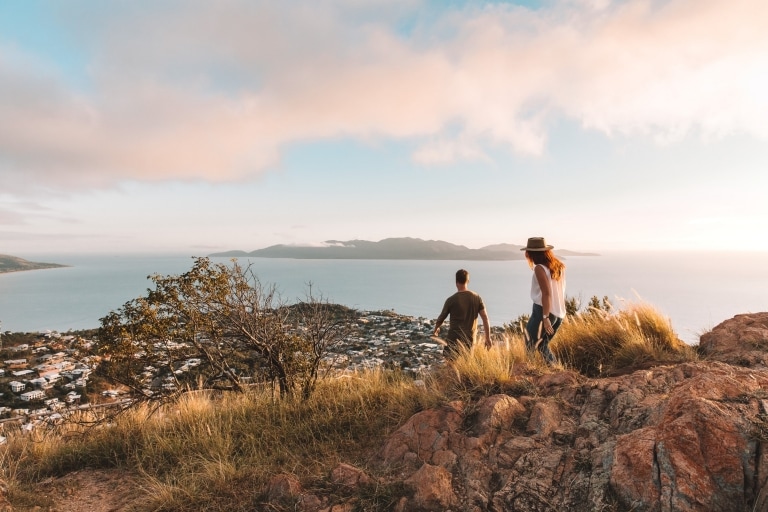

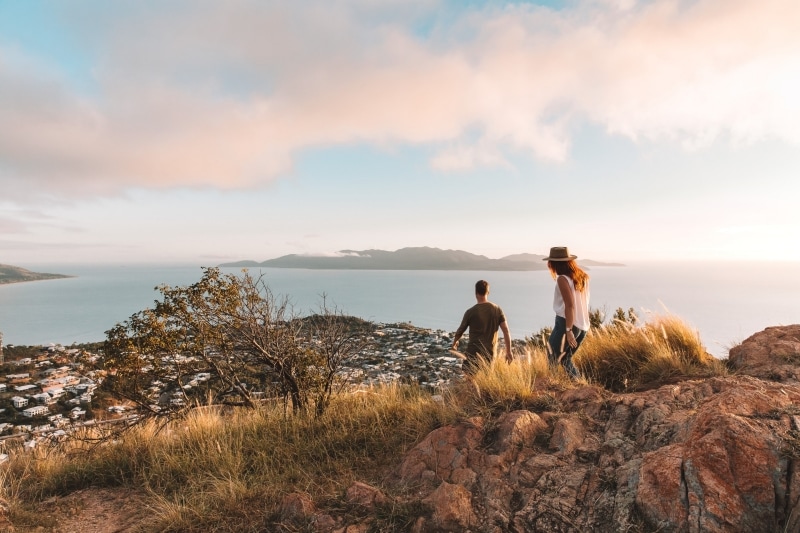
Castle Hill, Townsville, Queensland © Tourism and Events Queensland
Health and safety FAQs
Australia is a safe and welcoming country. Your top health and safety questions have been answered to help you prepare for your trip.
Australia is a very safe country to visit. The country has a stable political system and a low crime rate, and Australians generally experience a safe lifestyle. However, you should observe the same precautions with your personal safety and possessions as you would when travelling anywhere, whether at home or overseas.
Australia is a safe country to travel to alone. In fact, the welcoming locals and relaxed lifestyle make Australia a popular destination for solo travellers. There are also plenty of opportunities to meet new people once you arrive. Remember, it’s still important to use good judgement for your own health and safety, like you would at home.
When travelling to Australia with a disability, pre-planning can ensure you have an enjoyable holiday. If you have a medical condition or require assistance, you will find plenty of services available. Speak to your travel agent about your specific requirements or visit the People With Disability Australia website.
In the event of an emergency, dial Triple Zero (000) to speak with emergency services. Once connected, you can request ambulance, fire or police assistance. From a mobile phone you can also dial 112, the international standard emergency number, to speak to a Triple Zero operator.
If you don’t speak English, you can call Triple Zero (000) and ask for ‘police’, ‘fire’ or ‘ambulance’. Once you are connected to an operator, stay on the line and a translator can be organised for you.
Always be prepared while travelling in a remote location. Pack adequate supplies of water and food and bring provisions for warmth and shelter. Share your schedule with someone you trust and take communication devices such as a mobile phone and a long-range radio.
In the event of an emergency, dial Triple Zero (000) to request assistance. Advanced Mobile Location (AML) is available in Australia for upgraded Android and iPhone devices. This life-saving technology automatically sends your location details to emergency services when Triple Zero is called.
Australia’s national telephone warning system is used to warn the community in the event of a likely or actual emergency. Emergency Alert sends text messages to mobile phones within a geographic area defined by emergency services. International travellers can receive these notifications if their mobile phone is roaming on an Australia network.
Bushfires can occur in Australia’s bushland, typically in the warmer months of the year. Bushfires do pose a risk to travellers and property, for this reason it is recommended to check local conditions and reschedule trips within a bushfire radius. These bushfire safety tips include useful resources to stay up to date. Fortunately, Australia is a large country, and many areas will likely be unaffected.
Familiarise yourself with these tips for COVID-19 safe travel in Australia . There are also a few important measures to protect yourself from COVID-19 while travelling
- Wear a mask: in some states and territories, masks may be mandatory on public transport and indoor spaces.
- Physical distancing: keep 1.5 metres away from others where possible
- Soap up: wash your hands regularly for 20 seconds with soap and water
- Use cashless payment: use a credit or debit card to avoid handling cash
If you develop COVID-19 symptoms, get tested and follow the self-isolation guidelines of the state or territory you are visiting. Testing locations can be found here . For information about COVID-19 you can call Australia’s National Coronavirus Helpline on 1800 020 080.
While not mandatory, travel insurance is highly recommended. This will provide an extra level of security to cover for any unforeseen circumstances affecting your travel plans.
Australia has reciprocal health care agreements with eleven countries. If your country of origin is not in this list, you should consider taking out health insurance for your trip. It's not a requirement for travel to Australia, but it will protect you from high upfront costs if you need to see a medical professional. Having health insurance is always a good idea while travelling, even if just for peace of mind, but particularly if you have a health condition.
Nature and wildlife
Generally, swimming at the beach in Australia is safe. In fact, it’s one of our favourite activities! To stay safe, we recommend following the Surf Lifesavers’ water safety recommendations. These include:
- Only swim at patrolled beaches.
- Swim between the red and yellow flags. These areas are patrolled by Surf Lifesavers.
- Never swim alone, at night, or under the influence of alcohol.
- Always check water depth before diving in and never run and dive into the water from the beach.
The Australian sun is very strong, even on cloudy days. Be 'sun smart' and protect yourself from the sun by wearing a rash vest, applying water-resistant, reef-friendly sunscreen (SPF30 or higher) regularly, and wearing a hat and sunglasses. Protect yourself from heat exhaustion by sitting in the shade and drinking plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
The sun is strongest during the summer (December to February). However, UV levels are high all year round in Australia, even when the weather is overcast. Regularly apply sunscreen and take extra care between 10am and 3pm when UV levels are generally at their highest.
Australia is home to a plethora of incredible animals, some of which you might prefer to avoid, while others are a treat to meet. A good rule of thumb is to always follow advisory signs and don’t approach unfamiliar animals. Find out the facts about dangerous animals in Australia , there’s no need to be afraid. Our wildlife is wonderful, and responsible encounters in the wild will make your trip extra special.
Australia boasts a myriad of breathtaking bushwalks and hikes , all of which can be enjoyed safely. To avoid any danger, ensure that you:
- Only walk along marked trails and while you’re walking, stick to the path.
- Always bring plenty of water and food. It could be some time before you can top up on supplies.
- Bring appropriate clothing. Comfortable shoes, a hat to protect yourself from the sun, and layers are recommended.
- Tell someone where you are hiking.
Australia is a vast and diverse country, packing up the car and taking a long road trip is an immersive way to explore it. Driving long distances is a safe and stress-free adventure if you plan and pack safe. Make sure your vehicle is in good condition and take rest and stretching breaks every two hours. If you are driving in the outback there is often long distances between towns and facilities so it’s important to plan your trip before setting off. Be prepared by reading our guide to road safety and regulations.
More articles like this
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience. Find out more . By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
Acknowledgement of Country

We acknowledge the Traditional Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Owners of the land, sea and waters of the Australian continent, and recognise their custodianship of culture and Country for over 60,000 years.
- International (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- Canada (English)
- United Kingdom (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- Singapore (English)
- Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- 中国大陆 (简体中文)
*Product Disclaimer: Tourism Australia is not the owner, operator, advertiser or promoter of the listed products and services. Information on listed products and services, including Covid-safe accreditations, are provided by the third-party operator on their website or as published on Australian Tourism Data Warehouse where applicable. Rates are indicative based on the minimum and maximum available prices of products and services. Please visit the operator’s website for further information. All prices quoted are in Australian dollars (AUD). Tourism Australia makes no representations whatsoever about any other websites which you may access through its websites such as australia.com. Some websites which are linked to the Tourism Australia website are independent from Tourism Australia and are not under the control of Tourism Australia. Tourism Australia does not endorse or accept any responsibility for the use of websites which are owned or operated by third parties and makes no representation or warranty in relation to the standard, class or fitness for purpose of any services, nor does it endorse or in any respect warrant any products or services by virtue of any information, material or content linked from or to this site.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Australia Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for Australia.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Australia. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Australia.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis is mainly a concern in the Murray River, and the Outer Torres Strait Islands area.
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or traveling at times outside of the Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis (CDC Yellow Book)
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Australia is free of dog rabies. However, rabies may still be present in wildlife species, particularly bats. CDC recommends rabies vaccination before travel only for people working directly with wildlife. These people may include veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers working with specimens from mammalian species.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥1 year old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1 Travelers arriving from the Galápagos Islands of Ecuador are exempt from this requirement.
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
- Mosquito bite
Dengue outbreaks in Australia have only occurred in north and central Queensland.
- Avoid Bug Bites
Ross River virus disease
Ross River fever
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Australia, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Although Australia is an industrialized country, bug bites here can still spread diseases. Just as you would in the United States, try to avoid bug bites while spending time outside or in wooded areas.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Consider using permethrin-treated clothing and gear if spending a lot of time outside. Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Australia include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip:
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in the heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if you are driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance for things your regular insurance will not cover.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medicines you take.
- Bring copies of your prescriptions for medicine and for eye glasses and contact lenses.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Australia’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Make sure there are seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Australia, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Australia.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Australia for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory September 8, 2023
Australia - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with removal of major event information.
Exercise normal precautions in Australia.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Australia.
If you decide to travel to Australia:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Australia.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must be valid at time of entry
One page required for entry stamp
Amounts over AUD 10,000, or equivalent, must be declared
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. consulate general sydney.
Suite 2, 50 Miller Street North Sydney, NSW 2060 Australia Telephone: +(61) (2) 2 8219-2100 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (2) 4422-2201 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Embassy Canberra (The Embassy does not provide consular services.) Moonah Place Yarralumla, ACT 2600 Australia Telephone: +(61) (2) 6214-5600 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (2) 411-424-608 Fax: +(61) (2) 6214-5970
U.S. Consulate General Melbourne 553 St. Kilda Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Australia Telephone: +(61) (3) 9526-5900 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (3) 9389-3601 Fax: +(61) (3) 9526-5968 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Perth 4th Floor 16 St. George's Terrace Perth, WA 6000 Australia Telephone: +(61) (8) 6144-5100 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (8) 9476-0081 Fax: +(61) (8) 9325-5914 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
You must have a valid U.S. passport and a visa or an approved Electronic Travel Authority (ETA) to enter Australia. Most U.S. passport holders traveling to Australia for tourism or business purposes for less than 90 days can obtain an ETA. The ETA is an electronic label-free visa and can be obtained at the ETA website for a small service fee. Airlines and many travel agents in the United States are also able to apply for ETAs on behalf of travelers.
If you overstay your ETA or any other visa, even for short periods, you may be subject to exclusion, detention, and removal by the Australian Department of Home Affairs.
If you are travelling on a valid U.S. ePassport (a passport that contains an electronic chip) and are 16 years of age or older, you are eligible to use Australia’s automated border processing system, SmartGate, upon arrival in Australia (SmartGate kiosks are available only at participating airports). There is no additional enrollment process or fee to use SmartGate. Visit the SmartGate website for more information and for a list of participating airports in Australia.
Visit the Embassy of Australia website for the most current visa information.
HIV/AIDS restrictions. Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors and foreigners seeking permanent residence in Australia. Depending on the type of visa you apply for, the length of your stay, and your intended activities in Australia, you may be required to undergo a medical examination before the Australian Department of Home Affairs will issue you a visa.
If you are in the application process, and are found to be HIV positive, a decision on the application will be considered on the same grounds as any other pre-existing medical condition (such as tuberculosis or cancer), with the focus on the cost to Australia’s health care and community services.
Additional information about Australian immigration health requirements can be found here.
Please verify this information with the Embassy of Australia in Washington D.C. before you travel.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorists have targeted, and could continue to target, Australia.
- Australia has an alert system for possible terrorist attacks. The threat levels range from “not expected” to “certain.” The Australian National Security website has up-to-date information regarding the current terrorism threat level. You may also contact the Australian National Security Hotline at 61-1-800-123-400.
- U.S. citizens in Australia should remain vigilant toward their personal security and exercise caution.
- Australian law protects the right of individuals and groups to engage in peaceful protest and to publicly express their views. Demonstrations and political rallies are generally approved by local authorities and well publicized. However, please be cautious of any possible confrontation that could escalate into violence. You should attempt to avoid the areas of demonstrations and be careful within the vicinity of any demonstrations. You should stay current with media coverage of local events and always be aware of your surroundings.
- You should be aware that robberies, burglaries, assault, and auto theft are common in Australia’s larger cities.
- Foreign visitors in popular tourist areas are targets for pickpockets, purse-snatchers, and petty thieves. Most petty crime can be avoided if basic security precautions are taken.
- Be careful when visiting bars or clubs in the entertainment areas of major cities, as “bar brawls” and other assaults sometimes occur. You should watch out for drink spiking when consuming alcohol with unfamiliar people.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
Victims of Crime:
- Report crimes to the local police at 000 and contact the U.S. Consulate in your district.
- The local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes.
- See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide information about Australian Victim Assistance programs.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution.
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the U.S. consulate in your district for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is generally regulated, and rules and safety inspections are regularly enforced. Hazardous areas/activities are identified with appropriate signage, and professional staff is typically on hand in support of organized activities. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is widely available throughout the country. Outside of a major metropolitan center, it may take more time for first responders and medical professionals to stabilize a patient and provide life-saving assistance. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, imprisoned or deported.
- It is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings, such as inside certain areas of Australian airports, near prisons, and at military bases.
- Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Alcohol and Drugs:
- Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of drugs are strict. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy sentences and fines. Please see Australia’s Department of Health webpage for further information.
- Driving under the influence of alcohol can result in jail time.
- Random breath testing of a driver's blood alcohol level is a common occurrence.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Potential Health Screening: Australian authorities have broad powers to prevent the entry of diseases and other materials into Australia that might pose a threat to its welfare. In the event of a public health emergency involving a communicable disease, passengers arriving in Australia may be subject to strict health screening measures, including testing, monitoring, and assessment for possible quarantine.
Customs: Australian customs authorities enforce very strict regulations concerning the importation from all countries of items such as agricultural goods, including plants and food products, and wood products, as well as very strict quarantine standards for animals and pets. Can you bring it in?
Contact the Embassy of Australia in Washington, D.C., or one of Australia's consulates in the United States for specific information regarding customs requirements, and visit the Australian Government’s Department of Agriculture website for additional information.
Natural Disasters:
Australia experiences a range of natural disasters, including bushfires, floods, and severe storms. These events are difficult to predict and can result in loss of life. You should be aware of conditions around you and monitor local weather and safety reports so you can take appropriate action when needed.
See our webpage for information on storm preparedness and response.
Safety Concerns:
Outdoor Recreation/Adventure
- Be aware that Australian fauna can be dangerous. From jellyfish to crocodiles, sharks, poisonous insects, and snakes, the continent and its waters host wildlife that merit awe and respect in equal doses.
- Visit the Wet Tropics Management Authority visitor information guide for information on Australian wildlife and marine life.
- Take important safety precautions when swimming, such as swimming only between the flags where a lifeguard is present, and never swimming alone.
- Further information on beach safety can be found on the Surf Life Saving website.
Follow recommended precautions when snorkeling and scuba diving and never dive alone. Over the past few years, there have been numerous deaths related to snorkeling and scuba diving incidents.
Faith-Based Travelers : See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in Australia. Australian federal law prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation.
As of December 9, 2017 Australia defines marriage as “the union between two people.” Australia grants temporary and permanent visas to same-sex partners of Australian citizens.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance
- Australia enforces laws prohibiting discrimination against access to premises, facilities, and accommodation.
- Many of the downtown areas of Australian cities were built in the 1800s. These areas often have narrow sidewalks crowded with pedestrians and tourists.
- Most public transit, parking, streets, and buildings are accessible for disabled travelers.
- Tourist spots at the beach or in the Australian outback can have varying degrees of accessibility.
- Many accommodations and venues provide accessibility information on their websites.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
For emergency services in Australia, dial 000.
Ambulance services are widely available.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
- Excellent medical care is available in Australia.
- Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services.
- Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on overseas insurance coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
Prescriptions:
- If traveling with prescription medication, check with the government of Australia to ensure the medication is legal in Australia .
- Always, carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of hospitals and a link to the Australian National Health Services Directory at Medical Assistance - U.S. Embassy & Consulates in Australia (usembassy.gov) . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for information on Medical Tourism, the risks of medical tourism, and what you can do to prepare before traveling to Australia.
Pharmaceuticals:
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
Air Quality
Air pollution is a significant problem during certain months in Australia due to bush fires. Consider the impact seasonal bush fire season pollution may have on your health and consult your doctor before traveling.
The air quality varies considerably and changes with the season. It is typically at its worst in the bush fire season. People at the greatest risk from particle pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema;
- People with heart disease or diabetes
- People who work or are active outdoors
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety:
- Traffic operates on the left side of the road, and all vehicles use right-hand drive.
- Use caution when crossing streets and when driving.
- When crossing roads on foot, make sure you look carefully in all directions.
- Seat belt use by drivers and all passengers is mandatory, and fines apply for not wearing them.
- Motorcyclists must wear helmets.
- Speed limits and laws are rigorously enforced. Speed limits vary throughout Australia and are measured in kilometers, not miles. Be aware that speed cameras are everywhere and you will be ticketed for driving over the speed limit.
- Roads and streets are frequently narrower and less graded than U.S. highways.
- Outside major metropolitan areas, most highways are two-lane roads with significant distances between destinations.
- When driving in Australia, exercise caution while passing or merging with adjacent traffic.
- If driving in rural areas, be alert to free-roaming animals, such as kangaroos, and "road-trains" (several semi-truck trailers connected together).
- Passing road-trains is dangerous, and you should pull over to allow on-coming road-trains to pass to avoid being sideswiped.
- If you have no experience with a 4-wheel drive vehicle, you should exercise common-sense when driving in the Australian outback.
Traffic Laws:
- Each state/territory has different rules about using a foreign driver’s license and the conditions under which a visitor might have to get an international driver’s license. More information about driving rules and regulations is available by state .
- Texting or holding your phone while driving is against the law in Australia, but you can use a hands-free system to communicate while driving.
- For specific information concerning Australian driving permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, mandatory insurance, and the rental and operation of motor vehicles in Australia, visit the Australian Tourist Commission website.
Public Transportation: Australia has an extensive and safe public transportation network consisting of buses, streetcars, ferries, trains, and subways. Metered taxis and ride sharing services are also prevalent. Use common sense safety practices, such as guarding valuables and remaining aware of your surroundings, on all public transportation.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Australia’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Australia’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Australia should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings website portal select “broadcast warnings”.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Australia . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, australia map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:
- advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- information for women, LGBT+ and disabled travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Australia travel advice
Latest updates: Natural disasters and climate – removed information on Tropical Cyclone Megan
Last updated: April 10, 2024 05:31 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, australia - take normal security precautions.
Take normal security precautions in Australia.
Back to top
Violent crime is low.
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and bag snatching, occurs mostly in larger cities. Vehicle break-ins are common.
Robberies of safe-deposit facilities are common at inexpensive hotels and hostels.
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- Never leave personal belongings, such as money, credit cards, cell phones and other electronics, unattended
- Exercise caution in popular tourist areas
Online scam
Scammers have duped tourists into transferring money to an overseas bank account in exchange for renting accommodation in Australia.
When renting accommodation, beware of online scams.
Overseas fraud
Demonstrations
Demonstrations may occur. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
More about mass gatherings (large-scale events)
There is a threat of terrorism. The Government of Australia maintains a national terrorism threat advisory system. Individuals or groups have developed both the intent and capability to conduct a terrorist attack in Australia. Terrorist attacks could occur at any time.
Targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places.
Australian National Security – Government of Australia
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances, as they may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Water activities
Coastal waters can be dangerous. Riptides are common and can be dangerous. Several drownings occur each year.
In certain areas, sharks, crocodiles, jellyfish and other wildlife pose a risk to swimmers.
- Avoid unsupervised beaches
- Follow the instructions and warnings of lifeguards
- Respect the flag warning system, which provides notice of water conditions and safety risks on beaches
Beach safety – Government of Australia
Diving and snorkelling
You must provide a medical declaration for diving or snorkelling.
Follow the instructions and warnings of local authorities.
Safety information for divers and snorkellers – Government of Australia
Trekking and mountaineering
Weather conditions may be dry during the summer. You should be prepared for hot weather.
If you intend on trekking or mountaineering:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you’re properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back to camp
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails or slopes
Remote areas
Some regions in Australia’s interior are very isolated and have small populations. Services are scarce.
You may have difficulty getting adequate mobile phone coverage if you travel there by car.
- Avoid travelling alone
- Inform relatives of your itinerary
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are very good throughout the country. Exercise caution when driving in rural areas at night. Drivers often drive at excessive speeds. Roaming animals and road trains pose further hazards.
Access to some remote locations may be impossible during severe weather conditions. Due to the great distances between settlements and the isolation of many outback areas:
- avoid travelling in extreme heat conditions
- plan your overland route carefully
- provide a friend or relative with your itinerary, and ensure that your vehicle is in good repair
- carry a first-aid kit and personal medication
- carry sufficient fuel, water, and food supplies
- bring a satellite phone or an emergency position indicating radio beacon (EPIRB)
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Australian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid on the day of entry into the country.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays up to 90 days Business visa: required Student visa: required
Canadians entering Australia without a visa need to get an electronic travel authority (ETA) to visit Australia. Ensure that you travel with the same passport used to apply for your ETA.
A health examination might be necessary to obtain certain visas.
- Electronic Travel Authority – Government of Australia
- Department of Home Affairs – Government of Australia
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
In this destination, rabies may be present in some wildlife species, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who will be working directly with wildlife.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is excellent. Service is available throughout the country.
Payment is expected at time of service.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Canada and Australia are signatories to the Convention on the Transfer of Sentenced Persons. This enables a Canadian imprisoned in Australia to request a transfer to a Canadian prison to complete a sentence. The transfer requires the agreement of both Canadian and Australian authorities. This process can take a long time and there is no guarantee that the transfer will be approved by either or both sides.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy jail sentences and heavy fines.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Imports and exports
There are very strict rules and quarantine measures regarding the importation of food and animal products. Information about items which you can and cannot bring to Australia is available from Australia’s Department of Home Affairs.
Immigration and Citizenship – Government of Australia
Traffic drives on the left.
Local authorities accept your overseas driving licence if the names on your licence match exactly those in your passport.
You must apply for a local licence if you intend to stay in Australia longer than 3 months.
Permits are required when travelling on Aboriginal territory.
You should carry an international driving permit.
- Driving with an overseas licence – Government of Australia
- More about the International Driving Permit
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Australia.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Australia, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. The convention applies between Canada and Australia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Australia, and if the applicable conditions are met, you may apply for the return of your child to the Australian court.
If you are in this situation:
- act as quickly as you can
- contact the Central Authority for your province or territory of residence for information on starting an application under The Hague Convention
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Australia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- List of Canadian Central Authorities for the Hague Convention
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- The Hague Convention - Hague Conference on Private International Law
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The currency of Australia is the Australian dollar (AUD).
Bush and forest fires
Bush and forest fires are common between October and April, particularly in areas covered by bushes, long grass or coastal scrub. Elevated fire danger ratings and alert levels may be applied to affected areas. The air quality in areas near active fires may deteriorate due to heavy smoke.
In case of a major fire:
- stay away from the affected area, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- be prepared to modify your travel arrangements or even evacuate the area on short notice
- follow the instructions of local emergency services personnel
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
For current information, consult the relevant state or territory authorities.
Fire services
- Australian Capital Territory
- New South Wales
- Northern Territory
- South Australia
- Western Australia
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to April. Severe flooding occurs annually, especially in the inland parts of the following states:
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
- Monitor local news and weather reports
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
Australia Rainfall and river conditions – Bureau of meteorology, Australian government
Cyclones usually occur from November to April. They may occur along the coastal areas of Queensland, the Northern Territory and Western Australia.
During this period, even small storms can quickly develop into major cyclones. These severe storms can put you at risk and hamper the provision of essential services.
If you decide to travel to Australia during the cyclone season:
- know that you expose yourself to serious safety risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
- Bureau of Meteorology – Government of Australia
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
- Large-scale emergencies abroad
Seismic activity
Australia is located in a seismic zone. Earthquakes may occur.
Local services
Dial 000 for emergency assistance.
Consular assistance
Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, South Australia, Western Australia, Tasmania, Guam, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, New Caledonia, Northern Marianas, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu
New South Wales, Queensland and Northern Territory
For emergency consular assistance, call the High Commission of Canada in Australia, in Canberra, or the Consulate General of Canada in Sydney and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
COVID-19 however continues to pose a health risk in Australia and overseas. We strongly encourage wearing masks and being vaccinated while travelling internationally. You should practice good cough and hand hygiene, and physically distance from others where possible. Some countries, airlines and vessel operators may have COVID-19 travel ...
COVID-19 and the border. Updates to Australia's immigration and border arrangements during the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) pandemic. Latest updates. From 12:01am on Saturday 11 March 2023, people travelling to Australia from China, including Hong Kong and Macau, will not be required to show evidence of a negative pre-departure test for COVID-19. For ...
Here's what you need to know about new rules for close contacts and isolation will take effect in Western Australia today. Read more. Do tourists need a COVID-19 vaccine to travel to Australia?
Australia will reopen to all fully vaccinated visa holders, welcoming the return of tourists, business travellers, and other visitors from 21 February. ... including a recent 23 per cent decline in hospitalisations due to COVID, the National Security Committee of Cabinet today agreed Australia is ready to further progress the staged reopening ...
The Australian Government has announced changes to the COVID-19 testing requirements for inbound travel to Australia. You still need to provide evidence of a negative COVID-19 test before you board your flight. But more test types will now be accepted. Tests can be either: A rapid antigen test (RAT), taken under the supervision of a medical ...
Plan your trip with australia.com, the official Tourism Australia website, offering a wide range of travel information and planning tools including over 2000 images, a currency converter, daily weather updates, interactive maps, suggested holiday itineraries, holiday deals, specialist travel agents and more. Available in nine languages.
People travelling to Australia no longer need to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination or a negative COVID-19 test result. Some countries, airlines and ships may have their own testing, vaccination and face-mask rules. You should check with them before travelling. During your travel to Australia, you're encouraged to wear a face mask to reduce ...
Australia's border rules apply to everyone. Any individual seeking to enter Australia must comply with our strict border requirements. While the Victorian Government and Tennis Australia may permit a non-vaccinated player to compete in the Australian Open, it is the Commonwealth Government that will enforce our requirements at the Australian ...
All COVID-19 border restrictions to be lifted. People travelling to Australia will no longer have to complete a Digital Passenger Declaration (DPD) to declare their COVID-19 vaccination status, following changes to the Biosecurity Act, which come into effect from midnight AEST on Wednesday 6 July 2022. "This is great news for families coming ...
Queensland has the same rules, but mandates that you must use private transport to your place of isolation, while Western Australia limits travel to remote Aboriginal communities until June 15 ...
The rules are stricter for travel to Western Australia. The state requires that travelers are triple-vaccinated, complete a G2G pass before travel and take a COVID-19 test within 12 hours of arrival. The latest Australia health and safety information. Do children have to be vaccinated to travel to Australia?
See the Australian government's website for advice on COVID-19 and travelling. COVID-19 quarantine requirements Each state and territory determines its own quarantine rules.
Passengers arrive at Sydney airport on Monday. Australia's national cabinet will meet soon to discuss potential new border restrictions over the Omicron variant of Covid-19.
If you test positive to COVID-19, you may be required to quarantine or self-isolate depending on what country or city you're in. Many countries have penalties for breaking isolation rules, so it's important you check with local authorities what the requirements are. Some countries have government managed quarantine facilities or you'll ...
International travellers. People travelling to Australia no longer need to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination or a negative COVID-19 test result. The Australian Government controls Australia's international border. Visit the Department of Home Affairs for the latest advice on entering and leaving Australia.
Bars in Australia are . Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Australia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
This communique summarises the meeting of the Culturally and Linguistically Diverse (CALD) Communities Health Advisory Group (Advisory Group), held on 12 March 2024. 27 March 2024. View all resources. Find information on COVID-19, how to protect yourself and those around you, and the current situation in Australia.
Familiarise yourself with these tips for COVID-19 safe travel in Australia.There are also a few important measures to protect yourself from COVID-19 while travelling. Wear a mask: in some states and territories, masks may be mandatory on public transport and indoor spaces. Physical distancing: keep 1.5 metres away from others where possible Soap up: wash your hands regularly for 20 seconds ...
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information. COVID-19 vaccine. Hepatitis B: Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Australia. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Australia.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
30 April 2024. Updated: 26 March 2024. Latest update: Updated assessment that terrorist attacks in Australia cannot be ruled out ('Safety and security' page). The Foreign, Commonwealth ...
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination. ... Before travelling, verify your destination's COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care ...