Places the U.S. Government Warns Not to Travel Right Now
You may want to reconsider traveling to these countries right now.
Do Not Travel to These Countries

Getty Images
Crime, civil unrest and terrorism are common risk factors for countries that end up on the State Department's "Do Not Travel" advisory list.
In 2024, tourism across the globe is “well on track” to return to pre-pandemic levels, according to projections by UN Tourism.
Global conflicts and natural disasters , ranging from a series of coups across Africa to catastrophic earthquakes in the Middle East affected international travel patterns throughout 2023. Still, international tourist arrivals reached 87% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023, according to estimates by UN Tourism .
In January 2024 alone, about 4.6 million U.S. citizens left the country for international destinations, 17% higher than the same month in 2019, according to the International Trade Administration . But some destinations warrant more caution than others.
On Oct. 19, 2023, following the outbreak of war between Israel and Gaza and flaring tensions in the region, the U.S. State Department issued a worldwide caution advisory due to “increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.” Prior to this update, the most recent worldwide caution advisory was issued in 2022 after a U.S. strike killed Ayman al-Zawahiri, Osama bin Laden’s successor as leader of Al Qaeda, causing “a higher potential for anti-American violence.” The worldwide caution advisory remains in effect.
The U.S. State Department also issues individual travel advisory levels for more than 200 countries globally, continually updating them based on a variety of risk indicators such as health, terrorism and civil unrest. Travel advisory levels range from Level 1, which means exercise normal precautions, to Level 4, which means do not travel there.
About 10% of countries – 19 total – have a Level 4: “Do Not Travel” advisory as of Mar. 4. In Level 4 countries, the U.S. government may have “very limited ability” to step in should travelers’ safety or security be at risk, according to the State Department. Crime, civil unrest, kidnapping and terrorism are common risk factors associated with Level 4 countries.
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list.
Places With a Level 4 Travel Advisory
These are the primary areas the U.S. government says not to travel to right now, in alphabetical order:
Jump to Place: Afghanistan Belarus Burkina Faso Central African Republic Myanmar (formerly Burma) Gaza Haiti Iran Iraq Libya Mali Mexico North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) Russia Somalia South Sudan Sudan Syria Ukraine Venezuela Yemen
Afghanistan: The Central Asian country is wrestling with “terrorism, risk of wrongful detention, kidnapping and crime,” according to the State Department. U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for wrongful detention and kidnapping. In 2022, the government reinstituted public floggings and executions, and women’s rights are disappearing under Taliban control. The U.S. Embassy in Kabul halted operations in August 2021. Since the Taliban took control , many forms of international aid have been halted . Meanwhile, in 2023, some of the year’s deadliest earthquakes killed more than 2,400 in Afghanistan while the country continues to face a years-long extreme drought.
Belarus: Belarus, which shares a western border with Russia and a southern border with Ukraine, has been flagged for “Belarusian authorities’ continued facilitation of Russia’s war against Ukraine, the buildup of Russian military forces in Belarus, the arbitrary enforcement of local laws, the potential of civil unrest, the risk of detention, and the Embassy’s limited ability to assist U.S. citizens residing in or traveling to Belarus.” The U.S. Embassy in Minsk halted operations in February 2022.
Burkina Faso: Terrorism, crime and kidnapping are plaguing this West African nation. Terrorist attacks may target hotels, restaurants and schools with little to no warning, and the East and Sahel regions of the country are under a state of emergency. In late November 2023, hundreds died in clashes between state security forces and rebels near the country’s border with Mali. In June, more than 2 million people in Burkina Faso were displaced due to “violence linked to al-Qaida and the Islamic State group.”
Central African Republic: While there have not been specific incidents of U.S. citizens targeted with violence or crime, violent crime and sudden closure of roads and borders is common. The advisory states that “Embassy Bangui’s limited capacity to provide support to U.S. citizens, crime, civil unrest, and kidnapping” is a factor in its assessment. Recent data from UNICEF suggests the country has the worst drinking water accessibility of all countries in 2022.
Myanmar (Formerly Burma): Armed conflict and civil unrest are the primary reasons to not travel to this Southeast Asian country, which experienced a military coup in early 2021. Limited health care resources, wrongful detentions and “areas with land mines and unexploded ordnance” are also listed as risk factors. After Ukraine and Israel, Myanmar had the highest conflict-related death toll in 2023.
Gaza : Hamas, a foreign terrorist organization as designated by the State Department, controls much of the Gaza Strip, which shares borders with both Israel and Egypt. On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas fighters broke across the border into Israel, killing hundreds of civilians and soldiers in a brazen attack that stunned Israelis. On Oct. 10, Israel hit the Gaza Strip with “the fiercest air strikes in its 75-year conflict” according to Reuters . The conflict has since escalated into war between Israel and Hamas, with regular Israeli airstrikes leading to extensive civilian casualties in Gaza. As of mid-December, nearly 85% of Gaza’s population were displaced from their homes, according to UN estimates . The region continues to face shortages of food , water, electricity and medical supplies , with conditions deemed “far beyond a humanitarian crisis.” The State Department warns of terrorism and armed conflict within Gaza’s borders.
Haiti: In July 2023, the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Port-au-Prince in response to the increased risk of kidnapping and violent crime in the country , as well as armed conflict between gangs and police. The travel advisory states that cases of kidnapping “often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings.” The travel advisory also states that “U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible” given “the current security situation and infrastructure challenges.” A series of gang attacks in late September 2023 caused thousands to flee their homes, and many aid groups have been forced to cut or suspend operations amid escalating violence in recent months.
Iran: Terrorism, kidnapping and civil unrest are risk factors for all travelers to Iran, while U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for “arbitrary arrest.” U.S.-Iranian nationals such as students, journalists and business travelers have been arrested on charges of espionage and threatening national security. Executions in Iran rose sharply between 2021 and 2022, bringing the country’s total to nearly 580 people over the year, according to a report by Amnesty International released in May 2023.
Iraq: The State Department cites “terrorism, kidnapping, armed conflict [and] civil unrest” as cause for the country’s Level 4 distinction. Iraq’s northern borders, and its border with Syria, are especially dangerous. Since the escalation of conflict in neighboring Israel in October, there has been an increase in attacks against Iraqi military bases, which host U.S. troops and other international forces. In October 2023, non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members were ordered to leave the U.S. embassy in Baghdad.
Libya: Following the end of its dictatorship over a decade ago, Libya has been wrought with internal conflict between armed groups in the East and West. Armed conflict, civil unrest, crime, kidnapping and terrorism are all risk factors. U.S. citizens have been targets of kidnapping for ransom, with terrorists targeting hotels and airports frequented by Westerners. The U.S. Embassy in Tripoli halted operations in 2014. In mid-September 2023, floods, which some say were intensified by climate change , killed thousands in eastern Libya. Clashes between armed factions escalated across the country in the latter half of 2023, including in the capital city of Tripoli and in Benghazi.
Mali: After experiencing military coups in 2020 and 2021, crime, terrorism and kidnapping are all prevalent threats in this West African landlocked nation. In July 2022, non-emergency U.S. government employees and their families were ordered to leave the country due to higher risk of terrorist activity. A U.N. report in August 2023 said that military groups in the country, including both Mali security forces and possibly Russian Wagner mercenaries, were spreading terror through the use of violence against women and human rights abuses. Democratic elections were supposed to occur in February 2024, but Mali’s military junta postponed the plans indefinitely. In December, the U.N. officially ended a decade-long peacekeeping presence in the country, which had been among the agency’s deadliest missions, with hundreds of the mission personnel killed since 2013.
Mexico: Each state in Mexico is assessed separately for travel advisory levels. Six of the 32 states in Mexico are designated as Level 4: Colima, Guerrero, Michoacan, Sinaloa, Tamaulipas and Zacatecas. Crime and kidnapping are listed as the primary risk factors throughout the country. Nearly 112,000 people were missing across the country as of October, a number the U.N. has called “alarming.”
North Korea (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea): U.S. passports are not valid for travel “to, in, or through” this country, home to one of the world's longest-running dynastic dictatorships. The travel advisory states that the Level 4 distinction is due to “the continuing serious risk of arrest and long-term detention of U.S. nationals.” In July 2023, a U.S. soldier fled across the border into North Korea, where he is believed to be in North Korean custody, the first American detained in the North in nearly five years. He was returned to U.S. custody in September 2023.
Russia: The travel advisory for Russia cites its invasion of Ukraine , harassment of U.S. citizens by Russian government officials and arbitrary law enforcement as a few of the reasons for the Level 4 designation. Chechnya and Mount Elbrus are specifically listed as Level 4 regions. Terrorism, civil unrest, health, kidnapping and wrongful detention are all noted as risks.

Russia Invades Ukraine: A Timeline

Somalia: A severe drought resulting from five failed rainy seasons in a row killed 43,000 people in 2022, and caused a famine amid conflict with Islamist insurgents . Violent crime is common throughout Somalia , pirates frequent its coast off the Horn of Africa, and medical facilities, where they exist, have limited capacity. Crime, terrorism, civil unrest, health and kidnapping are all risk factors. In January 2024, some passengers aboard a U.N.-contracted helicopter were taken hostage by al-Shabaab militants after the vehicle crashed in central Somalia.
South Sudan: Crime, kidnapping and armed conflict are the primary risk factors for South Sudan, which separated from Sudan in 2011, making it the world’s newest country . Weapons are readily available, and travelers have been victims of sexual assault and armed robbery.
Sudan: The U.S. evacuated its embassy in Khartoum in April 2023, and the country closed its airspace due to the ongoing conflict in the country, only permitting humanitarian aid and evacuation efforts. Fighting has escalated in the region between two warring generals seeking to gain control after a military coup in 2021 ousted the country’s prime minister. Civil unrest is the primary risk factor for Africa’s third largest country by area. Crime, terrorism, kidnapping and armed conflict are also noted. The International Criminal Court began investigating alleged war crimes and violence against African ethnic groups in the country in 2023. Millions have fled their homes due to conflict, and the U.N. has said its efforts to provide aid have been hindered by a lack of support, safety and resources. As recently as December 2023, the United Nations warned of catastrophic famine , with millions of children at-risk for malnutrition .
Syria: The advisory states that “No part of Syria is safe from violence,” with terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, armed conflict and risk of unjust detention all potential risk factors. U.S. citizens are often a target for kidnappings and detention. The U.S. Embassy in Damascus halted operations in 2012. Fighting in neighboring Israel has escalated since October, and the conflict has spilled over into Syria, where the U.S. has carried out air strikes following drone and rocket attacks against American troops in Syria and Iraq, triggered by the Israel-Hamas war.
Ukraine: Russian setbacks in their invasion of Ukraine buoyed hopes in Ukraine in 2023. However, Ukraine is a Level 4 country due to Russia’s invasion, with crime and civil unrest also noted as risk factors. The country’s forces shot down two Russian fighter jets on Christmas Eve 2023, in a move Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said “sets the right mood for the entire year ahead.”
Venezuela: Human rights abuses and lack of health care plague this South American nation, which has been in a political crisis since 2014. In 2019, diplomatic personnel were withdrawn from the U.S. Embassy in Caracas. Threats in the country include crime, civil unrest, kidnapping, wrongful detention and poor health infrastructure.
Yemen: Six of the nine risk factors defined by the State Department – terrorism, civil unrest, health risks, kidnapping, armed conflict and landmines – are all present in Yemen. Despite private companies offering tourist visits to the Yemeni island of Socotra, the U.S. government argues those arranging such visits “are putting tourists in danger.” Civil war and cholera are also both present throughout the country. The U.S. Embassy in Sanaa halted operations in 2015. The country has experienced a relative lull in the civil war fighting, but as peace negotiations have gotten traction, flare ups in the fighting have jeopardized progress. Most recently, the U.S. and U.K. have carried out a series of airstrikes in the country, targeting Iran-backed Houthi sites.
Other Countries to Watch
Since Jan. 1, the State Department has updated travel advisories for 17 different countries as well as for the West Bank and Gaza, adding information about specific regions or risk factors, or simply renewing an existing advisory. Travel advisory levels can change based on several factors in a nation, such as increased civil unrest, policies that affect human rights or higher risks of unlawful detention.
The State Department has given about 25 countries an assessment of Level 3, meaning it recommends people “reconsider travel” to those destinations.
On Oct. 14, one week after the deadly Hamas attack on Israel, Israel and the West Bank were both moved from Level 2 to Level 3, while Gaza remains at Level 4. The region’s travel advisory was updated in November to reflect travel restrictions for certain government employees who have not already left the area, and it was updated again on Jan. 3.
Following the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas war in early October, the U.S. State Department raised Lebanon ’s travel advisory level from a Level 3 to a Level 4 level due to “the unpredictable security situation related to rocket, missile, and artillery exchanges” between Israel and Hezbollah or other militant groups. In December, the U.S. Embassy in Beirut returned to normal staffing and presence, and on Jan. 29, the country was moved back to Level 3. Crime, terrorism, armed conflict, civil unrest, kidnapping and unexploded landmines are listed as the country’s primary risk factors. However, the country’s borders with Syria and with Israel, as well as refugee settlements within Lebanon, are specifically noted as Level 4 regions.
China became a Level 3 country in late 2020, with an update in December 2022 citing “the surge in COVID-19 cases, arbitrary enforcement of local laws, and COVID-19-related restrictions” as the reason for the advisory. In June 2023, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR) was moved from the Level 3 to the Level 2 list, but travelers are still advised to be cautious in the area due to “arbitrary enforcement of local laws.” Meanwhile, Macau remains at Level 3.
Following an attempted coup in August 2023, Niger was elevated to Level 4 in August and the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Niamey. In early January 2024, the overall risk level for the country was lowered back to Level 3. Despite the new classification, the State Department still asks non-emergency government personnel and eligible family members to depart the country.
In mid-December 2023 there was an explosion at Guinea’s main fuel depot which has since affected access to health care and basic goods and services. The country was subsequently designated a Level 3 nation after having previously been Level 2. Concerns about civil unrest, health, crime and fuel shortages impacting local infrastructure were listed as the primary risk factors contributing to the change.
Several Level 3 countries are among the worst countries for human trafficking, as designated by the State Department’s annual Trafficking in Persons Report . Level 3 countries on this list include Papua New Guinea, Guinea Bissau, China and Chad. There are also nine Level 4 countries designated as among the worst for human trafficking: Afghanistan, Belarus, Iran, Myanmar, North Korea, Russia, Syria, South Sudan and Venezuela.
Over 70 countries are currently at Level 2, meaning the State Department recommends travelers “exercise increased caution” when traveling to those destinations.
Botswana became the newest Level 2 country on Feb. 26 after having previously been Level 1, with crime noted as the primary risk factor.
France, which saw nationwide protests throughout 2023, has civil unrest and terrorism noted as risk factors for its Level 2 status, and Sweden’s Level 2 status is associated with risks of terrorism.
The Level 2 travel advisory for the Bahamas was updated in January to reflect water safety concerns. The advisory warns that “activities involving commercial recreational watercraft, including water tours, are not consistently regulated” and notes that government personnel are “not permitted to use independently operated jet-ski rentals on New Providence and Paradise Islands.” It also warns visitors to be mindful of sharks, weather and water conditions. The advisory also says that crime is a primary risk factor with gang-on-gang violence contributing to high homicide rates in some areas. Visitors are asked to “be vigilant” and to not physically resist robbery attempts.
Bangladesh 's Level 2 travel advisory was updated in October 2023 to add a note about the country’s general election , which took place Jan. 7, 2024. The advisory states “demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence.” The U.S. has since claimed the country’s election was not free nor fair.
In November 2023, several Level 2 travel advisories were updated with new cautionary information. The advisory for Ghana was updated to reflect threats against LGBTQI+ travelers specifically, noting “anti-LGBTQI+ rhetoric and violence have increased in recent years.” Meanwhile, the advisory for South Africa was updated in February to note that routes recommended by GPS may be unsafe with higher risk for crime.
Turkmenistan was moved off of the Level 2 list to become the newest addition to the Level 1 list on Jan. 22, meaning normal precautions are recommended but there are no risk factors causing travelers to practice increased caution.
The State Department asks travelers to pay attention to travel advisory levels and alerts , review country information pages for their destinations and read related country security reports before going abroad.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Russia , Ukraine , Travel , Coronavirus , Travel Tips , Israel , Gaza , violence , Civil War , crime , kidnapping
Recent Articles
Best countries.

Education News

Best Countries Rankings
- # 1 Switzerland
- # 5 Australia
- # 5 United States
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Switzerland is world's best country.
Julia Haines Sept. 6, 2023

Photos: Best Countries Around the World
Sept. 6, 2023

The 25 Best Countries in the World
Elliott Davis Jr. Sept. 6, 2023

Reactions to Court Overturning Harvey Weinstein NY Rape Conviction
Reuters April 25, 2024

US VP Harris Hosts Kim Kardashian to Discuss Criminal Justice Reform

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement.
Replace or Certify Documents
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- For Travelers
Travel Overseas
This section provides information for international travelers about planning for your trip, returning home, navigating passenger processing. You can also find brochures about traveling overseas.
Travel Alerts
Travel Alerts are issued when short-term conditions that pose risks to the security of U.S. citizens.
Travel Warnings
Travel Warnings are issued when long-term conditions make a country dangerous or unstable and U.S. citizens should avoid or consider the risk of traveling to that country.
Preparing for your Trip
A passport is required for overseas travel. It is recommended to make a copy of your passport and put it in a separate place. Carry your passport - do not pack it in your checked luggage. You must present it to the Customs and Border Protection officer upon arrival in the United States.
Find out if you need to get a visa. United States citizens don’t need a U.S. visa for travel, but when planning travel abroad may need a visa issued by the embassy of the country they wish to visit. If you have a visa, we recommend you make a copy and put it in a separate place. Carry your visa with you — do not pack it in your checked luggage.
Trusted Traveler Programs (TTP ) provide modified screening for pre-approved members, improve security by being more efficient during screenings at ports of entry.
Learn about the types of identification that are required for travel in the Western Hemisphere (Canada, Mexico, Caribbean, Central and South America). There are six types of acceptable documents for crossing US borders.
All children, including infants, must have their own passport or Trusted Traveler Program document for U.S. entry. Carry documents for traveling with minor children.
- If you are escorting a minor child without the parents, have a letter from both parents indicating that you have permission to travel with the minor.
- If the child is accompanied by only one parent, the parent should have a note from the child's other parent. For example, "I acknowledge that my wife/ husband is traveling out of the country with my son/ daughter. He/She/ has my permission to do so."
- If a single parent has sole custody, a copy of the court custody document can replace a letter from the other parent.
If bringing a dog, have a health certificate and proof of rabies vaccinations from a veterinarian in your country of residence. Prior to your trip, check with your airline for its rules on transporting animals – many airlines require a health certificate.
Returning Home
Find out what is prohibited or restricted before you pack for your trip. Products that would harm community health, public safety and domestic plant and animal life are restricted from entering the United States and are subject to seizure by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection Agency .
Other considerations for packing:
- Carry only medication needed for the trip in its original container. Do not pack it.
- Carry only the jewelry needed for the trip. Do not pack it.
Navigating Passenger Processing
When planning connecting flights to or from the United States, allow at least two hours between flights. Allow time for CBP processing that must be completed at your first port of entry.
If entering the United States by air or sea, you will receive en route a CBP Declaration Form 6059B and, if you are not from a Visa Waiver Program country, a CBP Form I-94 Arrival/Departure Record . Complete all sections of the forms.
Review the CBP Inspection Process before your travel. Listed below are general steps for the inspection process.
- On your U.S. arrival, go to the primary CBP passport control area. The CBP officer will ask to see all of your travel documents and the completed CBP forms. The officer may refer you for a secondary screening.
- Proceed to baggage claim to pick up luggage.
- Go to the CBP customs inspection checkpoint and show your declaration to the CBP officer, who may examine your bags and refer you for a secondary inspection.
- Pay duty, if applicable.
Traveling Overseas Resources
These resources can help navigate traveling overseas.
- Know Before You Go – Regulations for International Travel
- International Travel Tips – Online resources for common questions about international travel
- Welcome to the United States – A Guide for International Visitors
- Import/Export Forms – Travel documents and forms
- Ports of Entry (Air, Land, Sea) – Locate the ports of entry into the United States
- How Do I - For Travelers
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Coronavirus Updates
The coronavirus crisis, u.s. issues more than 115 'do not travel' advisories, citing risks from covid-19.
Bill Chappell

Global travel continues to be risky because of the coronavirus. Earlier this year, passengers from Taiwan wear protective gear as they arrive at France's Charles de Gaulle Airport, and just this week, the U.S. issued over 100 new travel advisories. Francois Mori/AP hide caption
Global travel continues to be risky because of the coronavirus. Earlier this year, passengers from Taiwan wear protective gear as they arrive at France's Charles de Gaulle Airport, and just this week, the U.S. issued over 100 new travel advisories.
The U.S. State Department has vastly expanded its "Do Not Travel list," issuing new Level 4 advisories for more than 115 countries and territories this week. The agency cites "ongoing risks due to the COVID-19 pandemic."
The U.S. Do Not Travel list now includes Canada, Mexico, Germany and the U.K. A Level 3 warning is in place for a smaller group of nations, such as China, Australia and Iceland. Japan is also on the Level 3 list, despite a worrying rise in new coronavirus cases there.
Just a week ago, only 33 countries were on the U.S. Do Not Travel list, according to a cached version of the advisory site . But the State Department warned on Monday that the list would soon include roughly 80% of the world's countries.
More than 150 highest-level travel advisories are in effect — more closely reflecting guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the State Department says.
The CDC's own travel health notices also use a four-tier warning system. For many countries newly added to the State Department's Level 4 list, the CDC cites "a very high level of COVID-19."
As of last week, Brazil and Russia were two of the only large COVID-19 global hotspots on the State Department's most serious warning list. They're now joined by India and virtually all of Europe — places that have seen alarming spikes in new cases.
Bhutan is the only international destination designated as Level 1 — "exercise normal precautions" — on the State Department's travel advisory list.
Sixteen countries are categorized as Level 2 — meaning travelers should exercise increased caution when visiting places such as Thailand, Vietnam, South Korea, Belize and Grenada.
Many of the new or updated Do Not Travel notices cite high levels of coronavirus transmission in the relevant country. But the State Department says it also takes other factors into account, from the availability of coronavirus testing to any travel restrictions the countries might have against U.S. citizens.
In roughly 35 countries or destinations, the CDC says, details about the level of COVID-19 risk are unknown. The health agency urges Americans to avoid traveling to those spots, which include Afghanistan, Nicaragua and the Solomon Islands.
Regardless of a particular country's advisory status, the State Department wants all U.S. citizens to reconsider any travel abroad.
"The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose unprecedented risks to travelers," the agency said.
More than 3 million people have died from COVID-19 worldwide, according to the World Health Organization . Nearly 144 million coronavirus cases have been reported globally, according to data compiled by Johns Hopkins University .
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Routine Vaccines
It’s important to be up to date on recommended routine vaccines prior to travel, including Flu, RSV and COVID-19.

Find a Clinic
Advice for Travelers
Personalized Health Information Tool for Global Travel
Disease Directory
Frequently Asked Questions
CDC Yellow Book
Pre-travel Rapid Evaluation Portal for Patients
Clinician Resources
Research and Surveillance
- Medical Tourism
- Cholera Information for Health Care Professionals
- COVID-19 Travel Information
- Travel Industry Resources
Learn about CDC’s Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country.
Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips.
See the full list of Travel Health Notices , including:
Level 2 - Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Diphtheria in Guinea April 23, 2024
- Chikungunya in Timor-Leste April 05, 2024
- Yellow Fever in Nigeria March 28, 2024
Level 1 - Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Oropouche Fever in South America April 24, 2024
- Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands April 18, 2024
- Dengue in Africa and the Middle East April 18, 2024
There are no Warning , Alert, Watch, COVID-19 Very High, COVID-19 High, COVID-19 Moderate, COVID-19 Low, COVID-19 Unknown, Level 4, or Level 3 notices currently in effect.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here
Is it safe to go there? The U.S. travel advisory system, explained
If you’re planning an international trip, here’s how to use the State Department’s country-by-country guide to minimize your risk of encountering crime, violence, or civil unrest.

On October 19, the U.S. Department of State issued a rare advisory that Americans overseas “exercise increased caution” due to heightened tensions and chances of terrorism around the world, spurred by the Israel-Hamas war. It’s part of a system of travel warnings that’s been around in some form since 1978, designed to help citizens assess how safe a destination might be at a given time.
The current version of the system, which launched in 2018, gives fluid rankings from Level 1 (exercise normal precautions) to Level 4 (do not travel), indicating how risky countries (and in some cases, regions) are for Americans to visit. Rankings are based on factors such as crime rates, civil unrest, and the threat of terrorism. They are meant to give “clear, timely, and reliable information about every country in the world so they can make informed travel decisions,” says a State Department spokesperson.
Not surprisingly, on October 14, the State Department moved Israel and the West Bank to Level 3 (reconsider travel) and Gaza to Level 4.
Here’s how the advisories work and how to use them.
What is a travel advisory?
The U.S. State Department inaugurated the travel advisory system in 1978, initially aiming warnings at airlines and travel companies. The system was scrutinized after the 1988 bombing of a Pan Am flight from London to New York , which exploded over Lockerbie, Scotland , killing all 259 passengers and crew plus 11 people on the ground.
Investigations found U.S. authorities had been aware of a credible threat to a Pan Am flight but hadn’t informed the public. In response, the media and consular offices began issuing travel warnings. In 2018 the U.S. introduced its current four-tier advisory system. There are near-identical versions in Canada , Australia , and New Zealand .
To determine rankings, the State Department considers a nation’s political volatility, crime trends, medical care standards, and the threat of kidnappings or terrorism. (Politics also ends up playing an unspoken role.) Some countries, such as Russia , receive a Level 4 ranking partly because the U.S. government may have limited ability to assist citizens there. Others rise to Level 4 due to a crisis, such as the military coup that recently rocked Niger .
When the travel advisory system relaunched in 2018, it also included state-by-state evaluations for Mexico , which draws more than 11 million American travelers a year. “Some Mexican states are quite safe for U.S. tourists, while others are riskier due to narco-trafficking violence,” says Ryan Larsen , executive director of the Institute for Global Engagement at Western Washington University. Yucatán and Campeche states are currently at Level 1, while six other Mexican states are at Level 4, including Sinaloa.
( Solo female travelers share tips for staying safe on the road .)
Epidemics and natural disasters also can prompt a travel advisory number to rise. Americans may be prompted to reconsider visiting a country recovering from a tsunami or major wildfires, since their presence could hinder rehabilitation efforts. This occurred after the February 2023 earthquakes in Turkey . Such advisories can remain in place for weeks or months.
The strictest-ever advisories came in April 2021, amid the COVID-19 pandemic , says Larsen, who did a thesis on U.S. travel warnings. At that time, about 80 percent of the world’s countries were at Level 4.
At press time, about 70 percent of the world’s countries were rated Level 1 or Level 2 by the State Department, indicating they’re relatively safe. There are currently 21 countries at Level 3 and 21 at Level 4.
How to use travel advisories
Before booking an international trip, consult the State Department website to see where your destination ranks. While Level 1 and 2 countries are considered relatively safe, you should still register with the U.S. Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) . This lets Americans overseas use their smartphone to receive travel advisory updates and alerts about emerging dangers in their destination (protests, extreme weather).
Level 3 countries are considered more dangerous for foreign visitors, who should “reconsider travel,” according to the State Department. If you are headed to a Level 3 country, which currently includes Pakistan and Colombia , do wider research on its safety and on the places you’ll visit there, advises Jun Wen , a professor of tourism at Australia’s Edith Cowan University. For instance, while some remote areas in the Colombian Amazon still suffer from drug-related violence, cities such as Cartagena and Medellín are relatively safe. Going on a fully guided group or individual tour can also help you navigate destinations where political unrest or crime might impact your safety.
Travelers should study not only the advisories provided by their own country, but also by the U.S., United Kingdom, and Australia to broaden their understanding of the risks in Level 3 countries, Wen says. As for Level 4 countries, that “Do Not Travel” advice couldn’t be any clearer.
Other countries also issue warnings to their citizens about visiting the U.S. Canada recently informed its LGBTQ travelers they may be affected by laws in certain U.S. states. Australia, meanwhile, cautions its citizens visiting the U.S. to be wary of higher crime rates and gun violence, and even to learn safety strategies for active shooter scenarios.
People who visit countries with Level 3 or Level 4 travel advisories don’t just risk their safety. They also may have travel insurance complications, says Linchi Kwok , tourism management professor at California State Polytechnic University Pomona.
( How travel insurance can—and can’t—help when your plans change .)
They must pay much higher premiums, and their insurance can be invalidated if the advisory for their destination is elevated. “Medical coverage can be minimal, too, particularly if the travel advisory is put up against a disease or an outbreak,” says Kwok. “I encourage Americans to think twice before they travel to Level 3 and especially Level 4 destinations.”
Warnings and their impact on tourism
Travel advisories can be biased, Larsen argues. His research found that, while the U.S. didn’t often overstate the risk of travel to countries with which it had poor relations, it did often understate the danger of visiting nations that were its close allies. Elevating a travel advisory can stoke diplomatic tensions between two countries. Once a country is raised to Level 3 or 4, many tourists will avoid visiting, and many American universities won’t let students join study abroad programs.
The economic ramifications of a level change impact individual businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and travel agencies. For instance, J 2 adventures , a Jewish-focused tour company, saw most of its fall group trips to Israel canceled after the start of the Israel-Hamas war (and the higher advisory level), says cofounder Guy Millo. “This is not just because of the violence on the ground, but because of practical considerations like accessibility of commercial airline flights,” he says. “Most tourists from North America and places around the globe simply couldn’t get here even if they wanted to.”
Related Topics
- ADVENTURE TRAVEL
- BORDER REGIONS
You May Also Like


PreCheck, Global Entry, CLEAR: We explain U.S. expedited travel programs

The 8 best travel backpacks of 2024
Free bonus issue.

The best Easter gift ideas for adults who love travel

9 travel stories our readers loved in 2023

10 whimsical ways to experience Scotland

The essential guide to visiting Scotland

Ready to plan your fall hike? Read this safety advice first.
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
- History & Culture
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- First Name is a required field.
- Last Name is a required field.
- Please enter your email address.
- Please enter a valid email address.
- At least one Country must be selected.
- Travel.State.Gov
- U.S. Embassies & Consulates
- Country Information
- Latest Travel Advisories
24 Hour Consular Emergency Line: U.S. 1.888.407.4747 / Outside the U.S. 1.202.501.4444
This site is managed by the Bureau of Consular Affairs, U.S. Department of State. External links to other Internet sites should not be construed as an endorsement of the views contained therein.
OMB Control No: 1405-0152, Estimated Burden: 20 minutes, Expiration Date: 6/30/2026.
State Department issues ‘worldwide caution’ alert to Americans overseas
The State Department on Thursday issued a rare “worldwide caution” advisory to all Americans overseas, urging them to “exercise increased caution due to the potential for violence and increased tensions” globally.
It said that there is a potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests. “Stay alert in locations frequented by tourists,” it advised.
The State Department most recently issued a worldwide caution alert in August 2022 following the death of al-Qaeda’s No. 2 leader Ayman al-Zawahiri out of caution for potential “anti-American violence,” according to an archived release.
Similar advisories have been issued over the years when the State Department has warned Americans against increased risks for terrorist attacks, political upheaval and violence. An alert was issued in 2016 when the agency cautioned travel into Burkina Faso and the surrounding Sahel region in Africa following an attack at a hotel in Ouagadougou that killed 30 people, including one U.S. citizen.
The State Department has urged U.S. travelers to “reconsider travel” to Israel and the West Bank and placed a “do not travel” advisory — its most severe warning — on the Gaza Strip due to “terrorism, civil unrest, and armed conflict.”
Americans have been fleeing the country on charter flights and cruise ships since the Hamas attacks earlier this month. Over 7,000 U.S. citizens have departed Israel and the West Bank, a State Department spokeswoman told The Washington Post on Wednesday.
On Tuesday, the State Department raised its travel warning for Lebanon to “do not travel” because of rocket, missile and artillery exchanges between Israel and the Iranian-backed militant group Hezbollah .
Karen Schwartz contributed to this report.
Israel-Gaza war
The Israel-Gaza war has gone on for six months, and tensions have spilled into the surrounding region .
The war: On Oct. 7, Hamas militants launched an unprecedented cross-border attack on Israel that included the taking of civilian hostages at a music festival . (See photos and videos of how the deadly assault unfolded ). Israel declared war on Hamas in response, launching a ground invasion that fueled the biggest displacement in the region since Israel’s creation in 1948 .
Gaza crisis: In the Gaza Strip, Israel has waged one of this century’s most destructive wars , killing tens of thousands and plunging at least half of the population into “ famine-like conditions. ” For months, Israel has resisted pressure from Western allies to allow more humanitarian aid into the enclave .
U.S. involvement: Despite tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and some U.S. politicians , including President Biden, the United States supports Israel with weapons , funds aid packages , and has vetoed or abstained from the United Nations’ cease-fire resolutions.
History: The roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and mistrust are deep and complex, predating the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 . Read more on the history of the Gaza Strip .

What to know about the State Department worldwide travel advisory

The U.S. State Department announced a global travel advisory for those traveling internationally due to the ongoing conflict in the Middle East. The agency cited extra caution against traveling in "risk" areas, such as Israel, Gaza, and the West Bank.
Fighting broke out on Oct. 7 in Israel after Hamas launched an attack, killing and capturing more than 1,000 people. Israeli Defense Forces mounted a swift response, triggering a war between the nation and Hamas, which controls the besieged Gaza Strip.
Since the attack, the death count for Palestinians exceeded 5,000, according to the Palestinian Ministry of Health, as of Monday. The Associated Press reported that the death count for Israelis totaled 1,400 .
The conflict is playing out against the backdrop of religious tensions, an Israeli government in turmoil over judicial reform, and increased Israeli military raids within Palestinian territories.
What is a travel advisory?
The State Department issues travel advisories in incidents involving war, political turmoil, civil unrest, and other cases that may impact global travel.
On Oct. 19, the agency issued a worldwide caution advisory due to “increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.”
Stay safe while traveling: Here are 17 CIA tips, advice to think like a spy on vacation
Who does the travel advisory affect?
According to Arizona's former Director of Homeland Security Tim Roemer, this warning impacts all Americans traveling abroad, even outside the Middle East. Now the chief security officer for a private sector company, Roemer spent 18 years in government service, including his duty as a C.I.A. agent and running cyber security for the state of Arizona.
These types of situations have the risk of spilling over into other regions, he said.
"Lots of copycat violence takes place in the world whenever you have international incidents like this," Roemer said. "These types of wars tend to spark a lot of outrage."
The travel advisory was heightened to a worldwide scale due to the increased violence not just being concentrated in one specific region but could affect areas even in Europe, according to Roemer.
"It's a serious advisory to come from the state department. They don't take these things lightly."
What can international travelers do to stay safe while the advisory is in effect?
Roemer believes it's important to exercise caution now more than ever before and when traveling abroad, which includes always paying attention to your surroundings, having a heightened sense of alertness, and regularly communicating with friends and family back home. He also said it is imperative to pay attention to the news.
"Watch what's happening. You don't want to get stuck somewhere by being unaware of what's going on in the world," said Roemer.
While the advisory will remain active as long as the State Department believes it is relevant, Roemer advised Americans traveling internationally to remain vigilant, especially if they witness any unusual or suspicious activity.
"If you see something that seems out of the ordinary, say something. Don't just keep it to yourself," Roemer said. "Report it (to local law enforcement). It could actually be really important and make a huge difference."
Roemer also encouraged travelers to be more organized and have contingency plans when traveling internationally, especially for those who may already be abroad. This includes knowing all of the airports in your region and being prepared for the unexpected.
"In an emergency, you're not going to have good communication," said Roemer. "Your devices will likely not connect in certain situations. Any number of things could happen." For those planning on traveling internationally, including to regions in Europe that border West Asian territories, Roemer suggested possibly postponing or reconsidering at this time, depending on the location.
Travelers can also enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ), a free service that allows U.S. citizens traveling and living abroad to connect with the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate. The federal program also sends out alerts in the event of an emergency, which can be sent to your email and any smart device.
US issues level 3 travel advisory to China amid safety concerns. Here's what to know

Are you thinking about traveling to China to visit or study abroad? The U.S. government suggests reconsidering your trip for now.
According to the U.S. Department of State , traveling to China is under a level 3 travel advisory , warning Americans to reconsider. The State Department has four warning levels. The fourth is “Do not travel.”
Is it safe to travel to China right now?
The U.S. is asking Americans to reconsider traveling to China due to various reasons, including concerns about health and safety, such as the prevalence of contagious diseases like COVID-19, as well as political tensions or security risks in certain regions.
As of April 12, there are some specific areas that the U.S. is asking people to reconsider travel to. Those areas include:
- Mainland China due to the arbitrary enforcement of local laws, including exit bans and the risk of wrongful detentions.
- Exercise increased caution when traveling to the Hong Kong SAR due to the arbitrary enforcement of local laws.
- Reconsider travel to the Macau SAR due to a limited ability to provide emergency consular services.
Additionally, the U.S. government may issue travel advisories based on factors like civil unrest, natural disasters, or other hazards that could affect travelers' well-being.
Americans detained in China
Mark Swidan — a man from Houston, Texas — has been detained in China for over 10 years on drug charges. According to The Texas Tribune , Swidan was detained in China in 2012 while on a trip looking for materials for his home and business in Houston. Chinese authorities arrested him after his driver and translator were found in possession of drugs. The driver blamed Swidan, who is accused of trafficking and manufacturing methamphetamine.
A review of Swidan’s case said there were no drugs on him or in his hotel. Last year, the Republic of China’s Jiangmen Intermediate Court denied Swidan’s appeal and upheld his death penalty with a two-year suspended death sentence.
Other Americans considered wrongfully detained include Chinese American businessman Kai Li from Long Island, N.Y., and California pastor David Lin.
What countries have a Level 3 travel warning?
- Trinidad & Tobago
- El Salvador
- South Sudan
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Papua New Guinea
- Saudi Arabia
What countries have a Level 4 travel warning?
- Afghanistan
- Central African Republic
- North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
- Burkina Faso
Traveling abroad? Here are some safety tips
U.S. citizens are encouraged to enroll in the State Department’s free Smart Traveler Enrollment Program and to prepare contingency plans for emergencies.
Safety tips if you're traveling outside the U.S.:
- Don't travel alone.
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Keep a low profile.
- Try not to be flashy.
- Avoid going to places at night, especially by yourself.
What Does the US State Department’s Worldwide Travel Advisory Actually Mean?
By Matt Ortile

On Thursday, October 19, the US State Department issued a worldwide travel advisory urging American citizens to “exercise increased caution” while overseas, “due to increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, [and] demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.”
The alert comes as the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas escalates in the Middle East. According to the New York Times , the advisory is also in response to protests worldwide that have, in some cases, led to “violent clashes at U.S. diplomatic compounds.” Throughout this week, protesters all over the world have held demonstrations in solidarity with Palestinian civilians in the Gaza Strip, calling for an end to Israel’s airstrikes and blockade of the territory, according to the AP . There are also protests in New York City calling for the release of Israeli hostages held by Hamas, and in Washington, DC calling for President Biden to press for an Israel-Hamas war cease-fire.
But what does the State Department's warning mean for anyone currently traveling, or with an upcoming trip? And does it actually suggest that you shouldn't travel… at all?
The short answer is no. But the advisory is a fair reminder to do exactly as it instructs, which is, for the time being, to be cautious while in environments unfamiliar to you.
“I don’t think the advisory is asking people to cancel their planned travel, but it is asking us all to be more alert when we are traveling,” says Mei Zhang, founder of the travel company WildChina and a member of Condé Nast Traveler ’s Global Advisory Board . “To me, that means being more alert in airports, avoiding super crowded iconic tourist places, not having your eyes glued to your phone while traveling. Look around.” As a precaution, Zhang recommends signing up for the State Department’s STEP program , as well as keeping your friends and family informed of your travel plans. “Just take a little extra caution,” she says. “This is a good idea regardless of the warning.”
As for changing travel plans, Catherine Heald, the co-founder and CEO of the travel company Remote Lands , says that many of her clients have canceled their upcoming travel plans to Israel, Egypt, Lebanon, and Jordan, among others, and pivoted their trips toward destinations geographically far away from active conflict zones. (Read more about navigating upcoming travel to countries bordering Israel and Gaza here .)
While reconsidering itineraries, Heald advises all travelers to not panic: “Look at the facts,” Heald says. “Study a map and avoid the danger zones. Buy travel insurance so if the situation spreads or escalates—and we all sincerely hope it won’t—you are covered.”
Luis Vargas, CEO and founder of travel operator Modern Adventure , recommends equipping yourself with information. Read up on the local news in the area of your intended destination to get a better sense of what’s actually happening on the ground. “In many cases, major events—both political and natural—are locally or regionally concentrated, meaning nearby areas can be unaffected,” Vargas says. For example, during and in the aftermath of the earthquake in Morocco in September , some communities experienced the worst of it, while Marrakech and other parts of the country were largely unaffected. An event in one part of a country or region does not mean it is happening everywhere in that country or region.
The last time the State Department issued a similar worldwide travel advisory was on August 2, 2022 , due to a "higher potential for anti-American violence given the death of Ayman al-Zawahiri,” the al-Qaeda leader killed on July 31 in a US drone strike in Afghanistan .
The US State Department’s travel advisories are most often specified by country. This month, the State Department has raised the travel advisory for Lebanon to the highest level, “Level 4: Do not travel;” the travel advisory for Israel and the West Bank has been raised to “Level 3: Reconsider travel.” Jordan and Egypt, which share borders with Israel, are at Level 2 and Level 3, respectively.
Wherever you are headed, take stock of a number of factors before you cancel or reschedule any travel plans: Consider your destination’s relative risk and your own personal risk tolerance—and that of your travel companions. Evaluate the level of access you will have to consulate services and information, as well as to your own personal safety network; if you have friends and family in the area of your destination, ask them for tips on how to stay safe and up-to-date on local news developments.
From there, make an informed decision about your travel plans that you—and your travel companions, if you have them—will be comfortable with. Traveling is an exercise in preparedness. As with all trips, make sure you feel ready to navigate whatever may come your way, no matter where you go. And of course, follow the worldwide travel advisory’s directive, brief and broad as it may be, to “stay alert in locations frequented by tourists” and to “enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive information and alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency overseas.”
Taking a long-term view, Vargas offers a reminder that tourism is an integral part of many economies—in the Middle East and all over the world. "When travel advisories are adopted, more broadly than intended, the effects can also be devastating over time,” says Vargas. If you aren't comfortable traveling now, consider postponing your trip rather than canceling it; and, if you must cancel, see if you can redirect some of your financial resources to organizations offering aid to people who need it most.
At the end of the day, “trust your gut,” Vargas says. “If you are feeling uneasy to the point where enjoyment of the trip is compromised, postponing may be the right choice for you.”
This is a developing story and will be updated with more information.
By signing up you agree to our User Agreement (including the class action waiver and arbitration provisions ), our Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement and to receive marketing and account-related emails from Traveller. You can unsubscribe at any time. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Airlines must cough up cancellation cash and can no longer hide fees under new federal rule
A federal rule announced Wednesday will require airlines to quickly give cash refunds — without lengthy arguments — to passengers whose flights have been canceled or seriously delayed, the Biden administration said.
“Passengers deserve to get their money back when an airline owes them — without headaches or haggling,” Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said in a statement.
The rule from the Transportation Department says passengers who decline other reimbursement like travel credits are to get cash refunds.

It applies when a flight is canceled or has a “significant change,” the administration said.A “significant change” includes when departure or arrival times are three or more hours different from the scheduled times for domestic flights or six hours for international flights, and when the airport is changed or connections are added, it said.
Passengers are also to get refunds when their baggage is 12 hours late in delivery for domestic flights.
The new rule comes after promises to hold airlines accountable after major disruptions that made travel hell for passengers, including the 2022 Southwest Airlines meltdown , which resulted in almost 17,000 significantly delayed or canceled flights and a missing baggage nightmare.
The Transportation Department said that the new rule means refunds are automatic and that "airlines must automatically issue refunds without passengers having to explicitly request them or jump through hoops."
Also announced Wednesday was a rule requiring airlines to more clearly disclose so-called junk fees upfront, such as surprise baggage or other fees, the department said.
It said that rule is expected to save fliers around $500 million a year.
The surprise fees are used so tickets look cheaper than they really are, and then fliers get the unwelcome surprise of fees on checked bags, carry-on bags or reservation changes — or even discounts that are advertised but apply to only part of the ticket price, officials said.
Airlines will also have to tell fliers clearly that their seats are guaranteed and that they don't have to pay extra to ensure they have seats for flights, according to the Transportation Department.
Airlines for America, an industry trade group, said that its member airlines “offer transparency and vast choice to consumers from first search to touchdown” and that they do offer cash refunds.
The 11 largest U.S. airlines returned $10.9 billion in cash refunds last year, an increase over $7.5 billion in 2019 but slightly down from $11.2 billion in 2022, the group said.
“U.S. airlines are providing more options and better services while ticket prices, including ancillary revenues, are at historic lows,” Airlines for America said.
Left out of the federal changes announced Wednesday are those involving "family seating fees," but the Transportation Department said in a statement that "DOT is planning to propose a separate rule that bans airlines from charging these junk fees."
Travelers have complained to the Transportation Department that children weren’t seated next to accompanying adults, including in some cases young children, department officials said last year.
Fees on bags specifically have made up an increasing amount of airline revenues, the Transportation Department said Wednesday in announcing the new rules.
A Transportation Department analysis found that airline revenue from baggage fees increased 30% from 2018 to 2022, while operating revenue — which is from the flights themselves — increased by only half that amount, the department said.
Jay Blackman is an NBC News producer covering such areas as transportation, space, medical and consumer issues.
Phil Helsel is a reporter for NBC News.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
5 facts about presidential travel abroad
American presidents and other world leaders frequently travel internationally, most commonly for conferences and bilateral meetings. This face-to-face diplomacy can offer insights into political priorities, partnerships and tensions, as well as key international issues.
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted international travel in 2020 and 2021, but diplomatic travel picked up significantly in 2022. Here are five facts about presidential travel abroad:
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to examine the international travel history of recent U.S. presidents and other heads of government through Jan. 20, 2023.
Dates and destinations of U.S. presidential travel prior to 2021 are from the U.S. Department of State’s Office of the Historian, which has recorded international presidential travel since 1901. Travel data for 2021 and 2022 was compiled from White House press briefings. Information on visits to Ukraine by other world leaders were independently verified through official government websites.
Only trips where the head of government met face-to-face with another head of government are included. For example, Biden’s trip to the UK for Queen Elizabeth II’s funeral is excluded as Biden did not hold any diplomatic meetings with the British prime minister or other world leaders. Visiting leaders were only counted if they were the head of government at the time of their visit. Depending on the country’s political system, “head of government” could mean president or prime minister, but not both. Heads of state, monarchs and interim leaders are excluded from the visiting leaders count.
U.S. President Joe Biden has traveled internationally less frequently than his last two predecessors did. Biden traveled to 17 places outside the United States in his first two years in office, visiting some more than once. He made six international trips in 2021, all of them to Europe. In 2022, he made 12 trips, including to Europe, the Asia-Pacific region and the Middle East. And in early 2023, Biden traveled to Mexico for the North American Leaders’ Summit.

All told, Biden’s international visit count trails those of former Presidents Donald Trump, who made 23 international trips to 20 places during his first two years in office, and Barack Obama, who made 32 trips to 24 places in the first two years of his presidency.
Biden’s first presidential trip abroad was to the United Kingdom, while Trump’s was to Saudi Arabia and Obama’s was to Canada. A president’s first trip is often used to signal the importance of a strategic alliance. On his trip to the UK in June 2021, Biden reaffirmed the U.S.-UK partnership and committed to close cooperation throughout his presidency. Typically, U.S. presidents visit a close ally on their inaugural trip: Canada was the first international destination for both Obama and Bill Clinton, while Mexico was the first destination for George W. Bush.
U.S. presidents have visited the UK the most in the past decade – a total of eight times. American presidents have worked closely with their British counterparts over the past decade, cooperating on issues from defense and counterterrorism to climate policy . Travel to the UK has largely centered around conferences and summits, but in 2019, Trump made a ceremonial state visit to the UK .
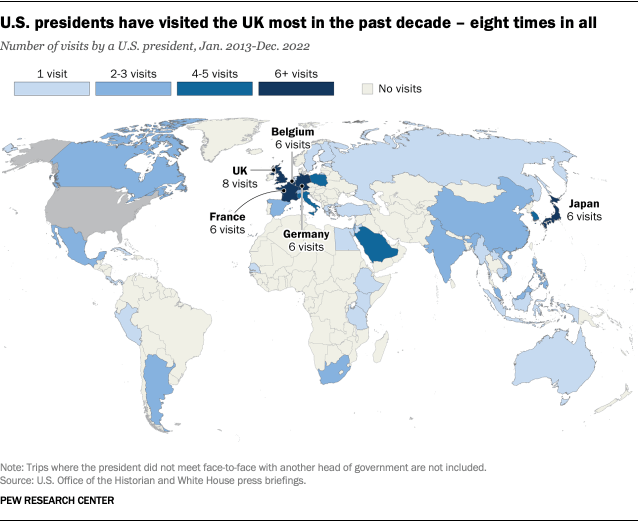
In the past decade of presidential travel, Belgium (home to NATO headquarters ), France, Germany and Japan are the second-most visited destinations, at six times each.
So far, Biden has made the most trips to the UK and Belgium – two each. (Biden’s additional visit to the UK to attend the funeral of Queen Elizabeth II is not included in this count, since he did not hold any diplomatic appointments.) Just as these two European allies stand out in Biden’s presidential travel thus far, France stands out in Trump’s administration and Germany stands out in Obama’s – they visited those respective countries four times while in office.
Biden is among 38 heads of government who have visited Ukraine since the beginning of the war there. Biden traveled to Kyiv as part of a surprise trip in February, days before the first anniversary of Russia’s invasion .
While many heads of government visiting Ukraine have come from neighboring countries or countries in Europe (such as Poland’s prime minister, who has visited five times since the beginning of the war) that is not always the case. For example, Guatemala’s President Alejandro Giammattei and Guinea-Bissau’s President Umaro Sissoco Embaló traveled to Ukraine in July 2022 and October 2022, respectively.
Biden hosted 28 heads of government at the White House as of the end of 2022. Foreign leaders come to the U.S. for events including conferences, summits and bilateral meetings. Among those to visit the White House in 2021 and 2022 were then-Prime Minister Magdalena Andersson of Sweden, who met with Biden to submit her country’s application for NATO membership ; Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, who traveled to the White House on his first known wartime trip abroad ; and French President Emmanuel Macron, whose trip marked the first state visit of Biden’s presidency . In fact, the president of France has been the first leader to make a state visit to the U.S. for the past three presidential terms, with Macron visiting Trump in April 2018 and his predecessor, François Hollande, visiting Obama in February 2014. In April 2023, Biden hosted the second state visit of his administration , meeting with South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol.
- International Affairs

Sarah Austin is a research assistant focusing on global attitudes research at Pew Research Center
A growing share of Americans have little or no confidence in Netanyahu
Fewer americans view the united nations favorably than in 2023, what are americans’ top foreign policy priorities, rising numbers of americans say jews and muslims face a lot of discrimination, younger americans stand out in their views of the israel-hamas war, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
US mandates new airline refund rules, fee disclosures
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by David Shepardson; editing by Miral Fahmy and Aurora Ellis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Dollar sags after US GDP and inflation surprise, except against yen
The U.S. dollar eased against most currencies on Thursday in tight seesaw trade after data showed the economy grew at a surprisingly slow pace and inflation came in hotter than expected in the first quarter, potentially tying the Federal Reserve's hands on easing interest rates in coming months.

Advertisement
Supported by
Hot Oceans Worsened Dubai’s Dramatic Flooding, Scientists Say
An international team of researchers found that heavy rains were intensifying in the region, though they couldn’t say for sure how much climate change was responsible.
- Share full article

By Raymond Zhong
Scenes of flood-ravaged neighborhoods in one of the planet’s driest regions stunned the world this month. Heavy rains in the United Arab Emirates and Oman submerged cars, clogged highways and killed at least 21 people. Flights out of Dubai’s airport, a major global hub, were severely disrupted.
The downpours weren’t a total surprise — forecasters had anticipated the storms several days earlier and issued warnings. But they were certainly unusual.
Here’s what to know.
Heavy rain there is rare, but not unheard-of.
On average, the Arabian Peninsula receives a scant few inches of rain a year, although scientists have found that a sizable chunk of that precipitation falls in infrequent but severe bursts, not as periodic showers. These rains often come during El Niño conditions like the ones the world is experiencing now.
U.A.E. officials said the 24-hour rain total on April 16 was the country’s largest since records there began in 1949 . And parts of the nation had already experienced an earlier round of thunderstorms in March.
Oman, with its coastline on the Arabian Sea, is also vulnerable to tropical cyclones. Past storms there have brought torrential rain, powerful winds and mudslides, causing extensive damage.
Global warming is projected to intensify downpours.
Stronger storms are a key consequence of human-caused global warming. As the atmosphere gets hotter, it can hold more moisture, which can eventually make its way down to the earth as rain or snow.
But that doesn’t mean rainfall patterns are changing in precisely the same way across every part of the globe.
In their latest assessment of climate research , scientists convened by the United Nations found there wasn’t enough data to have firm conclusions about rainfall trends in the Arabian Peninsula and how climate change was affecting them. The researchers said, however, that if global warming were to be allowed to continue worsening in the coming decades, extreme downpours in the region would quite likely become more intense and more frequent.
Hot oceans are a big factor.
An international team of scientists has made a first attempt at estimating the extent to which climate change may have contributed to April’s storms. The researchers didn’t manage to pin down the connection precisely, though in their analysis, they did highlight one known driver of heavy rain in the region: above-normal ocean temperatures.
Large parts of the Indian, Pacific and Atlantic Oceans have been hotter than usual recently, in part because of El Niño and other natural weather cycles, and in part because of human-induced warming .
When looking only at El Niño years, the scientists estimated that storm events as infrequent as this month’s delivered 10 percent to 40 percent more rain to the region than they would in a world that hadn’t been warmed by human activities. They cautioned, however, that these estimates were highly uncertain.
“Rainfall, in general, is getting more extreme,” said Mansour Almazroui, a climate scientist at King Abdulaziz University in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, and one of the researchers who contributed to the analysis.
The analysis was conducted by scientists affiliated with World Weather Attribution, a research collaboration that studies extreme weather events shortly after they occur. Their findings about this month’s rains haven’t yet been peer reviewed, but are based on standardized methods .
The role of cloud seeding isn’t clear.
The U.A.E. has for decades worked to increase rainfall and boost water supplies by seeding clouds. Essentially, this involves shooting particles into clouds to encourage the moisture to gather into larger, heavier droplets, ones that are more likely to fall as rain or snow.
Cloud seeding and other rain-enhancement methods have been tried across the world, including in Australia, China, India, Israel, South Africa and the United States. Studies have found that these operations can, at best, affect precipitation modestly — enough to turn a downpour into a bigger downpour, but probably not a drizzle into a deluge.
Still, experts said pinning down how much seeding might have contributed to this month’s storms would require detailed study.
“In general, it is quite a challenge to assess the impact of seeding,” said Luca Delle Monache, a climate scientist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in La Jolla, Calif. Dr. Delle Monache has been leading efforts to use artificial intelligence to improve the U.A.E.’s rain-enhancement program.
An official with the U.A.E.’s National Center of Meteorology, Omar Al Yazeedi, told news outlets that the agency didn’t conduct any seeding during the latest storms. His statements didn’t make clear, however, whether that was also true in the hours or days before.
Mr. Al Yazeedi didn’t respond to emailed questions from The New York Times, and Adel Kamal, a spokesman for the center, didn’t have further comment.
Cities in dry places just aren’t designed for floods.
Wherever it happens, flooding isn’t just a matter of how much rain comes down. It’s also about what happens to all that water once it’s on the ground — most critically, in the places people live.
Cities in arid regions often aren’t designed to drain very effectively. In these areas, paved surfaces block rain from seeping into the earth below, forcing it into drainage systems that can easily become overwhelmed.
One recent study of Sharjah , the capital of the third-largest emirate in the U.A.E., found that the city’s rapid growth over the past half century had made it vulnerable to flooding at far lower levels of rain than before.
Omnia Al Desoukie contributed reporting.
Raymond Zhong reports on climate and environmental issues for The Times. More about Raymond Zhong

COMMENTS
TRAVEL ADVISORIES AND ALERTS: THE DETAILS ... Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad. Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome. ... entities on this page are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as the U.S. Department of State or U.S. government ...
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list. Places With a Level 4 Travel ...
Office of the Spokesperson. April 19, 2021. State Department Travel Advisory Updates. In order to provide U.S. travelers detailed and actionable information to make informed travel decisions, the Department of State regularly assesses and updates our Travel Advisories, based primarily on the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC ...
Please enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive alerts and be located in an emergency. Please call 1 (888) 407-4747 (U.S. and Canada) or 1 (202) 501-4444 (overseas) or contact the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate. As a first step in planning any trip abroad, check the Travel Advisories for your intended destination.
× External Link. You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State. Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein.
Below are travel alerts and airport wait times from the Department of Homeland Security and other federal agencies. Airport Security Checkpoint Wait Times from TSA. Airport Wait Times from U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) Current International Travel Warnings from the Department of State. Health Alerts from the Centers for Disease ...
U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories. COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
If entering the United States by air or sea, you will receive en route a CBP Declaration Form 6059B and, if you are not from a Visa Waiver Program country, a CBP Form I-94 Arrival/Departure Record. Complete all sections of the forms. Review the CBP Inspection Process before your travel. Listed below are general steps for the inspection process.
The CDC's own travel health notices also use a four-tier warning system. For many countries newly added to the State Department's Level 4 list, the CDC cites "a very high level of COVID-19."
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
It's part of a system of travel warnings that's been around in some form since 1978, designed to help citizens assess how safe a destination might be at a given time. The current version of ...
The Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) is a free service to allow U.S. citizens and nationals traveling and living abroad to enroll their trip with the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate. Receive important information from the Embassy about safety conditions in your destination country, helping you make informed decisions about your travel ...
What to Know: U.S. Travel Restrictions. Lauren Hard 📍 Reporting from New Jersey. Reuters. The new policy ends an 18-month ban on nonessential travel from 33 countries, including China, Brazil ...
141. The State Department on Thursday issued a rare "worldwide caution" advisory to all Americans overseas, urging them to "exercise increased caution due to the potential for violence and ...
However, if the CDC raises a country's COVID-19 THN to a Level 4, the State Department's Travel Advisory for that country will also be raised to a Level 4: Do Not Travel due to COVID-19. This update will leave approximately 10% of all Travel Advisories at Level 4: Do Not Travel. This 10% includes Level 4 Travel Advisories for all risk ...
Arizona Republic. 0:00. 2:08. The U.S. State Department announced a global travel advisory for those traveling internationally due to the ongoing conflict in the Middle East. The agency cited ...
The U.S. government suggests reconsidering your trip for now. According to the U.S. Department of State , traveling to China is under a level 3 travel advisory , warning Americans to reconsider.
Travel Advisories include a level for each country, ranging from Level 1: Exercise Normal Precautions to Level 4: Do Not Travel. Each Travel Advisory also includes specific risk indicators to provide additional context for the advice level. Risk indicators include C for crime, T for terrorism, and U for civil unrest, among others.
The US government has sent out a rare global travel warning—we ask experts how to interpret it. On Thursday, October 19, the US State Department issued a worldwide travel advisory urging ...
Blinken will raise with Chinese officials steps they must take before the State Department lowers its Level 3 travel warning for American tourists, which urges Americans to "reconsider travel ...
Assistance: U.S. Embassy Nassau, The Bahamas #42 Queen Street, Nassau 1-242-322-1181 [email protected] U.S. Embassy Nassau webpage: Services for U.S. and Local Citizens - U.S. Citizen Services - U.S. Embassy in The Bahamas (usembassy.gov) For U.S. Citizens in an Emergency: Call State Department - Consular Affairs at: 1-888-407-4747 ...
The 11 largest U.S. airlines returned $10.9 billion in cash refunds last year, an increase over $7.5 billion in 2019 but slightly down from $11.2 billion in 2022, the group said.
Marine One costs between $16,700 and almost $20,000 per hour to operate, according to Pentagon data for the 2022 budget year. Air Force One is even more expensive: roughly $200,000 per hour. But ...
Biden traveled to 17 places outside the United States in his first two years in office, visiting some more than once. He made six international trips in 2021, all of them to Europe. In 2022, he made 12 trips, including to Europe, the Asia-Pacific region and the Middle East. And in early 2023, Biden traveled to Mexico for the North American ...
Item 1 of 2 Passengers line up to check bags before their flights at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. June 28, 2022.
April 18, 2024. Leer en español. Scenes of flood-ravaged neighborhoods in one of the planet's driest regions have stunned the world this week. Heavy rains in the United Arab Emirates and Oman ...