
Sustainability Success


10 Sustainable Tourism Examples
Tourism is fun; you get to meet new people, learn about new cultures and build beautiful memories that will last forever. However, as a tourist, have you ever paused to think that the areas you visit are actually people’s homes? And, of course, you wouldn’t want to ruin the homes and environments of other people, right?
This is where green tourism comes in. Sustainable tourism factors in the economic , environmental , and social aspects of tourism, ensuring that it does not have any negative consequences on the environment. In addition to protecting the environment, sustainable tourism also protects the local communities and businesses.
In this article, I will go through 10 sustainable tourism examples around the world!
Here are 10 remarkable examples of sustainable tourism for environmentally conscious persons, including both luxury travel and budget options! Responsible tourism examples:
1. Feynan Ecolodge – Jordan
The first ecolodge of its kind in Jordan, Feynan Ecolodge was designed to reflect the architectural style of the ancient caravanserai and was built in 2005 by the Royal Society for the Conservation of Nature.
In 2009, EcoHotels took over the management and operation of the lodge, offering travelers an opportunity to experience the wild nature of Jordan, meet its natives and explore its ancient history. All of this with minimal impact on the environment!
Feynan Ecolodge is found deep in the Dana Biosphere Nature Reserve; a mountainous place located in Jordan.
It is one of the best examples of sustainable tourism globally, with the National Geographic Traveler Magazine ranking it among the top 25 ecolodges globally.
The lodge has partnered with the Royal Society for the Conservation of Nature to provide solar-powered accommodation. The use of solar as the main source of energy greatly reduces the carbon footprint released and led them to win the World Responsible Tourism Award in 2019. Therefore, guests who use these accommodation services play a role in protecting the environment.
Dana Biosphere Reserve is one of the largest nature reserves in Jordan. It was established in 1989 to protect the area’s diverse wildlife, geology, and landscape. The reserve encompasses four different bio-geographical zones: Mediterranean, Irano-Turanian, Saharo-Arabian, and Sudanian. It is home to 800 plant species and 449 animal species, including several globally threatened/endangered species.

The Bedouin people are the original inhabitants of Jordan and are considered the backbone of the country. The Bedouin culture has transformed over time, as many people have left the traditional lifestyle and migrated to cities. However, there is still a small community of Bedouins who continue to live in the Feynan area, and geotourism has been helpful in preserving this culture.
As you can see, the Feynan Ecolodge is acting on all three pillars of sustainability (or the 3 E’s of sustainability ) by supporting the local culture (promoting cultural sustainability ), preserving the environment, and improving the local economy.
The Feynan Ecolodge is without a doubt one of the great examples of sustainable tourism, as well as an example of environmental responsibility !
2. Mdumbi Backpackers Hostel – South Africa
The Mdumbi Backpackers Hostel is specifically designed for people who like sustainable tourism.
Mdumbi Backpackers is a community-driven backpacker hostel located in the Transkei with panoramic views of the coast. They promote community involvement and sustainable eco-tourism.
The nearby beach was voted the best beach in Southern Africa, with world-class surf and incredible hiking and exploration opportunities, Mdumbi is a hidden gem not to be missed.
It provides an ideal base for whale-watching, hiking, and doing other outdoor tourist activities. The hostel uses multiple eco-friendly tools and practices, all of which are aimed to encourage more sustainable green tourism.
For example, all the accommodations use solar power and include a waste management system that is sustainable.
Besides, the hostel has a special ownership model, so that even local employees can own shares in the hostel.
3. Six Senses Resort – Fiji
The Six Senses Resort in Fiji resort is located on Malolo island at a secluded bay. The 5-star luxury resort can be said to meet all the sustainable tourism guidelines and principles.
Six Senses Fiji is committed to sustainability , with 100% solar power, programs to conserve energy and rainwater, make high-quality drinking water, and locally grow organic produce.
For example, Six Senses Resort uses solar energy to power the entire resort . Also, it established rain capture and efficient water filtration systems that help to reduce the usage of plastic bottles.
The resort has one of the largest off-grid solar installations in the Southern Hemisphere, using batteries to power the resort and the desalination plant.
In addition, the resort encourages recycling and re-using of materials, minimizing overall wastage and the release of harmful gases due to wastage.
Furthermore, the Six Senses Resort greatly supports different causes and programs aimed to help the local communities lead a more sustainable life.
For example, the resort works with Rise Beyond the Reef , an NGO that teaches women in remote communities to create marketable goods using traditional skills.
The Six Senses Resort in Fiji is clearly an amazing luxury eco-tourism example and a great option for those who can afford it!
4. Bom Bom Water Project – Príncipe Island – Africa
This water project is controlled and managed by the Bom Bom Resort . This luxury resort can be found in Príncipe and Sao Tome, an island that is located off the western coast of Gabon, West Africa.
This resort has a recycling scheme that involves replacing used water bottles with a stainless steel bottle (known as the “Biosphere Bottle”) that can be refilled.
So far, this recycling scheme has led to the removal of over 300,000 plastic bottles; a result that has contributed to a cleaner and more sustainable island.
More so, the Bom Bom Resort supports the water purification fountains and recycling projects established by UNESCO and the Príncipe Island World Biosphere Reserve.
It has established 13 water stations in different parts of the island, where tourists can refill their Biosphere Bottles. Besides, the resort encourages tourists and guests to take part in the sustainable programs available.
If you are interested in visiting this luxury eco-tourism option, then you can check a detailed review by some of their guests!
5. Inkaterra Hotels – Peru
Inkaterra Hotels is a 100% carbon-neutral organization with 47 years of experience in practicing sustainable tourism with its eco-lodges. Not bad for those luxury ecolodge options!
These hotels can be found in different parts of Peru, such as Tambopata, Machu Picchu Pueblo, Cusco, and Sacred Valley.
They were crowned by Greeninitiative , an organization endorsed by the United Nations (UN), as the very first “Climate Positive” hotel brand in the world.
All the lodges in these hotels are built using locally-sourced products; eliminating any transportation which would’ve led to a high carbon footprint.
Besides, the lodges are built in such a way that they do not ruin the environment or cause permanent damage.
Also, the Inkaterra Hotels provide support to education, scientific research, and local efforts aimed to conserve the environment and boost the economic condition of the locals.
Inkaterra Hotels is a great example of ecotourism , because the organization is truly aiming at sustainable development, by acting on all the 3 Ps of sustainability : people, profit, planet!
6. Atlantis Submarines – Hawaii
Sustainable tourism is not just about ecolodges, but also about experiences. Atlantis submarines in Hawaii offers the possibility to explore the submarine world in a more eco-friendly way.
The Atlantis Submarines are located in three different regions in Hawaii. They provide the thrill of diving up to 30 meters underwater to tourists and adventurous people.
Having been operational since 1988, the submarines are powered by environmental-friendly batteries. Therefore, they do not emit any pollutants or release harmful greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Furthermore, all the Atlantis Submarines move quietly via the water without causing any environmental disturbance.
The company has also installed environmental-friendly artificial reefs in two different locations; these reefs help to re-establish healthy habitats for Marine life and fish.
Indeed, the Atlantis Submarines provide an eco-friendly way of exploring the deep sea.
7. BEES Elephant Sanctuary – Thailand
The BEES Elephant Sanctuary is located in rural Thailand in the Maechaem district. Most animal sanctuaries are considered unsustainable since most of the activities only function to exploit the animals kept there. However, the BEES sanctuary is different from these other sanctuaries, since it takes a different approach that aims to improve sustainability.
BEES was founded in 2011 by Burm Pornchai Rinkaew and Emily Rose McWilliam.
Emily traveled to Thailand as a teen in early 2009 and was appalled by the living conditions and hardships elephants experienced working in tourist camps. She made a promise to the elephants to do something about their plight and, at just 18 years of age, co-founded BEES with her partner Burm.
BEES provides a safe, natural home for elephants to just BE elephants and also rescues and provides care for local cats and dogs.
This sanctuary has adopted a sustainable approach known as the “No Contact – Hands Off Approach.” The hands-off policy prevents humans from forcing elephants into contact.
Also, all the elephants in the sanctuary have either been rented from the owners, retired, or rescued in the wild, in turn giving them a break from all the tough work that they do.
More so, the BEES sanctuary has set up different programs that allow people to work for the sanctuary, providing them with the opportunity to give back to nature.
8. Summit Expeditions & Nomadic Experience (SENE) – Tanzania
SENE is a tour operator company based in Tanzania . It offers a wide range of tours, such as around Zanzibar island, climbing up to the top of Mt. Kilimanjaro, Mbahe farm cottages , and other wildlife safaris. Since the company was established in 1998, it has been offering sustainable tours to tourists and jobs to the locals.
The SENE tour company is a member of “Leave No Trace”; a set of ethics whose main goal is to promote a sustainable world that will support many generations to come.
Also, they use portable toilets whose disposal systems are biodegradable.
In addition, the company encourages tourists to take alternative routes to their destination, so that they give the busier routers a chance to recuperate.
All these sustainable activities help to promote a healthier local environment in Tanzania.
9. Wavelength tours – Australia
Wavelength is a family-operated firm with a team made of local marine biologists or people who have spent most of their lives on the barrier reef. It provides snorkeling tours on the great barrier reef of Australia. However, unlike other similar snorkeling tour firms, Wavelength offers more environmentally friendly tours.
For example, the company takes only a small group of people for snorkeling. They also have a “no-touch” policy that prevents unnecessary disturbance of nature.
Also, all tourists are recommended to use environmental-friendly sunscreen that won’t have any negative impact on the corals and marine life.
All these sustainable solutions help to protect the great barrier reef, ensuring that it is not put under much pressure, which would in turn have significant effects on the environment.
Of course there is still more that could be done, but this company is surely doing some steps in the right direction.
10. Trash Hero – Thailand/Global
Trash Hero is a volunteer-led movement whose mission is to drive positive change within communities all over the world. It does so by encouraging communities globally to pick up rubbish and prevent plastic waste being dispersed in the local environment.
While Trash Hero was first started in Thailand, they have been establishing in 12 more countries.
They combine the effort of local communities and eco-friendly tourists by encouraging both parties to clean rubbish wherever they see it and work together to create a healthy, trash-free world.
Trash Hero also produces steel bottles that are more sustainable; the movement sells these bottles and also works with other businesses to make them more sustainable and greener.
Why is Sustainable Tourism Important?
The main goal of sustainable tourism is to minimize the negative impact that tourism has on the environment and local communities. It ensures that all resources are used in an optimal way, preventing over-consumption and wastage. In turn, sustainable tourism helps to preserve the natural world, as well as local traditions, culture and heritage.
Besides, sustainability tourism provides social and economic benefits to the local communities. This contributes to a mutually beneficial relationship of “give and take” where both locals and tourists gain equal benefits.
What’s even better, the sustainable activities involved with this form of tourism ensure the long-term future of travel, such that the environmental, economic, and social benefits are enjoyed now and by many more generations to come.
Sustainable tourism is not only good for business; it is also good for the environment, ensuring sustainability now and in the future. Therefore, unless you want to promote an unsustainable world, you need to ditch mass tourism and apply to tours that support sustainable tourism.
However, did you know that soon we may be getting also new ways to travel sustainably and enjoy an eco-friendly luxury vacation on the water? This may soon become available thanks to the new solar catamarans that are starting to become more mainstream!
Here are the 10 sustainable tourism examples I went through in this article:
- Feynan Ecolodge – Jordan
- Mdumbi Backpackers Hostel – South Africa
- Six Senses Resort – Fiji
- Bom Bom Water Project – Príncipe Island – Africa
- Inkaterra Hotels – Peru
- Atlantis Submarines – Hawaii
- BEES Elephant Sanctuary – Thailand
- Summit Expeditions & Nomadic Experience (SENE) – Tanzania
- Wavelength tours – Australia
- Trash Hero – Thailand/Global
I hope you enjoyed learning about those responsible tourism examples, and if you are not sure where to start, simply pick one of the 10 sustainable tourism examples discussed above. These destinations will not only give you the best time of your life, but also give you the opportunity to make a positive contribution to the world while you’re having fun!
Related topics
- Mexico Ecotourism (Discover 10 Hidden Gems!)
- The Magic Of Ecotourism In Belize (Unmissable Experiences!)

Hand-Picked Top-Read Stories

Vision Zero: A Comprehensive Guide
- Environment
- Transportation

Advantages of Public Transport: 20 Reasons to Make the Shift Today
- Planet earth

CNG Fuel: A Comprehensive Guide
Trending tags.
- Zoning Laws
- Zero-waste living
- zero-waste kitchen
- workplace safety
- workplace charging
- WineTasting
- Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable Tourism Practices and Destinations: Examples from Around the World
Sustainable Tourism Practices: Sustainable tourism is a growing trend in the travel industry that focuses on minimizing the environmental and social impact of tourism while providing economic benefits to local communities. From eco-friendly accommodations to responsible travel practices, there are many ways that tourism can be made more sustainable. Around the world, destinations and businesses are implementing sustainable tourismthat support conservation, reduce carbon emissions, and promote local cultural heritage. These efforts not only benefit the planet, but also provide a unique and authentic travel experience for visitors. In this context, we will explore some of the sustainable tourism and destinations from around the world that are leading the way in promoting responsible and ethical tourism.
Here are 40 examples of sustainable tourism and destinations from around the world:
- The Galapagos Islands, Ecuador – A protected wildlife sanctuary that limits visitor numbers to prevent environmental damage and promote sustainable tourism.
- Costa Rica – A country that has made a strong commitment to sustainable tourism, with a focus on eco-tourism, community-based tourism, and conservation efforts.
- Bhutan – A country that measures its economic success through a Gross National Happiness index, which includes the protection of the environment and cultural heritage.
- Norway – A country that is known for its sustainable tourism, including eco-friendly transportation, green energy, and sustainable tourism certification programs.
- The Netherlands – A country that is promoting sustainable tourism through initiatives such as green hotels, bike-friendly cities, and nature conservation programs.
- New Zealand – A country that has a strong focus on sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism, conservation efforts, and responsible travel practices.
- The Amazon Rainforest, Brazil – A region that has adopted sustainable tourism to promote conservation and support local communities.
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia – A protected marine park that promotes sustainable tourism, such as reducing carbon emissions and protecting the natural environment.
- Kenya – A country that has implemented sustainable tourism, including wildlife conservation, community-based tourism, and eco-friendly lodges.
- Iceland – A country that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-friendly transportation, renewable energy, and eco-certification programs.
- South Africa – A country that is known for its conservation efforts, including wildlife protection and community-based tourism.
- The Azores, Portugal – A group of islands that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-tourism, whale watching, and nature conservation programs.
- The Serengeti, Tanzania – A protected wildlife sanctuary that promotes responsible tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Cook Islands, Pacific Ocean – A group of islands that is committed to sustainable tourism, including protecting the environment and supporting local communities.
- Thailand – A country that has implemented sustainable practices, including community-based tourism, wildlife conservation, and responsible travel.
- The Faroe Islands, Denmark – A group of islands that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-friendly transportation, sustainable seafood, and nature conservation programs.
- The Lake District, England – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Annapurna Region, Nepal – A region that is promoting sustainable tourism through community-based tourism, conservation efforts, and responsible trekking practices.
- The Maasai Mara, Kenya – A protected wildlife reserve that promotes sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Blue Mountains, Australia – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- Guna Yala, Panama – A protected indigenous territory that promotes sustainable tourism, such as supporting traditional livelihoods and preserving cultural heritage.
- The Isle of Eigg, Scotland – An island that is promoting sustainable tourism through renewable energy, eco-friendly accommodations, and community-based tourism initiatives.
- The San Blas Islands, Panama – A group of islands that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-tourism, community-based tourism, and responsible travel practices.
- The Burren, Ireland – A protected national park that promotes sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Bay of Fundy, Canada – A protected marine park that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Lofoten Islands, Norway – An archipelago that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-friendly transportation, responsible fishing, and community-based tourism initiatives.
- The Tongariro National Park, New Zealand – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Danube Delta, Romania – A protected wetland that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-tourism and responsible travel practices.
- The Douro Valley, Portugal – A region that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-tourism, responsible wine tourism, and community-based tourism initiatives.
- The Lake Titicaca, Peru/Bolivia – A protected lake that promotes sustainable tourism, such as preserving cultural heritage and supporting traditional livelihoods.
- The Everglades, United States – A protected wetland that promotes sustainable tourism, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Cinque Terre, Italy – A protected coastal area that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Mekong Delta, Vietnam – A region that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-tourism, responsible travel practices, and community-based tourism initiatives.
- The Lake District, Chile – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Sinharaja Forest Reserve , Sri Lanka – A protected rainforest that promotes sustainable tourism, such as eco-tourism and responsible travel practices.
- The Jasper National Park, Canada – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Arctic, various countries – A region that is promoting sustainable tourism through eco-tourism, responsible travel practices, and nature conservation programs.
- The Torres del Paine National Park, Chile – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting local communities.
- The Sagarmatha National Park, Nepal – A protected national park that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-tourism and responsible trekking practices.
- The Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve, Costa Rica – A protected cloud forest that promotes sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-tourism and nature conservation programs.
These are just a few more examples of the many destinations and businesses around the world that are adopting sustainable tourism. With a growing focus on responsible and ethical tourism, sustainable tourism is becoming an increasingly important industry worldwide.
Similar Articles
- Green Hiking
- How To Save Water
- What is an Eco Lodge?
Frequently Asked Questions About Sustainable Tourism Practices
What is sustainable tourism?
Sustainable tourism is a form of tourism that focuses on minimizing the environmental and social impact of travel while providing economic benefits to local communities.
What are some sustainable tourism practices?
Some sustainable tourism practices include supporting conservation efforts, reducing carbon emissions, promoting local cultural heritage, and supporting local communities through community-based tourism initiatives.
Why is sustainable tourism important?
Sustainable tourism is important because it helps to preserve natural and cultural resources, provides economic benefits to local communities, and promotes responsible and ethical travel practices.
How can travelers practice sustainable tourism?
Travelers can practice sustainable tourism by supporting eco-friendly accommodations, engaging in responsible travel practices, supporting local communities, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
What are some examples of sustainable tourism destinations?
Some examples of sustainable tourism destinations include national parks, protected areas, eco-tourism lodges, and community-based tourism initiatives.
How can tourism businesses implement sustainable tourism practices?
Tourism businesses can implement sustainable practices by reducing their carbon emissions, supporting local communities, promoting conservation efforts, and adopting eco-friendly practices.
What is community-based tourism?
Community-based tourism is a form of tourism that involves local communities in the tourism industry, providing economic benefits while preserving local culture and traditions.
What is responsible tourism?
Responsible tourism is a form of tourism that focuses on minimizing the environmental and social impact of travel while providing economic benefits to local communities and promoting cultural awareness.
What is the difference between sustainable tourism and ecotourism?
Sustainable tourism is a broader concept that encompasses all forms of tourism that are socially, economically, and environmentally responsible, while ecotourism is a specific form of tourism that focuses on nature-based experiences that support conservation efforts.
How does sustainable tourism benefit local communities?
Sustainable tourism benefits local communities by providing economic benefits through job creation and supporting local businesses, while also preserving cultural heritage and traditions.
How can tourists ensure they are practicing sustainable tourism?
Tourists can ensure they are practicing sustainable tourism by choosing eco-friendly accommodations, engaging in responsible travel practices, supporting local communities, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
What role do governments play in promoting sustainable tourism?
Governments play an important role in promoting sustainable tourism by establishing policies and regulations that support conservation efforts, promoting sustainable practices, and providing funding for sustainable tourism initiatives.
What are some challenges to implementing sustainable tourism practices?
Some challenges to implementing sustainable tourism practices include the high cost of implementing eco-friendly practices, lack of awareness among tourists, and limited resources in developing countries.
What is the role of tourism businesses in promoting sustainable tourism?
Tourism businesses play a critical role in promoting sustainable tourism by adopting eco-friendly practices, supporting conservation efforts, and engaging with local communities to ensure their economic benefits are sustainable.
What is the impact of sustainable tourism on the environment?
Sustainable tourism aims to minimize the impact of tourism on the environment by reducing carbon emissions, supporting conservation efforts, and promoting eco-friendly practices. This can have a positive impact on the environment by preserving natural resources and reducing pollution.
What is the role of tourists in promoting sustainable tourism?
Tourists have a crucial role to play in promoting sustainable tourism by supporting eco-friendly accommodations, engaging in responsible travel practices, supporting local communities, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
What is the role of local communities in sustainable tourism?
Local communities play a vital role in sustainable tourism by providing unique cultural experiences, supporting conservation efforts, and benefitting from the economic opportunities that tourism can bring. Sustainable tourism initiatives often involve working with local communities to ensure their voices are heard and their needs are met.
How can sustainable tourism help preserve cultural heritage?
Sustainable tourism can help preserve cultural heritage by supporting local cultural practices and traditions, promoting cultural awareness, and providing economic benefits to local communities. In doing so, it helps to maintain and celebrate cultural diversity and promote the value of cultural heritage.
What is the impact of sustainable tourism on the economy?
Sustainable tourism can have a positive impact on the economy by providing job opportunities, supporting local businesses, and promoting economic growth in tourism-dependent communities. It can also encourage investment in infrastructure and services, leading to long-term economic benefits.
What is the role of education in promoting sustainable tourism?
Education plays a critical role in promoting sustainable tourism by raising awareness among tourists, tourism businesses, and local communities. It can help to promote best practices, encourage responsible travel behavior, and foster a culture of sustainability.
How can technology be used to promote sustainable tourism?
Technology can be used to promote sustainable tourism by supporting digital platforms that provide information and resources for sustainable travel, reducing the need for paper-based materials and promoting more efficient and eco-friendly travel methods.
What is the role of sustainable tourism in climate change mitigation?
Sustainable tourism can contribute to climate change mitigation by promoting low-carbon travel options, reducing carbon emissions, and supporting conservation efforts that help to mitigate the impact of climate change on natural resources.
How can sustainable tourism be measured?
Sustainable tourism can be measured using a range of indicators, such as carbon emissions, waste reduction, water conservation, and economic impact. There are also several certification programs and sustainability standards that can be used to assess the sustainability of tourism businesses and destinations.
How can travelers support sustainable tourism initiatives?
Travelers can support sustainable tourism initiatives by choosing eco-friendly accommodations, engaging in responsible travel practices, supporting local communities, and minimizing their carbon footprint. They can also seek out sustainable tourism certification programs and support businesses that are committed to sustainable tourism practices.
- Carbon emissions
- community-based tourism
- conservation
- Cultural Heritage
- Eco-friendly travel
- ethical tourism
- Local Communities
- Responsible Tourism
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Previous Post

Benefits of Ecotourism: How Responsible Travel Can Make a Positive Impact

20 Sustainable Tourism Practices and Destinations in India to Visit Now
Related posts.

Impact of Tourism Pressure: A Closer Look at Environmental and Sociocultural Effects

Khajuraho Sustainable Tourism: A Guide to Responsible Travel

- Climate Crisis
The Profound Effects of Climate Change and How to Mitigate Them
What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
Sustainable management and socioeconomic, cultural, and environmental impacts are the four pillars of sustainable tourism
- Chapman University
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/HaleyMast-2035b42e12d14d4abd433e014e63276c.jpg)
- Harvard University Extension School
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
What Makes Tourism Sustainable?
The role of tourists, types of sustainable tourism.
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved by protecting natural environments and wildlife when developing and managing tourism activities, providing only authentic experiences for tourists that don’t appropriate or misrepresent local heritage and culture, or creating direct socioeconomic benefits for local communities through training and employment.
As people begin to pay more attention to sustainability and the direct and indirect effects of their actions, travel destinations and organizations are following suit. For example, the New Zealand Tourism Sustainability Commitment is aiming to see every New Zealand tourism business committed to sustainability by 2025, while the island country of Palau has required visitors to sign an eco pledge upon entry since 2017.
Tourism industries are considered successfully sustainable when they can meet the needs of travelers while having a low impact on natural resources and generating long-term employment for locals. By creating positive experiences for local people, travelers, and the industry itself, properly managed sustainable tourism can meet the needs of the present without compromising the future.
What Is Sustainability?
At its core, sustainability focuses on balance — maintaining our environmental, social, and economic benefits without using up the resources that future generations will need to thrive. In the past, sustainability ideals tended to lean towards business, though more modern definitions of sustainability highlight finding ways to avoid depleting natural resources in order to keep an ecological balance and maintain the quality of environmental and human societies.
Since tourism impacts and is impacted by a wide range of different activities and industries, all sectors and stakeholders (tourists, governments, host communities, tourism businesses) need to collaborate on sustainable tourism in order for it to be successful.
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) , which is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of sustainable tourism, and the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) , the global standard for sustainable travel and tourism, have similar opinions on what makes tourism sustainable. By their account, sustainable tourism should make the best use of environmental resources while helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity, respect the socio-culture of local host communities, and contribute to intercultural understanding. Economically, it should also ensure viable long-term operations that will provide benefits to all stakeholders, whether that includes stable employment to locals, social services, or contributions to poverty alleviation.
The GSTC has developed a series of criteria to create a common language about sustainable travel and tourism. These criteria are used to distinguish sustainable destinations and organizations, but can also help create sustainable policies for businesses and government agencies. Arranged in four pillars, the global baseline standards include sustainable management, socioeconomic impact, cultural impacts, and environmental impacts.
Travel Tip:
The GSTC is an excellent resource for travelers who want to find sustainably managed destinations and accommodations and learn how to become a more sustainable traveler in general.
Environment
Protecting natural environments is the bedrock of sustainable tourism. Data released by the World Tourism Organization estimates that tourism-based CO2 emissions are forecast to increase 25% by 2030. In 2016, tourism transport-related emissions contributed to 5% of all man-made emissions, while transport-related emissions from long-haul international travel were expected to grow 45% by 2030.
The environmental ramifications of tourism don’t end with carbon emissions, either. Unsustainably managed tourism can create waste problems, lead to land loss or soil erosion, increase natural habitat loss, and put pressure on endangered species . More often than not, the resources in these places are already scarce, and sadly, the negative effects can contribute to the destruction of the very environment on which the industry depends.
Industries and destinations that want to be sustainable must do their part to conserve resources, reduce pollution, and conserve biodiversity and important ecosystems. In order to achieve this, proper resource management and management of waste and emissions is important. In Bali, for example, tourism consumes 65% of local water resources, while in Zanzibar, tourists use 15 times as much water per night as local residents.
Another factor to environmentally focused sustainable tourism comes in the form of purchasing: Does the tour operator, hotel, or restaurant favor locally sourced suppliers and products? How do they manage their food waste and dispose of goods? Something as simple as offering paper straws instead of plastic ones can make a huge dent in an organization’s harmful pollutant footprint.
Recently, there has been an uptick in companies that promote carbon offsetting . The idea behind carbon offsetting is to compensate for generated greenhouse gas emissions by canceling out emissions somewhere else. Much like the idea that reducing or reusing should be considered first before recycling , carbon offsetting shouldn’t be the primary goal. Sustainable tourism industries always work towards reducing emissions first and offset what they can’t.
Properly managed sustainable tourism also has the power to provide alternatives to need-based professions and behaviors like poaching . Often, and especially in underdeveloped countries, residents turn to environmentally harmful practices due to poverty and other social issues. At Periyar Tiger Reserve in India, for example, an unregulated increase in tourists made it more difficult to control poaching in the area. In response, an eco development program aimed at providing employment for locals turned 85 former poachers into reserve gamekeepers. Under supervision of the reserve’s management staff, the group of gamekeepers have developed a series of tourism packages and are now protecting land instead of exploiting it. They’ve found that jobs in responsible wildlife tourism are more rewarding and lucrative than illegal work.
Flying nonstop and spending more time in a single destination can help save CO2, since planes use more fuel the more times they take off.
Local Culture and Residents
One of the most important and overlooked aspects of sustainable tourism is contributing to protecting, preserving, and enhancing local sites and traditions. These include areas of historical, archaeological, or cultural significance, but also "intangible heritage," such as ceremonial dance or traditional art techniques.
In cases where a site is being used as a tourist attraction, it is important that the tourism doesn’t impede access to local residents. For example, some tourist organizations create local programs that offer residents the chance to visit tourism sites with cultural value in their own countries. A program called “Children in the Wilderness” run by Wilderness Safaris educates children in rural Africa about the importance of wildlife conservation and valuable leadership development tools. Vacations booked through travel site Responsible Travel contribute to the company’s “Trip for a Trip” program, which organizes day trips for disadvantaged youth who live near popular tourist destinations but have never had the opportunity to visit.
Sustainable tourism bodies work alongside communities to incorporate various local cultural expressions as part of a traveler’s experiences and ensure that they are appropriately represented. They collaborate with locals and seek their input on culturally appropriate interpretation of sites, and train guides to give visitors a valuable (and correct) impression of the site. The key is to inspire travelers to want to protect the area because they understand its significance.
Bhutan, a small landlocked country in South Asia, has enforced a system of all-inclusive tax for international visitors since 1997 ($200 per day in the off season and $250 per day in the high season). This way, the government is able to restrict the tourism market to local entrepreneurs exclusively and restrict tourism to specific regions, ensuring that the country’s most precious natural resources won’t be exploited.
Incorporating volunteer work into your vacation is an amazing way to learn more about the local culture and help contribute to your host community at the same time. You can also book a trip that is focused primarily on volunteer work through a locally run charity or non profit (just be sure that the job isn’t taking employment opportunities away from residents).
It's not difficult to make a business case for sustainable tourism, especially if one looks at a destination as a product. Think of protecting a destination, cultural landmark, or ecosystem as an investment. By keeping the environment healthy and the locals happy, sustainable tourism will maximize the efficiency of business resources. This is especially true in places where locals are more likely to voice their concerns if they feel like the industry is treating visitors better than residents.
Not only does reducing reliance on natural resources help save money in the long run, studies have shown that modern travelers are likely to participate in environmentally friendly tourism. In 2019, Booking.com found that 73% of travelers preferred an eco-sustainable hotel over a traditional one and 72% of travelers believed that people need to make sustainable travel choices for the sake of future generations.
Always be mindful of where your souvenirs are coming from and whether or not the money is going directly towards the local economy. For example, opt for handcrafted souvenirs made by local artisans.
Growth in the travel and tourism sectors alone has outpaced the overall global economy growth for nine years in a row. Prior to the pandemic, travel and tourism accounted for an $9.6 trillion contribution to the global GDP and 333 million jobs (or one in four new jobs around the world).
Sustainable travel dollars help support employees, who in turn pay taxes that contribute to their local economy. If those employees are not paid a fair wage or aren’t treated fairly, the traveler is unknowingly supporting damaging or unsustainable practices that do nothing to contribute to the future of the community. Similarly, if a hotel doesn’t take into account its ecological footprint, it may be building infrastructure on animal nesting grounds or contributing to excessive pollution. The same goes for attractions, since sustainably managed spots (like nature preserves) often put profits towards conservation and research.
Costa Rica was able to turn a severe deforestation crisis in the 1980s into a diversified tourism-based economy by designating 25.56% of land protected as either a national park, wildlife refuge, or reserve.
While traveling, think of how you would want your home country or home town to be treated by visitors.
Are You a Sustainable Traveler?
Sustainable travelers understand that their actions create an ecological and social footprint on the places they visit. Be mindful of the destinations , accommodations, and activities you choose, and choose destinations that are closer to home or extend your length of stay to save resources. Consider switching to more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as bicycles, trains, or walking while on vacation. Look into supporting locally run tour operations or local family-owned businesses rather than large international chains. Don’t engage in activities that harm wildlife, such as elephant riding or tiger petting , and opt instead for a wildlife sanctuary (or better yet, attend a beach clean up or plan an hour or two of some volunteer work that interests you). Leave natural areas as you found them by taking out what you carry in, not littering, and respecting the local residents and their traditions.
Most of us travel to experience the world. New cultures, new traditions, new sights and smells and tastes are what makes traveling so rewarding. It is our responsibility as travelers to ensure that these destinations are protected not only for the sake of the communities who rely upon them, but for a future generation of travelers.
Sustainable tourism has many different layers, most of which oppose the more traditional forms of mass tourism that are more likely to lead to environmental damage, loss of culture, pollution, negative economic impacts, and overtourism.
Ecotourism highlights responsible travel to natural areas that focus on environmental conservation. A sustainable tourism body supports and contributes to biodiversity conservation by managing its own property responsibly and respecting or enhancing nearby natural protected areas (or areas of high biological value). Most of the time, this looks like a financial compensation to conservation management, but it can also include making sure that tours, attractions, and infrastructure don’t disturb natural ecosystems.
On the same page, wildlife interactions with free roaming wildlife should be non-invasive and managed responsibly to avoid negative impacts to the animals. As a traveler, prioritize visits to accredited rescue and rehabilitation centers that focus on treating, rehoming, or releasing animals back into the wild, such as the Jaguar Rescue Center in Costa Rica.
Soft Tourism
Soft tourism may highlight local experiences, local languages, or encourage longer time spent in individual areas. This is opposed to hard tourism featuring short duration of visits, travel without respecting culture, taking lots of selfies , and generally feeling a sense of superiority as a tourist.
Many World Heritage Sites, for example, pay special attention to protection, preservation, and sustainability by promoting soft tourism. Peru’s famed Machu Picchu was previously known as one of the world’s worst victims of overtourism , or a place of interest that has experienced negative effects (such as traffic or litter) from excessive numbers of tourists. The attraction has taken steps to control damages in recent years, requiring hikers to hire local guides on the Inca Trail, specifying dates and time on visitor tickets to negate overcrowding, and banning all single use plastics from the site.
Traveling during a destination’s shoulder season , the period between the peak and low seasons, typically combines good weather and low prices without the large crowds. This allows better opportunities to immerse yourself in a new place without contributing to overtourism, but also provides the local economy with income during a normally slow season.
Rural Tourism
Rural tourism applies to tourism that takes place in non-urbanized areas such as national parks, forests, nature reserves, and mountain areas. This can mean anything from camping and glamping to hiking and WOOFing. Rural tourism is a great way to practice sustainable tourism, since it usually requires less use of natural resources.
Community Tourism
Community-based tourism involves tourism where local residents invite travelers to visit their own communities. It sometimes includes overnight stays and often takes place in rural or underdeveloped countries. This type of tourism fosters connection and enables tourists to gain an in-depth knowledge of local habitats, wildlife, and traditional cultures — all while providing direct economic benefits to the host communities. Ecuador is a world leader in community tourism, offering unique accommodation options like the Sani Lodge run by the local Kichwa indigenous community, which offers responsible cultural experiences in the Ecuadorian Amazon rainforest.
" Transport-related CO 2 Emissions of the Tourism Sector – Modelling Results ." World Tourism Organization and International Transport Forum , 2019, doi:10.18111/9789284416660
" 45 Arrivals Every Second ." The World Counts.
Becken, Susanne. " Water Equity- Contrasting Tourism Water Use With That of the Local Community ." Water Resources and Industry , vol. 7-8, 2014, pp. 9-22, doi:10.1016/j.wri.2014.09.002
Kutty, Govindan M., and T.K. Raghavan Nair. " Periyar Tiger Reserve: Poachers Turned Gamekeepers ." Food and Agriculture Organization.
" GSTC Destination Criteria ." Global Sustainable Tourism Council.
Rinzin, Chhewang, et al. " Ecotourism as a Mechanism for Sustainable Development: the Case of Bhutan ." Environmental Sciences , vol. 4, no. 2, 2007, pp. 109-125, doi:10.1080/15693430701365420
" Booking.com Reveals Key Findings From Its 2019 Sustainable Travel Report ." Booking.com.
" Economic Impact Reports ." World Travel and Tourism Council .
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Some Advice on How to Travel More Intentionally
- 'The Last Tourist' Film Will Make You Approach Travel Differently
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- What Is Experiential Tourism?
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Food Sovereignty: Definition, Principles, and Importance
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Tech
- 10 Ways to Be an Eco-Conscious Tourist
- Travel + Leisure's Global Vision Awards Are a Win for the Planet
- Spain Starts a School for Shepherdesses
Latest Stories
Today's picks.
- History & Culture
- Perpetual Planet
- Photographer
Discover More on Disney+
- Queens with Angela Bassett
- Arctic Ascent with Alex Honnold
- The Space Race
- Genius: MLK/X
- A Real Bug's Life with Awkwafina
- Incredible Animal Journeys with Jeremy Renner
- TheMissionKeyArtDisneyPlusCard
- Animals Up Close with Bertie Gregory
- Secrets of the Elephants
- The Territory
- Never Say Never with Jeff Jenkins
- Extraordinary Birder with Christian Cooper
- A Small Light
Port Protection Alaska
Wicked tuna.
- Paid Content
May 2024 Issue
In this issue, the national geographic society mission, national geographic’s nonprofit work.
The National Geographic Society invests in innovative leaders in science, exploration, education and storytelling to illuminate and protect the wonder of our world.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Take advantage of the search to browse through the World Heritage Centre information.
Sustainable Tourism Toolkit
UNESCO World Heritage Sustainable Tourism Toolkit
- Toolkit About the Sustainable Tourism Toolkit How to use this guide? Our Objective Resource Library
- Guides Strategic foundations Guide 1: Understanding Guide 2: Strategy Guide 3: Governance Guide 4: Engagement Core Delivery Guide 5: Communication Guide 6: Infrastructure Guide 7: Value Guide 8: Behaviour Guide 9: Investment Guide 10: Monitoring
- Case Studies Guide 1: Historic Town of Vigan Guide 2: Angkor Guide 2: Ichkeul National Park Guide 3: Melaka and George Town Guide 4: Avebury Guide 4: Old and New Towns of Edinburgh Guide 4: Great Barrier Reef Guide 4: Røros mining town and the circumference Guide 5: Røros Mining Town and the Circumference Guide 6: Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape (United Kingdom) Guide 7: Røros Mining Town and the Circumference Guide 8: Wadi Al-Hitan Guide 9: Land of Frankincense
Sustainable planning and management of tourism is one of the most pressing challenges concerning the future of the World Heritage Convention today and is the focus of the UNESCO World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme.
These 'How To' guides for World Heritage Site managers and other key stakeholders will enable a growing number of World Heritage Site communities to make positive changes to the way they pro-actively manage tourism.
How to use this guide
These easily accessible 'How To' guides are focused on best practice approaches to sustainable economic development through tourism. The first of their kind, the 'How To' resources offer direction and guidance to managers of World Heritage tourism destinations and other stakeholders to help identify the most suitable solutions for circumstances in their local environments and aid in developing general know-how for the management of each destination.
The 'How To' guides bring best practice knowledge to the full WH community, so that site managers, tourism professionals, conservation professionals, and communities around the world understand the possibilities of sustainable tourism and what key issues have already been achieved. These resources are a valuable asset to site managers in particular, who often lack the tools and know-how to effectively manage and maximise tourism benefits, while minimising its negative impacts.
Our series of guides have been structured as a step-by-step process for site managers.
- Guides 1-4 establish the basic foundations for sustainable tourism (these are coloured yellow).
- Guides 5-10 are tailored to more specific issues, which will have greater relevance at some sites than at others (these are coloured orange).
We recommend that site managers explore each guide, however, as sustainable tourism is a holistic process, addressing all issues in a strategic manner.
Our Objective
The goal is to stimulate local solutions in communities through capacity-building in best practice. With the immense scale and variation of World Heritage Properties around the globe, coupled with scarce human and financial resources, this is now more important than ever. Site managers and other stakeholders in the tourism sector must have access to these types of innovative sustainability tools in order to develop and formulate their own successful results.
Ideally, site managers and other users will begin to navigate through this system by learning basic ideas and guidance. The system then enables the user to delve deeper into any given subject that falls in line with their local interests, needs, and aspirations.
Our objective for these guidance resources is to enable the growth and success of an entire community of World Heritage Properties, making positive changes to their local surroundings and pro-actively managing tourism in their areas. In parallel, by establishing this community, we aim to facilitate knowledge exchange of the most progressive ideas, and encourage their implementation and evolution.
The driving ethic for the 'How To' guides is to explain critically important ideas for sustainable tourism in World Heritage sites in a clear and concise manner, conveying the key knowledge and processes in a reading time of under 20 minutes per idea. Our goal is to make implementing the ideas of sustainable tourism easier to understand and put into practice for all parties involved.
Getting started
We understand the complex range of different societies in which World Heritage sites exist, and the many challenges site managers face on a daily basis. While the intention is to encourage each site to undertake most, or at least many, of the tasks included in the guides, considering them together all at once may seem daunting and even impossible.
We have developed this tool as a source of guidance and inspiration. It is a menu of ideas from which you, the user, may choose to put into practice, helping your World Heritage site become more sustainable for its current and future visitors.
Getting to know these 'How To' guides will move your site towards better self-management and sustainability rather than demand a level of sophistication that might simply be unattainable for some World Heritage sites. We would urge all site managers to read through these resources thoroughly and begin to think about what positive steps can be taken to implement these changes. Again, we remind each user that results will differ for each site, and the circumstances of the local environment and community must always be taken into consideration.
Download all Guides
Pdf version.
All Case Studies
Resource library, global good practice examples.
Tourism, Culture and Sustainable Development
UNESCO (2006)
English French
IUCN World Heritage Advice Note. Environmental Assessment & World Heritage
IUCN (2013)
Guidance on Heritage Impact Assessments for Cultural World Heritage Properties
ICOMOS (2011)
Managing Tourism at World Heritage Sites: a Practical Manual for World Heritage Site Managers
UNESCO World Heritage Paper Series n°1 (2002)
Climate Change. Adaptation and Mitigation in the Tourism Sector: Frameworks, Tools and Practices
UNEP (2008)
Enhancing our Heritage Toolkit
UNESCO World Heritage Paper Series n°23 (2008)
Best Practice Guidelines for Great Ape Tourism
IUCN (2010)
Criteria for Sustainable Tourism for the three Biosphere Reserves Aggtelek, Babia Góra and Šumava
Ecological Tourism in Europe (ETE) and UNESCO-BRESCE (2009)
Practical, profitable, protected. A starter guide to developing sustainable tourism in protected areas
ECEAT in partnership with the EUROPARC Federation (2012)
The contribution of tourism to sustainable development and achieving the Millennium Development Goals
BMZ Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development Position Paper 2|2011e (2012)
Guide on EU funding for the tourism sector (2014-2020)
European Commission, Directorate-General for Entreprise and Industry (2014)
Sustainable Tourism for Development Guidebook
UNWTO (2013)
World Heritage: Challenges for the Millennium
UNESCO (2007)
The Urban Rehabilitation of Medinas : The World Bank Experience in the Middle East and North Africa
The World Bank (2010)
Adapting to change: the state of conservation of World Heritage forests in 2011
UNESCO World Heritage Paper Series n°30 (2011)
UNESCO Pacific World Heritage Workshop (5-9 September 2011, Apia, Samoa)
UNESCO (2012)
Safeguarding Precious Resources for Island Communities
UNESCO World Heritage Paper Series n°38 (2014)
Terrestrial biodiversity and the World Heritage List: identifying broad gaps and potential candidate sites for inclusion in the natural World Heritage network
Culture & Development Nº 11
UNESCO (2014)
Sustainability is a complex system to navigate. Please feel free to ask any questions regarding the information provided in the 'How To' guides, or send us your feedback. We are here to help.
Supported by
Archive: Website before 15 Mars 2023

12 innovative sustainable tourism attractions you can visit around the world

Apr 4, 2022 • 5 min read

Check out these innovative sustainable attractions worldwide, like the Jewel at Changi Airport © Travel man / Shutterstock
More and more travelers are looking beyond the most affordable and comfortable way to travel and are putting more thought into how their choices might affect the destination they want to visit.
As travel priorities shift, on top of having a great time travelers increasingly want to do the right thing by the places they visit. In this extract from Sustainable Escapes , Lonely Planet looks at how 12 worldwide tourist attractions have approached sustainability in an innovative way.

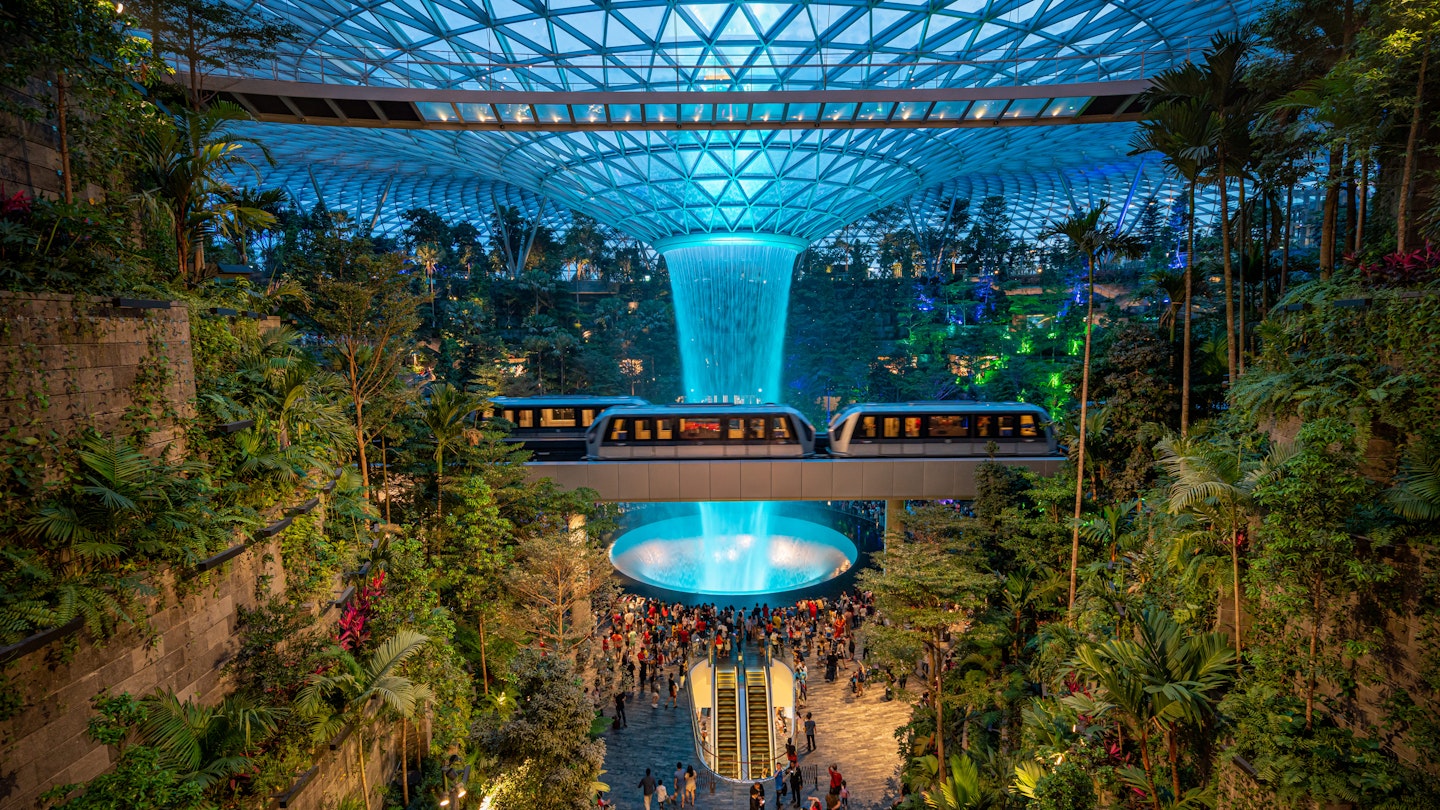
Jewel at Changi, Singapore, is an indoor oasis
First came Gardens by the Bay with its solar-harvesting Supertrees, and in 2019 Singapore upped its urban garden game with an airport terminal you’ll never want to leave. Harnessing cutting-edge sustainable technology, Jewel at Changi is a green oasis, complete with a hedge maze, a canopy bridge, and the world’s tallest indoor waterfall.
The Points Guy: 8 sustainable travel tips from expert green travelers
New York's Climate Museum aims to inspire action on the climate crisis
New York City ’s Climate Museum has won a legion of fans for over 200 innovative public exhibitions and events it has hosted around the city since 2017. Examples include youth spoken-word programs dedicated to themes of climate change; Climate Signals , a city-wide public art installation by US artist Justin Brice Guariglia, which flashed climate change alerts in five languages; and Beyond Lies , a public art exhibition by British illustrator and journalist Mona Chalabi, that examines climate disinformation from the fossil fuel industry.

Cape Town's Table Mountain cableway has been carbon-neutral since 2016
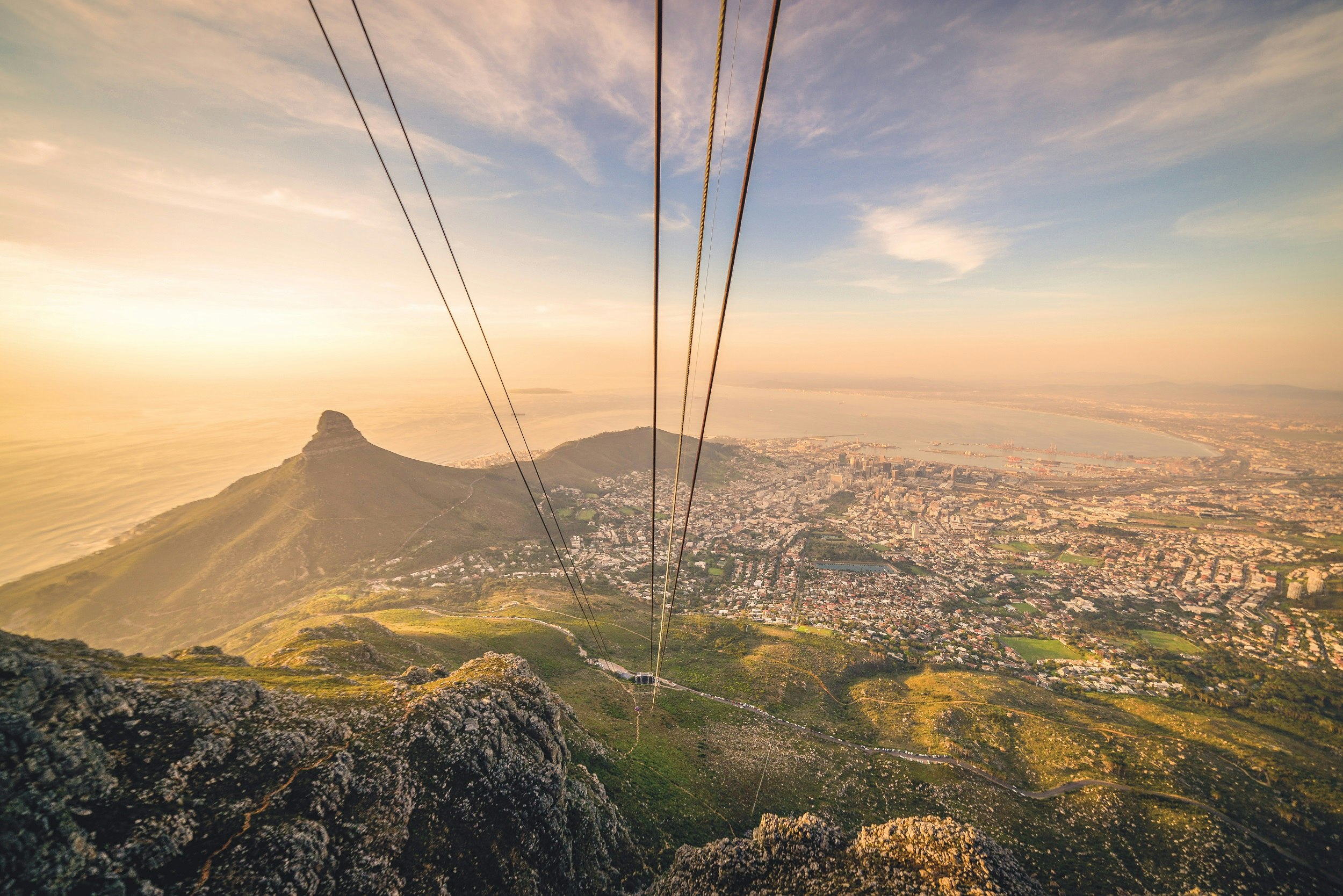
Hiking Table Mountain is a quintessential Cape Town experience. But those who prefer to ride the cable car can still feel good about it. The cableway has been carbon-neutral since 2016, and maintains one of the most cohesive responsible tourism policies around, with careful water management and waste reduction practices in place.
Copenhill, Copenhagen's ski slope, is on top of a power plant
Urban ski slopes typically take the form of emissions-emitting indoor centers. But not Copenhill . Opened in 2019, this artificial ski slope sits atop Amager Bakke, a waste-to-power plant central to Copenhagen ’s goal of becoming the world’s first carbon-neutral city . The complex also has a 280ft (85m) climbing wall (the world’s highest) and, like all good ski resorts, an après-ski bar.
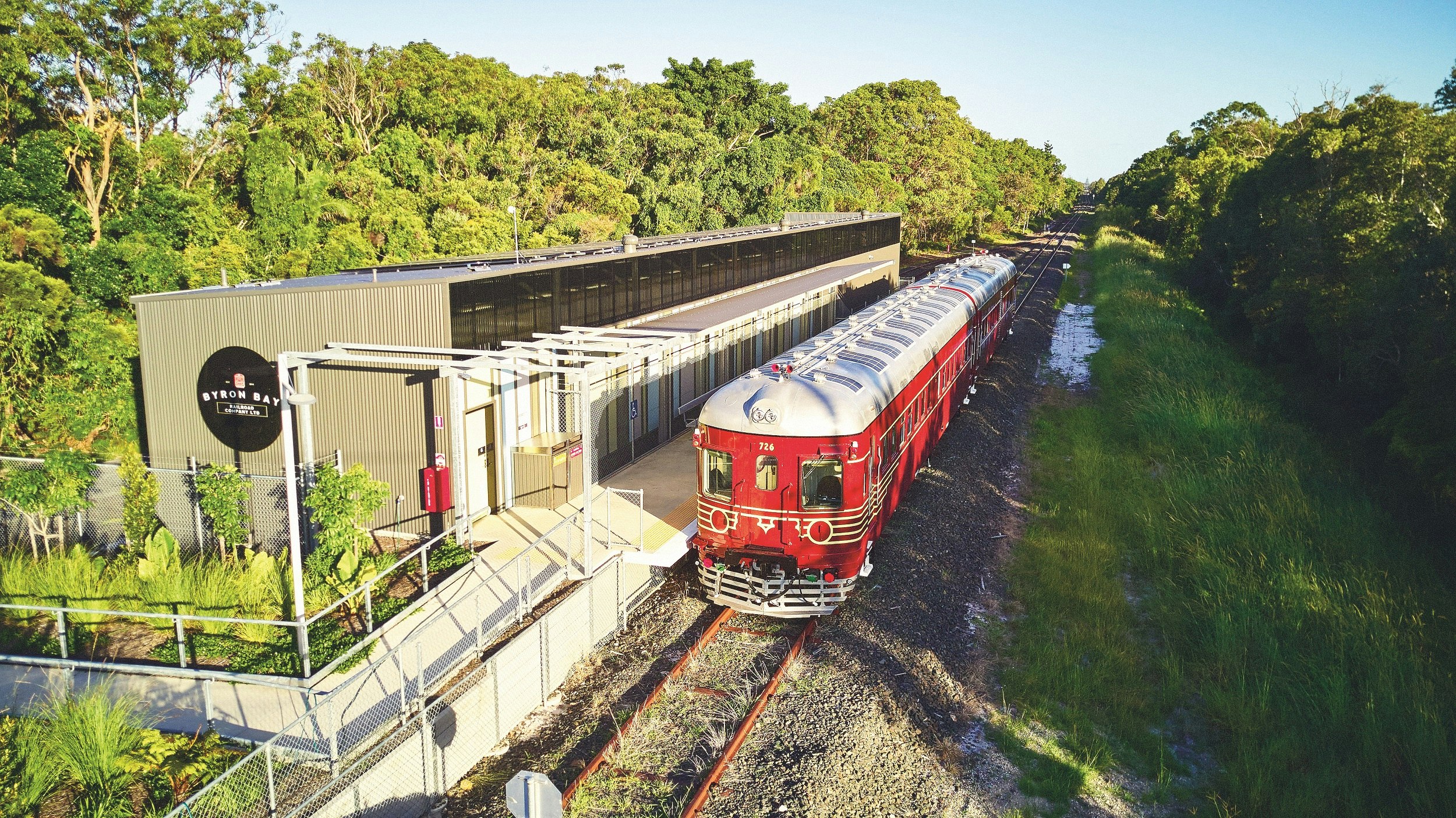

Byron Bay, Australia, has the world's first solar-powered train
Connecting the center of surf town Byron Bay to a vibrant arts estate, the world’s first solar-powered train made its maiden journey on a scenic 1.9 mile (3km) stretch of disused rail line in 2017. In lieu of ticket machines, fares are collected by a conductor on the beautifully refurbished heritage train.
Sustainability is central at the Azurmendi restaurant near Bilbao, Spain
Proving it’s haute to be sustainable, Azurmendi , a three-Michelin-star restaurant near Bilbao , has twice won the sustainable restaurant award from World’s 50 Best Restaurants . The hilltop atrium building harnesses solar and geothermal energy, and guests can tour the on-site greenhouses and vegetable gardens that supply the inventive menus.
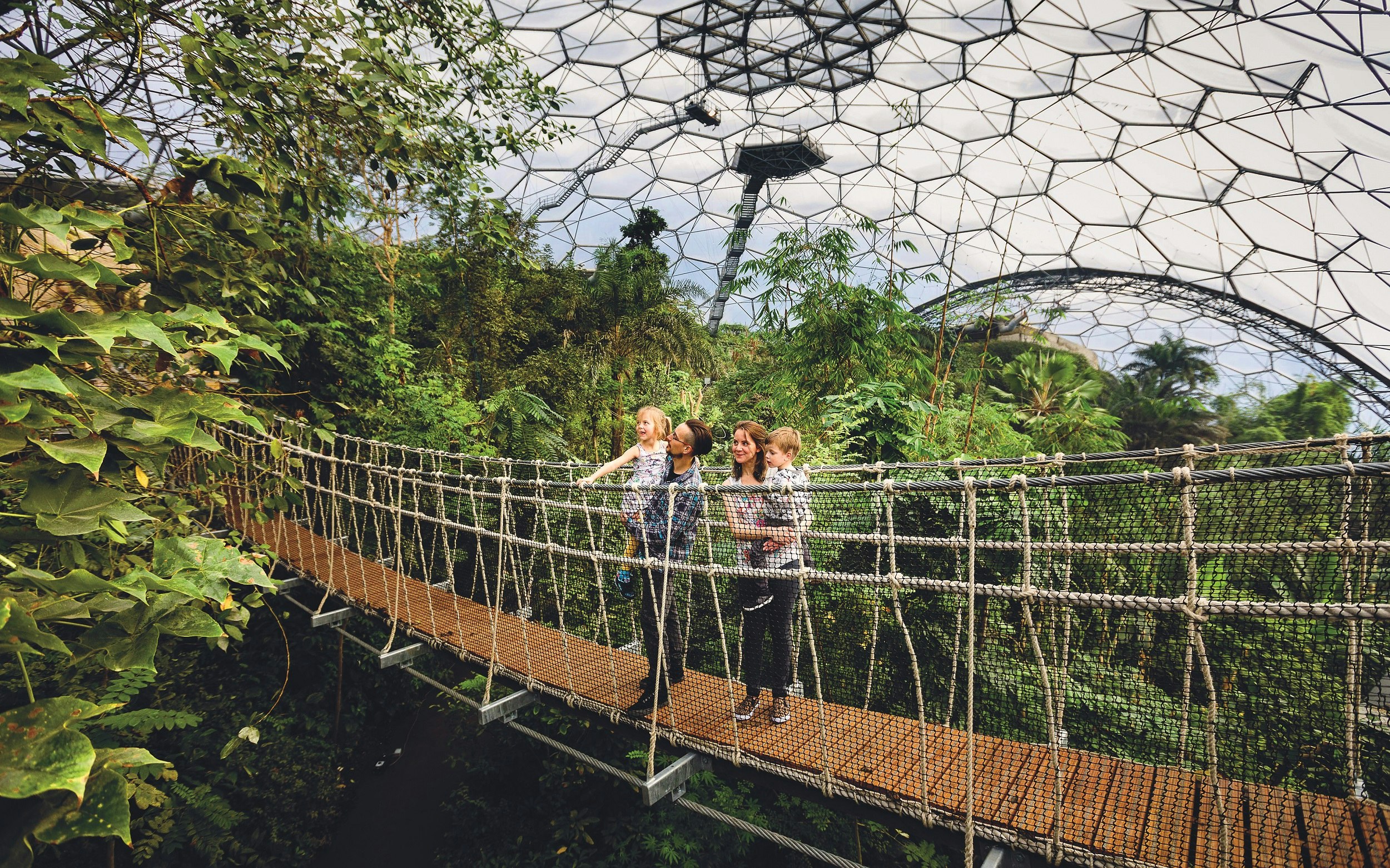

England's Eden Project recreates major climate systems
Occupying the site of an excavated china clay pit, the Eden Project education charity and visitor’s center in Cornwall , England , features huge biomes housing exhibitions, gardens, and the largest indoor rainforest in the world. It’s also home to the UK’s longest and fastest zip line, and a play tower for kids designed to introduce little ones to the concept of pollination.
Ocean Atlas in the Bahamas is an artwork and artificial reef
British sculptor and environmental activist Jason deCaires Taylor is famous for his surreal underwater sculptures that double as artificial reefs. Ocean Atlas – depicting a young girl supporting the ceiling of the water, much like the mythological Greek Titan shouldered the burden of the heavens – is a 60-plus-ton sculpture in Nassau , intended to symbolize the environmental burden we are asking future generations to carry.

A former nuclear reactor is now a theme park at Wunderland Kalkar, Germany
Following the 1986 Chernobyl disaster , German authorities decided not to put its new multi-billion-euro nuclear reactor near the Dutch border into operation. But it wasn’t a complete write-off. In the 1990s, the site was transformed into Wunderland Kalkar , an amusement park, complete with a swing ride inside the reactor’s cooling tower.
Vena Cava winery in Mexico is constructed from recycled materials
Vena Cava calls itself the hippest winery in Mexico , and when you lay eyes on this all-organic Baja winery – which was constructed from reclaimed fishing boats and other recycled materials – it’s difficult to disagree. Better yet, its cellar door is open for tastings every day of the week.
Minimize your impact when bird-watching from Tij Observatory, Netherlands
Taking its form from a tern’s egg, Tij Observatory is a stunning public birdwatching observatory in Scheelhoek Nature Reserve in Stellendam, the Netherlands , designed to rest as lightly on nature as possible. Built with sustainable wood and clad in thatched reeds, the observatory is reached via a tunnel built from recycled bulkheads to minimize disturbance to birds.
Jubileumsparken is a huge park project in Gothenburg , Sweden
The city of Lund might be getting a bicycle-powered museum in 2024, but there’s another great ecofriendly Swedish attraction you can visit now. Jubileumsparken is the ongoing redevelopment of a Gothenburg port area into an ultra-sustainable leisure hub to meet residents' requests for better access to the river and more green areas in the city. Two baths and a sauna were constructed, with ongoing work to introduce new children's play areas. Gothenburg has been ranked number one sustainable destination in the Global Destination Sustainability Index five times.
You might also like: 10 incredible places to learn to scuba dive 8 rewilding projects you can visit in Europe The world's eco-luxury resorts that are worth the hype
This article was first published October 2020 and updated April 2022
Explore related stories
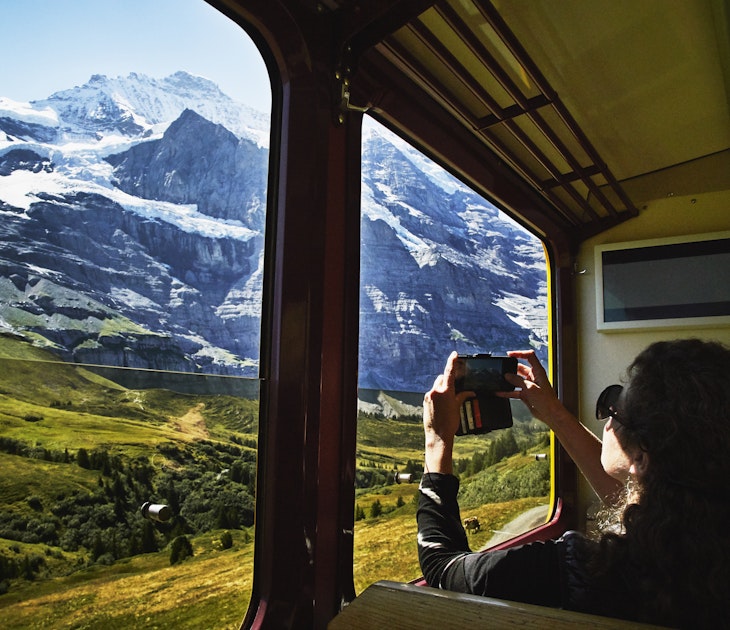

Sustainable Travel
Jan 16, 2024 • 8 min read
Rolling forests, saw-toothed mountains, bridges spanning river gorges - these European train rides put on quite a show.

Jan 2, 2024 • 11 min read

Nov 1, 2023 • 4 min read

Oct 19, 2023 • 8 min read

Oct 16, 2023 • 6 min read

Sep 12, 2023 • 9 min read

Jul 13, 2023 • 7 min read

Jun 30, 2023 • 6 min read

Jun 6, 2023 • 7 min read

May 17, 2023 • 12 min read
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
EU Guidebook on Sustainable Tourism for Development
In recognition of the considerable opportunities and issues involved in the development of tourism, in 2012 the European Commission's Directorate-General for Development and Cooperation – EuropeAid established the project “Enhancing capacities for sustainable tourism for development in developing countries”. The project was undertaken in collaboration with the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) which was commissioned to prepare a Guidebook on Sustainable Tourism, as an engine for development, trade in services, job creation and poverty reduction.
The Guidebook is intended to enhance the understanding of tourism in all its dimensions, how it relates to the EU Agenda for Change so as to enable EU services in Brussels and the EU Delegations in 180 countries as well as other development institutions to include sustainable tourism development in their programme cycles.
UNWTO endeavours to maximize tourism’s contribution to, inter alia, development and international understanding, while minimizing its negative impacts, paying particular attention to the growth potential of developing countries. Likewise, the European Union is well placed to support developing countries in identifying and implementing interventions in sustainable tourism.
The approach has been based on the experience of UNWTO and its work with a wide range of partner agencies and governments. In particular, the results of the study have been field tested in six countries during and following the preparation of the document, namely Kenya, India, Vietnam, Senegal, Botswana and Timor-Leste . The guidebook was publicly launched with the EU on the 27th of June 2013 in Brussels.
Background- Sustainable Tourism for Development
Over the last decades, tourism has experienced continued growth and increased diversification, becoming one of the fastest growing economic sectors in the world. The business volume of tourism today equals or even surpasses that of oil exports, food products or automobiles, offering millions of direct entry points into the workforce, particularly for youth and women, and a diversity of investment opportunities for young entrepreneurial talents. Tourism has become one of the major sectors in international trade, at the same time representing one of the main income sources for many developing countries. It is their only service sector with recorded surpluses in trade compared to the rest of the world.
However, tourism can also be a source of environmental damage and pollution, a threat to the socio-cultural structure, a heavy user of scarce resources and a potential cause of negative externalities in society. What must be done?
Tourism in the Global Development Agenda: The future we want Rio+20 outcome document
" Sustainable tourism is highlighted in the final outcome document of Rio+20 as a thematic area and a cross-sectorial issue within the framework for action and follow-up.
130. We emphasize that well-designed and managed tourism can make a significant contribution to the three dimensions of sustainable development, has close linkages to other sectors, and can create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities (…)
131. We encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential (…)"
- Rio+20: The Future We Want
- Green Economy Report leaflet
In recent years, sustainability has emerged as a critical concern that must be addressed in any viable tourism development strategy. Expressed simply, sustainable tourism can be defined as “Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment, and host communities”. Tourism is one of the ten economic sectors identified in the UNEP Green Economy Report, whose greening could increase prosperity, create employment and reduce poverty. In addition, tourists are increasingly demanding the greening of tourism. Tourism development should hence have a sustainable approach , to be able to promote growth in the long-term while maintaining a balanced use of resources. This should be supported at local, national, regional and international levels.
Developing Countries surpassing advanced economies’ international tourist arrivals in 2015
Although developed countries remain both the major tourism destinations and source of international tourism, developing countries are reducing the gap. In recent decades there has been a substantial diversification in international tourism destinations, and many developing countries have registered phenomenal growth in tourist arrivals and receipts. Tourism also particularly thrives on assets such as natural environment, warm climate, rich cultural heritage and plentiful human resources, where developing countries have a comparative advantage.
- Tourism is the first or second source of export earnings in 20 of the 48 LDCs
- In some developing countries, notably small island states, tourism can account for over 25% of GDP.
- From 2015, emerging economies will, for the first time receive more international tourist arrivals than advanced economies
- By 2030, 58% of international arrivals will be to emerging economy destinations of Asia, Latin America, Central and Eastern Europe, the Middle East and Africa

However, tourism can also be a source of environmental damage and pollution , a heavy consumer of scarce resources and a cause of negative impacts in society. For these reasons, it is imperative that it is well planned and managed , embracing the principles of sustainable tourism which is defined as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry the environment and host communities” .
The Purpose of the Guidebook- Sustainable Tourism for Development

The document is aimed at two main audiences:
- The EU and other development assistance agencies – to help them understand and identify opportunities to assist the tourism sector in delivering sustainable development.
- Governments and other stakeholders within developing countries – to help them identify where they may need to strengthen their approach to sustainable tourism, and if necessary to seek assistance, within the context of international priorities and policies for sustainable development.
In particular the document provides a basis for discussion between the above two groups in agreeing on priorities and actions for supporting sustainable tourism.
The study is seen as informing the existing cooperation frameworks and common assessment and coordination processes in Official Development Assistance and Aid for Trade . This applies particularly in the field of trade, in which tourism plays an important part, including the work of the Enhanced Integrated Framework in promoting Diagnostic Trade Integration Studies and in the delivery of Aid for Trade.
The study contributes to the positioning of tourism within the overarching framework for action on green growth, poverty eradication and sustainable development post-2015 , stemming from Rio+20 and addressed by the European Commission in Communication (2013) 92 A Decent Life for All: Ending poverty and giving the world a sustainable futur e
Related links
- A Decent Life for All: Ending poverty and giving the world a sustainable future
“Sustainable Tourism for development in developing countries”: A document in three interlinking parts
The Guidebook takes a comprehensive approach to tourism, covering a wide range of topics relating to its planning, development, management and impact. By working through the whole document, users are able to identify priorities for intervention across a spectrum of issues.
The Guidebook’s aim is to mainstream tourism by:
- Enhancing understanding and commitment to sustainable tourism.
- Providing guidance to assess the tourism sector’s importance, identifying opportunities for sustainable tourism development, planning actions, and enhancing sustainability of projects.
- Delivering a “Sustainable Tourism for Development Study” which will enable the EU and other development institutions to include sustainable tourism development in their programme cycles.
The guidebook is divided in the three parts described below:
- GUIDANCE NOTE: Relates the UE framework for development, e.g. the EU Agenda for Change and Tourism pillars (methodology) and relates to EU priorities. It aims at providing guidance to EU services on the approaches required to ensure the effective implementation of priorities for sustainable tourism in developing countries.
- SITUATION ANALYSIS : Describes the macro-economic dimensions of tourism; its contrubution to improve the situation of a country and its relation with other sectors; policies in place to develop the sector and its contribution to sustainable development and reviews the existing policies and programmes auming at developing sustainable tourism in developing countries.
- METHODOLOGY: Designes to ptovide EU delagrions with a sustematics approach to understand the impact and value of the tourism sector in the country and the way it is managed and operated; and to understand which actions are appropriate to improve the situation through tailored interventions.
“The Methodology”: How to assess priorities for Sustainable Tourism in Developing Countries?
The Methodology follows a systematic structure which, through a series of questions * under each issue, enables the situation to be assessed, weaknesses and gaps identified and possible actions considered, while also pointing to existing services that are available. It focuses on five key pillars of sustainable tourism in developing countries:

Assess your needs!
- Questionnaire Pillar 1- Tourism policy and governance
- Questionnaire Pillar 2- Trade Investment, Data and Competitiveness
- Questionnaire Pillar 3- Employment, Decent Work and Capacity Building
- Questionnaire Pillar 4- Poverty Reduction and Social Inclusion
- Questionnaire Pillar 5- Sustainability of natural and cultural environment

5 Examples of Sustainable Tourism around the World
Tourism is one of the fastest growing sectors in the world and can provide an essential economic boost for countries pitching themselves as holiday destinations. Tourism, however, has historically had devastating effects on the environment, people and their cultural identities.
Enter the concept of sustainable tourism, which according to the United Nations World Tourism Organisation must:
- Conserve environmental resources and protect biodiversity
- Respect and preserve the cultures of host communities whilst benefiting them
- Address the needs of the visitors and industry whilst providing socio-economic benefit to all
In order for tourism to continue and for us to live within our planetary bounds and respect all people, the only option is for the world to move away from unconscious, mass tourism and learn from the existing examples of thriving sustainable tourism models.
What are some examples of sustainable tourism?
- 1. Controlled tourism in Bhutan
Bhutan, located in the East of the Himalayas, is known as one of the happiest countries in the world. The country remains relatively untouched by colonialism which has ensured that the people’s sustainable way of life has remained in tact. Bhutan’s tourism operates on the principle of “high value, low impact”. This has been achieved by enforcing strict entry requirements and a daily visitor tariff. The daily tariff includes necessary expenses for the visit such as accommodation, a licensed tour guide, meals and hiking equipment. A large portion of the tariff, however, is used to maintain and develop the country’s infrastructure, as well as contribute towards Bhutan’s free health care and education.

- 2. A solar powered resort in Fiji
Six Senses Fiji , located on the tropical Malolo Island, is a five star resort with sustainable luxury and cultural awareness at its core. The resort runs on 100% solar power, equipped with rainwater capture and its own onsite water-filtration site to eliminate the use of single-use plastic bottles. The resort aims to be as low-waste as possible, encouraging the principles of reuse whilst also practicing recycling and composting with a “worm-based septic system” and growing as much of its own herbs and vegetables as possible. All handiwork and artwork at the hotel has been produced by local villagers and the hotel supports the Rise Beyond the Reef Charity which aims to bridge “the divide between remote communities, government and the private sector in the South Pacific, sustainably creating a better world for women and children.”

- 3. A community run backpacker in South Africa
Mdumbi , a backpackers on the Wild Coast of South Africa, aims to promote “community involvement and sustainable eco-tourism”. The backpacker prides itself in being fused with the amaXhosa culture of the Eastern Cape, situated deep in the heart of a traditional village. With a number of sustainability interventions onsite such as energy efficiency, solar power and waste management, Mdumbi has a unique ownership model, with the local employees, the amaxhosa community association, and TransCape (Mdumbi’s affiliated NPO) all holding shares in the business. Mdumbi’s NPO, TransCape, aims “ to provide access to the resources, support, and knowledge necessary for communities to initiate the process of change towards a better quality of life.” In 2017, the Backpacker was also awarded a silver prize by the World Responsible Tourism Awards for best in poverty reduction.

- 4. Conservation ‘Voluntouring’ in Belize

- 5. A sustainable tour operator come foundation in Switzerland
The Swiss Foundation for Solidarity in Tourism (SST) is a non-profit foundation that grew out of one of the leading tour operators in Switzerland. The foundation, founded in 2001, supports projects and organisations in Switzerland and worldwide which look to improve the livelihoods of people in tourist destinations, contribute to sustainable tourism development and contribute to “intercultural understandings” between travellers and locals. By providing grants to deserving projects, the foundation hopes to further develop sustainable tourism online and on the ground.
These are but a few of many varying examples of models for sustainable tourism development. As the world moves towards sustainability in every facet and every industry, there is no doubt that the tourism industry will need an unprecedented overhaul in order to move towards low-impact and meaningful travel experiences that do not detriment people or the world on which we rely.
Interested in doing your bit for sustainable tourism? Why not look at studying a sustainable tourism degree or look into sustainable tourism master programs? Here at SUMAS we offer a master of international sustainable tourism management and other courses fit to prepare you for a career in sustainable tourism anywhere in the world.
- Reference Links
http://sdt.unwto.org/content/faq-climate-change-and-tourism http://sdt.unwto.org/content/about-us-5 https://inhabitat.com/100-solar-powered-fiji-resort-combines-5-star-luxury-with-sustainability/ https://epicureandculture.com/bhutan-tourism-model/ https://www.sixsenses.com/resorts/fiji/sustainability https://www.mdumbi.co.za/about_us https://www.sstfoundation.org/ https://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/green-science/sustainable-tourism.htm

Sustainability Leaders United
Innovation for tourism sustainability: examples and solutions.

Innovation for sustainability is a key component on tourism’s journey towards a more sustainable development. Around the world, businesses and destinations are getting creative in their approach to achieving sustainability – or even regenerative tourism. How do they do it?
We asked our panel of sustainable tourism champions which destinations or organizations have done a particularly impressive job with regard to innovation for tourism sustainability. Here’s what they answered (highlighted respondents are available as consultants or speakers ).

Brian Mullis
It is well known that tourism has inherent negative environmental impacts and is extractive in nature when it’s not well managed. Sustainable tourism is usually focused on sustaining current tourism activities and / or limiting environmental damage and negative impacts on host communities.
Rather than sustaining an approach to tourism that is unsustainable by design, regenerative tourism is a holistic process that uses nature’s principles to restore degraded environments and uplift host communities helping both to flourish.
Good examples can be found in Hawai’i, New Zealand , Ireland, Rwanda and elsewhere. For example, the Regenerative Places Program .
Jonathon Day
Innovation comes in a variety of forms: Here are three examples that include technological innovation, and process innovation:
- EV [electronic vehicle] transportation will change tourism for the better. Hoteliers and other tourism organizations are working through the challenges of introducing these new technologies. That’s critical – because the EV change is happening (at scale), and we need to get in front of it.
- Groups in destinations all around the world are coming together and thinking through ways to make tourism better. These changes are co-created with a range of stakeholders and unique to each location. Even though the solutions are “local” – the regenerative approach is an example of innovation in how we approach challenges that are global in scope.
- Another innovation that is worth watching is the move to destination stewardship . This is a paradigm shift that a few “early adopters” have embraced.
Raj Gyawali
In 2020, Ethical Travel Portal won an innovation grant in Norway for the idea to research and develop a measurement tool for sustainable tour operations. The measurement itself might not be a big innovation but engaging the travellers as a decision making partner in sustainability is innovative, as the traveller is the one affecting change in the long run. The tool is being prototyped, and collaboratively formed in the community to help develop and nurture it. That itself is innovative, as sustainability is an issue that should be for everyone, and not about market shares.
In 2021, the same company won another innovation grant from Innovation Norway to prototype the first version of travel community engagement through a local storytelling website. This again is based on the principle to actively engage travellers – or intending travellers – in understanding destinations, through stories owned by the destinations and not by content generated by massive media machines which constantly misrepresent destinations. This is being prototyped and populated at www.resonate.travel .
In 2020, women in tourism in Manang, Nepal started agriculture as tourism dried out and rediscovered the joy of community agriculture. They then partnered with karma coffee in Kathmandu to get help on product packaging, marketing and exposure to the market. With an active focus on sustainable sourcing and packaging and smart marketing these products were launched as ManangDirect, and later KarnaliDirect also joined in from Far West Nepal. The spin off smart marketing via Instagram raised the profile of the product, and hence young people from Manang started owning their produce. And feeling a sense of pride. The produce was also used by chefs to create fusion food and presented at an exclusive dinner in Kathmandu, further raising its profile.
Post this, a further innovation was done by my own company, socialtours , in developing an agritourism experience of understanding this phenomenon, going back to the village to see the agriculture. This is an example of using tourism for regeneration.
Vicky Smith
- Climate : Tourism Declares a Climate Emergency has done a fantastic job growing from what was called a “specialist group” of nearly 30 travel organisation launch signatories to become the Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism, to more than 500 organisations today. Decarbonisation : we’ve seen EasyJet recently drop the bandaid of carbon offsets to focus on actual emission reduction. Our partners’ electric game drive vehicles aren’t just better for emissions, but quieter for watching wildlife and so a better customer experience. We’re also seeing meat-free menus (at least some days) pop up all over the world. Such reductions also help transition focus to restoration and regeneration.
- Collaborations : With such global, existential issues as Covid and climate crisis, we see how cross-sector and public/private partnerships are required to pool resources to support the wide-ranging, intense efforts and energy needed for big change. Tourism isn’t an island, and we are now seeing the intersection of the SDGs play out – not just SDG 17 (partnerships), but in implementations like Doughnut Economics in Amsterdam, really understanding how different priorities inter-depend, impact and are impacted by tourism, in order to deliver social needs within planetary resource boundaries.
- Consumers : are finally starting to demand sustainability. Where pioneering suppliers have led the charge for triple bottom line impacts, Covid and lockdown have increased public consciousness of wellness of community, economy and environment, and their ability to join the dots between issues of concern and how tourism can offer solutions. Annual surveys like Booking.com’s show yearly increases in interest and desire that the future of travel can only be sustainable.
- Greenwash : Unsurprisingly, as demand for sustainable tourism grows, so does greenwashing as companies try to appeal to the demand, without necessarily having the evidence to substantiate sustainability claims. Where in the past we’ve seen UK’s Advertising Standards Authority ban ads such as Ryanair’s claiming the ‘lowest emissions airline’ (based on per passenger per kilometre flown with little substantiated comparison), they’ve now taken the proactive positive step of publishing advertising guidance over misleading environmental claims and social responsibility. This gives tools to the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) and European counterparts to investigating misleading claims. Will our governments even stack up to their own policies?
Willy Legrand
If we take a look at the environmental pillar and in particular climate and biodiversity related issues, three innovations (which have actually been around for decades but increasingly being rediscovered and applied in the hotel and tourism settings) include:
- Nature-based solutions for urban destinations (a source of solutions to mitigate and adapt to climate change and protect biodiversity while ensuring human well-being with street trees, green roofs, green walls, green spaces which are particularly applicable to the urban building sector in general; some of this best represented by concepts such as green cover replacement or green plot ratio in urban settings)
- Biophilic design in hotels (related to the point above, plenty of application in the hotel settings with ROI on investment calculated environmentally, socially and psychologically as studies demonstrate the use of nature elements in a hotel minimizes employee burnout and increases productivity, work engagement satisfaction and employee retention, let alone the restoration benefits to guests)
- Blue roofs (the water cycles in urban areas are often broken with increased sealed spaces by building and asphalts; hotel buildings with blue roof allow for storage of rainwater which can be slowly drained, mitigating local flooding)
Gianna Moscardo
This is hard as since the pandemic I have seen almost no innovation in tourism in the areas I am familiar with. One that was emerging of interest was Istria In Spirit as a community based group engaging locals and tourists in regional stories.
Rachel Dodds
- Amsterdam : refocusing their campaigns to focus on ‘ Enjoy & Respect ’ rather than just attracting visitors.
- Intrepid Travel : The company offered vaccine equity. When someone booked a trip, they offered a vaccine to someone who didn’t have access. This supported safety and equity within the regions Intrepid was visiting.
- 4VI : Vancouver Island in Canada shifted their focus from just being a destination marketing organizations to a social enterprise.
Steve Noakes
Three examples from Indonesia .
Doing innovative environmental things: Urban Biologist Bali –
- A responsible waste management service for residents or business
- A chemical-free mosquito control for local community and private sector
- A wildlife exploration and education platform in the urban settings of Bali
Doing innovative things to change human behaviour: Greeneration Foundation , an Indonesian non-governmental organization that focuses on utilizing adaptive creative media in changing human behaviour to implement Sustainable Consumption and Production (SCP) in Indonesia.
Doing innovative good things for small scale (but important) economic benefit to local communities – Indonesia Conservation Foundation . One project during COVID shutdowns was to establish goat farming using zero grazing at the homes of the staff of the ecolodge that had to be closed (now reopened as Satwa Elephant Ecolodge).
Urs Wagenseil
Systemic innovations we are seeing more and more:
- Installation of Destination Management Organizations in tourism destinations with a clear task of sustainable development
- Adapting the tasks, duties and goals of already existing DMOs towards a more sustainable development
- Bridging DMOs and local governments with institutional structure to combine forces for a more sustainable development
- Installation of destination-specific monitoring systems
More about the sustainable tourism panel here – including previous sessions and answers to some of the most pressing issues linked to making tourism more sustainable and its development regenerative.

Beyond Greenwashing: Experts Weigh in on the Realities and Opportunities of Sustainable Tourism

Most Inspiring Sustainable Tourism Champions to Follow in 2023

Sustainable Tourism Development: Key Trends and Priorities in 2023

Innovation for Tourism Sustainability: Challenges to Overcome

Innovation for Tourism Sustainability: Priorities & Opportunities

Achieving Sustainable Tourism: These Are the Key Challenges

Sustainable Tourism 2022 and Beyond: These Are the Keys to Success

Career Choice: Why Focus on Tourism and Sustainability?

What Characterizes a Sustainability Leader in Tourism?

Sustainable, Responsible, Transformative, or Regenerative Tourism: Where Is the Difference?
Privacy Overview
For your kind of donation, destination, check-in date, check-out date.


Sustainable Tourism Planning and Why it Matters

Sustainable tourism is now an imperative focus for operators and communities. Major disruptions such as pandemics, climate change and new technology are influencing the way people feel about tourism, the way visitors are making decisions and the way industry responds to these changing expectations.
As connected global citizens, we are much more likely to seek out experiences which positively contribute to the people and places we choose to visit. How is your community taking notice of the shift toward sustainable tourism and making the most of what it has to offer?
What is Sustainable Tourism Planning?
Sustainable tourism planning is about finding the right balance between the needs of people and places. It involves clearly defining purpose, vision, and a point of difference or identity for your community. This form of destination planning in our communities enables us to think long-term, to be adaptable and proactive with changing target markets, trends and crisis like the Covid-19 pandemic. It also ensures we allocate resources appropriately while building local communities sustainably and ethically. Sustainability is at the heart of this approach to tourism planning, which benefits people and locations socially, economically, culturally and environmentally.
Planning with purpose is about prioritising the benefits tourism can provide for everyone and amplifying the quality of tourism over the quantity of tourism. It’s about maximising the quality of life for communities, protecting ecosystems, cultures, and the quality of experiences offered for visitors.
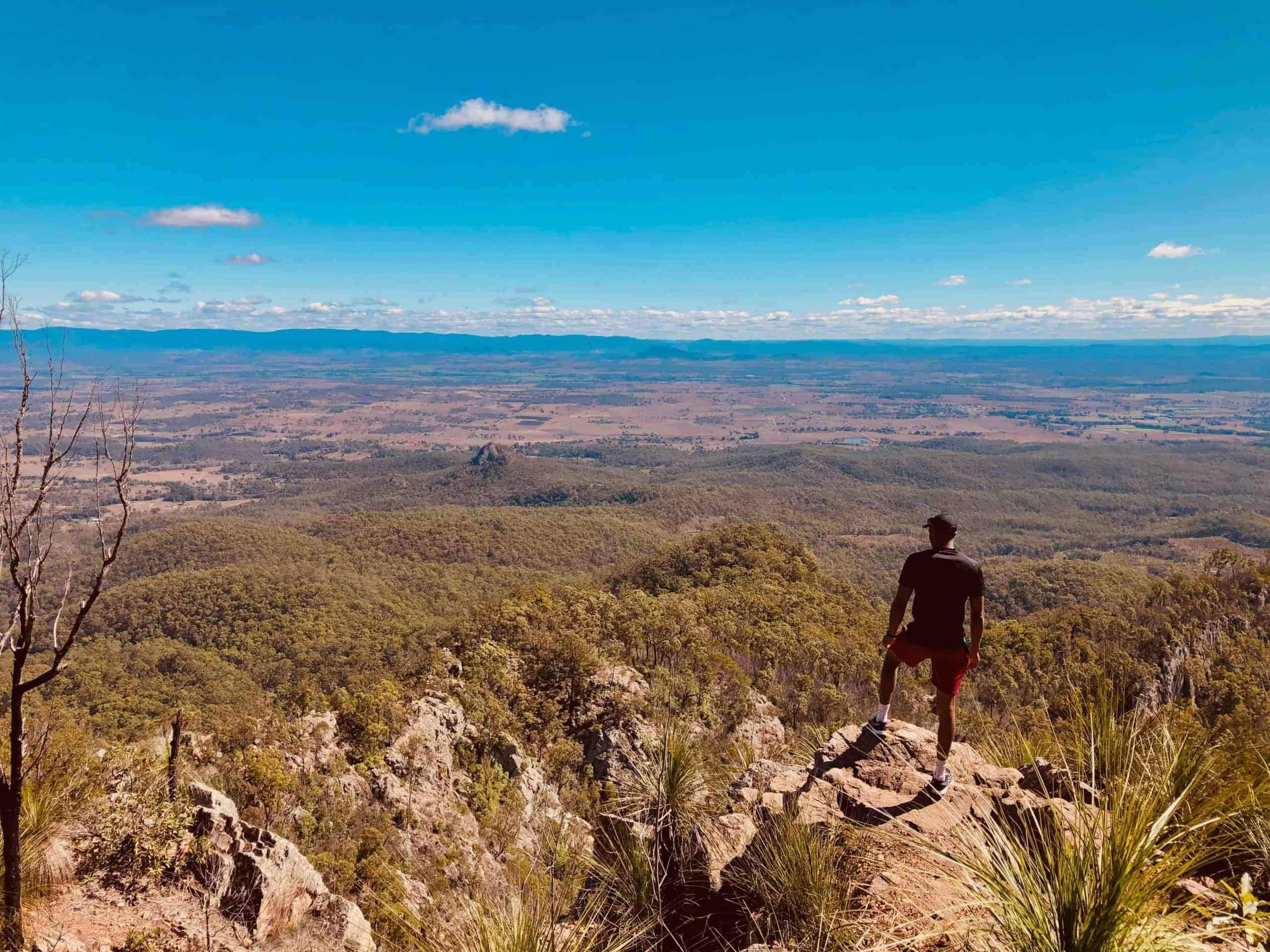

Our Top Sustainable Tourism Planning Tips:
- Use evidence to support decision making and let go of traditional approaches to your destination planning
- Articulate a strong united vision amongst your community, government and industry
- Identify the benefits you want to see in your area
- Focus on environmental and cultural advocacy and stewardship
- Connect with local Indigenous communities through purposeful engagement to capture their aspirations and further build the destination’s value proposition
- Build capability and strong, resilient local communities
- Seek out new products and experiences for ethical development opportunities
- Create new opportunities for investment and business development
- Collaborate with new partners and consider new organisational structures to get the best result
- Monitor and evaluate the environmental, social, cultural and economic benefits of tourism
- Consider risks and prepare for managing crisis and change.
Benefits of Sustainable Tourism Planning
Aside from attracting more interest in your community, your plan can extend across different sectors and attract the following benefits for your region:
- A good sustainable tourism strategy can preserve cultural and natural heritage for the benefit of locals and tourists alike
- The right planning can increase income thanks to tourist spending
- Planning for sustainable tourism allows you to implement strategies that increase people’s awareness and understanding of different cultures and ecosystems
- The money generated from the tourism industry can fund the construction of new infrastructures like educational and cultural centres that are of benefit to your community and to visitors.
The Bottom Line: The Importance of Sustainable Planning
Balancing the needs of the community with those of visitors is critical to protecting the very nature and culture of the places that make our world so special. This method of strategic, ethical tourism planning ensures you can maximise the benefits without causing disruption to local communities and leaving a negative mark on the region. READ MORE

Our Approach to Sustainable Tourism
Instead of thinking about how much value we can extract from experiences and places, at TRC Tourism , we focus on how many benefits we can create from tourism for the people and the places we love.
We provide support to communities with sustainable tourism planning services spanning sustainable destination planning , experience and product development , feasibility studies and business planning , indigenous tourism planning , and eco accreditation . From feasibility studies for wilderness trails to destination management plans and indigenous tourism programs, check out the hundreds of projects we’ve worked on for more than 20 years.
Ready to Explore Sustainable Tourism Planning for your Community?
Contact us today to see how we can take your destination and experience to the next level.
TRC is committed to the application of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the New Zealand Tourism Sustainability Commitment. TRC is a member of the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC), and our team holds GSTC Professional Certificates in Sustainable Tourism. Our team of sustainable tourism practitioners provide practical advice on how to maximise the social, economic, environmental and cultural benefits of tourism.
Share this story on your favourite social media platform.
Related posts.

Exploring the Sinai Trail with Trailblazer Chris Halstead

Meet the Speakers attending the 2024 Sustainable Trails Conference

Commonwealth Innovation Awards 2023 winners

Cultural Tourism is About Building for Our Future

Sustainable Tourism Development Plan Template
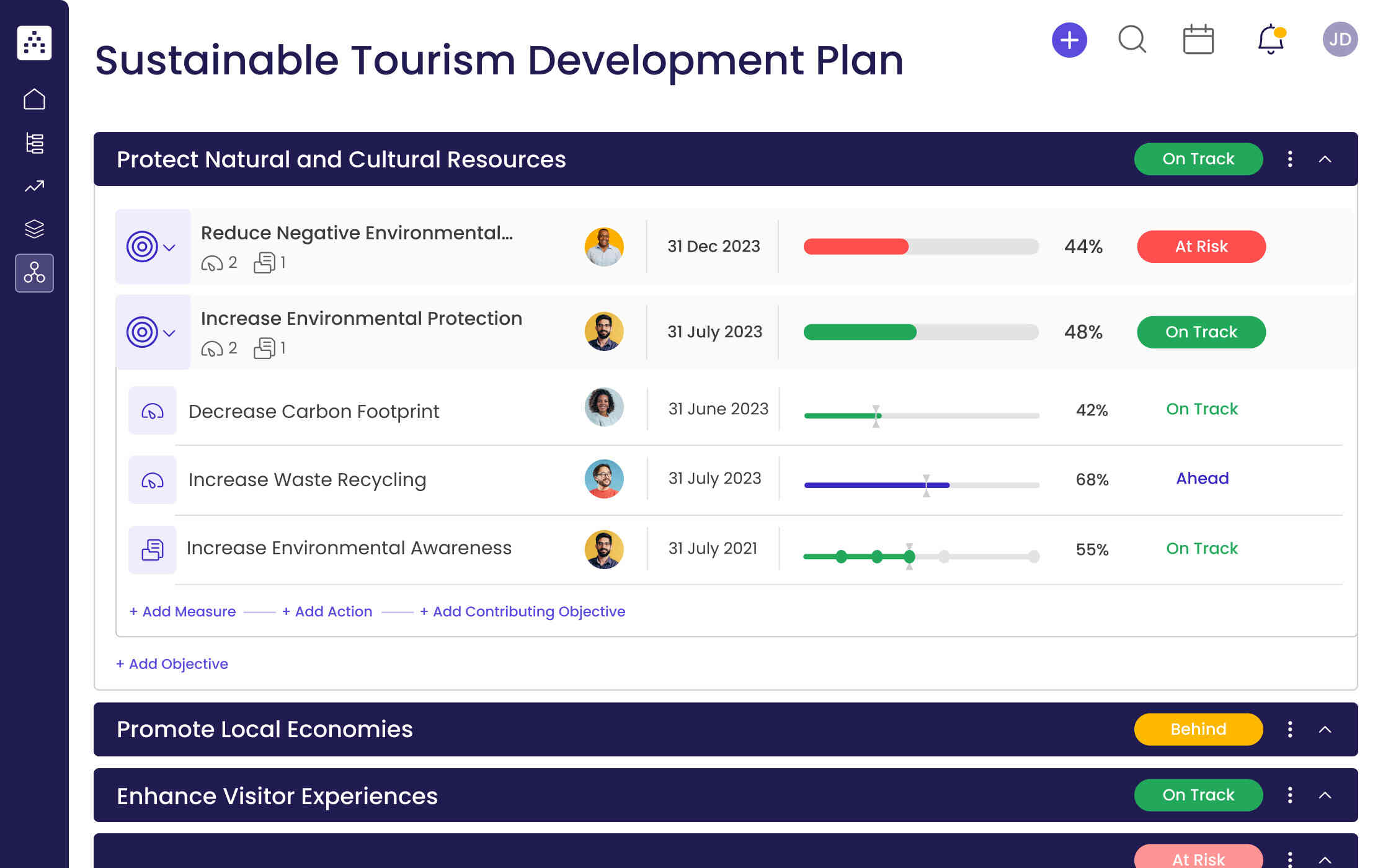
What is a Sustainable Tourism Development Plan?
A Sustainable Tourism Development Plan is a strategy designed to protect natural and cultural resources, promote local economies, and enhance visitor experiences. It is a roadmap for tourism boards, destination management organizations, and stakeholders in the tourism industry to ensure their development plans are sustainable and focused on the long-term success of the destination. This template provides a comprehensive guide for creating a plan that meets these goals.
What's included in this Sustainable Tourism Development Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Sustainable Tourism Development Plan template for?
This Sustainable Tourism Development Plan template is for tourism boards, destination management organizations, and stakeholders in the tourism industry who are looking for a comprehensive guide to create a sustainable tourism development plan for their destination. This template provides a straightforward and easy-to-follow structure that will help you create an effective plan.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a broad area of concern that you want to focus on when creating your plan. It is important to identify clear and specific focus areas so that you have a clear understanding of how to best achieve your goals. For example, in the Sustainable Tourism Development Plan, the focus areas are Protect Natural and Cultural Resources, Promote Local Economies, and Enhance Visitor Experiences.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
An objective is a specific goal that you want to achieve within a focus area. Objectives should be achievable and measurable. For example, under the focus area of Protect Natural and Cultural Resources, objectives could include reducing negative environmental impacts and increasing environmental protection.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
A key performance indicator (KPI) is a measurable target that you can use to track your progress toward achieving an objective. It should be specific and measurable. For example, under the objective of Reducing Negative Environmental Impacts, a KPI could be to decrease the carbon footprint by a certain number of tonnes.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
A project, or action, is a specific activity that you can implement to achieve a KPI. Projects should be related to the KPI and be achievable and measurable. For example, under the KPI of Decreasing the Carbon Footprint, a project could be to increase environmental awareness among employees and consumers.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade Strategy Execution Platform is an easy-to-use platform that enables you to set objectives, create projects, track progress, and measure success. It allows you to quickly and easily track the progress of your Sustainable Tourism Development Plan, so you can see faster results from your strategy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Feynan Ecolodge is without a doubt one of the great examples of sustainable tourism, as well as an example of environmental responsibility! 2. Mdumbi Backpackers Hostel - South Africa. The Mdumbi Backpackers Hostel is specifically designed for people who like sustainable tourism. Mdumbi Backpackers is a community-driven backpacker hostel ...
The Netherlands - A country that is promoting sustainable tourism through initiatives such as green hotels, bike-friendly cities, and nature conservation programs. New Zealand - A country that has a strong focus on sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism, conservation efforts, and responsible travel practices.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective ...
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved ...
1. Copenhagen, Denmark. Europe's sustainable city pioneer. The widespread inequalities revealed by the pandemic have ignited global interest in making cities more resilient, equitable and healthy. One example, Copenhagen, is set to become the world's first carbon-neutral capital by 2025.
Examples of sustainable tourism Companies and travellers, contributing to circular economy. A commitment to reuse and recycling when travelling redefines growth and tourism. To this can be added the idea of a reduction in consumption, always to the extent possible.It is about moving from a system where products have a short life span and resources are depleted, to one where, as in a circle ...
The sustainable tourism indicators are vital tools in the tourism planning, management and monitoring processes and also provide accurate information for decision making (UNWTO, Citation 2007). They focus on issues relating to economic sustainability, conservation and preservation of cultural assets and social values, and management of projects ...
Toolkit. Guides. Case Studies. Sustainable planning and management of tourism is one of the most pressing challenges concerning the future of the World Heritage Convention today and is the focus of the UNESCO World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme. These 'How To' guides for World Heritage Site managers and other key stakeholders will ...
Copenhill, Copenhagen's ski slope, is on top of a power plant. Urban ski slopes typically take the form of emissions-emitting indoor centers. But not Copenhill. Opened in 2019, this artificial ski slope sits atop Amager Bakke, a waste-to-power plant central to Copenhagen 's goal of becoming the world's first carbon-neutral city.
Sustainable Tourism Guide: Why Important, Examples & More. In this sustainable tourism guide, you can learn what sustainable tourism means and why it matters, including real-world examples.
UN Tourism is committed to accelerate progress towards low carbon tourism development and the contribution of the sector to international climate goals by: Strengthening the measurement and disclosure of CO 2 emissions in tourism. Accelerating the decarbonization of tourism operations. Engaging the tourism sector in adaptation and carbon removal.
Reducing tourism impacts- Work with the tourism supply chain on measuring and reducing its ecological footprint in Med coastal zones and Protected Areas. Market access for sustainable products- creating innovative ecotourism products in Med PAs as best practice examples, supporting local operators to gain market access through the community ...
If you're interested in this topic, you can learn more about the planning and development of tourism activities in our International Culture and Tourism Management ExpertTrack by Nankai University. You'll also discover strategies for sustainable tourism management. ... One example of sustainable tourism is the Six Senses Fiji resort, which ...
world's leading tourism destination. Integrated planning and sustainable management of tourism in the Mediterranean Tourism as a Threat vs Tourism as an Opportunity litres of waste 180 water/day 40% Tourist consumes between 300 and850 litres of water per day well above residents are urbanised - sun, sea and sand tourism infrastructure
The Guidebook's aim is to mainstream tourism by: Enhancing understanding and commitment to sustainable tourism. Providing guidance to assess the tourism sector's importance, identifying opportunities for sustainable tourism development, planning actions, and enhancing sustainability of projects. Delivering a "Sustainable Tourism for ...
1. Controlled tourism in Bhutan. Bhutan, located in the East of the Himalayas, is known as one of the happiest countries in the world. The country remains relatively untouched by colonialism which has ensured that the people's sustainable way of life has remained in tact. Bhutan's tourism operates on the principle of "high value, low ...
Jonathon Day. Innovation comes in a variety of forms: Here are three examples that include technological innovation, and process innovation: EV [electronic vehicle] transportation will change tourism for the better. Hoteliers and other tourism organizations are working through the challenges of introducing these new technologies.
Ivars (Citation 2004), in his analysis on tourism planning in Spain, discussed four broad approaches of tourism planning. For example, the earlier approaches to tourism planning (i.e. boosterism) generally reflect an uncomplicated view of tourism, while strategic planning has moved from the business environment to regional and urban planning in ...
Sustainable tourism planning is about finding the right balance between the needs of people and places. It involves clearly defining purpose, vision, and a point of difference or identity for your community. This form of destination planning in our communities enables us to think long-term, to be adaptable and proactive with changing target ...
A Sustainable Tourism Development Plan is a strategy designed to protect natural and cultural resources, promote local economies, and enhance visitor experiences. It is a roadmap for tourism boards, destination management organizations, and stakeholders in the tourism industry to ensure their development plans are sustainable and focused on the ...
Implementation and Action Plan 46 APPENDIX 1 - Supporting Resources 51 APPENDIX 2 - Action Plans for SPTO Partners 53. PACIFIC 2030 | SUSTAINABLE TOURISM POLICY FRAMEWORK ... Sustainable tourism is no longer optional - it is now an urgent imperative for every country in the Pacific. We want tourism to be resilient, prosperous, and ...