
- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone

golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Did You Know?

The Voyager mission was officially approved in May 1972. Through the dedicated efforts of many skilled personnel for over three decades, the Voyagers have returned knowledge about the outer planets that had not existed in all of the preceding history of astronomy and planetary science. The Voyager spacecrafts are still performing like champs.
It must come as no surprise that there are many remarkable, "gee-whiz" facts associated with the various aspects of the Voyager mission. These tidbits have been summarized below in appropriate categories. Several may seem difficult to believe, but they are all true and accurate.
Overall Mission
The total cost of the Voyager mission from May 1972 through the Neptune encounter (including launch vehicles, radioactive power source (RTGs), and DSN tracking support) is 865 million dollars. At first, this may sound very expensive, but the fantastic returns are a bargain when we place the costs in the proper perspective. It is important to realize that:
- on a per-capita basis, this is only 8 cents per U.S. resident per year, or roughly half the cost of one candy bar each year since project inception. the entire cost of Voyager is a fraction of the daily interest on the U.S. national debt.
- A total of 11,000 workyears was devoted to the Voyager project through the Neptune encounter. This is equivalent to one-third the amount of effort estimated to complete the great pyramid at Giza to King Cheops.
A total of five trillion bits of scientific data had been returned to Earth by both Voyager spacecraft at the completion of the Neptune encounter. This represents enough bits to fill more than seven thousand music CDs.
The sensitivity of our deep-space tracking antennas located around the world is truly amazing. The antennas must capture Voyager information from a signal so weak that the power striking the antenna is only 10 exponent -16 watts (1 part in 10 quadrillion). A modern-day electronic digital watch operates at a power level 20 billion times greater than this feeble level.
Voyager Spacecraft
Each Voyager spacecraft comprises 65,000 individual parts. Many of these parts have a large number of "equivalent" smaller parts such as transistors. One computer memory alone contains over one million equivalent electronic parts, with each spacecraft containing some five million equivalent parts. Since a color TV set contains about 2500 equivalent parts, each Voyager has the equivalent electronic circuit complexity of some 2000 color TV sets.
Like the HAL computer aboard the ship Discovery from the famous science fiction story 2001: A Space Odyssey, each Voyager is equipped with computer programming for autonomous fault protection. The Voyager system is one of the most sophisticated ever designed for a deep-space probe. There are seven top-level fault protection routines, each capable of covering a multitude of possible failures. The spacecraft can place itself in a safe state in a matter of only seconds or minutes, an ability that is critical for its survival when round-trip communication times for Earth stretch to several hours as the spacecraft journeys to the remote outer solar system.
Both Voyagers were specifically designed and protected to withstand the large radiation dosage during the Jupiter swing-by. This was accomplished by selecting radiation-hardened parts and by shielding very sensitive parts. An unprotected human passenger riding aboard Voyager 1 during its Jupiter encounter would have received a radiation dose equal to one thousand times the lethal level.
The Voyager spacecraft can point its scientific instruments on the scan platform to an accuracy of better than one-tenth of a degree. This is comparable to bowling strike-after-strike ad infinitum, assuming that you must hit within one inch of the strike pocket every time. Such precision is necessary to properly center the narrow-angle picture whose square field-of-view would be equivalent to the width of a bowling pin.
To avoid smearing in Voyager's television pictures, spacecraft angular rates must be extremely small to hold the cameras as steady as possible during the exposure time. Each spacecraft is so steady that angular rates are typically 15 times slower than the motion of a clock's hour hand. But even this was not steady enough at Neptune, where light levels are 900 times fainter than those on Earth. Spacecraft engineers devised ways to make Voyager 30 times steadier than the hour hand on a clock.
The electronics and heaters aboard each nearly one-ton Voyager spacecraft can operate on only 400 watts of power, or roughly one-fourth that used by an average residential home in the western United States.
A set of small thrusters provides Voyager with the capability for attitude control and trajectory correction. Each of these tiny assemblies has a thrust of only three ounces. In the absence of friction, on a level road, it would take nearly six hours to accelerate a large car up to a speed of 48 km/h (30 mph) using one of the thrusters.
The Voyager scan platform can be moved about two axes of rotation. A thumb-sized motor in the gear train drive assembly (which turns 9000 revolutions for each single revolution of the scan platform) will have rotated five million revolutions from launch through the Neptune encounter. This is equivalent to the number of automobile crankshaft revolutions during a trip of 2725 km (1700 mi), about the distance from Boston,MA to Dallas,TX.
The Voyager gyroscopes can detect spacecraft angular motion as little as one ten-thousandth of a degree. The Sun's apparent motion in our sky moves over 40 times that amount in just one second.
The tape recorder aboard each Voyager has been designed to record and playback a great deal of scientific data. The tape head should not begin to wear out until the tape has been moved back and forth through a distance comparable to that across the United States. Imagine playing a two-hour video cassette on your home VCR once a day for the next 33 years, without a failure.
The Voyager magnetometers are mounted on a frail, spindly, fiberglass boom that was unfurled from a two-foot-long can shortly after the spacecraft left Earth. After the boom telescoped and rotated out of the cannister to an extension of nearly 13 meters (43 feet), the orientations of the magnetometer sensors were controlled to an accuracy better than two degrees.
Each Voyager used the enormous gravity field of Jupiter to be hurled on to Saturn, experiencing a Sun-relative speed increase of roughly 35,700 mph. As total energy within the solar system must be conserved, Jupiter was initially slowed in its solar orbit---but by only one foot per trillion years. Additional gravity-assist swing-bys of Saturn and Uranus were necessary for Voyager 2 to complete its Grand Tour flight to Neptune, reducing the trip time by nearly twenty years when compared to the unassisted Earth-to-Neptune route.
The Voyager delivery accuracy at Neptune of 100 km (62 mi), divided by the trip distance or arc length traveled of 7,128,603,456 km (4,429,508,700 mi), is equivalent to the feat of sinking a 3630 km (2260 mi) golf putt, assuming that the golfer can make a few illegal fine adjustments while the ball is rolling across this incredibly long green.
Voyager's fuel efficiency (in terms of mpg) is quite impressive. Even though most of the launch vehicle's 700 ton weight is due to rocket fuel, Voyager 2's great travel distance of 7.1 billion km (4.4 billion mi) from launch to Neptune resultsed in a fuel economy of about 13,000 km per liter (30,000 mi per gallon). As Voyager 2 streaked by Neptune and coasts out of the solar system, this fuel economy just got better and better!
The resolution of the Voyager narrow-angle television cameras is sharp enough to read a newspaper headline at a distance of 1 km (0.62 mi).
Pele, the largest of the volcanoes seen on Jupiter's moon Io, is throwing sulfur and sulfur-dioxide products to heights 30 times that of Mount Everest, and the fallout zone covers an area the size of France. The eruption of Mount St. Helens was but a tiny hiccup in comparison (admittedly, Io's surface-level gravity is some six times weaker than that of Earth).
The smooth water-ice surface of Jupiter's moon Europa may hide an ocean beneath, but some scientists believe any past oceans have turned to slush or ice. In 2010: Odyssey Two, Arthur C. Clarke wraps his story around the possibility of life developing within the oceans of Europa.
The rings of Saturn appeared to the Voyagers as a dazzling necklace of 10,000 strands. Trillions of ice particles and car-sized bergs race along each of the million-kilometer-long tracks, with the traffic flow orchestrated by the combined gravitational tugs of Saturn, a retinue of moons and moonlets, and even nearby ring particles. The rings of Saturn are so thin in proportion to their 171,000 km (106,000 mi) width that, if a full-scale model were to be built with the thickness of a phonograph record the model would have to measure four miles from its inner edge to its outer rim. An intricate tapestry of ring-particle patterns is created by many complex dynamic interactions that have spawned new theories of wave and particle motion.
Saturn's largest moon Titan was seen as a strange world with its dense atmosphere and variety of hydrocarbons that slowly fall upon seas of ethane and methane. To some scientists, Titan, with its principally nitrogen atmosphere, seemed like a small Earth whose evolution had long ago been halted by the arrival of its ice age, perhaps deep-freezing a few organic relics beneath its present surface.
The rings of Uranus are so dark that Voyager's challenge of taking their picture was comparable to the task of photographing a pile of charcoal briquettes at the foot of a Christmas tree, illuminated only by a 1 watt bulb at the top of the tree, using ASA-64 film. And Neptune light levels will be less than half those at Uranus.
Through the ages, astronomers have argued without agreeing on where the solar system ends. One opinion is that the boundary is where the Sun’s gravity no longer dominates – a point beyond the planets and beyond the Oort Cloud. This boundary is roughly about halfway to the nearest star, Proxima Centauri. Traveling at speeds of over 35,000 miles per hour, it will take the Voyagers nearly 40,000 years, and they will have traveled a distance of about two light years to reach this rather indistinct boundary.
But there is a more definitive and unambiguous frontier, which the Voyagers will approach and pass through. This is the heliopause, which is the boundary area between the solar and the interstellar wind. When Voyager 1 crosses the solar wind termination shock, it will have entered into the heliosheath, the turbulent region leading up to the heliopause. When the Voyagers cross the heliopause, hopefully while the spacecraft are still able to send science data to Earth, they will be in interstellar space even though they will still be a very long way from the “edge of the solar system”. Once Voyager is in interstellar space, it will be immersed in matter that came from explosions of nearby stars. So, in a sense, one could consider the heliopause as the final frontier.
Barring any serious spacecraft subsystem failures, the Voyagers may survive until the early twenty-first century (~ 2025), when diminishing power and hydrazine levels will prevent further operation. Were it not for these dwindling consumables and the possibility of losing lock on the faint Sun, our tracking antennas could continue to "talk" with the Voyagers for another century or two!
Engineers Pinpoint Cause of Voyager 1 Issue, Are Working on Solution
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA’s Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe’s science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send the data to Earth.
In early March , the team issued a “poke” command to prompt the spacecraft to send back a readout of the FDS memory, which includes the computer’s software code as well as variables (values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status). Using the readout, the team has confirmed that about 3% of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations.
The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working. Engineers can’t determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years.
Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again.
Launched in 1977 , the twin Voyager spacecraft flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune. They are both exploring interstellar space, outside the bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun, called the heliosphere. Voyager 2 continues to operate normally.
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
NASA Engineers Make Progress Toward Understanding Voyager 1 Issue
Editor’s note: This blog post was originally published March 13, 2024, on NASA’s Sun Spot blog . Future Voyager blog posts will appear here, on NASA’s Voyager blog.
Since November 2023, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data. The source of the issue appears to be with one of three onboard computers, the flight data subsystem (FDS), which is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth by the telemetry modulation unit.
On March 3, the Voyager mission team saw activity from one section of the FDS that differed from the rest of the computer’s unreadable data stream. The new signal was still not in the format used by Voyager 1 when the FDS is working properly, so the team wasn’t initially sure what to make of it. But an engineer with the agency’s Deep Space Network, which operates the radio antennas that communicate with both Voyagers and other spacecraft traveling to the Moon and beyond, was able to decode the new signal and found that it contains a readout of the entire FDS memory.
The FDS memory includes its code, or instructions for what to do, as well as variables, or values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status. It also contains science or engineering data for downlink. The team will compare this readout to the one that came down before the issue arose and look for discrepancies in the code and the variables to potentially find the source of the ongoing issue.
This new signal resulted from a command sent to Voyager 1 on March 1. Called a “poke” by the team, the command is meant to gently prompt the FDS to try different sequences in its software package in case the issue could be resolved by going around a corrupted section.
Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach the spacecraft and another 22.5 hours for the probe’s response to reach antennas on the ground. So the team received the results of the command on March 3. On March 7, engineers began working to decode the data, and on March 10, they determined that it contains a memory readout.
The team is analyzing the readout. Using that information to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time.
Engineers Working to Resolve Issue With Voyager 1 Computer
Editor’s note: This blog post was originally published Dec. 12, 2023, on NASA’s Sun Spot blog . Future Voyager blog posts will appear here, on NASA’s Voyager blog. A previous version of this post identified the TMU as the telecommunications unit. It is the telemetry modulation unit.
Engineers are working to resolve an issue with one of Voyager 1’s three onboard computers, called the flight data system (FDS). The spacecraft is receiving and executing commands sent from Earth; however, the FDS is not communicating properly with one of the probe’s subsystems, called the telemetry modulation unit (TMU). As a result, no science or engineering data is being sent back to Earth.
Among other things, the FDS is designed to collect data from the science instruments as well as engineering data about the health and status of the spacecraft. It then combines that information into a single data “package” to be sent back to Earth by the TMU. The data is in the form of ones and zeros, or binary code. Varying combinations of the two numbers are the basis of all computer language.
Recently, the TMU began transmitting a repeating pattern of ones and zeros as if it were “stuck.” After ruling out other possibilities, the Voyager team determined that the source of the issue is the FDS. This past weekend the team tried to restart the FDS and return it to the state it was in before the issue began, but the spacecraft still isn’t returning useable data.
It could take several weeks for engineers to develop a new plan to remedy the issue. Launched in 1977, the spacecraft and its twin, Voyager 2, are the two longest-operating spacecraft in history. Finding solutions to challenges the probes encounter often entails consulting original, decades-old documents written by engineers who didn’t anticipate the issues that are arising today. As a result, it takes time for the team to understand how a new command will affect the spacecraft’s operations in order to avoid unintended consequences.
In addition, commands from mission controllers on Earth take 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is exploring the outer regions of our solar system more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth. That means the engineering team has to wait 45 hours to get a response from Voyager 1 and determine whether a command had the intended outcome.
Introducing the Voyager Mission Blog

Launched in 1977, NASA’s twin Voyager spacecraft are the agency’s longest-operating and farthest-flung probes. Voyager 1 visited Jupiter and Saturn, revealing new features of both planets and their moons. Voyager 2 followed its twin to Jupiter and Saturn before changing its trajectory to fly by Uranus and Neptune. It remains the only spacecraft to visit our solar system’s two ice giant planets.
Continuing their legacy as science pioneers, the Voyagers are the only two probes to journey into interstellar space – the space between stars. This region lies outside the heliosphere , the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields emitted by our Sun. By directly sampling the interstellar environment, the Voyagers are providing data that spacecraft closer to Earth can’t replicate. This helps scientists study both the shape of the heliosphere and its interaction with the ocean of interstellar material that the Sun is traveling through.
Readers of this blog can find occasional updates on mission science, the health of the spacecraft, and the creative solutions engineers have needed to come up with in order to keep the venerable spacecraft operating after nearly 50 years.
For more about Voyager, go to www.nasa.gov/voyager and follow along on X (formerly Twitter) at @NASAVoyager . Take Voyager’s Grand Tour with NASA’s Eyes .
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 calla.e. cofield @jpl.nasa.gov

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA’s Fermi Mission Sees No Gamma Rays from Nearby Supernova

The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA

The April 8 Total Solar Eclipse: Through the Eyes of NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now
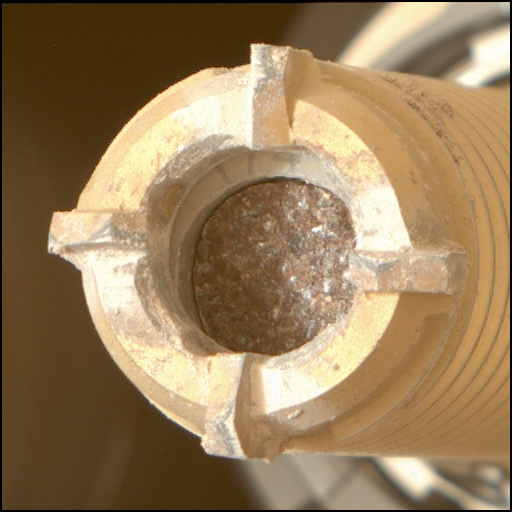
Comet Geyser: Perseverance’s 24th Rock Core
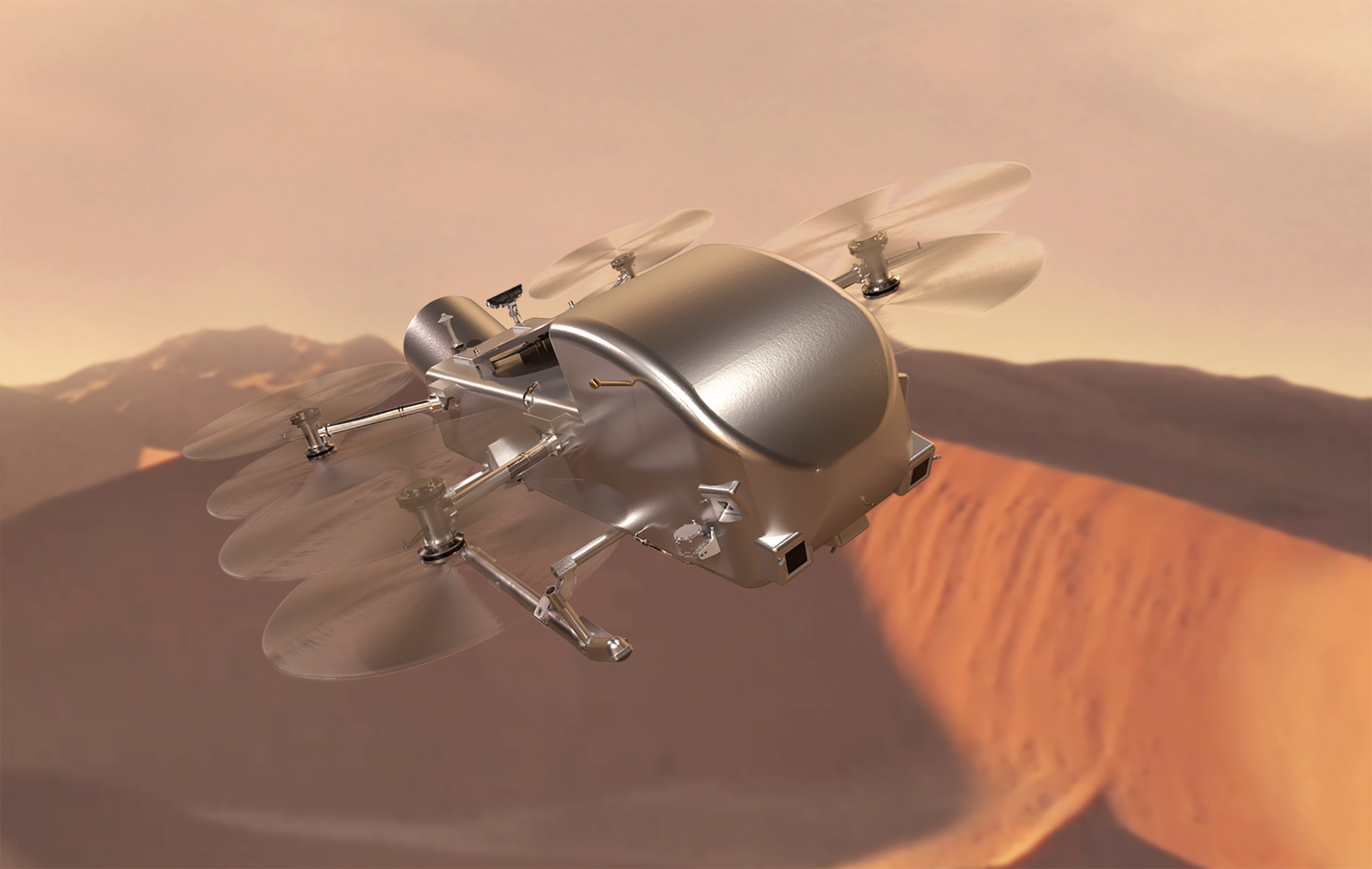

NASA’s Dragonfly Rotorcraft Mission to Saturn’s Moon Titan Confirmed

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin

NASA Motion Sickness Study Volunteers Needed!

NASA Selects New Crew for Next Simulated Mars Journey
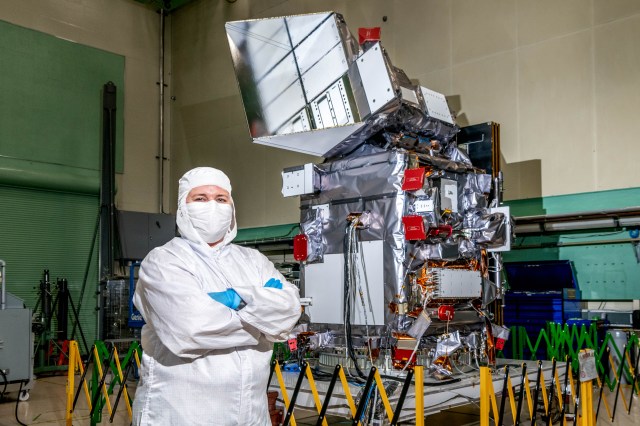

Kate A. McGinnis: Ready to “Go” with PACE Testing

A.3 Ocean Biology and Biogeochemistry Inclusion Plan Correction
A Solar Neighborhood Census, Thanks to NASA Citizen Science

Hubble Spots a Galaxy Hidden in a Dark Cloud
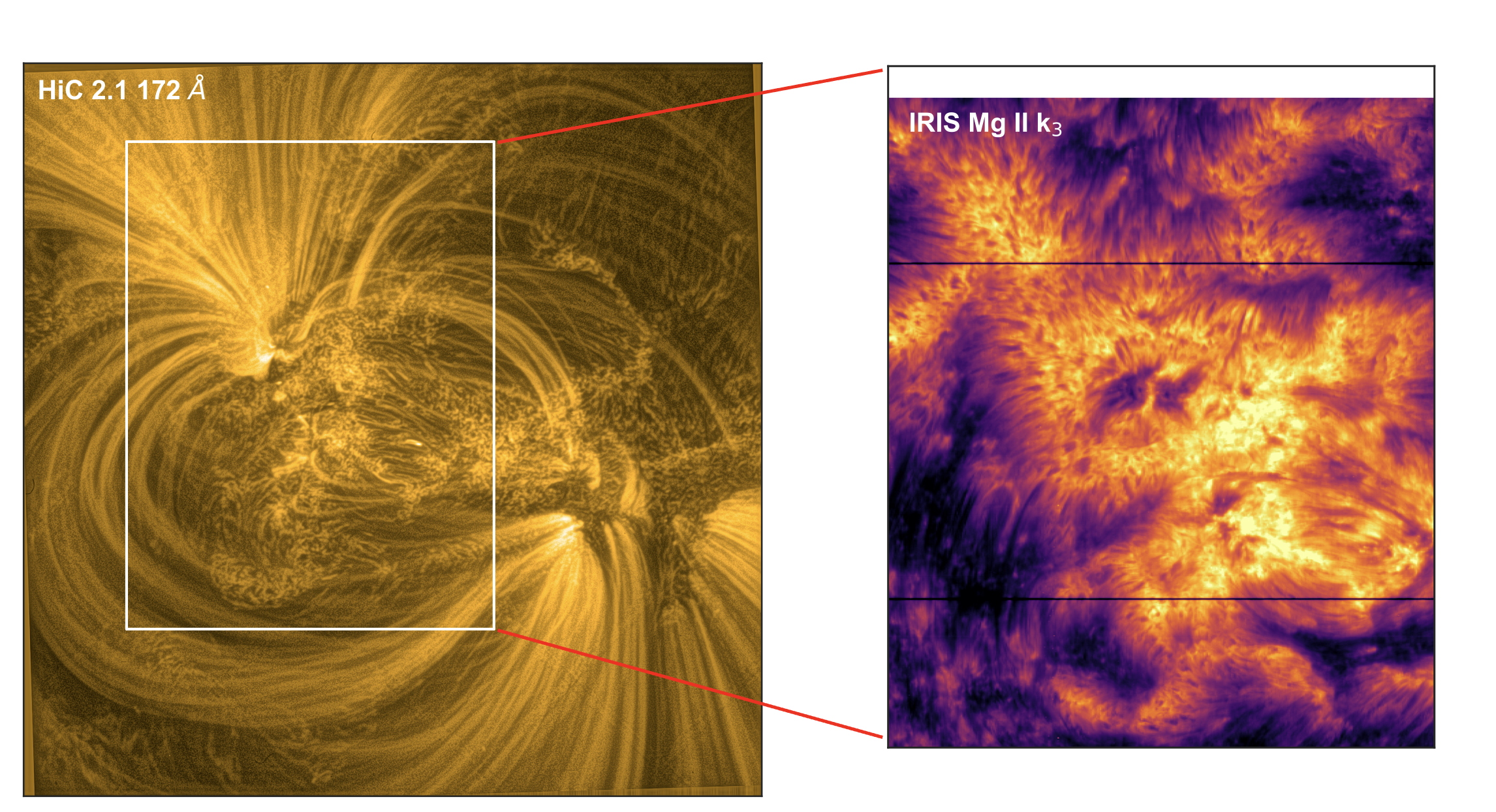
NASA Observations Find What Helps Heat Roots of ‘Moss’ on Sun

Amendment 9: New Opportunity: C.26 Rapid Mission Design Studies for Mars Sample Return

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations
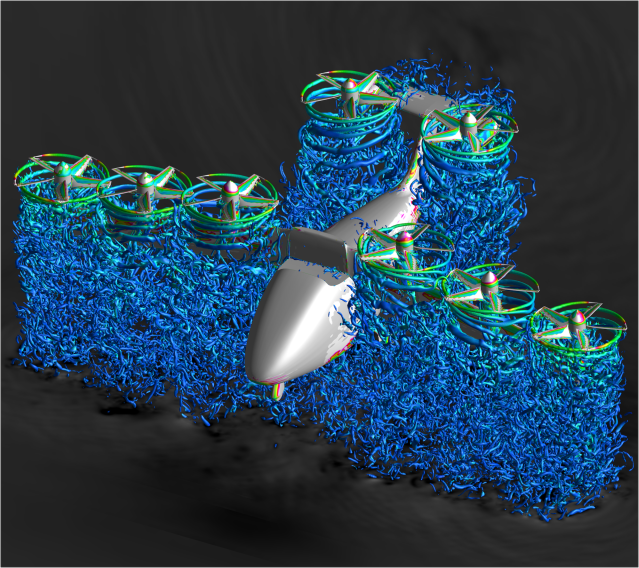
NASA Noise Prediction Tool Supports Users in Air Taxi Industry

NASA Goddard to Build Quake Detector for Artemis III Moon Landing

Tech Today: Folding NASA Experience into an Origami Toolkit
NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

NASA Receives 13 Nominations for the 28th Annual Webby Awards

La presentación del X-59 de la NASA personifica la tradición aeronáutica
Nasa mission update: voyager 2 communications pause, jet propulsion laboratory.
Once the spacecraft’s antenna is realigned with Earth, communications should resume.

UPDATE, Aug. 4, 2023: NASA has reestablished full communications with Voyager 2.
The agency’s Deep Space Network facility in Canberra, Australia, sent the equivalent of an interstellar “shout” more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) to Voyager 2, instructing the spacecraft to reorient itself and turn its antenna back to Earth. With a one-way light time of 18.5 hours for the command to reach Voyager, it took 37 hours for mission controllers to learn whether the command worked. At 12:29 a.m. EDT on Aug. 4, the spacecraft began returning science and telemetry data, indicating it is operating normally and that it remains on its expected trajectory.
UPDATE, Aug. 1, 2023: Using multiple antennas, NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN) was able to detect a carrier signal from Voyager 2. A carrier signal is what the spacecraft uses to send data back to Earth. The signal is too faint for data to be extracted, but the detection confirms that the spacecraft is still operating. The spacecraft also continues on its expected trajectory. Although the mission expects the spacecraft to point its antenna at Earth in mid-October, the team will attempt to command Voyager sooner, while its antenna is still pointed away from Earth. To do this, a DSN antenna will be used to “shout” the command to Voyager to turn its antenna. This intermediary attempt may not work, in which case the team will wait for the spacecraft to automatically reset its orientation in October.
Editor’s note: The following was posted on NASA’s The Sun Spot blog on July 28.
A series of planned commands sent to NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft July 21 inadvertently caused the antenna to point 2 degrees away from Earth. As a result, Voyager 2 is currently unable to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth.
Voyager 2 is located more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth, and this change has interrupted communication between Voyager 2 and the ground antennas of NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN). Data being sent by the spacecraft is no longer reaching the DSN, and the spacecraft is not receiving commands from ground controllers.
Voyager 2 is programmed to reset its orientation multiple times each year to keep its antenna pointing at Earth; the next reset will occur on Oct. 15, which should enable communication to resume. The mission team expects Voyager 2 to remain on its planned trajectory during the quiet period.
Voyager 1, which is almost 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, continues to operate normally.
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
Media Contact
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
We finally know why NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft stopped communicating — scientists are working on a fix
The first spacecraft to explore beyond the solar system started spouting gibberish late last year. Now, NASA knows why.

NASA engineers have discovered the cause of a communications breakdown between Earth and the interstellar explorer Voyager 1. It would appear that a small portion of corrupted memory exists in one of the spacecraft's computers.
The glitch caused Voyager 1 to send unreadable data back to Earth, and is found in the NASA spacecraft's flight data subsystem (FDS). That's the system responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send it back to mission control.
The source of the issue began to reveal itself when Voyager 1 operators sent the spacecraft a "poke" on March 3, 2024. This was intended to prompt FDS to send a full memory readout back to Earth.
The readout confirmed to the NASA team that about 3% of the FDS memory had been corrupted, and that this was preventing the computer from carrying out its normal operations.
Related: NASA finds clue while solving Voyager 1's communication breakdown case
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space in 2012. Voyager 2 followed its spacecraft sibling out of the solar system in 2018, and is still operational and communicating well with Earth.
After 11 years of interstellar exploration, in Nov. 2023, Voyager 1's binary code — the computer language it uses to communicate with Earth — stopped making sense. Its 0's and 1's didn't mean anything anymore.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Effectively, the call between the spacecraft and the Earth was still connected, but Voyager's 'voice' was replaced with a monotonous dial tone," Voyager 1's engineering team previously told Space.com .

The team strongly suspects this glitch is the result of a single chip that's responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory ceasing to work.
Currently, however, NASA can’t say for sure what exactly caused that particular issue. The chip could have been struck by a high-speed energetic particle from space or, after 46 years serving Voyager 1, it may simply have worn out.
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft to receive a response via the Deep Space Network's antennas. Solving this communication issue is thus no mean feat.
Yet, NASA scientists and engineers are optimistic they can find a way to help FDS operate normally, even without the unusable memory hardware.
Solving this issue could take weeks or even months, according to NASA — but if it is resolved, Voyager 1 should be able to resume returning science data about what lies outside the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
Rocket Lab to launch NASA's new solar sail technology no earlier than April 24
SpaceX launches Starlink satellites on record 20th reflight of a Falcon 9 rocket first stage
SpaceX launching 23 Starlink satellites from Florida this evening
- jcs Funny timing for this article, when I am streaming an old Star Trek movie. So, surely this didn't cause a 3 byte glitch removing the O, Y and A from Voyager's name buffer? Get it? Reply
- bwana4swahili It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment. Reply
bwana4swahili said: It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment.
- HankySpanky So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists. Reply
HankySpanky said: So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists.
- Classical Motion I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around. Reply
Classical Motion said: I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around.
- jcs ROFLOL! And a hot bald chick delivering the bad news! Reply
- View All 8 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Uranus and Neptune aren't made of what we thought, new study hints
- 3 Exotic 'Einstein ring' suggests that mysterious dark matter interacts with itself
- 4 Boeing Starliner spacecraft rolls out to Atlas V rocket ahead of 1st astronaut launch (photos)
- 5 'Star Trek: Lower Decks' Season 4 blasts onto Blu-ray and DVD on April 16
- Ask An Astrobiologist
- Resources Graphic Histories Coloring Pages Heroes Posters Life in the extremes Digital Backgrounds SciComm Guild

Voyager 1 and Voyager 2
Voyager interstellar mission.
- Launch Date August 19, 1977
- Arrival Date April 08, 1979
- Mission Type Outer Solar System
- Target Outer Solar System
Mission Overview
The primary mission of the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft was to explore the outer planets of Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 launched on August 20, 1977, from Cape Canaveral, Florida aboard a Titan-Centaur rocket. On September 5, Voyager 1 launched, also from Cape Canaveral aboard a Titan-Centaur rocket. The Voyager Interstellar Mission was the first to provide humankind with a close-up view of the outer planets. Between them, Voyager 1 and 2 explored all the giant planets of our outer solar system, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune; 48 of their moons; and the unique system of rings and magnetic fields those planets possess.
Relevance to Astrobiology
The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are now exploring reaches of space where nothing from Earth has flown before. The twin spacecraft are continuing on their more-than-37-year journey that began with their respective launches in 1977. Each spacecraft is now traveling further from the Earth and the Sun than Pluto.
After making a string of discoveries there — such as active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io and intricacies of Saturn’s rings — the mission was extended. Voyager 2 went on to explore Uranus and Neptune, and is still the only spacecraft to have visited those outer planets. The adventurers’ current mission, the Voyager Interstellar Mission ( VIM ), will explore the outermost edge of the Sun’s domain. And beyond.
NASA Astrobiology Involvement
The Voyager mission has dramatically shaped our understanding of the Solar System and the potential for life on our system’s planets and moons. It was data from Voyager that first raised questions about the potential for liquid water beneath the icy crust of Jupiter’s moon Europa. Voyager also revealed that Saturn’s moon Titan was shrouded in a thick atmospheric haze, a finding that ultimately led to the development of the Cassini-Huygens mission. Astrobiologists today still use data from Voyager, revealing more and more clues about the worlds that circle the Sun beyond the Asteroid Belt.

Observations from the twin Voyager spacecraft suggested that an ocean might exist beneath the cracked icy crust of Jupiter’s moon Europa.

Voyager discovered that Jupiter’s moon Io was active. The spacecraft spotted erupting volcanoes on Io’s surface, making it 100 times the volcanic activity of Earth. Voyager also discovered the Io torus, a thick ring of ionized sulfur and oxygen shed by Io that inflates Jupiter’s giant magnetic field
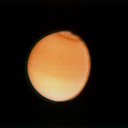
Voyager found Saturn’s moon Titan shrouded in a deep, smoggy nitrogen atmosphere. Titan was a high priority for the Voyager flybys at Saturn. The two spacecraft saw tantalizing hints of the structure and composition of the giant moon’s dense atmosphere. This Voyager 2 photograph of Titan, taken Aug. 23, 1981 from a range of 2.3 million kilometers (1.4 million miles), shows some detail in the cloud systems on this Saturnian moon.
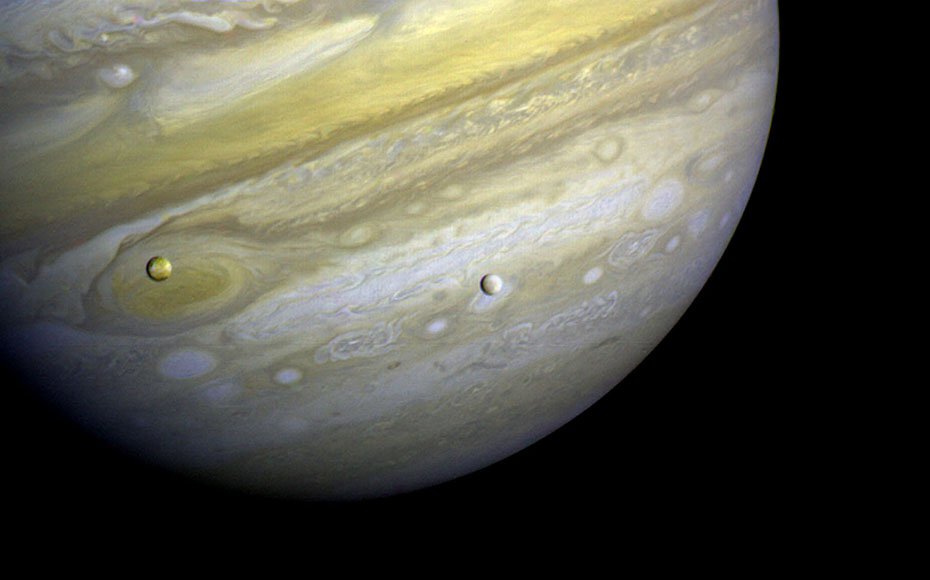

The closest approach to Jupiter occurred on March 5, 1979 for Voyager 1; July 9, 1979 for Voyager 2. Voyager 1 took this photo of Jupiter and two of its satellites (Io, left, and Europa) on Feb. 13, 1979.
The closest approach to Saturn occurred on November 12, 1980 for Voyager 1; August 25, 1981 for Voyager 2. Voyager 1 captured this image of Saturn on Nov. 16, 1980.
The closest approach to Uranus occurred on January 24, 1986 by Voyager 2. The spacecraft observed a bluish orb with extremely subtle features. A haze layer hid most of the planet’s cloud features from view.
The closest approach to Neptune occurred on August 25, 1989 by Voyager 2. This contrast-enhanced image of Neptune was taken 11 days before that encounter.
As of September 2013, Voyager 2 was at a distance of 15.3 billion kilometers (102.6 AU) from the Sun.
Voyager 2 is escaping the Solar System at a speed of about 3.3 AU per year.
A total of 11,000 work years was devoted to the Voyager project through the Neptune encounter. This is equivalent to one-third the amount of effort estimated to complete the great pyramid at Giza to King Cheops.
The Voyager spacecraft appear in Issue #4 of the Astrobiology Graphic History: https://astrobiology.nasa.gov/resources/graphic-histories/

Special Features
Vendor voice.
NASA tries to jog Voyager 1's memory from 15 billion miles away
Since you can't get a soldering iron out there, the fix will be in software.
Engineers at NASA have pinpointed some corrupted memory as the cause of Voyager 1's troubles and are working on a remote fix to deal with the hardware problem.
The veteran probe began sending unreadable data back to Earth in late 2023 , and engineers have tried to understand the nature of the issue. Last month, they sent a command – a "poke" to the spacecraft's Flight Data System (FDS) – and the resulting data stream contained a complete memory dump from the computer.
The team was able to use this readout, which contained the computer's code and variables, to ascertain that approximately 3 percent of the FDS memory had been corrupted. That corruption is preventing normal operation of the FDS, which is responsible for packaging the probe's engineering and science data before it gets passed to the Telemetry Modulation Unit (TMU), the radio transmitter and is sent back to Earth.
The Voyager team reckons that a single chip responsible for the corrupted portion of memory is at fault, although they can only make an informed guess with regard to what has happened.
Two leading theories are that the chip has simply worn out having spent 46 years in space, or that an energetic particle might have damaged it.
As Voyager 1 is well out of the reach of any physical intervention, the issue will need to be addressed in software.
According to NASA: "Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again."
- Hundreds of workers to space out from NASA's JPL amid budget black hole
- The Reg chats with Voyager Imaging Team member Dr Garry E Hunt
- Maverick Mars chopper has survived way past its warranty – now it's time for a sequel
- NASA just patched Voyager 2's software but spared Voyager 1 the risky rewrite
Computer problems caused by cosmic rays and energetic particles have long challenged spacecraft designers. Some might merely result in a bit flip, while others can leave satellites inoperable or damaged.
Voyager 2 suffered a bit flip in 2010 , which caused problems with science data transmitted from the spacecraft and was traced to the FDS. A computer reset dealt with the problem.
This time, however, the hardware appears to have become inoperative, requiring engineers to devise something more complicated than a simple turn-it-off-and-on-again solution. ®
Narrower topics
- Hubble Space Telescope
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory
- Perseverance
Broader topics
- Federal government of the United States
- Semiconductor Memory
Send us news
Other stories you might like
Nasa needs new ideas and tech to get mars sample return mission off the ground, nasa taps trio of companies to build the next generation of lunar rover, nasa confirms florida house hit by a piece of iss battery pack, industrial systems integrating digitalisation.
65 years ago, America announced the names of its first astronauts
Tsmc shrugs off impact of taiwan earthquake, us reckons it's about time the moon had its own time zone, nasa gives ixpe observatory the ctrl-alt-del treatment to make it talk sense, nasa to shoot rockets at april solar eclipse to see how it messes with the atmosphere, voyager 1 starts making sense again after months of babble, samsung preps inferencing accelerator to take on nvidia, scores huge sale, nasa missions are being delayed by oversubscribed, overburdened, and out-of-date supercomputers.
- Advertise with us
Our Websites
- The Next Platform
- Blocks and Files
Your Privacy
- Cookies Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Ts & Cs

Copyright. All rights reserved © 1998–2024
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, right, stands near the apex of a sand ripple in an image taken by Perseverance on Feb. 24, about five weeks after the rotorcraft’s final flight. Part of one of Ingenuity’s rotor blades lies on the surface about 49 feet (15 meters) west of helicopter (left of center in the image).
The final downlink shift by the Ingenuity team was a time to reflect on a highly successful mission — and to prepare the first aircraft on another world for its new role.
Engineers working on NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter assembled for one last time in a control room at the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Tuesday, April 16, to monitor a transmission from the history-making helicopter. While the mission ended Jan. 25, the rotorcraft has remained in communication with the agency’s Perseverance Mars rover, which serves as a base station for Ingenuity. This transmission, received through the antennas of NASA’s Deep Space Network , marked the final time the mission team would be working together on Ingenuity operations.
Now the helicopter is ready for its final act: to serve as a stationary testbed, collecting data that could benefit future explorers of the Red Planet.
Throughout its mission on the Red Planet, NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter received thousands of electronic postcards filled with well wishes from all over the world via the mission’s website. In this video, members of the helicopter team read some of those messages.
“With apologies to Dylan Thomas, Ingenuity will not be going gently into that good Martian night,” said Josh Anderson, Ingenuity team lead at JPL. “It is almost unbelievable that after over 1,000 Martian days on the surface, 72 flights, and one rough landing, she still has something to give. And thanks to the dedication of this amazing team, not only did Ingenuity overachieve beyond our wildest dreams, but also it may teach us new lessons in the years to come.”
Originally designed as a short-lived technology demonstration mission that would perform up to five experimental test flights over 30 days, the first aircraft on another world operated from the Martian surface for almost three years, flew more than 14 times farther than the distance expected, and logged more than two hours of total flight time.
Ingenuity’s mission ended after the helicopter experienced a hard landing on its last flight , significantly damaging its rotor blades. Unable to fly, the rotorcraft will remain at “ Valinor Hills ” while the Perseverance rover drives out of communications range as it continues to explore the western limb of Jezero Crater.
Bytes and Cake
The team enjoyed some “Final Comms” chocolate cake while reviewing the latest data from over 189 million miles (304 million kilometers) away. The telemetry confirmed that a software update previously beamed up to Ingenuity was operating as expected. The new software contains commands that direct the helicopter to continue collecting data well after communications with the rover have ceased.

Engineers working on NASA’s Ingenuity together monitored a transmission from the history-making helicopter in a JPL control room on April 16. They confirmed the operation of a software patch that will allow the helicopter to act as a stationary testbed and collect data that could benefit future Mars explorers.
With the software patch in place, Ingenuity will now wake up daily, activate its flight computers, and test the performance of its solar panel, batteries, and electronic equipment. In addition, the helicopter will take a picture of the surface with its color camera and collect temperature data from sensors placed throughout the rotorcraft. Ingenuity’s engineers and Mars scientists believe such long-term data collection could not only benefit future designers of aircraft and other vehicles for the Red Planet, but also provide a long-term perspective on Martian weather patterns and dust movement.
During this final gathering, the team received a farewell message from Ingenuity featuring the names of people who worked on the mission. Mission controllers at JPL sent the message to Perseverance the day before, which handed it off to Ingenuity so that it could transmit the farewell back to Earth.
Need Some Space?
Decades of Room
If a critical electrical component on Ingenuity were to fail in the future, causing data collection to stop, or if the helicopter eventually loses power because of dust accumulation on its solar panel, whatever information Ingenuity has collected will remain stored on board. The team has calculated Ingenuity’s memory could potentially hold about 20 years’ worth of daily data.
“Whenever humanity revisits Valinor Hills — either with a rover, a new aircraft, or future astronauts — Ingenuity will be waiting with her last gift of data, a final testament to the reason we dare mighty things,” said Ingenuity’s project manager, Teddy Tzanetos of JPL. “Thank you, Ingenuity, for inspiring a small group of people to overcome seemingly insurmountable odds at the frontiers of space.”
Tzanetos and other Ingenuity alumni are currently researching how future Mars helicopters — including the Mars Science Helicopter concept — could benefit explorations of the Red Planet and beyond.
More About the Mission
The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley and NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity’s development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System . At NASA Headquarters, Dave Lavery is the program executive for the Ingenuity Mars helicopter.
For more information about Ingenuity:
https://mars.nasa.gov/technology/helicopter

News Media Contact
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-9011
Karen Fox / Alana Johnson
NASA Headquarters, Washington
301-286-6284 / 202-358-1501
[email protected] / [email protected]

Rosatom Starts Production of Rare-Earth Magnets for Wind Power Generation
TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom has started gradual localization of rare-earth magnets manufacturing for wind power plants generators. The first sets of magnets have been manufactured and shipped to the customer.

In total, the contract between Elemash Magnit LLC (an enterprise of TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom in Elektrostal, Moscow region) and Red Wind B.V. (a joint venture of NovaWind JSC and the Dutch company Lagerwey) foresees manufacturing and supply over 200 sets of magnets. One set is designed to produce one power generator.
“The project includes gradual localization of magnets manufacturing in Russia, decreasing dependence on imports. We consider production of magnets as a promising sector for TVEL’s metallurgical business development. In this regard, our company does have the relevant research and technological expertise for creation of Russia’s first large-scale full cycle production of permanent rare-earth magnets,” commented Natalia Nikipelova, President of TVEL JSC.
“NovaWind, as the nuclear industry integrator for wind power projects, not only made-up an efficient supply chain, but also contributed to the development of inter-divisional cooperation and new expertise of Rosatom enterprises. TVEL has mastered a unique technology for the production of magnets for wind turbine generators. These technologies will be undoubtedly in demand in other areas as well,” noted Alexander Korchagin, Director General of NovaWind JSC.
For reference:
TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom incorporates enterprises for the fabrication of nuclear fuel, conversion and enrichment of uranium, production of gas centrifuges, as well as research and design organizations. It is the only supplier of nuclear fuel for Russian nuclear power plants. TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom provides nuclear fuel for 73 power reactors in 13 countries worldwide, research reactors in eight countries, as well as transport reactors of the Russian nuclear fleet. Every sixth power reactor in the world operates on fuel manufactured by TVEL. www.tvel.ru
NovaWind JSC is a division of Rosatom; its primary objective is to consolidate the State Corporation's efforts in advanced segments and technological platforms of the electric power sector. The company was founded in 2017. NovaWind consolidates all of the Rosatom’s wind energy assets – from design and construction to power engineering and operation of wind farms.
Overall, by 2023, enterprises operating under the management of NovaWind JSC, will install 1 GW of wind farms. http://novawind.ru
Elemash Magnit LLC is a subsidiary of Kovrov Mechanical Plant (an enterprise of the TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom) and its main supplier of magnets for production of gas centrifuges. The company also produces magnets for other industries, in particular, for the automotive
industry. The production facilities of Elemash Magnit LLC are located in the city of Elektrostal, Moscow Region, at the site of Elemash Machine-Building Plant (a nuclear fuel fabrication facility of TVEL Fuel Company).
Rosatom is a global actor on the world’s nuclear technology market. Its leading edge stems from a number of competitive strengths, one of which is assets and competences at hand in all nuclear segments. Rosatom incorporates companies from all stages of the technological chain, such as uranium mining and enrichment, nuclear fuel fabrication, equipment manufacture and engineering, operation of nuclear power plants, and management of spent nuclear fuel and nuclear waste. Nowadays, Rosatom brings together about 350 enterprises and organizations with the workforce above 250 K. https://rosatom.ru/en/

U.S. Added Less New Wind Power in 2021 Than the Previous Year — Here’s Why

Airborne Wind Energy Developer Kitemill Prepares for 24HOUR Operation and Multi-Device Demonstrations

Vietnam's Largest Wind Power Plant Starts Operational

Vietnam Plans to Double Wind Power Generation by 2030

Developer Lines up Support for Vietnam Wind Build

Trung Nam Group Inaugurates Wind Power Plant in Vietnam

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.
13 Facts About CdLS Awareness Day May 11th
12 Facts About Coin Week Apr 21st To Apr 27th
40 facts about elektrostal.
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett
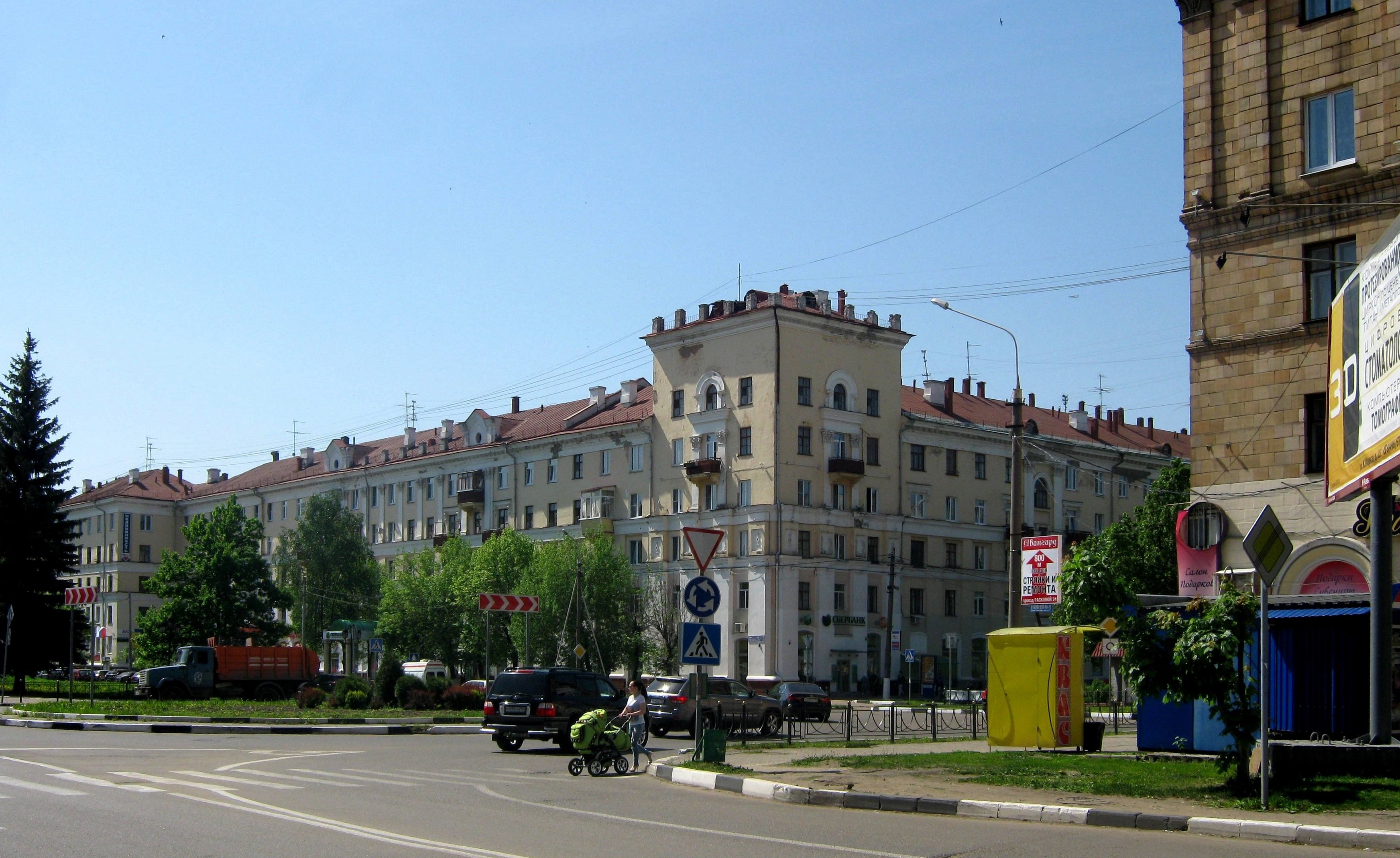

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:
- Phone: +90 (212) 875 19 08
- E-Mail: [email protected]
- Company Profile
- Company Policy
- Mission and Vision
- Certificates
- Aluminium Windows
- Aluminium Doors
- Aluminium Sliding Elements
- Aluminium Curtain Walls
- Aluminium Skylight Elements
- Aluminium Frames for Safety and Security
- Aluminium Conservatories
- Metal Panel Sheet Claddings
- Aluminium Entrance Frames
- Glass Structures
- Complementary Items
- Lightweight Steel Structures
- Human Resources OPEN
First successful projects, then lasting relationships!
As it has been in the past 40 years, Mimsa believe in providing competitive prices without compromising their principles of quality. We have managed to create lasting relationships based on honesty and cooperation while adding new customers each year.
Nothing is more important for us than Customer satisfaction!
Mimsa prioritizes customer satisfaction in the services they provide, and strives to understand the customers’ requests thoroughly in order to fulfil their needs and expectations. According to Mimsa Aluminium, every single customer should always be provided with the quality and services above expectations.
Every single completed project is the beginning of a lasting relationship for us.
Mimsa executes every project with experience and knowledge, while continuously improving itself and its high-quality production. Therefore, Mimsa never regards a project as a completed business. Every single project is a successful representation of lasting relationships. Thus, Mimsa pay great attention to post-sale support and keep on supplying uninterrupted support to their customers after completion.
It is very important for us that every single project we execute creates value to our workers, community and environment!
Aiming to create value for the community, environment and humankind in each project. Mimsa perceive that the occupational training of its employees and the new entrants to the workforce gets these individuals well equipped for the industry and community, and so does whatever needed without second thoughts.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time. For a full 3D, immersive experience click on View Voyagers link below to launch the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app. View Voyager.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
NASA's Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy. Article. 7 Min Read. NASA Missions Study What May Be a 1-In-10,000-Year Gamma-ray Burst. Multimedia Go To Galleries Go To Galleries Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test Mission Overview Earth Day Poster 2024 ...
What. Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018.
Voyager 1 was the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere, the boundary where the influences outside our solar system are stronger than those from our Sun. Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. Voyager 1 discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and two new Jovian moons: Thebe and Metis.
About the mission. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
A quarter-century after NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft departed Earth to visit outer planets, the historic mission is flying a race against time. During the first 12 years after launch in 1977, the Voyagers chalked up a wealth of discoveries about four planets and 48 moons, including fast winds on Neptune, kinks in Saturn's rings and […]
The mission objective of the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) is to extend the NASA exploration of the solar system beyond the neighborhood of the outer planets to the outer limits of the Sun's sphere of influence, and possibly beyond. This extended mission is continuing to characterize the outer solar system environment and search for the ...
Voyager, NASA's Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space. This archival image taken at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 23, 1977, shows engineers preparing the Voyager 2 spacecraft ahead of its launch later that year. Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 ...
The twin spacecraft Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were launched by NASA in separate months in the summer of 1977 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. ... The Voyager mission was designed to take advantage of a rare geometric arrangement of the outer planets in the late 1970s and the 1980s which allowed for a four-planet tour for a minimum of propellant and ...
NASA extended the mission so that Voyager 2 could visit Neptune and Uranus; it is still the only spacecraft ever to have encountered the ice giants. In 1990, NASA extended the mission again, this time with the goal of sending the probes outside the heliosphere. Voyager 1 reached the boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a ...
NASA's Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space. On Dec. 10, 2018, the spacecraft joined its twin - Voyager 1 - as the only human-made objects to enter the space between the stars. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range. Voyager 2 discovered a 14th moon at ...
The Project Begins. "Mariner Jupiter/Saturn 1977," the name of the mission before it became Voyager, is approved by NASA, with day-to-day management by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The original plans commit only to flybys of Jupiter and Saturn and build upon the heritage of earlier Mariner spacecraft that flew by ...
Voyager's fuel efficiency (in terms of mpg) is quite impressive. Even though most of the launch vehicle's 700 ton weight is due to rocket fuel, Voyager 2's great travel distance of 7.1 billion km (4.4 billion mi) from launch to Neptune resultsed in a fuel economy of about 13,000 km per liter (30,000 mi per gallon).
About the mission. The Voyager 2 spacecraft, which has been in operation since 1977 and is the only spacecraft to have ever visited Uranus and Neptune, has made its way to interstellar space, where its twin spacecraft, Voyager 1, has resided since August 2012. During its travels through the outer solar system, Voyager 2 visited all four gas ...
Launched in 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft are the agency's longest-operating and farthest-flung probes. Voyager 1 visited Jupiter and Saturn, revealing new features of both planets and their moons. Voyager 2 followed its twin to Jupiter and Saturn before changing its trajectory to fly by Uranus and Neptune. It remains the only ...
A series of planned commands sent to NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft July 21 inadvertently caused the antenna to point 2 degrees away from Earth. As a result, Voyager 2 is currently unable to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth. Voyager 2 is located more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth, and this change has ...
In November 2023, the first spacecraft to journey to interstellar space, Voyager 1, started spouting gibberish. Now, NASA knows why. The team is working on a fix.
The adventurers' current mission, the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM), will explore the outermost edge of the Sun's domain. And beyond. NASA Astrobiology Involvement. The Voyager mission has dramatically shaped our understanding of the Solar System and the potential for life on our system's planets and moons.
Richard Speed. Mon 15 Apr 2024 // 15:02 UTC. Engineers at NASA have pinpointed some corrupted memory as the cause of Voyager 1's troubles and are working on a remote fix to deal with the hardware problem. The veteran probe began sending unreadable data back to Earth in late 2023, and engineers have tried to understand the nature of the issue.
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-393-9011. [email protected]. Karen Fox / Alana Johnson. NASA Headquarters, Washington. 301-286-6284 / 202-358-1501. [email protected] / [email protected]. 2024-044. The final downlink shift by the Ingenuity team was a time to reflect on a highly successful mission — and to prepare the ...
06 Nov 2020 by Rosatom. TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom has started gradual localization of rare-earth magnets manufacturing for wind power plants generators. The first sets of magnets have been manufactured and shipped to the customer. In total, the contract between Elemash Magnit LLC (an enterprise of TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom in Elektrostal ...
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
Mission and Vision. Mission. First successful projects, then lasting relationships! As it has been in the past 40 years, Mimsa believe in providing competitive prices without compromising their principles of quality. We have managed to create lasting relationships based on honesty and cooperation while adding new customers each year.
The new production site was established for fulfillment of the contract between TVEL and the Chinese company CNLY (a subsidiary of CNNC Corporation) for supply of uranium fuel for the CFR-600 reactor, including start-up loading, as well as refueling for the first seven years of the power unit operation.