18 Biggest Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
President Donald Trump announced his desire in 2018 to create a sixth branch of the U.S. military that he colloquially called the Space Force. Although Congress has yet to act on this desire to take the armed forces beyond the atmosphere of our planet, in February 2019, Trump signed Space Policy Directive 4 to have these forces organize underneath the umbrella of the U.S. Air Force.
The directive formally allows the Air Force to organize, train, and equip a corps of military space personnel for actions that take place in space. “Today I’m thrilled to sign a new order taking the next step to create the United States Space Force,” Trump said during the signing ceremony. “It’s so important. When you look at defense, when you look at all of the other aspects of where the world will be some day. I mean, this is the beginning. This is a very important process.”
The initial version of the Space Force will be overseen by a civilian undersecretary and a four-star general serving as the Chief of Staff. Although this structure is not as ambitious as having a separate branch of the military, space exploration experts feel like this is a step in the right direction.
The pros and cons of exploring space are complex simply because we have limited knowledge of what lies beyond our solar system. There are still mysteries to discover about our own planet! These are the key points to consider when we begin to look at what life might look like in the vastness of space.

List of the Pros of Space Exploration
1. It is an opportunity which is available to anyone. If you have a telescope, then you have an opportunity to start exploring space. For more than 300 years, we have looked to the stars with this technology as a way to learn more about our planet and ourselves as a species. When the Hubble space telescope was launched in 1990, it gave us our first views without atmospheric interference on what the vastness of our universe was like.
With millions of images taken and tens of thousands of papers written based on the observations made from simple telescope technologies, we have learned more about the structure of our universe, its age, and the composition of our solar system in the last 20 years than our ancestors would have ever dreamed was possible.
2. It gives us an opportunity to foster genuine cooperation. Because we are a world of nation states, the investments that we make in space exploration tend to have a patriotic feeling to them. Some efforts in this scientific area are still nationally-based, but for most projects there is a spirit of cooperation between the countries of the world who have made this realm of science a top priority. We work together as the human race to operate the international space station, fund research projects, and look outward beyond the stars to see what is there. It is one of the few areas in our lives today where we set aside our boundaries to work together toward a common good.
3. It is an effort which requires us to become innovative. The 100-year Starship Program has the ultimate goal of creating a technology that will allow us to explore space. No idea is off-limits with this project. What we have found in our quest to achieve specific goals in this area of science is that there are numerous discoveries which become possible to improve our lives here at home. Everything from athletic shoes to water purification systems came about because of our push to look beyond our planet. By tackling the technological needs to stay safe in space, we can make life better for everyone down on our planet at the same time.
4. It is an opportunity to explore something new. Although there are still regions of our planet that we rarely study because of technology limitations, the vastness of the universe is a much more significant prize. Only the Voyager spacecraft have gone beyond the first boundaries of our solar system. The information they provide us nearly four decades after their launch continues to enlighten our knowledge of the universe. There are so many unanswered questions when we think about space, especially now that scientists can determine which stars have planets orbiting around them.
Is there life somewhere else in the universe? If so, would those beings look like us? There are numerous technological barriers we must cross before we could travel for long distances in the vacuum of space, but we are getting one step closer every day.
5. It creates numerous employment opportunities in a variety of fields. There are more than 18,000 people employed in the United States by NASA, along with countless contractors, freelancers, and specialists not counted in those figures. The private company SpaceX provides about 7,000 full-time high-skill positions that support the economy. Then there are the astronauts, engineers, and flight specialists who manage the actual mechanisms of space flight to consider.
Numerous indirect employment opportunities are possible because of our efforts at space exploration too. We need caterers, designers, nutritionists, personal trainers, astronomers, scientists, and many other positions to support these activities. Even though the budget for NASA is $21 billion for FY 2020, the economic returns can be five times greater because of these activities.
6. It allows us to understand our planet better. When we can observe the full scale of our planet from a high orbital position, then we can see changes that are not always possible from the ground. It gives us a way to track the changes to our environment, study ozone depletion, and measure the impacts of a warming planet. We can provide accurate prediction models for weather patterns, observe troop movements, and install safety equipment that guards against an attack. When we take full advantage of this benefit, it becomes possible to create a place in the universe that is healthier for many years to come.
7. It gives us a new perspective on our place in the universe. It took several centuries for the scientific world (back by religious zealots) to accept the fact that the Earth was not the center of the universe. When we saw that first picture from a distance of what our planet looks like from a distant point in our solar system, it became clear to see that a small, pale blue dot in the middle of the vastness of our universe puts our daily issues into a new perspective. Until we discover otherwise, this is the only home that we have. It is up to each of us to share resources, reduce conflict, and work toward a common good.
8. It allows us to identify potential dangers before they strike. The asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars is only one source for these deadly rocks in our solar system. There may even be threats that travel through the universe to interact with our region of space from time-to-time. It would only take one significant impact to change life on our planet forever, which is why space exploration makes threat identification a top priority. If we can locate and move threatening asteroids or comets before they threaten an impact, we could stop the apocalypse before it ever gets a chance to begin.
9. It would give us access to new minerals, precious metals, and other useful items. Thanks to the asteroids which occasionally make it to the surface of our planet, we know that many of them contain iron and carbon. We also know that there is nickel, cobalt, silicon, magnesium, calcium, and several other elements present. Some might have water or oxygen contained beneath their surface. There may even be gold, platinum, and other precious metals there. We might even discover something that we’ve never encountered before.
Space exploration gives us an opportunity to access new mineral resources, allowing for the privatization of this venture. It would also give us an opportunity to start building in space because the raw materials are easy to haul and transport.
10. It gives us an opportunity to see what lies beyond in the final frontier. Unless circumstances change somehow, there will come a point in time when our species will outgrow our planet. We must begin to look for colonization opportunities in our solar system and beyond to help support the future of our race. As our scientific and technological discoveries begin to open up opportunities to visit distant stars, we can start to discover even more mysteries that will help us to answer the meaningful questions in life.
11. It could change our approach to medicine. Discovering new organic elements in space could help us to discover cures for some of our worst diseases. We really don’t know what is possible in our universe beyond the scope of basic physics. There could be untold treasures just waiting beyond our solar system to discover. Although there is always an element of risk to any exploration venture, there are great rewards often waiting for those who embrace their courage to start pressing forward. At the rate of development that we’ve seen in the 21st century, we could be looking at a very different human race in our children’s lifetimes based on the possibilities of discovery.
List of the Cons of Space Exploration
1. It could cause us harm or provide harm to other species in space. We know from experience what happens when one group of humans comes into contact with another group after generations of isolation. The diseases that transferred back and forth between Europe and the New World devastated some cultures. There were times that smallpox would kill over 90% of the local population by itself. If we encounter life on a different planet (or if they visit us), the threat of disease transmission is real. Their viruses, bacteria, and potentially unknown invaders could do as much damage to us as we could to do them. First contact would be an exciting experience, but it could also be a deadly one even though no one has any ill intent toward the other.
2. It creates high-level pollution events. We must consume fossil fuels when we launch rockets into space, which means we’re creating a significant level of pollution every time we expend fuel for exploration purposes. Even on a light load, it costs about $300,000 to fuel a rocket. Larger models could hold a half-million gallons of fuel that would be used during an entire mission. That means we are creating roughly 4 million pounds of carbon pollution with every action that we take to reach space. Then we must find a way to place these fuels safely into orbit to make our exploration efforts useful, creating even further potential problems for our atmosphere.
3. It gives us more ways to be paranoid about what others are doing. There are only five treaties which currently govern how we operate in space. Our original goal as the human race was to make it so that no one could claim a territory in orbit or our solar system that could give one nation a distinctive advantage. The creation of a Space Force could work to upset the balance that we’ve worked to create for the last 50 years. We’re already using satellites to spy on one another, monitor communications networks, and potentially target cities with weapons.
This paranoia will only increase as we push further into the stars. The only real solution to this disadvantage is to start thinking of ourselves as a planetary nation instead of one that is built on nation-states alone.
4. It will create a large amount of garbage that we must manage. Did you know that NASA tracks over a half-million pieces of space junk that orbits our planet right now? Unless we physically remove these items in some way, this garbage will linger until it falls into our atmosphere to burn up. Every item we leave behind creates a future risk for someone else. If we are going to start exploring space, then we must begin to look at ways to clean up our act before we get going. It’s bad enough that we’ve polluted our oceans with microplastics. Should a spaceship encounter that debris, it could be a deadly experience.
5. it may cause our planet to face unknown perils. A common theme in many science-fiction novels, shows, and movies is the idea that an alien race is hostile towards us. It is widely believed that water may be one of the scarcest commodities in the universe, but here we are with a planet that is more than 70% water. If we start venturing out beyond our solar system, it is entirely possible that we could encounter a species who decides that our resources are ripe for the taking. We assume that an advanced culture who could invent real-time space travel would be peaceful, but there are no guarantees. Exploring space could become an invitation for interstellar war.
6. It will always entail risk. Human beings were not meant to be in the vacuum of space. We must wear extensive protective gear to survive those conditions. Even one small leak or crack in a helmet or suit would be enough to create an adverse health condition. This issue applies to the planetary environments which we know of right now as well. Then there are the health issues to consider when the human body experiences a lack of gravity for an extended time.
NASA studied identical twins Scott and Mark Kelly when Scott took a long trip to space. Scientists monitored their bodies to see how being in a weightless environment could change the physical chemistry of a person. They discovered that genomic instability occurs, including gene expression changes, and spending a year in that environment caused a thickening of the carotid artery, DNA damage, and reduced cognitive abilities.
7. It is expensive to start exploring space. Even though the budget for NASA has not changed that much in recent years, we are spending about $200 billion per decade on our current space exploration efforts. Privatization of the industry has helped to reduce some costs, especially as SpaceX continues to work on a recoverable rocket. When you add in the costs from other countries and their space programs, our planet spends about $60 billion per year on this effort. In comparison, the United Nations suggests that it would only take half of that amount to end global hunger permanently. Should exploring space be our top priority if we’re struggling to take care of ourselves here at home?
When we examine these space exploration pros and cons, there is a certain nobleness to the idea of seeking what lies beyond the next horizon. Our society was built on the desire to explore the planet where we live. Now our culture has the itch to start pushing beyond the next boundary. Whether that means we colonize the moon, establish a community on Mars, or push toward Alpha Centauri, there is something waiting to be discovered. We’re closer than ever before to finding out what that might be.

10 Benefits of Space Exploration. (Including Medical and Economical)
On April 12, 1961, the Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to journey to outer space. The age of space exploration started that day.
But why are we so interested in spending so much time, money, and resources to visit chunks of rock that are most likely empty? Why purposely go to environments that are dangerous and even deadly to humans?
Well, the answer is simple.
The benefits of space exploration outweigh the dangers of it. Becoming a space-faring civilization is the most important goal we must achieve for humanity to survive long-term .
In this article, we’ll the major 10 benefits of space exploration. These include medical, technological, and economic benefits. They are listed in no particular order of importance.
Economic benefits of space exploration

10. Creation of STEM Jobs
NASA employs more than 18,000 people. SpaceX more than 12,000. And that’s not counting outside contractors with whom those numbers at least double.
A lot of those jobs are positions for engineers, data analysts, mathematicians, physicists, astronomers, doctors, biologists, geologists, etc.
Space exploration is one of the industries that require the largest percentage of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) jobs.
These positions require highly qualified people to fill them but are also some of the highest-paid jobs in the market. The average entry-level STEM job pays approximately 26% higher than non-STEM fields for college graduates.
So, in summary, the growing space industry creates high-paying jobs.
9. Space mining and asteroid capturing
In space, there are many valuable resources in big quantities that are scarce on Earth. For example, the asteroid Pysche 16 is estimated to contain over $700 quintillion dollars worth of gold. Enough to give each person on Earth more than $100 billion dollars. And that’s not even close to being the most valuable object.
Economists have predicted the space mining industry will create the first trillionaire.
But the real benefit for the advancement of humankind might come from a much more unlikely substance. Water.
Learning to capture asteroids full of ice and crashing them safely, could help us solve one of the biggest challenges of inhabiting planets. The lack of liquid water.
8. Space tourism industry
The biggest dream some of us have is being able to take a trip to outer space. It is the ultimate destination. And because unfortunately, not many people can become astronauts, the rest of us will have to wait until the space tourism industry develops a bit more. It is still too expensive to go to space .
In 2021, a trip in one of the first trips offered by Blue Origin, the space company created by Jeff Bezos, was auctioned. The winner paid $28 million for the privilege to be one of the first space tourists.
As reusable rockets improve, the costs of these trips will become significantly lower. Hopefully one day they’ll be within the reach for all of us.
The space tourism industry will indubitably create tens of thousands of jobs. From travel agents to pilots, to manufacturing jobs in the factories that make the rockets.
Medical benefits of space exploration

7. Learning more about the human body
Studying the effects of space travel has helped us better understand the human body. For example, analyzing the effects of zero-gravity on blood circulation led to many discoveries on how arteries age and how to prevent some types of heart failure.
The experiments and measurements of bone strength and bone loss in astronauts have helped doctors better understand osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
The medical benefits of space exploration extend to pretty much every area of the human body. From muscle physiology to mental health.
6. Improving medical assistance in remote areas
One of the biggest challenges of space travel is solving problems when you can’t send any new equipment, experts, or any other help. You have to fix things with whatever is available on the ship.
So what happens when there’s a medical emergency on a spaceship?
This question has led doctors and engineers to develop tools and machines that can perform medical procedures and diagnostics remotely.
That same technology has many applications on Earth too. It allows doctors to assist patients that are located in remote rural areas or villages that are difficult to access.
5. Development of new medical procedures
All this knowledge that has been collected has yielded many developments in medical procedures.
Some examples of medical advancements that have been created thanks to space exploration are:
- Heart pumps
- Programmable pacemakers
- Fiber-optic catheters to perform laser angioplasty
- Digital imaging breast biopsy used to detect breast cancer
- Fetus monitoring transmitters
- Cooling suits made to lower a person’s temperature
The NASA spinoff site keeps track of some of the health and medicine advancements that have been made possible thanks to space exploration.
Other benefits of space exploration
4. development of new technologies.
The space race is one of the eras that has birthed the most technological advancements in the shortest period of time. It is probably only third behind both world wars. Throughout the years, companies have found consumer uses for many of these developments. To this day we still use them in our day-to-day lives without even knowing that some NASA engineers originally developed them for the Apollo program that took humankind to the Moon.
Listing all the technologies that have been derived from space exploration would be impossible, but here are some notable examples.
- Vacuum sealed food.
- Shock-absorbing sneaker soles. That’s right, the comfy running soles were originally developed for astronaut spacesuits.
- Fireproof materials used in firefighter uniforms
- Quake-proofing technology used in bridges and buildings to resist Earthquakes
- Heat-repellent blankets. There’s a reason why they are also known as “space blankets”. Fun fact, they can also double as DIY telescope covers.
- Rechargeable hearing aids
- Autonomous drone navigation
- Modern vacuum cleaners
- The lenses used in “action cameras”
- Water purification technology
As you can see, it is important for us to keep pushing the limits of space exploration. Who knows what kind of new technologies could be developed that will make our lives easier in the future.
3. Inspire the next generation
Space exploration sparks the curiosity of children who will become the next Elon Musk, Neil Armstrong, Sally Ride, or Guion Bluford.
It inspires students to dream and gets them interested in science and technology.
Not only is this good for them as STEM jobs can secure them a comfortably future, but it also helps humanity. It is through invention, research, and knowledge that humanity will be able to overcome the big challenges it will be facing in the future.
2. Protecting Earth
We only have one planet where we can live without the help of spacesuits. It would be nice to keep it in good condition until we can figure out a way to find other habitable planets or terraform others.
To do that, we need to learn more about the dangers of space. We know about extinction events like asteroids, but that’s not the only potential threat to our survival. Solar flares, radiation, magnetic pole changes, and greenhouse effects are just some of the challenges Earth might face at some point.
Exploring space is the only way we will learn more about them so we can develop strategies and technology that could help save us from such events.
1. Increase humanity’s odds of survival
There’s one thing we are certain of about when it comes to space. If we – humanity – don’t become a space-faring civilization. We will become extinct sooner or later.
Earth will eventually become uninhabitable and will probably be devoured by the Sun as it expands during the later years of its life cycle. And that’s hoping nothing else happens before, like an asteroid impact, an ice age, atmospheric loss, climate change, or any other potential threats that could wipe us out, to put it bluntly.
Space exploration is not a luxury for the richest nations. It should be a worldwide priority and every country needs to come together in this effort. It is simply the only way we can hope to survive as a species.
We don’t know if we have millions of years or hundreds of years before any of these events happen. So it’s better to get started today.
- Space exploration can be the doorway to many growth industries such as asteroid mining or space tourism.
- Many medical advancements have been made possible thanks to the aerospace industry.
- Space exploration is critical and the only path to the survival of the human race.
Elena is a Canadian journalist and researcher. She has been looking at the sky for years and hopes to introduce more people to the wonderful hobby that is astronomy.
Related Posts

What Happened to the Mars Helicopter? (Ingenuity)

What is the Purpose of the International Space Station?

Who Owns The International Space Station?

Is There Gold On The Moon? Yes! And Here’s Why It Matters.

Is There Gold On Mars? Yes! And The Discovery Was Very Curious…
Have We Landed On Venus?
- Buying Guides
- Telescope Accessories
- Magnification Calculator
- Field of View Calculator
- Constellations
- Solar System
- Space Exploration
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
The Planetary Society • Aug 30, 2021
Why space exploration is always worthwhile
Your guide to advocating for space in a complicated world.
Most people who love space and believe in exploration have probably heard this once or twice: “We shouldn’t waste money on space exploration when there are problems to deal with here on Earth.”
While public health concerns, social injustices, climate change, and other urgent issues are important to address, solving these problems doesn’t depend on defunding space programs.
This can be a difficult conversation to navigate, so we’ve outlined a few ideas here that you can share when advocating for space.
Space research isn’t as expensive as people think
Many countries around the world invest in space science and exploration as a balanced part of their total federal budget. Public opinion research has shown that people estimate NASA to take up as much as a quarter of the U.S. federal budget, but in fact, NASA’s budget only represents about 0.5% of the total federal budget and the proportion is even smaller for other spacefaring nations . The correct information may go a long way to reassuring critics that space spending isn’t eating up as many public resources as they think.
The United States government spent approximately $6.6 trillion in fiscal year 2020, of which just 0.3% ($22.6 billion) was provided to NASA. In this chart, shades of blue represent mandatory spending programs; shades of orange are discretionary programs that require annual appropriations by Congress. "Defense and related" includes both the Department of Defense and Veterans Affairs. Source: Office of Management and Budget Historical Tables 8.5 and 8.7.
Space spending pays off
If someone is arguing that public funds should be spent on solving the world’s problems, they should know that money spent on NASA positively impacts the U.S. economy . We get the same kind of payoff for space spending in other countries. Spending on space supports highly skilled jobs, fuels technology advancements with practical applications, and creates business opportunities that feed back into the economy. This in turn grows the pool of public money that can be spent on solving the world’s most pressing problems.
Space research directly impacts Earthly problems
When people apply themselves to the challenges of exploring space, they make discoveries that can help the world in other ways too. Studying how we might grow food in orbit or on Mars yields insights into growing food in extreme conditions on Earth , generating knowledge that can help mitigate the impacts of climate change. Medical research conducted on the International Space Station helps us understand the human body in new ways, helping save lives and improve quality of life .
This content is hosted by a third party (youtube.com), which uses marketing cookies. Please accept marketing cookies to watch this video.
Studying space helps us understand our own world
Studying the cosmos gives us an important perspective shift. When we learn about what lies beyond Earth, it gives us context for understanding our own planet. Studying the other worlds of our solar system and beyond makes it clear that Earth is a precious oasis for life. When we sent spacecraft to Venus we saw how a runaway greenhouse effect turned the world from a habitable planet to an absolute hellscape. When astronauts travel into space they see just how thin and tenuous Earth’s atmosphere is, appreciating the fragile balance in which we live . A cosmic perspective underscores the importance of protecting our planet’s habitability and encourages investment in that effort.
Studying space may one day save us all
All the social and environmental progress in the world won't help us if an asteroid impacts the Earth. We have to explore space to find and study the asteroids and comets in our cosmic neighborhood if we want to make sure we can defend our planet if an object ever heads our way.
Space is inspiring
Not every child who dreams of becoming an astronaut will get that opportunity. This is a sad truth that many of us know from experience. But to be inspired to aim for something so grand gives kids the motivation to study hard and gain skills in science, engineering, medicine, or other fields that benefit humanity and directly help overcome problems that we face as a species.
And inspiration isn’t just for kids. When we marvel at the beauty of Jupiter’s clouds or the mystery of Enceladus’ oceans , we get an opportunity to appreciate the wonder and majesty of this cosmos that we inhabit. The idea that life might exist elsewhere in the universe reminds us that we might not be the only planet struggling to achieve balance, justice, and sustainability. And even in the bleakest of times, there’s something beautiful about still striving to achieve something great and discover something that could change how we see ourselves and our cosmos forever.
There’s plenty of room at the table
There’s no denying that there are many important issues facing humanity that need fixing. But to deal with those problems doesn’t mean we have to stop looking up, stop exploring, and stop making discoveries.
Human civilization has astonishing capacity, and we can do more than one important thing at a time. If someone thinks that a particular issue should get more attention and investment, they can and should advocate for that. The problems we face don’t persist because we’re spending money on space science and exploration. And there’s no reason to pit our aspirations against one another.
Let’s Go Beyond The Horizon
Every success in space exploration is the result of the community of space enthusiasts, like you, who believe it is important. You can help usher in the next great era of space exploration with your gift today.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .

Universe Today
Space and astronomy news

What Are The Benefits Of Space Exploration?
Why explore space? It’s an expensive arena to play in, between the fuel costs and the technological challenge of operating in a hostile environment. For humans, a small mistake can quickly become fatal — something that we have seen several times in space history. And for NASA’s budget, there are projects that come in late and over budget, drawing the ire of Congress and the public.
These are some of the drawbacks. But for the rest of this article, we will focus on some of the benefits of going where few humans have gone before.
Perhaps the most direct benefit comes from technologies used on Earth that were first pioneered in space exploration. This is something that all agencies talk about, but we’ll focus on the NASA Spinoff program as an example. (NASA will be used as the prime example for most of this article, but many of these cited benefits are also quoted by other space agencies.)
The program arose from NASA’s desire to showcase spinoffs at congressional budget hearings, according to its website. This began with a “Technology Utilization Program Report” in 1973, which began as a black-and-white circular and progressed to color in 1976 following public interest. Since that year, NASA has published more than 1,800 reports on spinoffs.
The agency has several goals in doing this. “Dispelling the myth of wasted taxpayer dollars” is one NASA cites, along with encouraging the public to follow space exploration and showing how American ingenuity can work in space.
There are many commercialized advances the program says it contributed to, including “memory foam” (first used for airline crash protection), magnetic resonance imaging and smoke detection. In many cases, NASA did not invent the technology itself, but just pushed it along, the agency says.
But as counterpoint to NASA’s arguments, some critics argue the technology would have been developed anyway without space exploration, or that the money spent on exploration itself does not justify the spinoff.
Job creation
Another popularly cited benefit of space exploration is “job creation”, or the fact that a space agency and its network of contractors, universities and other entities help people stay employed. From time to time, NASA puts out figures concerning how many associated jobs a particular project generates, or the economic impact.
Here’s an example: in 2012, NASA administrator Charles Bolden published a blog post about the Curiosity Mars rover landing, which was picked up by the White House website . “It’s also important to remember that the $2.5 billion investment made in this project was not spent on Mars, but right here on Earth, supporting more than 7,000 jobs in at least 31 states,” he wrote.
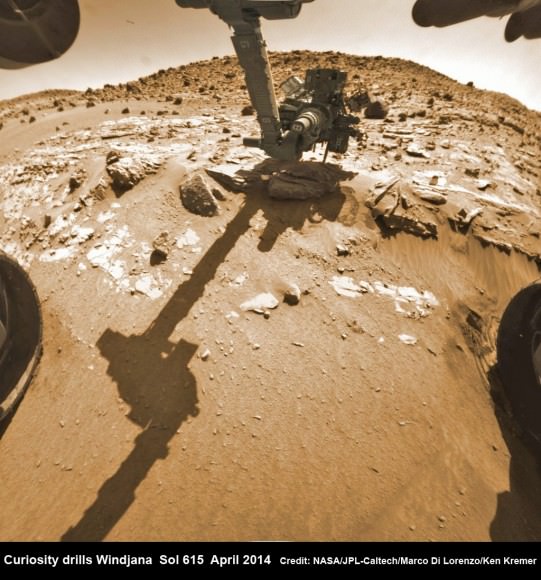

But the benefit can cut in a negative way, too. NASA’s budget is allocated by Congress, which means that the amount of money it has available for employment fluctuates. There are also some programs that are highly dependent on grants, which can make stable jobs challenging in those fields. Finally, as the priorities of Congress/NASA change, jobs can evaporate with it. One example was the space shuttle’s retirement, which prompted a job loss so massive that NASA had a “transition strategy” for its employees and contractors.
It’s also unclear what constitutes a “job” under NASA parlance. Some universities have researchers working on multiple projects — NASA-related or not. Employment can also be full-time, part-time or occasional. So while “job creation” is cited as a benefit, more details about those jobs are needed to make an informed decision about how much good it does.
Teaching has a high priority for NASA, so much so that it has flown astronaut educators in space. (The first one, Christa McAuliffe, died aboard the space shuttle Challenger during launch in 1986. Her backup, Barbara Morgan, was selected as an educator/mission specialist in 1998 and flew aboard STS-118 in 2007 .) And to this day, astronauts regularly do in-flight conferences with students from space, ostensibly to inspire them to pursue careers in the field.

NASA’s education office has three goals : making the workforce stronger, encouraging students to pursue STEM careers (science, technology, engineering and mathematics), and “engaging Americans in NASA’s mission.” Other space agencies also have education components to assist with requirements in their own countries. It’s also fair to say the public affairs office for NASA and other agencies play roles in education, although they also talk about topics such as missions in progress.
But it’s hard to figure out how well the education efforts translate into inspiring students, according to a National Research Council report on NASA’s primary and secondary education program in 2008. Among other criticisms, the program was cited as unstable (as it needs to change with political priorities) and there was little “rigorous evaluation” of its effectiveness. But NASA’s emphasis on science and discovery was also praised.
Anecdotally, however, many astronauts and people within NASA have spoken about being inspired by watching missions such as Apollo take place. And the same is true of people who are peripherally involved in the field, too. (A personal example: this author first became interested in space in the mid-1990s through the movie Apollo 13 , which led to her watching the space shuttle program more closely.)

Intangible benefits
Added to this host of business-like benefits, of course, are the intangibles. What sort of value can you place on better understanding the universe? Think of finding methane on Mars, or discovering an exoplanet, or constructing the International Space Station to do long-term exploration studies. Each has a cost associated with it, but with each also comes a smidgeon of knowledge we can add to the encyclopedia of the human race.
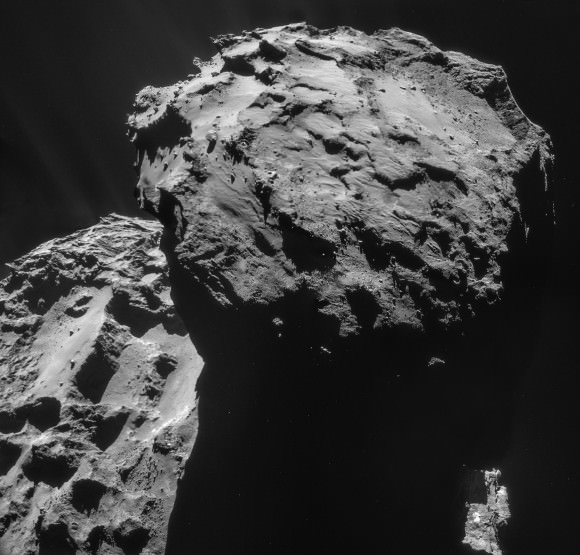
Space can also inspire art, which is something seen heavily in 2014 following the arrival of the European Space Agency Rosetta mission at Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. It inspired songs, short videos and many other works of art. NASA’s missions, particularly those early space explorers of the 1950s and 1960s, inspired creations from people as famous as Norman Rockwell .
There also are benefits that maybe we cannot anticipate ahead of time. The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) is a network that advocates looking for life around the universe, likely because communicating with beings outside of Earth could bring us some benefit. And perhaps there is another space-related discovery just around the corner that will change our lives drastically.
For more information, here is a Universe Today article about how we really watched television from the moon. We also collected some spin-offs from the Hubble Space Telescope. You can also listen to Astronomy Cast. Episode 144 Space Elevators.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
8 Replies to “What Are The Benefits Of Space Exploration?”
Nice article, and thanks for the links. A little off topic, I love the lead photo on top but you might want to give Harrison Schmitt photo credit for taking it.
Ha, good point. We all “know” it’s Schmitt as he was the only other one there and able to take the picture. I think you can even see him in the visor! But the official credit on NASA’s website is it’s a NASA photo, so that’s the style we stuck with. (It’s generally best practice to use the same credit that the organization does.)
Sorry, speaking as a photographer, I couldn’t disagree more with you. Saying what Harrison Schmitt did isn’t important enough to give him credit is an insult to him and what he accomplished. And just because some clerk at NASA was lazy doesn’t mean you should be too. Unlike him, your a journalist and should know better. I don’t mean to come off so accusatory, I like your reporting, but his work is as important as yours on this story. That’s why you lead with it. StevenGeorges.com
How about survival of the human race – such as finding dangerous asteroids, finding and using space based resources, figuring out how and where to build, protect and supply space colonies. I believe our long term survival depends on us moving off this planet. We can’t do it unless we explore the environment we are potentially moving into.
Spot-on and well said… INDEED! 😉
“What is the benefit of…” Sorry, but that’s a “stupid” question. What is the benefit of a… car? Now imagine one would have asked this 200 years ago! The benefit of a … computer – asked in the late 1950 (John Doe wouldn’t understand what you were asking). The benefit of having… sonar (beside the chance of catching enemy subs)? We never would have accepted Alfred Wegeners idea of plate tectonics (moving continents – ridiculous!!!)
Stupid question indeed, but none-the-less because so. many. people. ask it and accompanying ones such as, “Why spend millions of dollars to go to Mars and look at rocks instead of spending it to help poor people eat here on Earth?”, is why articles like this need to be published. My best answer to those is, “One could say there are more pressing issues here at home all throughout history; just ask the same about the starving folks in Spain back in the late 1400’s…..” Give a billion dollars to a nation’s poor and they’ll eat for a lifetime. Spend it to give them more cultivatable land elsewhere and they’ll eat for generations.
You’re right, Jeff. I have given this answer mostly because I’m kinda “fed up” with this question. It always comes up / asked by “ignorant” people who normally don’t give a damn about what’s going on around them… only if it takes some money away from them.
Comments are closed.
Why We Should Be Spending More on Space Travel

L et’s stipulate one thing: there’s absolutely no reason for us to go to space. It does nothing to feed us, to clothe us, to protect us, to heal us. It’s dangerous and hideously expensive too, a budget-busting luxury that policy makers and administrators have spent decades trying to defend—always unsuccessfully because the fact is, there’s no practical defense for it. So stand down the rockets, take down the space centers, pocket the money and let’s move on. Still want the adventure of going to space? That’s what they make movies for.
Now that we’ve established that, let’s stipulate the opposite: Space is precisely where the human species ought to be going. We accept that we’re a warring species. We accept that we’re a loving species. We accept that we’re an artistic and inventive and idiosyncratic species. Then we surely must accept that we’re a questing species. Questing species don’t much care for being stuck on one side of an ocean and so they climb aboard boats—indeed they invent boats—to cross it. They don’t much care for having their path blocked by a mountain and so they climb it for no reason other than finding out what’s on the other side. Accept that, and you can’t not accept that we have to embrace space.
April 12 marks the 60th anniversary of the day Yuri Gagarin became the first human being in space , taking off in his Vostok 1 spacecraft, spending 88 minutes making a single orbit of the Earth, and returning home to a species that seemed forever been changed by his efforts. The date will mark, too, the 60th anniversary of the by-now familiar argument that journeys like Gagarin’s and all of the ones that followed achieve nothing that can be touched and pointed to as a practical dividend of the effort made and the resources expended.
I found myself turning the old debate this way and that over the last week, when I was reading a column in the Guardian with the provocative headline, “Revive the U.S. space program? How about not,” by essayist Nicholas Russell. It opens with a mention of Gil Scott-Heron’s 1970 spoken word poem, “Whitey on the Moon,” which compellingly lamented the hard social truth that the U.S. was spending $24 billion in 1960s money on the Apollo program at the same time 10% of Americans were living in poverty, with Blacks suffering at three times the rate of whites.
“Was all that money I made last year (for Whitey on the moon?)” Scott-Heron wrote. “How come there ain’t no money here? (Hm! Whitey’s on the moon.)”
Russell goes on to cite the estimated cost of the new Artemis lunar program , which some analysts have placed at $30 billion; the role—a troubling one as he sees it—of the military in so many space projects, and the ongoing scourge of racism and inequality on Earth that persists while we still keep looking spaceward. Then he mentions, by way of caution, a University of Arizona proposal to send seed, spore, sperm and egg samples of 6.7 million terrestrial species to the moon as a sort of space ark in case life on Earth should come to an end. “When the vastness of space is cited as a means of escape from disaster, it’s exceedingly difficult not to believe nihilism acts as the prime motivator,” Russell argues. “Rather than sparking inspiration, it speaks of blatant fatalism about what is worth saving, a preference for the lofty and unpopulated … with delusions of innovation and heroism.”
Russell is right about some things—especially about the continuing blight of racism. But expenditures on space and expenditures on social programs have never been a zero-sum proposition, any more than any dollar the U.S. government spends on anything at all—the military, farm subsidies, tax cuts for corporations—is by definition a dollar not spent on something else. And the Artemis price tag is indeed high—but only if you look at it as a standalone figure. In the context of the federal budget? NASA funding currently accounts for just 0.4% of the total the government spends each year—down from 4% in the golden era of Apollo. The military’s role in the space program is inevitable, even if Russell sees it as regrettable. Rockets are rockets, after all, and physics is physics, and if the first machines that blasted humans off the Earth were originally designed as ballistic missiles, well, that was what the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. had on the shelf. What’s more, every Soviet R-7 rocket or American Atlas that was used to send an astronaut or cosmonaut to orbit was one fewer that could be used in a theater of war.
And as for that space ark? Well yes, it does suggest a certain fatalism. But the fact is, we are eminently capable of screwing the global pooch, to paraphrase the old Mercury astronauts. Unless you’re confident that no autocrat or hermit king with nuclear weapons and a button in reach won’t do something impulsive, storing the Earth’s genetic essence for safekeeping does not seem like a completely insane idea.
That doesn’t mean space exploration is inherently nihilistic, however. Look at the old footage of the global reaction to the Apollo 11 moon landing . Watch the worldwide relief when the Apollo 13 crew —three people the vast majority of the planet had never met—made it home safely. Consider the reaction today when a rover lands on Mars or a spacecraft whizzes past Pluto or a pair of women aboard the space station perform the first all-female spacewalk.
Yes, we can live without traveling to space. Indeed, we did perfectly well over all of the millennia that preceded April 12, 1961. We can meet most of our needs when we stay on Earth—we can raise our families and earn our salaries and feed our bellies. But we feed something less literal, more lyrical when we extend ourselves as far as we can. Once that meant crossing an ocean. Now it means more. Space is out there—and we should be too.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Jeffrey Kluger at [email protected]

Why explore space?
Why should we explore space? Why should money, time and effort be spent researching something with apparently so few benefits? Why should resources be spent on space rather than on conditions and people on Earth?
Perhaps the best answer lies in our history. What made our ancestors move from the trees onto the plains? Did a wider distribution of our species offer a better chance of survival?
Nearly all successful civilisations have been willing to explore. In exploring, the dangers of surrounding areas may be identified and prepared for. Without knowledge, these dangers have the ability to harm us. With knowledge, their effects or consequences may be lessened.

While many resources are spent on what seems a small return, the exploration of space allows new resources to be created. Resources translate into success at survival. Resources may be more than physical assets.
Knowledge or techniques acquired in exploring or preparing to explore always filter from the developers to the general population.
Techniques may be medical applications, such as new drugs or ways of living to increase the quantity or the quality of time lived. Techniques may be social, allowing the people in a society to better understand those within or outside that culture.
ESA’s space programme is a strategic asset. ESA does what individual European nations cannot do on their own.
Scientists from European nations can function at world-class level in their specialist fields, in co-operation rather than competition.
By studying alien worlds, such as Venus, Mars or Saturn’s moon Titan, we can place our own world in context. ESA’s exploration of the Solar System is focused on understanding the Earth’s relationship with the other planets, essential stepping stones for exploring the wider Universe.
While space may hold many wonders and explanations of how the universe was formed or how it works, it also holds dangers. The chance of a large asteroid or comet hitting the Earth is small. But given time, it will happen.
Some explanations for extinctions and evolution include strikes by asteroids or comets. Our technology is reaching the point where we can detect such a threat and might be able to do something about it.
The dangers exist and knowledge can allow us as a species to survive. Without the ability to reach out across space, the chance to save ourselves might not exist.

Earth is the only planet known to sustain life, but our ability to adapt could eventually allow us to inhabit other planets and moons.
Our lifestyles would be different, but human life and cultures have adapted in the past and surely could in the future. Space allows us to expand and succeed.
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!
Related Links

About Exploring space

Our environment in the context of space
Threats from space
Language selection
- Français fr
Everyday benefits of space exploration
Some examples of how space benefits Canadians and all of humanity.

Improving health care
Experiments performed in space help us understand health problems on Earth.
Protecting our planet and our environment
Satellites provide data on climate change, measure pollution, and help protect our planet.
Creating scientific and technical jobs
The space sector generates high-tech jobs for Canadians.
Improving our day-to-day lives
Space technologies improve products we use every day, weather forecasts, and communications worldwide.
Enhancing safety on Earth
Satellites data can be used to predict natural disasters and to support emergency relief efforts.
Making scientific discoveries
Scientific breakthroughs are challenging our assumptions and pushing our boundaries by exploring the unknown.
Sparking youth's interest in science
Astronauts encourage young people to study science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
Cooperating with countries around the world
Canada is a partner of the International Space Station, a research laboratory in space.
- Facebook: CanadianSpaceAgency
- X: @csa_asc
- Youtube: Canadianspaceagency
- Instagram: canadianspaceagency
- Linkedin: Canadian Space Agency
The Space & Beyond Blog
The benefits of space exploration, though only a lucky few have experienced space for themselves, all of humanity has prospered thanks to space travel..
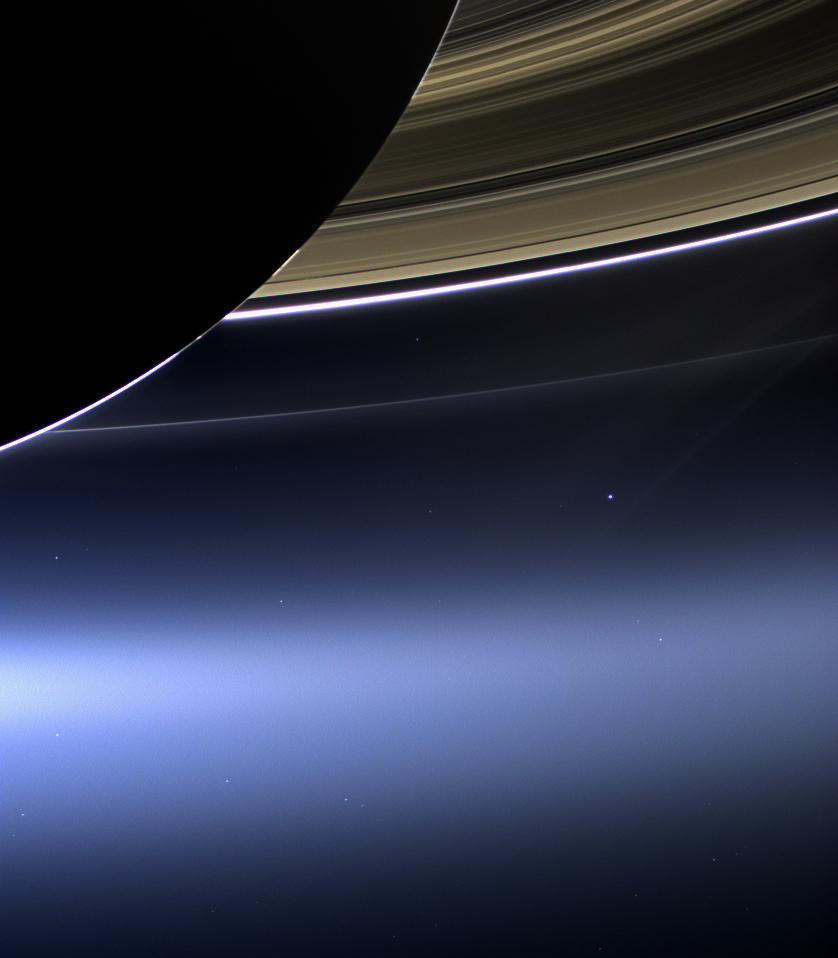
In 2006, the international Cassini spacecraft this image titled In Saturn’s Shadow – The Pale Blue Dot . The bright blue dot just below Saturn’s rings is Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute
For more than 50 years humanity has been active in space and though the number of people to visit space for themselves are few, the entire world has reaped the benefits of space exploration. From our modern telecommunications system to modern computers to solar cells, the innovations made to rise to the challenges of exploring our solar system have tangible effects on Earth as well.
Now humanity is at the edge of a new frontier with countries around the world reaffirming their dedication to space exploration. A trio of Mars-bound missions reached the Red Planet in early Feb. The United Arab Emirates’ al-Amal (Hope) orbiter — the first interplanetary mission undertaken by an Arab nation — arrived first. Hope was followed by China’s Tianwen-1 mission which will deliver the country’s first martian rover sometime in May. And last, but not least, NASA’s Perseverance rover which successfully touched down Feb. 18.
MOUSE OVER TO INTERACT WITH THE PANORAMA: Perseverance captures its first 360-degree panorama of its new home. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
But the new era of space travel is only the beginning, NASA has reaffirmed their dedication to returning humans, and the first woman, to the Moon by 20XX. Turkey’s president, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, recently announced the country will launch a lunar rover in 2023 as part of a new 10-year plan to develop their own space program. The next decade is proving to be an excited and groundbreaking time for space exploration. So, what can those of us on Earth expect to see?
More space travel means more challenges. But space agencies have proven themselves more than capable, developing knowledge and new technologies every step of the way. Past space exploration has given rise to a number of innovations that we take for granted today, including solar panels, implantable heart monitors, cancer therapy, and water-purification systems.
More space exploration promises to bring new and serendipitous benefits to a variety of areas, such as power generation and energy storage, recycling and waste management, advanced robotics, health and medicine, transportation, computing, and engineering. It’s hard to predict exactly what new technology may arise, but if history is any indication it will be life altering for many of us.
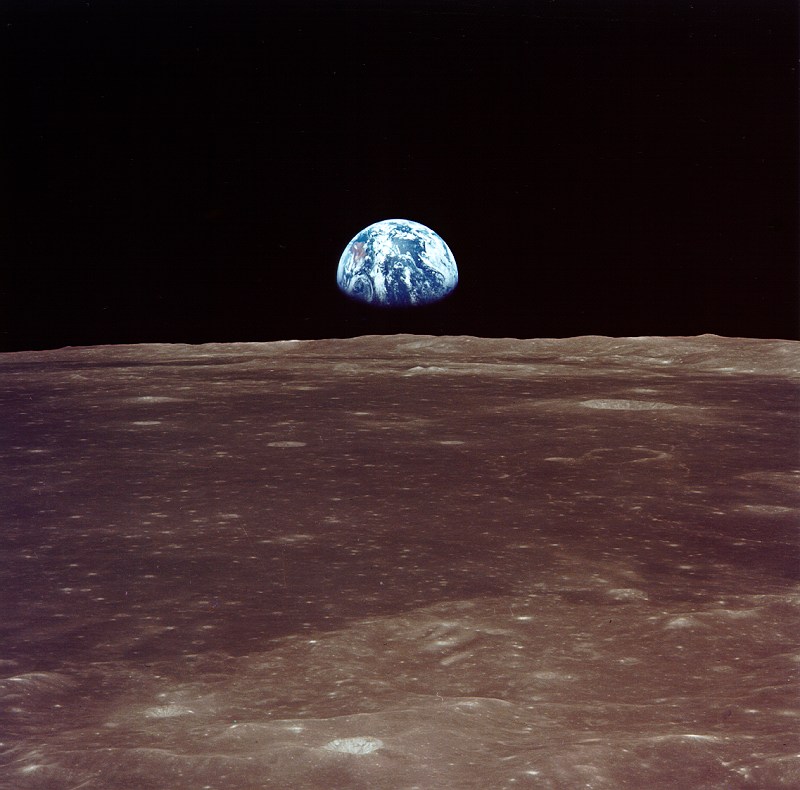

Taken from Apollo 11 spacecraft, this image shows Earth rising over the Moon’s horizon. Credit: NASA
Inspiration
Cultures around the world have long looked up at the night sky and dreamed. When NASA astronauts first landed on the Moon in 1969, they captured an image of Earth prior to landing. It changed humanity’s understanding of our place in the Universe.
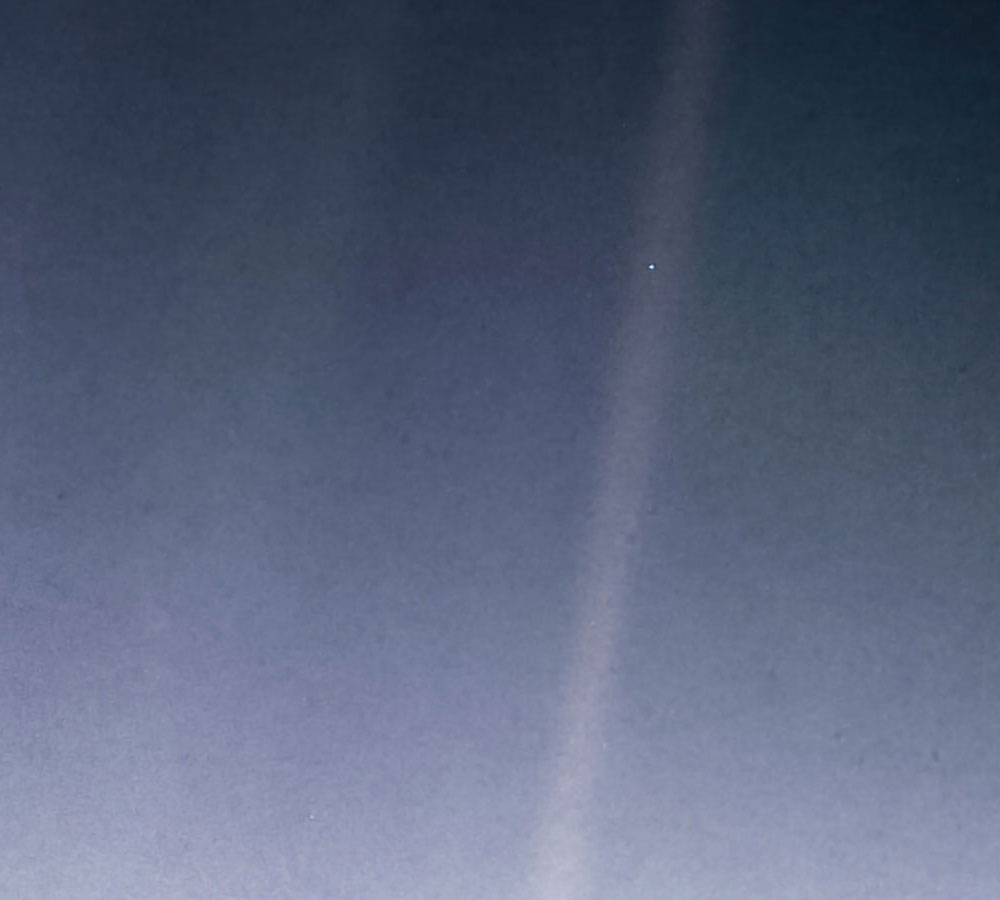

On Feb. 14, 1990, Voyager 1 captured this photograph of Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Then in 1990, the Voyager 1 craft captured an image of our pale blue dot at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers). The image inspired the title of Carl Sagan’s book Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space . He wrote, “Look again at that dot. That’s here. That’s home. That’s us.”
Those first five decades of space activity have expanded humanity’s views on the limits of exploration and inspired new thinking as to how life may exist beyond Earth. In 2013, NASA’s Curiosity rover detected preliminary signs of Mars previously hosting an environment capable of supporting life. Their most recent rover, Perseverance, will soon begin collecting promising samples to return to Earth one day with the hopes of seeing direct evidence of ancient microbial life on the Red Planet. To find past or present life either in the solar system or even beyond would forever changes our understanding of our pale blue dot’s place in the cosmos.
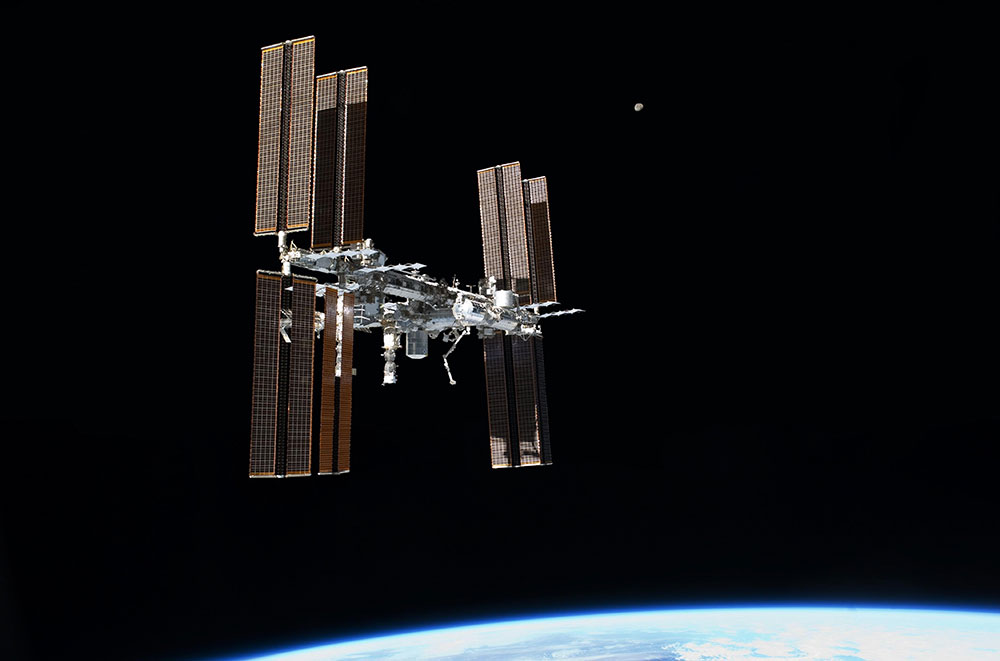

The International Space Station photographed by ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli. Credit: ESA/NASA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Combining innovation with a new appreciation for our world lays a foundation for international cooperation. Space exploration may have started as a race, but now it is the bedrock for partnerships and diplomacy around the globe.
The International Space Station (ISS), at nearly 30 years old, is the prime example of continuous and successful international cooperation. Originally 15 nations signed the international agreement for the ISS, but that has expanded over the years to include participation from 68 nations.
The ISS proves what humanity can accomplish when we agree to work together towards and single goal. As missions become more complex and ambitious more extensive international cooperation will be required, providing opportunities for peaceful, global-coordinated activities in space and on Earth. At home, international corporation is needed to tackle global threats such as Near-Earth Objects, solar storms, and global warming.
Enjoying our blog?
Check out the space & beyond box : our space-themed subscription box.

Join our mailing list and get 10% off your first box + a free Mars ebook
Connect with us on instagram, check out our latest blogs.

Tour the inner solar system
Take a deep dive into the rocky planets that make up our local neighborhood.
Pin It on Pinterest

19 Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
One of the reasons why fictional universes like those in Star Wars or Star Trek are popular is because they show us a reality where hope is possible anywhere. In the former, space exploration leads to an independent spirit where the fate of one’s culture and identity are at risk of being overrun by a zealous government. In the latter, humanity overcomes its core problems of conflict, hunger, and poverty to become great explorers of space.
Numerous science-fiction novels and stories over the years show us that exploring space could be exciting and profitable. What we don’t always discuss are the potential dangers and expenses that such an action would bring to us as well. When European settlers came to the Caribbean as explorers, some tribes lost up to 90% of their population because of the introduction of new diseases.
If we were to begin exploring alien worlds or encountering new life, our entire planet could experience the same problems as those island tribes.
That is why it is critical to examine the advantages and disadvantages of space exploration before launching these missions to ensure that we can all achieve the best possible result.
List of the Advantages of Space Exploration
1. Space exploration allows us to prepare for potential hazards. The universe is a vast place where hidden dangers could be lurking almost anywhere. Even if you consider only our solar system, there are asteroid and comet threats which could devastate our planet if an impact were to occur. Exploring space gives us an opportunity to locate these hazards in advance to prepare an encounter that could help to preserve our race.
Then there are the interstellar items to consider. Oumuamua, or 11/2018 U1, was discovered by the Pan-STARRS1 telescope in 2017 by the University of Hawaii through funding from the Near-Earth Object Observations Program. It was originally thought to be an asteroid, then a comet since it was accelerating, and up to 10 times as long as it was wide. These items could create interstellar impacts as well.
2. It gives us more information about our solar system, galaxy, and universe. When we take on the effort to start exploring space, then we can discover new truths about our planet and culture simultaneously. The information we obtain from these studies can then be applied to our STEM resources here at home. NASA technologies that were originally developed for space programs include infrared ear thermometers, LED lighting, ventricular-assist devices, anti-icing systems, and even temper foam.
Because it requires us to innovate to reach to the stars, our efforts to solve critical problems create opportunities to make life better here on our planet at the same time.
3. Exploring space is one of the few human endeavors that crosses borders. There are currently 72 countries who claim to have a space program, but there are only three which have an operating government space agency: China, Russia, and the United States. Despite the political conflicts that occur between these nations, their capability of producing human spaceflight provides the gold standard for future exploration efforts. Only 14 of the 72 nations who operate in this space even have a basic launch capacity and six (adding Europe, India, and Japan) have the capability to launch or recover multiple satellites.
Because of the expenses and resources necessary to achieve space flight, the remaining nations work together with those who have the capability of a full launch to manage this aspect of human existence. This endeavor is one of the few ways that humans from all nations cooperate without conflict.
4. We can see humanity in a different way with space exploration. Carl Sagan suggested that Voyager 1 take a picture of Earth while it was 4 billion miles away at more than 30 degrees above the ecliptic plane. In that image, our planet appears as a 0.12 pixel crescent. All of our conflicts, political battles, successes, failures, love, loss, and life occur on this one-tenth of a pixel. In the scope of a universal lens, we are but one small point of light amount countless others.
“Look again at that dot,” wrote Sagan. “That’s here. That’s home. That’s us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. The aggregate of our joy and suffering, thousands of confident religions, ideologies, and economic doctrines, every hunter and forager, every hero and coward, every creator and destroyer, every king and peasant… every saint and sinner in the history of our species lived there – on a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam.”
5. Space exploration provides us access to new raw materials. When we began to launch satellites into space, it allowed us to find new raw material deposits on our planet that we could access to make life easier here. If we apply this technology as an extension to the rest of our solar system, then it gives us the same benefit to find minerals, precious metals, and even new materials that we can use. Although the expense of exploring space is admittedly high, this advantage gives us a way to offset those costs somewhat. There is even the potential that it could become profitable one day if we can provide these efforts with enough capital.
6. Investments into space exploration create real economic benefits at home. The governments which provide the majority of our space exploration infrastructure employ over 20,000 people per agency who make direct positive economic impacts on their community. There are private companies who look at the potential benefits of this industry and contribute to this advantage as well, such as SpaceX and their thousands of staff.
People from all walks of life contribute to space exploration every day, ranging from astronomers to actual rocket scientists. Even though many of these programs receive taxpayer funding, the wages, manufacturing, and indirect investments contribute over 70% more in overall value at the local level compared to each dollar spent in the United States. These opportunities allows us to explore many different fields of study in addition to what is waiting in the universe as well.
7. Anyone can become a space explorer. Space exploration doesn’t need to involve starships, space stations, or intergalactic travel. If you own a telescope and can look up at the sky, then you can embrace this element of human existence. Our scientists have taken this advantage to the next level with the Hubble Space Telescope, which has made over 1 million observations in almost 30 years of service. We have made some incredible discoveries with this technology already.
- We have a better idea about the age of the universe (around 13.7 billion years).
- Images of the deep universe show that there are thousands of galaxies out there.
- It helped us to discover four of the five moons that orbit Pluto.
- We have a better understanding of planetary seasons in our universe.
- It works to peer into the atmospheres of alien planets so that we know what is waiting for us in our future exploration efforts.
8. Space exploration encourages us to share instead of being selfish. Being human-first from a space exploration standpoint isn’t about dominating other cultures that we might find waiting for us in the universe. It is a way for us to find common ground outside of our physical appearance, cultural differences, or religious preferences. For far too long, we have allowed ourselves to be consumed by our petty problems instead of looking at the big picture.
If someone is hungry, then we should feed them. If they are cold, then we should clothe them. If they need a job, then we should help to train them. Space exploration unites us in ways that other global efforts do not because we see ourselves as humans first. This advantage won’t solve our problems, but it can shift our attitude toward something that is healthier than our current state.
9. We know more about our planet thanks to our efforts to explore space. Because space exploration gives us a different perspective, it allows us to look at our planet in a different way. The view from outside of our atmosphere allows us to see the big picture instead of trying to extrapolate information from micro-scale research. This advantage allowed us to discover the problem of ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, begin the conversations on global warming, and examine the current and future impact of weather pattern changes that may happen because of a changing climate.
Space exploration helps us to look inward as well as outward, helping us all to find the changes that are necessary to keep our planet healthy for our children, grandchildren, and beyond.
List of the Disadvantages of Space Exploration
1. Our current technology makes it dangerous to get into space in the first place. Several agencies are developing “space tourism” packages that can take people in a comfortable aircraft to the very outer layers of our atmosphere, but that is not an exploration effort. We currently strap astronauts into a vehicle that gets attached to a very large rocket so that there is enough speed available to break the grasp of gravity.
Starting with Theodore Freeman, who was killed in the crash of a T-38 in October 1964, there have been over 20 individuals who lost their lives in the line of duty while advancing U.S. space program interests. There have been two individuals (Gus Grissom and Peter Siebold) who were able to survive a problem that resulted in the loss of a space vehicle.
2. There are cost considerations to look at with space exploration. The cost of exploring space is one of the biggest criticisms of the efforts to launch a program that takes us beyond our planet. When the space shuttle program was active in the United States, the total cost of the launch was about $500 million. That figure does not include the expenses of postponement that often occurred because the conditions were not right to send a rocket into space.
Manned missions in our solar system could cost 10 times that amount, and that might get us to Mars or one of Jupiter’s moons. Technology advancements in recent years could make this issue cheaper for the next generation, but we should ask ourselves if spending billions on space exploration is the right thing to do if we have people dying of hunger on our planet.
3. Astronauts receive exposure to natural dangers while in space. If the launching process doesn’t kill you during a manned space exploration effort, then the natural dangers that are present outside of our planet’s atmosphere could become problematic in a variety of ways. The radiation that comes from the sun is a constant danger to astronauts when they are in space, and the weightless environment can change their physical conditioning. Experiments with identical twins, with one staying on our planet and the other spending a lengthy assignment in space, show that there are changes at the cellular and genetic level that occur with space travel as well.
4. Current space exploration efforts could be a one-way trip. When we sent astronauts to the moon, our technology provided them with a chance to land on the surface and return to their spacecraft. It is possible that we could perform a similar action for asteroids, moons around other planets, and other celestial bodies that do not have an atmosphere. If we are going to start exploring Mars, then that journey could be a one-way trip for the astronauts.
Even if this journey does not become a one-way trip, the amount of time necessary to reach a destination beyond the moon makes it virtually impossible to mount a rescue mission if something goes wrong. Our current vision of space exploration requires perfection to create a successful result.
5. There may not be a reason to start exploring at this time. Human cultures have always had a fascination with exploring space because it satisfies our need to learn more about the universe. Taking long-distance pictures with the Hubble telescope is not the same as visiting the location in-person. What we must ask ourselves right now is if there is a valid reason to begin this effort, and the truth is that there are few pragmatic applications to consider.
We could start mining asteroids for their raw materials and mineral content in the future. Planetary colonization could be necessary in future generations. Since we are still dealing with issues like crime and poverty here at home, addressing our immediate concerns might be better than looking at future needs which might never be necessary.
6. Unmanned probes are even a waste of resources. One of the ways that we attempt to limit expenses with our space travel needs is to send unmanned probes into the dark vastness that lies beyond. There have been some successes with these efforts, most notably the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 missions that allow us to peer outside of our solar system. This option allows us to almost eliminate the risk to human life entirely as well.
There are also disadvantages to consider with this approach, starting with the fact that there is little adaptability to changing circumstances. The Mars Climate Orbiter is an excellent example of this problem. When it received incorrect coordinates for landing, it burned up while entering the atmosphere before sending any data at a cost of more than $120 million.
7. Our current information is well out-of-date. On February 22, 2017, NASA announced that it had found seven planets the size of Earth in a single solar system. Three of the planets were in the so-called Goldilocks Zone, which means they are at a distance from their star that is not too hot and not too cold. It is called the Trappist-1 group, and this set of planets lies in the Aquarius system. That’s about 235 trillion miles away, which is at least a measurable distance.
The problem is that this planetary system is 40 light-years away from us. That means the information that we can observe right now took forty years to get to our scientists. Think about all of the changes that have happened in your life in just the past 5 years, and then apply that concept to a planetary scale. When we start exploring space, we must take into account that this delay is present so that we don’t fly into an unexpectedly dangerous situation.
8. It may lead us into future conflict with beings who have superior technology. Space exploration makes us think in noble terms about what lies in wait for us in the universe. When we sent the Voyager spacecraft into our solar system and beyond, there were two records placed on the devices to communicate with whoever might find them to let that intelligent life know that we exist.
Most theorists who seriously consider the pros and cons of meeting alien life say that there are only two possible outcomes that can occur with first contact. That alien species will either be so advanced that their technological presence as led to a peaceful society where an exchange of information may one day be possible, or it will be aggressive and want to access our planetary resources.
9. Space exploration creates a lot of trash around our planet. There are over half-a-million items of trash from over 50 years of space travel and satellite placement which orbit our planet right now. Unless these items fall into the atmosphere and burn up, they will stay in place forever. The ring of debris that we have created makes space exploration more dangerous because an impact with a ship’s hull could have deadly results. We will need to clean up this mess in the future to provide better safety to our future explorers, and we have no idea what the expense might be.
Verdict on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
Space exploration is beneficial even if we only look at it through the lens of hope. It is an idea that unites us as one race instead of over 190 different countries. We can proceed into the universe as one people, taking the first steps toward new experiences just like we did when we placed astronauts on the moon for the first time.
Explorers always face danger, and space is no exception to that rule. The vacuum of the universe was not meant for humans, which means we must constantly adapt and protect ourselves when we are outside of our atmosphere. Then there is the risk of an encounter with alien life to consider too.
The advantages and disadvantages of space exploration must come from a common sense perspective. Other races could harm us, but there is also the possibility that we could be dangerous to other life as well. We should continue with these efforts, but with the understanding that this work is not a race. It is a cooperative effort that will eventually define our humanity.
Pros and Cons of Space Tourism
People put space tourism in the same bracket as flying cars as little as twenty years ago. The starting point of space tourism can be traced back to 2001 and the first space tourist, Dennis Tito. However, this term didn’t become a buzzword until 2021, when two billionaires, Sir Richard Branson and Jeff Bezos, set off to space in separate spacecraft in the same week. These two events marked the beginning of the new-generation space race.
Space tourism became available in February 2022, when Virgin Galactic started selling tickets for the next trip to space. While many people jumped on the space tourism bandwagon, others are beginning to wonder whether traveling to space as a tourist is a good idea.
This article will discuss the basics of commercial space travel, outlining its most essential advantages and disadvantages.
What Is Space Tourism?
A completely new level of sightseeing, it will become more widely available, you don’t need to be an astronaut to travel to space, new opportunities for space exploration, it will inspire more people to become astronauts, passengers will be able to experience weightlessness, it can boost scientific research, a new perspective of our planet, the possibility of finding additional resources, the possible discovery of extraterrestrial life, we may find other planets to colonize, more opportunities for employment, it could identify potential dangers to our planet, major technological advancements, endless opportunities, it contributes to global warming, few people can afford it right now, limited space, it’s not available for everyone, space tourism costs a lot of money, it’s not 100% safe, you pay a lot of money for a short trip, the issue with space junk, wasting natural resources, exposure to radiation, not going above the kármán line, out-of-date information, space sickness, all those resources could be invested elsewhere, it could put our planet at risk, space tourism – should we do it.
Before we go into the details regarding the pros and cons of space tourism, let’s talk about what this newest form of travel means.
Space tourism and space travel are not the same. What sets them apart is their purpose. Astronauts are sent to space to conduct various types of scientific research and experiments, and they go through rigorous training and preparation before they’re allowed to leave Earth. As a result, becoming an astronaut is incredibly challenging. Every year, NASA chooses a handful of people among tens of thousands of applicants.
Space tourism, or commercial space travel, refers to traveling to space for recreational reasons. People who want to become space tourists must satisfy three requirements: They must be 18 or older, physically fit, and rich. For example, one ticket for a 90-minute trip with Virgin Galactic costs $450,000, but we’ll get to that later.
There are three types of space tourism: orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism. The main difference between orbital and suborbital spacecraft is speed. Orbital space travel reaches an altitude of 1.3 million feet (400 kilometers), for which a spacecraft would need to travel at 17,400 miles per hour (28,000 kilometers per hour).
Suborbital rocket ships can only fly to a certain altitude (330,000 feet or 100 kilometers) because they don’t have enough power to orbit around the planet. As a result, these spacecraft must fly at a minimal speed of 3,700 miles per hour (6,000 kilometers per hour).
Most people assume that space tourism is pioneered by NASA and other government agencies. However, privately owned aerospace companies are now leading the global space tourism market. The three most important are Sir Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin, and Elon Musk’s SpaceX. The first two companies offer suborbital space travel, both licensed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for passenger space travel.
On the other hand, SpaceX plans to introduce orbital space tourism to the public. SpaceX rockets can reach 120 miles above the Earth, while Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic can’t achieve half that distance. Aside from SpaceX, Space Adventures, an American space tourism company is another enterprise that plans to introduce tourism flights to Earth’s orbit.
The final form of space tourism is lunar space travel, which includes orbiting around the moon or even landing on it. Space Adventures wants to introduce circumlunar flyby tours, but one ticket will be estimated at $150 million. SpaceX will also organize a space trip around the moon, which will be reached via the Starship.
Space tourism isn’t only in the hands of privately owned aerospace companies. NASA announced that space tourists, formally called private astronauts, will be allowed on board the International Space Station. They’ll be able to get there with the SpaceX Crew Dragon and the Boeing Starliner, which is currently being developed. Space tourists will be required to pay $35,000 for this trip to space.
Pros of Space Tourism
Many people are looking forward to the development of space tourism. In fact, the PEW Research Center surveyed the public’s opinion on space tourism in 2018. The survey revealed that 42% of participants stated they were definitely or probably interested.
It won’t only benefit people who want to be a part of this new era of space exploration but also space scientists. The advantages aren’t just limited to scientific and technological advancements. The dream will come true for many people who have always wanted to go to space.
Here are some of the most essential advantages of space tourism.
People have always been drawn to brand-new, unique experiences, and what could be better than viewing the Earth from a spaceship? Whether you’re a fan of science fiction or deeply fascinated by the endless wonders of our galaxy, traveling to outer space sounds like an unattainable fantasy. However, it’s closer than you might think.
People who said they were interested in space tourism in the 2018 PEW survey named three main reasons. Most participants (45%) said they wanted to experience something unique, while 29% of those surveyed wished to view the Earth from space. The others said they wanted to travel to space to learn more about our world.
Space tourists will be able to see the Earth, the Moon, the International Space Station, the Kármán Line, and many other parts of our solar system. Traveling to space will undoubtedly be a once-in-a-lifetime experience for many.
Since the beginning of space travel, only about 600 people have been to space. However, the development of space tourism will make traveling to space available for many people. According to a study by Northern Sky Research, there will be almost 60,000 space tourists by 2031.
There are currently long waiting lists for Virgin Galactic flights due to take place by the end of 2022. Although it’s nearly impossible to get a seat on this cutting-edge space vehicle right now, Virgin Galactic hopes to conduct 400 flights a year.
Even though prices for space tourism are currently going through the roof, it’s believed they will be significantly reduced when commercial space exploration becomes mainstream. One day, it may even become affordable for ordinary people.
You don’t need to be a trained astronaut to become a space tourist. Previously, the opportunity to fly to outer space was only available to astronauts. However, it will be possible for everyone who can afford it in the future.
Astronauts undergo years of preparation for a single flight, whereas space tourists receive the proper training a few days or even hours before the trip. If you want to fly with Blue Origin, you’ll only need one training day. On the other hand, Virgin Galactic’s training takes five days to complete.
The requirements for becoming a space tourist vary depending on the company. For example, if you want to fly with Virgin Galactic, you must be 18. Another important factor in traveling to space is physical fitness. You need to be relatively healthy for this adventure. People with heart problems or those who are overweight or underweight won’t be able to go.
Exploring outer space has been the goal of many government agencies and privately owned space companies ever since the 1950s. One of the most notable events of space exploration was the space race between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. This 20-year battle gave rise to many technological advancements and scientific achievements. It was also when the two nations sent the world’s first-ever satellites, rockets, and astronauts into space.
Space tourism and space exploration are inherently connected, where one directly influences the other. Therefore, increasing interest in space tourism will renew the global interest in space exploration, leading to more opportunities.
Many children want to be astronauts when they grow up. Kids usually start with sci-fi movies and space camps before pursuing educational opportunities in engineering, science, or technology. The chance to go to space when they grow up can inspire many young minds. Many people who have visited space as tourists have stated that the experience was life-changing.
Going to space will inspire many more people to become astronauts or contribute to the space industry in another way.

Other than being able to view our planet from outer space, passengers will also get a chance to experience weightlessness. Of course, zero-gravity simulators have already been developed on Earth, like the Zero G Experience , where people can experience weightlessness without going to space.
Space tourism allows people to sample the real thing. Once the spacecraft is launched, passengers will go through a similar experience to roller coaster rides. Space tourists who booked a flight with Blue Origin will be in zero-gravity for three minutes before the space vehicle descends to Earth.
Space tourism can help collect valuable research data. Such information will be essential in the development of space travel and space exploration. This kind of data wouldn’t be provided by space tourists but by people who organize the trip to space. Scientific research could encourage various innovations and solutions to problems.
Seeing our planet from space is a unique experience that will make us realize how small we are. We tend to think that we are the center of the universe and that the problems we face in life are insurmountable. However, going into space, even for a few minutes, puts things like conflicts and other issues that can be easily solved into perspective.
Another advantage of space tourism is the possibility of finding resources that are being depleted from our planet. If spacecraft take frequent trips to the moon or other locations in outer space, there is a greater chance of finding valuable resources that can be used for various applications.
For example, resources such as water, metals, minerals, atmospheric gases, and volatile elements can be found on various celestial bodies surrounding the Earth. For example, water was already found on the moon, Mars, and in some asteroids. Oxygen is another valuable resource that’s necessary for rocket propellants.
Not only can we use the raw materials to make life easier on Earth, but those resources can be put into improving aerospace technology. In other words, space tourism might pay off in the long run.
Space tourism brings us closer to finding extraterrestrial life. The subject of aliens has always been controversial, sparking many arguments about their existence. However, even though there is no solid proof of extraterrestrial life, many scientists agree that the odds of life on other planets are high.
The more money and resources that are invested into the commercial space travel industry, the further we will be able to explore. One of the goals of space exploration is discovering life outside of Earth, and space tourism can make this happen.
Space tourism may even bring us closer to finding new planets to colonize. But unfortunately, there haven’t been any discoveries of planets that are habitable and safe for human life yet. The planet closest to Earth in terms of habitability is Kepler-452b, which seems to be the most promising candidate.
The Mars colonization project is already on the way. Elon Musk plans to take SpaceX to Mars in five to ten years. So even though moving to a new planet seems like a plot from a movie right now, who knows what the future might bring? One thing is sure – space tourism will open new doors for us and allow us to explore more of the universe.
Hundreds of thousands of people are employed in the space industry, government agencies, and private companies. The growth of space tourism will open new doors for many individuals. As a result, the sector will likely see an increase in employment in the next couple of years.
Traveling to space lets us view the Earth from a different perspective. This will help us identify dangers to our planet and prepare for potential hazards. For example, if an asteroid or a comet is heading toward Earth, we would have more time to prepare. By exploring space, we could locate some of those hazards before they even come close and prevent a potential disaster.
As interest keeps growing in space tourism, more and more private companies will want to be a part of the new-generation space race. This will lead to significant technological advancements in the aerospace sector, facilitating space tourism even more. As a result, we can expect to see bigger, faster, and better rockets in the future, which will be made for suborbital space tourism and orbital space travel.
The future of space exploration through space tourism presents countless opportunities. The Northern Sky Research space tourism study suggests that the global space tourism market will be worth $20 billion in revenue.
Space tourism may replace long-air flights. Instead of traveling 16 to 17 hours from one continent to another, space travel will enable passengers to reach their destinations in under an hour.
One day, there might even be hotels in space, allowing space tourists to enjoy the wonders of space for a longer time. This is the goal of the Orbital Assembly Corporation. Their space hotels, the Voyager Station and the Pioneer Station, will orbit the Earth. Blue Origin and Orion Span are also working on building hotels in space called the Aurora Station and the Orbital Reef.
Cons of Space Tourism
Now that we’ve gone through all the advantages of space tourism let’s look at some downsides. Space tourism is extremely expensive and inaccessible, but it can also be dangerous in several ways.
Launching a rocket creates a significant carbon footprint. Spacecraft generate soot, a harmful substance of large amounts of carbon. Once it’s released into the atmosphere, the soot from a spacecraft is absorbed by sunlight, which increases the warmth in the atmosphere.
A spacecraft must burn excessive fuel to reach space and overcome Earth’s gravity. We’re talking hundreds of tons, which can leak through the rocket and spill into the atmosphere. The harmful chemicals, along with rocket fumes, harm the ozone layer.
It’s already possible to purchase tickets for space. However, it’s costly. One ticket for a ride with Virgin Galactic costs $450,000, and that’s only for a 90-minute trip. Now, becoming a space tourist is only possible if you’re a multi-millionaire. The only people who have become space tourists are billionaires like Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, and Sir Richard Branson. That’s why space tourism has been dubbed “the billionaire space race.”
Right now, both Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have enough room for a maximum of six passengers. However, if we were to include the two pilots, they could only accommodate four more people. For that reason, those who wish to participate in the space exploration experience must book tickets several years in advance. More than 600 reservations have already been made for Virgin Galactic space tours.
In other words, if you were thinking about buying a ticket for a space trip that will take place this year, you can forget about it. That being said, SpaceX announced they were working on a spacecraft with enough room for up to 100 passengers.
As mentioned before, not everyone will be able to become a space tourist. Even if you have the money and you’re old enough, your health and physical condition could prevent you from participating in space tourism.
Those allowed to travel to space need to be in pretty good shape. Aerospace companies have different rules and requirements. For example, Blue Origin only lets you buy tickets if you can climb seven flights of stairs in under 90 seconds. People who fail to meet their requirements are automatically eliminated.
There are also different height and weight requirements. For example, you can’t weigh less than 110 pounds or more than 223 pounds to become a space tourist.
Space tourism isn’t only expensive for the passengers but for the private space company as well. For example, a return trip to the International Space Station with the Boeing Starliner or the SpaceX Crew Dragon will cost around $50 million.
The trips to the International Space Station carried out by Space Adventures from 2001 to 2009 cost $20 to $30 million for eight- to 14-day trips. The more recent trip to the International Space Station cost $55 million when Axiom Space sent the Crew Dragon Endeavor spacecraft in June 2022. The space tourists were there for 17 days.
Space tourism is still a generally new concept. In fact, Blue Origin has only carried out three space tourism launches so far, while Virgin Galactic went just once. Space travel continues to be dangerous due to many factors, such as inadequate safety protocols and lack of proper regulation. Traveling to space isn’t safe, so we must consider the worst-case scenario. If the spacecraft crashes, there won’t be a way to save any passengers.
Space tourists will be required to pay a ridiculous amount of money for a short time in space. For example, if you choose to travel with Blue Origin, you will only spend a few minutes in zero gravity, for which you would have to pay $200,000.
Other aerospace companies offer longer trips. For example, Virgin Galactic will send their spacecraft into space for three hours. Similarly, the New Shepard will be in space for approximately 11 minutes, while the Virgin VSS Unity flight takes two and a half hours.
Space junk refers to man-made debris and satellites that are no longer active and always orbit around our planet. While testing new rockets, launching them into space, and even on space missions, these rockets create a large amount of waste. In the 60 years of human space travel, we have generated over half a million items of space junk.
Space junk is another form of pollution that directly affects the Earth. Not to mention that space junk can also damage active satellites and spacecraft that might be close by. Space junk is dangerous because all those micro shards accumulate into larger piles of debris.
If the space mission is successful, all the investments and resources put into the project will pay off one way or another. However, if the experimentation fails, the resources will have been spent for nothing. The same applies to space tourism. If we were to look at a trip to space from that perspective, we would have to ask ourselves, is it worth spending so much money and resources just to send six people to space for three minutes?
One of the dangers of being an astronaut is constant exposure to harmful radiation from the sun, which leads to a greater risk of cancer and other health problems. Of course, space tourists who only spend a few minutes or hours in space shouldn’t have anything to worry about. But those who spend days or weeks in space might want to consider this factor.
The Kármán Line is a widely accepted border between the Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. It’s roughly 100 kilometers (62 miles) above sea level, located in the Earth’s thermosphere. Although no globally accepted law defines where space begins or ends, most regulatory agencies agree that the Kármán line is the closest we have to a border.
Suborbital spacecraft belonging to Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic won’t be able to cross the Kármán Line, which is considered “real” space. However, this may change in the future.
No matter how fast space technology might be developing, space scientists still use outdated information for some matters. Unfortunately, outdated information is useless and can also be dangerous and cause serious issues.
The problem with space research is that most of the celestial bodies that aren’t in our solar system are light-years away. Unfortunately, measuring time and distance in space is difficult, so we often receive inaccurate information.
Even for three minutes, exposure to zero gravity can affect the human body. To be more specific, passengers won’t have any side effects while they’re in space. The issues start when they return to Earth when space tourists experience space adaptation syndrome (SAS).
This is more commonly known as space sickness, like the space version of motion sickness. Space sickness manifests itself through loss of muscle power, bone resorption, loss of consciousness, and other short- and long-term effects. However, such symptoms are more likely to affect astronauts who spend months in space.
Space tourists may experience mild symptoms, like headaches, nausea, puffiness, temporary anemia, loss of appetite, and similar. They can even feel sick a few days after their journey to space. That’s why space tourism will only be available for passengers who are in good health.
Space tourism is a multibillion-dollar industry, and its revenue is only expected to grow. Since so much money is being invested, it raises many controversies. The Earth is in a lot of trouble, financially, politically, and environmentally. As a result, many politicians, humanitarians, and public figures have tried to highlight other matters that require our immediate attention. This includes poverty, global warming, world hunger, and many more issues that could benefit from these resources.
Last but not least, space tourism can be dangerous because it puts our planet at risk. This is another scenario that could be taken from a sci-fi movie. But in the future, traveling to space might have grave consequences.
Space tourism is a controversial topic. On the one hand, it can be a wonderful experience that allows us to view our planet and other celestial bodies from space. In addition, it opens up new doors for space exploration, inspires technological advancements, and boosts scientific research. But on the other hand, space tourism is extremely expensive; it accelerates global warming, is only available for a limited number of people, and can be very dangerous.
Whatever your opinion on space tourism, there’s no stopping its advancement. People will always be drawn to new things no one has experienced before, which is just one of the reasons the commercial space travel industry will grow. One day, we might even have hotels on the moon or other planets. There’s no telling what the future might bring.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get your Space Exploration And Astronomy Free Guide
We will never send you spam. By signing up for this you agree with our privacy policy and to receive regular updates via email in regards to industry news and promotions
8 ways that SpaceX has transformed spaceflight
SpaceX has changed the spaceflight landscape during its first 20 years of existence.

- 8) Made big spaceflight dreams mainstream
7) Put billionaires front stage of space exploration
- 6) Awesome launch webcasts
- 5) Brought new style to spaceflight
- 4) Ramped up orbital space tourism
- 3) Returned crewed orbital spaceflight to U.S.
- 2) Reduced launch costs
- 1) Reusing rockets and landing boosters
Falcon. Dragon. Starlink. Starship. Starman.
SpaceX has contributed a lot to our spaceflight vernacular, showing just how far the company has come in its first 20 years.
Elon Musk founded SpaceX on March 14, 2002, with big dreams of creating reusable rockets, commercial spacecraft and other advanced technology. Musk has said that few believed it was possible, during an era when space agencies still dominated the industry and space hardware was mostly expendable, save for a few examples like NASA's space shuttle and its solid rocket boosters.
Now, 20 years later, SpaceX is a dominating force of its own. The company aims to build out its 2,000-satellite-strong Starlink internet constellation to hold perhaps 30,000 spacecraft. It's ramping up an orbital space tourism program and is the sole U.S. provider for crewed missions to the International Space Station. And as Musk envisioned, SpaceX is now regularly launching and landing rockets while carrying payloads for a wide range of customers, from private companies to NASA and the United States Space Force.
Musk and SpaceX are in the headlines a lot, and the coverage isn't always positive. In 2018, for example, the billionaire entrepreneur sipped whiskey and took a puff of marijuana during his 2.5-hour live appearance on The Joe Rogan Experience , prompting a NASA safety review of SpaceX practices. That same year, Musk insulted an individual involved in rescuing Thai boys from a flooded cave. The Starlink constellation is causing worries about orbital debris and interference with astronomy observations . And yet Musk persists in being himself, and his company is one of the most powerful in the space industry.
Here are eight ways in which SpaceX rose from relative obscurity to "Saturday Night Live"-level fame .
8) SpaceX made big spaceflight dreams mainstream again

Readers of a certain age may remember German-American rocket scientist Wernher von Braun partnering with entities like Disney to popularize space stations and future crewed space travel in the 1950s, in the years before the Saturn V rocket, whose design he led, launched people to the moon during NASA's Apollo program.
Such big dreaming rapidly became uncool in the 1970s as Apollo faded into history, NASA's budget was slashed and the agency's human spaceflight focus shifted to (supposedly) low-cost missions to low Earth orbit. The space shuttle was a remarkable machine, but it never came through on the low launching costs NASA wanted.
Enter Musk. He had remarkable independence for a spaceflight player, given that he received $180 million in 2002 (roughly $280 million in today's dollars) when eBay bought Paypal. He poured much of this fortune into starting up SpaceX and from the beginning talked about the need for humans to go interplanetary to reduce the threat of extinction. Mars, he said, would be a great place for us to go.

Musk has said that, around 2002, he began researching NASA's plans to land people on the Red Planet and couldn't believe there was no published timeline available. (In more recent years, NASA has suggested the 2030s as a goal.) That's when Musk says he envisioned a Mars mission "to spur the national will," Wired reported.
Meanwhile, Musk worked on accumulating reputation and contracts closer to home to launch satellites, International Space Station cargo and people. It took years to demonstrate that the reliability of SpaceX could rival that of big companies such as Arianespace and United Launch Alliance, but (as we'll talk about below) Musk's ability to spend a lot of money testing reusable rocket technology helped in that effort.
In latter years, Musk and SpaceX have poured much of their energy into developing Starship , a huge rocket-spaceship duo designed to get people to Mars and other distant destinations.
Multiple Starship prototypes went boom during high-altitude test flights, but one finally nailed its landing in May 2021. And NASA picked Starship as the first crewed lander for its Artemis program of lunar exploration, which aims to put boots back on the moon in the middle of this decade.
Starship still has a number of hurdles to clear, however. For example, the system has yet to launch on an orbital test flight; SpaceX is awaiting regulatory approvals before making the first attempt, which could come in the next month or so.

Musk isn't the only billionaire playing a large role in the space industry, of course. Jeff Bezos established the spaceflight company Blue Origin in 2001, for example, and the suborbital space tourism company Virgin Galactic is part of Richard Branson's Virgin Group.
But Musk has been in the public eye more than his fellow space billionaires, partly because of SpaceX's many high-profile successes and partly because he's a very active (and sometimes controversial) Twitter user.
Blue Origin , by contrast, operated in relative secrecy for much of its existence, making few public announcements. (That has changed in recent years, however, as the company has begun flying tourists to suborbital space on its New Shepard vehicle.) Branson is a colorful personality, but Virgin Galactic's suborbital tourist system isn't fully up and running; the company has four spaceflights under its belt but has yet to fly a paying customer.
Meanwhile, Musk has regularly provided updates about SpaceX's various systems on Twitter, given livestreamed Starship progress reports that quickly became must-watches for space fans and inserted himself into the cultural mainstream in a variety of other ways. For instance, he hosted "Saturday Night Live" in 2021, playing the Nintendo supervilllain Wario during his appearance.

Space tourism made a big leap in 2021, with individuals flying to space with SpaceX, Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin . Branson and Bezos themselves flew on their respective company's systems. Inevitably, given that a seat on Virgin Galactic (for example) now costs $450,000 , tremendous wealth is associated with these various opportunities. That means that very wealthy people are the key audience for selling tickets.
There are ethical issues with having the super-rich on spacecraft, to be sure. People have raised questions about what it means to have an industry in which rich people, or people who have received favors from rich people, are the only ones who get to take part. But then there is the example of Inspiration4 , which flew to Earth orbit for three days aboard a SpaceX Dragon in September 2021.
Inspiration4 — the first-ever all-private crewed trip to Earth orbit — was funded and commanded by billionaire Jared Isaacman, who (similar to Musk) made his fortune with a payment system, called Shift4. Isaacman opened the other three seats on his spacecraft to regular folks, two of whom won their opportunities through contests, with the third flying on behalf of a charity: St. Jude's Children's Research Hospital in Memphis.
Isaacman wanted to raise millions of dollars for St. Jude, and he achieved that goal, along with a healthy dose of publicity. Isaacman recently announced a set of new private missions with SpaceX, which will be run under the Polaris Program . Isaacman hasn't yet named the crews for all the opportunities, but has said each of these missions will also be charity-focused.

6) SpaceX made launch webcasts appointment viewing

Numerous space companies today run their own spaceflight broadcasts, but SpaceX's tend to stand out. Over the years, millions of people have tuned in to the company's broadcasts to see rocket stages landing on ships at sea and, in one particularly spectacular example, a spacesuit-clad mannequin launching into orbit around the sun.
The mannequin was one of the stars of the debut Falcon Heavy launch in February 2018. The huge rocket lifted off without a hitch, and its three first-stage boosters came back to Earth within view of a huge crowd at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the biggest such group since the space shuttle program ended in 2011.
When the webcast shifted back to an in-space view, the Falcon Heavy's upper stage had a spectacular reveal: a mannequin astronaut, driving a Tesla Roadster . SpaceX began playing David Bowie's "Starman" on the broadcast, dubbing the mannequin with the same name as it began a road trip around the sun.
The "astronaut" caught tremendous international attention; this reporter received a message about it from an individual in Mariupol, Ukraine, who didn't usually follow spaceflight, for example. But it's just a singular example of what the webcasts have offered to long-time SpaceX fans.
SpaceX has been strategic in offering camera views of staging, high-definition glimpses of its rockets during launches and at-sea landings, and numerous statistics that fans enjoy parsing on channels such as Twitter and Reddit.
In a sense, the company is borrowing from the earliest days of NASA, when the agency was running open television broadcasts during an era when crewed rocket reliability was far less than what is possible today. NASA and SpaceX, in fact, tend to have competing broadcasts during joint launch efforts of the Crew Dragon system, which creates a considerable (but fun) challenge as space fans split their attention among their social media channels and livestreams.

5) SpaceX brought new style to spaceflight

In 2017, Musk revealed the long-awaited spacesuits that NASA astronauts and others aboard his spaceships would don during future flights. True to his tradition of breaking news on social media, he posted the first images on Instagram (although the link doesn't work today.)
While Musk noted that it was "incredibly hard" to balance aesthetics and function in the spacesuits, right away people began commenting on its movie-star look. The SpaceX suit was so thin, in fact, that Musk had to reassure his Instagram followers: "It definitely works. You can just jump in a vacuum chamber with it, and it's fine."
The design was no Hollywood coincidence; it came from legendary costume designer Jose Fernandez, who created outfits for blockbusters such as "Wonder Woman," "Wolverine," "Batman vs. Superman" and "Captain America: Civil War."

SpaceX picked flashy opportunities to test its spacesuit in space, along with the usual pressure tests and vacuum chamber tests. One flew with Starman on the Falcon Heavy rocket in 2018, and another was used on the dummy Ripley that flew aboard the uncrewed SpaceX Crew Dragon Demo-1 test flight to the ISS in 2019.
There also are the sleek controls for Crew Dragon, which features touchscreens instead of dials and switches. The Crew Dragon console offered interesting experiences for NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley , who were used to the space shuttle's controls (parts of which date from the 1970s, although much was updated as the program evolved.)
"As a pilot, my whole career having a certain way to control a vehicle, this is certainly different," Hurley said during a news conference in May 2020. "But we went into it with a very open mind."


4) SpaceX ramped up orbital space tourism

We've already spoken about Inspiration4's mandate, but other aspects of the orbital space tourism mission are worth mentioning. The Crew Dragon Resilience and its spaceflyers circled Earth for three days at an altitude higher than any human has achieved since a Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission in 1999.
At 367 miles (590 kilometers) above our planet, Inspiration4 experienced a much higher view than astronauts receive on the ISS (about 250 miles, or 400 km). The crew also had the advantage of a domed window , rather than the little portholes that previous generations of NASA and Soviet astronauts had in the 1960s and 1970s.
SpaceX's marketing efforts for space tourism also extend to the dearMoon project , for which Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa is seeking eight crew members to join him on a trip around the moon using SpaceX's Starship spacecraft. The project received some early negative press, as Maezawa asked for a girlfriend to come with him, but a swift marketing shift had Maezawa instead asking for "people from all kinds of backgrounds to join." The targeted launch date is 2023.

In the nearer term, SpaceX will fly paying customers to the International Space Station for Houston-based company Axiom Space, which has booked several missions using the Falcon 9-Dragon system. The first of those flights, Ax-1 , is scheduled to launch on March 30.
And Isaacman's Polaris Project is providing a unique opportunity for SpaceX to show its stuff in orbital spaceflight. The first mission with four private astronauts will include two individuals from SpaceX highly experienced in crewed and uncrewed missions: Sarah Gillis and Anna Menon, who assist in matters ranging from crewed spaceflight development to taking the helm in SpaceX's Mission Control.
It's too early to say yet how SpaceX will position the marketing of its own personnel flying on space missions, but this may be done with some flare given how SpaceX showcased Starman. That said, SpaceX allowed Isaacman to take the lead in promoting Inspiration4, so it may be part of the arrangement to allow Isaacman to handle the work again for Polaris.

3) SpaceX returned crewed orbital spaceflight to U.S.

When NASA retired its space shuttle fleet in 2011, the agency was in the midst of supporting several American space companies working to develop the vehicles' replacement, including SpaceX. SpaceX and Boeing won out in 2014, splitting NASA's $6.8 billion Commercial Crew Transportation Capability award.
At award time, NASA hoped to have SpaceX's Crew Dragon and Boeing's CST-100 Starliner capsule flying by 2017, but technical and funding issues pushed the timeline back by several years. In May 2020, SpaceX launched its historic Demo-2 test mission, which sent a Crew Dragon carrying Behnken and Hurley to the International Space Station as the world was in the grips of the coronavirus pandemic, providing some hope and excitement for a captive audience looking for such things.
It was the first crewed orbital liftoff from American soil in nine years, although Florida could not see the usual launch crowds due to safety protocols associated with the pandemic. Still, the livestreams from NASA and SpaceX showed the spacecraft flawlessly sending Behnken and Hurley to the International Space Station for a two-month stay.

The splashdown on Aug. 2, 2020, the United States' first crewed one since the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975, also went technically well. Unfortunately, however, the area was swarmed by boaters eager to see the procedures up close. (NASA and SpaceX have since changed their protocols to advertise less specifically where the splashdown will occur.)
SpaceX has since run several operational crewed flights to the ISS with few issues, in contrast to Boeing's Starliner. Starliner ran into numerous snags during its uncrewed test flight to the orbiting lab in late 2019 and hasn't had the chance yet to return to space for another try. Numerous issues, including launch windows, the pandemic and technical concerns , mean Starliner likely won't launch until at least May 2022 . Crewed flights may not follow until 2023 or so.
This means that for now, Crew Dragon is the only option for NASA astronauts (or space tourists) to leave for orbital space from American soil.
After the space shuttle retired and before Demo-2 lifted off, NASA was completely dependent on Russian Soyuz vehicles to take its astronauts to and from the space station. Relations between NASA and Russia have been rocky in recent weeks after Russia's invasion of Ukraine on Feb. 24, prompting numerous international sanctions. ISS operations are normal for the time being, but NASA doubtless is breathing a sigh of relief that an American crewed orbital capability is up and running in case, as the relationship with Russia could well deteriorate further.
SpaceX may also be able to replace some Russian services to the ISS, such as reboosting the orbiting complex periodically to avoid drag from Earth's atmosphere pulling the station back to the planet. (Northrop Grumman's Cygnus cargo spacecraft will also test out this capability during its current mission to the ISS, which began in February.)

2) SpaceX helped reduce launch costs

Reusable rocket and spacecraft technology is the backbone upon which SpaceX builds its cost estimates, which tend to be lower than those of its competitors.
For example, the per-seat cost for SpaceX's Crew Dragon is around $55 million, NASA's Office of the Inspector General said in 2019 , which is roughly 60% less than both Boeing Starliner (projected at $90 million) and the Russian Soyuz (then $85 million).
For further perspective, SpaceX sells Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches for $62 million and $90 million , respectively, well below the prices of their chief competitors. In late 2020, for example, it cost a little more than $100 million to book a ride on United Launch Alliance's workhorse Atlas V rocket. (The Atlas V is not quite as powerful as the Falcon 9 .)

Launch customers also pay varying amounts for getting aboard Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy depending on the size of their satellite, in line with industry practice. So a fleet of tiny cubesats from different organizations, as an example, may typically pay lower costs for their "rideshare" than the operator of the main satellite that is also atop a Falcon 9 on the same launch.
Low costs may extend to future systems, too. The super-heavy Starship system , for instance, is projected to use only $900,000 worth of propellant to make it to Earth orbit. Operational costs overall could be as low as $2 million per flight, Musk suggested in 2019 . If that's the case, Starship will be truly revolutionary, slashing the cost of access to space like never before.
The caveat with all these costings as that some are theoretical and others may be subject to change with recent supply issues induced by the pandemic. But overall, SpaceX is still pointed to as an example of reliably allowing lower-cost launches than its competition.

1) SpaceX is reusing rockets and landing boosters

In a stunning bit of rocket tech now considered routine, SpaceX recovers and reuses the first stages of both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets. Indeed, such reuse is key to the company's ability to keep costs down.
The returning boosters come to the ground for soft vertical landings about nine minutes after liftoff, either on solid ground near the launch pad or on autonomous "drone ships" mid-ocean.
The company realized its 100th rocket landing in December 2021, six years after notching its first successful touchdown on an orbital mission. SpaceX also seeks to launch frequently, especially with regard to getting its Starlink constellation operational, and stresses that reusable rockets are key to boosting launch cadence as well as lowering costs.
At the moment, Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets are only partially reusable; their upper stages are still discarded after launch. The Starship-Super Heavy system, however, will be fully reusable. And the Super Heavy landings will be quite a sight to see.
"We’re going to try to catch the Super Heavy booster with the launch tower arm, using the grid fins to take the load," Musk said via Twitter on Dec. 30, 2021. .
Yes: SpaceX plans to bring the giant Super Heavy back to Earth directly on the launch tower. While Musk has talked about this idea before , the new tweak adds some interesting design challenges. In fact, when you think about it, Super Heavy won't actually be touching down, as it will be caught midair by the tower arm.
What this change would mean is that Super Heavy wouldn't need landing legs. Musk also listed additional benefits to this strategy: "Saves mass and cost of legs and enables immediate repositioning of booster onto launch mount — ready to refly in under an hour," he said in another Dec. 30 tweet .
Reusability is the key breakthrough needed to make the settlement of Mars economically feasible, Musk has repeatedly stressed. He recently estimated that SpaceX could get people on the Red Planet's surface by 2026 , if Starship development and testing go well. While the timeline is optimistic, his goal to put boots on Mars has not changed in decades and continues to fuel the work that SpaceX does.
Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter @howellspace . Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or on Facebook .
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mission — Live updates
How to watch Boeing's 1st Starliner astronaut launch webcasts live online
Watch SpaceX's Crew-8 astronauts move their Dragon at the ISS May 2 to make way for Boeing's Starliner
Most Popular
- 2 'It almost feels unreal': NASA astronauts excited for 1st crewed Boeing Starliner launch May 6
- 3 NASA prepares for intense sun storms on Mars during 'solar maximum'
- 4 James Webb Space Telescope forecasts clouds of melted rock on this blisteringly hot exoplanet
- 5 A Switzerland-size hole opened in Antarctica's sea ice in 2016-17. Now we know why
33 Main Pros & Cons Of Space Exploration
“Space exploration is a force of nature unto itself that no other force in society can rival.”
Neil deGrasse Tyson, Scientist
Advantages & Disadvantages of Space Exploration
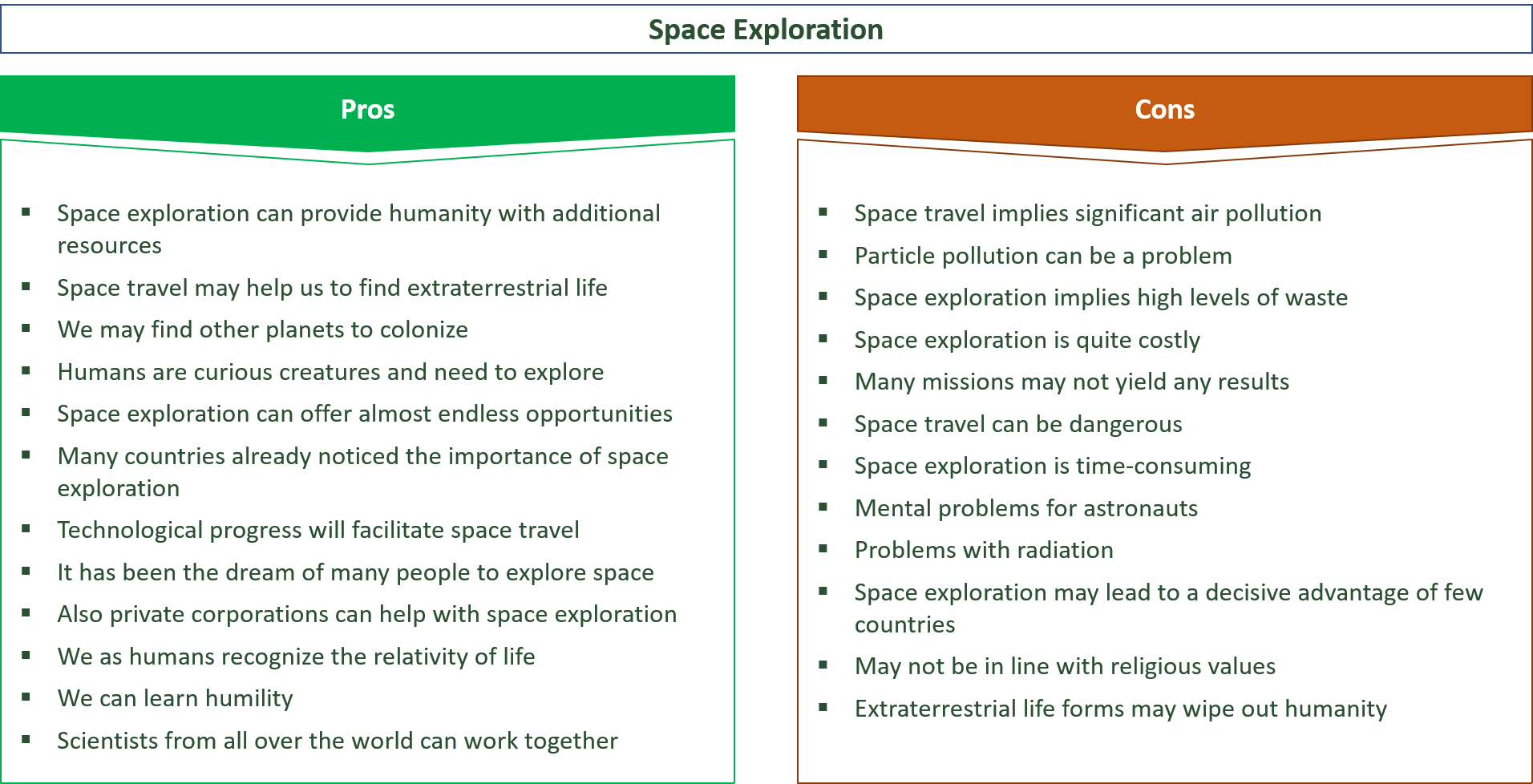
Space exploration is a rather controversial topic.
While the majority of people think it is a good idea to explore space, there are also opponents of space travel who claim that space exploration may potentially wipe out humanity in the long run.
In this article, the pros and cons of space exploration are discussed in detail.
Please enable JavaScript

Audio Lesson
Advantages of space exploration, space exploration can provide humanity with additional resources, space travel may help us to find extraterrestrial life, we may find other planets to colonize, humans are curious creatures and need to explore, space exploration can offer almost endless opportunities, many countries already noticed the importance of space exploration, technological progress will facilitate space travel, it has been the dream of many people to explore space, also private corporations can help with space exploration, we as humans recognize the relativity of life, we can learn humility, colonizing other plants may help to mitigate the overpopulation problem, scientists from all over the world can work together, can help us to install satellites, helpful to create maps and pictures, we can collect important research data, may help us to detect serious threats to our earth, space travel may become available also to private persons, space exploration may speed up technological progress, space travel industry provides many job opportunities, may help humanity not to go extinct in the far future.
One important advantage of space exploration is that it gives humanity the opportunity to exploit additional resources in outer space.
As many of us know, our fossil resources will become depleted sooner or later and when we run out of natural resources , chances are that our technological progress will suffer significantly.
Hence, if we want to continue to progress as a species and want to develop our technologies forward, the additional resources that can be extracted from asteroids are crucial in this regard.
Space exploration can also help us to find extraterrestrial life, at least if it really exists.
The idea of extraterrestrial life is fascinating for many people around and in order to improve the chances to get contacted by those life forms, it is crucial that we leave as many traces as possible in space.
Always remember that space is huge and that it will be not easy to find each other.
However, through space travel, we could at least increase the chances to get in touch with other extraterrestrial life forms a little bit.
Another benefit of space travel is that we may also find planets that we could colonize in the near future.
Yes, there are already plans to colonize Mars.
However, colonizing Mars implies many important problems and scientists are not sure yet whether Mars is really a promising option when it comes to populating other planets.
Therefore, we may have to search for other planets that are better suitable for colonization and space exploration is crucial in this regard since only if we explore space, we will find these additional colonization opportunities.
In general, we as humans are curious creatures and want to learn and explore.
In fact, when we take a look back at human history and see where we are now, we realize the enormous technological progress we made over the past centuries.
This indicates how big the human drive to invent new things really is and we as humans can only be happy and satisfied if we are the best versions of ourselves.
Consequently, space exploration can give us the opportunity to really move forward as a species and to satisfy the need to always progress and extent our knowledge.
Space travel also gives us the opportunity to always experience and explore new things.
In fact, space is so big that we as humans will never be able to explore all of it.
In fact, the size of our universe is enormous and gives us almost endless opportunities to always make new findings.
Indeed, scientists believe that we as humanity only scratched the surface of what is still to explore out there and we may know little to nothing up to this point in time about how the universe really works.
Space exploration is not only important for humanity as a whole, it is also crucial on a country level.
In fact, many countries around the world have already noticed how important space travel really is and try their best to conquer space and to claim territories up there.
Many people might not know it yet, but space provides us with pretty high amounts of resources and the country that conquers those resources will likely have quite a lot of power over the next decades and centuries.
While it was quite hard to explore space just a few decades ago, it has become much easier thanks to our technological progress.
We now know much more about the dynamics of rockets and space stations and the risk related to space exploration is much smaller compared to the significant risk that had been present in the past.
Since our technological progress advances at rapid speed, chances are that space travel will become even easier and more cost-efficient in the future.
Many people who have seen science fiction movies are also quite keen on exploring space.
In fact, many people think that it is our human duty to do our best we can in order to explore space and to learn about the dynamics of our whole universe.
Hence, space travel can also make this collective dream of many people come true.
At our current state of the world, not only countries, but also private corporations engage in the space travel market.
In fact, the United States currently rely on private space missions since they abandoned their own space programs in the past.
However, if private space corporations can help us to achieve our space missions, this can be a great way to improve our overall chances for success of space missions in the future.
In fact, the space travel market is huge and many other companies may enter this market sooner or later.
In turn, chances are that the resulting competition will benefit humanity as a whole since space companies will be more eager to invent new technologies and to make processes much more efficient.
Another upside of space exploration is that we as humans can realize our place in the universe.
In fact, we often think that we are the center of everything and that we are the superior species in our universe.
However, through space travel, we soon realize how big the universe really is and that we are indeed just a tiny grain of sand on a big beach.
In turn, many of us will realize how relative life is and that we are not superior in any kind of way.
In turn, we will also be able to learn a great level of humanity.
In fact, it is astonishing how small our earth really is compared to other planets, stars, galaxies or even the whole universe.
By realizing this fact, many people who currently have a rather arrogant attitude will be more likely to change their minds since they will realize that we are actually apes that don’t really know what’s happening around us.
Space travel can also help us to reduce our overpopulation problem .
In fact, until the end of the 21 st century, the number of people on our planet will likely exceed the 10 billion mark.
However, it is yet rather unclear how we are able to feed all those people.
Hence, it is crucial to look out for proper alternatives.
If our planet will no longer be suitable to provide for us, we may have to colonize other planets.
Sure, this will be a long-term goal and will not be feasible in the near future.
Yet, it can make sense that we look out for suitable alternatives to our earth in order to feed as many people as possible in the long run.
Space exploration also provides a unique opportunity for scientists all over the world to work together for a bigger goal.
In fact, in order to make space travel missions successful, we need the smartest people from all over the world.
Those people have to exchange their ideas to invent new technologies and to make space travel more efficient and also safer.
Space exploration is also quite helpful for rather basic things.
For instance, space exploration can help us to install satellites in space so that we can access different TV channels.
Hence, space exploration can also be helpful to make our daily lives easier and more fun.
Space exploration can also be helpful to provide us with nice pictures of our planet and of the universe.
Moreover, it can also be quite helpful to create 3-D maps that can be accessed via the internet.
By creating those maps, we get a better impression of the structure of our earth and of its location in our universe.
Space exploration is also crucial to provide important research data to leading scientists from all over the world.
In fact, the more data we get, the better we will be able to understand how the universe works and what is still missing for a comprehensive understanding of how the cosmos actually works.
Another important advantage of space travel is that it allows us to detect serious threats that could potentially wipe out humanity.
For instance, through space exploration, we may be able to detect a meteorite that is on collision course with our earth.
In turn, we could take measures to prevent this collision.
However, this will only be possible if we detect the meteorite in time and therefore, space exploration can be crucial to prevent catastrophic disasters in the future.
Space travel is not only accessible for astronauts on official missions, it will also become possible for private persons in the near future.
In fact, there are companies out there who will offer space travel for private people.
This also implies that not only astronauts, but also private people will be able to see the true beauty of space, at least if they have the money to do so.
Space travel is not easy and needs plenty of technology in order to be successful.
In fact, over the past decades, numerous important inventions have been made.
Those inventions have not only been beneficial for space exploration, these technologies had also been important to facilitating our daily lives.
Thus, inventions from space travel can also indirectly benefit the general public.
The space travel industry has become increasingly important over the past decades.
In fact, in our current state of the world, numerous jobs depend on this industry and chances are that many additional jobs will be created in the field of space exploration in the near future.
Space exploration also has the big goal to protect the human species from going extinct in the future.
In fact, our Earth will likely not provide us with a suitable living space forever and due to global warming and other environmental problems, we may have to leave our Earth behind sooner or later.
In turn, this also implies that we have to explore space and to find new planets that we may be able to colonize in order to secure the survival of the human species.

Disadvantages of Space Travel
Space travel implies significant air pollution, particle pollution can be a problem, space exploration implies high levels of waste, space exploration is quite costly, many missions may not yield any results, space travel can be dangerous, space exploration is time-consuming, mental problems for astronauts, problems with radiation, space exploration may lead to a decisive advantage for few countries, may not be in line with religious values, extraterrestrial life forms may wipe out humanity.
Apart from the many important advantages of space exploration, there are still some issues with space travel.
For instance, one important problem with space exploration is that it implies significant air pollution.
In fact, in order to launch a rocket, it takes large amounts of fossil fuels.
Moreover, also in the production process of rockets, significant amounts of fossil fuels have to be used.
In turn, space travel implies significant air pollution and especially people who live close to those facilities may suffer quite a lot from fumes in the air.
Particle pollution is closely related to the air pollution problem.
In fact, if large amounts of fossil fuels are burned, also large amounts of fine particles are emitted into our atmosphere .
In turn, people who live in those areas with significant particle pollution may suffer from several pulmonary issues like asthma or lung cancer.
Another downside of space exploration is that it also implies significant levels of waste .
In fact, in the testing process of new rockets, plenty of waste is produced.
Moreover, also on space missions, large amounts of waste are produced.
In fact, plenty of waste is circling around the earth in outer space and we have to be careful not to make space a gigantic garbage dump.
Space missions also imply significant costs.
In fact, it is quite expensive to explore space and depending on the lengths and the goal of the respective mission, many millions or even billions of dollars have to be used.
Opponents of space missions often claim that this money could be far better used for projects that would facilitate the energy transition process from fossil to renewable energy sources on our earth instead of wasting it for space travel.
Another disadvantage of space travel is that those space missions also often do not deliver any results.
In fact, all attempts to find extraterrestrial life have failed up to this point in time and there is little reason to believe that this might change in the near future.
While space travel has become much safer over the past decades, it is still a rather risky project and the chances for accidents are still present.
Hence, astronauts still have to enter a rocket with the knowledge that there will be the risk that they will never come back home from their missions.
Another issue with space exploration is that those missions are often quite time-consuming.
Especially for longer missions, it can take several months or even years to complete those missions and therefore, space travel con be considered as a long-term project that will not deliver too many immediate results.
Due to the overall high level of insecurity of space missions, astronauts also often suffer from mental problems .
This is not only due to the fact that there will be a significant risk for those astronauts to never come back home, it is also due to the fact that astronauts often feel quite lonely in space.
Yes, there are other astronauts on space stations.
Yet, this is not the same as being together with your family.
There is also still plenty of controversy when it comes to the true long-term health effects of space travel for astronauts.
While some scientists claim that space travel does not lead to too many severe long-term health issues, other scientists claim that radiation is a serious problem in space travel and that the chances to suffer from cancer will be much higher for astronauts compared to the average person in our society.
Hence, there might also be a significant health risk for astronauts from those space missions.
While space exploration can be extremely helpful for a few big countries, other countries may be greatly harmed by it.
For instance, if a few big countries control space and extract resources, other countries will likely lose their competitiveness in the global market.
In turn, this can also lead to higher wealth and income inequality across the planet.
Space missions may also conflict with religious values.
In fact, many people who believe in god do not advocate space exploration at all since they feel that humans should stay on earth and should not explore outer space.
Consequently, space missions may also be problematic from a religious point of view.
There is also no guarantee that extraterrestrial life forms will be peaceful.
In fact, those life forms may have the potential power to wipe out humanity and therefore, exploring space may also not be a good idea in this regard.

Top 10 Space Exploration Pros & Cons – Summary List
Should we explore space.
We can conclude from the previous discussion that space travel has many important advantages and disadvantages.
In my opinion, it can make sense to explore space in order to secure the survival of the human species.
However, we should also make sure that we reduce the pollution levels related to space missions as best as possible in order to protect our environment in the long run.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_exploration
https://www.britannica.com/science/space-exploration
https://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/space-travel/index.html

About the author
My name is Andreas and my mission is to educate people of all ages about our environmental problems and how everyone can make a contribution to mitigate these issues.
As I went to university and got my Master’s degree in Economics, I did plenty of research in the field of Development Economics.
After finishing university, I traveled around the world. From this time on, I wanted to make a contribution to ensure a livable future for the next generations in every part of our beautiful planet.
Wanna make a contribution to save our environment? Share it!
Terms & Privacy Policy
Affiliate Disclosure
As an associate, I may earn commissions from qualifying purchases from Amazon or other programs.
Please note that all the information I provide on this website is to my best knowledge. However, I will not take any responsibility for incorrect information and will not be liable for any negative consequences that might occur due to the reliance on this information.
Pin It on Pinterest

Everything you need to know about space tourism
Posted: April 4, 2024 | Last updated: April 4, 2024

Between floating in weightlessness, witnessing 16 sunrises a day and gazing into the infinite void, space travel sure sounds like an out-of-this-world experience. And now, it’s no longer a thing of the future.
That’s right, soon interstellar awe will be open to (almost) anyone, as billionaires Richard Branson, Jeff Bezos, and Elon Musk are pushing the space tourism industry to a higher orbit.

What is space tourism?
Well, it’s almost like regular tourism: travel for recreational and leisure purposes… but in outer space. Some organizations like the Commercial Spaceflight Federation and the Citizens in Space project prefer to use the terms “personal spaceflight” or “citizen space exploration,” though.
In a nutshell, it’s space travel for non-astronauts.

Who can travel to space?
Anyone ! Well, that is, anyone with enough money. No need to have any previous science qualifications or NASA training, especially since a trained crew will escort tourists on their galactic journey.
According to Virgin Galactic, future space tourists will be between 10 and 90 years old, and come from diverse professional and cultural backgrounds.
The only thing you need? The desire to explore the universe!

What is orbital travel?
The main difference between orbital and suborbital flights lies in the trajectory and speed of the vessels.
To go into orbit, a rocket or spaceship needs to follow a path that goes around the Earth at the very fast minimum speed of 7.7 kilometres (4.8 miles) per second, in order to keep circling and never fall back down.
It allows astronauts and travellers to stay in space for extended periods of time, hence it is for now the preferred type of flight.
What is suborbital travel?
A suborbital flight , which is what Branson and Bezos did, “just” requires enough energy to blast off to space and then naturally fall back to Earth, making a huge arc.
It requires less energy and is less costly than orbital flights, thus opening doors for relatively affordable space tourism in the future.
Passengers would experience up to six minutes of weightlessness and a grandiose view.

How do you prepare?
Although Virgin Galactic doesn’t explicitly list its physical requirements, they did say astronauts would have to pass certain medical checkups and training programs. Blue Origin, on the other hand, has said that training for suborbital trips will only take a day.
And of course, any space tourist will also have to pass a series of thorough tests to determine whether they’re fit to fly up there.
Once in space, you may have to perform small bouts of exercise to prevent muscle wasting , which takes place after just seven days.

What is lunar tourism?
As its name hints, lunar tourism is the project of sending paying travellers to the moon. The first one could happen as soon as 2023, and would consist of a loop flight.
But three types of lunar tourism could be available in the near future: circumlunar trajectory, lunar orbit, and even lunar landing.
How cool would it be to say to someone, upon returning from a lunar vacation, “I’ve literally loved you to the moon and back”?

Where does space tourism take place?
Admittedly, space is a vast place. So where exactly would tourists go ?
First, any space travel begins with the Kármán line , which lies at 100 kilometres (62 miles) above sea level and is commonly accepted as the limit between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
Then, there are several options: orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism.

Have touristic space travels already occurred?
Yes! From 2001 to 2009, the Russian space agency and the U.S.-based space tourism company Space Adventures took seven (very wealthy) members of the public for several orbital space travels to the International Space Station.
The flights took place aboard the famous spacecraft Soyuz but stopped in 2010, since the crew of actual astronauts grew bigger and left no more seats available for paying space tourists.

Who were the first space tourists?
The American businessman Dennis Tito became officially the first space tourist in April 2001, when he stayed for seven days on the International Space Station.
He was followed by six multimillionaire fellows from various countries: South African entrepreneur Mark Shuttleworth, American scientist Gregory Olsen, Iranian engineer Anousheh Ansari (the first female space tourist), Hungarian-American computer programmer Charles Simonyi, British video game mogul Richard Garriott, and Canadian businessman Guy Laliberté.
On July 11, 2021, billionaire Richard Branson, along with three Virgin Galactic employees and two pilots, reached an altitude of 85 kilometres (53 miles) above Earth aboard his Virgin Galactic rocket plane, the Unity. Less than 10 days later, on July 20, the world’s richest man, Amazon’s Jeff Bezos, briefly entered space on Blue Origin , his private space company’s reusable rocket. He was joined by his younger brother Mark, Dutch teenager Oliver Daemen, and Wally Funk, who, at 82 years old, became the oldest astronaut.

Who would be the space tourism “agencies”?
Unlike past tourism experiments, which took place aboard vessels sent off for scientific purposes, future travels will happen on private companies’ flights set up solely for space tourism.
Those pioneering aerospace companies are Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic ; SpaceX, founded by Tesla co-founder Elon Musk ; and Blue Origin , created by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos.

When will space tourism happen?
Sooner than you think. According to Forbes , Virgin Galactic’s successful trip means the company could start sending civilians up into space as soon as early 2022. Likewise, Blue Origin, which has a Federal Aviation Administration licence for human space travel through August 2021, could officially enter the space tourism game by early 2022.

How much will it cost?
It’s not exactly clear at the moment, but there have been some indications. For example, Virgin Galactic began selling ticket reservations for US$250,000 and sold roughly 600, before a test crash in 2014 brought sales to a halt. They’re expected to start selling tickets again in 2022, but at a much higher price.
It was reported in 2018 that seats on Bezos’s Blue Origin would also cost in the ballpark of US$200,000 to US$300,000, but that could change given how high demand is. At a recent auction, the winning bid for a seat aboard the company’s first spaceflight was a whopping US$28 million .
The bottom line is, those hoping to take a trip around the stars will either need to know someone or have hundreds of thousands (likely even millions) of dollars to spare.
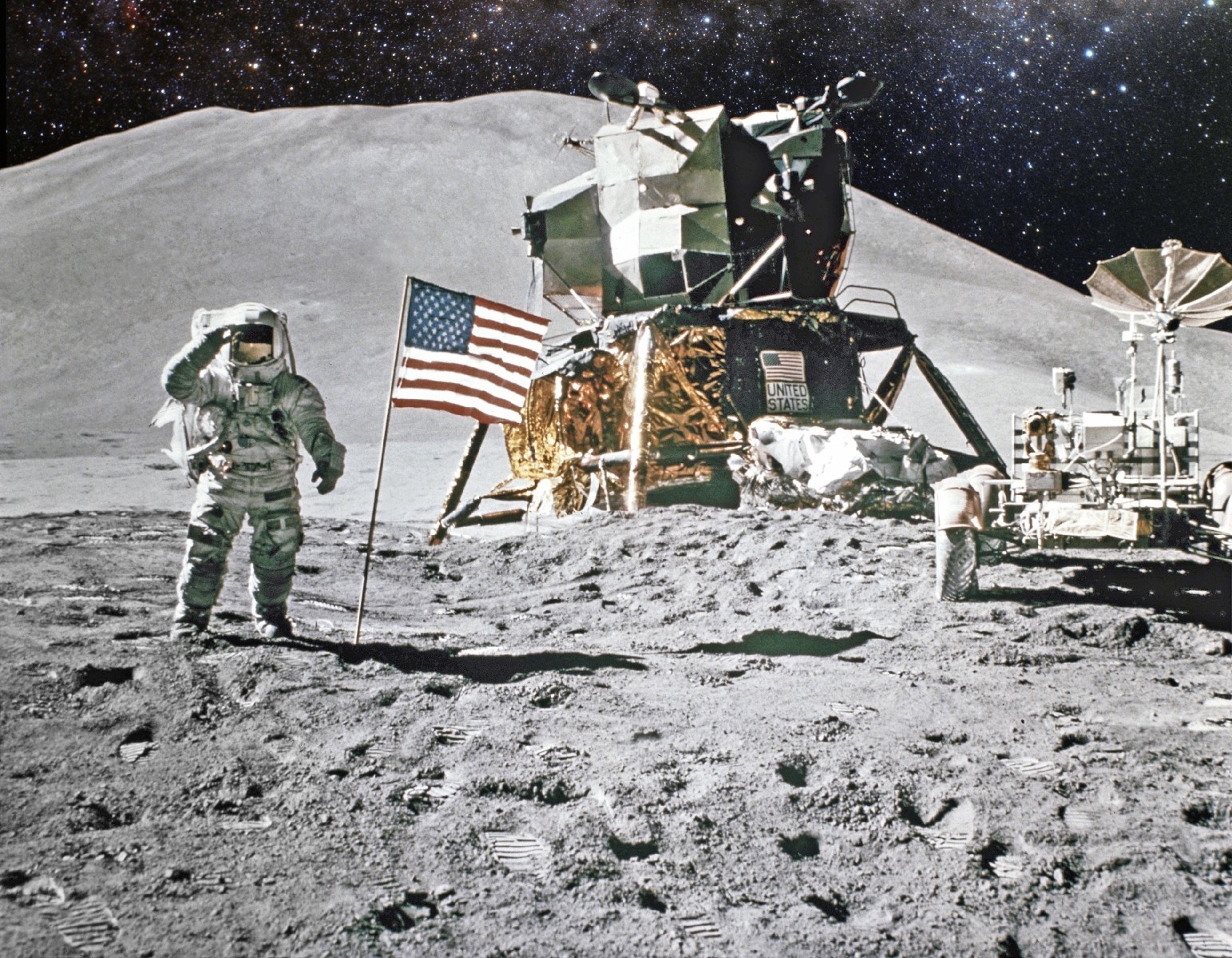

How do we get there?
The development of space tourism vehicles is still an ongoing project.
But a few options already exist, like Virgin Galactic’s spaceplanes that can carry up to eight people, or SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft , launched by the Falcon Heavy rocket.
Blue Origin’s New Shepard looks more like a regular rocket that takes off and lands vertically, but also claims to offer the biggest windows of any spacecraft—a good selling point. It comfortably sits six people and is fully autonomous, meaning no pilot onboard.

What does it feel like?
Needless to say, travelling to space is no walk in the park.
You’re eager to experience the joys of floating in microgravity? You better also get prepared to endure several physical discomforts: nausea and sea sickness, dizziness, headache, disorientation, puffy face, and bloodshot eyes.
But astronauts and previous space tourists agree that the body adjusts fairly quickly, getting used to its spatial environment in about three days.

Is it safe?
Safety is a reasonable concern , considering the many hazards involved in space travel: the probability of a crash, exposure to cosmic radiation, and even unknown dangers that could emerge with this new industry. But here is the real question for any adventurer: is the thrill worth the risk?

What is the food like?
For many tourists, food is a crucial criterion for a successful vacation. But outer space is no place for gourmets, at least not yet. Interstellar tourists can expect to enjoy mostly canned, modified, and pre-packaged meals (such as space burritos and freeze-dried ice cream). But soon, thanks to NASA’s veggie farm , space tourists might be able to savour space-grown salads.

What about the accommodations?
Orbital space travel allows you to stay up there for a few days or even weeks. At that point, you might want to stretch your legs outside of the spacecraft, right? Well, in the future, space stations could be used as hotels: the Genesis inflatable habitats by Bigelow Aerospace and the Space Island Project are existing examples. Make sure to book a room with a view of planet Earth!

How to pack a space suitcase?
Packing a suitcase for a trip through the cosmos is actually less of a headache than doing so for a weekend vacation on Earth. Just keep in mind that it’s impossible to do laundry in space, so pack clothes accordingly : stock up on underwear, light clothing (space station temperature is controlled at about 22 degrees Celsius, or 72 degrees Fahrenheit), and exercise outfits. Outerwear will be provided: an orange suit for takeoff and re-entry, and a white one for potential space strolls.
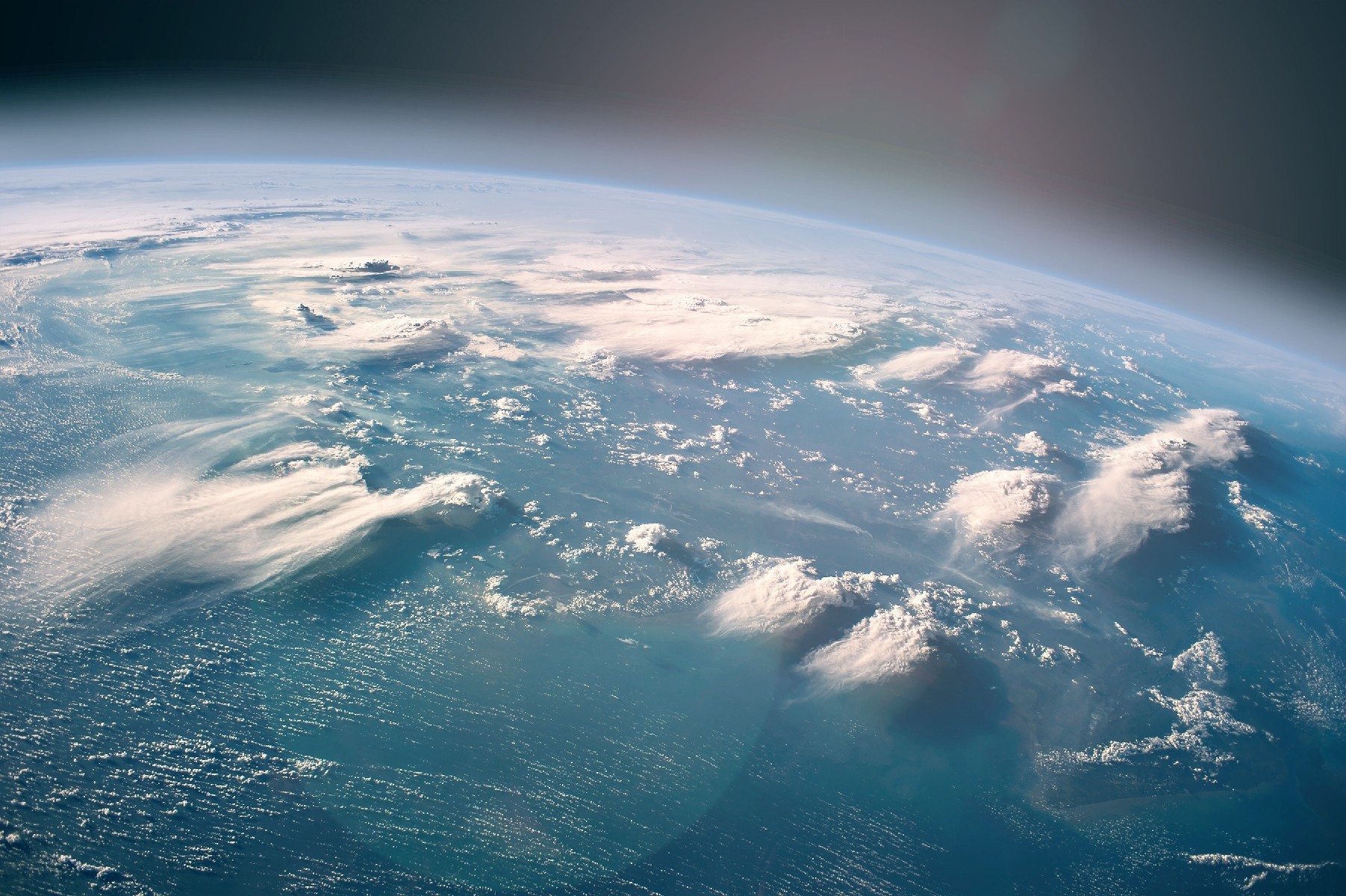

Is it eco-friendly?
With ecotourism being a growing trend and concern over the last few years, the question is legitimate. Well, bad news: space travel could have a negative impact by accelerating global warming . This would be caused by the black carbon released into the stratosphere after suborbital launches. But of course, entrepreneurs in the industry claim that the carbon footprint of space tourism would be minimal. The truth is, rockets emit 50 to 100 times more CO₂ per passenger than a regular flight. Considering that Virgin Galactic plans to do 400 trips per year, that’s a lot of CO₂ entering the atmosphere.
More for You
One of these pictures of me is real and the other is AI – but which is which?
Eleven States Hit With 50% Capital Gains Tax Under Biden's Plan
5 inflammatory foods to avoid if you have arthritis or are at risk of arthritis
Fox anchor pushes back on Mace’s claim of George Soros funding student protests
We Ordered 7 Fast-Food Breakfast Sandwiches to Find the Best One
Analyst makes bold claims about Russell Wilson's struggles with Broncos: 'All the play calls had to be two words'
This is one of the most advanced humanoid robots in the world
Pokemon and Krispy Kreme Collaborate on Exclusive Donut Release
3 reasons you keep waking up in the middle of the night
Eating one type of fruit regularly could reduce diabetes risk in women, study suggests: 'Incredibly healthy'
I became a millionaire at age 27—here are 4 'unpopular' rules rich people follow that most don't
30 food items that you might not know are banned in America
Meet one of the world's most advanced humanoids
McDonald's Says It's Creating Its Biggest Burger Yet

“A real smoking gun”: How Trump reacted as secret Cohen recording played in court
Here is the true value of having a fully paid-off home in America — especially when you're heading into retirement
How bad is alcohol for you really?
14 fascinating things most Americans don’t even know about the USA
Actor starred in a film about a nuclear accident days before a real-life accident
Best Online Computer Science Programs of 2024

- [ May 4, 2024 ] HOT OFF THE PRESS! Enjoy Space Coast Daily, Brevard County’s Best and Most Read Magazine Brevard Business News
- [ May 4, 2024 ] U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Confidence Celebrates 58 Years of Service During Ceremony At Port Canaveral Brevard News
- [ May 4, 2024 ] Former NASA Center Director Ellen Ochoa and Scientist Jane Rigby to Receive Presidential Medal of Freedom Brevard News
- [ May 4, 2024 ] WATCH: Platinum Coast Orchid Society 59th Annual Orchid Show Underway at Kiwanis Island Park on Merritt Island Brevard Business News
- [ May 4, 2024 ] Eastern Florida Titans Softball to Face Florida Southwestern State in South Atlantic District Tournament Brevard News
Home » Home » Why Neck Gaiters Should Be at the Top of Your Travel Packing List
Why Neck Gaiters Should Be at the Top of Your Travel Packing List
By Space Coast Daily // April 26, 2024

As travelers, we understand the importance of packing efficiently to ensure a smooth and enjoyable journey. While there are countless items that vie for space in our luggage, one accessory stands out for its versatility, convenience, and practicality: the neck gaiter.
In this article, we’ll explore why neck gaiters deserve a prime spot at the top of your travel packing list, covering everything from their multifunctional use to their lightweight design and durability.
The Versatility of Neck Gaiters
Protection from the elements.
Neck gaiters are a traveler’s best friend when it comes to facing unpredictable weather conditions. Whether you’re trekking through rugged terrain or strolling through city streets, a neck gaiter offers versatile protection against the sun’s rays, biting winds, swirling dust, and even chilly temperatures. 4inbandana offers a diverse selection of options to choose from. Explore their range of neck gaiters and find the perfect companion for your next adventure. Their seamless designs provide coverage for your neck, face, and head, ensuring you stay comfortable and protected in any environment.
Multifunctional Use
What sets neck gaiters apart from other travel accessories is their incredible versatility. Not only can they be worn as a neck warmer or face mask, but they also double up as a headband, beanie, scarf, or even a makeshift hair tie in a pinch. This multifunctional aspect eliminates the need to pack multiple items, saving precious space in your luggage and streamlining your travel gear. With a neck gaiter, you have a single accessory that adapts to a multitude of situations, making it an indispensable companion for any journey.
Lightweight and Compact Design
Space-saving advantage.
One of the most significant benefits of neck gaiters for travelers is their lightweight and compact design. Made from thin, breathable materials, they take up minimal space in your luggage, leaving more room for other essentials. Unlike bulky scarves or hats, neck gaiters can be rolled up or folded neatly to fit into the smallest compartments of your bag, making them an ideal choice for travelers who prioritize efficiency and organization.
Easy to Carry and Pack
Another advantage of neck gaiters is their portability. Whether you’re backpacking through Europe or embarking on a weekend getaway, you’ll appreciate the convenience of carrying a lightweight and packable accessory like a neck gaiter. Its small size allows you to slip it into your pocket or clip it onto your bag for easy access whenever you need it. Plus, since neck gaiters are wrinkle-resistant, you won’t have to worry about ironing or reshaping them after unpacking, saving you time and hassle on your travels.
Comfort and Breathability
Enhanced comfort.
Comfort is key when it comes to travel, and neck gaiters excel in this department. Made from soft, stretchy fabrics like microfiber or polyester, they provide a snug yet comfortable fit that stays in place throughout the day. Unlike traditional scarves or bandanas, which can be bulky and restrictive, neck gaiters offer a lightweight and seamless alternative that won’t weigh you down or cause discomfort, even during extended wear.
Breathable Fabric Technology
In addition to comfort, breathability is essential, especially in warm and humid climates. Neck gaiters are designed with moisture-wicking properties that help regulate your body temperature by wicking away sweat and moisture from your skin. This keeps you cool, dry, and comfortable, whether you’re hiking in the tropics or exploring a bustling city in the height of summer. Plus, since neck gaiters are quick-drying, you won’t have to wait long before they’re ready for your next adventure.
Durability and Longevity
High-quality construction.
When it comes to travel gear, durability is paramount. Neck gaiters are built to withstand the rigors of travel, thanks to their high-quality construction and resilient materials. Whether you’re hiking through rugged terrain or navigating crowded airports, a well-made neck gaiter will hold up to whatever adventures come your way, ensuring long-lasting performance trip after trip.
Easy Maintenance
Despite their rugged construction, neck gaiters are surprisingly easy to care for. Most can be machine washed and dried, making them a low-maintenance addition to your travel gear. To keep your neck gaiter in top condition, simply toss it in the laundry with your other travel clothes and let it air dry. With proper care, your neck gaiter will remain a reliable companion for countless journeys to come.
In conclusion, neck gaiters are a must-have accessory for travelers seeking comfort, versatility, and peace of mind on their journeys. From protecting you against the elements to streamlining your travel gear and keeping you comfortable in any environment, neck gaiters offer a myriad of benefits that make them worthy of a prime spot in your packing list. Whether you’re embarking on a weekend getaway or a globetrotting adventure, don’t leave home without a trusty neck gaiter by your side. With its lightweight design, multifunctional use, and durable construction, it’s sure to become your go-to travel companion for years to come.
Similar Stories
FEATURED STORIES

Click Here to Sign Up for Text Alerts
Or Signup Below For Email Alerts!
Ukraine-Russia war latest: Moscow rages over Cameron strike remarks, warns of 'direct escalation' and threatens Denmark
During a visit to Kyiv, Lord Cameron said Ukraine has a "right" to strike inside Russia, just as Moscow's forces are doing. Meanwhile, the fall of the eastern town of Chasiv Yar looms closer. Listen to a Daily podcast on whether the UK should send troops to Ukraine as you scroll.
Friday 3 May 2024 19:17, UK
- Cameron: Ukraine has 'right' to strike Russia using British-supplied weapons
- Fall of Ukrainian city a 'matter of time', Ukrainian intelligence officer says
- Russia's 'three-point plan' to victory
- Moscow rages over Cameron remarks
- Exclusive: UK plans to ramp up weapons production for Ukraine
- Analysis: Will US aid help turn tide on Russia?
- Your questions answered: Why can't Ukraine destroy key Crimean bridge?
- Listen to the Sky News Daily above and tap here to follow wherever you get your podcasts
- Live reporting by Lauren Russell
That's it from our live coverage for today - thanks for following along.
Before we go, here is a quick reminder of today's updates:
- Lord Cameron has been in Ukraine where he told Sky News that the UK will appoint a new envoy to oversee a plan to ramp up the production of weapons and ammunition, which is now a "national priority";
- Russia is planning to launch a three-factor plan to destabilise and claim victory in Ukraine, a top Ukrainian military intelligence officer has said;
- The Kremlin branded Lord Cameron's comments about Ukraine striking inside Russia "dangerous and worrying";
- Russian Defence Minister Sergei Shoigu has praised the "new regions" troops have taken control of in Ukraine since the start of the year.
Now to Georgia, which is not directly involved in the war in Ukraine, but whose future is seen as highly significant in the context of Vladimir Putin's ambitions for Russia.
Draft legislation, known as the "foreign agents" law, is winding its way through the Georgian parliament and would require organisations receiving more than 20% of their funding from abroad to register as agents of foreign influence.
The proposed law has been attacked by opponents as authoritarian and Kremlin-inspired.
Protesters have taken to the streets of capital Tbilisi for weeks to show their opposition, while the European Union and the United States have urged Georgiato drop the legislation or risk harming its chances of EU membership and a broader Euro-Atlantic future.
The stand-off is seen as part of a wider struggle that could determine whether Georgia, a country of 3.7 million people that has experienced war and revolution since the fall of the Soviet Union, moves closer to Europe or back under Moscow's influence.
Video below shows protesters in Tbilisi blocking traffic as part of their efforts to prevent the bill being passed.
A regular feature of news coverage surrounding the war in Ukraine has been the frequently bellicose statements that have emanated from one of Vladimir Putin's most prominent allies, Dmitry Medvedev.
The deputy chairman of the security council of the Russian Federation is notorious for his inflammatory language and repeated invocation of Cold War-style nuclear threats, which tend to be widely dismissed by most Western commentators.
Indeed, some analysts have suggested the former president's penchant for such wild outbursts are specifically designed to frame himself as an erratic character who could not be considered a viable rival to Mr Putin - thus avoiding the fate of other figures considered a threat to the leader's authority.
It is through that lens that many will view his latest comments, which ostensibly cover his thoughts on the Ukraine peace conference due to take place in Switzerland in June - to which Russia has not been invited.
His assessment is perhaps unsurprisingly dismissive, even going as far as to imply the summit represents positive news for Moscow.
"What is Russia's gain of the Swiss 'peace conference'?" he asks in his post on social media.
"It's actually threefold. First, it will come as yet another proof of failure of the so-called peace plan by the halfwit zelensky (sic)."
He follows that by referring to Ukraine's leader as "the bandera b******", seeking to associate him with a Ukrainian far-right leader of the mid 20th century.
The Kremlin has long sought to depict Ukraine's leadership as far-right neonazis, efforts that have been widely dismissed by commentators on the region.
"Second, it will be visible evidence of the full impotence of the present-day western elites, who have performed painful self-castration of their own potential to stop the military conflict," Mr Medvedev continues.
"What's more, it has been done on direct orders given by a group of senile doctors from Washington.
"Third, it will allow our Armed Forces to further cleanse Malorossia's [little Russia's] territories from neonazis without any hindrance and regard for some c***'s 'peace initiatives'."
After forecasting "the final collapse of the former Ukraine’s political regime", he concludes: "Thank you, the land of cheese and watches!"
Russian officers has been welcoming foreign military attaches in Moscow today during their visit to an exhibition of Western military equipment captured from Kyiv forces during the fighting in Ukraine.
The event organised by the Russian Defence Ministry features more than 30 pieces of Western-made heavy equipment, including a US-made M1 Abrams tank and a Bradley armoured fighting vehicle.
More now from Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova, who has been speaking to journalists this afternoon.
She has said any move by Denmark to restrict the freedom of navigation of Russian ships in the Baltic straits will be seen as a hostile act and draw retaliation.
It is unclear exactly what prompted the threat, but we'll bring you any more detail as we get it.
Denmark has played down suggestions it will begin checking Russian tankers moving through its waters to establish whether they have the correct documentation.
The country allows ships calling at Russia to use its waters due to a longstanding freedom of navigation treaty, although the country's armed forces have said it is standard procedure to track them.
The Baltic straits - the only natural exits from the Baltic sea to the North Atlantic - are notoriously difficult to navigate and international maritime authorities strongly recommend the use of pilots with specialist local knowledge.
However, it is believed more than 20 tankers - so-called shadow vessels - transporting Russian oil but with unknown ownership, have declined offers to use Danish pilots since the start of 2024.
And the Danish Maritime Authority said in a statement in March that a tanker from Russia's shadow fleet was involved in a collision near Denmark.
The incident involving the 15-year-old Andromeda Star oil tanker took place on 2 March.
A Russian activist has been sentenced to 15 years in prison for attempting to set fire to a military conscription office in protest against the war in Ukraine.
Angel Nikolayev, 39, was convicted on charges of terrorism for placing two bottles of a flammable substance in the windows of a conscription office in the eastern city of Khabarovsk and setting them alight.
He was also convicted of damaging Russian flags that were put on the graves of soldiers killed in Ukraine at a local cemetery and removing symbols of Russian military action from a bus stop and several vehicles.
Since 2022, hundreds of people have faced criminal charges in Russia over protests and remarks condemning the war in Ukraine, and thousands have been fined or briefly jailed.
Russia is ready to consider "serious" peace talk proposals to settle the conflict in Ukraine, Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova has said.
Speaking at a press briefing this afternoon, Ms Zakharova said the talks must be based on existing "realities" and Moscow's security concerns.
She said part of the proposal would include Ukraine pledging to remain militarily neutral in future.
Russia proposing the possibility of peace talks is nothing new.
Despite suggesting it is open for discussion, it always seems to blame Ukraine or the West for the breakdown of negotiations.
Russian Defence Minister Sergei Shoigu said troops have taken control of 211 square miles (547 square kilometres) of Ukrainian territory this year.
He referred to the territory as Russia's "new regions".
Mr Shoigu told a group of senior military commanders that Ukrainian forces were retreating along the frontline and that Russian troops were breaking a network of "Ukrainian strongholds".
"Over the past two weeks, the Russian armed forces have liberated the settlements of Novobakhmutivka, Semenivka and Berdychi in the Donetsk People's Republic," he said.
"The Ukrainian army units are trying to cling on to individual lines, but under our onslaught they are forced to abandon their positions and retreat."
Ukraine's top commander said last week that a number of troops had fallen back to new positions in villages on the eastern front.
The advances mean Russia now controls around 18% of Ukraine.
As reported here earlier, Moscow has had a predictably indignant reaction to Lord Cameron's statement's yesterday during his trip to Ukraine (see 10.34am post).
Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova has offered a further reflection of displeasure within Vladimir Putin's regime, claiming the British foreign secretary's comments amounted to an acknowledgement that the West was waging a war against Russia using "Ukrainian hands".
Lord Cameron said yesterday that Ukraine had a right to use weapons provided by London to strike targets inside Russia, and that it was up to Kyiv whether to do so.
"Cameron's words are further evidence of the hybrid war the West is waging against our country," Ms Zakharova said.
"Russia is responding to that and will continue to respond."
Russian's Vladimir Putin is planning to visit China later this month to meet President Xi Jinping, according to a report by Bloomberg News.
The visit is scheduled for 15-16 May, Bloomberg reported, citing a person familiar with the Kremlin's plans.
It comes after the White House said it remained "deeply concerned" that it was not seeing China make any changes amid accusations it is helping Russia's military with its war in Ukraine.
Next week, Mr Xi will visit Europe for the first time in five years.
Beginning in Paris, France, he will visit Hungary and Serbia, the latter of which is a close ally to Mr Putin.
China has always maintained that it remains an objective and just party over the war, adding that its trade relations are "above-board".
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA’s Commercial Partners Deliver Cargo, Crew for Station Science

Hi-C Rocket Experiment Achieves Never-Before-Seen Look at Solar Flares

NASA Is Helping Protect Tigers, Jaguars, and Elephants. Here’s How.
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Hubble Hunts Visible Light Sources of X-Rays

NASA Selects Students for Europa Clipper Intern Program

NASA Mission Strengthens 40-Year Friendship
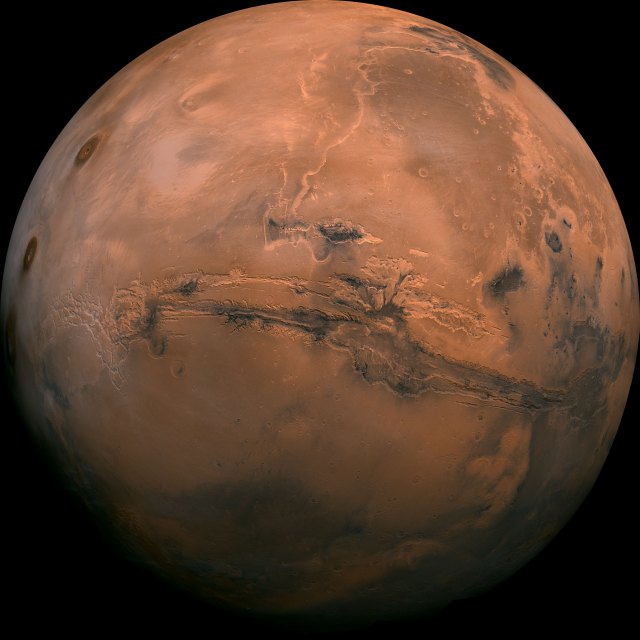

NASA Selects Commercial Service Studies to Enable Mars Robotic Science

Two Small NASA Satellites Will Measure Soil Moisture, Volcanic Gases

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers
Orbits and Kepler’s Laws
X-ray Satellite XMM-Newton Sees ‘Space Clover’ in a New Light
NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels

Researchers Develop ‘Founding Document’ on Synthetic Cell Development

ARMD Solicitations

NASA Uses Small Engine to Enhance Sustainable Jet Research

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

Big Science Drives Wallops’ Upgrades for NASA Suborbital Missions

Tech Today: Stay Safe with Battery Testing for Space

NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars

Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest

Asian-American and Native Hawaiian Pacific Islander Heritage Month

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Space travel.
The path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond requires technologies to get us where we need to go quickly, safely and efficiently. Space travel includes launch and in-space propulsion systems, cryogenic fluid management, and thermal management, as well as navigation and landing systems to get our supplies, equipment, and robotic or human explorers to diverse surface destinations.
Quick Facts
NASA’s Space Launch System is 17 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty and produced 15% more thrust than the Saturn V at liftoff.

The last nuclear thermal rocket engine tests conducted by the United States occurred more than 50 years ago. NASA and DARPA are partnering on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, program and together, we’ll develop and demonstrate advanced nuclear thermal propulsion technology as soon as 2027.

Mission and Impact
NASA seeks to improve our ability to access and travel through space; land more mass in more locations throughout the solar system; live and work in deep space and on planetary bodies; build next generation air vehicles, and transform the ability to observe the universe and answer profound questions in earth and space sciences.

Latest Space Travel News
NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’
NASA Announces Semifinalists of Power to Explore Challenge

NASA Artemis Mission Progresses with SpaceX Starship Test Flight

Peregrine Mission One
How Do Spacecraft Slow Down? We Asked a NASA Technologist
How do spacecraft slow down? Rigid heat shields and retropropulsion have been the favorites of engineers for years. Now NASA is testing a new inflatable heat shield technology that could allow us to carry even larger payloads to worlds with atmospheres.
NASA Technology

Explore Technology Areas
Space technology mission directorate.
Space Technology Mission Directorate. Technology drives exploration and the space economy.

@NASA_Technology

@NASATechnology

NASA Space Tech Channel

COMMENTS
It would also give us an opportunity to start building in space because the raw materials are easy to haul and transport. 10. It gives us an opportunity to see what lies beyond in the final frontier. Unless circumstances change somehow, there will come a point in time when our species will outgrow our planet.
Space exploration unites the world to inspire the next generation, make ground-breaking discoveries, and create new opportunities. Technologies and missions we develop for human spaceflight have thousands of applications on Earth, boosting the economy, creating new career paths, and advancing everyday technologies all around us.
The medical benefits of space exploration extend to pretty much every area of the human body. From muscle physiology to mental health. 6. Improving medical assistance in remote areas. One of the biggest challenges of space travel is solving problems when you can't send any new equipment, experts, or any other help.
When you become a member, you join our mission to increase discoveries in our solar system and beyond, elevate the search for life outside our planet, and decrease the risk of Earth being hit by an asteroid. Your role in space exploration starts now. $4 /month. $10 /month. $20 /month.
Space agencies, governments, researchers and commentators have isolated a large number of direct and indirect benefits of space exploration programs including: New technologies that can be utilized in other industries and society (such as the development of communications satellites) Improved knowledge of space and the origin of the universe.
We have now entered the decade of results. With more than 20 years of experiments now conducted on the station, more breakthroughs are materializing than ever before. Explore 15 of the ways the space station is benefiting humanity. 1. Producing the next generation of medical scanning technology. In their quest to study neutron stars, the team ...
Job creation. Another popularly cited benefit of space exploration is "job creation", or the fact that a space agency and its network of contractors, universities and other entities help ...
Why We Should Be Spending More on Space Travel. 6 minute read. NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Expedition 33 commander; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Aki Hoshide, flight ...
Benefits for Humanity. The International Space Station is an unprecedented achievement in global human endeavors to conceive, plan, build, operate, and utilize a research platform in space. With assembly of station at completion, continuity of visiting vehicles, and support of a full-time crew of six, the era of utilization for research advances.
ESA's exploration of the Solar System is focused on understanding the Earth's relationship with the other planets, essential stepping stones for exploring the wider Universe. While space may hold many wonders and explanations of how the universe was formed or how it works, it also holds dangers. The chance of a large asteroid or comet ...
Space exploration - Applications, Benefits, Technology: Space visionaries in the early 20th century recognized that putting satellites into orbit could furnish direct and tangible benefits to people on Earth. For example, Arthur C. Clarke in 1945 described a way in which three satellites in orbit about 35,800 km (22,250 miles) above the Equator could relay communications around the globe.
The space sector generates high-tech jobs for Canadians. Improving our day-to-day lives. Space technologies improve products we use every day, weather forecasts, and communications worldwide. Enhancing safety on Earth. Satellites data can be used to predict natural disasters and to support emergency relief efforts. Making scientific discoveries
space exploration, investigation, by means of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft, of the reaches of the universe beyond Earth 's atmosphere and the use of the information so gained to increase knowledge of the cosmos and benefit humanity. A complete list of all crewed spaceflights, with details on each mission's accomplishments and crew, is ...
More space travel means more challenges. But space agencies have proven themselves more than capable, developing knowledge and new technologies every step of the way. Past space exploration has given rise to a number of innovations that we take for granted today, including solar panels, implantable heart monitors, cancer therapy, and water ...
List of the Disadvantages of Space Exploration. 1. Our current technology makes it dangerous to get into space in the first place. Several agencies are developing "space tourism" packages that can take people in a comfortable aircraft to the very outer layers of our atmosphere, but that is not an exploration effort.
And by the time the last Apollo mission was flown ( Apollo 17, in 1972), the program had cost a pretty penny. According to the NASA authorization Hearings held by the Ninety-third Congress in 1974 ...
space needs and benefitted many sectors on Earth. 5. The first satellites, designed to study the space environment and test initial capabilities in Earth orbit, contributed critical knowledge for developing space telecommunications, global positioning, and advances in weather forecasting.
Orbital space travel reaches an altitude of 1.3 million feet (400 kilometers), for which a spacecraft would need to travel at 17,400 miles per hour (28,000 kilometers per hour). ... Another advantage of space tourism is the possibility of finding resources that are being depleted from our planet. If spacecraft take frequent trips to the moon or ...
It is fairly well known that space exploration has resulted in significant innovations, contributing to the creation of GPS, solar panels, implantable heart monitors, cancer therapy, water-purification systems, improved computing, and more (Benefits Stemming from Space Exploration, 2013, p. 1). Since 1976, NASA has recorded over 2,000 spinoff ...
SpaceX has changed the spaceflight landscape during its first 20 years of existence. SpaceX's Starship is stacked atop its Super Heavy for the first time in August 2021 during tests of the new ...
Space Exploration Cons. Space exploration can provide us with resources. Space exploration is expensive. Space travel can teach us about space. Space exploration is time-consuming. Humans are curious creatures. Space travel can be dangerous. Space travel provides endless opportunities.
The technology development path is a two-way street and sometimes what is created as a concept for human space exploration is applicable today on Earth. NASA works with dozens of space agencies and thousands of companies around the world to develop innovative technologies to advance human space travel. The technical leaps and bounds since the ...
First, any space travel begins with the Kármán line, which lies at 100 kilometres (62 miles) above sea level and is commonly accepted as the limit between Earth's atmosphere and outer space ...
Space-Saving Advantage. ... From protecting you against the elements to streamlining your travel gear and keeping you comfortable in any environment, neck gaiters offer a myriad of benefits that ...
During a visit to Kyiv, Lord Cameron said Ukraine has a "right" to strike inside Russia, just as Moscow's forces are doing. Meanwhile, the fall of the eastern town of Chasiv Yar looms closer.
Space Travel. The path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond requires technologies to get us where we need to go quickly, safely and efficiently. Space travel includes launch and in-space propulsion systems, cryogenic fluid management, and thermal management, as well as navigation and landing systems to get our supplies, equipment, and robotic or human ...