We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory October 19, 2023
Brazil - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with updates to Country Summary.
Exercise increased caution in Brazil due to crime . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to:
- Any areas within 150 km/100 miles of Brazil’s land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay due to crime . (Note: This does not apply to the Foz do Iguacu National Park or Pantanal National Park.)
- Informal housing developments (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or conglomerados) at any time of day due to crime (see additional information below).
- Brasilia’s administrative regions (commonly known as “satellite cities”) of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa during non-daylight hours due to crime (see additional information below).
Country Summary: Violent crime, such as murder, armed robbery, and carjacking, is common in urban areas, day and night. Gang activity and organized crime is widespread. Assaults, including with sedatives and drugs placed in drinks, are common. U.S. government personnel are discouraged from using municipal buses in all parts of Brazil due to an elevated risk of robbery and assault at any time of day, and especially at night.
If you decide to travel to Brazil:
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not accept food or drinks from strangers.
- Use caution when walking or driving at night.
- Avoid going to bars or nightclubs alone.
- Avoid walking on beaches after dark.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry.
- Be extra vigilant when visiting banks or ATMs.
- Use caution at, or going to, major transportation centers or on public transportation, especially at night. Passengers face an elevated risk of robbery or assault using public, municipal bus transportation throughout Brazil.
- Use increased caution when hiking in isolated areas.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Brazil.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
International Borders – Level 4: Do Not Travel
U.S. government personnel are not permitted to travel to areas within 150 km/100 miles of the international land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay without advance approval from security officials due to crime. Travel to the Foz do Iguacu National Park and Pantanal National Park is permitted.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Informal Housing Developments (commonly known as “Favelas”) – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Do not travel to informal housing developments (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or conglomerados), even on a guided tour. Neither the tour companies nor the police can guarantee your safety when entering these communities. Even in these communities that the police or local governments deem safe, the situation can change quickly and without notice. While some informal housing developments have clear boundaries or gates, or even names such as “favela”, “vila”, “comunidade”, or “conglomerado”, other such developments may be less obvious, and may be identified by crowded quarters, poorer conditions, and/or irregular construction. In addition, exercise caution in areas surrounding these communities, as occasionally, inter-gang fighting and confrontations with police move beyond the confines of these communities. Except under limited circumstances and with advance approval, U.S. government personnel are not permitted to enter any informal housing developments in Brazil. Read the Safety and Security Section on the country information page and consult the maps on the Embassy’s website for further information regarding favelas.
Visit our website for Travel High-Risk Areas .
Brasilia’s Administrative Regions (commonly known as “Satellite Cities”) – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Without advance approval from security officials, U.S. government personnel are not permitted to travel to Brasilia’s Administrative Regions of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa between the hours of 6:00 p.m. and 6:00 a.m. (non-daylight hours) due to crime.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must be valid on the date of entry
One page required for entry stamp
Yes, beginning April 10, 2025
None required, but see Health section
More than 10,000 BR must be declared to Customs
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Brasilia SES 801- Avenida das Nacoes, Lote 03 70403-900 - Brasilia, DF Brazil Telephone: 011-55-61-3312-7000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 011-55-61-3312-7400 Fax: (61) 3312-7651 Email: [email protected]
Embassy Branch Office in Belo Horizonte Avenida do Contorno, 4520 / 2nd floor – Funcionários 30110-028 Belo Horizonte, MG – Brazil Telephone: +55 (31) 3338-4000 E-mail: [email protected] Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Embassy in Brasilia
Consular Agency in Brasilia’s Consular District Manaus Consular Agency Edificio Atrium, Suite 306 Rua Franco de Sá, 310 69.079-210 Manaus, AM Brazil Telephone: 011-55-92-3611-3333 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Embassy in Brasilia
U.S. Consulate General Porto Alegre Avenida Assis Brasil, 1889 Passo d' Areia 91010-004 - Porto Alegre, RS Brazil Telephone: 011-55-51-3345-6000 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Recife Rua Goncalves Maia, 163, Boa Vista 50070-125 - Recife, PE Brazil Telephone: 011-55-81-3416-3050 or 011-55-81-3416-3080 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 011-55-81-3416-3060 or 011-55-81-9916-9470 Email: [email protected]
Consular Agency in Recife’s Consular District U.S. Consular Agency Fortaleza Avenida Santos Dumont 2828, Aldeota, Suite 708 60150-162- Fortaleza, CE Brazil Telephone: 011-55-85-3223-4902 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Consulate General in Recife
U.S. Consulate General Rio de Janeiro Avenida Presidente Wilson, 147, Castelo 20030-020, Rio de Janeiro, RJ Brazil Telephone: 011-55-213823-2000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 011-55-21-3823-2029 Email: [email protected]
Consular Agency in Rio de Janeiro’s Consular District U.S. Consular Agency Salvador da Bahia Avenida Tancredo Neves, 1632, Caminho das Arvores Salvador Trade Center-Torre Sul, Room 1401 41820-020 - Salvador, Bahia Brazil Telephone: 011-55-71-3113-2090/2091/2092 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Consulate General in Rio de Janeiro: (21) 3823-2029
U.S. Consulate General Sao Paulo Rua Henri Dunant, 500 Chacara Santo Antonio 04709-110 - Sao Paulo, SP Brazil Telephone: 011-55-11-3250-5000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 011-55-11-3250-5373 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
See the Department of State’s Fact Sheet on Brazil for information on U.S.-Brazil relations.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
There are no COVID-related entry requirements for U.S. citizens.
Effective midnight on April 10, 2025 , a visa will be required for U.S. citizens to travel to Brazil, regardless of the purpose of travel. For more information about visa requirements, visit the Brazilian government-authorized website, https://brazil.vfsevisa.com
You will need:
- A valid U.S. passport.
- A valid Brazilian visa or e-visa, beginning April 10, 2025 for tourists and currently for all other types of travel.
- Visit the Brazilian government-authorized website to obtain your e-visa: https://brazil.vfsevisa.com
Find a Brazilian consulate abroad .
Brazilian law requires any minor who is a Brazilian citizen (even dual nationals who are both U.S. and Brazilian citizens) to have permission from each parent to travel within Brazil or exit the country. When a minor travels with both parents, no written authorization is needed. When the minor travels with only one parent or without either parent, s/he must have two original written authorization letters from each absent parent and carry a copy* of the child’s birth certificate or have an annotation in his/her Brazilian passport authorizing travel alone or with only one parent. Brazilian citizen minors without authorization letters and a birth certificate* or an annotated Brazilian passport likely will not be allowed by authorities to pass through immigration or to board a flight departing Brazil.
The U.S. Embassy and its consulates cannot intervene in Brazilian immigration matters or request that this requirement be waived for U.S. citizen travelers.
Written Authorization Letter: If the absent parent is in Brazil, written authorization letters must be in Portuguese and notarized by a Brazilian notary. If the absent parent is in the United States or elsewhere outside of Brazil, the authorization must be done at the nearest Brazilian Embassy or Consulate using the form provided by that office. Again, please note that Brazilian law requires two original authorizations for each absent parent. This is important, because Federal Police may request and retain one authorization upon the minor’s entry into Brazil. Authorities may then request the second original document upon the minor’s departure. Authorizations written in English or executed before a U.S. (or any non-Brazilian) notary public are not accepted by the Brazilian Federal Police. Similarly, birth certificates issued outside of Brazil that are not apostilled * and translated by a certified translator may not be accepted.
Brazilian Passport Annotation: In lieu of carrying authorization letters, parents of dual U.S.-Brazilian citizen minors may instead request an annotation be placed in the minor’s Brazilian passport authorizing the minor to travel with only one parent, or to travel alone or with a third party. This annotation replaces the requirement for written authorization letters until the passport expires. Parents residing in Brazil should contact the Brazilian Federal Police for details on obtaining an annotated passport. Parents residing abroad should contact the nearest Brazilian Embassy or Consulate. The annotated Brazilian passport must not be expired and must be carried along with the minor’s U.S. passport at all times for Brazilian Federal Police to accept it in lieu of an authorization letter. There is no comparable annotation available in U.S. passports.
Children who are not dual citizens of Brazil: Please note that, while Brazilian law related to travel authorization does not explicitly apply to non-citizens of Brazil, Federal Police have, at times, delayed the travel of non-Brazilian minors who lack appropriate authorization from both parents. For this reason, we recommend that families of non-Brazilian minors who may travel through Brazil without one or both parents execute written authorizations (following the instructions in the preceding paragraph) in advance of travel and ensure that the minor, or the minor’s traveling companion, carries the original or notarized copy** of the minor’s birth certificate.
An exemplar of the form used by Brazilian authorities to document parental permission for minors to travel without one or both parents may be found here.
*There is a useful pamphlet published by the Hague Conference called “ The ABCs of Apostilles .” The Brazilian competent authority that issues apostilles is the Conselho Nacional de Justiça .
**If the birth certificate was issued in Brazil, copies must be notarized by a Brazilian notary. If issued outside of Brazil, copies must be apostilled and translated by a certified translator into Portuguese.
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Brazil.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Crime: The violent crime rate is high in most Brazilian urban centers. Public transportation, hotel sectors, and tourist areas report high crime rates, but these incidents can happen anywhere and at any time. Be aware of your surroundings.
- Informal housing developments in Brazil (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or satellite cities), even on a guided tour, at any time of day due to crime. Neither the tour companies nor the police can guarantee your safety when entering these areas. Even in favelas that the police or local governments deem safe, the situation can change quickly and without notice. In addition, exercise caution in areas surrounding favelas, as occasionally, inter-gang fighting and confrontations with police move beyond the confines of these communities.
- Brasilia’s administrative regions (commonly known as “satellite cities”) of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa during non-daylight hours due to crime.
- Any areas within 150 km of Brazil’s land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay due to crime. (Note: This does not apply to the Foz do Iguacu National Park or Pantanal National Park.)
- Consider avoiding the use of public, municipal buses in Brazil at any time of day, and especially at night. Crime trends indicate an elevated risk of robbery or assault on public bus systems throughout Brazil. The U.S. government recommends against personnel using public, municipal buses in all parts of Brazil.
- Avoid going to bars or nightclubs alone and avoid leaving with strangers.
- Before going on a date with someone you met on a dating app, tell a loved one who you are meeting, where you are going, and the details of the dating application account.
- Be wary about inviting individuals to your residence. If inviting a new acquaintance to your residence, speak to your door attendant in advance about your invited guest.
- Trust your instincts – if something does not feel right or if you suddenly feel ill, walk away from the situation.
- If you believe you may have been drugged, seek immediate medical attention. Some people can have life-threatening reactions to these drugs. After that, report the crime to local police and contact us at the numbers listed below.
- Traveling Outside Metropolitan Areas After Dark: Travelers are encouraged to organize their trips so that they can travel during daylight hours. Road conditions throughout Brazil can vary widely, and travelers must exercise caution due to debris in the road, horse-drawn carriages, unmarked speed bumps, and other infrastructure deficiencies.
- Armed hold-ups of pedestrians and motorists can happen, including at or near public beaches. Personal belongings, left unattended even for a moment, are often taken. If you are robbed, hand over your personal belongings without resisting. Resisting will increase your risk of injury.
- Carjackings and hold-ups can occur at any time of the day or night, especially at intersections and in tunnels. Some robberies involve individuals robbed at gunpoint and taken to make purchases or to withdraw as much money as possible from one or more ATMs.
- Crime on public transportation occurs. Registered taxis have red license plates and openly display company information and phone numbers.
- Credit card fraud and ATM scams are common in Brazil. Work closely with your financial institutions to monitor accounts and keep your credit card in view while it is scanned at a point of sale.
- Avoid using ATMs in unfamiliar, secluded, or lightly protected areas. Be aware that criminals often target ATMs and businesses in the early hours of the morning when there are fewer witnesses and law enforcement response times may be delayed. If you opt to use an ATM, select those that are located inside of secure facilities, such as an airport, hospital, bank, or government building.
- Avoid openly displaying your cell phone. When using a ride share service or taxi, wait for its arrival in a secure area.
- Avoid large groups or events where crowds have gathered. Public events of any nature, including concerts and sporting events, can unexpectedly turn violent.
- Travel to any areas within 150 km of the international borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay, except in limited circumstances with the appropriate U.S. Department of State approvals. Individuals with ties to illegal criminal networks operate along Brazilian borders. Travel to the Foz do Iguaçu National Park and Pantanal National Park is permitted.
- Enter any informal housing developments in Brazil (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or satellite cities), except in limited circumstances with the appropriate approvals.
- Enter Brasilia’s administrative regions (commonly known as “satellite cities”) of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa during non-daylight hours.
To reduce the chance of becoming the victim of a crime, in addition to the above recommendations, please review the below precautions:
- Limit the personal belongings you carry with you. Carry your money in your front pockets and limit the number of credit cards you carry. Make copies of all of your personal documents – including your credit cards, license, passport, etc. – and keep them in a safe place. This will be helpful if you lose your documents.
- Do not carry or wear valuable items that will attract the attention of thieves. If you need to wear expensive jewelry or carry a camera, conceal it until you arrive at your destination.
- Be aware of the street environment and avoid contact with those who may be looking for robbery targets. Seek a safer location. Go into a store, bank, or simply cross the street.
- Do not walk on beaches after dark. Assaults are common.
- Use increased caution when hiking in isolated areas, particularly near popular tourist locations in the city of Rio de Janeiro.
Demonstrations and strikes are common in urban areas, may occur unexpectedly, disrupt transportation, and may escalate into violence.
- Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and possibly become violent.
- Avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
- Check the website of the Embassy or Consulate nearest you for current information on demonstrations.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Victims of Crime:
U.S. citizen victims of crime should contact the local authorities to file a Brazilian police report before departing Brazil. In most instances, you can report crimes to the tourist or civil police. U.S. citizens should also inform the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate, but local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting the crime.
- Police number - 190
- the U.S. Embassy at 011-55-61-3312-7000
- the U.S. Consulate General in Porto Alegre at 011-55-51-3345-6000
- the U.S. Consulate General in Recife at 011-55-81-3416-3050 or 011-55-81-3416-3080
- the U.S. Consulate General in Rio de Janeiro at 011-55-21-3823-2000
- the U.S. Consulate General in Sao Paulo at 011-55-11-3250-5000
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Replace a lost or stolen passport
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Provide information on victims' compensation programs in the U.S .
- Provide a list of local lawyers who speak English
The local equivalent to the “911” emergency line in Brazil is divided among four services:
- 190 - Policia (Police)
- 191 - Policia Rodoviaria (on interstate roads)
- 192 - Ambulancia (Ambulance)
- 193 - Bombeiros (Fire Department)
Victims of Domestic Violence or Sexual Assault: Contact the nearest Embassy or Consulate for assistance after contacting local authorities.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities are inconsistent. Inquire with property management about the presence and functionality of safety equipment, such as fire alarms and carbon monoxide detectors. Hazardous areas/activities are normally identified with appropriate signage in major urban centers but may not be in other locations. Tourism industry staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate and timely medical treatment is consistently available only in or near major cities. First responders can face delays accessing areas outside of major cities to quickly provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy or Consulate immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Firearms: Brazil forbids importing, exporting, and possessing firearms without prior authorization of the Brazilian Government. U.S. citizens are subject to arrest and prosecution in Brazil for possession of unauthorized firearms or firearm components anywhere in the country, including airports. This prohibition extends to spent shell casings or ammunition, even if inside luggage during transit, regardless of whether those items were legally purchased in the United States or elsewhere.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Water Hazards: Many of Brazil’s beaches have very dangerous riptides, even if the water looks safe. Ocean currents and waves are unpredictable, even in popular beaches frequented by tourists. Shark attacks are reported in the waters of some beaches in northeastern Brazil, particularly near Recife. Always observe posted warnings and never swim while under the influence of alcohol. Follow local authorities’ guidance and refrain from swimming alone in areas marked with red warning signs or at beaches where there are no municipal lifeguards or first responder services.
Electricity Blackouts: Power failures in large urban centers are common and sometimes followed by increased crime. Most tourist hotels are equipped with generators, minimizing the impact of a blackout, but you should remain cautious.
Natural Disasters: Flooding and mudslides occur throughout the country and can be fatal. Monitor news and weather reports and adhere to municipal advisories before traveling to areas prone to flooding or landslides. Many of Brazil’s larger cities have frequent heavy rainstorms that cause flash flooding and can disrupt traffic.
Customs Restrictions : Contact the Brazilian Embassy in Washington, D.C. or one of Brazil's consulates in the United States for specific information regarding import and export regulations. Please also refer to our information on customs regulations .
- Brazilian customs authorities may enforce strict regulations concerning temporarily importing or exporting items such as firearms, antiquities, mineral samples, tropical plants, wildlife, medications, and business and communication equipment.
- In the Amazon region, there is special scrutiny of exporting biological material. People raising, growing, or exporting biological materials without permits can be charged with “biopiracy.”
Faith-Based Travelers: See our following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: Brazil does not have legal restrictions on same-sex marriage, relations, or events coordinated by LGBTI organizations. However, according to the 2019 Human Rights Report, violence against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and intersex (LGBTI) individuals was a serious concern, with local NGOs reporting 297 LGBTI persons were victims of hate killings. See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance: Brazilian law prohibits discrimination against persons with physical and mental disabilities in employment, education, and access to health care. However, accessibility to public transportation and the ability to accommodate the needs of physically disabled persons are limited in most areas.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
COVID-19 Testing: Brazil is a very large, diverse country with varying medical resources, both private and public, throughout the country. Many private labs perform COVID-19 testing at various prices, typically between $20 and $100. PCR, serology-based antibody tests, and antigen tests are available. Turn-around time varies widely depending upon location. Please verify turn-around time with your chosen lab before taking the test. Express results within 2-4 hours are available in many locations at an increased fee, including in the Guarulhos International Airport in São Paulo and Galeão International Airport in Rio de Janeiro. Testing is available in the private sector without a doctor’s prescription, but a prescription may be required for insurance payment.
In the public healthcare system, each Brazilian state has its own COVID-19 testing plan. We recommend that you contact local/state authorities for more information. Typically, a COVID-19 test is ordered by an emergency room physician and then sent to a public lab. Turnaround time is much slower and can take up to seven days, but tests are generally free. Information on testing sites and procedures is available through the official app of the Ministry of Health.
COVID-19 Vaccines: The COVID-19 vaccine is available for U.S. citizens to receive in Brazil once they register with the public Unified Health System (SUS) . According to the Ministry of Health, available vaccines include AstraZeneca/Oxford (Fiocruz), CoronaVac (Butantan), Janssen (Johnson & Johnson), and Pfizer (BioNTech). For more information on local availability of COVID-19 vaccines, please see the Brazilian Ministry of Health’s website and also contact local health authorities .
For emergency services in Brazil, dial 192.
Ambulance services are not present throughout the country or are unreliable in most areas except in state capitals and other large cities.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on overseas insurance coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
If traveling with prescription medication, check with the Government of Brazil to ensure the medication is legal in Brazil. Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Though the yellow fever vaccine is not required to enter Brazil, travelers wishing to be vaccinated should consider receiving it prior to travel, as local supplies are limited. Please note that the yellow fever vaccine should be administered ten days prior to travel for it to be effective.
Also note that, while yellow fever vaccine is not required to enter Brazil, some neighboring countries (French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Bolivia, and Paraguay) do require travelers with recent entries in Brazil to show proof of yellow fever vaccination.
All travelers to the country are advised to carry documentation, such as a vaccination card, that they have been appropriately vaccinated for yellow fever.
The following diseases are prevalent in Brazil:
- Chikungunya
- Leishmaniasis
- Travelers' diarrhea
- Tuberculosis
- Schistosomiasis
In recent years, outbreaks of these diseases have also been detected in certain areas of Brazil:
- Yellow fever
Elective Surgery : Although Brazil has many elective/cosmetic surgery facilities that are on par with those found in the United States, the quality of care varies widely. If you plan to undergo surgery in Brazil, make sure that emergency medical facilities are available and professionals are accredited and qualified. Some “boutique” plastic surgery operations offer luxurious facilities but are not hospitals and are unable to handle emergencies.
Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for information on Medical Tourism, the risks of medical tourism, and what you can do to prepare before traveling to Brazil.
Non-traditional Medicine: Several U.S. citizens have died while seeking medical care from non-traditional “healers” and practitioners in Brazil. Ensure you have access to licensed emergency medical facilities if seeking such services.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Travel and Transportation
Public Transportation: Consider avoiding the use of public, municipal buses in Brazil at any time of day, and especially at night. Crime trends indicate an elevated risk of robbery or assault on public bus systems throughout Brazil. The U.S. government recommends against personnel using public, municipal buses in all parts of Brazil.
Public buses are one of the main modes of inter-city road travel. Buses can range (depending on route and price) from luxurious and well-maintained to basic and mechanically unsound. Bus hijacking can occur at random.
Road Conditions and Safety: Driving on Brazil's roads poses significant risks. Poor driving skills, bad roads, and high-density traffic make road travel more hazardous than in the United States. Road maintenance is inadequate in many areas and some long-distance roads through the Amazon forest are impassable much of the year due to flooding.
Apart from toll roads, which generally have their own services, roadside assistance is available only sporadically and informally through local mechanics. The fastest way to summon assistance in an emergency anywhere in the country is to dial 193, a universal number staffed by local fire departments. This service is in Portuguese only.
Traffic Laws: Travelers planning on staying for more than 180 days should obtain an Inter-American Driving Permit to carry with their valid U.S. license if they plan to drive in Brazil. Such permits can be obtained through AAA or other sources. Please note:
- Everyone in the vehicle must wear a seatbelt. Brazilian federal law requires child seats for all children under the age of 7 ½. From age 7 ½ years to 10, children must only ride in the back seat.
- Drivers must yield the right of way to cars on their right. Compliance with stop signs is rarely enforced, so many motorists treat them as yield signs. It is common for drivers to turn or cross one or more lanes of traffic without warning.
- Drivers often flash their lights or wave their hand out the window to signal other drivers to slow down.
- Pedestrian crossings are only observed in some places, such as Brasilia.
- Drivers must have their daytime running lights on during the day and headlights on at night on Federal Highways.
- Under Brazil’s Lei Seca (“Dry Law”), you cannot operate a vehicle with any measurable blood-alcohol level. Checkpoints are often set up in urban areas, and randomly chosen drivers are required to perform a breathalyzer test. Those in violation are subject to legal penalties and having their vehicle impounded.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of Brazil’s national tourist office and national authority responsible for road safety .
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Brazil’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Brazil’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Brazil should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Brazil was cited in the State Department’s 2022 Annual Report to Congress on International Child Abduction for demonstrating a pattern of non-compliance with respect to international parental child abduction. Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Brazil . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Brazil Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Brazil
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to brazil, find stays in brazil, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Brazil from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
Can I travel to Brazil if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Brazil without restrictions.
Can I travel to Brazil without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Brazil without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Brazil?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Brazil.
Can I travel to Brazil without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Brazil?
Mask usage in Brazil is not required in public spaces.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Brazil?
Restaurants in Brazil are open. Bars in Brazil are .
- Human rights
- International
Ex. Saúde, Presidente, Governo
- TVBrasilPlay
- Carta de Serviços
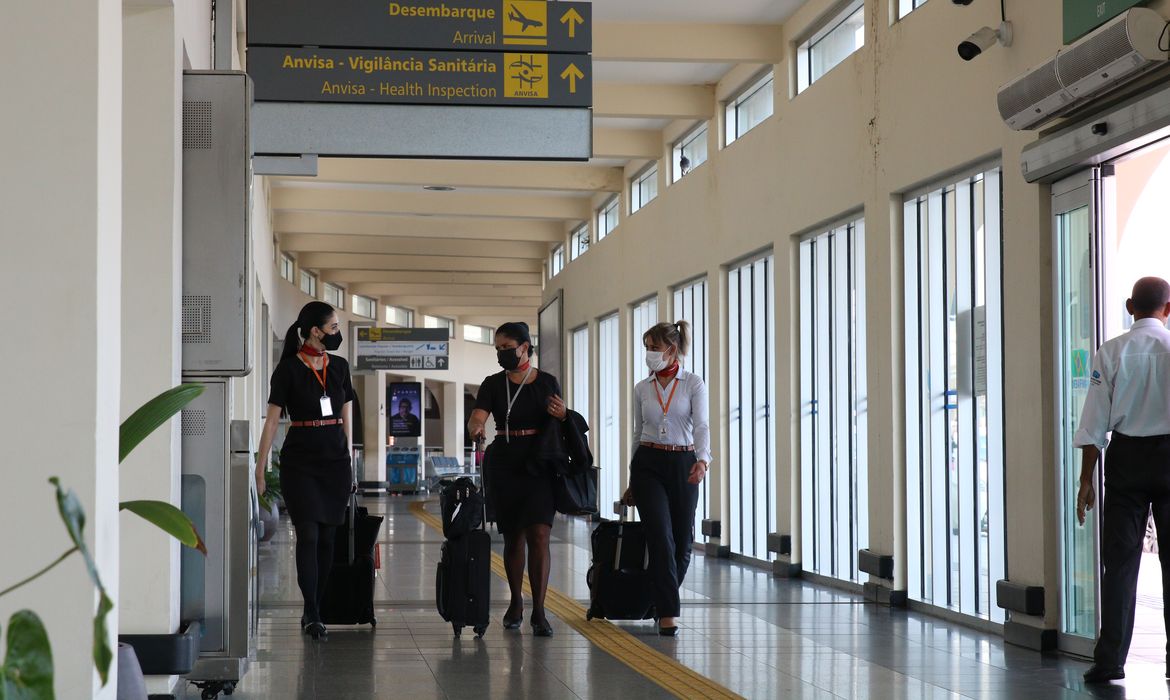

COVID-19: Brazil simplifies measures for entry of travelers
Proof of vaccination or a negative rest result may now suffice.
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Linkedin
Published on 13/09/2022 - 15:07 By Pedro Peduzzi - Brasília
Click to listen:.

Per national sanitary body Anvisa, travelers are now only required to meet some of the requirements for entry into the national territory.
For instance, visitors may choose to only procure proof of vaccination or a test with a negative result, when arriving in Brazil.
The new rules are already in force and must be observed by travelers and operators in air, waterway, and land transportation.
Anvisa adds that the recommendation is reiterated by the World Health Organization (WHO), which stresses that the “policies for testing and quarantine should be reviewed regularly” to ensure they are lifted when no longer necessary.
Despite the move, Anvisa reinforces the alert from the WHO on the need for alternatives for unvaccinated people, such as a COVID-19 test.
Translation: Fabrício Ferreira - Edition: Nádia Franco
Destaques EBC
Conteúdos extras dos outros veículos de comunicação da EBC para lhe informar mais
PEC do Quinquênio deve ser analisada no plenário do Senado nesta terça
Domingo do bom pastor, brasília 64 anos: trigo vira cultura emergente no setor agrícola do df.

Civilians killed per officer murdered more than doubled from 2020
Brazil has a higher rate of civilians killed by on-duty police officers than countries such as Colombia, El Salvador, and Venezuela. For this indicator, Brazil is surpassed only by Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago.

Lula homologates indigenous lands in Bahia, Mato Grosso
The original right of traditional indigenous occupation is provided for in the 1988 Federal Constitution, which guarantees permanent possession for these peoples.

Brasília to have direct flight to Bogotá as of October
The new flights should link travelers from Colombia to over 30 Brazilian cities, while passengers boarding in Brasília will get access to another 30 destinations from Bogotá.

Indigenous peoples demand priority in protection
Brazil is home to about 1.7 million self-declared indigenous individuals belonging to 305 ethnic groups. This population accounts for 0.83% of the total population.

Eliane Potiguara: "I believe in the changing power of education"
Potiguara is an advocate for high-quality public education that embraces Brazil's ethnic and cultural diversity, rooted in the indigenous self-affirmation movement.

Finance Minister Haddad expects G20 deal by Nov. to tax super‑rich
On a trip to the US, the minister said that President Joe Biden’s government backs the measure, proposed by Brazil. The world could be on the brink of a debt crisis, he added.

Author Daniel Munduruku: Non‑indigenous vision of future is alienating
“Looking to the future alienates people from the more immediate need to build our existence in the present. It’s a vision that educates people to selfishness,” he said in an interview to Agência Brasil .

Justice Moraes authorizes depositions of X representatives in Brazil
This action follows a request from the Attorney General's Office, which has initiated an investigation into the conduct of Elon Musk, the owner of the social network.

Brazil announces agrarian plan to settle 295,000 families by 2026
As per the government's plan, 73,200 families will be settled this year, followed by 81,000 next year and 90,500 in 2026, the final year of the current administration.

Brazil has lost 34 mi of the 82.6 mi hectares of caatinga
The president of the national environmental authority Ibama, Rodrigo Agostinho, spoke during a scientific seminar on the biome, attended by Minister for the Environment and Climate Change Marina Silva.
Brazil judge mandates proof of vaccination for foreign visitors
Supreme Court justice rules all travellers arriving in Brazil must present proof of vaccination to enter the country.

A Supreme Court justice in Brazil has ruled that all travellers arriving in the country must show proof of vaccination against COVID-19.
The decision from Luis Roberto Barroso on Saturday challenges a more lenient rule announced by the government of President Jair Bolsonaro, who has opposed mandatory immunisation against the virus that can cause COVID-19.
Keep reading
Brazil orders probe into bolsonaro linking covid vaccine and aids, brazilian football icon pele hospitalised again for colon tumor, brazil court convicts four for nightclub blaze that killed 242.
Barroso’s ruling must be reviewed by all 11 judges of the Supreme Court next week.
The federal government announced on Tuesday that travellers arriving in Brazil did not have to produce a vaccine passport, though they would have to undergo a five-day quarantine.
The government later delayed the regulation for a week, due to a hacker attack on the Health Ministry on Friday.
In ruling on a petition filed by the Sustainability Network party, Barroso said monitoring the quarantine of thousands of travellers would be too difficult and would put Brazilians at risk.
“The threat of promoting anti-vaccine tourism, due to the imprecision of the regulations that require the voucher, represents an imminent risk,” Barroso said in the ruling.
The justice said the requirement for proof of vaccination could be waived only when the traveller comes from a country where no vaccines are available or the individual was prevented from vaccination due to health reasons.
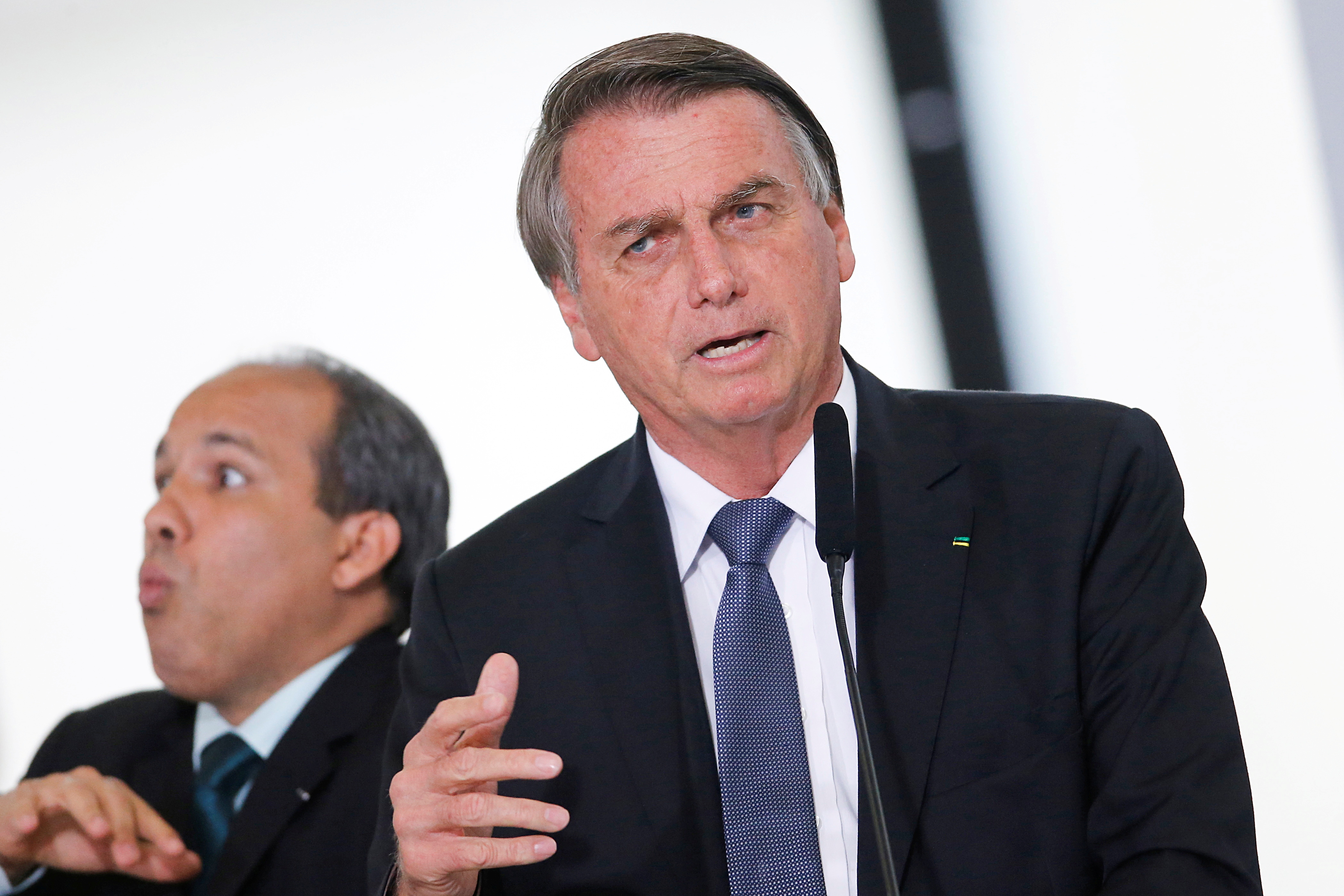
Brazil’s president has argued that those backing the use of vaccine passports want to restrict the freedoms of the population.

“Where is our freedom? I’d rather die than lose my freedom,” Bolsonaro said on Tuesday.
More than 616,000 people have died of COVID-19 in Brazil, the country with the second most deaths from the disease.
The pandemic has waned in recent months and the nation’s seven-day average is approaching 200 deaths a day. But many of Brazil’s major cities, including Rio de Janeiro, have either cancelled or scaled back their New Year’s Eve festivities due to fears of a new outbreak of the virus.
Bolsonaro dismisses vaccination requirement for entry into Brazil
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Lisandra Paraguassu Writing by Anthony Boadle; Editing by Bill Berkrot and Sandra Maler
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

US VP Harris hosts Kim Kardashian to discuss criminal justice reform
U.S. Vice President Kamala Harris hosted reality-television star Kim Kardashian at the White House on Thursday to discuss criminal justice reform, after the Biden administration granted clemency to people convicted of nonviolent drug offenses.

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 10 - Tanzania & Zanzibar
- Section 10 - Cusco & Machu Picchu
CDC Yellow Book 2024
Author(s): Alexandre Macedo de Oliveira
Destination Overview
Infectious disease risks, environmental hazards & risks, safety & security, availability & quality of medical care.
At nearly 3.3 million square miles in size, Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world and the largest country in South America, occupying nearly half the land area of the continent. With >210 million people, Brazil is home to the world’s largest Portuguese-speaking population. The world’s eighth largest economy, Brazil is classified as an upper-middle-income country. Nearly 85% of Brazilians live in urban areas.
Brazil is the most popular tourist destination in South America, and the second most popular in all Latin America. In 2018, >6 million international visitors traveled to Brazil; the country hosted the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) World Cup in 2014 and the Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games in 2016. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil’s second-largest city (population >7 million) and most frequently visited tourist destination, is famous for its beaches, landmarks, and annual Carnival festivities. São Paulo, one of the world’s largest cities with >21 million people in the greater metropolitan area, is the economic center of Brazil and the most visited destination for business travel. Brazilian people prize many of their major cities, including Florianópolis, Fortaleza, Manaus, Recife, and Salvador, for their coastlines and regional culture.
The country also boasts multiple UNESCO World Heritage sites, including Iguaçu National Park in Paraná, home to the largest waterfalls in the Americas; the historic towns of Olinda (Pernambuco), Ouro Preto (Minas Gerais), Salvador (Bahia), and São Luis (Maranhão); the modern capital of Brasília; and natural areas of the Amazon Forest and the Pantanal Conservation Area, which extends from one state (Mato Grosso do Sul) into another (Mato Grosso) and into portions of two countries (Bolivia and Paraguay). The Atlantic forests and the archipelago of Fernando de Noronha in the Atlantic Ocean are World Heritage sites (see Map 10-06 ).
The Amazon Forest, large portions of which extend into the countries that neighbor Brazil, attracts travelers in search of exotic adventures. The region presents unique risks, and careful planning and attention to travelers’ health needs before, during, and after the trip is critical. Because mosquito-borne diseases (chikungunya, dengue, malaria, yellow fever, and Zika) are endemic throughout the Amazon, advise travelers to complete all relevant vaccinations and provide them with detailed instruction on the proper use of chemoprophylaxis and mosquito avoidance. The hot and humid climate throughout the forest increases the risks for dehydration and heat stroke; travelers should practice extreme caution and, whenever possible, resist the temptation to consume potentially unsafe food and beverages.
Map 10-06 Brazil
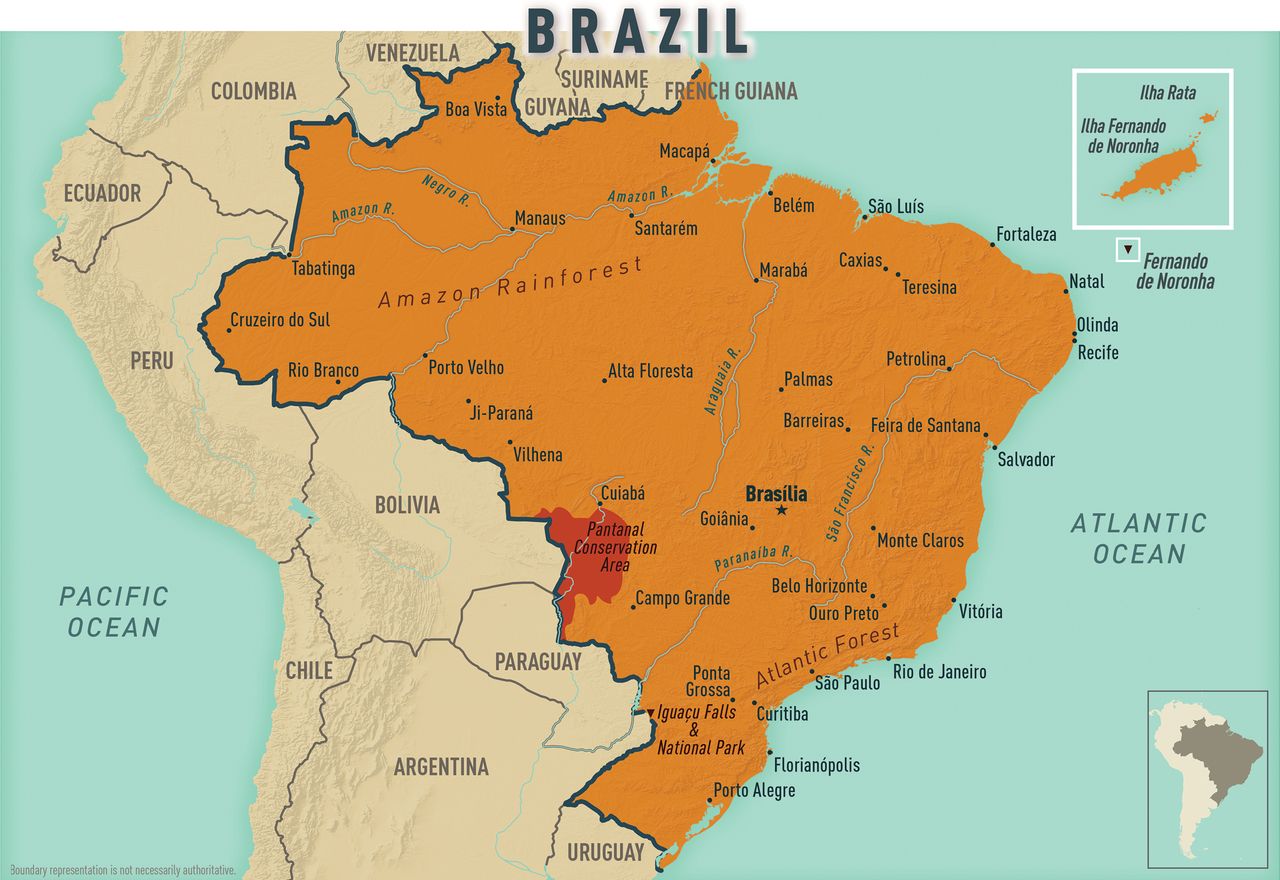
View Larger
Travelers to Brazil should be up to date on routine vaccines, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), influenza, measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), and diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis. Hepatitis A vaccination also is recommended. Consider hepatitis B vaccination for most travelers, but especially for anyone who could be exposed to blood or other body fluids (e.g., through medical services, sexual contact, tattooing).
Enteric Infections & Diseases
Travelers’ diarrhea.
Travelers should take food and water precautions throughout Brazil, including in the big cities (see Sec. 2, Ch. 8, Food & Water Precautions ). Travelers’ diarrhea (TD) is the most common travel-related ailment, and visitors consuming raw fruits and vegetables, unpasteurized dairy products, and food from street vendors increase their risk for foodborne infections. Oral rehydration salts are available from public health clinics and in almost all pharmacies in Brazil. For further information about travelers’ diarrhea, see Sec. 2, Ch. 6, Travelers’ Diarrhea .

Typhoid Fever
Consider vaccinating “adventurous eaters” against typhoid, along with travelers who stay with friends or relatives or who visit smaller cities, villages, or rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 24, Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever ).
Respiratory Infections & Diseases
Coronavirus disease 2019.
All travelers going to Brazil should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
Endemic Fungi
A variety of fungi (e.g., Paracoccidioides in the south and southeast) are endemic to Brazil. Inhaling the spores of fungi typically present in the soil (e.g., Coccidioides , Cryptococcus neoformans , Histoplasma , P aracoccidioides ) can cause respiratory illness and occasionally more severe disease (e.g., meningitis, bone infections). For more details, see Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 1, Coccidioidomycosis / Valley Fever , and Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 2, Histoplasmosis . Travelers should beware of bat guano in caves and use caution before disturbing soil, particularly if contaminated by bat or bird feces.
Peak influenza circulation occurs during April–September in most of Brazil but can occur throughout the year in tropical areas. The influenza vaccine recommended for use in the Northern Hemisphere each year confers protection against the virus strains circulating in the Southern Hemisphere that same year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends seasonal influenza vaccination ≥2 weeks before travel, and pneumococcal vaccination for people ≥65 years of age, and for younger adults and children with chronic medical conditions.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is prevalent in Brazil, but short-term travelers are not considered to be at high risk for infection unless visiting specific crowded environments. Before they leave the United States, consider TB testing for travelers who anticipate prolonged exposure to people known to have, or at high risk for having, TB (e.g., people in clinics, hospitals, prisons, homeless shelters). For more detailed information, see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 22, Tuberculosis , and Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 23, . . . perspectives: Testing Travelers for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.
Sexually Transmitted Infections & HIV
The HIV infection rate in Brazil is 0.5% among adults aged 15–49 years, comparable to other countries in South America. Discuss options for preexposure prophylaxis with travelers at greater risk for acquiring HIV infection (see www.cdc.gov/hiv/prep, and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 11, Human Immunodeficiency Virus / HIV ). In Brazil, people who use drugs, men who have sex with men, and female sex workers are more likely than the general population to be infected with HIV.
In Brazil, condoms are available free of charge in public health clinics, tourist service centers, and other distribution points in many cities. Male condoms are also available throughout Brazil in pharmacies, convenience stores, and supermarkets; female condoms are available in some locations.
Soil- & Waterborne Infections
Leptospirosis.
In urban areas of Brazil, outbreaks of leptospirosis have occurred after heavy flooding (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 10, Leptospirosis ). Travelers who have contact with standing water or mud after heavy rainfall are at increased risk. Advise travelers to avoid entering bodies of freshwater potentially contaminated with animals’ body fluids.
Schistosomiasis
Schistosoma spp. are parasites found in freshwater lakes and rivers in many states of Brazil, especially in the northeast. Advise travelers to avoid bathing, swimming, or wading in fresh, unchlorinated water, where they could contract schistosomiasis (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 20, Schistosomiasis ). Bathing or swimming in saltwater is not a source of infection.
Vectorborne Diseases
Vectorborne diseases (bacterial, viral, parasitic) are present in many areas of Brazil; these infections are among the leading causes of febrile illness in travelers returning from South America.
Chikungunya & Dengue
Risk for chikungunya and dengue infection is increased in many large Brazilian cities due to large populations of Aedes mosquitoes, which transmit these viruses (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 2, Chikungunya , and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 4, Dengue ). During 2000–2015, cases of dengue surged throughout Brazil, with epidemics reported in large cities, including Rio de Janeiro and Salvador. Preliminary data show that in 2019, Brazil recorded ≈132,000 cases of chikungunya and ≈1.5 million probable cases of dengue. Travelers to Brazil should take measures to protect themselves from mosquito bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis occur in Brazil and are most common in the Amazon and northeast regions (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 14, Cutaneous Leishmaniasis , and Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 15, Visceral Leishmaniasis ). The risk for transmission is greatest from dusk to dawn because the sand fly vector typically feeds (bites) at night and during twilight hours. Ecotourists and adventure travelers might be at increased risk, but even short-term travelers in endemic areas have developed leishmaniasis. Travelers should take measures to avoid insect bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Lymphatic Filariasis
Brazil is actively participating in the global program to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (LF); LF is considered endemic to only 4 cities in Brazil, all located in the Recife Metropolitan Region (northeastern coast) of the country. As of 2020, all regions had achieved the targets set by the World Health Organization (WHO) to stop annual treatment, suggesting low likelihood of ongoing disease transmission and minimal risk to travelers. Brazil is still working to achieve all targets demonstrating elimination of LF as a public health problem (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 9, Lymphatic Filariasis , and the WHO website .
Almost all malaria in Brazil occurs in the Amazon Basin, although less competent malaria vector species are present in other parts of the country. Plasmodium vivax is the main malaria species; only ≈10%–20% of malaria cases are caused by P. falciparum . CDC recommends chemoprophylaxis for travelers going to malaria-endemic areas of Brazil (see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country ; Map 2-04 ; and the CDC Malaria webpage. No malaria transmission occurs in the cities of Brasília (the capital), Rio de Janeiro, or São Paolo, or at Iguaçu Falls.
Map 2-04 Malaria prevention in Brazil
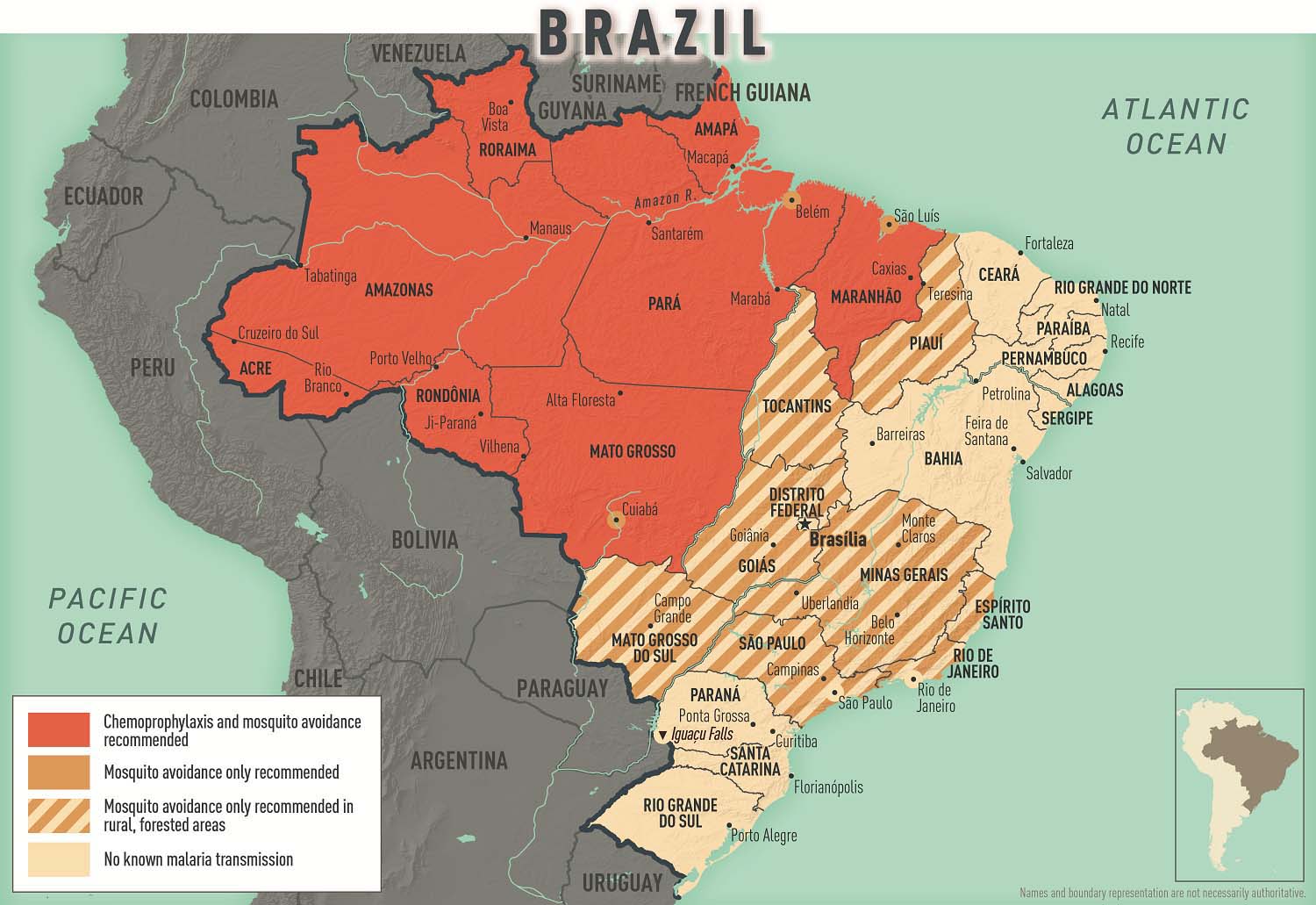
Rickettsial Diseases
Tickborne rickettsial diseases in Brazil include febre maculosa and Brazilian spotted fever, which are caused by etiologic agents from the same genus (Rickettsia) that causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever in the United States (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 18, Rickettsial Diseases ). Travelers should take precautions (e.g., wearing appropriate clothing, applying insect repellants on clothes and skin) to avoid tick bites both indoors and outdoors (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Trypanosomiasis
Except in the north of the country where cases continue to rise, most states in Brazil have eliminated Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) through improved housing conditions and insecticide spraying for the vector. Although the risk is extremely low, travelers and ecotourists staying in poor-quality housing, especially in the Amazon region, might be at greater risk for this disease.
Outbreaks have been associated with consuming food or beverages containing açaí, an Amazonian fruit eaten throughout Brazil, and sugar cane juice ( caldo de cana ). Oral transmission occurs when people consume food or beverages contaminated with triatomines—the bloodsucking insects that transmit the etiologic agent of Chagas disease ( Trypanosoma cruzi )—or their feces (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 25, American Trypanosomiasis / Chagas Disease ).
Yellow Fever
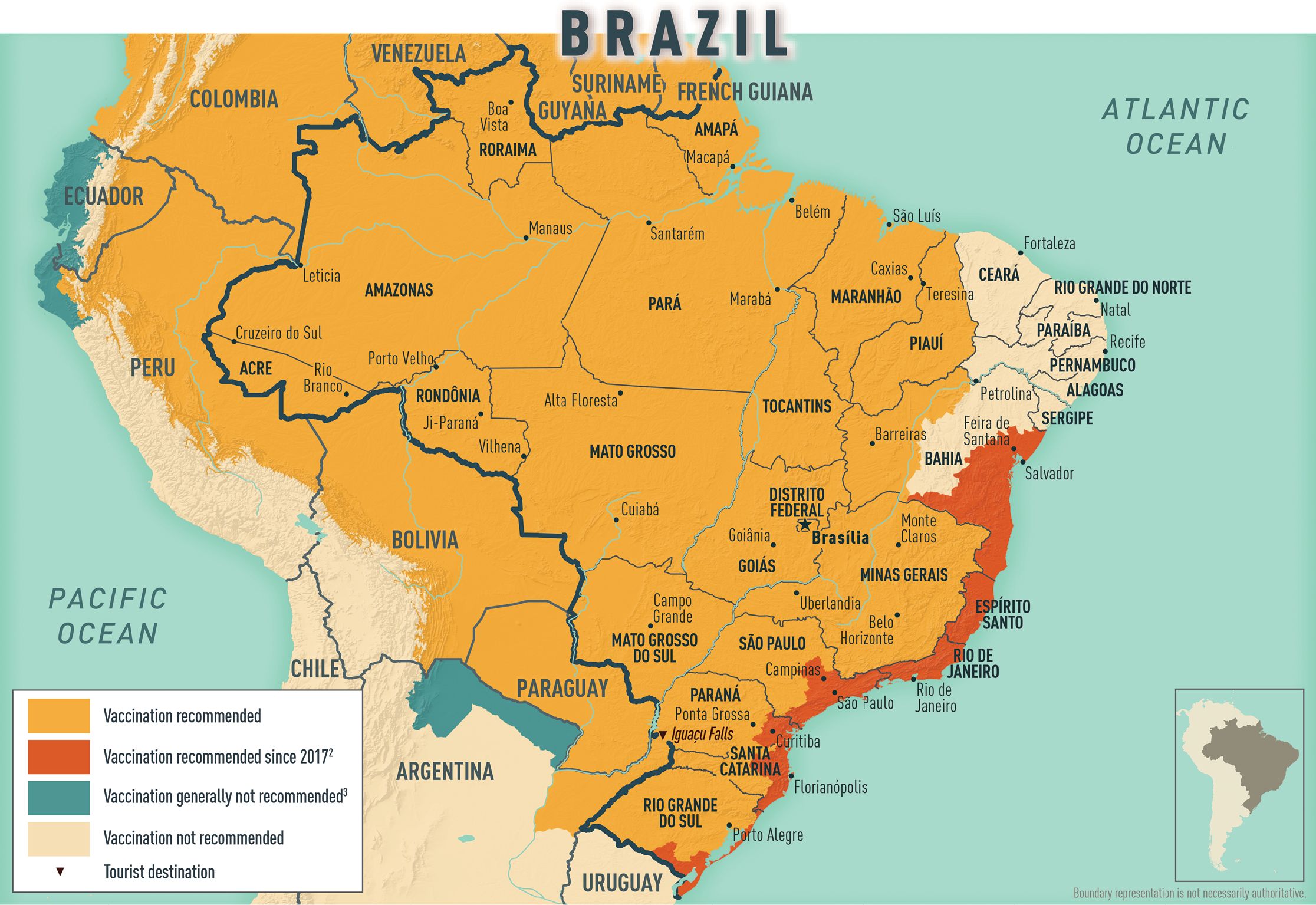
Mosquitoes that transmit yellow fever virus can be found throughout the Amazon Basin and in forested regions along all major river basins in Brazil, including Iguaçu Falls and as far south as Rio Grande do Sul. During 2016–2017, outbreaks of sylvatic yellow fever extended to the southeastern coast of Brazil, including the cities of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo, areas with historically low risk for transmission. Several unvaccinated travelers visiting these areas became ill with the disease, and some died.
Evidence of an expanded range of yellow fever transmission in Brazil led WHO and CDC to broaden their vaccination coverage recommendations for the country in 2017. Although Brazil does not require proof of vaccination against yellow fever for entry into the country, CDC recommends yellow fever vaccination for all travelers aged ≥9 months going to areas with risk for transmission. Updated information on areas of risk can be found on the CDC Travelers’ Health website; see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country .
People planning travel to other countries in South America (e.g., Colombia) could be required to show proof of yellow fever vaccination at airline counters before exiting Brazil.
Map 2-03 Yellow fever vaccine recommendations for Brazil & neighboring countries
Zika virus is an arbovirus (genus Flavivirus ) transmitted mainly by mosquitoes, typically, although not exclusively, Aedes aegypti . Zika virus also can be sexually transmitted and transmitted during pregnancy to a fetus. First reported in Brazil in 2015, Zika was likely introduced to the country 2 years prior. A large Zika outbreak occurred in 2016, and >215,000 probable cases were reported. By 2019, the number of cases had dropped to 10,000.
Most Zika infections are asymptomatic and, when present, symptoms are mild. Commonly reported signs and symptoms include arthralgia, conjunctivitis, fever, and maculopapular rash; Guillain-Barré syndrome and encephalopathy have also been reported (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 27, Zika ).
Vertical transmission leads to congenital Zika virus infection; sequelae can include microcephaly with central nervous system anomalies, other serious neurologic consequences, and fetal loss. Because of the risk for birth defects in infants born to people infected with Zika during pregnancy, CDC encourages a pretravel discussion of risks with anyone who is pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Zika travel information is available at the CDC Travelers’ Health website.
Animal Bites
Overall, the risk for rabies infection in Brazil is very low. Preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for travelers with extended itineraries, particularly children, and people planning trips to rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 18, Rabies ). For shorter stays, preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for adventure travelers, those who might be occupationally exposed to animals, and people staying in locations >24 hours away from access to rabies immune globulin (e.g., the Amazon Forest).
Poisonous snakes are a hazard in many places in Brazil, although deaths from snake bites are rare (see Sec. 4, Ch. 7, Zoonotic Exposures: Bites, Stings, Scratches & Other Hazards ). Counsel travelers to seek immediate medical attention any time a bite wound breaks the skin, or if a snake sprays venom into their eyes. In some areas of the country, specific antivenoms are available, and being able to identify the snake species (or taking a picture) might prove critical to delivery of optimal medical care. The national toll-free number for intoxication and poisoning assistance is 0800-722-6001 (in Portuguese only).
Climate & Sun Exposure
Ensure travelers to Brazil are familiar with climatic conditions at their destinations before they go. Except in the south, where temperatures peak at 85°F (30°C), temperatures >104°F (40°C) are common in cities along the coast and in the Amazon region during October–March (see Sec. 4, Ch. 2, Extremes of Temperature ).
Travel in Brazil is generally safe, although crime remains a problem in urban areas and has spread to rural areas. The incidence of crime against tourists is greater in areas surrounding beaches, hotels, nightclubs, and other tourist destinations (see Sec. 4, Ch. 11, Safety & Security Overseas ). Drug-related violence has resulted in clashes with police in tourist areas. Several Brazilian cities have established specialized police units that patrol areas frequented by tourists and provide assistance to crime victims.
Political Unrest
Political demonstrations might disrupt public and private transportation. Encourage travelers to register with the US Department of State’s Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive advisories and alerts for areas they plan to visit.
Prostitution
Although commercial sex work is legal in Brazil, operating a brothel and financial exploitation of sex workers are both against the law.
Traffic-Related Injuries
As in many foreign countries, motor vehicle accidents in Brazil are a leading cause of injury and death among US travelers (see Sec. 8, Ch. 5, Road & Traffic Safety ). Road conditions in Brazil differ significantly from those in the United States, and driving at night can be dangerous. The national toll-free number for emergency roadside assistance (193) is in Portuguese only. Driving after drinking alcohol, even small quantities, is illegal, and travelers can expect police checkpoints during evenings and nights in many urban areas. Seatbelt use is mandatory, and motorcyclists are required by law to wear helmets.
Children aged ≤10 years must be seated in the back seat. Brazilian federal law requires infants ≤1 year of age to use rear-facing car seats, children 1–4 years of age to use forward-facing car seats, and children 4–7.5 years of age to use booster seats. Anyone traveling with small children should bring their own car or booster seats, in the event these are limited or unavailable.
Quality health care is available in most sizable Brazilian cities. Brazilian public health services are free, even for visitors. Foreign visitors can seek treatment in the emergency care network of Brazil’s public health system, known as the Unified Health System, or by its Portuguese acronym, SUS, or through private facilities. A non-comprehensive list of private medical services can be found on the US Embassy in Brazil website. The toll-free emergency number for ambulance services throughout Brazil is 192. The Brazilian Ministry of Health provides information in Portuguese for international visitors , including a list of reference hospitals for mass gathering events in Brazil.
Medical Tourism
Brazil has a growing number of private clinics that cater to international clientele and offer medical procedures using advanced technologies. Travel to Brazil for cosmetic surgery, assisted reproductive technology, or other elective medical procedures has increased in recent years, becoming a major part of the medical industry. Although the quality of care overall can vary widely, Brazil has many cosmetic surgery facilities on par with those found in the United States. Travelers seeking cosmetic surgery or other elective procedures should do their research and make sure that emergency medical services are available at their clinic of choice (see Sec. 6, Ch. 4, Medical Tourism ).
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Joanna Gaines, Ana Carolina Faria e Silva Santelli
Bibliography
Hamer DH, Angelo K, Caumes E, van Genderen PJJ, Florescu SA, Popescu CP, et al. Fatal yellow fever in travelers to Brazil, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(11):340–1.
Malaria Atlas Project. Country profile: Brazil. Available from: https://malariaatlas.org/trends/country/BRA .
Melo CFCAE, Vasconcelos PFDC, Alcantara LCJ, Araujo WN. The obscurance of the greatest sylvatic yellow fever epidemic and the cooperation of the Pan American Health Organization during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20200787.
Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin: special issue. Chagas disease World Day, 14 April; year 2 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2021. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/especiais/2021/boletim_especial_chagas_14abr21_b.pdf .
Ministry of Health. Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin 41. Monitoring of cases of urban arboviruses transmitted by Aedes aegypti (dengue, chikungunya and Zika), epidemiological weeks 01 to 52 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2020. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/edicoes/2020/boletim_epidemiologico_svs_41.pdf .
Nobrega AA, Garcia MH, Tatto E, Obara MT, Costa E, Sobel J, et al. Oral transmission of Chagas disease by consumption of acai palm fruit, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15(4):653–5.
Petersen E, Wilson ME, Touch S, McCloskey B, Mwaba P, Bates M, et al. Rapid spread of Zika virus in the Americas—implications for public health preparedness for mass gatherings at the 2016 Brazil Olympic Games. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;44:11–5.
Possas C, Lourenço-de-Oliveira R, Tauil PL, Pinheiro FP, Pissinatti A, Cunha RVD, et al. Yellow fever outbreak in Brazil: the puzzle of rapid viral spread and challenges for immunisation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113(10):e180278.
Sabino EC, Buss LF, Carvalho MPS, Prete CA Jr, Crispim MAE, Fraiji NA, et al. Resurgence of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, despite high seroprevalence. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):452–5.
Silva MMO, Tauro LB, Kikuti M, Anjos RO, Santos VC, Gonçalves TSF, et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Brazil: clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(8):1353–9.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Brazil set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Brazilian Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Brazil.
Passport validity requirements
To enter Brazil, your passport must have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Visa requirements
You can visit Brazil without a visa for up to 90 days for tourism.
If you want to extend your tourist visa, contact the Federal Police (in Portuguese) before your visa expires.
For more information about visas, contact the Brazilian Consulate in London .
If you overstay your visa, you’ll face a daily fine. You have the option to pay this fine either when you leave Brazil or during your next visit. You will not be allowed to re-enter Brazil if you do not pay the fine. Overstaying your visa will result in a 6-month ban from re-entering the country.
Make sure you get your passport stamped.
Make sure the border control officer puts a stamp in your passport. If it is not stamped, you may be fined when you leave.
Read about passport stamping if you live in Brazil (in Portuguese).
At Brazil border control, you must be able to show:
- information about the purpose of your visit
- evidence you have enough money for your whole stay
- details of your accommodation
- evidence of return or onward travel
British-Brazilian dual nationals
Brazilian immigration authorities often require dual British-Brazilian nationals visiting Brazil to travel on Brazilian (rather than British) passports.
Travelling with children
Children with dual british-brazilian citizenship.
British-Brazilian dual nationals under the age of 18 who are travelling without all parents or legal guardians need authorisation from all parents or legal guardians to travel in Brazil or leave the country.
If they travel with only one parent (or guardian) or without any parent, they must have 2 original written authorisations from all parents or guardians. Read more about the formal travel authorisation process for Brazilian minors and the frequently asked questions .
You must show this permission when the under-18 leaves Brazil. One copy will be kept by the Federal Police inspection agent, together with a copy of the under-18’s identification document, and the other must stay with the under-18 or the adult accompanying them on the trip.
Children who are not dual British-Brazilian nationals
The Federal Police have sometimes delayed the travel of non-Brazilian under-18s who travel without authorisation from both parents. Families of non-Brazilian under-18s travelling through Brazil without one or both parents should follow the instructions for dual British-Brazilian under-18s. Make sure the under-18 or their travelling companion also carries the original or notarised copy of the under-18’s birth certificate. Contact the Brazilian Consulate in London for more information.
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need in TravelHealthPro’s Brazil guide . Depending on your circumstances, this may include a yellow fever vaccine.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
May 18, 2022
What the U.S. Can Learn from Brazil’s Successful COVID Vaccination Campaign
Despite similar leadership at the start of the pandemic, Brazilians are more trusting of government and view vaccination as a necessity and a right
By Adriana de Souza e Silva & Claudio Araujo
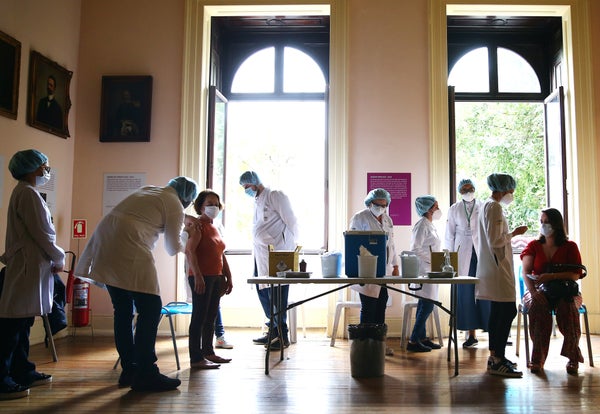

Public health workers vaccinate people at a COVID-19 vaccination clinic at Museu da Republica (Museum of the Republic) on May 24, 2021 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Mario Tama/Getty Images
During the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, media outlets, health experts and scholars have explained the COVID-19 vaccine divide in the U.S. as partisan , educational , racial or socioeconomic . As it stands, the overall U.S. adult vaccination rate has hovered around 65 percent for months now. But this division may go back to the founding ideals of democracy in the U.S.: Americans simply aren’t accustomed to expecting much from their government.
Vaccinating everyone depends on more than the availability of vaccines; it depends on health infrastructure woven into the fabric of society. If preventing further pandemics is truly a goal of the U.S. public health system, then instead of investing in private health care and subsidizing private research for vaccine development, the U.S. should invest in the development of public health systems and develop strategies to include social rights in the principles of its democracy.
Brazil, our homeland, is a prime example of how that can be done and how vaccine acceptance can become a matter of course.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
In July 2021, a group of drug traffickers approached the staff of a public vaccination site in a slum of Rio de Janeiro called Maré. A friend of ours who works in Maré shared the story: Armed with shotguns, the drug dealers demanded to be vaccinated against COVID-19, even though at that time, Rio was only vaccinating people above 50 years old (most drug traffickers are in their teens or 20s).
“We know there is this Delta variant going around, and we want to be protected,” they told the vaccination staff, who had no choice but to vaccinate everyone.
At first, the drug traffickers’ eagerness to get vaccinated might seem surprising, but the truth is, Brazilians from all walks of life welcome vaccines as a public health right. In the 2020 H1N1 pandemic, for example, Brazil vaccinated more people than any other country . Citizens are used to lining up in public health centers for routine vaccinations, despite the anti-vax attitude of its president, Jair Bolsonaro.
Although COVID-19 vaccines were slow to arrive in Brazil, as of March 2022, virtually 100 percent of the adult population in Rio and São Paulo are fully vaccinated. This is a stark difference from the U.S. In New York, one of the most vaccinated megacities, 78.2 percent of the adult population has received two doses—despite having no shortage of vaccines. Brazil has about two thirds the population of the U.S., but in November 2021, Brazil surpassed the U.S . in the share of its population that is fully vaccinated. And that gap keeps increasing .
The reason most Brazilians embrace vaccines, and about a quarter of Americans resist them, is deeply rooted in how these two democracies developed.
Since the 19th century, political analysts, such as Alexis de Tocqueville, have remarked on the decentralized democratic structure in the U.S., which has pushed the role of the state to the periphery and heavily relied on associations among civil society . During the formation of the U.S., there was a focus on civil and political rights, with an emphasis on individual liberty and freedom.
While Brazil is also a democracy and a federation, with grassroots political associations of its own, Brazilian political history has emphasized the role of the state in ensuring social rights. In short, Brazilians expect health and other services to come from the government. Even before the current 1988 constitution, which establishes public health as a human right, previous governments ensured labor rights and social welfare for everyone in the country.
The development of the Brazilian democratic process created the infrastructure for a free nationwide public health system. This, in turn, has supported people’s acceptance of top-down public health measures—even among drug traffickers. Even if this system is often precarious, and at risk of dismantlement by Bolsonaro’s government, people still expect the government to provide free health care. This is very different from the U.S., where government-funded health care is directed mainly to people living below the poverty line and to seniors.
Years ago, when one of us (Araujo) worked as a teacher in Rio’s Vidigal slum, his students used to share stories about stopping by the public health care center to greet the doctor on their way to school. This daily interaction created a relationship of trust. When someone felt ill, they did not hesitate to ask for help; help was inside their community. This trust in the public health system has now translated to public acceptance of COVID-19 vaccines.
These health care providers are part of SUS, Brazil’s public health system, created in 1988 as a human right with the intent to serve everyone in the country. The service, which includes a decentralized network of providers, including doctors, hospitals and urgent care centers, is free. Most of the favela and low-income population in Brazil depend entirely on the SUS for health care, and many middle-class citizens use SUS for routine vaccinations and emergency care.
SUS is not perfect. Public hospitals, for example, deal with funding shortages and long waiting lines for treatment. But everyone has access to basic health care. SUS providers represent a continuously present institution and are often members of the community themselves. More than an inconvenient step to getting a prescription, SUS providers are trusted liaisons, connecting community members with health researchers, government officials and grassroots interventions.
The U.S. has no such system. For many Americans, regular health care is financially out of reach. Half of Americans carry medical debt —and the government has little role in ensuring access to health care. Health care is, explicitly, a luxury, rather than a right.
It has been clear for months throughout this pandemic that vaccine acceptance is not only a scientific issue, but also a public health and communication problem. What has been less clear, however, is how the acceptance of public health measures is deeply rooted in each country’s own historical political process. We cannot change history, but we can learn from it in order to implement policy changes that improve people’s lives.
This is an opinion and analysis article, and the views expressed by the author or authors are not necessarily those of Scientific American.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Clinical Trials
Brazil Orders 12.5 Million mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines

Moderna, Inc. today announced a contract with Brazil's Ministry of Health (Ministério da Saúde) to supply its monovalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
Under the new contract, 12.5 million doses of Moderna's mRNA COVID-19 vaccine ( SpikeVax ) are anticipated for delivery in the second quarter of 2024.
This contract follows the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency's approval of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine (XBB.1.5 sublineage) in March 2024 to prevent COVID-19 in children from six months of age and adults.
"We are proud to partner with the Ministry of Health to provide our mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for the first time in Brazil as part of the national vaccination campaign," said Stéphane Bancel, Chief Executive Officer of Moderna, in a press release on April 22, 2024.
"This agreement underscores our commitment to global health and our role in supporting Brazil's efforts to protect its citizens against COVID-19."
"We look forward to working with the Ministry of Health to help maintain health security in Brazil."
Previously, Moderna generated preclinical and clinical data of its monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccine candidate, which showed an immune response against XBB sublineages and currently circulating strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including JN.1.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee

- The Power of mRNA
- Responsibility
News Details
Moderna announces contract with brazil to supply 12.5 million covid-19 vaccines as part of national vaccination campaign.
CAMBRIDGE, MA / ACCESSWIRE / April 22, 2024 / Moderna, Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) today announced a contract with the Ministry of Health in Brazil (Ministério da Saúde) to supply its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine as an integral part of Brazil's 2024 national vaccination campaign against COVID-19. This contract follows the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency's (ANVISA) approval of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine in March 2024, which encodes the spike protein of the XBB.1.5 sublineage of SARS-CoV-2 for active immunization for the prevention of COVID-19 in children from six months of age and adults.
"We are proud to partner with the Ministry of Health to provide our mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for the first time in Brazil as part of the national vaccination campaign," said Stéphane Bancel, Chief Executive Officer of Moderna. "This agreement underscores our commitment to global health and our role in supporting Brazil's efforts to protect its citizens against COVID-19. We look forward to working with the Ministry of Health to help maintain health security in Brazil."
Under the contract, 12.5 million doses of Moderna's mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are anticipated for delivery in the second quarter of 2024, marking a significant milestone in Brazil's ongoing efforts to combat COVID-19. The partnership between Moderna and the Ministry of Health reflects a shared commitment to public health and the importance of national immunization campaigns. This contract is expected to bolster Brazil's national vaccination campaign and contribute to the global effort to combat the enduring threat of COVID-19.
The World Health Organization (WHO) determined that the ancestral strain and related variants no longer circulate in humans. To ensure updated vaccines provide the most robust immune response against the dominant circulating variants, regulators and global public health agencies have recommended that COVID-19 vaccines be updated to a monovalent XBB.1.5 composition. Moderna has generated preclinical and clinical data of its monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccine candidate showing an immune response against XBB sublineages and currently circulating strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including JN.1.
About Moderna
Moderna is a leader in the creation of the field of mRNA medicine. Through the advancement of mRNA technology, Moderna is reimagining how medicines are made and transforming how we treat and prevent disease for everyone. By working at the intersection of science, technology and health for more than a decade, the company has developed medicines at unprecedented speed and efficiency, including one of the earliest and most effective COVID-19 vaccines.
Moderna's mRNA platform has enabled the development of therapeutics and vaccines for infectious diseases, immuno-oncology, rare diseases and autoimmune diseases. With a unique culture and a global team driven by the Moderna values and mindsets to responsibly change the future of human health, Moderna strives to deliver the greatest possible impact to people through mRNA medicines. For more information about Moderna, please visit modernatx.com and connect with us on X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including statements regarding: the Company's contract with the Ministry of Health in Brazil to supply Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine as part of Brazil's national vaccination campaign; the planned delivery of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccines; and the ability of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine to trigger an immune response against current circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as "will," "may," "should," "could," "expects," "intends," "plans," "aims," "anticipates," "believes," "estimates," "predicts," "potential," "continue," or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. The forward-looking statements in this press release are neither promises nor guarantees, and you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements because they involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, many of which are beyond Moderna's control and which could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. These risks, uncertainties, and other factors include, among others, those risks and uncertainties described under the heading "Risk Factors" in Moderna's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and in subsequent filings made by Moderna with the SEC, which are available on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov . Except as required by law, Moderna disclaims any intention or responsibility for updating or revising any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation in the event of new information, future developments or otherwise. These forward-looking statements are based on Moderna's current expectations and speak only as of the date of this press release.
Moderna Contacts:
Media: Luke Mircea Willats Senior Director, Corporate Communications [email protected]
Investors: Lavina Talukdar Senior Vice President & Head of Investor Relations 617-209-5834 [email protected]
SOURCE: Moderna, Inc.
Quick Links
- SEC Filings
- Investor FAQs
- Information Request Form
Investor Email Alerts
To opt-in for investor email alerts, please enter your email address in the field below and select at least one alert option. After submitting your request, you will receive an activation email to the requested email address. You must click the activation link in order to complete your subscription. You can sign up for additional alert options at any time.
At Moderna, we promise to treat your data with respect and will not share your information with any third party. You can unsubscribe to any of the investor alerts you are subscribed to by visiting the ‘unsubscribe’ section below. If you experience any issues with this process, please contact us for further assistance.
By providing your email address below, you are providing consent to Moderna to send you the requested Investor Email Alert updates.
Email Alert Sign Up Confirmation
Investor overview
Press releases
Media Center
Partnerships.
Strategic collaborators
Company culture
People behind the science
Join our team
Innovation Incubator
New venture labs
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Contact Moderna
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Stock Market
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Investment Ideas
- Research Reports
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit Cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash-back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Moderna announces contract with brazil to supply 12.5 million covid-19 vaccines as part of national vaccination campaign.
CAMBRIDGE, MA / ACCESSWIRE / April 22, 2024 / Moderna, Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) today announced a contract with the Ministry of Health in Brazil (Ministério da Saúde) to supply its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine as an integral part of Brazil's 2024 national vaccination campaign against COVID-19. This contract follows the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency's (ANVISA) approval of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine in March 2024, which encodes the spike protein of the XBB.1.5 sublineage of SARS-CoV-2 for active immunization for the prevention of COVID-19 in children from six months of age and adults.
"We are proud to partner with the Ministry of Health to provide our mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for the first time in Brazil as part of the national vaccination campaign," said Stéphane Bancel, Chief Executive Officer of Moderna. "This agreement underscores our commitment to global health and our role in supporting Brazil's efforts to protect its citizens against COVID-19. We look forward to working with the Ministry of Health to help maintain health security in Brazil."
Under the contract, 12.5 million doses of Moderna's mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are anticipated for delivery in the second quarter of 2024, marking a significant milestone in Brazil's ongoing efforts to combat COVID-19. The partnership between Moderna and the Ministry of Health reflects a shared commitment to public health and the importance of national immunization campaigns. This contract is expected to bolster Brazil's national vaccination campaign and contribute to the global effort to combat the enduring threat of COVID-19.
The World Health Organization (WHO) determined that the ancestral strain and related variants no longer circulate in humans. To ensure updated vaccines provide the most robust immune response against the dominant circulating variants, regulators and global public health agencies have recommended that COVID-19 vaccines be updated to a monovalent XBB.1.5 composition. Moderna has generated preclinical and clinical data of its monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccine candidate showing an immune response against XBB sublineages and currently circulating strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including JN.1.
About Moderna
Moderna is a leader in the creation of the field of mRNA medicine. Through the advancement of mRNA technology, Moderna is reimagining how medicines are made and transforming how we treat and prevent disease for everyone. By working at the intersection of science, technology and health for more than a decade, the company has developed medicines at unprecedented speed and efficiency, including one of the earliest and most effective COVID-19 vaccines.
Moderna's mRNA platform has enabled the development of therapeutics and vaccines for infectious diseases, immuno-oncology, rare diseases and autoimmune diseases. With a unique culture and a global team driven by the Moderna values and mindsets to responsibly change the future of human health, Moderna strives to deliver the greatest possible impact to people through mRNA medicines. For more information about Moderna, please visit modernatx.com and connect with us on X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including statements regarding: the Company's contract with the Ministry of Health in Brazil to supply Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine as part of Brazil's national vaccination campaign; the planned delivery of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccines; and the ability of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine to trigger an immune response against current circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as "will," "may," "should," "could," "expects," "intends," "plans," "aims," "anticipates," "believes," "estimates," "predicts," "potential," "continue," or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. The forward-looking statements in this press release are neither promises nor guarantees, and you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements because they involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, many of which are beyond Moderna's control and which could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. These risks, uncertainties, and other factors include, among others, those risks and uncertainties described under the heading "Risk Factors" in Moderna's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and in subsequent filings made by Moderna with the SEC, which are available on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov . Except as required by law, Moderna disclaims any intention or responsibility for updating or revising any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation in the event of new information, future developments or otherwise. These forward-looking statements are based on Moderna's current expectations and speak only as of the date of this press release.
Moderna Contacts:
Media: Luke Mircea Willats Senior Director, Corporate Communications [email protected]
Investors: Lavina Talukdar Senior Vice President & Head of Investor Relations 617-209-5834 [email protected]
SOURCE: Moderna, Inc.
View the original press release on accesswire.com

IMAGES
COMMENTS
COVID-19 travel regulations change frequently and at times without warning. The Government of Brazil updated its vaccination requirements for children subsequent to our February 18 MASCOT message and, as of February 22, returned the minimum age to present proof of vaccination to 12 years of age.
COVID-19: All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information. COVID-19 vaccine. Hepatitis A: Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Brazil. Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A.
COVID-19 Vaccines: The COVID-19 vaccine is available for U.S. citizens to receive in Brazil once they register with the public Unified Health System (SUS). ... Though the yellow fever vaccine is not required to enter Brazil, travelers wishing to be vaccinated should consider receiving it prior to travel, as local supplies are limited. ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Brazil such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Brazil's government today (Dec. 20) enacted a norm requiring a negative COVID-19 test and proof of vaccination from international travelers flying into the country. The new rules take effect ...
Over 88% of the population in Brazil has received at least one dose of a Covid vaccine as of November 25, 2022. What's on offer Brazil is a bucket list destination - a country that really does ...
Visitors may choose to only show proof of vaccination or a test with a negative result. The change applies to travelers and air, waterway, and land operators. COVID-19: Brazil simplifies measures ...
Brazil has announced a new ordinance regarding entry for international travelers amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic following a recent supreme court ruling in favor of requiring proof of vaccination. As a result, visitors must now present proof of COVID-19 vaccination approved by Anvisa, Brazil's National Health Surveillance Agency, a negative ...
12 Dec 2021. A Supreme Court justice in Brazil has ruled that all travellers arriving in the country must show proof of vaccination against COVID-19. The decision from Luis Roberto Barroso on ...
The supreme court of Brazil has just ruled that inbound international travelers will be required to provide proof of full COVID-19 vaccination in order to enter the country-a decision that directly contradicts the express wishes of Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro. The president himself remains unvaccinated (though he contracted COVID-19 last ...
The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Brazil is an ongoing mass immunization campaign for the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil. It started on January 17, 2021, when the country had 210 thousand deaths. ... Even so, many European countries accept travelers vaccinated with Covishield variants, including the Fiocruz vaccine. Vaccination progress
Brazil will require international arrivals to show proof of vaccination against COVID-19 and for unvaccinated travellers to quarantine for five days. The decision issued by a Supreme Court judge ...
Brazilian health agency Anvisa on Saturday issued a new set of rules for incoming international travelers, easing restrictions related to the COVID-19 pandemic as the health crisis subsides in the ...
BRASILIA, Dec 7 (Reuters) - Brazil will require that unvaccinated travelers entering the country go on a five-day quarantine followed by a COVID-19 test, its health minister said on Tuesday, after ...
Brasilia, Brazil, March 21, 2021 - Today Brazil will receive 1,022,400 doses of COVID-19 vaccine through the COVAX Mechanism, a global effort by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (Gavi), the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO).
Travelers to Brazil should be up to date on routine vaccines, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), influenza, measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), and diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis. Hepatitis A vaccination also is recommended. Consider hepatitis B vaccination for most travelers, but especially for anyone who could be exposed to blood or other ...
A nurse has received Brazil's first Covid-19 vaccine dose after regulators gave emergency approval to two jabs. Regulator Anvisa gave the green light to vaccines from Oxford-AstraZeneca and China ...
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. ... COVID-19 rules. There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for ...
Although COVID-19 vaccines were slow to arrive in Brazil, as of March 2022, virtually 100 percent of the adult population in Rio and São Paulo are fully vaccinated. This is a stark difference ...
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lowered its Covid-19 travel advisory for Brazil by one notch as the pandemic wanes in Latin America's largest economy. Brazil is now ranked as ...
Moderna, Inc. today announced a contract with Brazil's Ministry of Health (Ministério da Saúde) to supply its monovalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Under the new contract, 12.5 million doses of Moderna's mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (SpikeVax) are anticipated for delivery in the second quarter of 2024.
CAMBRIDGE, MA / ACCESSWIRE / April 22, 2024 / Moderna, Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) today announced a contract with the Ministry of Health in Brazil (Ministério da Saúde) to supply its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine as an integral part of Brazil's 2024 national vaccination campaign against COVID-19. This contract follows the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency's (ANVISA) approval of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine ...
Under the contract, 12.5 million doses of Moderna's mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are anticipated for delivery in the second quarter of 2024, marking a significant milestone in Brazil's ongoing efforts to ...