The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!

Exploring the Speed of Starlink Satellites: How Fast Do They Travel?
By Happy Sharer

Introduction
Starlink satellites are a network of thousands of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites created by SpaceX, which is an aerospace manufacturer and space transportation services company founded by Elon Musk. The main purpose of the Starlink satellites is to provide high-speed internet access to people in remote areas around the world. With this ambitious project, SpaceX is revolutionizing the way people access the internet.
In order for the Starlink satellites to be effective, they need to travel at certain speeds. But how fast do Starlink satellites actually travel? In this article, we’ll explore the speed of Starlink satellites and examine how fast they can travel.
Exploring the Speed of Starlink Satellites: How Fast Can They Travel?
The speed of Starlink satellites is determined by the laws of physics. According to Newton’s first law of motion, objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force. This means that the speed of Starlink satellites is determined by the amount of thrust provided by the rocket engines, as well as the gravitational pull of the Earth’s atmosphere.
There are several factors that can affect the speed of Starlink satellites. These include the size and weight of the satellite, the type of rocket engine used, the altitude of the satellite, and the atmospheric conditions such as air temperature, humidity, and wind speed.

A Closer Look at the Speed of Starlink Satellites
The typical speed of Starlink satellites is about 18,000 mph (28,968 km/h). This is enough speed to make orbits around the Earth in just 90 minutes. However, the maximum speed that Starlink satellites can reach is much higher than this. At its peak, a Starlink satellite can reach speeds of up to 22,000 mph (35,406 km/h).
How Quickly Do Starlink Satellites Move Through Space?
Starlink satellites move through space at different orbital speeds. As they get closer to the Earth, their speed increases, and as they move away from the Earth, their speed decreases. This is due to the fact that the gravitational pull of the Earth affects the speed of the satellite. Additionally, the satellites must accelerate and decelerate in order to maintain their orbits.
Examining the Velocity of Starlink Satellites
The velocity of Starlink satellites can be measured in terms of meters per second (m/s). To calculate the velocity of a Starlink satellite, you must take into account the distance it travels and the time it takes to travel that distance. The velocity of a Starlink satellite is then calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time it took to travel that distance.
What is the Velocity of Starlink Satellites?
The average velocity of Starlink satellites is about 5.8 m/s. This means that on average, a Starlink satellite will travel 5.8 meters in one second. However, the peak velocity of Starlink satellites can be much higher. At its highest speed, a Starlink satellite can reach velocities of up to 11 m/s.
In conclusion, Starlink satellites travel at a variety of speeds. The typical speed of a Starlink satellite is 18,000 mph (28,968 km/h), while the maximum speed is 22,000 mph (35,406 km/h). The average velocity of a Starlink satellite is 5.8 m/s, while the peak velocity can reach up to 11 m/s. The speed of a Starlink satellite is determined by the laws of physics and is affected by various factors such as the size and weight of the satellite, the type of rocket engine used, the altitude of the satellite, and the atmospheric conditions.
Further research should be done on the speed of Starlink satellites and the factors that affect their speed. This research could help improve the efficiency of the Starlink satellite system and lead to better internet access for people in remote areas around the world.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Exploring japan: a comprehensive guide for your memorable journey, your ultimate guide to packing for a perfect trip to hawaii, the ultimate packing checklist: essentials for a week-long work trip, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.
We have completed maintenance on Astronomy.com and action may be required on your account. Learn More

- Login/Register
- Solar System
- Exotic Objects
- Upcoming Events
- Deep-Sky Objects
- Observing Basics
- Telescopes and Equipment
- Astrophotography
- Space Exploration
- Human Spaceflight
- Robotic Spaceflight
- The Magazine
How do spaceX’s Starlink satellites actually work?

SpaceX witnessing a conga line of dozens of bright satellites marching through the night sky has surprised — and occasionally unsettled — many around the world in recent years. And as much as the sight of SpaceX’s Starlink satellites passing overhead might mystify the unacquainted, exactly how they work remains a riddle to many of those who already know about the ambitious project.
The Starlink constellation, which is intended to provide high-speed internet to underserved rural areas, depends on a huge network of interlinked satellites. For the past several years, every couple weeks or so, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket has blasted off and carried a new batch of some 60 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit. As those desk-sized satellites travel to their final positions, they brightly reflect light, irking many skygazers.
As of June 2021, there are over 1,500 Starlink active satellites, making Starlink the largest satellite constellation around Earth. In fact, SpaceX now owns more than half of all active satellites circling our planet. Ultimately, Elon Musk plans for Starlink to consist of many thousands — or even tens of thousands — of satellites, providing the entire globe with high-speed, low-latency internet.
Despite the attention received by SpaceX’s Starship and Crew Dragon capsule launches, Starlink has quietly become the company’s most frequently launched project. Musk frequently talks about putting humans on Mars, yet it’s clear that Starlink is a top priority — even if only to fund Musk’s multi-planetary goals. Leaked documents show that by 2025, SpaceX expects to earn five times as much revenue from Starlink as it does from all other launches combined.
That potential cash is igniting a commercial space race to build the satellite-based internet that many think is the future. Companies like Amazon and OneWeb are working on their own satellite internet constellations, known as megaconstellations, too. Even China has plans for a Starlink-like project in the coming years.
So, how do satellite megaconstellations like Starlink work? And why do they need so many darn satellites?

Solving slow satellite internet
Satellite internet can be notoriously laggy. So, to move more data with minimal delays, Starlink satellites occupy much lower orbits than traditional satellites — orbiting only some 340 miles (550 kilometers) above Earth’s surface. As a result, Starlink is useful for things like video calls and online games, which challenge current space-based internet providers. Ultimately, Starlink is expected to deliver speeds up to about one gigabit per second with no caps. That’s more than enough for even data-hungry households.
But that same low orbital position is also one of the main reasons why Starlink satellites shine so bright in our night sky: They’re close to us.
Once launched, a Falcon 9 launch vehicle deploys its batch of 60 Starlink satellites into an initial “parking orbit” at around 270 miles (440 kilometers) above Earth. From there, the individual satellites unfurl their solar panels and slowly start to spread out around the planet. Each satellite also uses its thrusters to gradually boost itself to a higher altitude, climbing into its eventual final orbit some 100 miles (160 km) above the International Space Station’s orbit. As the satellites climb, they grow dimmer, reflecting less sunlight back toward Earth.
In the past, communications satellites for things like TV utilized much higher orbits. This is because sitting relatively far from Earth makes them “visible” to satellite dishes across a larger geographical area. But because Starlink orbits closer in, the network requires thousands of satellites to provide simultaneous global coverage.
Of course, Starlink’s spacecraft are much smaller than conventional satellites — dubbed smallsats — weighing a mere 550 pounds (250 kilograms) each. Some have even referred to them as flying routers. That’s partly why customers must also purchase a ground-based antenna to tap into Starlink’s internet service.
This antenna is confusingly branded as a “Starlink,” but more commonly referred to as a “UFO on a Stick” or “Dishy McFlatface.” When it’s powered up, the self-pointing antenna quickly scans the sky and locks onto the nearest overhead satellite — that is, if the ambient temperature is below 122 degrees Fahrenheit, according to r ecent reports by ArsTechnica ). Then, it seamlessly maintains that connection as each new Starlink satellite comes into view and the previous one fades beyond the horizon.

The future of megaconstellations
Originally, SpaceX planned to connect every satellite to its neighbors using lasers that would let the spacecraft communicate with one another. But the first batch of Starlink satellites launched without this ability.
So for now, service relies on a system of ground stations called gateways. These stations are positioned around the world and exchange signals with the Starlink satellites, tapping them into existing fiber-optic infrastructure. So, a user’s home antenna connects to a Starlink satellite as it passes overhead, which in turn links them into the nearest gateway. As a result, in addition to their own antenna, users need to have a ground station within roughly 500 miles of their location to get service.
Things wont stay that way for long, though. Starlink engineers have already experimented with a batch of test satellites that uses lasers to communicate. Instead of connecting people to a nearby ground station, the lasers would let the satellites talk to each other directly at the speed of light, which is faster in the vacuum of space than in fiber optic cables. In a Reddit AMA (“Ask Me Anything”) session, company engineers said the tech is still too expensive and challenging to manufacture in volume, but they expect it to roll out in future generations of satellites.
Of course, it wasn’t too long ago that this whole project was too technically challenging to pull off. In the 1990s, several companies tried and failed, ultimately going bankrupt. Those services were hobbled by costly launches and electronics that weren’t quite ready for the task. That disappointing history forced even Musk to take a measured tone when discussing Starlink during the projects infancy.
Yet, the Starlink launches have now become so routine that last month, SpaceX marked its 100th consecutive successful Falcon 9 launch. Even with just a portion of the eventual constellation deployed, more than 10,000 customers already have been given access to a beta version of Starlink’s internet service. It’s now clear that SpaceX not only has revolutionized the rocket launch industry, but also figured out how to use those rockets to take advantage of the rapid miniaturization of modern electronics.
It’s looking increasingly likely that Starlink will help solve high-speed internet problems in at least some rural areas. And with Musk planning to eventually launch hundreds of Starlink satellites with each launch of SpaceX’s Starship vehicle, much of the planet could someday get its internet signal from space. At one point, the company said it was making six Starlink satellites every single day.
The lingering question now is how many competitors will follow suit, and how many satellites will ultimately make up these megaconstellations?
NASA’s snake-like EELS robot impresses in early testssssssss

NASA is taking astronaut applications. Here’s how to apply

It’s hard to grow food in space. These sensors can help.

Mariner 10, a mission of firsts, used gravity to bend its way from Venus to Mercury

Remembering Tom Stafford, the Apollo commander who did his part to thaw the Cold War

Dwarf galaxies turned on the lights near the dawn of time, JWST reveals

What are the smallest brown dwarfs? The JWST has a new answer

The upgrades to spacesuits that need to be made sooner rather than later

JWST data show intense bursts of radiation are vaporizing parts of a young star’s disk in the Orion Nebula
Starlink internet coverage, cost, speeds and the latest news — what you need to know
Elon Musk’s Starlink satellite internet service is seeing rapid speed gains and increased adoption

Elon Musk’s satellite internet company Starlink is already approaching broadband speeds. Actually, Starlink Premium, a new higher-end tier, surpasses some of the best broad speeds available in the U.S., albeit, at an absurdly high price .
While it’s still somewhat early on, Starlink is already having an impact on people living in rural parts of the world. In our Starlink review , we were thoroughly impressed by the new satellite internet service but there are still lots of questions and variables that need to be taken into account.
SpaceX has also launched Starlink RV which is a service meant for users on-the-go or who live in campers. While you can skip the line and get Starlink's RV plan instantly, there is a downside though as network services are de-prioritized for Starlink RV compared to other Starlink products – which means a degraded service and slower speeds.
So far, SpaceX has launched more than 5,300 Starlink satellites with new launches scheduled quite frequently. These satellites will continue to help cover the continental U.S., Canada and the U.K. At the same time, NASA and SpaceX have come to an information-sharing agreement to help avoid orbital collisions .
SpaceX also revealed its next-gen Starlink V2 Mni satellites which now use the E-band for backhaul. This will allow Starlink to provide four times more capacity per satellite compared to its previous iterations.
Starlink is also moving beyond providing satellite internet as SpaceX is also working on a Direct-to-Cell service that will start with text messages first before moving on to actual phone calls. In fact, the company sent out its first text messages at the beginning of 2024.
You can currently order Starlink , which promises to deliver broadband speeds of up to 300 Mbps to anyone in the world regardless of where they are. Whether it be a rural farm in Iowa or a remote village in Canada, customers are reporting greatly improved internet speeds with Starlink.
Sign up to get the BEST of Tom’s Guide direct to your inbox.
Upgrade your life with a daily dose of the biggest tech news, lifestyle hacks and our curated analysis. Be the first to know about cutting-edge gadgets and the hottest deals.
SpaceX is continuing to launch more satellites and service is already reaching more parts of the continental U.S., Canada and parts of Europe. We now have an even better indication of how rollout is going, thanks to a new coverage map .
But what is Starlink? Below you'll find a rundown of this project that aims to get everyone in the world connected to high speed internet.
Latest Starlink news (updated Jan 26)
- Starlink is also working on bringing satellite cell service to its customers and SpaceX recently sent out its first text messages using new satellites equipped with Direct to Cell capabilities
- SpaceX has launched an additional 23 Starlink satellites using a Falcon 9 rocket
- An FCC application has been filed by SpaceX ahead of the release of a new Starlink Wi-Fi router that supports Wi-Fi 6 and could come with built-in Ethernet ports
- SpaceX has launched an additional 50 Starlink satellites to further build out its constellation
- Starlink has unveiled a new suite of Priority plans for those who need the fastest internet available
Starlink release date
Starlink officially exited beta two years ago but it’s currently only available in select regions and countries. However, the company plans to make its satellite internet service available worldwide soon.
As of right now, Starlink is available in the U.S., Canada, the UK, France, Germany, Austria, the Netherlands, Ireland, Belgium, Switzerland, Denmark, Portugal, Australia and New Zealand. According to Starlink’s pre order agreement though, its satellite internet service will also launch in Italy, Poland, Spain and Chile but no release date has been set yet.
Back in May of 2022, Starlink completed its first deployment in Asia by launching in the Philippines. After making preorders available in India in October, 2021, the company’s Sanjay Bhargava revealed that the Indian government had halted pre orders until SpaceX received the regulatory approval in the country.
While it’s still difficult to get Starlink satellite internet coverage at the moment, a filing with the FCC in May of 2022 revealed that the service already has over 400,000 subscribers. If you live in an area that’s currently unsupported, you can still order Starlink on the company’s website to hold your place in line. Once the service expands to more areas this year, you’ll receive a notification that your Starlink is ready to ship.
Even if you have no plans to use Starlink as your home internet provider, you will soon be able to use the service’s satellites with your smartphone. T-Mobile President and CEO Mike Sievert announced back in August that the mobile carrier would begin working together with SpaceX on a plan to provide its customers with text coverage everywhere in the continental U.S. Likewise, Elon Musk revealed in a post on Twitter that he had discussions with Apple about using Starlink’s satellite service on the iPhone. This makes a lot of sense, especially now that the iPhone 14 includes a new Emergency SOS via Satellite feature.
Starlink availability and coverage

Although Starlink initially prioritized “high latitudes” or areas in the northern part of the Earth like Canada and the upper parts of the United States, that seems to have changed. According to a few coverage maps available online, Starlink coverage now seems to be readily available in the lower hemisphere of the Earth as well. In a tweet from back in 2020, Musk explained that Starlink would arrive in cities like Seattle first and then “get progressively closer to the equator”.
According to BroadbandNow , Starlink currently has more than 400,000 subscribers and Space X has launched a total of 2,700 LEO satellites into orbit. However, 750,000 pre orders have been submitted to Space X for Starlink satellite internet and the company is working to fulfill them all by the end of the year.
In the U.S., Starlink is currently available in 32 states including Alaska, California, Hawaii, New York, Texas and others which have a max download speed of 350 Mbps. In these states, big cities with Starlink coverage include New York City, Las Vegas, San Francisco, Portland, Philadelphia, Seattle and El Paso.
Starlink price
Starlink preorders currently cost $99 a month. But the service will require an up-front hardware fee of $499. That includes the small satellite dish that can be set up at a home or business, as well as a router and power supply. There's also a shipping and handling fee of $50.
For anyone wanting to preorder, all it requires is a refundable $99 deposit. Order fulfillment can take up to six months or more.
Starlink's Standard service now costs $120 per month for 24-220 Mbps. Meanwhile, its Business plans are available in three different packages: Priority 40GB for $140 per month, Priority 1TB for $250 per month and Priority 2TB for $500 per month.
If you want to use Starlink on the go, then you're going to need one of the company's Land Mobility packages which offer 40-220 Mbps. Mobile Priority 50GB costs $250 per month, Mobile Priority 1TB costs $1,000 per month and Mobile Priority 5T costs $5,000 per month.
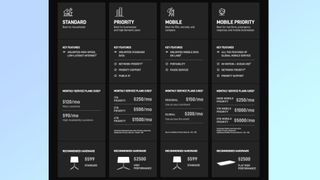
SpaceX has also unveiled a new suite of "Priority" plans for customers who need the fastest internet possible. All of these plans also come with unlimited standard speed data. The 1TB Priority plan comes in at $250 per month, the 2 TB Priority plan costs $500 per month and the 6TB Priority plan costs $1,500 per month. Starlink recommends that users of these new Priority plans pair them with its High Performance dish.
SpaceX has now rebranded Starlink RV as Starlink Roam . It's available in two different versions, one costs $150 per month and is intended to be used regionally while the other can be used for global roaming for $200 per month. Regadless of which option you choose, the dish itself still costs $599.
To get top speeds, it's a good idea to pair Starlink with one of the best Wi-Fi routers .
Starlink Premium
Elon Musk is never shy when it comes to launching faster models at high prices, and Starlink Premium is no different. Starlink Premium is a $500 monthly internet tier that offers speeds of up to 500 Mbps. It will also require a new $2,500 antenna and a $500 deposit for those wanting orders as quickly as possible. This tier is designed for, "small offices, storefronts, and super users across the globe," or what SpaceX calls "high demand users."
Starlink Premium customers in the mid-west and southern U.S. can expect their shipments to arrive this year. However, there is immediate availability in most other U.S. states.
What Starlink users are saying
The response to Starlink's internet service has been overwhelmingly positive from the few customers receiving service. Head on over to the Starlink subreddit , and you'll find users posting images of their new satellites, with accompanying speed tests. In Missouri , users are reporting download speeds of 150 Mbps. Another user in Idaho uploaded 72 hours worth of test results, and found speeds to be an average of 71 Mbps.
A user in the U.K. saw a massive leap in internet speed after installing Starlink. Aaron Wilkes from Kent, went from 1 Mbps to 175 Mbps. While Wilkes is paying more for Starlink, he feels the price is worth it .
"The ability to be able to download content so quickly compared to our standard BT line is amazing,” said Wilkes in an interview with the PA news agency.
Mega popular YouTube channel Linus Tech Tips was also able to procure a Starlink satellite system. They were able to stream four 4K videos at once and successfully played through a game of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive with little issue.
And director Jesse Senko, who lives in a rural Ontario, Canada, detailed how Starlink massively upgraded his workflow in the video below.
Starlink specs and IPO
Unlike other satellite internet providers, Starlink's LEO satellites promise to offer low-latency broadband speeds regardless of where you are. While Starlink was first boasting speeds of 1 Gbps, it's since upped that target to 10 Gbps . To put that into context, users would be able to download a 4K movie in less than 30 seconds. Starlink would be a major boon for people living in rural parts of the world.
Speed test analysis by Ookla shows Starlink seeing major gains in speed in the past few months. Median download speed has jumped from 65.72 Mbps to 97 Mbps. Actually, Starlink is creeping up on average median broadband speeds of 115.22 Mbps. The second leg of the Starlink network should see even faster speeds,
Latency on Starlink is surprisingly low considering its satellite internet. Early beta tests show that Starlink averages 34 milliseconds . While that may not be as fast as fiber, which can get as low as 17ms , any latency under 40ms is solid for most applications. Certain types of online games, most notably shooters and fighting games, benefit most from low latency. But sports games or MOBAs will work well on Starlink. Musk has admitted as such, aiming to bring pings down below 20ms.
It goes without saying, Starlink absolutely destroys other satellite internet companies like HughesNet and Viasat. Both offer download speeds at a fifth of Starlink with latency that's ten times higher.
Because of this, it's no surprise that OneWeb (half-owned by the UK government), Amazon's Project Kuiper , Boeing , Telesat , and the Russian and Chinese governments are all planning satellite internet constellations.
Still, getting a project of this magnitude literally off the ground and into profitability is a monumental task. While the Russian and Chinese governments can bear the brunt of the cost, companies like Starlink and Amazon take on significant risk. Past satellite internet constellations have gone bankrupt.
There's also a lot of interest in when a Starlink IPO would go live. In a tweet, Musk replied that an IPO is planned, but it would come after SpaceX has a more predictable cashflow. For Musk and Starlink, the goal right now is not to go bankrupt.
Starlink in your Tesla?
It seems that SpaceX has made a request with the Federal Communications Commission to bring Starlink satellite internet service to jets and ships. In a letter to the FCC by SpaceX director of satellite policy, as acquired by CNBC , David Goldman states, "This application would serve the public interest by authorizing a new class of ground-based components for SpaceX’s satellite system that will expand the range of broadband capabilities available to moving vehicles throughout the United States and to moving vessels and aircraft worldwide."
The company would handle vehicle installation through "qualified installers" and cited the need for quality internet "while on the move."
SpaceX has also made a second filing with the FCC regarding a more rugged satellite dish, one that can handle moving conditions or more extreme climates. Already, Starlink satellites are shutting down in extreme heat , forcing users to water their "Dishys" like they would flowers.
There is the issue of internet access varying between countries. Some countries, like China, have a strictly controlled internet infrastructure. Sites that might be okay to view in the U.S. likely would not be in China. But this is satellite internet, meaning it can be accessed from anywhere. It seems that Starlink will default to the rules of the country you're in, "whichever is more constraining."
This is all academic right now, though. Because of the size of the Starlink satellite terminal, at the moment it will not be possible on cars. Elon Musk stated so in a tweet.
Starlink outlook
Given that broadband companies lack rivals in many cases, Starlink and other satellite internet constellations are a welcome injection of competition. More important, the service enables regions to get connected at broadband speeds where there were no options previously.
For example, the Hoh Tribe, a Native American tribe located in Western Washington state along the Pacific coast, said Starlink was like being "catapulted into the 21st century." Per the Newsweek article, the Hoh Tribe tweeted that faster internet speeds helped with remote learning and access to healthcare.
Starlink's wireless nature allows it to enter any part of the world, subverting the need for cables. By doing so, rural areas that remain neglected can now be connected at broadband speeds. The cost of $99 is still too high for many parts of the globe, but given that Starlink will see competition from other companies, prices will likely drop over time.
Elon Musk hopes to complete the Starlink internet constellation sometime in 2023.

Anthony Spadafora is the security and networking editor at Tom’s Guide where he covers everything from data breaches and ransomware gangs to password managers and the best way to cover your whole home or business with Wi-Fi. Before joining the team, he wrote for ITProPortal while living in Korea and later for TechRadar Pro after moving back to the US. Based in Houston, Texas, when he’s not writing Anthony can be found tinkering with PCs and game consoles, managing cables and upgrading his smart home.
Don't wait! Get Apple AirTags for just $18 a piece in this 4-pack deal at Amazon
I love this Anker 10,000mAh power bank — and it just crashed to $13
Microsoft believes Snapdragon X Elite will beat Apple M3 — and the Surface Pro 10 could prove it
admin said: Star is Elon Musk's ambitious satellite internet service that promises broadband speeds anywhere in the world with new satellites being launched regularly. Here's everything you need to know. Star internet coverage, speed, cost, satellites, IPO and latest news : Read more
- View All 1 Comment
Most Popular
By Rory Mellon April 09, 2024
By Charlotte Henry April 09, 2024
By Dave LeClair April 08, 2024
By Don Reisinger April 08, 2024
By Ryan Epps April 08, 2024
By Nicholas Fearn April 08, 2024
By Camilla Sharman April 08, 2024
By Jessica Downey April 08, 2024
By Tom Pritchard April 08, 2024
- 2 Forget iPad Pro 2024 — the iPad Air just crashed to lowest-ever price
- 3 Apple AirPower prototype video shows an Apple Watch being charged for the first time
- 4 Meta's Llama 3 is coming this summer — but a small version could drop next week for you to try early
- 5 I test security cameras for a living and trust Wyze Cams in my home
PCMag editors select and review products independently . If you buy through affiliate links, we may earn commissions, which help support our testing .
Starlink Speed: How Much Faster Is Elon's Satellite Internet in 2023 vs. 2022?
Living with starlink: our tester in idaho crunches the speed test numbers to show how his satellite service has changed over the last 6 months. (spoiler: it's become much better.).

About a year ago, I moved to a new house. Relocating from a well-connected city to a very rural part of Idaho forced me to change my internet service, but the local options weren't going to support my work-from-home needs. The solution, SpaceX's Starlink satellite internet , has been an essential part of my life and work ever since.
After the first few months of living with Starlink and testing the service over a period of several days, I gave it my vote of approval . The service earned an Editors' Choice award, and it's one of the best quality-of-life improvements to happen to people living in rural areas in a long time.
But since then, there have been some changes. New plans have been introduced, prices have increased, and some reports have claimed that Starlink performance has gone down over time. (Because of location differences and many other variables, not every Starlink user experiences the exact same internet speed.) So, as we reached the six-month mark from our first review, we decided to re-test and revisit Starlink's internet service with some Starlink speed tests to see if it's still worth it.
After Living With Starlink for Months, It's Better Than Ever
Having used Starlink for the better part of a year now, I can speak to a lot of the questions people have about the service. Is it easy to set up Starlink ? (Yes.) Will I need any Starlink accessories to get started? (Almost definitely.) Is Starlink fast enough for gaming? (Yes.) Will it work in winter weather ? (Yup.) Can you do your own repairs on a damaged cable ? In theory, yes, if your dog makes it a necessity.
The biggest concerns to come out of this extended use are mostly around the availability of equipment, the pricing for Starlink service, and concerns about the overall quality of service. Let's look at each.
The Equipment Situation
One of the biggest complaints I had about my Starlink experience at the outset was the process of getting the necessary equipment. It involved buying the dish, router, stand, and cables up front—a $599 outlay—and then still required additional accessories for proper installation. I was able to get things up and running with a temporary setup that placed the dish at ground level in my yard, but a more permanent installation on my roof required some additional accessories.

You can definitely get your Starlink service set up and running with this basic equipment package, but it is highly unlikely that it will have everything you need to install your Starlink dish in its long-term, permanent location. Whether that's on a roof, mounted on a pole in the middle of a field, or any other setup, you're going to need some accessories to properly mount your dish.
Ideally, this would be emphasized as part of the initial purchase process, but it's not. You do need to assess your home, determine your ideal mounting situation, and figure out what additional accessories you may need, such as special mounts for different types of roofing, construction materials, and distances. Check out our guide to Starlink accessories to get some help figuring out what additional gear you'll need for your installation.
One positive development is an improvement on the initial equipment buying process, with standard Starlink kits now selling at Home Depot . They're still $599, and it looks like you'll still need to buy accessories through the Starlink app, but it removes one big headache from the initial setup process.
Pricing: Up, Up, and Away
If there is one complaint I've had as a Starlink user, it's been the price increases. When I initially signed up a year ago, the price was a simple $100 per month. Now, 12 months and two price increases later, it's up to $120 a month, for ostensibly the exact same service.

Starlink operates as something of a contract-free, month-to-month service, though you do plunk down a fair amount of money up front for your equipment. It would be nice to be able to lock in a price for longer service periods if you're so inclined, something that many other ISPs offer. Two price increases within a single year is a bit much.
That said, I do still get a great deal of value for my money, even at the current cost. It's also in line with what you'd be charged by any other satellite internet provider , and those services are markedly slower than Starlink.
Network Performance: The State of Expansion
Finally, there's the question of performance. Starlink has been adding users like crazy in the last year, but the performance always seemed satisfactory to me. That might not be the case for every subscriber, however. There are credible reports that the performance has gotten worse for some users in North America. Others mention a slight increase in speeds , but note that this improvement hasn't been consistent year-over-year. We'll look more closely at this below, using our own test numbers.
Aside from the quality of the service, SpaceX is clearly pouring a lot of money, time, and effort into expanding and improving the Starlink experience. New plans added over the past year include the Roam option aimed at RV users, the Best Effort tier that offers a more-affordable option for slightly less-impressive service, and increasingly numerous options for boats, airplanes, and even trains.

All of this is on top of major strides made with opening up service in formerly waitlisted areas, as well as launching more low Earth orbit satellites to the Starlink constellation that are the backbone of Starlink service. And the best news from Starlink's many recent developments? A long-anticipated data cap has been nixed , causing users with high data consumption to breathe a sigh of relief.
Rising Satellite Speeds Lift All Subscribers
Obviously, any specifics about service speeds and performance are subject to some caveats. In the case of Starlink internet service, those caveats are location-based. I live in a relatively low-population area in Idaho, with fewer local users than you'd get in, say, California or Virginia. There's a reason large portions of the country are seeing new users put on waitlists instead of simply adding new customers, and that's because each Starlink satellite has a limited amount of bandwidth to divide up among the users immediately below it on Earth. While my testing uses the same hardware and satellites that other Starlink subscribers use, my results may be different from people who live where user saturation is already slowing down service.
But don't worry about those differences too much. The connection speed changes I saw in testing, which we'll discuss below, should still carry over to any other Starlink user, even if their total speeds don't match mine. Faster is faster, even if the improvements don't translate to exactly the same increases for every user in every place. Additionally, as Starlink's network improves, SpaceX has opened up more service areas in previously waitlisted areas. The improvements made not only will be seen in better speeds for every user, but more new users can join the service in areas that were previously closed.
Finally, it's always worth pointing out that Starlink isn't really meant for high-population areas, but for rural locales without other high-speed internet alternatives. If you have cable or fiber available in your area, get that. Those options generally offer better service at better prices. Starlink's service is specifically tailored to providing connectivity where other options are scarce, rather than a cheap alternative to established ISPs.
Starlink Performance in 2023: Significantly Improved
Since my initial review of Starlink, my day-to-day internet usage has remained the same. I'm online all day for work, with frequent video calls and sizable downloads being part and parcel of my job here at PCMag. My kids still stream their favorite shows; my wife and I listen to music and podcasts; and I do a bit of gaming here and there. And, aside from patching a damaged cord and then swapping it out for an official Starlink cable, everything else remains identical to the day I set it up last year. Same dish, same router, same roof-mounted position.
For our six-month follow-up testing, we used the same testbed PC that we used the first time around. It's a small desktop computer set up exclusively to run our testing software. Over the test periods, this testbed has been constantly running a test script that periodically checks Ookla's Speedtest.com to record download and upload speeds, and sends pings to specific servers every minute to measure latency. (Ookla is owned by Ziff Davis, PCMag's parent company.) Running this Starlink speed test 24 hours a day over the course of two weeks, we gathered thousands of data points.
Where our initial (2022) tests were cut slightly short by a global outage (we omitted part of our two-week test results to keep the event from skewing our performance analysis), there was no such outage this time, giving us a full 14-day test period.
In our two weeks of testing, we saw a wide range of download and upload speeds offered by my Starlink connection. With highs up to 261Mbps, and lows dipping lower than 5Mbps, the speeds aren't always blazing fast, but they were, for the most part, right in line with what Starlink promises.

Mean download speeds were excellent, averaging higher than 100Mbps nearly every day of testing. With our home using this single internet connection for work, streaming TV and music, and even online gaming, the consistent speed and quality was absolutely necessary.
Our next set of charts looks specifically at the performance consistency of download and upload speeds, as well as the latency offered by the Starlink satellite internet service.
Here we can see that the bulk of recorded download-speed tests (which number in the several hundred) fall between the 50Mbps and 200Mbps advertised for the service, with only a few outliers trailing slower. That's just what we expected, given Starlink's service claims, but we were surprised to see a significant number of download tests that register higher than 200Mbps. In the aggregate, you're more likely to see faster-than-promised speeds than you are slower ones.
Aside from premium fiber connections, it's exceedingly rare to see upload speeds that are close to download speeds, and Starlink is no exception. However, most of the test results over two weeks peg Starlink's upload speeds between 10Mbps and 20Mbps, with a fair number of results in the 20Mbps-to-50Mbps range. In rural areas where DSL and satellite providers promise upload speeds in the 2Mbps-to-5Mbps range, that's a massive improvement over local options.
Finally, there's the question of latency, measured in milliseconds. The tests recorded almost nothing slower than 100ms, and most results were in the 20ms-to-50ms range. That's low enough to enjoy gaming, and to be active in a video call without any noticeable lag.
Breaking out ping results to the two servers we tested on— Cloudflare's 1.1.1.1 and Google's 8.8.8.8—we see that the destination server will have a slight effect on the overall latency results, but both offered a similar overall distribution of results. That suggests our analysis above holds up, even when accounting for the fact that we got faster pings on Google's servers.

These numbers are still right within the range of Starlink's promised throughput, and deliver exactly the service quality I expected when I signed up. Our original review noted that speeds like these are simply unmatched in many parts of the country, and that still holds true.
But how do these newer test numbers compare to last year's test results?
Starlink Speed Tested: Uploads Are Still a Fraction of Downloads
When we look at the performance results from our Starlink review in 2022, and measure them against the new performance results from 2023, one thing becomes very clear: Starlink got better.
Just looking at raw averages, we see that the average download speed jumped from 89.38Mbps to 129.64Mbps, roughly 30Mbps faster. Upload speeds also bumped up, from 10Mbps to 15Mbps, a welcome change. And, despite using the same dish and router, Starlink has managed to drop the latency a full 10ms, making everything faster and more responsive.
Looking more closely at the numbers, we see that the 30MBps of average improvement is reflected across our testing period. For comparison's sake, we looked at nine days' worth of data for these point-by-point comparisons, but it holds true for the full 14-day stretch—download speeds are roughly 40% to 50% faster on any given day.

But that's merely the mean download speed, an averaged number from multiple test results. What if we look at the lowest and highest download speeds?
Comparing the lowest recorded speed for each day of testing, we see that most days are indeed higher than what we saw in 2022. Even though both wallow down in the 20Mbps-or-less range from time to time, our 2023 results were consistently higher, while our 2022 numbers rarely climbed above 20Mbps. Even at its slowest, Starlink is offering better download speeds in 2023 than it did last year.

It's a tighter comparison between highest download speeds, if only because the performance is bumping against the upper limits of what Starlink's hardware (both on Earth and in space) can handle. Starlink promises speeds up to 200Mbps, and last year's testing showed that was about right, with results ranging between 185Mbps and 246Mbps. But in this latest batch of tests, we saw consistently higher top numbers, generally exceeding 220Mbps. Obviously this isn't sustained throughout the day, but it raises the ceiling just enough to make a real difference.

However the highs and lows shake out, the bigger question is one of consistency: How reliably will Starlink give you 100Mbps or higher download speeds? Well, according to our numbers, the odds are way better than they were last fall. (I should point out here that even though we have more days worth of tests in this recent batch of results, we've averaged them by day to more directly compare against our 2022 numbers.)
Last year's numbers (in blue) covered much of the same overall range, but the majority of test results fell between 20Mbps and 100Mbps. This time around, our testing showed most results fell easily within the 60Mbps-to-200Mbps range, marking a big shift toward faster speeds in general.

Upload speeds don't have the same dramatic improvements, if only because they continue to be a fraction of what download speeds offer, but the trend continues here. Where most uploads measured between 0Mbps and 20Mbps last fall, our more recent tests show a marked shift toward faster speeds—far more in the 10Mbps-to-20Mbps range, and a significant number between 20Mbps and 30Mbps. And there were proportionally more results at even higher speeds, of 30Mbps, 40Mbps, or even 50Mbps.

The one area where we expected test results to stay relatively unchanged was in latency, since there are so many bottlenecks in the Starlink system that would have to be improved, from the speed of the router and dish to the satellites in space and the terrestrial units that SpaceX uses to actually connect those satellites to the greater internet. But, somehow Starlink service has even improved here, offering faster speeds and lower latency, effectively eliminating the lag times in excess of 100ms seen in our first round of testing last fall. While the majority of service still measures between 30m and 50ms of lag, the fact is that you're more likely to get better, faster ping measurements now than you were six months ago.

Add it all up, and what Starlink has managed is pretty impressive: Everything got better.
Verdict: You'll Have to Pry My Starlink From My Cold, Dead Hands
Even as the number of users grew, Starlink has managed to open up more service areas, trim waitlists, and improve service across the board (the last, at least in my rural area). I may grumble about it costing me an extra $20 per month over its original rate when I signed up, but there's zero chance I'd give it up.
It's hard to appreciate just how good Starlink is compared with every other option for rural internet users until you've tried them side by side. While DSL and other satellite providers are still popular, SpaceX's Starlink network is really the best choice for people who don't have access to fixed broadband like cable or fiber. And, as our test numbers clearly show, it's a service that is actively improving. Combine the faster download and upload speeds, better latency, and growing access to equipment, and that's more than enough for me to say that Starlink remains a winner.
More Inside PCMag.com
- Starlink Installers Unite, But Can They Compete With SpaceX?
- Starlink Rival Astranis Debuts Next-Gen Satellite With 5x More Capacity
- Major ISPs Required to Display 'Nutrition Fact' Labels for Broadband Starting Today
- Internet Activity Plummeted As People Went Outside to Watch Solar Eclipse
- SpaceX to Light Up Starlink on Upcoming Private Space Station
About Brian Westover
If you’re after laptop buying advice, I’m your man. I’ve been reviewing PCs and technology products for more than a decade. I cut my teeth in PC Labs, spending several years with PCMag.com before writing for other outlets, among them LaptopMag.com and Tom’s Guide. While computers are my main focus, I am also the resident Starlink expert, and an AI enthusiast. I’ve also written at length about topics ranging from fitness gear and appliances to TV and home theater equipment. If I’ve used it, I have opinions about it, whether somebody’s paying me to write them up or not.
More From Brian Westover
- The Best 2-in-1 Laptops for 2024
- Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Fold 16
- The Best Ultraportable Laptops for 2024
- The Best Work Laptops for 2024
- The Magazine
- Stay Curious
- The Sciences
- Environment
- Planet Earth
How Do SpaceX's Starlink Satellites Actually Work?
Take a closer look at elon musk’s orbiting constellation of satellites, which are built to deliver high-speed, low-latency internet across the globe..

Witnessing a conga line of dozens of bright satellites marching through the night sky has surprised — and occasionally unsettled — many around the world in recent years. And as much as the sight of SpaceX's Starlink satellites passing overhead might mystify the unacquainted, exactly how they work remains a riddle to many of those who already know about the ambitious project.
The Starlink constellation, which is intended to provide high-speed internet to underserved rural areas, depends on a huge network of interlinked satellites. For the past several years, every couple weeks or so, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket has blasted off and carried a new batch of some 60 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit. As those desk-sized satellites travel to their final positions, they brightly reflect light, irking many skygazers.
As of June 2021, there are over 1,500 Starlink active satellites, making Starlink the largest satellite constellation around Earth. In fact, SpaceX now owns more than half of all active satellites circling our planet. Ultimately, Elon Musk plans for Starlink to consist of many thousands — or even tens of thousands — of satellites, providing the entire globe with high-speed, low-latency internet.
Despite the attention received by SpaceX’s Starship and Crew Dragon capsule launches, Starlink has quietly become the company’s most frequently launched project. Musk frequently talks about putting humans on Mars, yet it’s clear that Starlink is a top priority — even if only to fund Musk's multi-planetary goals. Leaked documents show that by 2025, SpaceX expects to earn five times as much revenue from Starlink as it does from all other launches combined.
That potential cash is igniting a commercial space race to build the satellite-based internet that many think is the future. Companies like Amazon and OneWeb are working on their own satellite internet constellations, known as megaconstellations, too. Even China has plans for a Starlink-like project in the coming years.
So, how do satellite megaconstellations like Starlink work? And why do they need so many darn satellites?
Solving Slow Satellite Internet
Satellite internet can be notoriously laggy. So, to move more data with minimal delays, Starlink satellites occupy much lower orbits than traditional satellites — orbiting only some 340 miles (550 kilometers) above Earth's surface. As a result, Starlink is useful for things like video calls and online games, which challenge current space-based internet providers. Ultimately, Starlink is expected to deliver speeds up to about one gigabit per second with no caps. That's more than enough for even data-hungry households.
But that same low orbital position is also one of the main reasons why Starlink satellites shine so bright in our night sky: They're close to us.
Once launched, a Falcon 9 launch vehicle deploys its batch of 60 Starlink satellites into an initial "parking orbit" at around 270 miles (440 kilometers) above Earth. From there, the individual satellites unfurl their solar panels and slowly start to spread out around the planet. Each satellite also uses its thrusters to gradually boost itself to a higher altitude, climbing into its eventual final orbit some 100 miles (160 km) above the International Space Station's orbit. As the satellites climb, they grow dimmer, reflecting less sunlight back toward Earth.
In the past, communications satellites for things like TV utilized much higher orbits. This is because sitting relatively far from Earth makes them "visible" to satellite dishes across a larger geographical area. But because Starlink orbits closer in, the network requires thousands of satellites to provide simultaneous global coverage.
Of course, Starlink's spacecraft are much smaller than conventional satellites — dubbed smallsats — weighing a mere 550 pounds (250 kilograms) each. Some have even referred to them as flying routers. That's partly why customers must also purchase a ground-based antenna to tap into Starlink's internet service.
This antenna is confusingly branded as a "Starlink," but more commonly referred to as a “UFO on a Stick” or "Dishy McFlatface." When it's powered up, the self-pointing antenna quickly scans the sky and locks onto the nearest overhead satellite — that is, if the ambient temperature is below 122 degrees Fahrenheit, according to recent reports by ArsTechnica ). Then, it seamlessly maintains that connection as each new Starlink satellite comes into view and the previous one fades beyond the horizon.
The Future of Megaconstellations
Originally, SpaceX planned to connect every satellite to its neighbors using lasers that would let the spacecraft communicate with one another. But the first batch of Starlink satellites launched without this ability.
So for now, service relies on a system of ground stations called gateways. These stations are positioned around the world and exchange signals with the Starlink satellites, tapping them into existing fiber-optic infrastructure. So, a user's home antenna connects to a Starlink satellite as it passes overhead, which in turn links them into the nearest gateway. As a result, in addition to their own antenna, users need to have a ground station within roughly 500 miles of their location to get service.
Things wont stay that way for long, though. Starlink engineers have already experimented with a batch of test satellites that uses lasers to communicate. Instead of connecting people to a nearby ground station, the lasers would let the satellites talk to each other directly at the speed of light, which is faster in the vacuum of space than in fiber optic cables. In a Reddit AMA ("Ask Me Anything") session, company engineers said the tech is still too expensive and challenging to manufacture in volume, but they expect it to roll out in future generations of satellites.
Of course, it wasn't too long ago that this whole project was too technically challenging to pull off. In the 1990s, several companies tried and failed, ultimately going bankrupt. Those services were hobbled by costly launches and electronics that weren’t quite ready for the task. That disappointing history forced even Musk to take a measured tone when discussing Starlink during the projects infancy.
Yet, the Starlink launches have now become so routine that last month, SpaceX marked its 100th consecutive successful Falcon 9 launch. Even with just a portion of the eventual constellation deployed, more than 10,000 customers already have been given access to a beta version of Starlink’s internet service. It’s now clear that SpaceX not only has revolutionized the rocket launch industry, but also figured out how to use those rockets to take advantage of the rapid miniaturization of modern electronics.
It's looking increasingly likely that Starlink will help solve high-speed internet problems in at least some rural areas. And with Musk planning to eventually launch hundreds of Starlink satellites with each launch of SpaceX's Starship vehicle, much of the planet could someday get its internet signal from space. At one point, the company said it was making six Starlink satellites every single day.
The lingering question now is how many competitors will follow suit, and how many satellites will ultimately make up these megaconstellations?
Already a subscriber?
Register or Log In

Keep reading for as low as $1.99!
Sign up for our weekly science updates.
Save up to 40% off the cover price when you subscribe to Discover magazine.

New Speedtest Data Shows Starlink Performance is Mixed — But That’s a Good Thing
Get the latest ookla research™.
Satellite providers are playing no small part in the rapid expansion of global connectivity. Some experts predict there will be 58,000 satellites orbiting the earth by 2030 — a nearly 725% increase from 2023. Ookla® is back with our ongoing satellite internet series with compelling, fresh data for satellite providers in Africa, Europe, and Oceania during Q2 2023, including SpaceX’s Starlink, Viasat, and Skylogic.
This analysis includes Starlink Net Promoter Score (NPS) data for France, Germany, Italy, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom, year-over-year data for satellite providers in Europe and Oceania from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023, and new Q2 2023 data from Starlink in Africa.
Starlink users across different continents continue to love the service
Using Speedtest Intelligence ®, we examined NPS ratings data for Starlink users against an aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined.
NPS is based on Speedtest® user responses after being asked how likely they are to recommend their provider to friends or family on a 0 to 10 scale. NPS ratings are categorized into Detractors (score 0-6), Passives (score 7-8), and Promoters (score 9-10), and is calculated as (% Promoters – % Detractors) x 100. Any NPS score above 0 indicates that a provider’s audience is more loyal than not.

As you can see from the above image, Starlink users in France, Germany, Italy, New Zealand, and the U.K. had an NPS score much higher than the aggregate score for all fixed broadband providers combined during Q2 2023. France had the highest NPS among the aggregate of fixed broadband providers for the countries we surveyed at -15.98 and fixed broadband providers had a much faster median download speed at 165.37 Mbps to Starlink’s 107.56 Mbps. In New Zealand there was a similar story with the aggregate of fixed broadband providers having a -20.40 NPS to Starlink’s 48.83, while having a faster median download speed 147.86 Mbps to 113.78 Mbps during Q2 2023.
Germany, which had the lowest NPS rating of aggregate of fixed broadband providers in Europe at -30.10, also had the smallest difference in NPS with Starlink scoring 38.19. Interestingly, the aggregate of fixed broadband providers and Starlink both had similar median download speeds at 83.16 Mbps and 82.56 Mbps, respectively, during Q2 2023.
Of note, Starlink had much higher NPS ratings and median download speeds than the aggregate of all fixed providers combined in Italy and the U.K., respectively, during Q2 2023. Starlink’s NPS was 50.20 to -25.61 for the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers in Italy during Q2 2023, while the median download speeds were 100.68 Mbps to 63.99 Mbps. In the U.K., Starlink’s NPS was 47.18 to -26.88 for the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined, with the median download speeds a little closer, 100.11 Mbps to 77.38 Mbps, respectively.
In our last report , we found a wide NPS gap between U.S. rural Starlink users — who often have fewer options for fixed broadband access — and the corresponding aggregate of fixed broadband providers. Given that all five of these countries have rural or remote regions that are underserved or not served by traditional broadband offerings, it may be no surprise that Starlink users who reside in those areas may feel positive about having access to fast broadband internet.
Starlink speeds over 100 Mbps in 14 European countries during Q2 2023, speeds stabilizing across Europe
Key takeaways:
- Starlink results were the fastest among satellite providers we surveyed.
- Starlink quarter-to-quarter speeds improved or remained about the same (between 5% and -5%) in 23 countries, while decreasing in 4 countries.
- Among the 27 European countries we surveyed, Starlink had median download speeds greater than 100 Mbps in 14 countries, greater than 90 Mbps in 20 countries, and greater than 80 in 24 countries, with only three countries failing to reach 70 Mbps.
- Skylogic, while delivering speeds slower than Starlink, showed stabilized broadband speeds over the past year for those seeking a Starlink alternative.

Over the past year, we’ve seen huge developments in the global satellite market, Europe notwithstanding, with Amazon’s Project Kuiper moving forward, the EU creating its own satellite constellation, and OneWeb and Eutelsat merging. While Starlink continues to lead for performance among satellite providers we surveyed, Starlink has experienced some major hurdles over the past year as users flock to the service and speeds have subsequently dipped — but of note those concerns seem to have started allaying in most of Europe during Q2 2023.
At first glance, year-over-year median download speeds for Starlink are about the same (-5% to 5%) or better (greater than 5%) from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023 in 15 countries and slower (decreasing more than 5%) in 8 countries. But among the 27 countries we surveyed during Q2 2023, Starlink had speeds faster than the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined in 11 countries (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Estonia, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, and the U.K.) Those speeds were most notably faster in Croatia and Greece for Starlink at 94.41 Mbps to 45.24 Mbps and 108.97 to 44.09 Mbps , respectively, during Q2 2023. Speeds were about the same in four countries (Finland, Slovenia, Germany, and Lithuania), and speeds were slower than the aggregate of fixed broadband providers in 12 countries, most notably in Poland, Spain, Romania, Denmark, and France which saw between 50% and 105% faster aggregate fixed broadband speeds than Starlink.
Quarterly download speeds stabilizing or improving
Looking at results from Q1 2023 to Q2 2023, median download speeds for Starlink remained about the same (between 5% and -5%) in 23 countries, while decreasing in four countries . That’s a big deal, especially given Starlink had median download speeds greater than 100 Mbps in 14 countries, and greater than 90 Mbps in 20 countries, and greater than 80 in 24 countries — with only three countries failing to reach 70 Mbps.
While trailing Starlink speeds, Skylogic recorded median download speeds in Italy at 29.21 Mbps during Q2 2023, a roughly 27% statistical increase year-over-year from 22.28 Mbps during Q2 2022. Notably, Skylogic recorded a median download speed of 68.44 Mbps in Italy during Q1 2023. Among the various countries we recorded Skylogic data for during the past year, the range of median download speeds varied between 19.53 Mbps and 68.44 Mbps, with most speeds between 28 and 50 Mbps, all fast enough to stream 4K video online. Viasat, had relatively similar download speeds in Germany and Italy at 17.22 Mbps and 17.45 Mbps, respectively, during Q2 2023.
Top 10 fastest Starlink download speeds in European countries

Starlink in Switzerland had one of the fastest median download speed among countries with Starlink during Q2 2023 at 122.47 Mbps, followed by Denmark (117.38 Mbps), Austria (111.91 Mbps), Belgium (111.20 Mbps), Hungary (108.97 Mbps), France (107.56 Mbps), Ireland (104.42 Mbps), Estonia (102.38 Mbps), Portugal (101.75 Mbps), and Latvia (100.94 Mbps). Sweden, Italy, Bulgaria, and the U.K. all followed but had speeds greater than 100 Mbps.
Upload speeds for Starlink are down year over year, but quarterly speeds almost all improved or were about the same
Upload speeds for Starlink mostly decreased notably year over year, with only the U.K. showing an improved median upload speed in Q2 2023 out of 27 countries surveyed. However, looking quarter to quarter, Q2 2023 upload speeds for Starlink stayed about the same or improved in 25 out of 27 countries, with only Greece and Ireland showing declines . For upload speeds, Starlink all 27 countries we surveyed had upload speeds between 10 Mbps and 15 Mbps except Portugal (17.70 Mbps), Hungary (16.91 Mbps), Croatia (16.12 Mbps), Bulgaria (15.93 Mbps), Romania (15.82 Mbps), Spain (15.79 Mbps), and Poland (9.11 Mbps). Starlink in Greece was the only instance of a satellite provider in Europe having an upload speed greater than the aggregate of all fixed providers combined, 12.97 Mbps for Starlink to 7.85 Mbps for the aggregate of fixed broadband providers combined. Skylogic showed upload speeds lower than 4 Mbps in both Austria and Italy during Q2 2023. Viasat had upload speeds of 3.51 Mbps in Germany and 4.69 Mbps in Italy during Q2 2023.
Multi-server latency is stabilizing for Starlink users across Europe
As an low-earth orbiting (LEO) satellite internet provider, Starlink has a leg up on some satellite competitors who rely on further away geosynchronous-earth orbit (GEO) and medium-earth orbit (MEO) satellite constellations. However, once again, all the aggregates of all fixed broadband providers in Europe had much lower multi-server latencies than Starlink, Viasat (which had latencies over 600 ms) and Skylogic (which had latencies over 700 ms). That being said, Starlink still saw multi-server latencies under 60 ms in the U.K. (51.26 ms), Spain (53.37 ms), Portugal (55.84 ms), and Belgium (59.34 ms). Starlink saw most countries’ multi-server latencies between 60 and 90 ms.
Starlink speeds stabilize in Oceania

Oceania, the second least densely populated continent in the world to Antarctica, has rural and remote populations that benefit from (and even rely on) satellite internet connections. Luckily for rural and remote Starlink users, they’ve probably seen a good amount of stability over the past year with Q2 2023 median download speeds in New Zealand at 113.78 Mbps (105.99 Mbps in Q2 2022) and Australia at 104.92 Mbps (102.76 Mbps in Q2 2022). Tonga, which is very remote, saw download speeds drop from 45.25 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 37.95 Mbps in Q2 2023.
Upload speeds also showed some stability with Australia going from 10.45 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 11.33 Mbps during Q2 2023 and New Zealand going from 12.31 Mbps to 14.62 during the same time period. Tonga saw a notable drop in speeds year over year from 19.26 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 6.66 Mbps Q2 2023.
Multi-server latency, which usually will be higher for satellite internet options, showed promising results for Starlink in Oceania during Q2 2023. Multi-server latency dropped noticeably in New Zealand year over year, going from 89.38 ms in Q2 2022 to 46.42 ms in Q2 2023. Australia saw a more modest drop with multi-server latency going from 63.04 ms to 59.78 ms from Q2 2022 to Q2 2023. Tonga saw an increase in multi-server latency from 125.24 ms to 137.16 ms during the same time period.
Starlink in Africa is off to a promising start

Starlink, which first launched on the African continent in Nigeria this past January, is showing intriguing early results. Speedtest Intelligence showed that Starlink in Nigeria had a faster median download speeds than all aggregate fixed broadband providers combined at 63.69 Mbps to 15.60 Mbps during Q2 2023. Upload speeds were more similar during the same time period with Starlink at 13.72 Mbps and the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined at 10.60 Mbps. Starlink did have a marginally higher multi-server latency at 55.88 ms to 50.26 ms during Q2 2023.
In Rwanda, median download speeds were a little closer with Starlink recording a median download speed at 63.10 Mbps in Q2 2023 compared to the aggregate of all fixed broadband providers combined at 34.55 Mbps. Starlink trailed behind for median upload speed at 6.88 Mbps to 10.05 Mbps for fixed broadband providers during Q2 2023. Multi-server latency for Starlink was much higher at 320.45 ms to 29.04 ms for fixed broadband providers during the same time period.
The 2023 space revolution is off to a huge start
Here are some major updates about what’s next for various different satellite competitors:
After delays, Amazon’s Project Kuiper aim to launch prototype satellites this fall
Facing a series of rocket-related delays, Amazon recently announced it could send its first two Project Kuiper prototypes into orbit in late September . That news follows a recently announced $120 million 100,000-square-foot satellite processing facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Planning on offering internet service in 2025 , Amazon is slated to have half of its 3,236 LEO satellite constellation in space by 2026.
China’s grand ambitions to provide internet connectivity to over 362 million people
According to the Wall Street Journal, over 362 million people in China don’t have access to the internet — which is about 1 in every 4 people in China, a large portion of which live in rural or remote communities. In order to overcome that connectivity gap, China is looking to the sky to create its own satellite constellation with potentially over 12,000 satellites . China’s biggest gap seems to be with recreating the success of SpaceX’s reusable rockets — however, initial tests are far underway and a host of reusable rockets are slated for test launches in 2024.
SpaceX’s Starlink service offerings are about to rapidly expand
While Starlink continues to lead among satellite providers in most areas of the world, their expansion is only starting. Looking at the Starlink availability map , Starlink has an incredibly busy rest of 2023 and 2024 in Africa, Asia, and South America — and they’re marking their intent to expand into most of the world. That comes as Starlink marked launching over 5,000 satellites into space at the end of August . With some wiley entrepreneurs already renting out their Starlink “Dishy McFlatfaces” to vacationers and campers for $25-30 dollars a day, satellite connectivity is truly becoming a full-time gig.
Viasat’s bad luck might affect entire industry
Viasat launched the first of its three long-awaited Viasat-3 arrays — but then their first satellite suffered an antenna anomaly , which prevented a large reflector to deploy that affects whether or not the satellite can operate as intended. While Viasat is rushing to solve the issue, this could ultimately trigger a $420 million insure claim for the loss of the $700 million satellite . With such a high-value loss, this could send ripples through the satellite industry, causing insurance premiums to skyrocket for companies looking to mitigate potential losses through insurance. All of this comes on the heels of acquiring Inmarsat in May for $7.3 billion to expand its satellite arrays and spectrum holdings. We’ll be watching to see whether or not Viasat can find a solution.
Eutelsat and OneWeb merger imminent, big moves abound
The Eutelsat and OneWeb merger should make competitors take notice — combining satellite networks, expanding enterprise offerings, and competing in emerging markets has big revenue potential — with OneWeb having an already established LEO network of 630 satellites and Eutelsat offering 36 GEO satellites. Of note, OneWeb recently inked a deal with Telstra in Australia to provide satellite backhaul for locations “where satellite backhaul is a preferred or only viable option.” OneWeb is also partnering with the European Space Agency to develop a next-gen 5G beam-hopping satellite, which could quickly increase connectivity for people traveling or for disaster areas that need emergency connectivity. Shareholders are set to vote on approving the merger on Sept. 28 .
European Union greenlights multi-orbit constellation
With grand ambitions to launch a multi-orbit, €6 billion constellation in 2024, the European Union is partnering with a consortium of industry players including Airbus, SES, Eutelsat, Hispasat, and Thales to develop the EU’s IRIS² project. The EU still expects to have the first of its satellites go live by the end of 2024 and have a fully operational constellation by 2027 .
HughesNet aiming to launch Jupiter 3 array in Q2 2023
HughesNet successfully launched its Jupiter 3 array on July 29 , which aims to provide U.S. and Latin America consumers with higher broadband download speeds. While the actual satellite will take some time to reach its geosynchronous orbit and deploy, this satellite adds 500 Gbps of Ka-band capacity for HughesNet, which could see consumers reaching download speeds between 50 Mbps and 100 Mbps. We’ll be eagerly awaiting Speedtest ® results from HughesNet’s Jupiter 3 array.
Ookla will continue monitoring new satellite internet developments
2023 continues to be an important year for satellite internet providers. Satellite connectivity is something we’ll be watching closely and we’ll continue our series next quarter with Q3 2023 data from select continents including North America. In the meantime, be sure to download the Speedtest app for Windows and Mac computers or for iOS or Android for devices and see how your satellite internet stacks up to our results.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.
About the Author

Ookla® is a global leader in connectivity intelligence that provides consumers, businesses, and other organizations with data-driven insights to improve networks and connected experiences.
- More Articles
Starlink: SpaceX's satellite internet system
Starlink is a space internet project run by aerospace company SpaceX

Satellite positioning
How does it work, starlink controversy, additional resources, bibliography.
In 2019, SpaceX launched the first 60 satellites of Starlink. Since then, over 2,000 have reaches orbit, set to become part of a constellation of more than 12,000. Known as Starlink, the project aims to bring high-speed internet to every corner of the planet.
SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk announced the Starlink concept in Jan. 2015, explaining the company intended to launch only about 4,000 broadband satellites into low-Earth orbit to provide low-cost internet . For perspective, there were only about 2,000 operational satellites in orbit before Starlink, and humanity have launched only around 9,000 craft into space in all of history.
Currently, fast internet access is only available in places with fibre optic cables. In remote locations, communications satellites provide links to the internet, but the connections are notoriously slow.
These satellites sit in geostationary orbit, meaning they travel at the same speed as Earth's rotation and therefore remain positioned above the same point on the ground, according to the European Space Agency (ESA) . This makes it easy for receiving satellite dishes to connect with them, but the downside is that transferring data in this way takes time.
The internet: History, evolution and how it works
How will Ukraine keep SpaceX's Starlink internet service online?
How are asteroids, space weather and space debris detected before they hit Earth?
SpaceX aims to change that by surrounding Earth with low-orbiting satellites, according to Starlink.com . Individually they won’t cover as much of Earth's surface, and they won’t be geostationary, so there will need to be thousands of them to ensure complete coverage of the globe. But, because they fly low, it will cut the time it takes for a signal to travel from the ground to space and back again.

Achieving this is no mean feat. The closer a satellite is to Earth, the more drag it will experience from the edges of the atmosphere . To get around this, SpaceX has designed the satellites to look like vertical shark–fins, according to their website , with a knife-like edge that cuts through the wind.
Each one weighs just 550 pounds (250 kilograms), and it works a bit like a router. Its job is simply to receive signals, work out where they're going, and pass them on. On the ground, users will have special dishes that lock on to whichever satellite is closest.
The project is not without controversy. Each satellite has a solar array that sticks out like a wing. At sunrise and sunset, it catches the light, making it glint like a shooting star. As the constellation moves overhead, it leaves streaks on telescope images, obscuring the stars and planets behind. Space X has been working with astronomers to minimize the impact by shading and tilting the satellites to reduce the light reflected back towards Earth, according to Space.com .
The high-profile project most likely to be affected is the Vera Rubin Observatory, scheduled to come online in October 2023 in the Chilean Andes, according to Space.com . This will be impacted by bright satellite trails because of its wide field of view and high sensitivity.
The satellites also pose a potential threat to other orbiting objects, Live Science previously reported. They are already responsible for over half of close encounters in Earth’s orbit, and that proportion is only set to rise, Live Science previously reported .
In December 2021, the Chinese government lodged a formal complaint with the United Nations after two near-misses with the China Space Station, Space.com reported. And, with at least 11 other companies already entering the satellite constellation race, space is likely to get more complicated and more crowded in years to come.
To learn more about the goals of Starlink internet, you can visit the satellite page at Starlink.com . Additionally, you can read more details about the Starlink internet speed and coverage at Tom's Guide .
- " Types of orbits ". The European Space Agency (2020).
- " World's most advanced broadband internet system ". Starlink (2022).
- " Astronomy discussion with National Academy of Sciences ". SpaceX (2020).

Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Laura Mears is a biologist who left the confines of the lab for the rigours of an office desk as a keen science writer and a full-time software engineer. Laura has previously written for the magazines How It Works and T3 . Laura's main interests include science, technology and video games.
NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
The moon is getting its own time zone, White House memo to NASA reveals
Viking Age women with cone-shaped skulls likely learned head-binding practice from far-flung region
Most Popular
By Anna Gora December 27, 2023
By Anna Gora December 26, 2023
By Anna Gora December 25, 2023
By Emily Cooke December 23, 2023
By Victoria Atkinson December 22, 2023
By Anna Gora December 16, 2023
By Anna Gora December 15, 2023
By Anna Gora November 09, 2023
By Donavyn Coffey November 06, 2023
By Anna Gora October 31, 2023
By Anna Gora October 26, 2023
- 2 Here are the best photos of the April 8 total solar eclipse over North America
- 3 Pregnancy may speed up 'biological aging,' study suggests
- 4 Part of the San Andreas fault may be gearing up for an earthquake
- 5 NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
- 2 Part of the San Andreas fault may be gearing up for an earthquake
- 3 Extremely rare marsupial mole that 'expertly navigates' sand dunes spotted in Western Australia
- 4 Giant 'toe biter' water bugs discovered in Cyprus for the 1st time
- 5 Low tides reveal Bronze Age fortress that likely defended against Irish mainland
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
Starlink speed tests —
Spacex starlink speeds revealed as beta users get downloads of 11 to 60mbps, ookla tests aren't showing the gigabit speeds spacex teased, but it's early..
Jon Brodkin - Aug 14, 2020 5:00 pm UTC

Beta users of SpaceX's Starlink satellite-broadband service are getting download speeds ranging from 11Mbps to 60Mbps , according to tests conducted using Ookla's speedtest.net tool. Speed tests showed upload speeds ranging from 5Mbps to 18Mbps .
Further Reading
The same tests, conducted over the past two weeks, showed latencies or ping rates ranging from 31ms to 94ms. This isn't a comprehensive study of Starlink speeds and latency, so it's not clear whether this is what Internet users should expect once Starlink satellites are fully deployed and the service reaches commercial availability. We asked SpaceX several questions about the speed-test results yesterday and will update this article if we get answers.
Links to 11 anonymized speed tests by Starlink users were posted by a Reddit user yesterday . Another Reddit user compiled some of the tests to make this graphic:
Update at 11:18pm ET : A new Reddit post listing more speed tests shows some Starlink users getting even lower latency of 21ms and 20ms .
Beta testers must sign non-disclosure agreements , so these speed tests might be one of the only glimpses we get of real-world performance during the trials . SpaceX has told the Federal Communications Commission that Starlink would eventually hit gigabit speeds, saying in its 2016 application to the FCC that "once fully optimized through the Final Deployment, the system will be able to provide high bandwidth (up to 1Gbps per user), low latency broadband services for consumers and businesses in the US and globally." SpaceX has launched about 600 satellites so far and has FCC permission to launch nearly 12,000 .
While 60Mbps isn't a gigabit, it's on par with some of the lower cable speed tiers and is much higher than speeds offered by many DSL services in the rural areas where SpaceX is likely to see plenty of interest. On the Reddit thread, some Internet users said they'd love to get the speeds shown in the Starlink tests as they are currently stuck at 1Mbps or even less. An Ookla report on fixed-broadband speeds in December 2018 found average download speeds in the US of 96.25Mbps and average uploads of 32.88Mbps. SpaceX is planning for up to 5 million home-Internet subscribers in the US.
SpaceX latency
In March, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk said , "We're targeting latency below 20 milliseconds, so somebody could play a fast-response video game at a competitive level." SpaceX satellites have low-Earth orbits of 540km to 570km, making them capable of much lower latency than geostationary satellites that orbit at about 35,000km.
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai doubted Musk's latency claims and in May 2020 proposed to classify SpaceX and all other satellite operators as high-latency providers—i.e. above 100ms—for purposes of a rural-broadband funding distribution. The FCC backed off that plan but said companies like SpaceX will have to prove they can offer low latencies, and it continued to express " serious doubts " that SpaceX and other similar providers will be able to deliver latencies of less than 100ms.
Ping and latency are the same thing in Ookla speed tests, one of the service's help documents says . It measures the round-trip time in milliseconds when a client device sends a message to a server and the server sends a reply back. "This test is repeated multiple times with the lowest value determining the final result," Ookla says.
As the FCC wrote , the latency of a satellite network "consists of the 'propagation delay,' the time it takes for a radio wave to travel from the satellite to the earth's surface and back, and the 'processing delay,' the time it takes for the network to process the data." The FCC also noted that "propagation delay in a satellite network does not alone account for latency in other parts of the network such as processing, routing, and transporting traffic to its destination." FCC tests found that "Cable latencies ranged between 18ms to 24ms, fiber latencies between 5ms to 12ms, and DSL between 27ms to 55ms." Traditional broadband satellites using geostationary orbits have FCC-measured latency of about 600ms, but that is not indicative of the lower latencies to be expected from low-Earth orbit satellites.
Although the Ookla speed-test latencies for Starlink don't hit Musk's target of below 20ms, they are below the FCC's 100ms threshold. For competitive online gaming, Ookla says players should be in "winning" shape with latency or ping of 59ms or less, and "in the game" with latency or ping of up to 129ms. The 35 best cities in the world for online gaming have ping rates of 8 to 28ms, an Ookla report last year said.
Latency tests are affected by the distance between the user and the server. The Ookla tests revealed on Reddit showed the tests going to servers in Los Angeles and Seattle; SpaceX's beta tests are slated for the northern US and southern Canada , but a Stop the Cap story says that testers so far are in rural areas of Washington state only.
reader comments
Channel ars technica.

Starlink Satellite Train Explained: Decoding the Linear Formation in the Sky
Product manager by day, Starlink enthusiast by night.

People all across the globe have reported seeing a straight line of white dots traveling across the night sky.
Before you freak out now: no, aliens are not taking over just yet. Instead, the phenomena, made possible by SpaceX’s Starlink, is commonly referred to as satellite trains.
In this article, I’ll detail what Starlink’s satellite trains actually are, how they can be spotted, and how many of those are roaming earth at any given time.
What Is a Starlink Satellite Train?
Starlink satellite trains are a collection of satellites that roam low-earth orbit (LEO) at close distances to each other.
This is how a satellite train I recently spotted from my backyard (sorry for the lackluster video quality) looks like out in the wild:
The fact that you can see Starlink’s satellites isn’t anything unique to the internet service provider (ISP). Whether it’s the International Space Station (ISS) or even the James Webb telescope, objects in space are visible due to the sunlight they attract.
However, what separates Starlink from other objects in space is the vastness of its constellation, which currently boasts close to 3,600 satellites in orbit.
SpaceX, as you can see on our dedicated launch statistics page , normally deploys around 50 or so satellites during a single launch.
Starlink has since reached the maximum number of version 1.5 satellites permitted by the FCC. It has now gone over to exclusively launch its so-called V2 Mini satellites – normally in groups of 20 to 22.
Those satellites initially orbit earth in multiple groups and take advantage of a concept called plane drift, thus enabling Starlink to cover various parts of our globe.
Recent Starlink launches are using plane-drift to share sats from a launch among even more orbit planes. This also increases the amount of time sats spend in orbit raising. Here is the launch from Feb 4, with 23% of sats still not at final altitude after over 4 months pic.twitter.com/XdrZbboB3E — Jonathan McDowell (@planet4589) June 16, 2021
The initially grouped together satellites then form the trains that we see back down on earth. Unfortunately, that sight is only of temporary nature.
According to Harvard scientist Jonathan McDowell (see tweet above), Starlink’s satellites remain in their train-like position for a few months after which they each go their separate ways.
More precisely, satellites operate in what McDowell calls the “intermediate orbit”, namely around 400km (~248 miles) distance to earth.
They then rise to an operational orbit, at a height of 550km (~341 miles), using the satellite’s thrusters. Around 80 or so percent of all satellites reach their designated orbit location while the rest malfunction for a variety of different reasons.
Luckily, people do not need to worry , though. The overwhelming majority of Starlink’s satellites burn up when re-entering earth’s atmosphere.
This is also why the trains have ‘holes’ in them, meaning the distance between each satellite isn’t equal as some have already departed for operational orbit.
Why Are Starlink Satellites in a Train?
The reason why Starlink’s satellites are roaming Earth in a train-like structure is manifold. First of all, releasing them in one sequence simply minimizes collision risk and thus space debris.
Here you can see a release sequence for Starlink’s Gen2 Mini satellites, which are grouped together as one:
Video of last night’s @Starlink satellite deployment pic.twitter.com/K7ezZLLusz — SpaceX (@SpaceX) September 16, 2023
Over time, those satellites are separating from each other, forming the train-like structure that you can then see back down on Earth.
Apart from the safety aspect, fuel efficiency is also of importance. Each satellite only has a limited amount of fuel, so sending them immediately to their designated orbit (550km) would use up even more of it.
Being grouped together in a train early on also allows ground controllers to more easily track them and make precise orbital adjustments.
For example, satellites can malfunction sometimes for different reasons. Being located in lower orbital shells and within the confinement of the train thus enables them to deorbit faster.
How to Spot a Satellite Train
There are a variety of online tools that enable you to track Starlink satellites as they roam the skies. The one that I used can be accessed here .
Simply add your country and city of residence, or alternatively longitude and latitude, and the tool shows you when to expect a satellite train.
Keep in mind that all of these tools are mere approximations given that their creators do not have access to real-time navigation data.
For example, Starlink relies on an autonomous collision avoidance system that changes a satellite’s direction whenever necessary.
SpaceX previously revealed that its Starlink satellites performed over 26,000 collision avoidance maneuvers in a span of two years (11/2020 – 11/2022). Therefore, on any given day, its satellites perform 75 maneuvers.
Another aspect to keep in mind is your environment. Satellite spotting works best in areas of low light pollution. So, small towns and nature are likely your best bet to spot a train of satellites.
Additionally, you want to make sure that the weather is on your side and thus offers a clear and cloud-free view of the night sky.
Lastly, keep in mind that the satellite train will only be visible for a few minutes, so simply being on time is essential to a great viewing experience.
How Many Starlink Trains Are There?
At any given time, there are a handful or more satellite trains that are visible to the human eye. The above-mentioned tracker page highlights their current location and projected directions.

Generally speaking, Starlink and SpaceX are incentivized to have as few spottable satellite trains as possible.
For once, satellites in intermediate orbit do not operate on the required frequency bands to provide internet services to customers back down on earth – thus not making money for Starlink.
Another aspect to consider is the mounting political pressure Starlink is facing. For example, its satellites are causing streaks in telescope images.
The fact that those trains are visible without relying on advanced technology only amplifies those concerns, regardless of how valid they may be.
Luckily, SpaceX has vowed to address those issues. In July 2022, it published a document highlighting the initiatives it already underwent and plans to undergo to mitigate the negative effects of its constellation.
Those include using a darker coating, adopting specular surfaces to deflect lighting into another direction, optimizing flight operations, and so forth. SpaceX also remains in constant exchange with those very same astronomers to ensure whatever it implements addresses their concerns.
Does Starlink Have Data Caps? Sort Of!
Starlink Best Effort Option Explained
37 thoughts on “Starlink Satellite Train Explained: Decoding the Linear Formation in the Sky”
First time here but for sure not the last. I really enjoyed your article regarding the Elon Musk Starlink Satellite Train explanation. Fascinating space insights and facts to learn about and sit in awe. Keep up the good work!
Thanks Bob!
Thank you sir!
Thanks for the excellent explanation of what the Starlink trains are. We saw it for the first time last night and were impressed with the sight.
Hi Keith, thank you & glad you enjoyed the article.
I observed Starlink and the ISS at the same time on August 1 2023! What a awesome sight
That’s awesome!
Great article, appreciate the insight. Hate that they are making them less visible. I love looking up in fascinated aww.
Thanks Chad!
Just saw the train tonite while I was out grilling. Was blown away and came in to ask my son what it might be – he said his friend had posted that he saw the same thing. We researched, and I found your informative article. Thanks!
Hi Scott, glad you enjoyed the article 🙂
Thank you for your article. I saw my first Starlink Train last night. What a sight! As it went directly over me the lights were blue. Is this part of the changes they are making? It was quite beautiful. I am curious to know the speed at which the trains travel. Do you happen to know?
Hi Kathleen, can’t comment on the light. However, the newer satellites should have not reflect as much, so glad that you still saw them! As far as speed, it takes SL satellites around 90 minutes to orbit around the earth. At an altitude of ~550km, that means they travel at a speed of approx. 7.7 km/s or 27,770 km/h (7.7 km/s x 3600 sec).
On August 11, 2023, about 21h30, I saw a Starlink Train over Hot Springs, SD. This was while camping, and sitting outside watching for the Perseid meteors. Had never heard of such a thing as this long column of blue dots, and thought it was a drone constellation from the Mt. Rushmore lighting display. But then, by coincidence, the next day I was researching Starlink Mobile (RV) service, and I came across the correct explanation.
Sounds like an awesome experience!
Saw satellite train over rural Missouri at 9.36 pm, on August 16. Had no idea what I was seeing. Was hesitant about saying anything until I found your site. Fun.
It’s always an awesome experience 🙂
Just saw them going over the city of Chicago!
I just saw this train in the clear skies of New Jersey this evening. I was just star gazing, but was treated to this amazing sight! Great article btw!
Hi Christine, awesome & big thanks for the flowers. 🙂
I was with a family group sitting around a bonfire, and the discussion had just turned to the possibility of extraterrestrial life. David, one member of our group, was arguing strongly that spaceship Earth was all alone when someone else spotted a strange set of moving dots high in the sky. Were they alien spaceships coming to prove David wrong, perhaps abduct him to prove it? He certainly fell silent, perhaps contemplating that possibility. Posing pictures of this phenomenon on Facebook led to a tip the next day, which led to this page. Thanks for clearing up the mystery.
Happy to be of help Doug 🙂
Also in New Jersey. Labor Day party grilling and hanging out. A group of about 14 people saw the train in the sky. About 20 minutes later (or less) we witness the meteor – a green fireball glowing as it came down to earth. (I did some research and determined it was somewhere overhead Hamilton, Maryland.)
Awesome sight during a party, that’s for sure! 🙂
Just spotted one for the 2nd time over Apache Junction AZ 9/06 2023at 8 PM. First time seeing one was December 03 2022 same place . So cool Thank you for your write-up
Hi Pamela, awesome & you’re welcome 🙂
Viktor, I saw a Starlink constellation on Sunday, Sept. 3, directly overhead at 9pm on Bethany Beach, DE. One of the persons I was with pointed up and then explained what it was after watching me for a minute marveling at it. I read a year ago that Starlink is a network of crosshatching orbiting satellites, I figured it was a pre-orbital pattern, which you confirm above.
I wonder about the astronomer’s who are complaining, considering airplanes, meteors, other satellites, and now drones filling the sky. What is your opinion? Are they just picking on Musk or is it a real complaint?
Hi Ron, the concerns that astronomers voice are somewhat legit. That said, a few points:
1) Starlink is doing a lot to diminish the light that its satellites reflect, for example applying darker coating. Their newer Gen2 sats specifically address some of those problems (feel free to have a read here: https://starlinkinsider.com/starlink-gen2-satellites/ ). 2) You can use various computer vision techniques to get rid of the streaks in images. 3) Many of most important and powerful telescopes, such as NASA’s James Webb or the proposed Lunar Crater Radio Telescope (LCRT) on the Far-Side of the Moon, are located above the altitude of Starlink sats.
If there’s one thing that SpaceX is great at, then it’s learning from past mistakes. I’d expect this issue to be figured out over time.
Just saw them go over Cornwall, England at 21.30 amazing sight
Awesome stuff David 🙂
Excellent article. It explains what we saw sitting around a campfire on our farm in Olean NY at approximately 9 pm last night. I’m used to seeing the space station and other satellites at much higher orbits and last nights “string of 20 pearls” seemed at a much lower orbit. Now I know why. Thank you.
Thanks Pierre, appreciate it 🙂
A month ago, the kids came in yelling about a space dragon… come look, come look. I didn’t get away from under the trees in time to see it. They were genuinely upset that i missed it, it had to be aliens. I discarded that event until tonight when another batch came across, this time i got to see it, awe inspiring for certain. This time i did some searching and we now know what they are. Musk is certainly the Tesla of our age (minus the destitute part). Wow.
Just outside of Allentown PA we saw a Starlink train pass overhead this evening. Really neat to see! It raised a question: about how long is a typical “train” way up there, and what is the distance between the individual “dots?” I know that will vary, But can you give an example?
Hi Chuck, Starlink normally deploys 20 to 23 V2 Mini satellites, so that should roughly be the train’s size. That said, satellites do have varying trajectories, depending on whether they function properly, designated orbital shells, and so forth. So, there’s no generalizable answer to that question except that it depends.
I saw the train a couple of nights ago I find it really hard to believe that I can easily see such small objects from 248 miles away
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
All things Starlink, SpaceX, and tech.
As an independent source of information, our aim is to assist users of the SpaceX Starlink satellite internet service. We are not connected with either SpaceX or Starlink in any official capacity. Our focus is on providing useful tips and tutorials for those interested in learning about Starlink.
© 2024 Starlink Insider
Last Updated on 2 months by Viktor
SpaceX launches 23 satellites on 1st leg of Starlink doubleheader
Liftoff occurred at 5:12 a.m. ET today (April 5).

SpaceX launched another batch of its Starlink broadband satellites this morning (April 5), on the first leg of a spaceflight doubleheader for the company.
A Falcon 9 rocket carrying 23 of SpaceX's Starlink spacecraft lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida today at 5:12 a.m. EDT (0912 GMT).
The Falcon 9's first stage then came back to Earth safely, making a vertical landing about 8.5 minutes after liftoff on the SpaceX droneship A Shortfall of Gravitas, which was stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.
Related: Starlink satellite train: How to see and track it in the night sky

It was the 14th launch and landing for this particular booster, according to a SpaceX mission description . The Falcon 9's upper stage, meanwhile, hauled the 23 Starlink satellites to low Earth orbit , deploying them there about 65 minutes after liftoff as planned.
— SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket ties 19 flight-record with launch from California (video)
— 8 ways that SpaceX has transformed spaceflight
— SpaceX launches Crew-8 astronaut mission to International Space Station for NASA (video)
This morning's launch was the 33rd orbital mission of the year already for SpaceX, and the 22nd of 2024 devoted to building out the giant Starlink megaconstellation.
The liftoff was also the first leg of a planned Starlink doubleheader: SpaceX plans to launch 21 more of the internet satellites from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California tonight during a four-hour window that opens at 10:31 p.m. EDT (0231 GMT on April 6).
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.
Trains, planes and a total solar eclipse! Watching the moon block the sun was a transportation adventure (exclusive)
Could these big expandable habitats help humanity settle the moon and Mars?
DJI Avata 2 drone review
Most Popular
- 2 Scientists identify origin of the 'BOAT' — the brightest cosmic blast of all time
- 3 My formal 2024 solar eclipse apology
- 4 Achoo! Baby star 'sneezes' tell astronomers a lot about their development
- 5 A NASA spacecraft spotted something weird orbiting the moon. It was just a lunar neighbor (photos)

ROAM WITH STARLINK
Work and play at remote locations. starting at $150/mo with a hardware cost of $599. 30 day trial with full refund if not satisfied..

WORK AND PLAY AT REMOTE LOCATIONS
Starlink offers high-speed internet almost anywhere across the world. Starlink connects within minutes and packs up quickly when it's time to move to your next destination.

GET ONLINE IN MINUTES
Set up Starlink with just two steps. Instructions work in either order:
1 PLUG IT IN
2 POINT AT SKY
Starlink requires an unobstructed view of the sky. Download the Starlink app to determine your best install location.
Download for android chevron_right Download for iOS chevron_right

USE STARLINK IN MOTION
In-motion use is supported with Mobile Priority service plans and the Flat High Performance hardware, which is designed for permanent installation on your vehicle.

WEATHER RESILIENT
Starlink is designed to endure the elements - it can melt snow and withstand sleet, heavy rain, and harsh winds.
"This is a must have item if you need to work remotely or like to travel off the grid but still want internet availability! Works very well!"
"As a full time RV customer we love our Starlink. We've had perfect internet everywhere we've been."
"Starlink has helped me with my online work, allowing me to go to different places with a reliable source of satellite internet and helping me decide to soon move and live in the countryside."

You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
- Moneycontrol Trending Stock
- Infosys INE009A01021, INFY, 500209
- State Bank of India INE062A01020, SBIN, 500112
- Yes Bank INE528G01027, YESBANK, 532648
- Bank Nifty
- Nifty 500
- Mutual Funds
- Commodities
- Futures & Options
- Cryptocurrency
- My Portfolio
- My Watchlist
- FREE Credit Score ₹100 Cash Reward
- My Messages
- Price Alerts
- Chat with Us
- Download App
Follow us on:
Starlink: What is Elon Musk’s satellite internet, how it works and more
Ahead of elon musk’s india visit, rumour mill is abuzz that he may announce the availability of starlink, a satellite-based internet service..

starlink elon musk
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is scheduled to visit India this month. Ahead of Musk’s visit, rumour mill is abuzz that he may announce the availability of Starlink, a satellite-based internet service. We explain what is satellite internet, how it works and other details
What is Starlink?
Starlink, as per the official website, is a constellation of thousands of satellites that orbit the planet much closer to Earth, at about 550km, and cover the entire globe. Starlink satellites are in a low orbit compared to other geostationary satellites, which makes it relatively easier to provide faster internet connectivity.
How does satellite internet work?
Your internet service provider — could be Starlink or any other — beams a signal to a high-flying satellite which bounces it off the antenna you have installed. The signal is then sent to a modem, which is installed in your house and that fires up the internet connectivity.
Related stories

Starlink does provide a whole kit to its subscribers. There are no cables or fibres, which is why it can be useful in remote areas. Musk has always emphasised Starlink reaching out in areas, where internet connectivity is a problem — like remote locations in India and other countries.
What do you need for Starlink satellite internet?
Starlink sells an installation/equipment kit depending on why you need satellite connectivity. There’s Starlink antenna — which is a dish that needs to be installed where you want satellite connectivity. There’s a router, a satellite link cable and an AC cable. Starlink also makes it clear that it “needs a clear view of the sky so it can stay connected with satellites as they move overhead. Objects that obstruct the connection between your Starlink and the satellite, such as a tree branch, pole, or roof, will cause service interruptions.”
How much does it cost, how fast is internet speed?
For those in remote and rural areas, satellite internet can be really useful. Starlink users typically experience download speeds between 25 and 220 Mbps, with a majority of users experiencing speeds over 100 Mbps. Upload speeds are typically between 5 and 20 Mbps, claims Starlink.
It’s not cheap. In the US, Starlink starts at $120 per month and depending on the plan you choose it can go up to $5,000. Not to forget the equipment cost which starts at $500 and goes up to $2,500.
Where is Starlink currently available?
The list of countries has grown over the last couple of years. USA, Canada, UK, France, the Netherlands, Denmark, Portugal, Australia, New Zealand are some of the countries where Starlink is currently available.

DAILY-EVENING

Discover the latest business news , Sensex , and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Trending news

- Swiggy delivery agent steals Nike shoes from Gurgaon flat, company reacts. Viral video
- His pitch on 'Shark Tank' was rejected. 5 years later, he returned to show as a judge
- Billionaire heiress stood in line for 2 hours to get job at her own store
- Why this startup is ‘returning cheques’ to its ‘Shark Tank India’ investors
You got 30 Day’s Trial of

- Ad-Free Experience
- Actionable Insights
- MC Research
- Economic Calendar

You are already a Moneycontrol Pro user.

Access your Detailed Credit Report - absolutely free
The News Of Tomorrow, Today
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Now you can get the top stories from Gizmodo delivered to your inbox. Enter your email below.
By subscribing you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
By subscribing you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Starlink: Everything You Need to Know About Elon Musk’s Satellite Internet Service in Australia
Here’s your guide to Starlink, how much it costs, and what you should know about SpaceX’s internet solution.
What is Starlink?
Starlink is a satellite internet service that operates internationally, reliant on a network of hundreds of low-Earth orbit satellites that beam an internet connection from space and to your home via a satellite dish. It’s a high-speed internet alternative to the NBN and 5G, although due to transmission distance, latency takes a hit, making it not an ideal solution for things like gaming.
Is Starlink available in Australia?
Starlink is out of beta, which means that you can now preorder the service in Australia. Head over to the website and see if your address is available. If you’re interested in the Starlink satellite map, you can find a handy third party tracking website here .
How much does Starlink cost in Australia?
Plugging your address into the website reveals that the total cost of the consumer service per month is $139. However, a $599 hardware fee and $30 shipping fee will also be incurred. That brings the price to start off to a total of $768, plus recurring monthly charges of $139.

The business plan offers speeds of between 150Mbps and 500Mbps for $750 per month, with a setup fee of about $3,740 (of course this is only available to business customers).
Additionally, you can also order a Telsa service that uses Starlink hardware. This costs $125 per month, plus a one-off $599 hardware fee, for 50Mbps download and 10Mbps upload speeds (slower than standard Starlink).
How many plans does Starlink offer?
At the moment, Starlink offers two plans. The normal plan offers unlimited data with speeds between 100Mbps and 200Mbps, billed at $139 per month. The business plan offers unlimited data with speeds between 150Mbps and 500Mbps for $230, $374 or $748 per month, depending on data allowance. Again, Telstra also offers a Starlink-leveraging plan , but it is not a Starlink-operated plan.
How fast is Starlink?
According to Starlink , users can expect speeds of between 100Mbps and 200Mbps on the service. Additionally, users can expect latency as low as 20ms “in most locations”.
According to Ookla , a website that measures internet speeds, Starlink users can experience download speeds of about 106Mbps on average and upload speeds of 11Mbps. Latency is reported at 66ms on average. This information comes from Ookla’s Q1 2023 Starlink report .
Additionally, Telstra’s new Starlink plan can supposedly achieve max speeds of 50Mbps download and 10Mbps upload.
How does Starlink compare to the NBN?
In terms of base speed, Starlink appears to offer a faster home internet experience than the NBN, with speeds of between 100Mbps and 200Mbps, depending on the conditions.
One of the most popular fast NBN plans, NBN 100, is capable of speeds up to 100Mbps, the low point of a Starlink plan (though this will likely be upgraded to NBN 500 in the coming year ). There are, however, NBN 250 and NBN 1000 plans available that will outpace Starlink, though these are limited to fibre and HFC connections.
That being said, it’s also more expensive than most NBN plans. At $139 per month, and with high starting costs, it’s difficult to say that it offers better value than the NBN.
Just on latency for a minute: NBN plans typically experience latency of between 8ms and 20ms , which is of course much better than what Starlink offers.
Due to the latency, it’s probably not worth getting a Starlink plan if you have a fixed-line NBN plan if you’re an avid gamer, however if you rely on satellite internet, you should consider it.
Does Elon Musk own Starlink?
Elon Musk himself doesn’t own Starlink, but Musk’s space company, SpaceX (of which he owns a 42 per cent stake and 79 per cent of voting power), operates the internet company.
How does this compare to NBN Sky Muster satellite plans?
Starlink’s biggest point of difference to the majority of the NBN is that it’s a satellite service. This means it can service areas that copper or fibre NBN can’t due to infrastructure limitations.
This is particularly relevant to a country as big as Australia, but we do already have Satellite internet.
Satellite NBN, or Sky Muster, is similar to Fixed Wireless in that it’s for rural areas that can’t connect to the NBN (or even 4G) in any other way. However, it takes it a step further as it’s able to service remote areas that don’t have stable 4G access.
The problem with Sky Muster is that it can really slow compared to other NBN services, though NBN Co has been working to improve this . Starlink does, at the time of writing, seem to offer higher base speeds.
Can I take my Starlink satellite dish elsewhere?
When you order a Starlink service, it will be tied to the property you order that service to. While the dish you receive from Starlink is widely portable, you’ll need to keep it at the same address for the service to work.
Starlink also allows customers to take the dish on the go for about $35 per month (local pricing is still to be confirmed).
Should I get a Starlink service?
If you live in a remote part of Australia and need a stable, reliable internet connection, you should probably consider Starlink. Though Skymuster offers a reasonable internet service, Starlink undoubtedly offers better performance, though it is far more expensive.
However, if you have a fixed-line internet service, it’s tough to recommend Starlink. You’ll be paying more for the setup and for ongoing costs than on most NBN plans, and although Starlink typically sees average speeds of 106Mbps (via Ookla), NBN 250 and NBN 1000 will outpace it – not to mention latency will certainly be better on a fixed-line service.
The Cheapest NBN 50 Plans
It’s the most popular NBN speed in Australia for a reason. Here are the cheapest plans available.
SpaceX launches latest Starlink missions, adding to low-orbit broadband satellite network

Two hours before sunrise, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket illuminated the predawn darkness during a Friday morning liftoff from Florida's east coast, marking another expansion of the company's Starlink network.
The early-bird Starlink mission lifted off at 5:12 a.m. EDT, shipping another payload of 23 Starlink broadband satellites into the company's ever-growing constellation in low-Earth orbit.
In a post on X last week, SpaceX officials announced Argentina is now the 72nd country worldwide — and seventh in South America — that can access Starlink high-speed internet service.
Following Friday's rocket stage separation, the Falcon 9 booster landed atop SpaceX's drone ship A Shortfall of Gravitas out on the Atlantic Ocean, wrapping up its 14th mission, Florida Today, part of the USA TODAY Network, reported. The booster previously launched CRS-24, Eutelsat HOTBIRD 13F, OneWeb 1, SES-18 and SES-19 and nine Starlink missions, according to SpaceX.
PHOTOS: See the best pictures from SpaceX southern California launch
SpaceX had a second Friday launch scheduled in California: A Falcon 9 was scheduled to send up 21 Starlink satellites — including six with direct-to-cell capabilities — at 10:31 p.m. EDT from Vandenberg Space Force Base.
In Brevard County, Air Force officials are preparing an environmental impact statement examining SpaceX's proposal to convert Launch Complex 37 into a Starship-Super Heavy launch facility by 2026 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Base. Public open houses were conducted last month in Cocoa, Titusville and Cape Canaveral to collect public comments about the massive rocket system.
Next on the launch calendar, SpaceX is targeting Sunday evening for its next mission from the Cape, Federal Aviation Administration and National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency navigational warnings show. More information:
- Mission: A SpaceX Falcon 9 will launch a Bandwagon-1 "rideshare" payload of small satellites from NASA's Kennedy Space Center.
- Launch window: 7:12 p.m. to 7:50 p.m.
- Location: Pad 39A.
- Live coverage: Starts 90 minutes before liftoff at floridatoday.com/space .
Then on Tuesday, United Launch Alliance continues to target 12:53 p.m. for the historic last launch of a Delta IV Heavy triple-core rocket on the NROL-70 national security mission from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
SpaceX’s high-flying Starlink still searching for stable financial orbit
Maxwell Nelson, a seasoned journalist and content strategist, has contributed to industry-leading platforms, weaving complex narratives into insightful articles that resonate with a broad readership.

SpaceX’s Starlink, lauded for its ambitious global internet service, is reportedly in a financial paradox, burning through cash at a rate that questions its profitability claims, according to Bloomberg reporting . Despite assertions from CEO Elon Musk and SpaceX executives of reaching “profitable territory,” insiders revealed to Bloomberg that the reality of Starlink’s finances is more complex, especially concerning the costs associated with its ground terminals and satellite launches.
Though it boasts over 2.6 million customers, Starlink allegedly omits the significant expenses of satellite deployment in its financial presentations to investors, creating an overly optimistic portrayal of its fiscal health. This accounting practice has led to skepticism about the satellite business’s operational profitability, contrasting Musk’s previous announcements of achieving “breakeven cash flow.”
As SpaceX continues to redefine the aerospace industry with its reusable rockets and the sheer number of satellites deployed , the financial sustainability of its satellite internet service comes under scrutiny. Valued near $180 billion, SpaceX’s reliance on Starlink for revenue is evident, especially as the company seeks to fund Musk’s vision of Mars colonization. Yet, the ambition of reaching millions more customers necessitates a network expansion that could exacerbate existing capacity and cost challenges.
Starlink’s capacity constraints and speed bumps
Starlink’s quest for global coverage faces hurdles, not just in the technological realm but also in market penetration. Urban saturation has begun to affect service performance, a situation SpaceX hopes to alleviate with the introduction of more advanced satellites. However, the promise of improved services with the upcoming Starship rocket launches remains contingent on overcoming significant testing milestones.
While Starlink’s appeal to major airlines has been limited, its success in rural and maritime sectors demonstrates the service’s potential. Partnerships with companies like Carnival Cruise Lines and Anglo-Eastern Ship Management highlight Starlink’s ability to offer vital internet services in areas traditionally underserved by traditional providers.
The path to consistent profitability for Starlink involves reducing manufacturing and operational costs while expanding its subscriber base. With revenue projections optimistic, SpaceX may explore additional financing or an IPO for Starlink, though such plans remain speculative. Yet, as Starlink navigates these financial and operational challenges, its impact on global internet access continues to grow
About ReadWrite’s Editorial Process
The ReadWrite Editorial policy involves closely monitoring the tech industry for major developments, new product launches, AI breakthroughs, video game releases and other newsworthy events. Editors assign relevant stories to staff writers or freelance contributors with expertise in each particular topic area. Before publication, articles go through a rigorous round of editing for accuracy, clarity, and to ensure adherence to ReadWrite's style guidelines.
Maxwell Nelson Tech Journalist
Related news.

Stream like you are in the Fallout Vault with this themed gear from Elgato

Niantic teases Necrozma ahead of Pokémon Go Fest 2024

Cool new city builder will let you construct the metropolis of your dreams across four distinct eras

Free Xbox games to play this weekend including Fallout 76
EA Play prices hiked – increases land on all tiers from next month
Most popular tech stories.
- GTA 6 – Release date, trailers, setting, and everything we know so far
- Samsung Galaxy S25: release date, specs and price
- 5 best AI content detectors
- iPhone 16 Pro: release date and rumors
- Most Trending Cryptocurrency Today – Ethena, Meme Ai, Dogwifhat
Latest News

LEGO 2K Drive races onto Xbox Game Pass
Xbox Game Pass is getting a Mario Kart-like in the brick-based form of LEGO 2K Drive this month. The popular racing sim was free for PlayStation Plus subscribers in December...

Fallout 4's next-gen update finally arrives, in time for Amazon's hit show

Humane AI pin reviews: Critics savage $699, no-screen wearable

Pepe Price Prediction: The Top Meme Coin Eyes $0.0000080 Ahead Of Bitcoin Halving; Time to Buy?

ESMA warns of crypto trading concentration on Binance
Popular topics, get the biggest tech headlines of the day delivered to your inbox.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy. Unsubscribe anytime.
Explore the latest in tech with our Tech News. We cut through the noise for concise, relevant updates, keeping you informed about the rapidly evolving tech landscape with curated content that separates signal from noise.
Explore tech impact in In-Depth Stories. Narrative data journalism offers comprehensive analyses, revealing stories behind data. Understand industry trends for a deeper perspective on tech's intricate relationships with society.
Empower decisions with Expert Reviews, merging industry expertise and insightful analysis. Delve into tech intricacies, get the best deals, and stay ahead with our trustworthy guide to navigating the ever-changing tech market.
SpaceX rocket launch sends advanced satellite into low orbit, brings booster back to Earth

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Early risers on California’s Central Coast and parts south were treated to a rocket launch Thursday morning, followed by a sonic boom.
SpaceX launched a weather satellite into low Earth orbit from the Vandenberg Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County at 7:25 a.m. Roughly 8 minutes later, the booster safely returned to Earth a little lighter after its payload separated in low orbit. The rocket’s launch and return was livestreamed and marked the 279th landing of an orbital rocket, according to SpaceX.
The United States Space Force mission carried out by SpaceX was considered a success and marked the company’s second national security mission for the year.
The spectacle was visible, and audible, to people in parts of San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara and Ventura counties.
The first stage of the company’s Falcon 9 rocket caused a sonic boom — which has been known to startle people — after the booster broke the speed of sound on the way down.
Instead of crashing to earth, the rocket fired again and powered itself to a soft — but very hot and smoky — landing.
Falcon 9 was the first reusable rocket to reach orbit, according to the company, and being able to use it repeatedly drives down the cost of space flight. Thursday’s mission marked the third launch for the reusable booster rocket, which helped get two previous Starlink missions into low orbit, according to SpaceX.

Rockets? Meteors? UFOs? Here’s what really caused Tuesday morning’s sky show
Debris from a Chinese spacecraft lit up the SoCal sky early Tuesday. Space junk is of growing concern as low earth orbits get increasingly clogged.
April 2, 2024
The satellite Falcon 9 carried is designed to monitor weather and environmental conditions such as sea ice, snow depth, soil moisture and wind.
More to Read

SpaceX is launching more rockets from a military base. Can the Coastal Commission impose a limit?
April 11, 2024

SpaceX rocket launches over Southern California after four-day delay
April 1, 2024
Look to the skies this weekend for another SpaceX rocket launch
March 29, 2024
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Jack Dolan is an investigative reporter for the Los Angeles Times. A winner of numerous national awards, he has twice been named a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize.

Nathan Solis is a Metro reporter covering breaking news at the Los Angeles Times. He previously worked for Courthouse News Service, where he wrote both breaking news and enterprise stories ranging from criminal justice to homelessness and politics. Before that, Solis was at the Redding Record Searchlight as a multimedia journalist, where he anchored coverage of the destructive 2017 fires in Northern California. Earlier in his career, he worked for Eastsider L.A.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Airbnb rentals could be harder to come by in Hawaii. Here’s why and when that might happen

San Francisco man arrested after allegedly vandalizing mosque, leaving community ‘living in fear’

From anger to appreciation, O.J. Simpson’s death elicits wide range of reactions

Paul Flores, Kristin Smart’s convicted murderer, attacked and stabbed in prison again
Astronauts get eerie view of Moon’s shadow as it trudges across Earth during solar eclipse
The astronauts living and working on the international space station orbit the earth about every 90 minutes, witnessing 16 sunrises and sunsets day, along with up to five eclipses a year. on monday, the massive black hole from the moon's shadow could be seen from space down on the planet below..

Watch: Colorful eclipse in Arkadelphia, Arkansas
Stephen Morgan and Kendall Smith take us to Arkadelphia, Arkansas during totality. The video is saturated with color.
Astronauts on the International Space Station had an eerie view during the total solar eclipse on Monday as the Moon's shadow raced across the planet's surface.
Waiting for totality on Earth took more than an hour after the partial eclipse began, but the low-Earth orbit's view provided context for how fast the Moon's shadow is moving. According to NASA , the eclipse shadow travels at 1,100 mph at the equator and up to 5,000 mph near the poles.
AMERICA’S TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE DAZZLES COUNTRY AS MILLIONS SCRAMBLE TO FIND BEST VIEW
The astronauts living and working on the ISS orbit the Earth about every 90 minutes, witnessing 16 sunrises and sunsets in 24 hours and up to five eclipses a year.
On Monday, the astronauts could not only see the eclipse as the Moon blocked the face of the Sun, but the Moon's shadow down on Earth as it blocked the sunlight over the path of totality – looking like a floating black hole on Earth down below.
The ISS wasn't the only view of the solar eclipse from space. SpaceX founder Elon Musk shared the video below, which was taken by a Starlink satellite in low-Earth orbit.
MISS THE APRIL 8TH TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE? HERE’S A LIST OF FUTURE CELESTIAL EVENTS
The video shows the Moon's umbra or shadow as it moves across the planet.
While the Moon was moving in front of the Sun's face, solar and Earth-observing spacecraft recorded the eclipse in real time.
NOAA's GOES-East satellite tracked the Moon's shadow moving across the Pacific Ocean and North America while the European Space Agency's Proba-2 satellite recorded the eclipse looking toward the Sun.

NOAA satellite captures total solar eclipse moving across America
Different views from NOAA's GOES East satellite show the umbra or shadow of the Moon during the eclipse sweeping from the Pacific Ocean to Atlantic Canada. (video credit: NOAA)
- Earth & Space
- Spaceflight
- Solar Eclipse

IMAGES
COMMENTS
While uhoh did the standard basic math, You can check public TLE data for almost all satellites, which contains an approximate orbital period. For Starlink satellites, you can find info here.So you'll see that the (approximate) periods are between 89.73 and 91.53 minutes as of 03Feb2020.. The reason for the "approximate" period, is that first, due to perturbations, there will always be slight ...
But the other trend is noticeable improvement in both upload speeds and latency. In the three years we have been testing Starlink, upload speeds have been trending upward, from 10Mbps in 2022, to ...
In conclusion, Starlink satellites travel at a variety of speeds. The typical speed of a Starlink satellite is 18,000 mph (28,968 km/h), while the maximum speed is 22,000 mph (35,406 km/h). The average velocity of a Starlink satellite is 5.8 m/s, while the peak velocity can reach up to 11 m/s. The speed of a Starlink satellite is determined by ...
Even though both wallow down in the 20Mbps-or-less range from time to time, our 2023 results were consistently higher, while our 2022 numbers rarely climbed above 20Mbps. Even at its slowest ...
A Starlink satellite's lifespan can also be cut short by powerful geomagnetic storms. On Feb. 3, 2022, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket made a routine and successful launch of 49 Starlink satellites from ...
So, a user's home antenna connects to a Starlink satellite as it passes overhead, which in turn links them into the nearest gateway. As a result, in addition to their own antenna, users need to ...
Order fulfillment can take up to six months or more. Starlink's Standard service now costs $120 per month for 24-220 Mbps. Meanwhile, its Business plans are available in three different packages ...
Starlink satellites are designed to offer users worldwide high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity. The satellites are placed in low Earth orbit, approximately 550 kilometers above the Earth ...
For many Starlink users, we suspect these changes are negligible. Starlink in Mexico was the fastest satellite provider in North America. Starlink in Mexico had the fastest satellite internet in North America during Q1 2022 with a median download speed of 105.91 Mbps, followed by Starlink in Canada (97.40 Mbps) and the U.S. (90.55 Mbps).
Starlink is the world's first and largest satellite constellation using a low Earth orbit to deliver broadband internet capable of supporting streaming, online gaming, video calls and more. Leveraging advanced satellites and user hardware coupled with our deep experience with both spacecraft and on-orbit operations, Starlink delivers high-speed ...
When we look at the performance results from our Starlink review in 2022, and measure them against the new performance results from 2023, one thing becomes very clear: Starlink got better. Just ...
As those desk-sized satellites travel to their final positions, they brightly reflect light, irking many skygazers. As of June 2021, there are over 1,500 Starlink active satellites, making Starlink the largest satellite constellation around Earth. In fact, SpaceX now owns more than half of all active satellites circling our planet.
Starlink speeds over 100 Mbps in 14 European countries during Q2 2023, speeds stabilizing across Europe. Key takeaways: Starlink results were the fastest among satellite providers we surveyed. Starlink quarter-to-quarter speeds improved or remained about the same (between 5% and -5%) in 23 countries, while decreasing in 4 countries.
Appearing as a string of bright lights in the sky, Starlink trains can look rather "otherwordly" and have prompted numerous UFO-sighting reports when they first took to the skies. But the long ...
Known as Starlink, the project aims to bring high-speed internet to every corner of the planet. SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk announced the Starlink concept in Jan. 2015, explaining the company ...
349. Beta users of SpaceX's Starlink satellite-broadband service are getting download speeds ranging from 11Mbps to 60Mbps, according to tests conducted using Ookla's speedtest.net tool. Speed ...
High-speed internet. Available almost anywhere on Earth. Personal. Business. ... Starlink can adjust terms and pricing as needed, and you can cancel at any time, for any reason. ENGINEERED BY SPACEX. As the world's leading provider of launch services - and the only provider with an orbital class reusable rocket - SpaceX has deep experience ...
See the night sky come alive with Starlink satellite trains, delivering fast internet across the globe with SpaceX's cutting-edge satellite technology. ... At an altitude of ~550km, that means they travel at a speed of approx. 7.7 km/s or 27,770 km/h (7.7 km/s x 3600 sec). Reply. J.R. Johnson. August 14, 2023 at 12:35 am On August 11, 2023 ...
As objects orbiting at 340-1150km in altitude, Starlink satellites will orbit at between 7.70km/s (orbit every 91 minutes) and 7.28km/s (orbit every 108 minutes). Reply reply mindbridgeweb
Get satellite internet on the go with Starlink Roam review. In our article, we break down Starlink Roam (also called Starlink Mobile) features, performance, and real-world experiences to make an informed decision for your travel experience. ... Screenshot of our next Starlink Roam speed test, where we got almost 80Mbps. Image credit: TJ Kolanko ...
Calculate when you can see the SpaceX Starlink satellites above your location. OK. Home. Live Map. Help. Results. Find Starlink. Check when you can see it! ... DIM means the satellite might not be very visible. ... The satellites move at an unbelievable speed. They travel nearly 500 km/300 miles EVERY MINUTE. But because they're so high up in ...
The liftoff was also the first leg of a planned Starlink doubleheader: SpaceX plans to launch 21 more of the internet satellites from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California tonight during a ...
Starlink coverage map of Europe (Credit: Starlink.com) For other parts of the world, the maps show that Starlink offers significantly better broadband quality in Europe, where the download speeds ...
Starlink offers high-speed internet almost anywhere across the world. ... "This is a must have item if you need to work remotely or like to travel off the grid but still want internet availability! ... allowing me to go to different places with a reliable source of satellite internet and helping me decide to soon move and live in the ...
How much does it cost, how fast is internet speed? For those in remote and rural areas, satellite internet can be really useful. Starlink users typically experience download speeds between 25 and ...
The normal plan offers unlimited data with speeds between 100Mbps and 200Mbps, billed at $139 per month. The business plan offers unlimited data with speeds between 150Mbps and 500Mbps for $230 ...
SpaceX had a second Friday launch scheduled in California: A Falcon 9 was scheduled to send up 21 Starlink satellites — including six with direct-to-cell capabilities — at 10:31 p.m. EDT from ...
Despite Starlink's 2.6 million subscriber base, insiders reveal SpaceX's satellite business is grappling with financial challenges. ... Starlink's capacity constraints and speed bumps.
SpaceX launched a weather satellite into low Earth orbit from the Vandenberg Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County at 7:25 a.m. Roughly 8 minutes later, the booster safely returned to Earth a ...
The video shows the Moon's umbra or shadow as it moves across the planet. While the Moon was moving in front of the Sun's face, solar and Earth-observing spacecraft recorded the eclipse in real time. NOAA's GOES-East satellite tracked the Moon's shadow moving across the Pacific Ocean and North America while the European Space Agency's Proba-2 ...