Breeze In Busan
- Send us your news
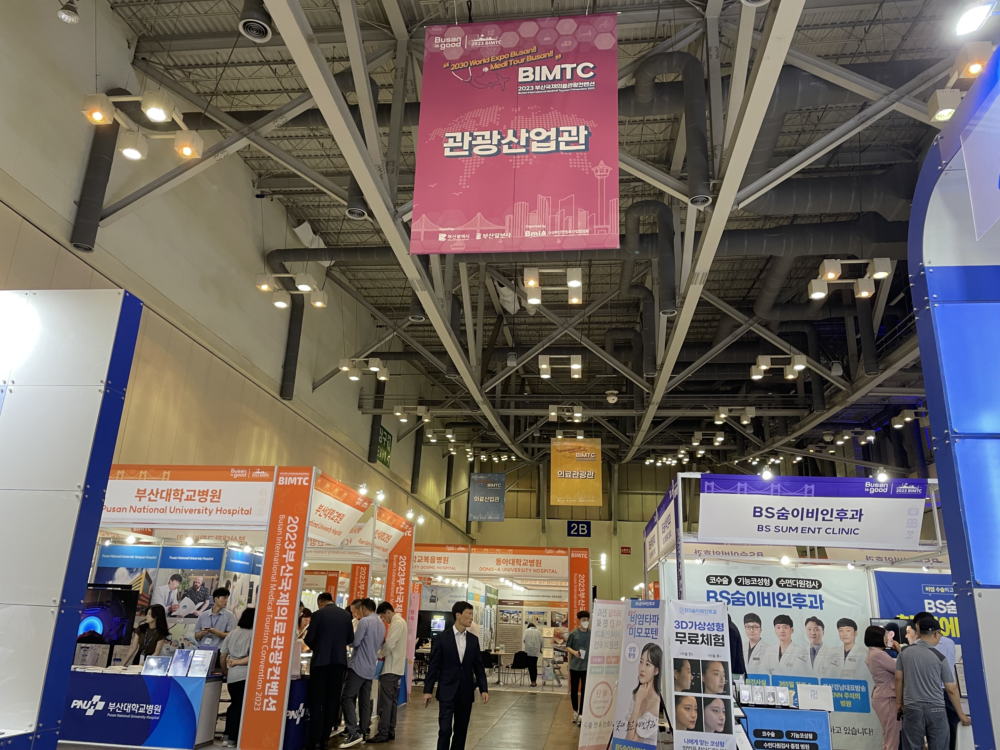


Busan’s Medical Tourism: Ambition, Reality, and The Path Forward
A reality check for busan's medical tourism vision global outreach and grand conventions can only succeed if underpinned by genuine expertise, preparation, and commitment to the cause..

In the rapidly evolving arena of medical tourism, cities across the globe are vying for a spot under the limelight. Busan’s stewardship of the International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 is more than a display of its medical prowess; it’s emblematic of a city in metamorphosis, poised to stake its claim in the expansive medical tourism domain. While Seoul may frequently capture the international spotlight, Busan’s initiatives mirror the ambitions of emerging global cities, each striving to etch its distinctive imprint on the world stage.
However, every ambitious tale has its underlying complexities. Enter Seo-gu, a pivotal district in Busan’s medical tourism strategy. With its arsenal of medical institutions, Seo-gu is more than equipped to be a medical hub. Yet, the district faces an impending demographic challenge: a declining population. The christening of Seo-gu as Busan’s Medical Tourism Special Zone was a dual-purpose strategy. While on one hand, it signaled Busan’s intent to upscale its medical offerings to international visitors, it also addressed an internal challenge — the need to rejuvenate a district facing population decline.
Busan’s officials have been vocal in promoting Seo-gu’s strengths. They point to the district’s top-tier hospitals and its picturesque landscapes, imagining a future where medical excellence and natural beauty coalesce. This vision received a significant boost in 2022 when Seo-gu was designated as a specialized development zone for the medical industry by the Ministry of SMEs and Startups. Hopes were high, with promises of state-of-the-art infrastructure and a thriving medical R&D ecosystem.
Busan’s Medical Tourism Proposition: Between Potential and Reality
The recent Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 shed light on Busan’s ambitions. The city’s aspirations were clear: to emerge as a leading global destination for medical tourism. But aspirations are one thing, reality another.
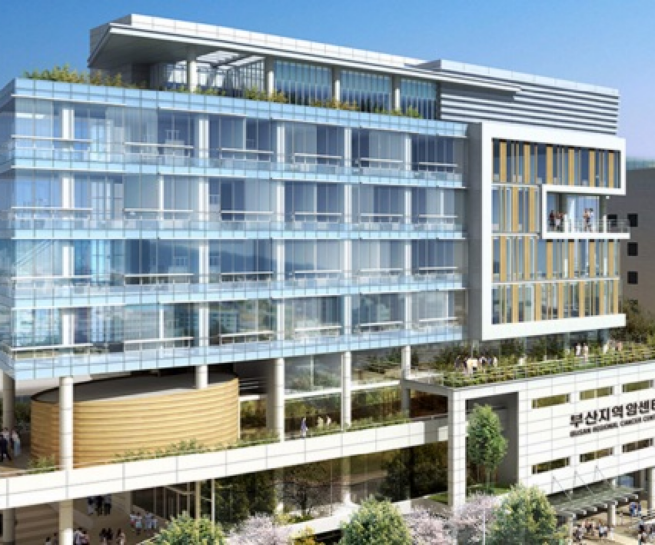
Busan’s medical infrastructure is undeniably impressive. The city prides itself on its robust healthcare network, comprising renowned university hospitals, comprehensive general hospitals, and a multitude of specialized clinics. This solid framework is a testament to Busan’s commitment to healthcare excellence. Tourists seeking medical intervention in Busan aren’t just assured of quality treatment. The city, with its natural wonders like Geumjeongsan and Haeundae, promises a holistic healing experience.
Furthermore, events like the Busan International Film Festival and the Busan Biennale amplify the city’s global allure, making it not just a medical destination but a cultural one.
However, a deeper dive into patient demographics presents a challenge. Unlike Seoul, which attracts North Americans and Japanese in droves, Busan’s clientele is predominantly from Central Asia. This demographic skew underscores the need for Busan to broaden its outreach.
The enthusiasm around Seo-gu’s designation as a Medical Tourism Special Zone was palpable. But is the district living up to its promise? Feedback from ground zero suggests a disparity between the anticipated growth trajectory and the present scenario.
Busan stands at an interesting crossroads. Its potential as a top-tier medical tourism destination is evident. However, realizing this potential requires strategic recalibration. The city’s stakeholders and policymakers must engage in introspective strategizing to bridge the gap between ambition and reality.
The Global Medical Tourism Landscape & Busan’s Intended Role
As we advance into the 21st century, the global medical tourism market has grown exponentially. This can be attributed to factors such as rising life expectancy and an aging global population. As a result, there’s an evident surge in individuals willing to cross borders to seek specialized and high-quality medical treatments. Korean medical institutions, sensing this wave, have actively endeavored to build overseas networks and partnerships.
Busan, a fresh entrant into this domain, has been zealous in its attempt to stake a claim. The ambition isn’t just reflected in the city’s medical infrastructure or the quality of services provided. It’s a holistic vision, one which aims to foster global collaborations, propagate knowledge exchange, and ensure patient-first initiatives.
Busan International Medical Tourism Convention (BIMTC): An Eye-Opener
In line with this vision, the 15th Busan International Medical Tourism Convention was anticipated to be a significant milestone. On paper, the event was impressive: participation from 13 countries, a setup of over 200 booths, and the expectation to attract approximately 40,000 visitors. It promised to be an arena for knowledge sharing and an epitome of international collaboration in medical tourism.
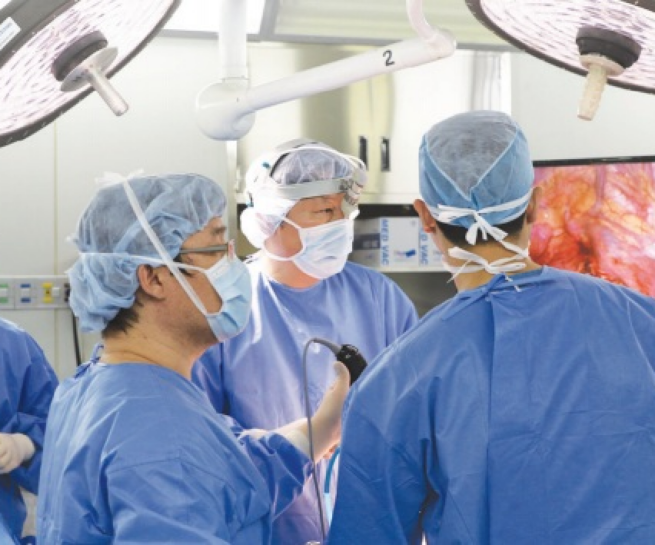
However, a ground-level visit and subsequent interviews with various hospital representatives painted a starkly different picture. Many of the booths were vacant, the footfall was significantly lower than anticipated, and the energy that should have crackled through such a convention was palpably absent. The aspiration to attract international patients seemed more of a distant dream than a present reality. Many hospitals, while present in body, seemed to lack a strategic vision and professional drive for international patient acquisition.
This dissonance between expectation and reality served as a wake-up call. The convention, which should have been a testament to Busan’s earnest endeavors in medical tourism, inadvertently highlighted the gaps in preparation, dedication, and execution.
A Reality Check for Busan’s Medical Tourism Vision
The learnings from the BIMTC are clear: while Busan has the infrastructure and the potential to become a frontrunner in the medical tourism sector, there’s a tangible need for a more concerted and professional approach. Global outreach and grand conventions can only succeed if underpinned by genuine expertise, preparation, and commitment to the cause.
Busan stands at a crossroad. It can either take the feedback from this convention constructively, addressing the gaps and bolstering its strategy, or continue with a veneer of ambition without the foundational commitment. The choice will dictate its place in the global medical tourism landscape.
The Pulse of Busan’s Medical Scene: A Reality Beyond The Facade
Busan’s Seo-gu, following its designation as the Medical Tourism Special Zone, has seen waves of anticipated change. This strategic move wasn’t just to thrust Seo-gu into the limelight but also to revitalize a district facing population decline. With its flourishing medical infrastructure and serene landscapes, the district promised an enticing blend of world-class health services within a leisure-filled environment.
However, upon a closer look, the narrative reveals some wrinkles. Direct conversations with representatives from the four major hospitals in the district showed a mixed bag of enthusiasm and concern. A glaring observation was the conspicuous absence of North American patients. While these hospitals have successfully catered to various international demographics, the North American segment remains largely untapped. More than just a demographic miss, it highlights a larger issue: a potential lack of readiness or strategic direction to cater to this specific patient group.
Charting the Road Ahead: Challenges and Vistas
It’s crucial to distinguish between intent and execution, and Seo-gu offers a case study in this distinction. The anticipation around its potential as a medical tourism hub is palpable, but the on-ground realities sometimes sing a different tune.
There’s an unmistakable urgency to bridge this gap. For Busan to genuinely compete on the global stage, it needs a robust, dedicated platform that can not only attract but also efficiently serve foreign patients. The emphasis on North America isn’t arbitrary; it represents a significant chunk of the global medical tourism market, and tapping into this demographic can change the game for Busan.
Embracing Global Potential: The Road to Becoming a Beacon in Medical Tourism
Every aspiring global city can benefit from looking beyond its shores, and Busan is no exception. By integrating its abundant medical and touristic offerings, Busan has the potential to offer a holistic experience that few global cities can rival.
There are lessons to be learned from global counterparts. Cities like Bangkok, Singapore, and Dubai have successfully etched themselves onto the global medical tourism map. Their success stories are grounded in the synergy of advanced medical care, effective international outreach, and an overall appealing environment for recuperation.
Busan stands poised with all the ingredients for success. The amalgamation of top-notch medical services with its diverse cultural and natural tapestry sets it apart. However, to truly shine on the global stage, Busan must engage in introspection, take stock of its strengths and weaknesses, and chart a path that mirrors global best practices while staying true to its unique offerings.
In essence, while the road ahead may seem daunting, with a diligent approach, Busan can very well morph into a global beacon for medical tourism. The task is to marry ambition with meticulous planning and execution.
Reflecting on Busan’s Ascent and Charting a New Path Forward
The burgeoning world of medical tourism presents a landscape rife with opportunity, driven by the intertwined elements of healthcare advancements and the allure of travel. At the heart of South Korea’s ambitions in this sector are two cities: Seoul and Busan. However, a dive into the statistics reveals a tale of two vastly different trajectories.
Seoul, with its established prominence, has successfully harnessed a wide-ranging international patient demographic, notably from North America and Japan. Its well-laid infrastructure, coupled with a focused approach to international outreach, has positioned it as a preferred destination for medical travelers.
Busan, on the other hand, while not short of ambition, currently draws its primary clientele from Central Asia, with China, Russia, and Mongolia taking the lead. The evident absence of a significant North American clientele, as mirrored in the interviews from Seo-gu’s major hospitals, paints a picture of potential untapped.
The recently concluded Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 was both a beacon of hope and a reflection of challenges. While it represented Busan’s commitment, firsthand observations relayed empty booths and a discernible lack of preparedness in some sectors. This chasm between anticipation and on-ground reality underscores a need for reevaluation.
Yet, the path ahead, while riddled with challenges, is also abundant in opportunities. Busan, with its enviable meld of medical excellence and touristic splendor, holds the potential to be more than just a secondary option. The key lies in adopting a two-fold strategy:
- Strategic Outreach: Leveraging the lessons from Seoul’s success, Busan must invest in a dedicated platform focused on comprehensive international outreach, particularly targeting North America. This includes language and cultural training for medical staff, enhanced international patient services, and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Synergizing Medical and Tourism Offerings: Beyond clinical excellence, Busan’s natural and cultural landscapes can offer a holistic recuperation experience. Packages that combine medical procedures with touristic exploration could be an innovative way to draw in more international patients.
In retrospect, our exploration into Busan’s medical tourism landscape has been enlightening. From the promises of the Busan International Medical Tourism Convention to the realities of Seo-gu, and the juxtaposition of Busan’s potential against Seoul’s achievements, the journey has been one of discovery. Busan stands on the precipice of a transformative era. With calculated steps, astute strategies, and a vision harmonized with ground realities, the city can not only compete with the likes of Seoul but also etch its unique legacy in the realm of global medical tourism. The narrative of Busan’s ascent is still being written, and with the right measures, it can be a story of unprecedented success.
You Might Also Like
Resignations surge among new “mz generation” public servants amid record low application rates, the dual edges of urban redevelopment in south korea, constructing urban rail systems in soft ground areas, south korea faces unprecedented low birthrate crisis, the battle over medical quotas in south korea.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Chinese (Simplified)
We recommend tour routes where medical tour patients and their families
Who are fatigued by covid can heal their minds and bodies with the beautiful nature and various experiences of busan., wellness busan.
- Blue Recovery
- Green Recovery
Ahopsan Forest Phytoncide Trekking
Enjoy the phytoncide as you trek through the bamboo and cypress trees of the Ahopsan Forest.
Jangan Temple Meditation Road
Have a quiet moment of meditation at the quiet Jangan Temple, located in a forest.
Gijang Market Snow Crab Street
The largest snow crab restaurants in Busan are located in Gijang Market. Try the snow crabs here, which are delicious and also good for the health.
Busan X the Sky Observation Deck
Enjoy the view of the sea of Haeundae and the Gwangan Bridge from the tallest building in Busan (100th floor).
Dalmaji Road Traditional Teahouses
Drink traditional tea at the various traditional teahouses along the Dalmaji Road and have some time to heal your mind and body.
Cosmetic Clinics & Hospitals

Enjoy Beauty, Catering and Scenery
Nowadays, more and more people consider cosmetic surgery a valuable self-investment. A pleasing appearance is the sublimation of rich connotations and is an expression of self-care and love, which can help open up a better future. With Korean dramas and K-pop sweeping the globe, the looks of Korean stars have also been the subject of fans' fervent pursuit, sparking strong interest in Korean cosmetic surgery among the public.
Busan, Korea has become a popular destination for people seeking cosmetic surgery. It is home to hundreds of Korean plastic surgery hospitals and is a place where Korean stars often frequent. In Busan, not only can you enjoy the latest and most advanced cosmetic surgery techniques, but you can also experience a life closest to that of Korean celebrities.
Follow us and easily embark on a medical tourism journey to Busan, Korea.
The Trend of Korean Medical Tourism
In recent years, the trend of traveling to Korea has been increasing. Statistics show that about 7.5 million people visit Korea every year, and more than 80,000 of them come for cosmetic surgery. Today, Korea's top medical equipment and top-notch plastic surgeons are gaining more recognition.
The Korean government is fully aware of the importance of medical tourism and is promoting it vigorously worldwide. Through medical tourism, Korea showcases its fascinating scenery, advanced medical facilities, and world-class doctors. CNN has already recognized Korea as one of the top destinations for medical tourism and a place of beauty, plastic surgery tourism, and will become the absolute core of Asia's medical tourism industry.

An unique tourism city
With 3.5 million citizens, Busan is 2nd biggest city to Seoul, and is the biggest port city in Korea.
Lonely Planet just named it the number one destination on its 2018 Best in Asia list. Busan, about a 2.5-hour journey from Seoul, is the country's second largest city and a popular summer destination famous for delicious seafood and picturesque beaches.
"A stunning confluence of scenery, culture and cuisine, Busan packs an eclectic offering of activities to suit all travelers: hike hills to Buddhist temples, settle into sizzling hot springs and feast on seafood at the country's largest fish market," reads Lonely Planet's top 10 list. "Poised to steal the spotlight, Busan is East Asia's Culture City for 2018 and will be at its most vibrant with colorful events showcasing the country's cultural heritage, from street art festivals to traditional dance shows."
1st place for the best medical cityby Korea’s National Brand
By focusing on medical industry, Busan is well-set to be a hot tourist site for medical trips in North-east Asia and has established world-class medical infrastructure, by employing heavy particle accelerator (2023) and robotic surgery center in Korea for the first time. In addition, the city has 5,000 medical institutes with outstanding experts, as well as brilliant medical clusters such as Seomyeon medical street, that enable such medical centers to create synergies together. High-quality medical services covering cosmetic surgery, dermatology, and dentistry, as well as severe diseases such as brain and heart disease and tumor are provided.

Our Principles
Experienced specialists provide you with professional medical beauty consultation and program planning, make the best choices for you, and arrange the most suitable medical beauty institutions, saving you a lot of time searching and screening.
Reasonable prices provide you with a variety of reception service options, helping you enjoy a wonderful and perfect journey, making your medical beauty trip in Korea worry-free from start to finish.
We provide professional medical translation and accompaniment personnel, so that you won't be lonely during your stay in Korea. From reception to the hospital, we provide the most intimate and special services for you.
We strictly control your relevant information to ensure privacy and security protection. The medical beauty institutions we arrange for you have joined the protection insurance organized and operated by the Korean government in accordance with the law, with a maximum compensation of up to 100-200 million Korean won.
Medical tourism in Busan
Full-service personalized assistance throughout the journey, inquiry & consultation.
- Registration
- Information provision
- Consultation & reservation
Travel Reception
- Schedule confirmation
- Visa application
- Pre-travel briefing
- Arrival reception
Medical Treatment
- Reception & Admission
- Medical Consultation
- Medical Observation
- Sightseeing
- Local special cusine
- Entertainment & Shopping
- Health management
Popular Clinics
JEONG SUNG HOON PLASTIC SURGERY

BSTHEBODY PLASTIC SURGERY

KANG DONG HOSPITAL
KOSIN UNIVERSITY GOSPEL HOSPITAL

KIM BYOUNG JOON LEDAS VARICOSE VEIN CLINIC

GOWOONSESANG KIMYANGCHE SKIN CLINIC

NUNEVIT EYE CENTER


DAEDONG HOSPITAL

DONGNAM INSTITUTE OF RADIOLOGICAL & MEDICAL SCIENCES

LINE-UP DENTAL CLINIC

PARK WEON WOOK HOSPITAL

BUSAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
- Useful Information
Preparing for a Trip

- Currency exchange/Roaming/ZIM CARRY
- Visa & Immigration
- Transportation
- Climate of Busan
Emergency Medical Services
- City Guide for Muslim Travelers
- Free interpretation mobile app
- VISIT BUSAN PASS
In Case of Accidents and Emergencies
Dial 112 or 119 to call an ambulance in English. An ambulance will be dispatched after a caller’s location is confirmed. If you call 119 wherever you are in Korea, your location will automatically show up.
- Find Emergency Rooms in Busan Link Shortcut
Pharmacy Services
You can purchase medicines at stores with “pharmacy” signs. Pharmacies are often well-stocked with prescription drugs and medical supplies while you can find basic medicines such as fever reducer, pain killer, digestive pills, and cold medicine at convenient stores.
- 24-hour Pharmacies Link Shortcut
International Medical Services
International medical centers.
- Privacy Policy
Meet ‘Visit Busan’ on social media

Copyright Busan Metropolitan City. All rights reserved.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Iran J Public Health
- v.52(10); 2023 Oct
- PMC10612551
Analyzing a New Model of Medical Tourism Policy: Target Country-Specific Models and Marketing Strategies
Kyoung-lee kim.
1. Asia Contents Institute, Konkuk University, Seoul, South Korea
Byung-Ro Seo
2. Korea Department of Global MICE, Konkuk University, Seoul, South Korea
Background:
The three-year the pandemic has increased the preference for “safer and healthier” medical tourism destinations at a global level. Busan in South Korea aims to increase its competitiveness as a “medical city” destination. This study aimed to explore the best marketing strategies designed based on country-specific attraction model.
We collected data from surveys with 10 participants of a focus group from the medical tourism field in Busan and 352 participants of doctors, stakeholders, and moderators working in the medical tourism field in Nov and Dec 2022 to investigate key success factors for the medical tourism in Busan.
The interview identified key target countries and effective strategies such as ease of visa acquisition, non-face-to-face care, insurance billing systems, foreign language expertise, win-win systems for agencies and healthcare organizations, and international accessibility. When participants were asked about their country-specific attraction for patients, they ranked healthcare quality and tourism resources as both important and satisfactory. Although cultural environment, economic support, and administrative support were ranked important, they were less satisfactory. For Japanese patients, the infrastructure showed high levels of importance and satisfaction.
Conclusion:
This study identified specific items for a new model of patient attraction customized to target countries. This model was based on cultural background and preferences of each target country. Strategies are needed to strengthen the cultural environment and administrative support. Results of this study can be used to promote medical cities through target specific policies.
Introduction
After more than two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, patients are searching for the most convenient and safest destination for medical tourism. While the pandemic has shown negative consequences in the form of an unprecedented downturn in medical tourism, it has also provided positive data on technological advancement of the digital healthcare industry ( 1 ). As a result, the pandemic has been influential in shifting standards of medical tourism destination to more ‘safe’ destination. For example, Iran used phone interviews for medical tourists who arrived during the pandemic to provide them practical help with their healthcare needs, demonstrating the country’s credibility as a medical tourism destination that could deliver quality medical tourism ( 2 ). In general, the quality of a medical tourism destination depends on several factors, including the quality of services and how patients can trust that system ( 3 ). Due to the pandemic, infection prevention policies and smart technology for digital healthcare are driving healthcare demand and growth in medical tourism ( 4 ).
Smart city strategies are getting more and more significant and preferred in healthcare. They will further influence medical tourism destination preferences in the future ( 5 , 6 ). South Korea have been advertising a digitalized medicine as a national brand. However, there has been a lack of research on a ‘medical city’ as a ‘medical hub’. Competitiveness of medical tourism destinations in Korea depends on medical treatments and services, destination attributes, and tourism-specific factors ( 7 ). Yet, there is lack of a comprehensive research on how a destination in Korea can design strategies based on specific factors of medical tourists.
Therefore, this study aimed to explore a new model for Busan to strengthen its competitiveness as a medical hub destination. To be more specific, this study aimed to develop a target country-specific attraction model for Busan through importance and satisfaction analysis. To accomplish this, a literature review of medical tourism in Korea from 2009 up to now was performed, the recent medical tourism status in Busan was searched, importance and satisfaction analyses were performed to find determinant factors for medical tourism development in Busan, and implications and designing policy for a target country-specific model for Busan were suggested. Findings of this study will provide practical implications for medical tourism policy makers and authorities(medical institutions, agencies, and tourism organizations) in cities aspiring to become ‘medical cities’.
Literature Review: Medical Tourism in South Korea
The global medical tourism market was valued at $44.8 billion in 2019. It grew at a CAGR(Compound annual growth rate) of 21.1% during the forecast period. It is expected to grow significantly over the next decade, accounting for a significant portion of national economies around the world ( 8 ). South Korea’s Ministry of Health and Welfare has also declared its intention to become a bio-health center. It has established a comprehensive plan to strengthen the digital medical infrastructure in Korea and support the entry of secondary medical care and attraction of foreign patients overseas ( 9 ). As of 2021, the United States, China, Vietnam, Mongolia, Thailand, and Russia are the top five countries for foreign patients visiting South Korea, with cancer, heart disease, critical illness, and cerebrovascular disease on the rise. In particular, the five-year survival rate for stomach cancer in Korea (73.1%) is more than double the U.S. rate of 29.3% and the five-year survival rate for thyroid cancer has recently reached 100% ( 10 ). Amid these changes in the healthcare landscape, KHIDI’s 2021 “Foreign Patients’ Experience and Satisfaction with Korean Healthcare” report has found that when it comes to satisfaction with medical tourism in Korea, patients from China, Mongolia, and the Middle East prioritize medical technology, CIS countries prioritize treatment outcomes and effectiveness, the United States prioritizes service, and Russia prioritizes trust in medical institutions ( 11 ). The overall satisfaction rate was 89.9%, broken down by nationality as follows: CIS, 93.8%; Mongolia, 91.4%; Russia, 90.9%; Middle East, 90.5%; US, 89.5%; and China, 83.6%.
This high level of satisfaction among foreign patients is a result of the Korean government’s medical tourism policies and promotional strategies such as KAHF (7.7%), Medical Fast Track, Medical Korea, (15%), and Medical Visa (26.7%), with Russia showing the highest results across all categories Fig. 1 .

Four ways to promote Korean medical tourism
Such generally high satisfaction and popularity are also due to the fact that Seoul is the preferred medical tourism destination for foreign patients. This is because Seoul has a high concentration of advanced hospitals with wellness tourism information provided through a promotional channel called ‘Medical Tour Seoul’ ( 12 ). In comparison, although Busan has 133 medical institutions and 74 agencies, it is ranked differently as a medical tourism destination by patients from the following countries. It is ranked 2 nd by patients from Japan and Russia, 3rd by those from Southeast Asia, 4 th by those from Middle East, 5 th by those from US, and 6th by those from China. Mongolia and Central Asia have very few medical tourists visiting Busan. In particular, the agency that attracts the most foreign patients is Busan’s 14.1%, which ranks second overall, but is still a far cry from Seoul’s 74.3%, which ranks first overall. Therefore, Busan needs a new model and promotion strategy for attracting foreign patients customized for target countries to bridge the gap with Seoul and enter the global ‘Medical City’.
‘SMART CARE MEDICAL BUSAN’ (SCMB) Brand Revitalization Plan
Busan is South Korea’s second-largest city with a mild four-season climate and abundant tourism resources. It has been named Lonely Planet’s #1 Best Destination in Asia (2018) and one of the New York Times’ “52 Must-See Global Attractions”. Busan is a digital medical city that aims for the ‘Smart Care Medical Busan’ brand. It has excellent infrastructure and enough potential for development as a ‘medical city’ ( 13 ).
Paradigm shift in Busan medical tourism after the pandemic
The number of foreign patients visiting Busan changed from Russia (29.7%), China (19.6%), Japan (13.8%), and the United States (7.6%) in 2019 to Russia (15.3%), China (12.4%), the United States (12.2%), the Philippines (10.6%), and Vietnam (5.6%) after the pandemic. In the last five years, from 2016 to 2021, the average annual growth rate of foreign patients decreased for Japan, Russia, China, and the United States, while that of Southeast Asia showed an increase. This change of foreign patients from Southeast Asia is noteworthy, with Myanmar increasing by 766% Year-on-Year(36.2% CAGR), Indonesia by 416.3% YoY (37.6% CAGR), the Philippines by 270.9% YoY (20.6% CAGR), and Vietnam by 67% YoY (31.7% CAGR) ( Table 1 ).
Status of foreign patients visiting Busan (unit: %)
*Source: [Korea Healthcare Industry Promotion Agency] 2021 Foreign Patient Attraction Performance Statistical Analysis Report
In Oct 2022, Busan announced its goals to strengthen health and medical care, including “globalization of Busan” and “attraction foreign tourists” ( 13 ). This city plans to improve the quality of Mediair, Medistay, and Medigo to “strengthen the healthcare system” and “build foreigner-friendly infrastructure”. Mediair operates information centers for the convenience of foreign patients. Medistay provides information on various accommodation facilities. Medigo provides medical services, culture, and tourism as one product to experience wellness medical tourism.
To address the most problematic communication issues in Korean medical tourism, foreign language courses and training programs have been established at 12 universities in Busan to train medical professionals and support international students from target countries. Busan is trying to provide medical tourism services based on target country-specific models and strategies.
To design the best target country-specific attraction model for medical tourism in Busan, this study was conducted with two different phases of data collection. The focus was on five main factors in the medical tourism system of Busan: medical service quality, tourism resources, infrastructure, cultural factors, and administrative support. The factors were adopted from two previous studies and then modified based on the aim of our study, one was searching for the satisfaction level in the health tourism sector in Korea ( 14 ), and the other one was about the activation of medical tourism in Korea using IPA ( 15 ).
In the first phase, information were collected through focus group interviews with medical tourism stakeholders who directly or indirectly were familiar with the system of medical tourism in Busan. The focus group consisted of 10 participants (3 hospital officials, 3 agency representatives, and 4 professors) with an average of 16.5 years of experience. Focus group interviews had three questions regarding changes of determinant factors in attracting foreign patients due to the pandemic, countries as main target countries for Busan medical tourism and characteristics of medical culture and patients in each target country, and determinants of attracting foreign patients after the pandemic. In the second phase, a survey was conducted using a questionnaire asking 352 participants, including people with experience in Busan medical tourism sector, employees of international medical centers, and hospital coordinators. More than 100 participants were multinational coordinators. Their nationalities were China, Russia, Japan, the United States, Vietnam, Mongolia, South Korea, Hong Kong, Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, Pakistan, Africa, Canada, and Turkey. Participants were asked about factors associated with ‘importance and satisfaction’ on decision-making determinants in Busan’s post-pandemic medical tourism program. The research period was six months, from Jul to Dec 2022, with questionnaire distribution and collection from Nov 30 to Dec 13, 2022 (three weeks). Patient and medical tourism stakeholder surveys were created and distributed in Korean, English, and Russian. The first section of the questionnaire included demographic questions. The questionnaire consisted of 42 questions on importance and 42 questions on satisfaction of decision-making items for attracting foreign patients to Busan. The focus was on the five factors mentioned above. The survey response rate was 237% (initial target 200, 473 respondents). Only countries with 60 or more respondents (China, Russia, and Japan) were used for sample analysis.
First phase: Focus group interview
Analysis results of responses and data are shown as follows.
For the first question to find changes of determinant factors in attracting foreign patients the two following were found for hospitals, “difficulty to issue visas” for agencies and “utilization of virtual care and changing national guidelines”.
For the second question to find main target countries and their characteristics, main target countries were found to be Russia, Japan, China, and Vietnam. Since countries in Americas (including diaspora), Central Asia (CIS), and the Middle East are new target countries, marketing strategies for medical specialties in new countries are needed. Main requested treatments were predicted to be major surgeries, especially cosmetic surgery, cardiovascular, cancer, and medical checkups.
For the third question to find determinants of attracting foreign patients after the pandemic, the following changes are predicted and requested:
- Agencies need to support the convenience of long-term stays for critically ill patients.
- Hospital officials should build host-country-friendly infrastructure and increase accessibility for fast-tracking.
- There is a need to secure the country’s insurance billing system.
- Content that utilizes Busan’s tourism resources should be created.
- The number of foreign language specialists should be expanded.
The focus group concluded that Busan would be differentiated from other cities in the future through city branding and high recognition as a ‘medical city’, with win-win system and systematic support for agencies and medical institutions, agency expertise, diverse tourism resources, and high overseas accessibility.
Second phase: Questionnaire analysis
The following shows results of analysis of 84 items on the “Importance and satisfaction” of the five main factors in the medical tourism system of Busan, including medical service quality, tourism resources, infrastructure, cultural factors, and administrative support. Only three countries (China, Russia, and Japan) with more than 60 participants were considered in the analysis.
China had 160 respondents, including 38 (24%) males and 122 (76%) females. Their preferred treatment in Korea were internal medicine (35%), checkup centers (21%), and plastic surgery (21%). Chinese patients have loyalty to the medical institution they visit since they visit one institute regularly. Healthcare professionals were: coordinators, hospitals, agencies, public organizations, and education & consulting.
There were 101 Russian respondents, including 34 (34%) males and 67 (66%) females. Their preferred treatments were internal medicine (31%), checkup center (19%), and plastic surgery (14%). There were 88 (87%) people involved in medical tourism, including 54 medical tourism coordinators, 11 doctors & nurses, 10 agencies, 10 hospital officials, 2 public institutions, and 1 consultant.
For Japan, 91 respondents participated in the data collection, including 19 (21%) males and 72 (79%) females. Their preferred treatment were plastic surgery, internal medicine, and checkups. There were 80 (88%) people involved in medical tourism, including 54 coordinators, 13 doctors and nurses, 8 hospital staff, 4 agencies, and 1 public organization.
All three countries ranked ‘healthcare quality’ and ‘tourism resources’ as both important and satisfactory. Although ‘cultural environment’ and ‘economic and administrative support’ were considered important, they were less satisfactory. The factor of ‘infrastructure’ was ranked similar by China and Russia, while Japan ranked its importance and satisfaction at higher levels.
Items for each factor are shows as follows. Table 2 presents the level of importance and satisfaction of each factor given by representatives of each country.
Five Factors that Determine International Patient Attraction (China, Russia, Japan) (Units, counts)
*H: High, L: Low.
- Medical service quality (14 items): after-sales service, state-of-the-art medical facilities, stability of technology, insurance application, provision of medical information, sanitary condition of medical institutions, kindness of medical staff and staff, excellent medical technology, reputed medical staff, organized medical service, coordinator competence, non-face-to-face and telemedicine efficiency, communication, and 1:1 customized medical care.
- Tourism resources (7 items): shopping tourism, food tourism, new tourism experiences, visiting tourist attractions, procedures and clear costs of medical tourism, various tour programs, and convenience of movement within Busan.
- Environment (8 items): safe security, simple immigration procedures, provision of convenience facilities for companions, international accessibility, visa issuance, possibility of re-entry, immigration policy and responsiveness, and pleasant climate.
- Cultural resources (4 items): economic and administrative support (9 items): traditional oriental medicine treatment experience, religious and ethical culture, traditional culture, Korean wave entertainment experience, low & clear medical cost, simple treatment procedure and short waiting time, insurance claim system establishment, consumer reviews and feedback, diversity of promotion channels, and easy and simple inquiry process.
Although there are diverse tourism resources in Busan, there is a lack of systematic support for medical institutions and agencies active in medical tourism. However, considering both high medical facilities and infrastructure for overseas accessibility in Busan, this city has potential to be recognized as a ‘medical city’. Though, it seems that such recognition depends on designing strategies in accordance with the needs of those tourists who are loyal to visit this destination.
Busan is trying to redefine its city brand to ‘Smart Care Medical Busan’ and to establish a new patient attraction model customized for target countries to increase its desirability as a medical tourism destination. Besides ‘performance risk’ and ‘quality risk’, ‘Health risk’ has been always one of the main dimensions of perceived risk for traveling ( 16 , 17 ). Moreover, the latest pandemic increased the level of uncertainty for selecting a destination ( 18 ), especially for medical tourists. For medical tourism, such an issue is likely to be more important since the perceived risk is defined as the perception of medical tourism that may influence their travel decisions ( 19 ). Though, South Korea as a medical tourism destination has several advantages. The public health of this country performed a successful action plan during the pandemic which increased the trust level for foreign patients, especially for those who had been familiar with this country. Hence, this country could already ensure its potential medical tourists about the low level of risk which has been even more significant after the pandemic ( 20 ). The result if this paper also confirms the importance of the perceived risk in selecting a destination since most of the participants mentioned the availability of virtual care in Korea.
Busan is already well known as a destination for foreign tourists, for instance, the high accessibility and the loyalty of tourists (especially from the neighborhood countries) are among the advantages of this city being recognized as a medical tourism destination. Yet, this city is still far from building a host-country-friendly infrastructure. The most significant advantage is that Busan is already a popular destination for visitors from China, Russia, and Japan. Loyalty is a factor that the authorities of Busan can use as a strength point in their policy planning. Chinese patients showed to have loyalty to the medical institution they visit since they visit one institute regularly. Hence, all they need is to improve the infrastructure as a ‘medical city’. Besides, new marketing strategies are required to increase the satisfaction of the tourists coming from new targeted countries. This study indicates that China, Russia, and Japan can be targeted as the countries with loyalty levels, and medical tourists from Central Asia and the Middle East would be the potential new target countries.
To attract patients from these countries, ease of entry and exit (visa, stay, and travel), professional staff (more foreign language training for coordinators), insurance claims systems and fast-tracks, cultural and tourism infrastructure tailored to each country, and digitalization of the medical environment are commonly needed. Besides the infrastructure factors, the cultural variables are likely to be more vital for the medical tourists to feel secure and satisfied. Cultural factors especially language has been always one of the main determinants of building trust in medical tourism ( 21 ). Likewise this study confirms that while the healthcare quality and tourism resources are both important and satisfactory for the visitors, cultural environment and administrative support are yet to be satisfactory by the customers, nevertheless, these factors are considered as highly important by the medical tourists from China, Russia, and Japan. Therefore, in order to continue to grow as a ‘medical hub’ in the future, in-depth analysis of the characteristics of customers from target country should be provided to policy practitioners. These significant findings on the possibility of segmentation and regionalization of medical tourism destinations can be used as concrete evaluations for many cities that aspire to become ‘medical cities’ in the future.
However, this study has several limitations. First, generalization of empirical analysis results needs caution due to an unbalanced distribution of gender ratio in socio-demographic characteristics and the convenience sampling method. Second, this study might have regional limitations as it analyzed opinions of those involved in and experienced with medical tourism in Busan. Third, the competitiveness of foreign patients as a whole could not be identified because only China, Russia, and Japan with more than 60 foreign patient respondents were targeted. Therefore, future research that complements limitations of this study is needed to confirm findings of this study.
We identified specific items for a new model of patient attraction customized to target countries. This model was based on cultural background and preferences of each target country. Strategies are needed to strengthen the cultural environment and administrative support.
Journalism Ethical considerations
Ethical issues (including plagiarism, informed consent, misconduct, data fabrication and/or falsification, duplicate publication and/or submission, and redundancy) have been completely addressed by authors.
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the Research Professor Program of Konkuk University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.
- Ulsan/Gyeongnam News
- National News
- Asia News – Media OutReach
- Business Wire
- GlobeNewswire
- PR Newswire
- Arts & Culture
Dine & Drink
- Food Delivery
- Local Destinations
- Seoul Events and Festivals
- Upcoming Concerts in Seoul
- Health, Fitness & Beauty
- Live Like a Local
- Shopping, Home & Living
- 10 Second Korean
- Eat Like a Local
- Domestic Destinations
- International Destinations
- Busan Museums
- Busan Subway Map
- Tourist Attractions
- Transportation — Getting Around Town
- Busan IPark Soccer
- KCC Egis Basketball
- Lotte Giants Baseball

Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023

The Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 will open at BEXCO Exhibition Hall 1 from September 1st to 2nd.
In its 15th year, this year’s event will feature a variety of programs including exhibitions, global academic seminars, health lectures by renowned physicians, and overseas buyer consultations.
Additionally, there will be a promotion area for the World Expo 2030 Busan, along with various medical device experience events.
Event Information
Period: September 1-2, 2023
Venue: BEXCO
Hours of Operation: 10:00 a.m. – 6:00 p.m.
Hosted by: Busan Metropolitan City, Busanilbo
Website: bimtc.busan.com/eng/html/main/main.php

Related Articles
Haeundae beach hot spring foot bath makes long-awaited return, daily hydration goals: water intake journey illustrated with photo editing using capcut’s online photo editor, two day beauty art festival gets underway today at bexco, barefoot walking becoming a popular hobby in busan, how to get a free covid-19 vaccine in korea, celebrate diverse fashion at 2023 korea-asean fashion week.

4th Busan Spring Flower Exhibition to be Held May 3-6
“star wars day” event to take place on haeundae beach may 4-5, seomyeon hosting its first “car-free street” cultural event of 2024 today, 40th sancheong hwangmaesan azalea festival begins today, build your own bloody mary/caesar day @ hq gwangan this sunday, busan home living and household goods exhibition.

Jr. Whopper Special at Burger King
Reminder: new zealand wine festival tickets for seoul and busan now on sale, eat like a local: craft makgeolli, soju and delicious eats at sulgotgan in suyeong.

Busan to Tsushima Izuhara Route Resumes
Korea destinations: 23rd jinju nongae festival celebrates korea’s gyobang culture, korea destinations: nighttime tours of gyeongbok palace return in may, korea in photos: wiyangji in full bloom.

Haps Korea Magazine features stories of people from all walks of life in Korea, covering news and trends in lifestyle, society and whatever else is happening on the peninsula.

About Us | Advertise ©2024 Haps Korea Magazine
BUSAN < invest Korea
- News & Event
- pdf Download
- img Download
- facebook Shortcuts
- twitter Shortcuts
- pinterest Shortcuts
- google Shortcuts
- weibo Shortcuts
- renrenwang Shortcuts
According to Yonhap News,
Busan-si said on December 24 that it signed 9 MOUs in medical tourism industry briefing session it held in Moscow, and others together with the Busan Economic Promotion Agency (BEPA) in Russia. The city held Busan medical tourism briefing session in St. Petersburg on December 3. It also ran the 2021 special pavilion for the Busan medical tourism industry in Moscow on December 6-9. During the briefing session it held on December 3, the Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (DIRAMS) opened a telemedicine center in a cancer center in St. Petersburg and signed a MOU. The DIRAMS, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan Adventist Hospital, other medical institutes and companies that attract foreign patients in Busan held the medical tourism briefing session and signed 3 MOUs. The 2021 Busan Medical Tourism Special Pavilion held in Moscow on December 6-9 was held in conjunction with the 2021 Russia Med Travel Expo. 10 companies from Busan had consultations with 69 local buyers, signing 6 MOUs. The city explained that Busan's excellent medical techniques and infrastructure were introduced, attracting great interest. [email protected]
Source Text
Copyrights Yonhap News. All Rights Reserved. Reprint or redistribution without permission is prohibited.
Source: Yonhap News (December 24, 2021)
- Go To Contents
- Go to Main Menu
Busan is good
- Introduction
- City Environment
- Four Seasons
- Origin of Busan
- Autonomous Districts
- Role & History
- City Symbols
- Busan Citizen's Charter
- History of Busan
- World Heritage in Busan
- On an average day in Busan
- Busan Statistics by Category
- Inaugural Address
- Vision of Busan
- Former Mayors of Busan
- City Organization
- Virtual Tour
- Floor Directory
- Busan Dream Space
- Construction Objectives
- Status and Expected Effects
- Vision Roadmap
- The Five Promotion Strategies
- Performance Goals and Area Strategy
- Overview of EDSC
- Vision and Objectives
- Ten Innovations
- Fine Dust Reduction Measures
- Honorary Citizenship
- List of Sister Cities
- Los Angeles
- Shimonoseki
- Rio de Janeiro
- Vladivostok
- Ho Chi Mihn
- Western Cape
- St. Petersburg
- Thessaloniki
- Dar es Salaam
- List of Friendship Cities
- Shenzhen(深圳市)
- Tianjin(天津市)
- Chongqing(重庆市)
- Bandar Abbas
- Ulaanbaatar
- Panama City
- Dili Municipality
- Liverpool City Region
- Belize City
- City of Rijeka
- Busan English Media Hub
- News & Notices
- Daily Busan
- Busan is good(English Newspaper)
- e-Newsletter
- Photo Gallery
- Website Satisfaction Survey
Calendar of Events
- Visit Busan
- Medical Tourism
- City Cruises
- Nakdong Estuary Eco Center
- Free Wi-Fi Service
- Arts & Culture
- Parks and Arboretums
- Busan’s Seven Bridges
- Busan Galmaet-gil
- Port Logistics
- Invest Busan
- Organizations and Facilities
- Festivals and Events
- Busan International Film Festival (BIFF)
- MICE Industry
- Exhibition & Convention
- Nurimaru APEC House
- Busan Global City Foundation
- Busan Foreign Residents Center
- Driving License
- Car Registration
- Two-wheeled Vehicle Registration
- Immigration
- Communication
- Land Purchase
- Maps of Busan
- Transportation Cards
- Public Transportation
- Demand Responsive Bus TABARA
- Prepaid Dongbaek Pass
- Bicycle Rental Shops
- Types of Housing
- Finding Housing
- Real Estate Agencies for Foreigners
- Jeonse and Monthly Rent Contracts
- Using a Moving Company
- Moving Overseas
- Acquiring Living Conveniences
- Garbage Disposal
- Education System
- Foreign Schools in Busan
- Colleges & Universities
- Learning Korean
- National Health Insurance
- Community Health Center
- Pharmacy Information
- Emergency Rescue Call 112, 119
- COVID-19 Busan Updates
- COVID-19 Vaccination Information
- Medical Care Assistance Program for Foreign Workers
- Multicultural Family Support Project
- Multicultural Family Support Centers
- Institution of Korean Education
- Sports Facilities
- Public Safety
- Earthquake Safety Tips
Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2021
○ Period: November 12-13, 2021
○ Venue: BEXCO
○ Hours of Operation: 10:00 a.m. - 6:00 p.m.
○ For more infor.: 070-5154-9941
○ Hosted by: Busan Metropolitan City, Busanilbo
○ Website: https://bimtc.busan.com/eng/html/main/main.php
- Jung-gu Office
- Seo-gu Office
- Dong-gu Office
- Yeongdo-gu Office
- Busanjin-gu Office
- Dongnae-gu Office
- Nam-gu Office
- Buk-gu Office
- Haeundae-gu Office
- Saha-gu Office
- Geumjeong-gu Office
- Gangseo-gu Office
- Yeonje-gu Office
- Suyeong-gu Office
- Sasang-gu Office
- Gijang-gun Office
- Related to Busan
- Affiliated Office
- Local Public Enterprises
- Busan Metropolitan Council
- City-Invested and -Funded Institutions
- Busan-based Public Institutions
- State of Victoria
- Ho Chi Minh
- Privacy Policy
- City Hall Hours & Directions
- 1001, Jungang-daero, Yeonje-gu, Busan, 47545, Republic of Korea
- Phone: +82 (51) 120
Copyright © Busan Metropolitan City. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2020-01-29 677 Views. The city of Busan launched the newly revamped Busan Medical Tourism website on January 29, 2020. The responsive design of the website allows users to be able to access it from different types of mobile devices as well as PC. The website is available in five languages: Korean, English, Chinese, Japanese and Russian.
The Medicall Center is a medical tourism service platform that provides various convenience services from airport pickup vehicles to hotel reservations, interpretation services, and introduction of wellness tour packages for medical tourists visiting Busan so that they can enjoy Busan medical tourism more comfortably and safely. If you want ...
The recent Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 shed light on Busan's ambitions. The city's aspirations were clear: to emerge as a leading global destination for medical tourism. But aspirations are one thing, reality another. Busan's medical infrastructure is undeniably impressive.
2024 Foreign Busan Traveler Contest. 2024-04-23; Announcement of Winners for the Second Event with Starry Night in Busan and Nikon. 2024-02-13; Announcement of Winners for the First Event with Starry Night in Busan and Nikon. 2024-01-19; Winners Announcement for [Magazine <B> EVENT] 2024-01-11
We recommend tour routes where medical tour patients and their families who are fatigued by COVID can heal their minds and bodies with the beautiful nature and various experiences of Busan. ... Busan X the Sky Observation Deck. Enjoy the view of the sea of Haeundae and the Gwangan Bridge from the tallest building in Busan (100th floor).
The 2022 Busan International Medical Tourism Convention, which is the nation's largest exhibition for international medical tourism and medical experience, takes place at the BEXCO for two days from September 30-October 1, 2022. The 14th Busan International Medical Tourism Convention is jointly hosted by Busan Metropolitan City and Busan Ilbo ...
If you finished the check-in process and customs report, move to the departure process to get security check. Carry-ons for the flight are allowed for only 55cm(W) x 40cm(L) x 20cm(H) (within total 115cm) and weight 10kg or less.
Busan Medical Tourism Information Center (Seomyeon) (Seomyeon Station Exit 9), 787, Gaya-daero, Busanjin-gu, Busan 051-818-1320. Busan Station Tourist Information Center. 206, Jungang-daero, Dong-gu, Busan 051-441-6565. Haeundae Tourist Information Center. 264, Haeundaehaebyeon-ro, Haeundae-gu, Busan 051-749-5700. 1 2 3.
Follow us and easily embark on a medical tourism journey to Busan, Korea. The Trend of Korean Medical Tourism. In recent years, the trend of traveling to Korea has been increasing. Statistics show that about 7.5 million people visit Korea every year, and more than 80,000 of them come for cosmetic surgery. Today, Korea's top medical equipment ...
Busan Medical Center: Equipped with a rehabilitation center for all medical specialties including internal medicine and surgery, an artificial kidney center, a cardiovascular center, etc. 08:30-16:30 (on weekdays) 08:30-12:00 (on Saturdays) 359, World cup-daero, Yeonje-gu, Busan / +82-51-507-3000: Pusan National University Hospital
The official website of Busan Metropolitan City. Find information about the city government, news, events, residents, business, recreation and tourism. Busan moves swiftly to be a hub for medical tourism : News > News & Notices
Busan Medi Tour, Busan, South Korea. 107,411 likes · 3 talking about this · 314 were here. Rich in human & material resources in its medical infrastructure, with convenient transportation and a...
There are Line 1 and Line 2 in Busan Metro station. A section of Line 3 (From Suyoung to Daejeo) is available. Metro station ticket price for 1 section (up to 10 km) is KRW900 and 2 section (over 10km) is ₩1,000.
To design the best target country-specific attraction model for medical tourism in Busan, this study was conducted with two different phases of data collection. The focus was on five main factors in the medical tourism system of Busan: medical service quality, tourism resources, infrastructure, cultural factors, and administrative support.
February 10, 2015. The City of Busan has announced a reorganization of its medical tourism policy, shifting from a focus on attracting foreign patients to an overall approach to medical care including anti-aging, bio, clinical tests, and health care industrialization. The city will also aim to attract domestic and overseas outstanding hospitals ...
The recent Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 shed light on Busan's ambitions. The city's aspirations were clear: to emerge as a leading global destination for medical tourism.
There's an issue and the page could not be loaded. Reload page. 3,338 Followers, 364 Following, 532 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from BUSAN MEDICAL TOURISM (@busan.medical.tourism)
The Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 will open at BEXCO Exhibition Hall 1 from September 1st to 2nd. In its 15th year, this year's event will feature a variety of programs including exhibitions, global academic seminars, health lectures by renowned physicians, and overseas buyer consultations. ...
Busan Medi Tour is at Busan Bexco. · November 24, 2019 · Seoul, South Korea ·. From 12th Nov. to 15th Nov, Busan Medical Tour held a Pam Tour for Russian medical tourism agencies and broadcasting officials. They visited Busan's University Hospitals and Clinics for medical experiences, and also tour several places in Busan City.
Find information about the city government, news, events, residents, business, recreation and tourism. Go To Contents; Go to Main Menu; eng. 한국어; 日本語; 简体中文; 繁體中文; WorldWide ... Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2023 . Period 2023-09-01 (Fri) ~ 2023-09-02 (Sat) Contents Period: September 1-2, 2023
The official website of Busan Metropolitan City. Find information about the city government, news, events, residents, business, recreation and tourism. Busan City developing its Medical Tourism Infrastructure : News > News & Notices
The 2021 Busan Medical Tourism Special Pavilion held in Moscow on December 6-9 was held in conjunction with the 2021 Russia Med Travel Expo. 10 companies from Busan had consultations with 69 local buyers, signing 6 MOUs. The city explained that Busan's excellent medical techniques and infrastructure were introduced, attracting great interest.
The official website of Busan Metropolitan City. Find information about the city government, news, events, residents, business, recreation and tourism. Busan International Medical Tourism Convention 2021 : Visit > Calendar of Events