- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
Design a better business


Linking the Customer Journey to your Business Model Canvas
March 30 by Erik van der Pluijm
Sometimes it can be difficult to specify the channels and customer relationships building blocks of the business model canvas. When you get stuck there, it can help to look at the customer journey for new ideas and clarity. There is a link between the business model canvas and the customer journey.
Don’t build your business model inside-out.
Especially when you’re working on a business idea from within an existing business or business model it can be tempting to think inside-out, with potentially disastrous results. The customer journey is a tool that helps you step into the shoes of the customer to prevent just that.

To build your customer journey start by imagining what the life of the customer is like. What is the problem the customer is trying to solve? How are they solving it today? What are they happy or frustrated about? Mapping this out will give you a number of (hypothetical) touch points to validate in the real world. These touch points are moments in the customer’s life where they are experiencing a problem, taking action, or planning their next steps. Going out of the building or doing a customer safari will tell you if the touch points you mapped are the ones that actually show up in your customer’s experience.
The link to the business model canvas: Channels
In the business model canvas, the building block ‘channels’ describes the ways your customers learn about your product or service, and how they receive their product or service. Usually, we will find ‘website’ or ‘advertising’ here, and those definitely could work – but then they have to also show up in your customer journey!
If you want to use a website as a channel, you better understand how and why customers visit that website first. How are you going to make sure that they do? What ideas and tricks do you have to influence their behaviour? Besides, looking at the customer journey, there may be smarter, less obvious ways to reach your customers. Looking through the customer journey in this way will help you better understand your channels.
The customer journey is a great way to map out the process where your customers become aware of the problem, look for a solution (hopefully yours!), and finally, make a purchase.
wait, there is more: customer relationships
Finally, looking at the customer relationships, the customer journey can help you as well. As soon as you understand the problem your customer has very well (and that means, understanding it in the terms in which the customer experiences it) it is possible to build a relationship around that – and that relationship also needs touch points.
When and where are you going to communicate with your customer? When and where can you grow the relationship?
It is more important to fall in love with the problem than with the solution.
Too often, businesses assume that in order for them to communicate to (not ‘with’!) their customers, they can freely add new touch points in the customer’s life: emails, notifications, and phone calls. Often those extra touch points are scheduled at times when the customer is definitely not in the mood or in the opportunity to do anything with them.
But, it doesn’t have to be like that. What if you would be able to take touch points that the customer already is used to and cares about and trigger communication at that moment? And, what if you can identify down time or idle time and use that to ask for feedback? Or if you can tell when the customer is delighted and interact at that time? Going over your customer journey with that in mind can certainly give you better ideas for the way in which your business creates and maintains relationships with your customer.
The way in which Nespresso built a very successful business model, without (initially) bringing their product to supermarkets, was for a very large part supported by the relationship they have with their customer – and the relationship their customer has with coffee. They removed a (very obvious) touch point in supermarkets, where the mood and reference frame of the customer may be unsuitable for them to decide to buy much more expensive coffee, and replaced it by another, more personal touchpoint, where the customer feels special.
Ideas like the one Nespresso came up with are much easier to find if you start looking at the relationship from the customer’s perspective, while staring at the ‘customer relationships’ building block of the business model canvas will probably make you come up with more pedestrian solutions.
Keep track of your customer journey, it will keep bringing value
Building and maintaining an accurate customer journey (backed up by real world evidence) is a vital tool to find new possibilities in your business model – not only in terms of ideas but also in terms of quality of execution.
Keeping track of the behaviours customers actually follow will keep informing your business model!
By Erik van der Pluijm - Designer
Erik is the owner of Pitchlab and Tech Perform Lead at Growth Tribe Academy. He is passionate about visual thinking and making complex things simple. He mixes design, code and strategy, using his experience from art and design, artificial intelligence, computer games, and the startup scene.

More blogposts
Strategic storytelling: bridging ideation and scaling.
January 17 by Maarten van Lieshout
When people think of running a business or working together, the last thing they would think of is storytelling as a major driver for the success of the business or the success of a team. Often time when we start a new project, the team is assembled <What should you look for when assembling a […]
Why the Business Model of Santa Claus is so successful
December 21 by Patrick van der Pijl
The business model of Santa Claus is an age-old business model over 200 years old. Santa is a legendary figure originating in West Christian culture who is said to bring gifts to the homes of well-behaved children on Christmas Eve. Santa Claus is generally depicted as a portly, joyous, white-bearded man, wearing a red coat […]
A journey to success with Design Thinking
December 20
Enexis is one of the 7 network operators in the Netherlands. The most important task of a network operator is to install and maintain the energy network in the Netherlands. Enexis carried out a survey among its employees, resulting in eight different personas. We as ISS wanted to start providing a service experience for those […]
Please fill in your details and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
- Name * First Last
- When would you like to book this speaker? * MM slash DD slash YYYY
- Where is the event? *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
GET YOUR FREE SAMPLE PDF !
Get the first 40 pages of Design A Better Business for free as a PDF! Includes the first chapter.
- First name *
- Emailaddress *
- Keep me up to date
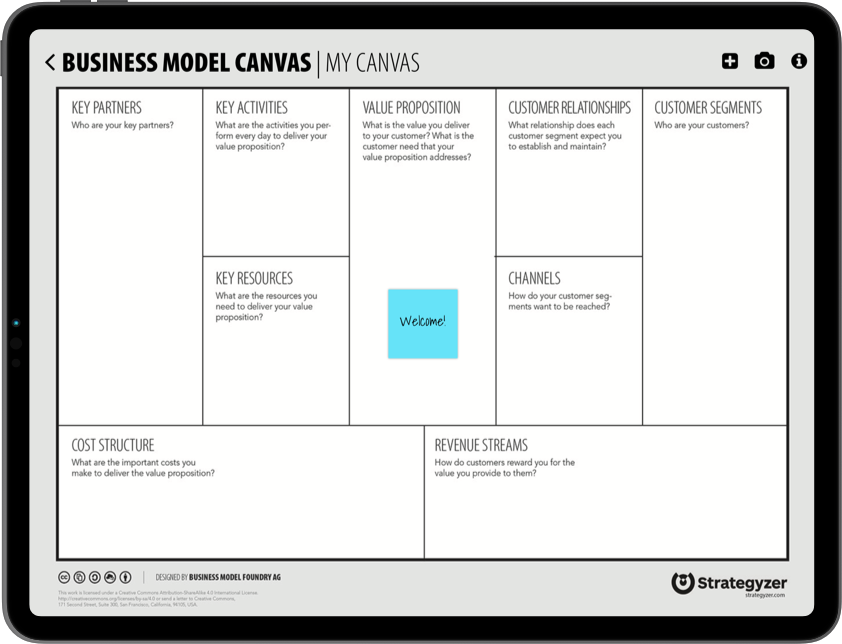
Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.
What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
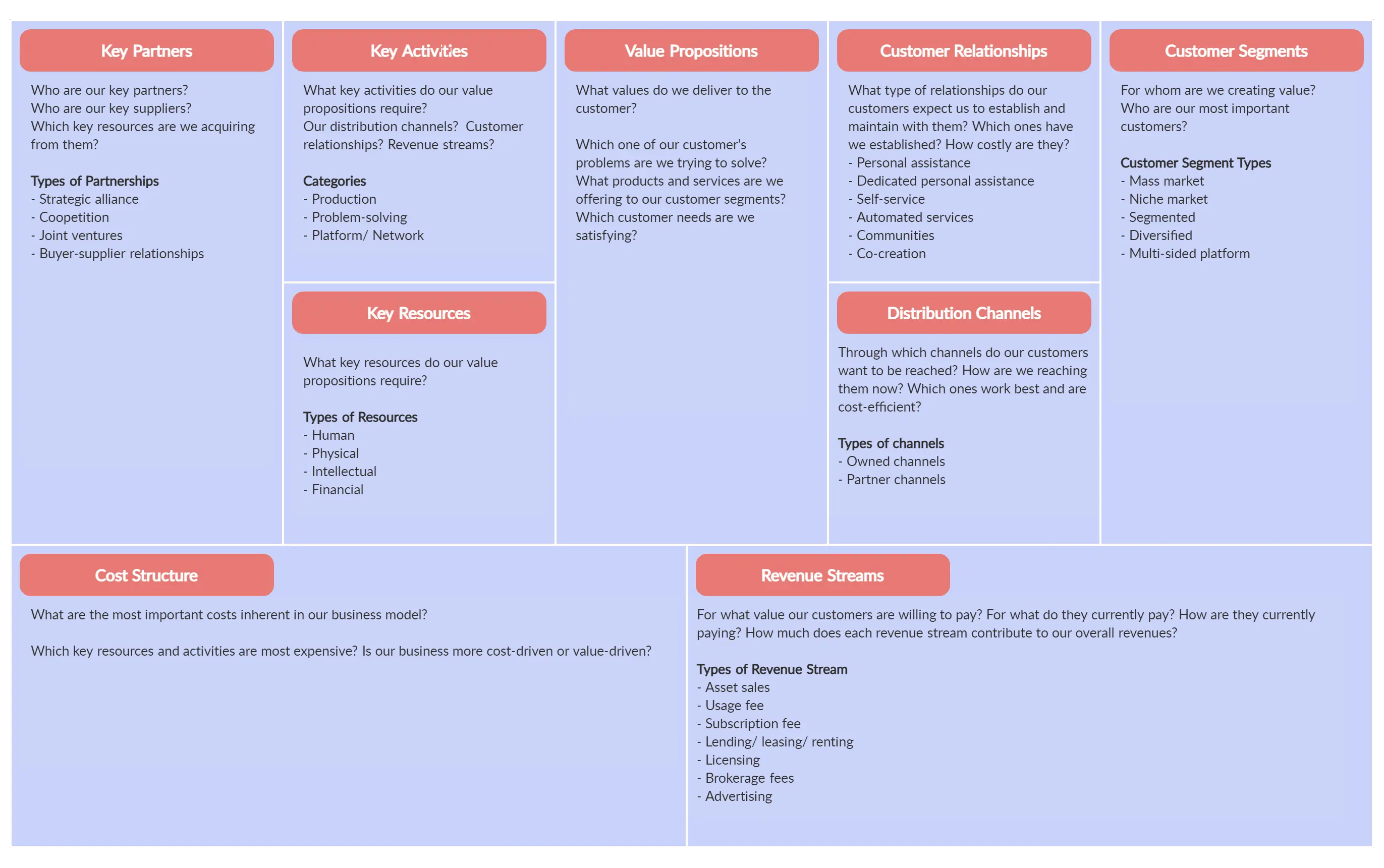
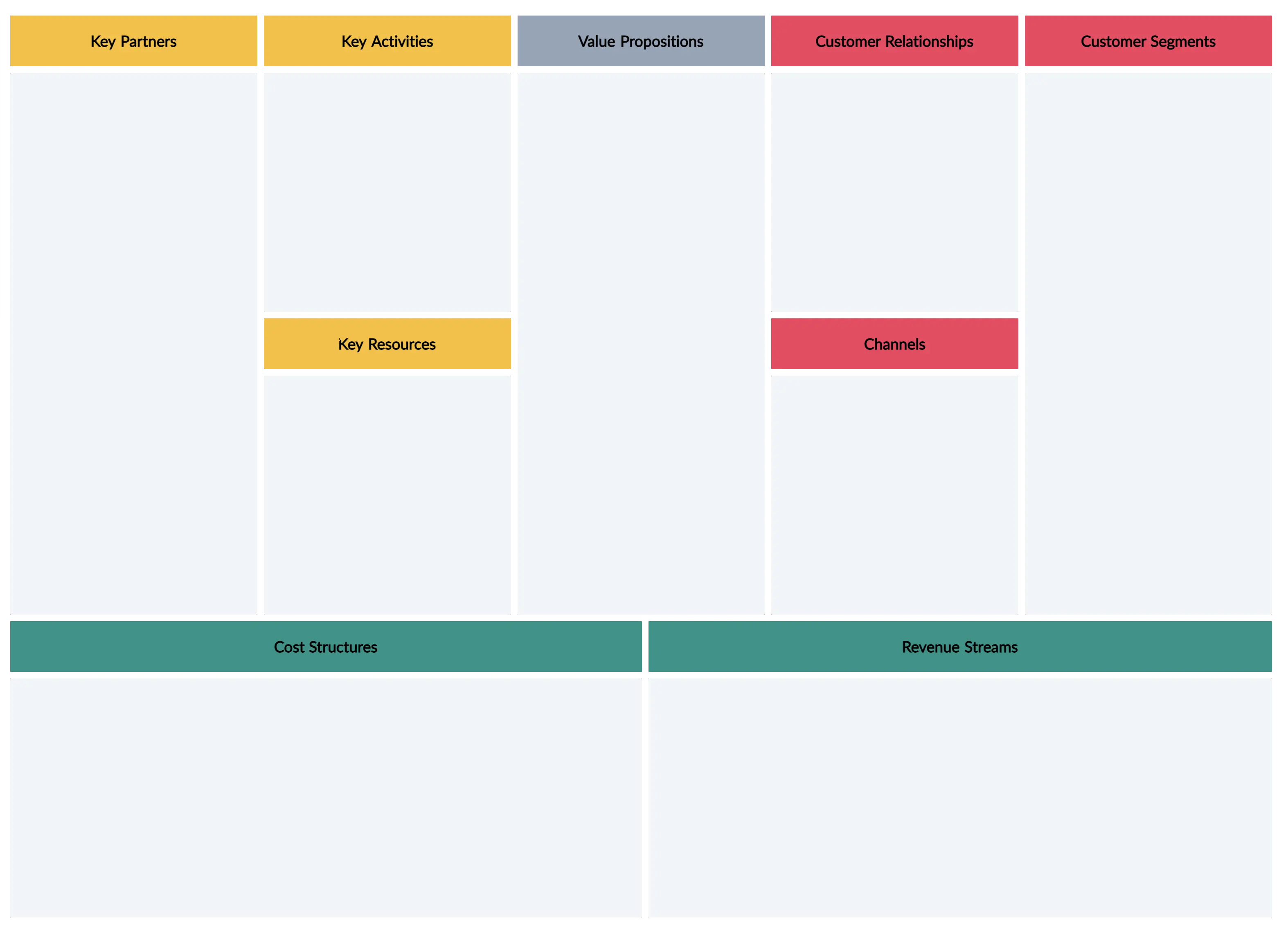
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
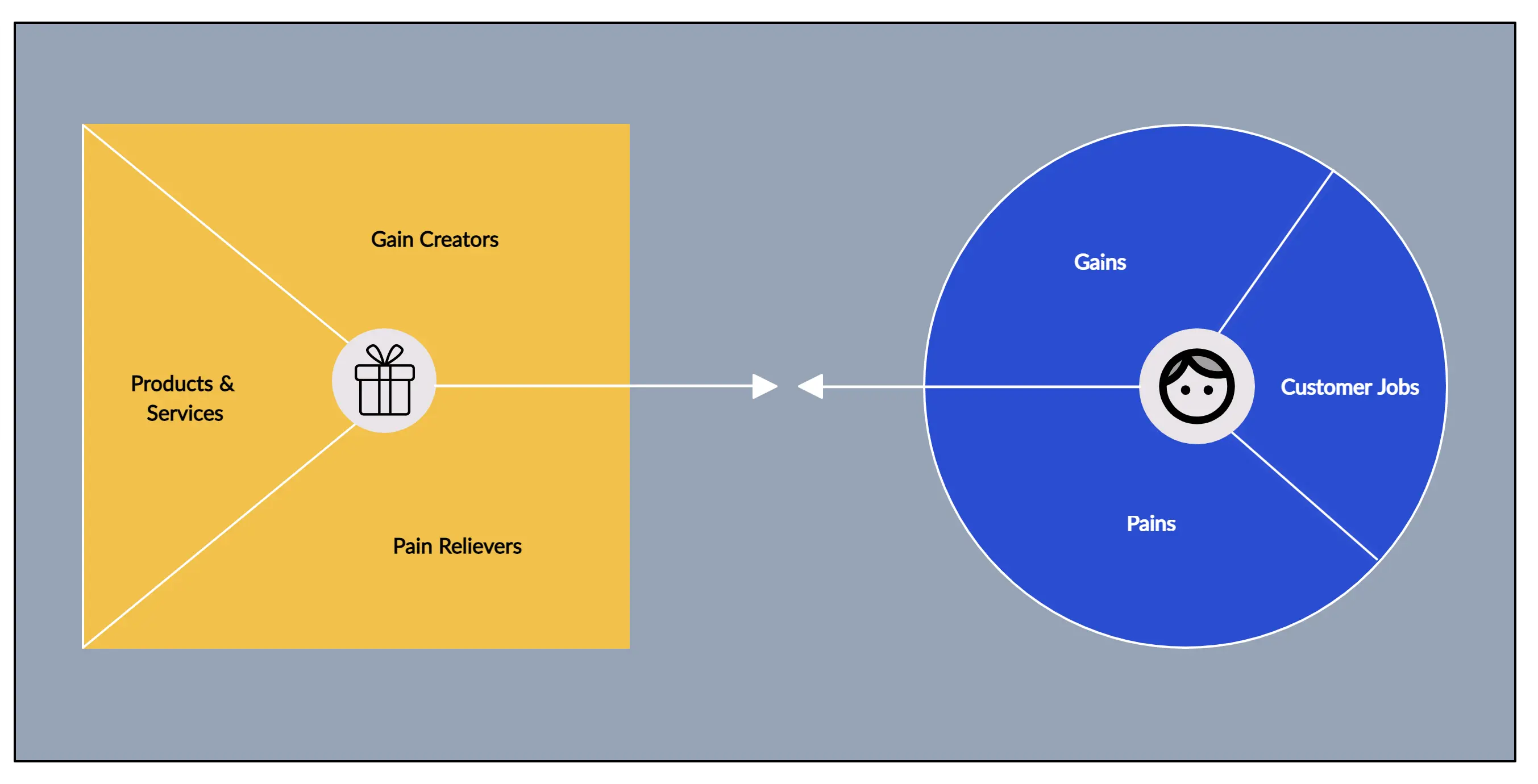
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
Customer Journey Canvas
Introduction.
The Customer Journey is a tool to help you get insight into, track, and discuss how a customer experiences a problem you are trying to solve. How does this problem or opportunity show up in their lives? How do they experience it? How do they interact with you?
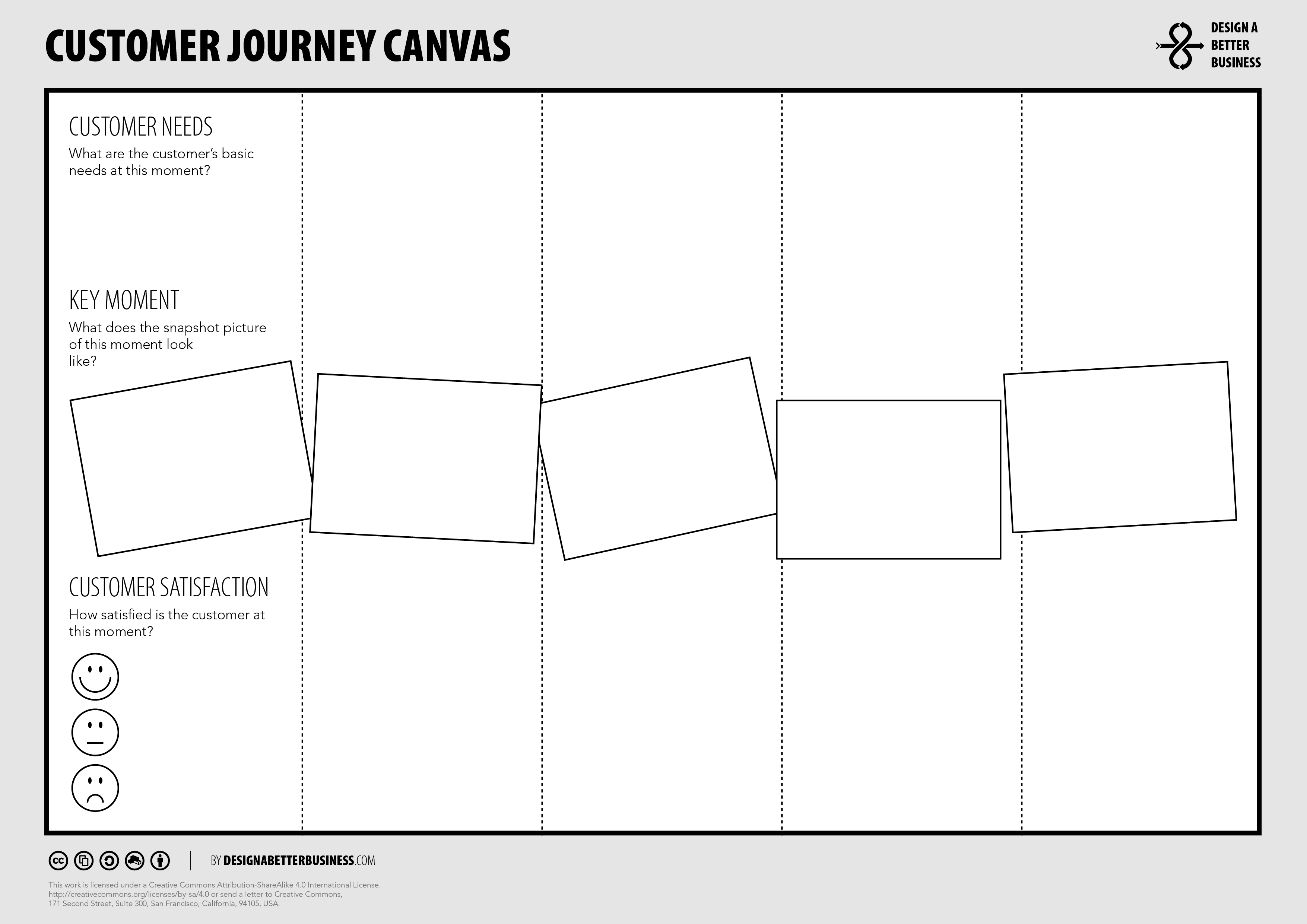
How To Use the Customer Journey Canvas
Mapping this journey will provide you with insights into how customers experience a product or service, as well as how they might be better served or even delighted. This is especially true when co-creating the journey together with your customers or when validating your assumptions with them. What are the circumstances? How do customers feel throughout? What are the moments when the experience can best be improved?
Customer journeys are not linear. A customer can jump from one phase to another depending on many factors. They interact with some touchpoints and miss out others. It is your job, as a designer, to understand the moments when customers engage so that you can design better experiences for them in the future. This tool helps in looking at your products and services through the lens of the customers.
Of course, no customer journey is totally complete or made without assumptions. Mapping the customer journey is based on the knowledge and insights of your team. This tool simply helps you understand and explore from the customer’s point of view.
The customer journey canvas helps make things real. Through the mapping exercise you can identify where customers get stuck, where they have great experiences, and why. One outcome of using this tool with your team will be the so-called low hanging fruit that you can deliver on immediately. Once you have co-created and assembled the customer journey maps, you can add real customer data gathered through customer safaris, interviews, and feedback. This will enable you to make informed decisions based on reality.
The customer journey is relevant for everyone. Everyone on the team, and in your company, must understand what your customers experience, how they feel, what they struggle with, and how you can improve the experience. The underlying goal: to solve our customers’ problems and make them happy.
Tool Overview
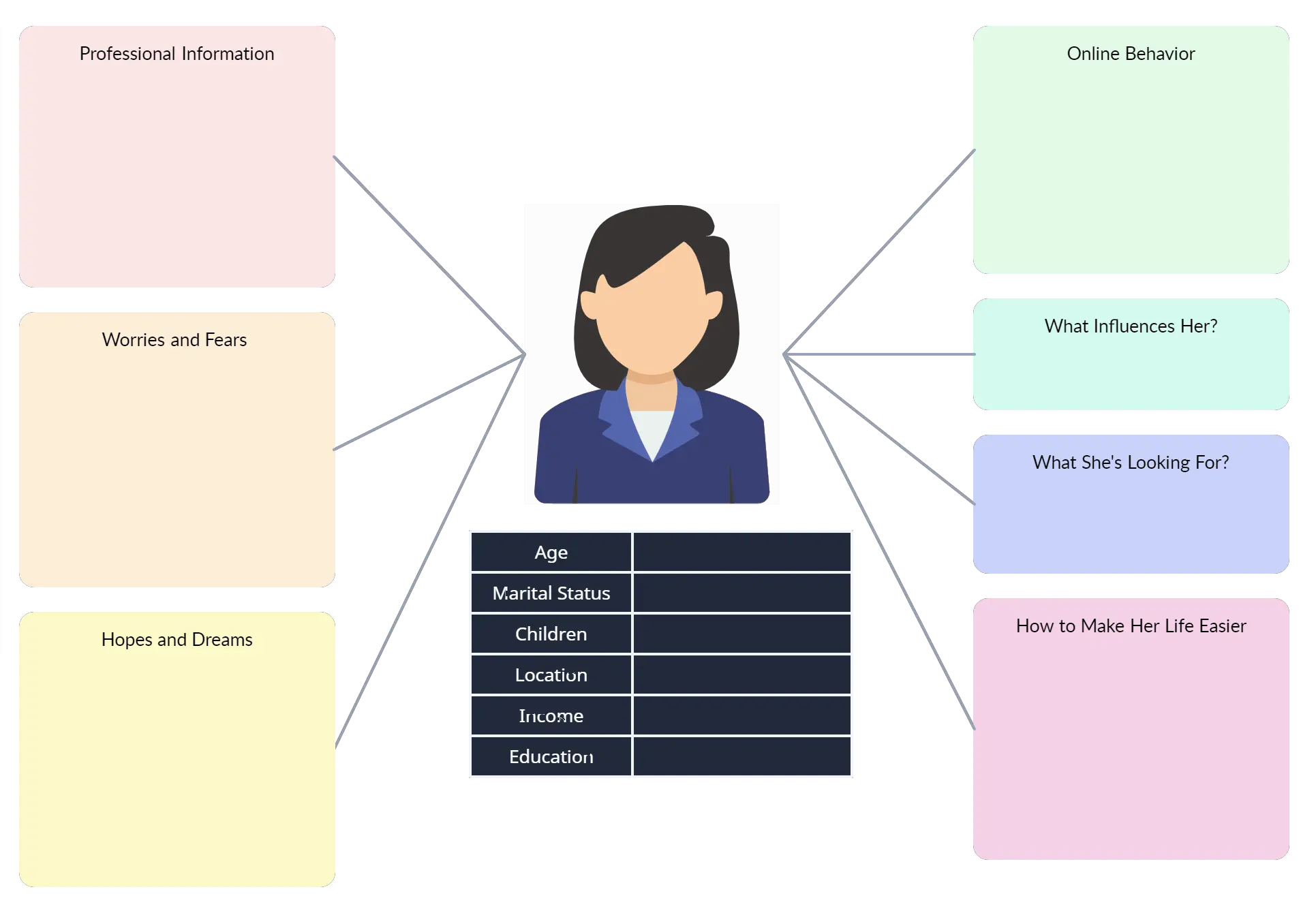
Persona Start with defining the Customer Personas that you are creating the journey for. Be specific (e.g., name, age, occupation, skills, interests).
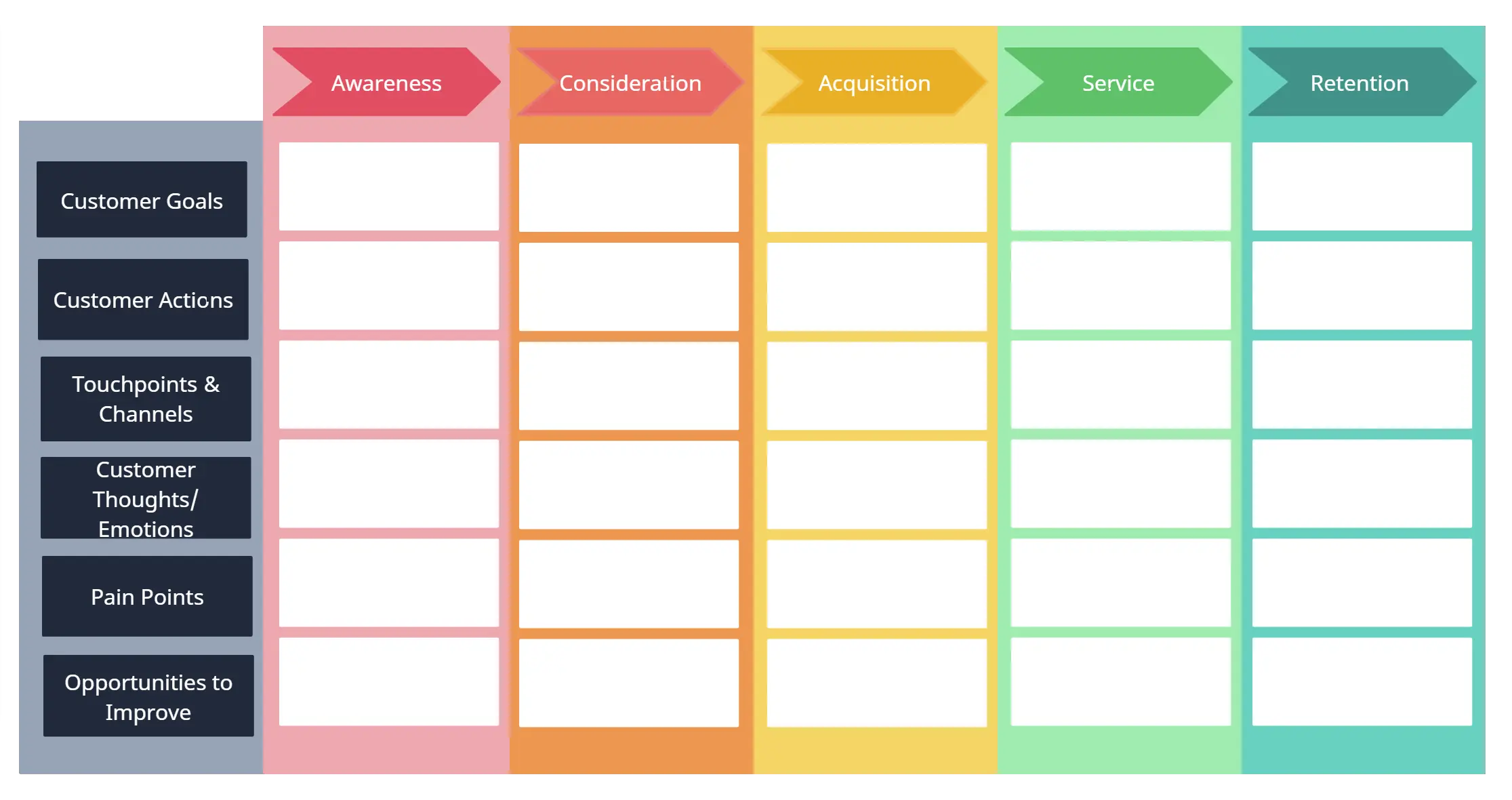
Touch Points What are the different moments of interaction with the customer (e.g., in a shop, online, via webinar, by phone, mail, or in contracts)? Some moments may be important to the customer, but are currently not touch points: map these moments as well! The customer is the primary focus.
Mood What is the customer’s mood at that very moment? Are they happy, frustrated, angry? What in the moment makes it so?
Timeline and Stages Define at least 5 moments in the journey. What is the timespan? What is the step-by-step experience for the customer? How much time has passed in the journey? Don’t overcomplicate: test with customers to see what to adapt.
Customer Needs What is the job the customer wants to get done in each of the stages? For example, if your customer seeks to identify the company they want to work with, we need to understand the various touch points. What are the questions customers have at each point?
Step-by-step guide
1 before you start.
Arrange for a comfortable environment. Definitely not a meeting room. Create a creative athmosphere and have plenty of colorful materials and magazines at the ready.
- Arrange a relaxed, positive and private environment
- Have markers (fine tip) and paper for everybody
- Print or draw the canvas on a big sheet of paper
- Have plenty of sticky notes and markers ready
- Allow yourself 45 minutes of undisturbed time
2 Define your Customer
To make a good customer journey, you need to define who it is for. Who is the customer you are going to follow? And easy way to do this is by using the persona canvas. You don't want to specify generic customer segments here, but start from specific customers, that you know. This will help enrich the journey. Generalizing it comes later.
3 Map the Journey
With the team, come up with moments in the journey of your customer. Think from that customer's perspective. His or her goal in life is not to buy your product or use your service, that is (usually) a means to an end. What end is that? How do they experience the problem you are trying to solve? And do they really experience it? What do they currently do to deal with that problem?
While you are defining moments for the customer, try to place them in an order. That could be a short interval, for example a day in the life of the customer, or a longer duration. The goal is to find the meaningful moments for the customer first, and then to look for the touchpoints where your product or service comes into the picture.
An easy way to build moments is to think of what happened first (what would be the movie frame for that moment?) and then to proceed what the customer thinks or feels, and ultimately what their needs are. Make sure it's their needs, don't sneak your product back in!
4 Challenge your Assumptions
Now that you have mapped out a lot of moments, it's time to challenge assumptions. So far, almost everything you have done is an assumption, starting from what you know about the customer, and going all the way to their needs in specific moments. Some of these assumptions are more impactful than others. They need to be checked before you start building product ideas on top of them. To do this, you need to go out of the building, and run experiments.
Show your journey to actual or potential customers, and see if they recognize themselves. What is their journey? Map it out with them. Once you have done that, you will start to see patterns and learn what the actual needs are that they have. Sometimes they may not even know it themselves!
5 Hack: Online Safari
In the age of the Internet it would be silly not to take an online safari. There are several tricks for getting a quick idea of what people are actually doing online. Take a look at your own user forum or that of a competitor. What are people complaining about? What conversations are they having? Use Twitter to get in touch with people that write about similar products. What kind of pictures do they post on social media? Are there any video blogs or YouTube channels that cover similar topics? How popular are they? What trends can you find there? You can get a lot of information in a very short amount time if you start following some online leads!
6 Hack: Do it yourself!
It pays to step into your customer’s shoes for a while. If you really want to understand your customers and their preferences, slip into their shoes, do what they do, and shop where they shop. We learned this trick from an expert retail food marketer. If you’re interested in understanding what attracts customers, go to the stores they shop at, observe them, and start pulling things off the shelf that attract you. Compare what you bought with what you see in customer’s shopping carts. You’ll likely find customer segments that stick together and look for similar qualities in the things they buy. Best of all, you’ll quickly learn what attracts customers to your competition.
7 Hack: Be the Barista
When you really want to surprise your customers and put them into a different state of mind, consider going the extra mile. Find (or build) a nice coffee cart and add to it everything you need to get people talking. Making the rounds in a place where your customers hang out is guaranteed to put a smile on their faces. You’d be surprised at what people tell their barista! What we’re actually saying: be a perfect host(ess) and facilitate the interaction.
8 Check your Customer Journey
Check the following items to see if you have worked enough on the Customer Journey.
- Is the persona you used specific enough?
- Is the journey complete? are there any moments missing?
- Ask yourself where the journey really starts and ends. Are there moments before and after?
- You can't think of moments you left out
9 Next Steps
- Use what you learned to inform your point of view.
- Go back and check your design criteria .
- Use the knowledge to work on new value propositions .
Additional Resources
design a better business ( patrick van der pijl, justin lokitz, lisa kay solomon, maarten van lieshout, erik van der pluijm ), contagious - why things catch on ( jonah berger ), hooked ( nir eyal ), made to stick ( dan heath and chip heath ), the mom test ( rob fitzpatrick ), you may also like, experiment cheat sheet.
A free overview of 25 Validation Experiment Recipes from WRKSHP.tools.
Free Canvases (A4)
All 20+ canvases from the book Design A Better Business, as print ready PDFs on A4 size (29.7x21 cm, 11.7x8.3 in), for free!
Design A Better Business

This book stitches together a complete design journey from beginning to end in a way that you’ve likely never seen before.
DBB Mobile App
Try the iOS App and have all 23 innovation tools in your pocket.
Design A Better Business Newsletter
Sign up for the Design A Better Business Newsletter and keep up to date with events and news!
Subscribers
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Customer Journey Canvas Explained

Mapping out a customer journey canvas is the best way to understand how to meet the customer’s needs. A basic way to diagram this is by using a customer journey . The customer journey canvas helps make things real. If you want to map out the different stages in the customer journey and the related user experience, keep reading to learn how to best use a customer journey canvas.
What Is a Customer Journey Canvas?
A customer journey canvas is a board that documents the user’s journey through your product/service. It is similar to a storyboard and maps out your user’s journey through different stages and emotions.
Customer journey canvases are similar to Customer Journey Map s but diagram elements on the surface level before diving deeper. In this template, you use sticky notes to build out customers experience and develop an understanding of areas where customer satisfaction is achieved.
How to Build a Customer Journey Canvas
Customer journeys are a straightforward way to define your customer’s journey and main expectations. In doing this, there are a couple of necessary stages you need to incorporate to accurately display their customer experience . We’ve gathered them here so you can build your own customer journey canvas.
Target Persona
The first stage in creating a customer journey canvas highlights the user persona you are targeting. Defining your persona is vital because it will narrow what you focus on, the user’s goals, and how you will meet them. The persona can help you identify and empathize with a customer segment. Start with individual clients you know, not generic customer segments.
LEARN ABOUT: Customer Journey Mapping Tools
If you have a predefined persona, you can insert it here, and if you need to create one, you can use a persona map.
The stages section is where you list each stage in the customer’s journey as they interact with your products and services. These stages should be very descriptive and record the user’s actions in their route to completion.
These stages should be critical in the journey but also to the customer. If there is a misalignment between what is important to the customer and what is emphasized in the product, this is a place you need to rethink your journey.
Customer Needs
The customer needs section is very important and asks you to specify what the customer requires from this stage of their interaction. This will mainly manifest in their actions, and it’s essential to look at what they do concerning their needs.
Additionally, two things are critical to emphasize when analyzing customer needs: intention and expectation.
Customer intention is not only the actions they take en route to completion but the reasons behind their actions. What motivates each action? Why do they do what they do?
When you analyze intention, you must also consider expectations. When the user does something, what result are they expecting? Does this line up with their intentions?
Addressing intention and expectation is vital to breaking down the customer’s needs.
- Customer Experience
Lastly, based on the stages and needs, you must analyze the customer’s overall experience. This process is mainly an emotional analysis, stating if they are happy, neutral, or dissatisfied. This real customer data is usually gathered through user research and product feedback.
After you map out this data, you will know where your customer is happy with the product and what pieces require improvement. Understanding this information is key to building a successful and trustworthy brand, and using a customer journey is the first step in that journey.
Customer Journey Canvas Template
Below we are providing you with a template that can serve as an example for you to start creating your own Customer Journey Map and identify the points to improve at each point of contact with the customer.

Download the customer journey canvas here
Customer Journey Canvas Tips
If you haven’t mapped out a customer journey, doing so can feel daunting. Follow these tips to make sure you create a practical customer journey canvas.
Do Your Research
Doing research is the core of everything that follows in a customer journey canvas. You cannot simply map out what you think the customer experiences. You need to know, from them, what the customer feels and goes through in order to address their needs adequately.
When creating a customer journey canvas, don’t skimp on your research.
Focus on a Persona
When creating a journey map, it can be easy to slip up and focus on a broad user base. For it to be effective, you have to do just the opposite.
Instead of focusing on a large group of users, it’s usually more effective to target a specific persona and alleviate their issues. Unless you have a large group of users expressing similar concerns, it’s usually best to start narrow and expand from there.
Try Mapping Your Assumptions
If you’re struggling to focus your map on your persona, it might be because your assumptions are getting in the way. As we previously mentioned, it’s dangerous to create these maps based on assumptions because they will rarely be accurate.
If this is the case, try creating another row for your personal/shared assumptions. This will help you compare them to the actual customer’s point of view and identify any discrepancies.
Don’t Stop at Customer Needs
The canvas stops here, but the optimization shouldn’t. After you’ve identified what the customer needs and where their experience is lacking, ensure that you conduct a brainstorming session to make each stage better. This can be done on the same board or as a different exercise, but each effectively creates the next steps for auditing your customer journey.
LEARN ABOUT: Consumer Decision Journey
If you need to audit your customer experience, a customer journey canvas is the perfect first step. To learn more about journey mapping , check out our other articles about improving CX.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities
Apr 26, 2024

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024

12 Best Employee Survey Tools for Organizational Excellence

Customer Experience Management Platform: Software & Practices
Apr 24, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Customer Journey Canvas Tutorial
Service design may come across as something intangible but the Customer Journey Canvas allows you to put your thoughts into words or diagrams in a structured manner. Once you fill up every aspect of the canvas, you will see everything coming together, just like assembling a jigsaw puzzle. A concept cafe is used as an example in the given Customer Journey Canvas. The first stage of service design is to plan how the service will be marketed and predict the reactions.
Pre-Service Period
Advertisement/public relations:.
Thinking about the core differences between advertisement and public relations campaign will help you make a decision on how you want people to perceive your upcoming services. Advertisements give you control over the creative direction and content of your message but your intended consumers know you are trying to sell to them. On the other hand, a successful PR campaign will gain the trust and attention of the consumers since they perceive the message as an independent, third party review of your upcoming service. The downside is that you have no control over how people are going to write about your services. Another marketing element to consider is if you plan to tap into both print media and the internet for your marketing campaign. Most companies tend to go both routes in order to reach out to a larger audience. In the example, the idea of having a short film that expounds on the cafe’s unique concept is an effective way to capture attention without advertising blatantly.
Social Media:
Twitter and Facebook are the leading social media platforms. You can go beyond these and release updates on your services on social media platforms that are related to your niche.
Word of Mouth:
Think in both the positive and negative context. Imagine yourself as the customer. If you are pleased with the services, which aspects are you likely to be satisfied with? What will you tell your friends and family? In contrast, if you are unhappy with the service, what is likely to have gone wrong? By anticipating these reactions, you can try to further fine-tune your service.
Past Experiences:
It can be hard to fill up this column if you are launching a whole new, unheard of service but you can trace it back to the inception of the service. Was something lacking in a service which customers often complain about, thus inspiring you to create a service to fulfill the needs?
Expectations:
Put yourself in the shoes of the customer who hears of the service. How would you react and what expectations you have in mind? Understanding customer expectations means that you can set well-defined goals.
New Customer Journey Canvas
Service Period
Service journey:.
The service journey details the entire experience of the customer from his arrival to departure. As you can see from the example, the three major touchpoints are: the entrance where the customer gets greeted by the staff and leaves his more bulky belongings, the place where he settles down to order from the menu, and when he exits the cafe. Your service journey may be a lot more detailed but one thing to keep in mind is that the touchpoint may not necessarily involve an interaction with the service staff.
Experiences:
As always, the evaluation of the service will lead to the conclusion of customer experience.
Post Service Period
Customer relationship management:.
CRM can manifest itself as a software or a system aimed at building a relationship with customers and maintaining it. A successful CRM model is imperative to the success of the business. Depending on your industry, your CRM model will differ but the three major aspects to consider remain the same. They are: 1) People Everyone in the company needs to breathe and live the CRM initiative. Customer service representatives are usually at the forefront of the initiative since they have direct contact with customers. 2) Process You should always ask yourself how a particular process can be streamlined to better serve the customer. Companies may often find themselves going back to review this aspect repeatedly because new situations always crop up to reveal a lapse in the service. 3) Technology Does the company have the technology to support its CRM initiative? This can be in the form of having a software to capture the personal data of customers so they can be sent updates on the service. The system should provide the management valuable insight into the demographic profile and preferences of their customers so they can add a personal touch to the service.
Social Media, Word of Mouth:
These two sections are pretty self-explanatory. Providing a social media platform means that customers will use it as a feedback channel to communicate their experiences and feelings towards the service. The response on the social media platform is likely to reflect the general word of mouth sentiments.
Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction:
As you list out what customers were satisfied and dissatisfied with, it is time to compare it with the customer expectations you have penned down during the first stage. Do the sentimentsmatch up with the expectations? A disparity is a telltale sign that the management need to go back to the drawing board and re-evaluate the entire service design.
The customer journey canvas is a clear overview of the entire service design process. You are likely to refer to it again and again because there are always improvements to be made and problems to be solved. An element of surprise is always possible. When it presents itself to you as a challenge to your business, the customer journey canvas helps you to clearly identify how the problem is related to the service design process. This will helps you stay focused and work on resolving the problem systematically.
The next level
You love working with canvases? How about bringing innovation and collaboration to the next level with great canvases and a great app.
Profitable Business Models > Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas Explained: Customer Relationships
- by Joanne Moyo
- January 20, 2022
Next, on the business model canvas explained, we will discuss the customer relationship segment. Once you’ve figured out your value proposition and defined your customer segment, the next step is to build, nurture, and grow the relationship between your business and your customers.
The key question here is how much effort you must make to deliver your value proposition to customer segments?
Think about the brands or businesses you feel loyal to or enjoy buying from. One of the things you’ll notice is how easy it is to get in touch with their customer service department. This is just one example of how companies manage their relationships with customers.
How your business interacts with its customers defines what customer relationships are. The structures you have in place are essential to maintaining good customer relationships.

Types of Customer Relationships
First, let’s look at the different types of customer relationships you could implement.
- Personal assistance
This type of relationship is concerned with human communication. You could choose to talk to your customers using the phone, email, face-to-face, or other means of personal contact.
For example, when LinkedIn was having issues with getting people to sign up and use the site, they launched a personal survey campaign. This allowed LinkedIn staff to take some customers out for lunch to discuss the issues they were having with the site.
- Dedicated personal assistance
This relationship is more personal and is tailored to the individual customer’s needs. This type of relationship includes assigning a customer representative to a specific customer who consistently engages with the same person.
This gives the customer familiarity, builds trust, and allows the customer representative to really get to know and understand that particular client. You can foster deep and meaningful relationships with influential customers over a prolonged period.
Let’s take a look at a real-life example. Conducting surveys is a common way for companies to get relevant and accurate customer feedback. But usually, most companies churn out online surveys, which tend to be impersonal. LinkedIn’s founder, Reid Hoffman, felt the same way.
When LinkedIn was just starting, they failed to get enough people to join the site. So they came up with the idea to hear firsthand from the LinkedIn user what issues they had with the site. Instead of impersonal online surveys, LinkedIn created a system where team members sought out users to have lunch with them and share their LinkedIn experience. This allowed the LinkedIn team to understand what their customer segment liked and disliked.
- Transactional
You might be familiar with this type of customer relationship. Transactional relationships are pretty impersonal; you hardly interact with the customer, and contact is limited to a specific transaction.
The Amazon online marketplace, for example, is mainly transactional. Most customers only interact with Amazon online while they order their product. This is the only interaction they’ll have with the brand for many customers.
- Co-creation
Nowadays, we’ve seen more companies going beyond the traditional customer-vendor relationship. Going back to our Amazon example, the initial interaction between the company and customers was transactional. But now, Amazon has gone a step further and invites customers to write reviews on products, thus creating value for other customers.
- Self-service
This type of relationship involves no direct relationship between a business and its customers. Clients are entirely self-sufficient, so there is no need to establish human interaction. You can start your business using the self-service model. Still, sometimes companies can move to self-service at a later stage.
For example, IKEA’s entry into self-service relationships with its customers was unique. In 1971 an electrical fault at the IKEA flagship store caused the sign on the roof to catch fire. The damage was substantial, but the company did not want to halt operations; instead, they came up with the idea for a self-service area and began selling most of their products this way. Customers could simply pay and pick up their furniture at the self-service area, without going into the damaged store to view the display.
- Automated services
This relationship is a combination of self-service with automated processes. Both processes can identify specific customers and provide them with accurate information on their transactions.
Additionally, automated services can be designed to mimic a personal relationship, providing excellent and efficient customer service. Netflix is famous for using automation and machine learning to improve its customer experience. Not only do they offer personalized viewing, but they also stimulate personal relationships by suggesting accurate movie or TV show recommendations.
- Communities
These relationships nurture community connections between customers, which can be done online, for example. More and more companies utilize user communities to become more involved with current and future customers. This can be done using third-party websites or applications such as Slack or Facebook to communicate with your customers and encourage interaction.
How to Develop Good Customer Relationships
In today’s business environment, the key to nailing this segment is to develop an effective communication system. People can instantly get in touch with the brand and engage with the company through new posts, images, and collections uploaded to social media.
Additionally, a crucial building block to mastering your customer relationships is to consider the perfect relationship between you and your customer. Should it be personal? Automated? Or a bit of both? For instance, it could be personal to one customer segment and automated to the other.
You also need to put yourself in your customer’s shoes as a company. Think about what the ideal relationship would look like from their point of view? For some customers, the ideal relationship would be that there is no self-service and that they have access to a dedicated personal assistant.
As you go through this process, you should also consider that this relationship you’re trying to create will heavily impact your customer’s experience. Additionally, your customers may have certain expectations about the type of relationship you should establish with them. Therefore the two key questions to ask are; how much assistance is actually needed? And what is minimum assistance required to sell to a customer?
So for example, in the case of IKEA, you shop at IKEA because it’s cheap. You can assemble
Furniture in your house to save some money, but it’s not really a pleasant experience spending the entire Saturday assembling furniture. Then again there are other customers who prefer assembling furniture themselves instead of hiring someone or buying custom-made furniture, which tends to be much more expensive.
Questions to ask
To help you define your relationship with your customers, there are a few questions you can ask. These include:
- What type of relationship does each customer segment expect you to establish?
- Which ones have we established?
- How much would it cost you to establish a relationship with each customer?
- How do your methods integrate with the rest of your business model?
- Does the customer have a dedicated personal contact they can contact in person, via phone, or email?
- Do you have physical or online channels that are dedicated to customer interactions?
- How could you automate some parts of the process, to scale up?
- Would moving to the left on the scale “personal – automated” help you differentiate from your competitors and allow to deliver or redefine value proposition?
Your customer relationships segment should answer the question of how you get, keep, and grow customers. Let’s talk about these factors briefly for a bit.
- Getting customers: Here, you’ll have to figure out how customers find out about you and make their initial purchase? So, for example, this could be through advertising on Google.
- Keeping customers: How do you keep your customers loyal? Excellent customer service is one of the ways you may be able to retain your customers.
- Grow: You’ll have to figure out how to get your customers to spend more? A good example will be using a monthly newsletter to keep them informed about your latest products. But this depends on the industry and the type of business you conduct. For some businesses a newsletter may not be such a good idea.
Examining the ways you propose to interact with your customers will help you define how your business will operate. Overall, the easiest way to develop good customer relationships is to walk through the entire customer journey in detail.
The Key Takeaway
Whatever types of customer relationships you choose, the most crucial point is that you must always keep your customers in mind. And lastly, think about the costs incurred for each type of relationship and how you can integrate these with the rest of your business model.
Most Popular

Netflix’s Business Model Canvas Evolution (2021)

McDonald’s: Business Model Canvas, its evolution and company’s history

18 Must-Read Business Books

Check how Amazon’s main focus allowed the company to thrive. Amazon’s Business Model Canvas and how it changed from the very beginning.
- Business books reviews (27)
- Business Ideas (8)
- Business Model Canvas (9)
- Business models of large companies (26)
Business Tools

Download Free Business Model Canvas Template in Word / docx / PDF / SVG format
Inspire yourself with Business Ideas Generator
Get INSPIRING stories and TIPS on making your business model PROFITABLE!
- Recently trending business ideas
- Inspiring business models
- Examples of profitable businesses from all over the world
Related Posts

Twitter: Becoming The World’s Fastest Information Hub
Today, Twitter is one of the most recognizable and influential social media platforms on the planet. As of February 2022, Twitter is valued at $27.48

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Cost Structure
The last (but not least) segment on the Business Model Canvas is the cost structures. In this segment, you must ask yourself, how much will

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Partners
No man is an island; the same goes for your business. They are other companies, 3rd parties, and people that you will need to achieve

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Resources
On the Business Model Canvas, the Key Resources segment refers to the supplies, assets, and materials required to deliver your value proposition to your customer
Privacy Overview
What is a Business Model Canvas: A Miro Insider Guide

Table of Contents
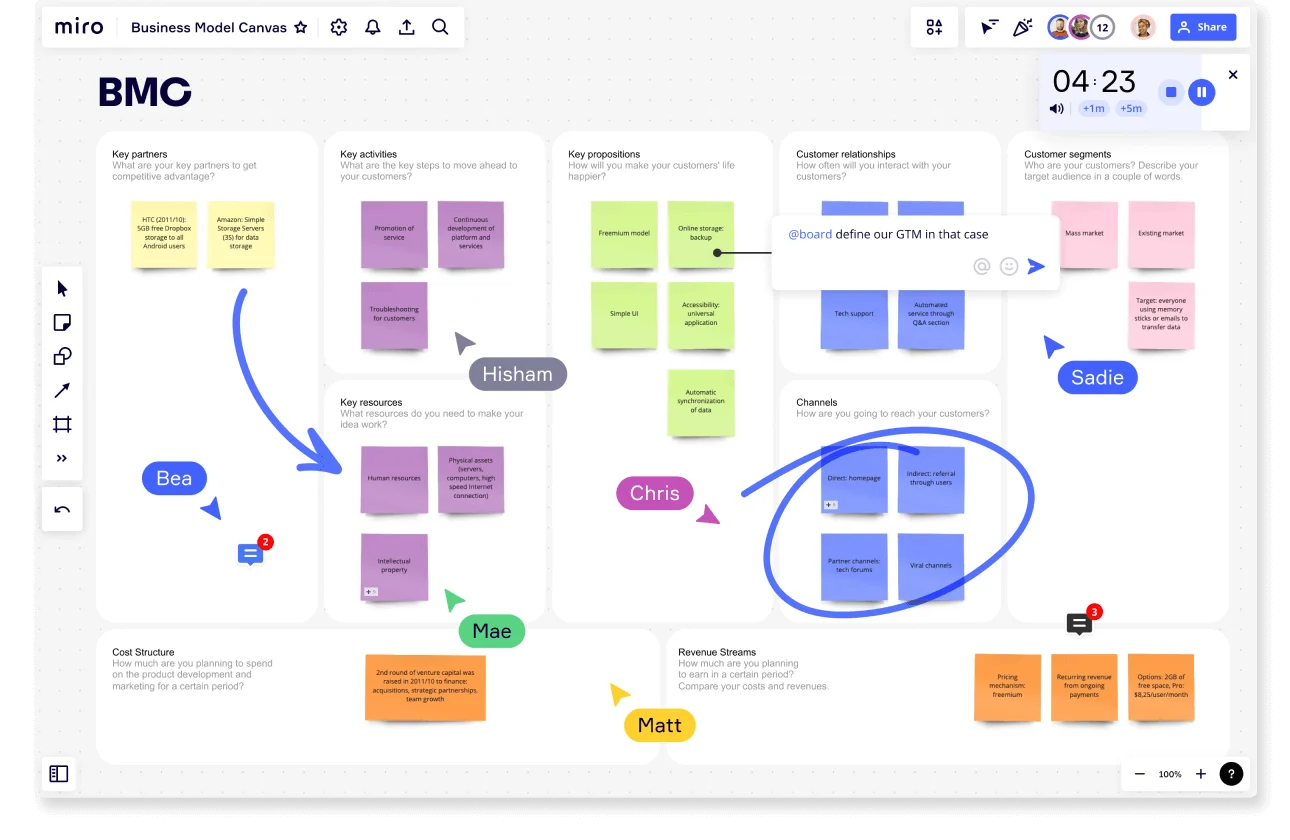
Diving into the business strategy and innovation world introduces various tools and methodologies to navigate current markets. Among these, the Business Model Canvas (BMC) stands out as a strategic management tool that has revolutionized how entrepreneurs, innovators, and business leaders visualize, design, and reinvent their business models.
The BMC provides a concise, visual framework that encapsulates how organizations create, deliver, and capture value. This article aims to explore the BMC in-depth, offering insights and practical advice on leveraging this tool to its fullest potential.
Decoding the Business Model Canvas
What is the Business Model Canvas? At its core, the Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool designed to visualize, design, and reinvent business models. It's your canvas (pun intended!) to paint a comprehensive picture of how your organization creates, delivers, and captures value. Alexander Osterwalder pioneered this concept, making it a cornerstone for entrepreneurs, innovators, and business leaders worldwide.
Key components of the Business Model Canvas:
1. value propositions.
Your value proposition is the core of your Business Model Canvas. It essentially answers the question: What sets you apart from your competitors, and why would customers choose you over them? It's more than just your products or services; it's about your exclusive benefits and solutions. A compelling value proposition is concise, straightforward, and directly addresses the customer's problem or need. So, it's like your pitch to your target market that you can deliver in an elevator ride.
2. Customer segments
Who are you creating value for? This section requires you to segment your market into groups of customers with similar needs, behaviors, or characteristics. Understanding your customer segments allows you to tailor your value propositions, communication, distribution channels, and more to each specific segment. It's about being precise in whom you serve to maximize your impact and efficiency.
3. Channels
Channels are the touchpoints through which you communicate with your customer segments and deliver your value propositions. They cover the entire customer journey, from awareness and evaluation to buy and post-purchase. Channels can be direct, like your website, or indirect, like retail partners. The goal here is to find the most effective and efficient way to reach your customers where they are.
4. Customer relationships
How do you intend to establish and sustain relationships with your customers? This aspect involves identifying the kind of relationship you wish to maintain with each customer group, ranging from personalized assistance to self-service, automated services, communities, and co-creation. Your chosen relationship strategy should align with customer expectations and your business model's cost structure.
5. Revenue streams
Revenue Streams refer to how your business can generate income by converting value into financial returns. These streams may include selling assets, lending, leasing, subscription fees, licensing, and advertising. It is important to associate each revenue stream with a specific customer segment and to clearly understand what your customers are willing to pay for and how they prefer to pay.
6. Key resources
Key resources are the assets required to make your business model work. They can be physical (buildings, vehicles), intellectual (brands, patents, data), human (expertise, knowledge), or financial. Identifying and securing these resources is vital for delivering your value propositions, reaching markets, maintaining customer relationships, and earning revenue.
7. Key activities
What must you do to ensure your business model functions effectively? Key activities in the Business Model Canvas could involve production, problem-solving, or platform/network maintenance, depending on your business type. These are the most important tasks your company must undertake to fulfill its value propositions, reach markets, and sustain operations.
8. Key partnerships
Few businesses operate in isolation. Key partnerships and networks can help you optimize your business model, reduce risks, or acquire resources and activities. Partners can include suppliers, manufacturers, collaborators, and even competitors in some cases. The aim is to forge alliances that help your business focus on its core value proposition and outsource or collaborate on the rest.
9. Cost structure
Finally, the cost structure outlines the major costs of operating your business model. Understanding your cost structure is crucial for ensuring your business is financially viable. Costs can be fixed (unchanged regardless of output), variable (scale with production volume), or a mix of both. The goal is to create a cost structure that allows your business to deliver its value propositions sustainably and competitively.
Each of these components interconnects to paint a comprehensive picture of your business model. When thoughtfully completed, the Business Model Canvas not only guides your strategic planning but also serves as a dynamic blueprint that evolves with your business.
Do you need a Business Model Canvas?
Whether you're a startup or an established company, BMC is your Swiss Army knife for business model innovation. It's particularly useful when:
Launching a new product or service, providing a holistic view of its potential.
Entering a new market , helping you understand your unique value proposition.
Pivoting your business , enabling rapid conceptualization of new directions.
Benefits of using a Business Model Canvas:
Clarity and focus.
The BMC provides a clear, concise framework that condenses complex business models into a single visual document. This clarity is invaluable, as it allows you to see the relationships between different business model components—how your value propositions align with your customer segments, how your channels and customer relationships support your value delivery, and how your revenue streams fit with your cost structure. This focused overview enables you to identify your business model's strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for innovation.
Alignment and communication
One of the BMC's greatest strengths is its ability to facilitate alignment and communication within teams and across departments. By having a shared, easily understandable visualization of the business model, everyone from the CEO to the newest intern can have a common understanding of the company's strategic direction. This alignment ensures that all efforts are coordinated towards the same objectives, reducing conflicts and enhancing productivity. It also makes it easier to onboard new team members and communicate with external stakeholders.
Flexibility and adaptability
Adaptability is key to survival and growth in today's fast-paced business environment. The BMC is inherently designed for flexibility, making it easier to pivot and iterate on your business model as market conditions change, new technologies emerge, or customer preferences evolve. This adaptability allows for rapid experimentation and validation, enabling businesses to effectively innovate and respond to opportunities or threats.

Streamlined strategy development and execution
The BMC streamlines the process of strategy development and execution. Breaking down the business model into nine fundamental components simplifies complex strategic considerations, making it easier to identify which areas require attention, improvement, or innovation. This streamlined approach helps businesses more efficiently allocate resources, prioritize initiatives, and execute their strategies more precisely.
Enhanced customer understanding
The BMC encourages a deep dive into who your customers are, what they need, and how they want to interact with your business. This enhanced understanding is crucial for creating value propositions that truly resonate with your target audience and developing customer relationships that foster loyalty and advocacy. You can maintain a customer-centric approach that drives sustained business growth by continuously refining your customer segments and value propositions based on feedback and market research.
Risk management and cost efficiency
The BMC helps identify potential risks and areas where costs can be optimized by providing a holistic view of your business model. Understanding the key activities, resources, and partnerships essential to your business model allows you to make informed decisions that minimize waste and reduce vulnerabilities. This proactive approach to risk management and cost efficiency can significantly improve your business's operational effectiveness and financial health.
Innovation and competitive advantage
Lastly, the BMC is a powerful tool for fostering innovation. By visualizing your business model, you can easily spot opportunities for disruptive innovation, whether through new value propositions, untapped customer segments, novel revenue streams, or more efficient channels. This ongoing pursuit of innovation helps maintain a competitive edge, ensuring that your business remains relevant and capable of capturing new market opportunities.
Application of BMC in different roles
Product managers.
Scenario: Launching a new app.
Validate customer needs and tailor the app's value proposition.
Identify key features as Key Activities.
Design a user acquisition strategy through Channels.
Business managers
Scenario: Expanding into a new market.
Assess the market's Customer Segments and adapt the value proposition accordingly.
Reevaluate Key Partnerships for local market access.
Adjust Cost Structure for market entry.
Strategists
Scenario: Exploring new revenue streams.
Analyze current Revenue Streams and brainstorm alternatives.
Evaluate new Customer Segments for expansion.
Consider innovative Channels and Customer Relationships to enhance value delivery.
How to complete a Business Model Canvas: Step-by-Step
1. start with the value propositions.
Clearly define the unique benefits your product/service offers.
Tools/Frameworks: The Value Proposition Canvas is an excellent tool here. It allows you to get into your customers' shoes, understanding their needs, pains, and gains deeply. This detailed exploration helps craft compelling value propositions that resonate strongly with your target market.
2. Identify your customer segments
Understand who your customers are and what they need.
Tools/Frameworks: Market Segmentation Analysis is crucial. Use data analytics tools like Google Analytics for an online audience or customer surveys and interviews for direct feedback. Personas and empathy maps also offer valuable insights into customer motivations and behaviors, helping you to segment your market more effectively.
3. Map out channels
Determine how you'll reach your customers.
Tools/Frameworks: The Five Channels Framework by Clayton Christensen is a powerful way to think about how you reach your customers. Additionally, A/B testing platforms can help you experiment with different channels and measure their effectiveness in reaching your customer segments.
4. Design customer relationships
Plan how to interact with your customers.
Tools/Frameworks: Customer Journey Mapping tools enable you to visualize the entire customer experience and identify key touchpoints where you can strengthen relationships. CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software can then help you manage these relationships at scale.
5. Define revenue streams
Explore how you'll make money.
Tools/Frameworks: For this component, Business Model Scenarios can be particularly useful. This involves creating various "what-if" scenarios to explore different revenue models and their implications. Financial modeling software or spreadsheets are essential tools for quantifying these scenarios and projecting their financial outcomes.
6. List key resources
Identify what you need to operate.
Tools/Frameworks: Resource Analysis is a systematic approach to identifying your essential resources. Tools like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis can help you critically assess your internal capabilities and resources.
7. Outline key activities
Pinpoint what actions are necessary.
Tools/Frameworks: Process Mapping tools can help you visualize and optimize the key activities required for your business model to succeed. Lean methodology and Kanban boards effectively identify and focus on value-adding activities, minimizing waste in your processes.
8. Select key partnerships
Choose who will help you succeed.
Tools/Frameworks: Partnership Mapping is a strategy that can clarify how and with whom you should collaborate. Tools like the Partner Ecosystem Canvas can help you identify potential partners and define the nature of these partnerships in alignment with your business objectives.
9. Analyze cost structure
Break down your costs.
Tools/Frameworks: Cost Analysis Tools , such as cost-benefit analysis frameworks and financial modeling software, are invaluable. They allow you to break down your costs into fixed and variable components, understand your cost drivers, and explore ways to optimize your cost structure for efficiency and sustainability.
Avoid these pitfalls when building your BMC
Overcomplication.
Problem: Adding too much detail or too many elements can make the BMC confusing and less actionable. It's essential to keep the model clear and concise to maintain focus and ensure it's easily understood by all stakeholders.
Solution: Stick to the core elements of your business model. Use simple language and avoid industry jargon. If necessary, create additional documents for in-depth analyses, but keep the BMC as your strategic overview.
Ignoring customer feedback
Problem: Building a BMC based on assumptions without validating these assumptions with real customer feedback can lead to a misalignment between your business model and market needs.
Solution: Regularly engage with your customers through surveys, interviews, and prototype testing. Use these insights to continually refine your value propositions and customer segments in your BMC.
Inflexibility
Problem: Treating the BMC as a static document rather than a living, evolving tool can stifle innovation and responsiveness to market changes.
Solution: Periodically review and update your BMC to reflect new insights, changes in the market, and strategic pivots. Encourage a culture of flexibility and continuous improvement.
Lack of alignment among team members
Problem: Without a shared understanding and consensus among team members regarding the BMC, there can be misalignment in execution, leading to inefficiencies and dilution of strategic efforts.
Solution: Regularly discuss and review the BMC with all team members and stakeholders. Ensure clear communication and alignment on the business model's key components and strategic direction.
Focusing only on the present
Problem: Focusing solely on current operations and ignoring future opportunities and threats can make your business vulnerable to disruption.
Solution: Use the BMC as a tool for both current state mapping and future scenario planning. Regularly brainstorm potential changes in customer needs, technological advancements, and market dynamics that could impact your business model.
Underestimating the importance of key partnerships
Problem: Neglecting to carefully consider and nurture key partnerships can lead to missed opportunities for leveraging external expertise, resources, and market access.
Solution: Identify and actively manage relationships with partners that can provide critical resources, channels, or customer access. View these partnerships as strategic assets.
Failing to prioritize and sequence activities
Problem: Attempting to tackle all components of the BMC simultaneously without clear priorities can lead to resource strain and loss of strategic focus.
Solution: Identify the most critical components of your BMC that will drive most of your value creation and revenue generation. Focus your efforts and resources on these areas before expanding to others.
Not leveraging technology and tools
Problem: Manually managing and updating your BMC without using digital tools can limit collaboration and reduce the efficiency of iterations.
Solution: Use platforms like Miro for collaborative BMC creation and iteration. These tools offer templates, easy updates, and the ability to share your canvas with stakeholders for feedback and collaboration.
By being mindful of these pitfalls and implementing the suggested solutions, you can ensure that your Business Model Canvas remains a dynamic, effective tool that drives your business strategy forward. Remember, the goal is to use the BMC not just as a planning tool but as a framework for ongoing innovation and strategic agility.
Building your BMC with confidence
Creating a Business Model Canvas is an ongoing journey, not a one-time task. Here are some final nuggets of wisdom:
Iterate Relentlessly: Your BMC should evolve as your business grows.
Seek Diverse Perspectives: Collaboration enriches your business model.
Use Visual Tools: Platforms like Miro offer an interactive way to build and share your BMC.
As we come to a close, it's important to emphasize that the Business Model Canvas is more than just a tool - it's a way of thinking that encourages creativity and innovation in your business strategy. Whether you're a product manager, business manager, or strategist, using the BMC framework can help you clearly articulate, develop, and pivot your business model with confidence. So embrace it, and discover how your business ideas can flourish in ways you never thought possible.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas In A Nutshell
The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in the book Business Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising : key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
Table of Contents
A quick intro to business models
A business model is a way in which organizations capture value. Not only the economic value but also the social values an organization can foster and the cultural values it can sustain in the long run.
In other words, generating a business model isn’t just about how companies make money but how they create value for several players. Unlocking profits for the organization that came up with that business model is one of the critical elements.
There isn’t a single way to design and assess a business model . However, the business model canvas is a holistic model that takes into account nine factors or building blocks.
Alexander Osterwalder proposed the Business Model Canvas. He’s a Swiss business theorist that in 2000 together with a team of 470 co-creators in an attempt to create a tool that entrepreneurs could use for their businesses.
The aim of having a sharp understanding of your business model is critical to provide strategic insights about your customers, product/service, and financial structure.
Thus, to take action and iterate the business model until it unlocks value for your organization as a whole.
Let’s take a real case study. I often mentioned the Google business model as a great example. You might like or not the giant from Mountain View.
Yet what made this company so profitable – I argue – was its ability to unlock value for several players in the digital marketing space.
In fact, on the one hand, with AdWords, Google allowed businesses to transparently bid on keywords based on the clicks those ads received.
This allowed companies to disintermediate advertising from intermediaries that were taking up most of the margins (of course now Google gets them).
On the other hand, with AdSense, Google allowed small publishers around the world to monetize their content. All they needed was an AdSense account and enough traffic to start earning money.
Of course, as of today, this model isn’t sustainable anymore for many businesses. In a way, AdSense democratized the ads revenues, which before were only taken by large players. With Google , those profits got shared with content creators.
Also, Google offered the best search experience compared to any other search engine.
Even though it wasn’t the first to take over the market (it was actually among the last movers ) Google offered a free service that worked wonders.
The focus on a great search experience was one the most crucial factor in Google ‘s success.

Little critical note: Just like professors study birds flight and go around the world to teach birds how to fly while they can’t. So entrepreneurs that tinker on a daily basis with business models might have a better feel for that compared to theorists trying to teach them what a business model is. In short, my point is that you don’t need to get bogged down on its definition or to stick with the business model canvas to assess your business model . You might want to develop your way to look at your business as – if you’re an entrepreneur – there’s none better than you to do that. In short, use the business model canvas as one of the many methods you can use to assess your business. What really matters is that you’ll be able to build a valuable business in the marketplace.
Going back to the business model canvas Alexander Osterwalder , outlined several prescriptions that form the building blocks for a business model .
Those building blocks enable entrepreneurs to focus on operational, strategic, and financial assessments of their business.
- Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
Business model canvas in a nutshell
The nine-building blocks of the business model canvas comprise vital partners, key activities, value propositions , customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
- Key partners
Who are your key partners/suppliers? What are the motivations for the partnerships?
It all begins with your partners. If you don’t have the right partnerships in place, you don’t have a business at all. That is the starting point of your business model . Finding the right partners is critical.
The success of your business and the traction depend upon your ability to identify and offer your partners a compelling reason to do business with you.
For instance, if you think about Google , the principal partners are the small publishers part of the AdSense program, together to the businesses that are part of the AdWords network and the users that daily keep going back to the Google search box by giving it critical data to sustain its business model .
If you think about Uber instead, you’ll notice how the key partners are its drivers for which Uber means an additional if not a full-time income as self-employed. Its engineers that keep the platform smooth and running and people that sustain the cause of Uber.
If you think instead at Airbnb , you’ll notice that those key partners aren’t only hosts and travelers that transact each day on the platform. Also, freelance photographers that travel the world to take professional pictures that enrich the user experience of Airbnb are also key players.
When it comes to partners “who” and “why” are critical questions. In short, who’s the niche of people that can sustain your business? And why, so what compelling reason are you giving them? What value do they get from this partnership? It doesn’t have to be just in terms of finances.
Of course, initially, a better deal would do. But it could also be about social values or personal values. For instance, initially for its drivers, Uber didn’t mean right away full-time income. But it also meant more freedom for its drivers to work when they wanted. So initially freedom might have been a critical aspect.
- Key activities
What key activities does your value proposition require? What activities are important the most in distribution channels , customer relationships, revenue stream…?
As innovationtactics.com explains, critical actions for Uber were:
- Remove friction from all interactions
- Scale driver and customer side to reduce idle times for drivers and waiting times for customers
- Reduce negative externalizes , e.g., bad behaviors on both sides
- Grow the platform by getting more participants joining
- Keep participants engaged and stimulate ongoing participation
- Continue improving the value proposition , e.g., cheaper rides for regular commuters through UberPOOL
- Look out for complementary value propositions (e.g., car financing, new customer segments, etc.)
- Deliver on the customer proposition
- Reduce churn (esp drivers)
- Expand to more cities (US and global)
- Analyze the data to fine-tune everything
- Enhance technological lead and intellectual property to steepen barriers of entry
In short, those are the activities needed to make your value proposition compelling for your key partners. Thus, they can vary from removing friction (think of a marketplace that is hard to use), add features, or make transactions smooth.
In short, the more your organization acts as an enabler of business relationships among several players the more its value proposition consolidates. Thus, anything that solves a customer problem, or satisfies an unfulfilled need would do.
Based on my personal experience from the case studies I’ve looked at the more the value proposition can adapt to several players’ needs, the more it makes a business model become the driver for organizational growth. Take Quora:

The Q&A social network can bring together several partners (users, writers, top writers, publishers/online businesses, and investors) with different value propositions ; all met on the same platform.
- Value proposition

What core value do you deliver to the customer? Which customer needs are you satisfying?
Although the value proposition is not listed as the first element. In reality, this is the first thing you should assess. I’d say this is the foundation of your business model . That is what keeps the blocks together.
Without knowing the core values for your customers or partners and what needs you’re satisfying, or what problems you’re solving for them you might have a product but not a business.
This is connected with the previous building blocks and with the next ones. This is the glue that keeps it all together. As explained in the last point a value proposition doesn’t have to be for only one player, partner, or type of customer.
Take the case of a multi-sided platform like LinkedIn. The value proposition can embrace both sides of the marketplace:

The value proposition isn’t marked in the stone, but it can change over time. As new partners join; and as you tinker with your business model and as new unforeseen needs come about your value proposition might also change.
- Customer relationship
What relationship that the target customer expects you to establish? How can you integrate that into your business in terms of cost and format?
Based on the identified partners and customers you need to assess how to manage those relationships to keep them aligned with their expectations and within your business model .
If you take Uber, as specified by innovationtactics.com it needs to consider four elements to manage their customer relationships.
(1) the customers(=riders),
(2) the drivers,
(3) the broader public and
(4) regulators.
Each of those relationships will have different dynamics. For instance, drivers might be concerned about safety risks while regulators might be worried about transparency and proper data management.
Another example, if you take the Airbnb business model , hosts are critical to the success of the platform, and concerns like liability coverages are essential for them to keep using it.
That is why hosts are provided with insurance and liability coverage, the “Host Protection Coverage” (of course that might have happened because of some accidents).
https://fourweekmba.com/airbnb-business-model-explained/
- Customer segment
Which classes are you creating values for? Who is your most important customer?
Once you have the previous building blocks in place, it shouldn’t be hard to define for which class of people you’re creating value and what are your most important customers.
It is important to stress that although this is a list of blocks, it is not necessarily meant to be read or assessed in order. In fact, at times you might have some blocks but miss others.
For instance, let’s take the case of a startup that has created an innovative software-based on new, emerging technologies. The startup founders might know for sure that technology is valuable and it will open up market opportunities.
Yet that same founder might not have a clue about who the potential customers might be. This shouldn’t surprise you. Starting up a business doesn’t necessarily mean starting from a problem people have.
That is true in more traditional industries. In tech, the opposite might apply. You have new technology and a product that does many things.
However, you struggle to have that business take off. How to find your customers? Often they will come to you as the interactions with the first customers become more intense. You’ll also refine your service to make it more focused on specific features and needs.
That process of iteration will bring you to the so-called “product-market fit.” This process can be at times painful and time-consuming.

Key resource
What key resources does your value proposition require? What resources are important the most in distribution channels , customer relationships, revenue stream…?
As we’ve seen the value proposition is the glue that keeps all the blocks of your business model together. Thus, it is critical to assess what financial and human resources to allocate to allow your value proposition to keep your business model going.
For instance, on Airbnb , it is critical to continue growing the offering and the quality of it to give more and more options to travelers. Also, Airbnb has noticed users wanted more experiences . It started to offer a whole new section focused on those experiences.
- Distribution channel

Through which channels that your customers want to be reached? Which channels work best? How much do they cost? How can they be integrated into your and your customers’ routines?
A Peter Thiel might say if you don’t have a distribution you don’t have a product. As engineers are running many successful tech companies, it’s easy to get deluded by the fact that engineering alone can generate a successful business model . This is false!
The business world is a competitive environment. It doesn’t matter if you’re technically skilled if you don’t have the guts to take action in critical moments your business might well sink with your technical skills.
If you take Bring and Page, Google ‘s founders, they are engineers, but they are businessmen.
When Google paid $300 million for keeping its search engine as default choice within Mozilla, when Microsoft was about to steal it, it was an aggressive move to keep one of the most important distribution channels (at the time).
Microsoft was trying to have Bing featured as the default choice of Mozilla. When Google’s founders understood what was happening, they didn’t stop thinking for a second. They didn’t build algorithms to make that decision. They acted out of their guts feelings.
If I had to name what’s the most important asset of any company, the distribution would come first. Finding the distribution channels that best fit your business isn’t a natural process. Traditional channels are word of mouth, paid marketing , and media coverage.
In the digital business world instead, there are channels like SEO, social media, and content marketing . I know you might look at them as marketing tactics and they are. However, those are meant to build distribution channels .
For instance, content can be used as a way to connect with key players in your industry that you’d want to have as business partners. Google can also act as a “distributor” as with a proper SEO strategy can bring a continuous stream of qualified traffic to enhance your business and so on.
Gabriel Weinberg, the author of “Traction” and founder of DuckDuckGo , a search engine that doesn’t track you, has identified 19 channels you can tap into to grow your business .
Zero to One: Sales and Distribution Lessons from Peter Thiel
- Cost structure

What are the most cost in your business? Which key resources/ activities are most expensive?
In the business community often growth is confused for profitability. That is not the case. Many companies that achieved staggering growth rates have failed to be profitable.
This isn’t necessarily bad, but a successful long-term business needs to become profitable as soon as possible. When Google opened its hood in 2004 after its IPO, the numbers were staggering. In terms of growth, revenues, and profitability.
A cost structure is then crucial to allow sustainable long-term growth.

Generally speaking, your customer acquisition cost has to be lower than the lifetime value of your customers. Easy said than done. This connects us to the next, critical building block, the revenue stream generation.
- Revenue stream

For what value are your customers willing to pay? What and how do they recently pay? How would they prefer to pay? How much does every revenue stream contribute to the overall revenues?
Until you don’t have a stream of revenues coming in you can’t say you have a business. This might seem a trivial point. Yet the way you monetize the company will also affect the overall business model .
There isn’t a single way to generate revenues. You might choose a subscription business model , a freemium , a fee, or membership model . That also depends upon the industry, product, and service you offer.
For instance, Facebook uses a hidden revenue generation model .
In short, the utterly free platform in a way “hides” to its users the way it monetizes. Of course, business people and marketers are well aware of how Facebook makes money as it has been so far a proper advertising channel for many businesses.
However, the average user doesn’t have a clue. Things are changing now that privacy issues and new regulations have brought attention to the Facebook , business model .
Yet for a decade Facebook has benefited from a vast stream of revenues and high profitability without most users ever noticing it.
https://fourweekmba.com/facebook-business-model/
Many might argue that the hidden revenue generation model is the most powerful. And in fact, it has proved so ( Google is another example).
Indeed, as Peter Thiel remarks in his book, Zero to One, sales works best when hidden. As none likes to be reminded of being sold something. However, a business model that works , in the long run, needs to be aligned with users’ interests.
Thus, the way you monetize isn’t only about the bottom line but also about the kind of organization you’re building. If the revenue streams you generate provides value and is in line with your users’ interests, there is no need for corporate slogans like “don’t be evil.”
What more? Once you’ve found a revenue stream the works and is in line with your business model you can’t stop there. You need to keep experimenting with new revenue models.
In short, the business model canvas is the starting point for your business, rather than the ending point of your entrepreneurial journey.
Read : Google Business Model Canvas

Key takeaways
The business model canvas is a model that helps you have an overall strategic vision of your business. It is comprised of nine building blocks. Those building blocks are critical to assessing your long-term strategy .
This is one of the methods you can use. To sum up, the nine building blocks are:
Each of those blocks is not independent of the other. In fact, in many cases, they are strictly tied to each other.
And from the interactions between them, you can build a sustainable business model able to unlock value for your organization and other players that are part of its growth.
Alternative ways to design, develop and understand a business model
The business model canvas is a good starting point to assess your business or a competitors’ business. It is also a simple tool to leverage if you need to design a sustainable and financially viable business model.
However, that is not the only tool. Alternative tools for business model innovation and design comprise the lean startup canvas , the growth hacking canvas , Blitzscaling business model innovation canvas , and many others.
Leaner canvas

The customer/problem quadrant from the LEANSTACK, also called by its author, Ash Maurya, “leaner canvas.”
A tool like the leaner canvas might be quite useful in the first stage. Where all the building blocks are still missing. And they will probably be lacking for a while.
Thus, at that initial stage, it becomes critical to focus on understanding the problem you’re trying to solve and who you’re solving that for. Once you fine-tune that process you’re ready to move to the next step.
The most important takes from Ash Maurya leaner canvas is a via negativa approach (as Nassim Nicholas Taleb explains in his book Antifragile, via negativa is about focusing on the things you might want to remove), where you need to limit your focus to the problem rather than having a pre-conceived solution to it. Thus avoiding to fall in what Ash Maurya called in our interview the “ Innovator’s Bias .”
Lean startup canvas
Once you fine-tune the process of truly understanding the problem, it might make sense to move to the next building blocks to test some of the assumptions underlying the business you’re building.
Assumptions can make or break a business.
While in the past or when financial resources are easily available to companies, it is possible to hold these assumptions for a long time (until you won’t run out of cash or potential investors interested in your business) in a beautifully drafted business plan.
For a company with limited resources, gathering feedback from customers, mastering the problem, and building a solution on top of that becomes a key element. Therefore, the Lean Canvas by Ash Maurya helps do that:

The Lean Canvas is a variation of the Business Model Canvas by Alexander Osterwalder, put together by entrepreneur and author (Running Lean and Scaling Lean) Ash Maurya.
The advantage of the lean startup canvas is the reduction in uncertainty and risk intrinsic to the initial stage of the launch of a business. It’s important to highlight that there is no tool that can remove all the risks.
And entrepreneurship is risky, that’s part of the game. And that is also what makes the opportunity worth it. What these tools should help us achieve is a focus on the things that matter and remove the rest.
The business world can be very noisy, and if we have a few tools that make us focus on a few key elements those are welcome. Thus, with a tool like the lean canvas, as you start reiterating on a measuring whether the product or service delivered to your audience is a solution to their problems.
You can track that by looking at key metrics. This model is well suited for those that want to grow a lean organization by limiting the risk of running a business based on too many assumptions and with an approach that is driven by your customers’ needs.
Growth hacking canvas
Another tool that might work instead, if you want to accelerate the growth process, via a framework that is designed to test and prioritize marketing channels to enhance growth, the growth hacking canvas :

The growth hacking canvas also built on top of the business model canvas and similar to the lean startup canvas, it has an additional layer in comparison to the latter as it allows to identify a set of actions to undertake to measure, assess and speed up growth.
Growth marketing is a key ingredient for the success of any business in the current landscape. It is also the first move toward a 10X growth thinking for your business.
Blitzscaling business model canvas
The last tool, you can use for your business is called Blitzscaling business innovation canvas . I put together this framework after reading the book Blitzscaling , by LinkedIn co-founder Reid Hoffman.
The Blitzscaling canvas aims to design an innovative business model to generate aggressive growth. More precisely Blitzscaling prioritizes speed over efficiency and makes of massive growth its primary objective.
Thus, in a climate of uncertainty where competition or the market might threaten your business, any delay might mean the death of your business. Then the Blitzscaling framework might be the best suited to face that scenario:

Blitzscaling tells you that – in some particular circumstances – if you want to scale a business, you’ll need to leverage a few elements, among which business model innovation plays a key role.
This business model will need to be built around four growth factors (market size, distribution, high gross margins, network effects) and to avoid the to primary growth limiters (lack of product/market fit and operational scalability).
Blitzcaling is well suited if you’re trying to scale a business and bring it to a billion-dollar business as quickly as possible. This is only suited to a few scenarios, where the company is in a place to doing or dying. Thus, this framework might be both a defense and an attack mechanism.
FourWeekMBA Two-Deimensional Business model

The key components of any business model according to the FourWeekMBA analysis are:
- A compelling value proposition: How do you want your people to think about your brand?
- A unique brand positioning: What do you offer to your people that make them want more?
- A 10x goal setting: Can you offer a 10X better product or service? (compared to existing solutions)
- Customer segments: Who is your customer? (to notice here we’re not talking anymore about people but customers, those willing to pay for your product or service)
- Distribution channels: How do you get your product or service to your customers?
- Profit formula: Is the business financially sustainable?
This business model framework by FourWeekMBA has four aims:
- simplicity : heuristics-based rather than complex models
- noise reduction : choosing a few key data points, rather than looking at a massive amount of data that only adds noise and paralyze decision-making processes
- branding and distribution : looking at a business model as a systematic way to build a strong distribution network and a strong brand. The two things walk hand in hand
- and profitability : the financial viability of a business model is a key element for its success
In short, according to this framework, there are two dimensions of a business:
- The people dimension
- The financial dimension
These two dimensions walk hand in hand.
Yet the people side is also what makes the business thick from the economic standpoint.
The people side comprises the following elements:
This people dimension will help you build a solid brand. A solid brand builds up a tribe, a group of people that can follow you anywhere. Once you have a solid brand, you can focus on the second dimension: the financial dimension.
The three elements of the financial dimensions are:
3c Business Model Analysis

Another way to look at business models is through the 3c model analysis , where the three components that make up the business model are customers, competitors, and company. The 3C Analysis Business Model was developed by Japanese business strategist Kenichi Ohmae.
Platform Canvas

VTDF Framework
What tool to use.
What tool to use to design your business model will depend on what is that you’re after. In this guide, you have enough material to get going with your business.
Business model tools can be used for several reasons:
- Analysis : imagine you are a business analyst trying to make sense of a company, a tool like the business model canvas is a great framework to start with as it gives you a clear path to follow.
- Entrepreneurship : if you’re an entrepreneur trying to build a valuable company than using tools like the leaner canvas or the lean canvas is probably a good starting point.
- Business innovation: if you’re looking for the recipe to build an innovative business, intended as a company that finds new ways to build value for its customers, both the business model canvas to study existing successful businesses, in other fields might be a good starting point. In many cases, business innovation is about finding the right mix of existing patterns. Or transposing things that have been done in other faster industries, in a slower, and less attractive industry.
- Business acumen: if you want to just improve your business acumen, I’d suggest not using any particular tool, but rather keep your mind open to the things you might stumble upon. Look at financials, at data, look at entire industries and try to absorb as much as you can. Once the process becomes automatic and almost unconscious your mind will know how to make sense of that!
Keep it creative

One of the biggest mistakes people make (I do it as well) is to fall in love with particular tools, methodologies, and instruments. But those are just tools, that while helpful to get us started and give us a clear path, they might also limit our understanding.
The real world is extremely messy and it requires an open approach, where you are able to look at different aspects, angles, and perspectives. Only when you leave the process creative, and you leave space to test many things out, eventually you might stumble on incredible business discoveries!
Alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
Fourweekmba squared triangle business model.
This framework has been thought for any type of business model , be it digital or not. It’s a framework to start mind mapping the key components of your business or how it might look as it grows. Here, as usual, what matters is not the framework itself (let’s prevent to fall trap of the Maslow’s Hammer ), what matters is to have a framework that enables you to hold the key components of your business in your mind, and execute fast to prevent running the business on too many untested assumptions, especially about what customers really want. Any framework that helps us test fast, it’s welcomed in our business strategy .
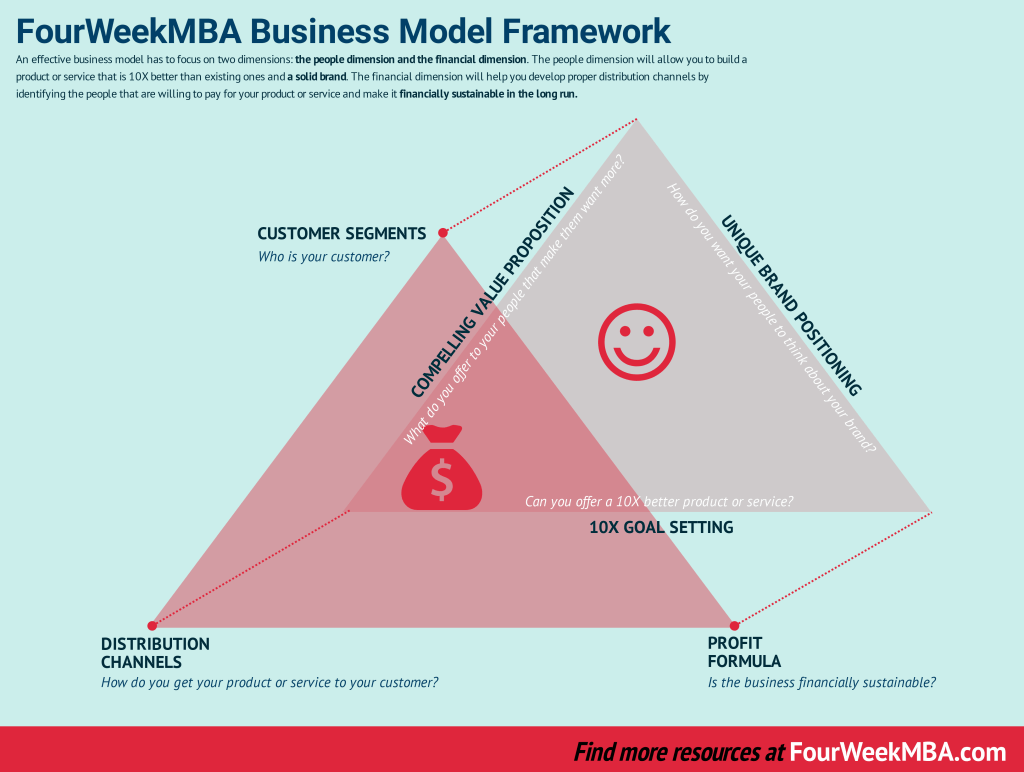
An effective business model has to focus on two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. The people dimension will allow you to build a product or service that is 10X better than existing ones and a solid brand . The financial dimension will help you develop proper distribution channels by identifying the people that are willing to pay for your product or service and make it financially sustainable in the long run.
FourWeekMBA VTDF Framework For Tech Business Models
This framework is well suited for all these cases where technology plays a key role in enhancing the value proposition for the users and customers. In short, when the company you’re building, analyzing, or looking at is a tech or platform business model , the template below is perfect for the job.

A tech business model is made of four main components: value model ( value propositions, mission , vision ), technological model (R&D management), distribution model (sales and marketing organizational structure ), and financial model (revenue modeling, cost structure, profitability and cash generation/management). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build a solid tech business model .

Download The VTDF Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA VBDE Framework For Blockchain Business Models
This framework is well suited to analyze and understand blockchain-based business models. Here, the underlying blockchain protocol , and the token economics behind it play a key role in aligning incentives and also in creating disincentives for the community of developers, individual contributors, entrepreneurs, and investors that enable the whole business model . The blockchain-based model is similar to a platform-based business model , but with an important twist, decentralization should be the key element enabling both decision-making and how incentives are distributed across the network.

A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model.

Download The VBDE Framework Template Here
Key Highlights
- Key Partners : Identify the key partners or suppliers who are crucial for the success of your business. Understand the motivations and reasons for forming partnerships.
- Key Activities : Determine the key activities your value proposition requires. These activities are essential for distribution channels , customer relationships, and revenue streams.
- Value Proposition: Define the core value you deliver to your customers and identify the customer needs you are satisfying. Your value proposition is the foundation of your business model.
- Customer Relationships: Establish the type of relationship your target customers expect you to establish. Understand how to integrate these relationships into your business in terms of cost and format.
- Customer Segments: Identify the different classes of people for whom you are creating value. Determine who your most important customers are.
- Distribution Channels : Determine the set of steps through which your product or service reaches your customers. Consider both direct and indirect distribution channels , as well as physical and digital distribution.
- Cost Structure : Identify the most significant costs in your business and the key resources or activities that are most expensive.
- Revenue Streams: Understand what value your customers are willing to pay for and how they prefer to pay. Assess the contribution of each revenue stream to your overall revenues.
- Key Resources: Determine the key resources your value proposition requires and those that are most important in distribution channels , customer relationships, and revenue streams.
Read Next: Business Model Innovation , Business Models .
Related Innovation Frameworks
- Business Model Innovation

Innovation Theory

Types of Innovation

Continuous Innovation

Disruptive Innovation

Business Competition

Technological Modeling

Diffusion of Innovation

Frugal Innovation

Constructive Disruption

Growth Matrix

Innovation Funnel

Idea Generation

Design Thinking

FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox
Business Engineering

Tech Business Model Template

Web3 Business Model Template

Asymmetric Business Models

Transitional Business Models

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Scaling

Market Expansion Theory

Speed-Reversibility

Asymmetric Betting

Revenue Streams Matrix

Revenue Modeling

Pricing Strategies

- Business Strategy Examples
- Business Models
- What Is a Value Proposition?
What is a business model canvas?
The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in the book Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising : key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
How do I create a canvas model for my business?
By going through the nine building blocks proposed by the business model canvas (key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams) you can have in one page the whole representation of a business.
What is cost structure in business model canvas?
The cost structure building block in the business model canvas asks the questions, “What are the most cost in your business?” and “Which key resources/ activities are most expensive?” Thanks to the cost structure building block, it is possible to look at the vital resources and cost centers of an organization.
What is Lean Canvas model?
The lean startup canvas is an adaptation by Ash Maurya of the business model canvas by Alexander Osterwalder, which adds a layer that focuses on problems, solutions, key metrics , unfair advantage based, and a unique value proposition. Thus, starting from mastering the problem rather than the solution.
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
6 thoughts on “what is a business model canvas business model canvas in a nutshell”.
Awesome stuff. Good explanation of the business model canvas. Thanks a million!
thanks a lot, Roman! Make sure to check this out too: https://fourweekmba.com/what-is-a-business-model/
Thank you so much for sharing all this.
Absolutely Roman 🙂
Significant article, every aspect clearly explained, will love to read more, thanks a lot!
Thanks a lot Antonio! Check this out then: http://fourweekmba.com/business-strategy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Our in-house rules:
- One game per user
- Cheaters will be disqualified.
Discover more from FourWeekMBA
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Customer Segments: The Foundation of the Business Model Canvas
The “customer segments” field describes the different groups customers your company might have. By identifying customer segments, you can design your products to more specifically satisfy the needs of these customers. In this article, we will take a closer look at how you can create, or identify customer segments.
Hint It is recommended to start with this field when filling in the Business Model Canvas.
What are customer segments?
“Customer segments are groups of customers who have similar needs, desires, behaviors, or characteristics and can be addressed in a similar way”.
A company can have multiple customer segments. Examples of customer segments could be specific age groups, geographic regions, etc…

Why customer segments?
When you identify and describe different customer segments, it makes it easier for you to find out what needs and desires these groups have and how best to address them. This allows your company to better target your products and services to these needs. And that, of course, might increase your chance of success.
When you have different customer groups it makes it easier for your marketing and sales teams to target these segments. For example teenagers need to be addressed in a completely different way then retired people.
Customer segments also help to meet the needs and wants of each customer segment in a unique way and thereby stand out from the competition . Only in this way can the company be successful and achieve competitive advantages over others.
Example 1: Sports equipment
A sportswear manufacturer could have different customer segments, such as professional athletes, amateur athletes and recreational athletes. These customer segments have different needs and wants in terms of the type and quality of sportswear. Therefore, the manufacturer must develop different products to meet the needs of each customer segment.
Example 2: Young professionals who eat consciously.
Another example of customer segments could be young professionals aged 25-35 who live in a large city and have a high interest in healthy eating. A company that specializes in providing healthy meals could focus on this customer segment and develop a marketing strategy that targets the needs and interests of this group.
How to create customer segments?
But, how do you make customer segments now? Well, there are several methods:
One way is to use demographics . Customers are divided into groups based on characteristics such as age, gender, income and education.
Another method is geographic segmentation : Customers are divided into different groups based on where they live.
Another one is psychographic segmentation , in which customers are grouped according to their attitudes, interests, and lifestyles.
Or maybe you want to use Behavioral segmentation : That means, customers are grouped according to their buying patterns and usage patterns.
If none of those methods seem to fit, you can also use various market research techniques such as surveys , customer feedback , and data analysis to identify and analyze customer segments.
You need to decide on your own which methods fits best. The most appropriate method depends on your company. It is important that customer segments are distinct from other segments. That means there should be a clear separation. They should also be large enough to represent a relevant target group for the business model, but small enough to be addressed and served individually.
- So-called “buyer personas” can also help in the creation of customer segments
Buyer Personas Buyer personas, or “buyer profiles”, are fictional characters that represent a company’s key characteristics, needs and behaviors. They are often used in marketing and product development to better understand and target a company’s audiences. Go to main article: Buyer Personas
Which customers are most profitable?
An important task for a company, especially at the beginning of its endeavour, is to find out which customer segments are most profitable and to focus on these groups. This enables the company to target its resources and tailor its products or services to the needs and wants of the customer groups that bring in the most money.
Tips for filling in
As mentioned earlier, it is recommended to start with the customer segments, as the other fields depend on these groups.
For example, the services you offer or your value proposition depend on the needs and desires of your customer segments. If you know your customer segments intimately, you can more specifically address their needs and tailor your offering accordingly.
The channels you use also depend on your customer segments. If you know where your target audience is and how best to reach them, you can select and target the appropriate distribution channels.
In addition, the relationships you build with your customers also depend on your customer segments. If you know who your customers are, you can build a closer and more lasting relationship with them.
Free PowerPoint Business Model Canvas Templates
By Courtney Patterson | April 3, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve collected the top PowerPoint business model canvas templates for entrepreneurs, startup leaders, and strategy architects. These customizable templates offer a comprehensive layout to define, evolve, and polish your business strategies. Included on this page, you’ll find a lean business model canvas template for PowerPoint, a business capability model canvas template for PowerPoint, a customer-focused business model canvas template , an e-commerce business model canvas template , and more. These PowerPoint business model canvas templates will help you effectively organize and present your business strategies.
PowerPoint Simple Business Model Canvas Template
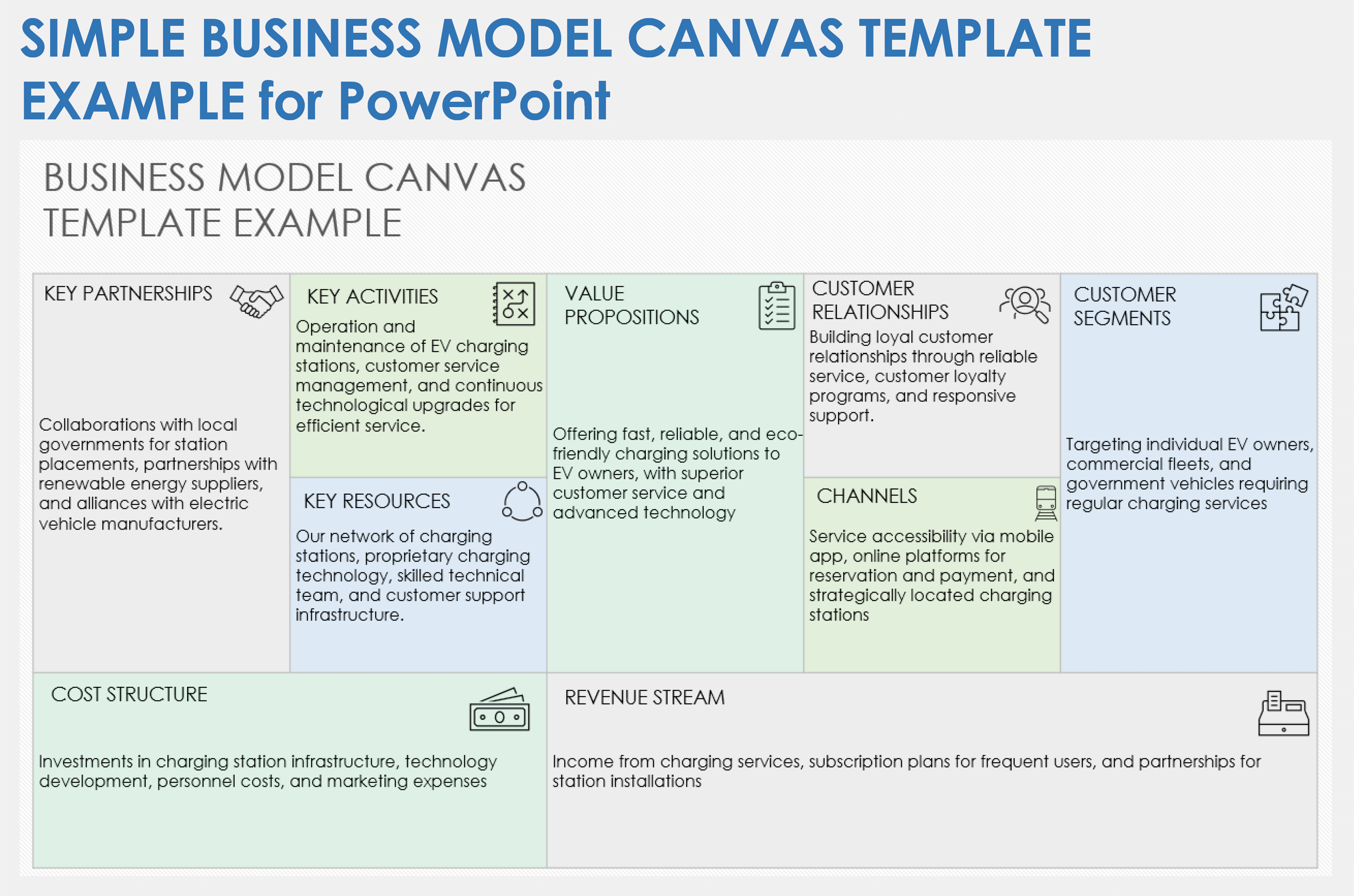
Download the Sample Simple Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank Simple Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
When to Use This Template:
This simple business model canvas template for PowerPoint is ideal for swift strategic sessions and perfect for startups, entrepreneurs, and educators that need a quick yet comprehensive overview of their business or project’s core aspects. Use the template with or without sample data during initial planning phases or workshops, or when refining an existing business model for clarity and direction. Notable Template Features:
This template’s streamlined layout highlights essential business model components — value propositions, customer segments, key activities, and more — in an easily digestible format. Its intuitive design facilitates quick modifications and collaborative discussions, making it a standout tool for visual strategy planning and presentation. Download our free business model and business model canvas templates to gain a clear, structured visualization of your business’s core components, so you can innovate, strategize, and align your operations for enhanced growth and competitiveness.
PowerPoint Lean Business Model Canvas Template
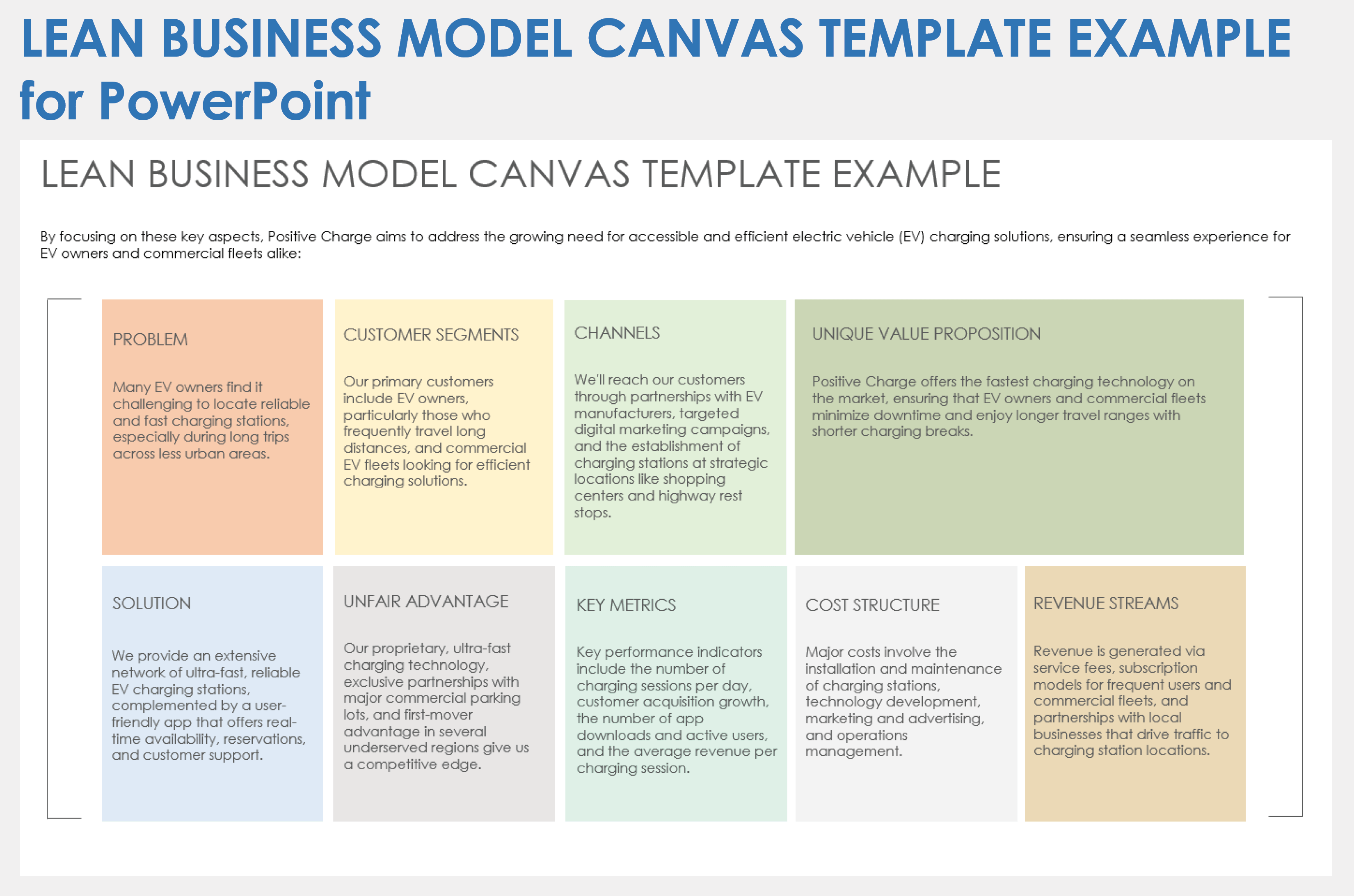
Download a Sample Lean Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download a Blank Lean Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
When to Use This Template:
This Lean business model canvas template for PowerPoint with or without sample data is best suited for agile startups and innovators looking to rapidly test and validate their business ideas. The template is particularly useful in fast-paced environments where the focus is on pinpointing the most critical elements of your business model to quickly adapt to market feedback. Notable Template Features:
This template distills the business model canvas to its essence, prioritizing lean startup principles such as problem-solution fit, unique value propositions, and key metrics for success. Its design encourages dynamic interaction and iteration, making it an invaluable asset for teams committed to Lean methodologies and continuous improvement. Need business model canvas templates in Google formats? Check out our article on free, editable Google Slides business model canvas templates to systematically understand, design, and refine your business strategy for improved clarity and strategic focus.
PowerPoint Business Capability Model Canvas Template
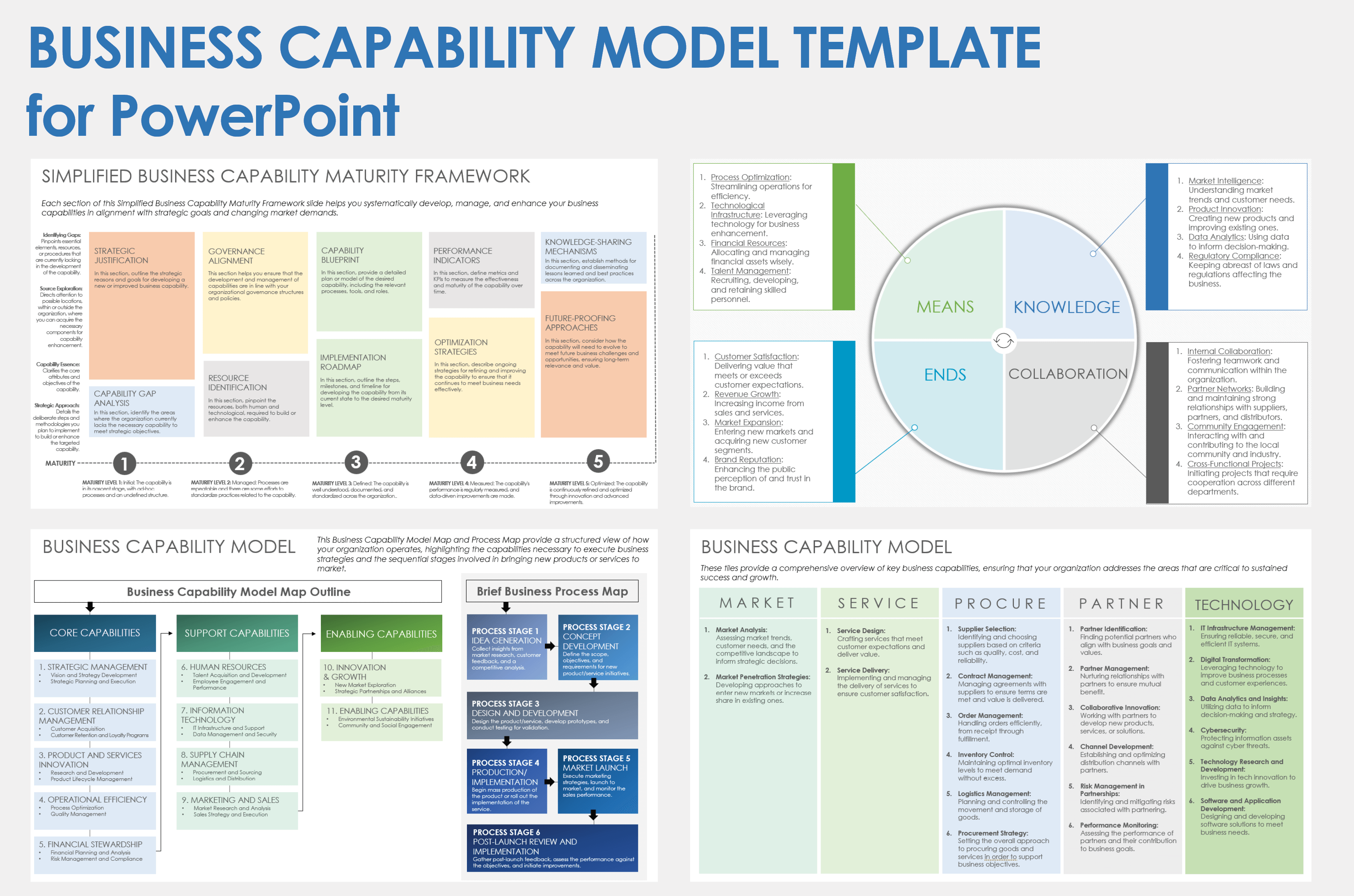
Download the Sample Business Capability Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank Business Capability Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
When to Use This Template:
This multi-slide business capability model canvas template for PowerPoint is designed for comprehensive strategic planning and analysis, ideal for evaluating your organization’s core business functions in detail. With or without sample data, the template is particularly useful for aligning business strategies with operational capabilities and identifying areas for improvement or investment. Notable Template Features:
This template offers a detailed breakdown of business capabilities across multiple slides, from operational processes to customer engagement strategies. The structured format supports a systematic approach to identifying strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for growth, facilitating clear communication and strategic alignment within teams and departments.
PowerPoint Social Enterprise Business Model Canvas Template
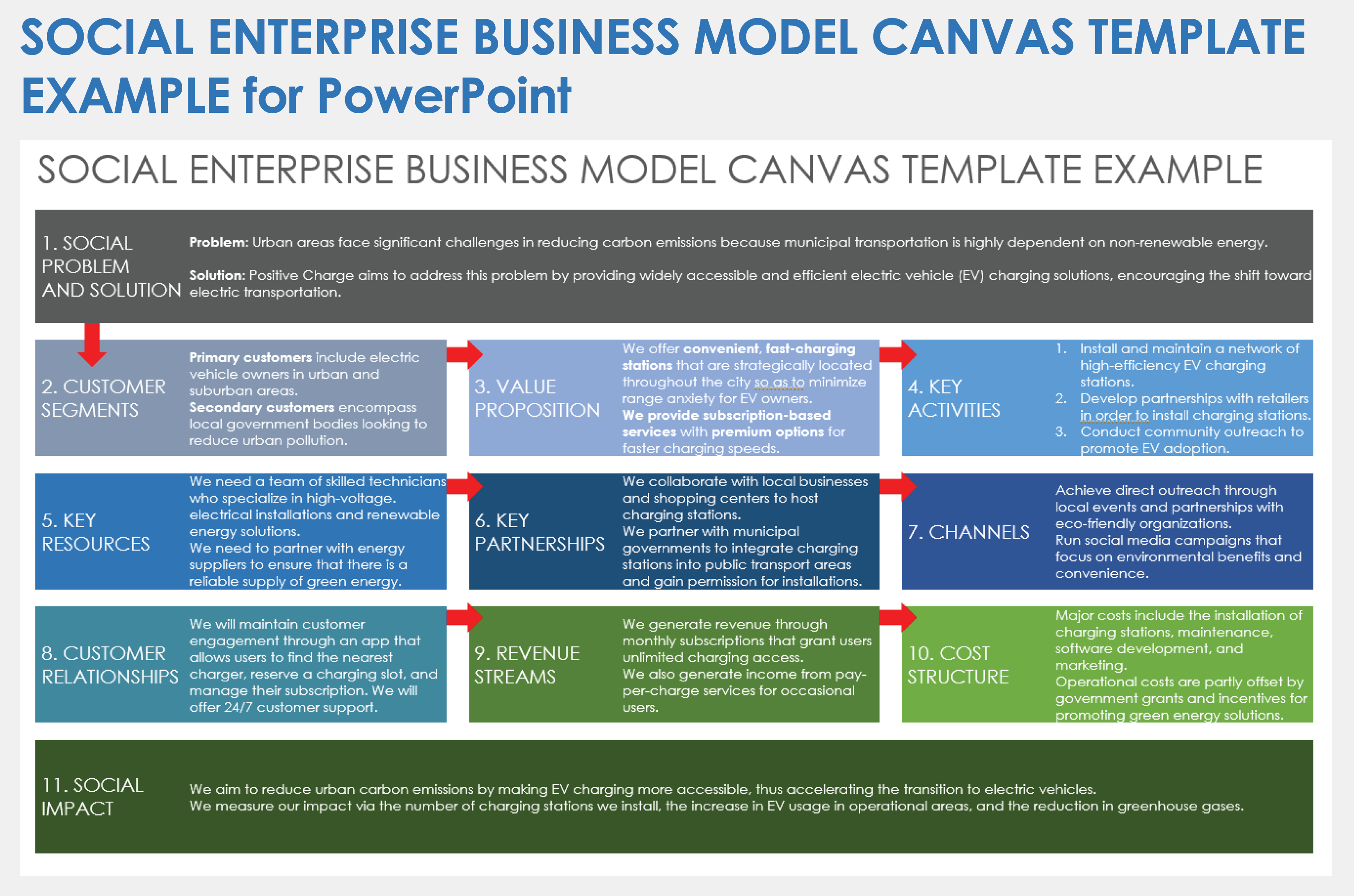
Download the Sample Social Enterprise Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank Social Enterprise Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
Tailored for social enterprises and mission-driven organizations, this social enterprise business model canvas template for PowerPoint with or without sample data is the go-to resource for blending social impact with financial sustainability. Use it when brainstorming or strategizing how to effectively address social issues while remaining economically viable. Notable Template Features:
Distinctive for its focus on social value alongside traditional business elements, this template enriches your strategic planning with sections dedicated to social goals, impact measurement, and community engagement. The holistic approach helps you visualize both the societal benefits and the economic model of your enterprise, fostering a balanced strategy for both making a difference and achieving business success.
PowerPoint Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template
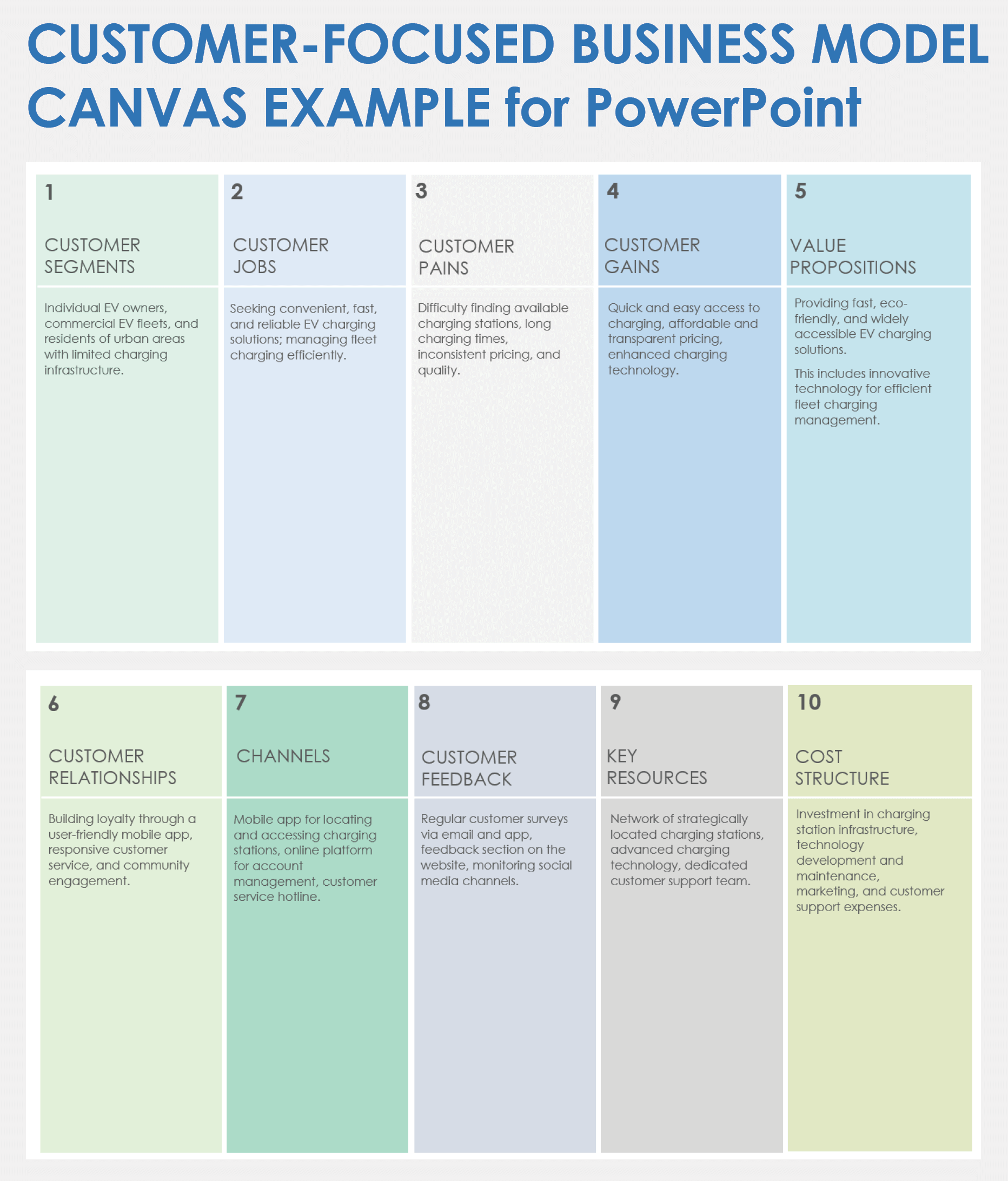
Download the Sample Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
Deploy this customer-focused business model canvas template with or without sample data for PowerPoint while creating or reevaluating your business strategy with a focus on the customer. This template excels in environments where understanding and meeting customer needs are pivotal to crafting competitive advantages and personalized experiences. Notable Template Features:
Uniquely designed to elevate the importance of customer insights in strategic planning, this template incorporates sections for customer journeys, preferences, and feedback loops. It enables a deep dive into how each aspect of your business model serves the customer, ensuring that customer satisfaction and engagement are prioritized during decision-making.
PowerPoint E-commerce Business Model Canvas Template
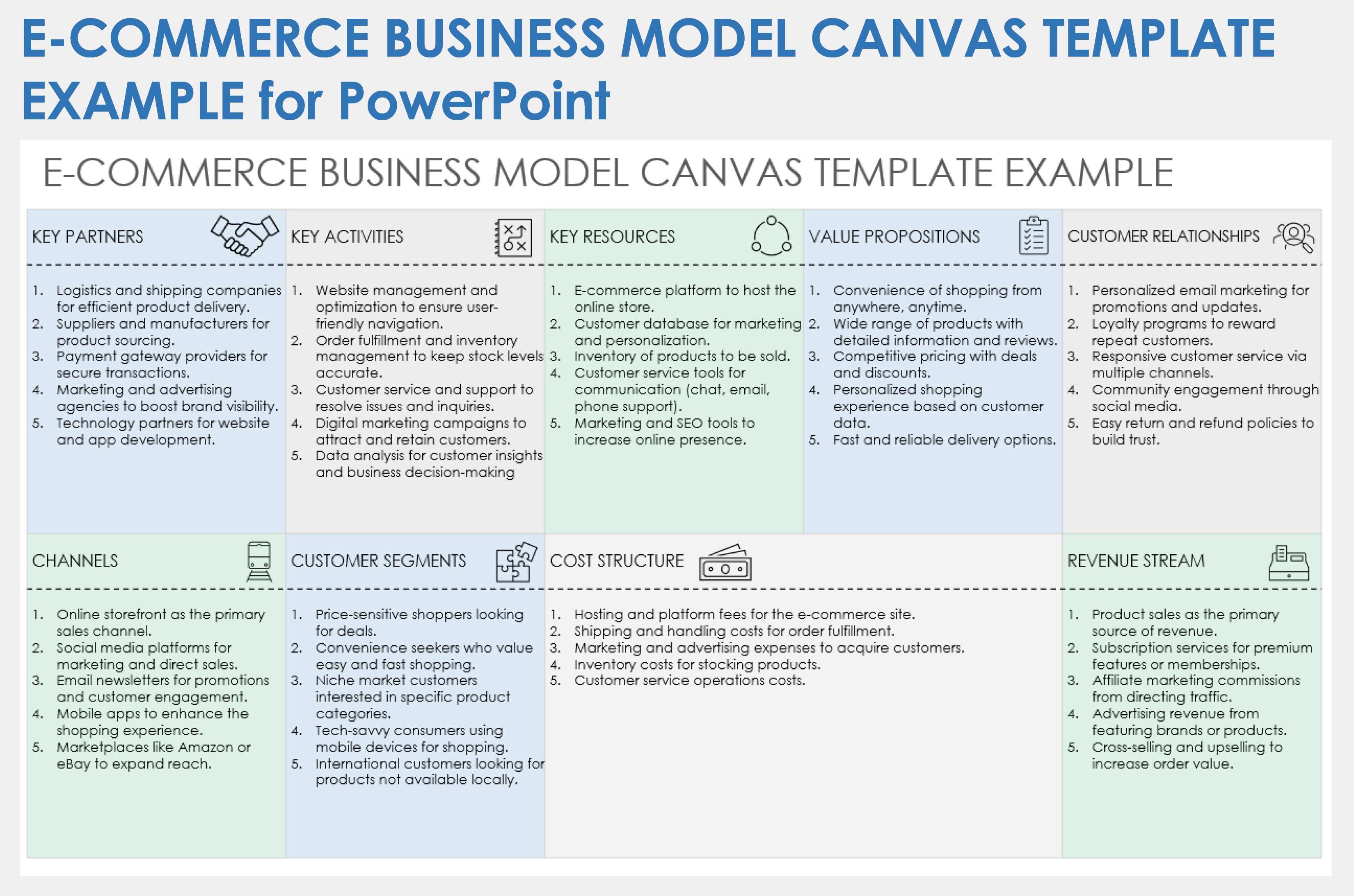
Download the Sample E-commerce Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank E-commerce Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
This e-commerce business model canvas template for PowerPoint is your ally when diving into the online retail world, whether you’re launching a new e-commerce platform or optimizing an existing one. With or without sample data, the template is particularly effective for sessions aimed at dissecting and enhancing the online shopping experience, from initial click to post-purchase support. Notable Template Features:
With a design that caters specifically to the digital marketplace, this template allows for an in-depth analysis of online customer behavior, digital marketing strategies, and logistics. Its comprehensive layout ensures that every facet of the e-commerce ecosystem — including user experience, payment processing, and customer service — is meticulously planned and aligns with your business objectives.
PowerPoint Tech Startup Business Model Canvas Template
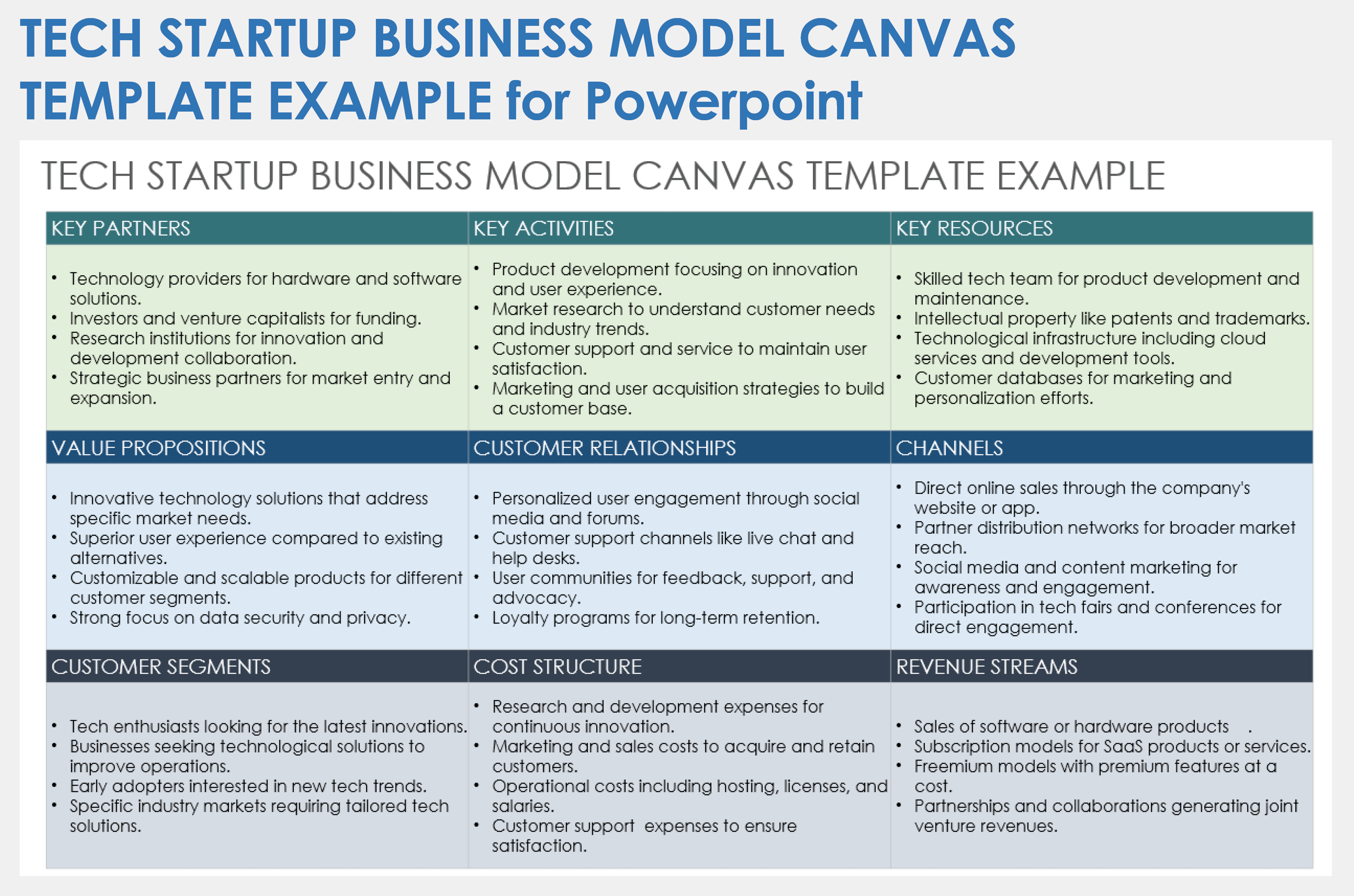
Download the Sample Tech Startup Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint Download the Blank Tech Startup Business Model Canvas Template for PowerPoint
This tech startup business model canvas template for PowerPoint is most useful when preparing your new idea for market entry or when adapting your technology venture to evolving market demands. The template, with or without sample data, is specially crafted for taking into account the interplay between innovative tech solutions and market needs. Notable Template Features:
This template is uniquely tailored to the dynamics of the tech industry, spotlighting areas such as R&D, IP strategy, and user acquisition. It helps you visualize how your technology fits within the market, and ensures that elements such as scalability, cybersecurity, and technological advancements are front and center in your planning process.
Refine Your Business Model with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
Design thinking tools.
Just like good craftsmen we use state-of-the-art tools to design, build and grow your businesses. but just like good samaritans we like to share. so here's our toolbox..

Emerging technology workspace.
This workspace equips you with the essentials to future-proof your business by merging three key elements: Business Reimagining , where we explore your business model's strengths and weaknesses; Technological Exploration , introducing you to cutting-edge technologies through an accessible deck of cards that reveal new opportunities; and Hands-on Exercises , involving interactive tasks that foster creativity, strategic thinking, and the discovery of practical opportunities. Elevate your efficiency and gear up for the future with our digital workshop on emerging technologies.

The portfolio map.
This is the Portfolio Map is a great tool to plot your different business models and business model innovation initiatives as a portfolio. It helps to understand where your business is today and how to manage both current and future value creation. Mapping your portfolio is a valuable exercise if you want to gain a better understanding of your business models and optimize your portfolio for long-term growth and success.
You can use all of these tools to design, build and grow your next business model.
Context map canvas..

Persona canvas.

Value prop canvas.

5 Bold steps canvas.

Design criteria canvas.

Business model canvas.
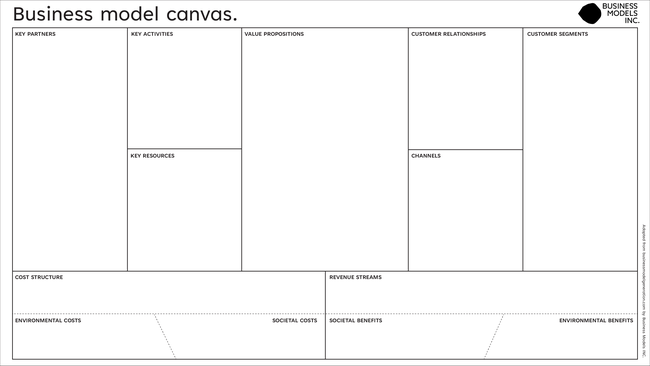
Looking for all the design thinking tools you need? Get your hand on our Design a Better Business Book.

- Search Search Search …
Business Model Canvas, Value Proposition Canvas, Customer Journey Map, Lean Canvas etc. with Archi-tool
Archi -tool provides ready-to-use canvas templates. E.g. Business Model Canvas (BMC) and Value Proposition Canvas for business model design, and Customer Journey Canvas for more detailed service design. These canvases utilize model elements that look like post-it chards. It is also possible to create custom canvases such as Kanban Board. All the canvases – as well as any other model artifacts (diagrams) – can be published in HTML or in document format from the Archi-tool.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
Value proposition canvas, customer journey canvas, lean canvas, kanban canvas.

Customer Journey Canvas
Een nieuwe week, een nieuwe tool. Dit keer een blog over het Customer Journey Canvas. Klantgedrag is enorm aan het veranderen en dat heeft een grote impact op de manier hoe je zaken doet. Als bedrijf moet je tijdig mee veranderen en je bedrijf afstemmen op voorkeuren van klanten. Je moet tijdig actief zijn op de kanalen waarop klanten in contact willen staan met je merk en over de gehele klantreis een goede ervaring bieden.
En die goede ervaring is erg belangrijk. Waardecreatie vormt de basis van jouw onderneming en die creëer je niet enkel met de aanschaf of het gebruik van je product of je dienst. Waarde creëer je gedurende de klantreis, het gehele proces waarop klanten interactie hebben met je merk. Het gaat hierbij in de consistentie in de totale klantreis en WOW-ervaringen en merkmomenten creëren bij klanten. Het Customer Journey Canvas helpt je om betere klantreizen te ontwerpen.

Download het Customer Journey Canvas: Powerpoint (invulformat) of A0 .
Uitleg Customer Journey Canvas
Dit is het Customer Journey Canvas. De kracht van deze tool zit in het feit dat het helpt om de klantreis inzichtelijk te maken en deze te verbeteren. Het visualiseert de essentiële touchpoints die klanten met je merk of bedrijf hebben. Een klantreis is elk contact (oriëntatie, aanschaf, gebruik & aanbeveling) dat de klant heeft met jouw merk en product. Het Customer Journey Canvas vormt een sterke basis om je marketing- & sales strategie mee op te stellen en helpt om van klanten ambassadeurs te maken.
- Helpt om de klantreis inzichtelijk te maken
- Je krijgt inzicht in de behoeften van de klant
- Helpt om de meest belangrijke touchpoints te identificeren
- Je doet waardevol inzichten op die helpen om je business te verbeteren
Voorbereiding
Voordat je met het Customer Journey Canvas aan de slag gaat, is het zinvol zin om vooraf een persona , een klanttype-piramide & een customer story gemaakt te hebben. Ook is het slim om onderzoek verricht te hebben naar klanten middels een klantsafari. Klanten op een een diep niveau begrijpen is namelijk een vereiste om fantastische klantreizen te ontworpen. Roep je team bijeen! In de ideale situatie betrek je naast je eigen team ook klanten en mensen die het klantsegment erg goed kennen bij de sessie. Regel een inspirerende omgeving en reserveer minstens 45 minuten tijd, zonder afleidingen. Print ook meerdere Customer Journey Canvassen uit op een groot formaat, plak deze op de muur en pak je stiften en post-its erbij.
1. Bepaal het doel
Voordat je aan de slag gaat met het Customer Journey Canvas, kan het zinvol zijn om eerst het doel scherp te stellen. Wat is de reden dat jullie het Customer Journey Canvas willen toepassen? Op basis van het doel kunnen de juiste stappen gedefinieerd worden.
2. Kies een persona
Kies een persona. Bepaal voor welk klantsegment en welk klanttype je de klantreis in beeld gaat brengen. Dit kan het klanttype zijn die over de aankoopbeslissing gaat, maar ook over een eindgebruiker of een andere belanghebbende. Zorg dat je de persona specifiek beschrijft en het is aan te raden een uitgewerkte persona en customer story als input te gebruiken voor de klantreis.
3. Bepaal de scope
Bepaal het begin en het eind van de klantreis die je in beeld gaat brengen.
4. Schets de klantreis
Schets de klantreis met behulp van de Customer Journey Canvas. Doorloop de volgende onderdelen:
I. Definieer de verschillende fasen
Gedurende de (afgebakende) klantreis doorloop de klant verschillende fasen. Definieer de verschillende fasen zoals oriëntatie, aanschaf, gebruik, aanbeveling & aftersale. Geef ook aan hoelang een fase duurt.
II. Touchpoints
Touchpoints zijn de essentiële contacten die je klanten met je merk of bedrijf hebben. Wat zijn de verschillende momenten van interactie met de klant? Op welke manieren heeft de klant per fase interactie met jouw merk? En welke relevante touchpoints zijn er voor de klant waar jouw bedrijf niet bij betrokken is?
III. Bepaal de emotie per touchpoint
Hoe is de stemming van de klant precies op dat moment? En wat is zijn/haar algemene ervaring per fase. Wat maakt de klant blij? Waarvan raakt de klant geïnspireerd? Wat frustreert? Wat maakt de klant boos?
IV. Bepaal de meest cruciale touchpoints per fase
Bekijk de schets van een afstandje. Kies de meest cruciale touchpoints en visualiseer deze. Wees niet bang om te tekenen. Het visualiseren van de meest cruciale momenten in de klantreis zal helpen om nieuwe inzichten op te doen en het moment scherp te stellen.
Doe een stap naar achter. Bestudeer de in kaart gebrachte klantreis met elkaar. Wees je ervan bewust dat Customer Journeys niet lineair zijn en nooit helemaal compleet. Een gebruiker kan van de ene naar de andere fase springen zonder al de touchpoints te doorlopen. Ook zullen er altijd aannames in staan. Het gaat erom dat de kennis en inzichten van het team gebruikt worden om de klantreis te schetsen en het bedrijf in staat stelt om te onderzoeken en ontwerpen vanuit het oogpunt van de beoogde klant of gebruiker.
Staan er zaken op die jou en je collega’s verrassen? Bij welke onderdelen missen er nog cruciale zaken? Op welke vlakken kan de klantreis nog flink verbeterd worden? En hoe verhoudt onze klantreis zich met die van de grootste concurrenten?
Maak een foto van het canvas om de schets vast te leggen en hang het Customer Journey Canvas op een zichtbare plek op kantoor. Zo kan iedereen ernaar kijken en aanvullen.
Vervolgstappen
Nadat de klantreis is uitgewerkt is het tijd om vervolgstappen te bepalen. Het is aan te raden om klantreizen te ontwerpen voor ieder klantsegment en de relevante klanttypes die daarbinnen vallen. Verder is waardevol om data toe te voegen. De vervolgstap die wij adviseren is om een klantsafari uit te voeren en het beeld van de klantreis te bevestigen of weerleggen met feitelijke informatie uit interviews, experimenten en feedback van klanten. Gebruik de inzichten die je continu opdoet om de klantreis te herontwerpen en te verbeteren. De ‘’onderzoekstap’’ is hierbij cruciaal om beslissingen te nemen op basis van realiteit in plaats van aannames.
Vind niet zelf het wiel uit. Laat je inspireren door klantreizen van andere bedrijven en doe waardevolle inzichten op die je helpen om betere Customer Journeys te ontwerpen voor jouw bedrijf. Bestudeer bijvoorbeeld de klantreis van Ikea en ontdek hoe zij de Peak-end rule toepassen. Of lees dit artikel over d e beste customer journeys in e-commerce .

Waar wacht je nog op?
Ga aan de slag met de tool en verbeter de klantreis.
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Lean Canvas Business Model (LCBM)
- Information Systems

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Keep track of your customer journey, it will keep bringing value. Building and maintaining an accurate customer journey (backed up by real world evidence) is a vital tool to find new possibilities in your business model - not only in terms of ideas but also in terms of quality of execution. Keeping track of the behaviours customers actually ...
Customer Journey Map Canvas and Business Model Canvas. The benefit of using business modelling is how it shifts thinking within an organization. In particular; ... Click to download free high-quality printable pdf's of the Business Model Canvas. width 3508 px x height 2480 px (300 dpi) width 7016 px x height 4960 px (300 dpi)
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Step 1 (of 10): Customer Segments. This sounds obvious, but when you get into the detail many people overly simply the customer and don't create a clear picture of who they are. As a result, the tendency is to make generalizations. Sections of the Business Model Canvas. 1.
Present the CJM's purpose & goals. Now it's time to kick off the customer journey map exercise. Start by speaking to the purpose and goals you've identified for the map. It's important to make sure your team understands what you're trying to accomplish, or else you run the risk of the session getting off track.
Map out your customer journey. Start mapping the current or future states of your customer journey in a template you've chosen from Canva. Organize in the diagram all the insights and touchpoints you've gathered and listed as a team earlier. You can arrange them in the most visually appealing way you can think of.
The customer journey canvas helps make things real. Through the mapping exercise you can identify where customers get stuck, where they have great experiences, and why. One outcome of using this tool with your team will be the so-called low hanging fruit that you can deliver on immediately. Once you have co-created and assembled the customer ...
A customer journey canvas is a board that documents the user's journey through your product/service. It is similar to a storyboard and maps out your user's journey through different stages and emotions. Customer journey canvases are similar to Customer Journey Map s but diagram elements on the surface level before diving deeper.
Published Apr 21, 2015. + Follow. This is less of a post and more of an extension of yesterday's post on the channel decision and a presentation of the channel element of the Business Model Canvas ...
The customer journey canvas is a clear overview of the entire service design process. You are likely to refer to it again and again because there are always improvements to be made and problems to be solved. An element of surprise is always possible. When it presents itself to you as a challenge to your business, the customer journey canvas ...
A customer journey map, also known as a user journey map, is a visual representation of how customers experience your brand and company across all its touchpoints. In a customer journey map template, interactions are placed in a pre-made timeline to map out the user flow. Since customers are the backbone of your business, it is important to ...
January 20, 2022. Next, on the business model canvas explained, we will discuss the customer relationship segment. Once you've figured out your value proposition and defined your customer segment, the next step is to build, nurture, and grow the relationship between your business and your customers. The key question here is how much effort ...
The Business Model Canvas and the Value Proposition Canvas are not only great tools in business modeling, they can help you get started at the right place in your Customer Journey work.
The Customer Relationship block of a Business Model is intrinsically dependent on the first block developed, Customer Segments. This is because this component deals exactly with the type of relationship that the company will establish with each of the previously defined segments. This block will determine the nature of each of the relationships ...
Among these, the Business Model Canvas (BMC) stands out as a strategic management tool that has revolutionized how entrepreneurs, innovators, and business leaders visualize, design, and reinvent their business models. The BMC provides a concise, visual framework that encapsulates how organizations create, deliver, and capture value.
The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising: key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
867 templates. Create a blank Customer Journey Map Whiteboard. Stakeholder Map Team Whiteboard in Green Yellow Purple Trendy Stickers Style. Whiteboard by Canva Creative Studio. SWOT Analysis Brainstorm Whiteboard in Orange Pink Modern Professional Style. Whiteboard by Canva Creative Studio. Meetings Whiteboard.
It is important that customer segments are distinct from other segments. That means there should be a clear separation. They should also be large enough to represent a relevant target group for the business model, but small enough to be addressed and served individually. So-called "buyer personas" can also help in the creation of customer ...
The Super Guide about Customer Journey is a complete guide on how understanding the customer journey has become essential to creating successful marketing strategies and delivering exceptional customer experiences. ... Home / Business Model Canvas Templates and Downloads / Super Guides Customer Journey. US$ 35 US$ 29.
Deploy this customer-focused business model canvas template with or without sample data for PowerPoint while creating or reevaluating your business strategy with a focus on the customer. This template excels in environments where understanding and meeting customer needs are pivotal to crafting competitive advantages and personalized experiences.
Business model canvas. Tell me more. Looking for all the design thinking tools you need? Get your hand on our Design a Better Business Book. read more Home; Services; About us; Jobs; Contact; Offices. Amsterdam +31 20 505 0600. Istanbul +90 5512821348. Brisbane +61 423 792 887. Taipei
The Customer Journey Map Canvas - 9 Steps To Powerful CX Design; OKR Canvas Free Templates - Empower Teams and Succeed Like Google; Blue Ocean Strategy: 5 Critical Points and Free Templates To Download ... Even Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, creators of the business model canvas, ended up creating more canvas models.
Business Model Canvas (BMC) and Value Proposition Canvas for business model design, and Customer Journey Canvas for more detailed service design. These canvases utilize model elements that look like post-it chards. It is also possible to create custom canvases such as Kanban Board. All the canvases - as well as any other model artifacts ...
Dit is het Customer Journey Canvas. De kracht van deze tool zit in het feit dat het helpt om de klantreis inzichtelijk te maken en deze te verbeteren. Het visualiseert de essentiële touchpoints die klanten met je merk of bedrijf hebben. Een klantreis is elk contact (oriëntatie, aanschaf, gebruik & aanbeveling) dat de klant heeft met jouw merk ...
Name The Lean Canvas Business Model with basic instructions Problem List your top 3 problems-Most vet clinics don't have certain doctors in at certain times-Vet clinics are overcrowded, and often can't help customers -Uncertain operating hours of service Solution Outline a possible solution for each problem-Show vet clinics near by with those certain vets and are currently open-Show top-rated ...