This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more


Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Asia (East)
- Asia (Central)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- Middle East
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Vietnam (Asia)
Advice for all destinations.
Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccinations and malaria risk
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: Diphtheria; Tetanus.
- Other vaccines to consider: Hepatitis A; Hepatitis B; Rabies; Typhoid.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: Japanese Encephalitis.
No yellow fever vaccination certificate required for this country
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Japanese Encephalitis : spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. This mosquito breeds in rice paddies and mainly bites between dusk and dawn. Risk is highest for long stay travellers to rural areas, particularly if unable to avoid mosquito bites.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
- Typhoid : spread mainly through consumption of contaminated food and drink. Risk is higher where access to adequate sanitation and safe water is limited.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk is low throughout the year in Kon Tum, Gia Lai, Dak Lak, Dak Nong, Binh Phuoc and western parts of Phu Yen, Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan, Binh Thuan and north west Lai Chau. In these areas, malaria tablets are not recommended, however, they may be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk (see below under Low risk areas with additional advice)
- Low to no risk in other areas including Ho Chi Min City and Hanoi, the Red River and Mekong deltas, Phu Quoc Island and coastal plains.
- Malaria precautions are essential. Avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Check with your doctor or nurse if antimalarial tablets may be required.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- Low risk with additional advice: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised, however, they can be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk e.g. longer stay in rural areas, visiting friends or relatives, those with medical conditions, immunosuppression or those without a spleen. Atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine is advised for those at risk.
- Low to no risk: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
- If travelling to an area remote from medical facilities, carrying standby emergency treatment for malaria may be considered.
Other Health Risks
Altitude and travel, dengue fever.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
Zika Virus Infection
This country has been categorised as having a risk of Zika (ZIKV) virus transmission.
ZIKV is mainly spread through mosquito bites. The mosquito responsible most commonly bites during daylight hours and is common in towns and cities.
The illness is usually mild but infection during pregnancy may lead to babies being born with birth defects. There is no vaccine currently available against ZIKV.
Advice for All Travellers
You should practice strict mosquito bite avoidance at all times. Do not travel without adequate travel insurance . Seek pre-travel health advice from a travel health professional 6 to 8 weeks in advance of travel.
Additional recommendations for pregnant travellers or those planning pregnancy
If you are planning pregnancy in the very near future you should consider whether you should avoid travel to this country.
- contact your GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- use barrier methods of contraception during and after travel and for the duration of your pregnancy, even in you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- If you develop symptoms of ZIKV infection, it is recommended that you avoid becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following your recovery
- 2 months afterwards if you are female
- 3 months afterwards if you are male or if both partners travelled
These measures reduce the chance of sexual transmission of ZIKV and/or the risk of ZIKV infection in pregnancy.
For further information, see Zika virus infection page.
- 74 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top
Vietnam Travel Restrictions
Traveller's COVID-19 vaccination status
Travelling from the United Kingdom to Vietnam
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to vietnam, find stays in vietnam, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, netherlands, new zealand, philippines, switzerland, united arab emirates, united states, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Vietnam from the United Kingdom?
Most visitors from the United Kingdom, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vietnam.
Can I travel to Vietnam if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United Kingdom can enter Vietnam without restrictions.
Can I travel to Vietnam without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United Kingdom can enter Vietnam without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Vietnam?
Visitors from the United Kingdom are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Vietnam.
Can I travel to Vietnam without quarantine?
Travellers from the United Kingdom are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Vietnam?
Mask usage in Vietnam is not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Vietnam?
Restaurants in Vietnam are open. Bars in Vietnam are .
Mon 29 Apr 2024
2024 newspaper of the year
@ Contact us
Your newsletters
Vietnam entry requirements: New travel restrictions welcome fully vaccinated with tourist ban to end in March
Travellers will still have to quarantine while awaiting their test result and must agree to download and use the country's contact tracing app.

Vietnam is to end its ban on vaccinated tourists three months early – although travellers will still have to quarantine while awaiting antigen test results.
The country, which has been inaccessible to foreign travellers since the start of the pandemic, will allow double-jabbed arrivals in from 15 March.
The decision follows the reopening of borders for leisure travellers by other Asian nations including Thailand , Cambodia and the Philippines, who all accept fully vaccinated arrivals from the UK.
Japan is also expected to loosen travel restrictions in March , but it is not yet clear if holidaymakers will be finally allowed in.
InsideAsia PR and partnerships manager James Mundy welcomed the announcement as “big piece in the south-east Asia jigsaw”.
He added: “This is great news for us as a specialist tour operator and something that we have been looking forward to for such a long time, along with our customers and partners on the ground.”
Zina Bencheikh, managing director EMEA for Intrepid, said the adventure escorted tour company expected to see a spike in bookings “as word spreads that the country is about to open its doors”.
She added: “This is fantastic news for the travel industry and for the many people in Vietnam who rely on tourism for their livelihood.”
Under the new rules, travellers over two years of age must take a negative PCR test 72 hours before arrival, an antigen test upon arrival and await the result while in hotel isolation.
All arrivals must also be able to prove that they have travel insurance with Covid-19 cover for at least $10,000.
More from Travel
While in Vietnam, holidaymakers must abide by the country’s strict Covid-19 regulations, including installing the Vietnam track and trace app on their phone for the duration of their stay.
It is not yet clear if an exception will be made allowing unvaccinated children travelling with fully-vaccinated parents to enter the country.
Currently, holidays to Vietnam are all but impossible from the UK, with the country only open to tourists booked onto a pilot programme of government-approved group tours. Visitors must also quarantine for at least three days upon arrival.
Foreign arrivals to Vietnam dropped from 18 million in 2019 to just 157,000 in 2021, according to local media .
Do you have a question about travel? Email us: [email protected]
Most Read By Subscribers

International Travel to Vietnam: Complete Guide from A to Z
According to Vietnam Briefing, Vietnam has reopened its doors to international tourists since March 15th, 2022 - after more than 2 years of dealing with COVID-19. Tourists from all over the world can now travel to Vietnam using various modes of transportation, such as by plane, train, bus, or private car.
Below, we will provide you with essential information for traveling to Vietnam.
Entry Requirements for Malaysian Citizens

Entry requirements for Malaysian citizens to fly to Vietnam
Here are the entry requirements for Malaysian citizens to Vietnam - in brief:
Note: As entry requirements may change over time, you should check the current regulations with the Vietnamese embassy or consulate or with your travel agency in advance.
Passport Validity

Understand the validity of your passport if you travel to Vietnam
As clearly stated at Vietnam-Immigration.Org.Vn , foreign citizens are required to have a passport that is valid for at least six months longer than the period you intend to stay in Vietnam. Thus, it is advisable to review your passport before the trip if it is set to expire within the next six months.
Supposing that you are traveling with your family and your children are under 14 years old, you can also replace a passport with a birth certificate and a stamped portrait picture.
Visa policy

Do you need to apply for a visa to Vietnam?
As mentioned, an entry visa can be either exempt or required - depending on how long you plan to stay in Vietnam.
How Do You Apply for a Vietnamese Visa in Malaysia?

You can apply for a regular visa, e-visa, or visa on arrival
Regular Visa
If you do not bother going to the Vietnamese embassy directly, you may apply for a regular visa in the form of a tourist visa, business visa, or diplomatic visa.
- A tourist visa is ideal if you are traveling to Vietnam solely for tourism.
- A business visa is granted if you are traveling to Vietnam to collaborate with legal businesses and organizations, provide services, establish a commercial presence, or conduct activities outlined in international treaties.
- A diplomatic visa is granted if you are invited by Vietnamese ministries or high-ranking government officials for official visits to Vietnam.
Vietnam also allows passengers to apply for an electronic visa, or for short, an e-visa.
Simply register for it online through the Vietnam Immigration website at xuatnhapcanh.gov.vn and receive an electronic visa document that permits entry into Vietnam.
Generally, an e-visa for Vietnam is valid for a single entry and allows a stay of up to 30 days.
Visa on arrival
Otherwise, you have the option to apply for a visa on arrival in Vietnam - at the designated entry points.
For this type of visa, you need to obtain a visa approval letter through a travel company or an online service prior to your arrival.
Upon arrival at any of the designated international airports in Vietnam, it is possible to present the visa approval letter, settle the visa stamping fee, and promptly obtain your visa.
Vietnam Travel Guide for Malaysian Tourists
We would like to share with you a travel guide to Vietnam so that you can take note of some popular destinations, cultural tips, transportation options, and other useful information.
- Entry Requirements: Please refer to the entry requirements for Malaysian citizens as mentioned above and ensure that you have all the necessary documents and procedures completed before your departure.
- Flights: Find flights from Malaysia to Vietnam and book your plane tickets at least 45 days prior to the departure date to choose the appropriate time with the best price and early purchase benefits from Vietnam Airlines.
Note: The flight information is current as of October 2023 and is subject to potential fluctuations.
- Currency: You should exchange for VND currency at the airport, local banks, or authorized currency exchange counters. This will enable you to shop and pay for services in Vietnam more easily.
- Language: Vietnamese and English are commonly spoken in Vietnam; however, it is advisable to carry a dictionary or install a translation app to communicate with locals who may not be fluent in English.
- Weather: Vietnam has diverse weather from the North to the South. Therefore, we recommend checking the weather conditions for the specific region you plan to visit and packing appropriate clothing and accessories based on the weather.
- Transportation: You have various options for transportation in Vietnam, such as taxis, motorbikes, buses, trains, or flights. For convenience and safety, we suggest that you use reputable taxi services or ride-hailing apps. If you want to rent a motorbike, make sure that you have a valid license and wear a helmet.
- Attractions: Vietnam offers countless attractions , including vibrant cities, stunning landscapes, historical landmarks, and beautiful beaches. Hanoi, Halong Bay, Hoi An, Nha Trang, Da Nang, and Ho Chi Minh City are among the well-liked destinations in Vietnam. Research and plan your itinerary by considering your personal preferences and the time you have at your disposal.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Vietnam - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Exercise normal precautions in Vietnam.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Vietnam.
If you decide to travel to Vietnam:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Vietnam.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must have six months’ validity remaining.
One visa page required for entry stamp.
Not required.
None. However, Vietnamese Dong in excess of VND 15,000,000 or foreign currency in excess of 5,000 U.S. dollars or equivalent must be declared.
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Hanoi - Consular Annex 170 Ngoc Khanh Ba Dinh District Hanoi, Vietnam Telephone: From outside Vietnam: +84-24-3850-5000 From the U.S.: 011-84-24-3850-5000 From landline within Hanoi: 3850-5000 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 024-3850-5000
Emergency: From outside Vietnam: +84-24-3850-5000 or +84-24-3850-5105 From the U.S.: 011-84-24-3850-5000 From landline within Hanoi: 3850-5000 or 3850-5105 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 024-3850-5000 or 024-3850-5105 Fax: (+84-24) 3850-5010 Email: [email protected] Facebook
U.S. Consulate General Ho Chi Minh City 4 Le Duan, District 1 Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Telephone: From outside Vietnam: +84-28-3520-4200 From the U.S.: 011-84-28-3520-4200 From landline within Ho Chi Minh City: 3520-4200 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 028-3520-4200
Emergency: From outside Vietnam: +84-28-3520-4200 From the U.S.: 011-84-28-3520-4200 From landline within Ho Chi Minh City: 3520-4200 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 028-3520-4200 Fax: (+84-8) 3520-4244 Email: Contact Us Here
EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS WITHIN VIETNAM
Police: 113 Fire brigade: 114 Ambulance: 115
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Entry Requirements: You must have a valid passport and a visa (or pre-approval for a visa on arrival) to enter Vietnam. Your passport must be valid for six months beyond your planned stay, and you must have at least one blank visa page (not including the endorsement page). Visit Mission Vietnam’s website for the most current information. If you arrive in Vietnam without an appropriate visa (which could be an e-visa) or pre-approval for a visa on arrival, you will be denied entry . The U.S. Mission to Vietnam cannot assist U.S. citizens who arrive in Vietnam without required visas. U.S.-Vietnam dual nationals should consult the Department of State’s information page for Travelers with Dual Nationality and the Embassy of Vietnam for travel requirements. You must enter and exit Vietnam on the same passport. If using a Vietnamese passport to enter and exit the country, your passport must have at least six months’ validity from your return date to the United States.
Visas: The Government of Vietnam requires a “visa sponsor” for all visa categories, except for E-visa. A visa sponsor is a local business or travel agent to apply for a pre-approval letter with a Vietnamese Immigration Office in Vietnam on behalf of the traveler. Only on receipt of the pre-approval letter can a foreigner apply for an appropriate visa at a Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate abroad, or for a visa on arrival. For more information about this process, please visit the website of the Vietnamese Embassy here . When you apply for a visa to enter Vietnam, be sure to request the visa category that corresponds to your purpose of travel. Please refer to Vietnam’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs website for information detailing visa categories. If you plan to work in Vietnam, you must obtain a work permit before applying for your visa. If you change the purpose of your visit after you have received your visa, you must obtain a new visa outside of Vietnam appropriate for your new activities before beginning those activities. Under local immigration law, employment-based visas are based on a petition from a specific employer, and workers may be unable to switch jobs without securing a new visa. In addition, employers may prevent the departure of contracted employees from Vietnam if they violate contract terms. Before accepting employment in Vietnam, make sure you understand the conditions of contracts and employment-based visas.
Note that travelers with a U.S. APEC Business Travel Card will still need a valid visa to enter Vietnam. The United States is a transitional member of APEC and does not reciprocate with other economies regarding full pre-clearance benefits to applicants. As such, no countries are listed on the back of U.S. APEC Business Travel Cards and card holders are required to present any travel or identity documentation, such as a passport and visa (where applicable), required by Vietnam. If a U.S. APEC Business Travel Card holder does not conform to Vietnam’s entry requirements, the card holder may be refused entry.
Please consult Mission Vietnam’s website for more information.
Please note that Vietnam requires a valid visa, residence card, or approval from the Immigration Department to leave the country. Immigration officials will apply a fee to replace lost/stolen visas or will assess a fine for any visa overstays. The Government of Vietnam has recently increased the penalties for visa overstays, and fines can be substantial. In addition, the processing of exit visas for cases involving visa overstays can take one to two weeks, and longer for more complex cases.
If your U.S. passport is lost or stolen in Vietnam, you will need both a replacement passport and a replacement Vietnamese visa to legally remain in or depart Vietnam. The U.S. Embassy in Hanoi and the Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City can usually issue you a limited validity replacement passport in as little as one business day for emergency purposes; however, the Vietnamese government requires three to five working days to issue a replacement visa. For lost and stolen passports, immigration officials will also request a police report. You must file a report of a lost or stolen passport with the police in the location where the loss or theft of your passport occurred, or authorities may refuse to accept the report. The U.S. Embassy and the Consulate General cannot expedite the replacement of your Vietnamese visa.
If you plan to travel from Vietnam to Laos by land, you should request that an adhesive visa be affixed to your passport instead of a detachable one. Lao immigration officials require proof that travelers have departed Vietnam, something that can only be shown with an adhesive visa. Vietnamese officials remove detachable visas from passports when travelers depart Vietnam, leaving travelers with no proof of their Vietnam departure. This situation can result in Lao officials requiring travelers to return to Vietnam.
Pre-approval for Visa on Arrival: The Government of Vietnam has authorized some businesses and travel agencies to arrange for pre-approval for a “visa on arrival” at the airport. On a receipt of a pre-approval letter, travelers may then travel to Vietnam and apply for a visa upon landing to Vietnam. Please be advised that you should not travel to Vietnam without having been issued a pre-approval letter as it may result in a denial of entry by immigration authorities. To avoid having to rearrange your travel date, please do not make travel arrangement before you receive your pre-approval letter.
E-visa: U.S. citizens can apply online for an E-visa on the Vietnam Immigration website . The E-visa is valid for a maximum of 90 days, single or multiple entry, and does not allow for renewal or extension from within the country. The E-visa is valid for a maximum of 90 days, single or multiple entry, and does not allow for renewal or extension from within the country. An E-visa is usually processed within three to five working days after the Vietnam Immigration Department receives the completed application and E-visa fee. E-visa holders must present the printed E-visa and valid passport at the port of entry. Prior to your travel with an E-visa to Vietnam, we recommend travelers to carefully check their E-visa to make sure all information is correct, and that you will enter/exit Vietnam through a port of entry that you had selected at the time of application. An error on E-visa, including minor differences between the information on the application and the biographical information on the passport, may result in a denial of entry by immigration authorities. The U.S. Embassy and Consulate General are unable to change the information on your E-visa or help expedite the process as Vietnamese E-visa is under the sole jurisdiction of the Vietnamese government.
Certificate of Visa Exemption: Vietnamese nationals residing abroad indefinitely, their spouses, and their children may apply for a Certificate of Visa Exemption. The certificate has a maximum validity of five years, during which time the holder can enter Vietnam and stay for up to six months without applying for a visa. More information can be found on the Vietnam Embassy website .
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Vietnam.
Immunization information for travelers can be found on the Centers for Disease and Control’s website .
Information about dual nationality or the prevention of international child abduction can be found on our website. For further information about customs regulations, please read our Customs Information page .
Safety and Security
The Department of State recommends that U.S. citizens overseas always maintain a high level of vigilance and take appropriate steps to increase their security awareness while traveling internationally. Please visit www.travel.state.gov for up-to-date information.
Messages regarding weather-related events are posted here and on the Embassy/Consulate General website .
While in Vietnam you are subject to Vietnamese laws. U.S. citizenship will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be arrested, expelled, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Vietnamese authorities routinely do not provide timely notification of the arrest of a U.S. citizen to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General or approval for consular officials to visit U.S. citizens. The delays for both – particularly for access – can take several weeks. Note that if you enter Vietnam with a non-U.S. passport, the Government of Vietnam has different notification and access responsibilities for the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General. See our webpage for further information.
Small-scale, peaceful protests occasionally occur in Vietnam’s major cities, but large-scale demonstrations are rare. As in any country, you should avoid large protests, as they can become violent with little or no warning.
The Government of Vietnam may not allow or authorize travel to certain areas of the country that are deemed sensitive. Check with local authorities before visiting border areas to see if you need to obtain a travel permit issued by local authorities. U.S. citizens have been detained after traveling in areas close to the Vietnamese borders with the People’s Republic of China, Cambodia, and Laos. These areas are not always marked, and there are no warnings about prohibited travel.
Safety standards in Vietnam are not at the same level as those in the United States and vary greatly from company to company and province to province. This is especially true for fire safety codes. Travelers should be aware that many buildings, including hotels, shops, and restaurants, have limited or no fire safety equipment or emergency exits. Ground and water transportation also lack safety regulations.
Travelers to Vietnam should have no expectation of privacy and should safeguard all personal documents and electronic devices. Exercise caution when discussing sensitive or proprietary information.
Crime: Crime in Vietnam is rated high. Exercise vigilance and the same commonsense security precautions you would in any major metropolitan city in the United States.
Violent crime against foreigners is rare; however, petty crimes, such as theft, bag grabs, and pickpocketing occur regularly, especially in crowded areas and tourist locations. Typically, there is a rise in petty crime during the Christmas and Tet (Lunar New Year) holiday seasons, including during the day and in well-lit areas. Motorcyclists are known to snatch bags, cameras, cell phones, and other valuables from individuals riding or walking on the street. If you are targeted by thieves, do not resist, and report the incident immediately to local police and to the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U.S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City. Keep a tight hold on bags as you enter and exit vehicles and as you walk around. Hold tightly to cell phones when using them outside and lock and stow phones until you actually need to use them.
Some U.S. citizens have reported threats of death or physical injury connected to business-related disputes. You should report such threats to local authorities and if you feel unsafe, you should depart the country.
Keep your passport and other important valuables in your hotel in a safe or another secured location at all times and carry both photo and digital copies of your passport. You should immediately report the loss or theft of your U.S. passport to the local police and the U.S. Embassy or the U.S. Consulate General. See section on “Visas” for information on what to do if your passport/visa are lost or stolen.
Sexual Assault: Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment and rape do occur. To minimize the risk avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Local authorities may not always respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Male violence against women and sexual harassment is often ignored by the police. In areas foreigners frequent, women have reported harassment and assault such as men exposing themselves, asking for sexual favors, and groping.
Drugs: Recreational drugs available in Vietnam can be extremely dangerous and can result in death. Drugs sold in Vietnam may be fake, synthetic, or laced with toxic ingredients undetectable to the buyer. This includes nitrous oxide balloons widely available in nightlife establishments. You should also avoid purchasing liquor or cigarettes from street vendors or strangers, as the authenticity of the contents cannot be assured.
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General for assistance. Vietnam’s local equivalent of an emergency line is 113. Local police will issue a report of a crime, but generally will only initiate investigations for crimes they determine serious, which do not always equate with U.S. standards. Investigations can take several months or even years to complete.
In the event you are a victim of a crime, local police will issue a crime report in Vietnamese, but generally will only initiate investigations for crimes they determine serious. While the overall situation is improving, some police have asked for bribes, ostensibly to support local police efforts or to facilitate investigation of a crime. If you are involved in a situation where a police officer is soliciting money, contact American Citizen Services at the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
We can:
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the United States.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited support in cases of destitution.
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the Embassy or Consulate General for assistance . Note that local authorities take a different attitude towards domestic violence cases and are hesitant to get involved in cases involving foreigners. Vietnam has very limited infrastructure to support victims of domestic violence.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to Vietnamese laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Vietnam are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines, or even the death penalty. Police periodically raid nightlife establishments suspected of engaging in the drug trade and during these raids will subject all patrons present to drug testing at the police station. A positive result, regardless of whether drugs were consumed in Vietnam or before entry, may result in criminal charges.
In Vietnam, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have proper ID, such as a passport or a copy of your visa. Driving under the influence of alcohol resulting in a fatal accident could lead to immediate imprisonment. If you break local laws in Vietnam, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Note that the Vietnamese legal system allows for lengthy criminal investigation periods that can lead to prolonged pre-trial detention; some investigations can last years without any explanation.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. You can be prosecuted in the United States for engaging in sexual conduct with children or for using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country regardless of the legality of these activities under the host country’s laws.
Arrest Notification in Vietnam: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General immediately. There are often delays in notification by the Vietnamese authorities to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General and officials have been known to delay consular access to prisoners for several weeks.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or forfeit them upon return to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Gambling: Gambling is highly regulated by the government and persons or businesses running games or gambling halls are required to be licensed. The Government of Vietnam pursues cases of running or playing in unlicensed games aggressively. There are currently U.S. citizens serving jail sentences of three to five years because of illegal gambling.
Dual Nationality: Dual nationality is accepted by the Vietnamese government in some, but not all, circumstances. However, dual nationals should be aware that Vietnam recognizes their Vietnamese citizenship as primary before others. In such cases, the U.S. Embassy and Consulate General may be limited in the consular services we are able to provide. U.S. citizens who also hold Vietnamese citizenship and are currently residing in Vietnam may wish to contact local authorities and/or seek competent legal advice on how local laws may affect their status. For detailed information on Vietnamese nationality law and other legal issues visit the Embassy of Vietnam website .
Work Authorization: The Government of Vietnam maintains strict laws with respect to foreign workers. U.S. citizens planning to work in Vietnam should make sure that they are in full compliance with Vietnamese regulations. Penalties can be severe and include deportation, fines, or detention. Vietnam immigration law allows for companies sponsoring foreign employees to exercise control over their employees’ visas, including prohibiting their exit from the country if they have any outstanding debts.
Teaching English: We advise those considering accepting an English teaching job in Vietnam to carefully review the terms of the contract regarding working and living conditions and to ask for multiple references from persons familiar with the institution, especially former U.S. citizen employees, before committing to contracts. Some U.S. citizens have reported their employers have reneged on contract terms, including offering significantly lower salaries than agreed or seizing their passports, and employers have caused complications with the exit visa process for employees who quit, complicating the exit visas required to depart the country.
Hotels: Hotels in Vietnam require you to present your passport (and visas, if issued separately) upon check-in so that your stay can be registered with local police. Every guest in a hotel room or private residence must be registered, regardless of nationality. If you stay at a private residence (i.e., at the residence of family or friends), you must comply with registration requirements by visiting the local police station and registering your stay within 24 hours. Some provinces allow registration online.
Exports: Vietnamese law prohibits the export of antiques. However, these laws are vague and unevenly enforced. Customs authorities may inspect and seize your antiques without compensating you, and the determination of what is an “antique” can be arbitrary. If you purchase non-antique items of value, you should retain receipts and confirmation from shop owners and/or the Ministry of Culture and the Customs Department to prevent seizure when you leave the country.
Imports: Vietnamese authorities have seized documents, audio and video tapes, compact discs, literature, and personal letters they deem to be pornographic or political in nature or intended for religious or political proselytizing. It is illegal to import weapons, ammunition, explosives, military equipment and tools (including uniforms), narcotics, drugs, toxic chemicals, pornographic and subversive materials, firecrackers, or children's toys that have "negative effects on personality development, social order, and security." For up-to-date information on Vietnam Customs information, please visit the Vietnam Customs website .
Freedom of Expression: The Government of Vietnam maintains strict control over all forms of political speech, particularly dissent or speech it deems as critical of the government and/or party. U.S. citizens have been detained, tried, and convicted for political activities (including criticizing the government or its domestic/foreign policies or advocating alternatives to Communist Party rule), possession of political material, and non-sanctioned religious activities (including proselytizing). Authorities have also detained U.S. citizens for posting messages on blogs or online chatrooms that are perceived to be political or critical of the government. U.S. citizens of Vietnamese descent should be especially careful with their online postings. Review the latest version of the Vietnam Human Rights Report for the latest information on Freedom of Expression in Vietnam.
Association with Groups: Persons whom the Government of Vietnam perceives to be associated with dissident or political groups may be denied entry to Vietnam, prevented from departing, detained, interrogated, placed under surveillance, or even tried and convicted. Note that if arrested, you could be subject to lengthy detention without access to an attorney or family members. U.S. citizens of Vietnamese descent should be especially careful about associating with dissident groups. U.S. citizen travelers have been summoned by immigration or local security officials for reasons that are unclear or not explicitly related to any suspected or alleged violation of law. We recommend that U.S. citizens finding themselves in this situation contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General immediately for further information and/or assistance.
Photography: Taking photographs of anything that could be perceived as being of military Taking photographs of anything that could be perceived as being of military or security interest may result in questioning by authorities, fines, or delayed travel. You should be cautious when traveling near military bases and avoid photography in these areas. Disputes: The Vietnamese government has occasionally seized the passports and blocked the departure of foreigners involved in commercial disputes. U.S. citizens whose passports have been seized by Vietnamese authorities should contact the Embassy or Consulate General for assistance .
Civil Procedures: Civil procedures in Vietnam, such as marriage, divorce, documenting the birth of a child, and issuance of death certificates, are highly bureaucratic and can be slow. Local authorities may refuse a request to include a non-Vietnamese name on a birth certificate. In addition, for those wishing to get married in Vietnam, you will need a notarized affidavit of single status. Please contact the Vietnamese Embassy in Washington, D.C. , or the Vietnamese Consulate General in San Francisco or Houston concerning documentary requirements for these services. Enforcement of civil orders is frequently difficult or non-existent.
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
LGBTQI+ Rights: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or in attending LGBTIQ+ events in Vietnam. See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Accessibility: Most public places and public transportation are not accessible to persons with disabilities. Sidewalks, curb ramps, restrooms, road crossings, and tourist areas are not equipped to assist such individuals. New, modern buildings and facilities in larger urban cities are regularly built with ramps and accessible entryways.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Medical facilities in Vietnam, including emergency response services, frequently do not meet international standards and may lack medicine and supplies. We strongly recommend travelers purchase medical evacuation insurance before visiting Vietnam.
- Medical personnel generally speak little or no English. Doctors and hospitals expect immediate cash payment for health services. You may obtain lists of local English-speaking physicians from the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U.S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City from our website .
- International health clinics in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City can treat minor illnesses and injuries, but more serious problems often require medical evacuation to other cities in the region.
- Although you can purchase many prescription and non-prescription medications at pharmacies, some common U.S. medications may not be available. You should bring adequate supplies of medications for the duration of your stay in Vietnam and ensure with the Ministry of Health that the medicine you need is allowed to enter Vietnam. You should carry a copy of your prescription if carrying medicine in a travel case or container.
- We strongly recommend travelers purchase medical evacuation insurance before visiting Vietnam.
- Travelers to Vietnam are at risk of the following diseases: Tuberculosis, Dengue Fever, Zika, Avian Influenza (H5N1), and HIV. You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the CDC website .
We do not pay medical bills. The U.S. government cannot pay medical bills and does not provide medical assistance. Also, be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept upfront payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage . Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas. If covered by TriCare, check the TriCare website ( https://www.tricare.mil/ ) for additional information about overseas coverage.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation as it can cost many thousands of dollars. Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription.
It is extremely important that travelers have sufficient funds and/or insurance to cover any potential medical costs. Frequently hospitals will hold onto a patient’s passport as collateral for payment, and patients may have difficulty getting their passport back without paying their medical bills in full. Patients who do not pay their medical bills in full also run the risk of being barred from departing the country.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Air quality: Air pollution is a significant problem in Vietnam’s major cities, and you should consult your doctor prior to travel and consider the impact that seasonal smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on you. To obtain information on the air quality in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City, please follow the link to the Environmental Protection Agency’s AirNow website . Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City’s Air Quality Index (AQI) can be observed either by clicking on the Vietnam location on the map, or by selecting Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City in the “Select a City” option on the upper right part of the page. The page provides AQI over the last 24-hour period as well as pollutant concentration and a downloadable historical document.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Traffic in Vietnam is dangerous, chaotic, and undisciplined. Road conditions are poor; traffic accidents are the leading cause of death, severe injury, and emergency evacuation of foreigners in Vietnam. Long-distance buses and trains do not meet U.S. safety standards. Buses and trucks are often overloaded and travel at high speeds with little regard to other modes of road transportation.
Traffic Laws: Driving in Vietnam is not comparable to driving in other countries. Vietnamese drivers routinely ignore traffic laws, causing traffic fatalities on a daily basis. We strongly discourage you from operating a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam. Vietnamese drivers and pedestrians may not behave in a manner to which Americans are accustomed. If you do choose to operate a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam, wear a helmet and always yield to larger vehicles. Motor bike fatalities are a leading cause of death or serious injury among foreign nationals visiting or living in Vietnam, with several fatalities having occurred on major roads and rural routes within the past year. If you are the victim of a serious motor bike accident in Vietnam, the prognosis for full recovery and survival is low due to Vietnam’s poor medical infrastructure. A motorbike license is required to operate a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam. Motor scooter drivers without a license can be held criminally liable for injuries to or death of a victim in an accident, and you may be held in custody for an extended period of time without the ability to speak to family or a lawyer during the investigation.
Pedestrians should always look carefully in both directions before crossing streets, even when using a marked crosswalk with a green “walk” light illuminated or when crossing what is believed to be a one-way street. When walking on sidewalks, be mindful of scooters that may be behind you. Vietnamese commonly drive their scooters against traffic and on sidewalks.
Because the United States is not a party to the Convention on Road Traffic, international driving permits and U.S. drivers’ licenses are not valid in Vietnam. Foreigners renting vehicles risk fines, prosecution, and/or imprisonment for driving without a Vietnamese license endorsed for the appropriate vehicle. If you wish to drive in Vietnam, contact the Provincial Public Transportation Service of the Vietnamese Department of Communications and Transport to obtain a Vietnamese driver’s license. Note that you may be required to take a medical examination as part of the driver license application process.
For more information, please refer to Vietnam’s national tourism office website.
Public Transportation:
Bus System: While Vietnam does have an extensive bus system, buses can be overcrowded and are often driven with little or no regard for passenger safety.
For-hire vehicles: Major taxi companies tend to be reliable. Occasionally boutique taxi companies have rigged meters, particularly on routes to and from the international airports. Exercise caution in choosing ground transportation upon arrival at the airport in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City. Some travelers have reported being robbed by drivers who greeted them upon arrival with a placard showing the traveler's name. If you are expecting to be picked up, ask the company for the driver’s name, phone number, and license plate number before you travel. Areas outside of large cities typically have only rudimentary public transportation and often do not have metered taxis. Travelers are advised to use caution in these situations.
We strongly discourage the use of motorcycle taxis (known as “xe om”). Motorcycle taxis are unregulated and unsafe, and the helmets provided to riders offer little to no protection against injury in the case of an accident.
Smartphone-based for-hire vehicle services: GrabTaxi and local taxi companies are readily available, accessible via Smartphone apps, and routinely utilized by foreigners and locals.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Vietnam’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Vietnam’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Vietnam should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) broadcast warnings website portal.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Vietnam . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, vietnam map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Check passport expiration dates carefully for all travelers! Children’s passports are issued for 5 years, adult passports for 10 years.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

UK unlikely to unlock travel to key European destinations, say sources
Government considers adding more destinations to England’s red list as it monitors Vietnam variant
- Coronavirus – latest updates
- See all our coronavirus coverage
The UK is unlikely to unlock significant new summer destinations this week when changes to travel restrictions are announced, with key holiday countries unlikely to be quarantine-free until later in the summer, Whitehall sources have said.
The changes to England’s travel advice are eagerly anticipated by the beleaguered travel industry, which is hoping for changes to the green list of destinations that do not require quarantine on return.
Portugal is the only mass tourism destination where no quarantine is required on either leg, but operators are pinning hopes on the reopening of holiday islands such as Malta, the Canaries or the Balearics , even if mainland Spain remains on the amber list.
Boris Johnson told Tory MPs at a Conservative backbench 1922 Committee meeting last week he expected “quite a few” destinations to be added to the list, but there are doubts over some of the most popular European countries such as Spain and France.
“We are still early in the summer, no one is expecting huge changes,” a Whitehall source said. “Very little has changed in terms of the risks in most places, including the risk from variants.”
Spain lifted all restrictions for UK travellers on 24 May, though France has tightened restrictions on British visitors owing to fears over the spread of the Delta variant first detected in India. Entry to France is limited to EU nationals, French residents and those travelling for essential purposes.
The changes are expected to be announced on Thursday after ministers receive advice from the Joint Biosecurity Centre. Those changes would then take effect the following week.
The UK government has confirmed it is monitoring a suspected Covid variant detected in Vietnam ahead of a decision on travel restrictions due later this week that could result in more destinations being added to England’s red list, which requires arrivals to go into hotel quarantine.
Vietnam is currently on the amber list, which requires self-isolation at home upon return, but is among the countries that could be upgraded to stricter quarantine measures.
“We continually run genomic testing on positive cases of the virus and we will continue to do so to spot new and emerging variants,” Downing Street said.
Vietnam’s containment of coronavirus had been a worldwide success story until the past few months, when cases have risen. The country has recorded about 7,000 total cases, with 47 deaths.
Vietnam’s health minister, Nguyễn Thanh Long, said on Saturday that a variant had been detected combining characteristics of two existing variants first found in India and the UK.
The Telegraph reported analysis by Robert Boyle, a BA strategist, suggesting Bahrain, Costa Rica, Trinidad and Tobago and Kuwait could also be added to the red list because of their case rates.
Heathrow airport in London has reopened a dedicated terminal for red-list passengers after significant concerns were raised about people mixing at border control.
Currently the red list requires hotel quarantine for arrivals from countries including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Brazil, South Africa, the UAE and Turkey.
From Tuesday, red-list arrivals will pass through the airport’s Terminal 3, which has been closed since April 2020 due to plummeting visitor numbers.
- Coronavirus
- Travel & leisure
- Health policy
- Public services policy
Most viewed
Pinpoint Travel Health

Foreign travel advice Vietnam
Table of Contents
Foreign Travel Advice Vietnam

Warnings and Insurance: This travel advice has been rewritten to make it easier to read and understand.
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) provides advice on travel risks to assist British nationals in making informed decisions. Learn more about FCDO travel advice.
ENTER YOUR DESTINATION FOR YOUR CUSTOM TRAVEL BRIEF
Before You Travel: No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide, as well as support for British nationals abroad, which includes:
- Advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- Information for women, LGBT+, and disabled travelers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. You can also sign up to receive email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel Insurance: If you decide to travel to Vietnam, conduct research on your destinations and obtain appropriate travel insurance. Your insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities, and expenses in case of an emergency.
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- women travellers
- disabled travellers
- LGBT+ travellers
- solo and independent travel
- volunteering and adventure travel
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
About FCDO travel advice
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
This information is for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK. It is based on the UK government’s understanding of the current rules for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Vietnam set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Vietnam.
Passport validity requirements
To enter Vietnam, your passport must have:
- an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive
- at least 2 blank pages
- no damage – British nationals have been denied entry and exit due to passport damage
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Make sure you get your passport stamped.
Check the visa expiry date written in your passport is correct before leaving border control. If it is wrong, you could be accused of overstaying.
Visa requirements
You can visit Vietnam without a visa for up to 45 days for tourism or business.
If you want to stay longer than 45 days, you can:
- book with a travel agent in Vietnam and ask them to apply for a visa pre-approval letter – your agent will tell you when to collect your visa from the embassy
- apply for other visa types from the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK
- apply for an e-visa that allows a 90-day stay and multiple entries
E-visas restrict you to the entry and exit points you select when you apply. If you get an e-visa while in Vietnam, you must exit the country and re-enter to start your e-visa.
The British Embassy will not assist with visa extensions.
Work or study
If you want to work or study, check which type of visa or work permit you need with the Vietnam Immigration Department .
Read about visas and work permits if you live in Vietnam .
If you overstay your visa or work illegally, the authorities can prevent you from leaving until you pay a fine. You could be deported and prevented from visiting Vietnam in the future.
Travelling through Vietnam
If you transfer from an international flight to a domestic flight in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City, you must go through immigration and enter Vietnam. You must do this even if your final destination is outside Vietnam.
Check with your airline before departing.
Vaccine requirements
For details about medical entry requirements and recommended vaccinations, see TravelHealthPro’s Vietnam guide
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Vietnam . You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
If you’re taking prescription medication into Vietnam, carry it in your hand luggage with a copy of the prescription. If it has a total import value greater than 100 US dollars, you must declare it at customs. For information about restrictions on medication, see Health .
Taking money into or out of Vietnam
If you’re taking cash into or out of Vietnam, you must declare amounts over:
- 15 million Vietnamese dong
- 5,000 US dollars (or the same value in other currencies)
If you’re leaving the country with more than these amounts, declare the money at customs and show either:
- confirmation you’re carrying cash abroad, issued by an authorised credit institution
- written approval to carry cash, issued by the State Bank of Vietnam
There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK interests and British nationals, including from groups and individuals who view the UK and British nationals as targets. Stay aware of your surroundings at all times.
UK Counter Terrorism Policing has information and advice on staying safe abroad and what to do in the event of a terrorist attack. Find out how to reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad .
Terrorism in Vietnam
Although there is no recent history of terrorism in Vietnam, attacks cannot be ruled out.
Attacks could be indiscriminate including in places visited by foreign nationals. Stay aware of your surroundings, keep up to date with local media reports and follow the advice of local authorities.
Political situation
Vietnam has a single-party political system, which does not welcome people disagreeing with the government. Some protests in recent years have turned violent or been violently suppressed by the authorities. Avoid all protests.
Protecting yourself and your belongings
Pickpockets and bag-snatchers operate in crowded areas and in places visited by tourists. Take care of your belongings and consider splitting important items between bags.
Do not give your passport to others as a guarantee – for example, to motorcycle rental shops or landlords. They can hold your passport against claimed damage.
There is a risk of petty theft on buses and trains, particularly while asleep on overnight trains.
Drink spiking and sexual assault
British nationals have reported rape and sexual assaults in tourist areas and places where foreigners live. Women have also reported indecent assaults and harassment. These include inappropriate touching and groping, particularly while walking alone.
In Vietnam there is a higher burden of proof for victims than in the UK. Victims must show they did not consent, particularly if they drank alcohol or knew the alleged attacker.
There is a risk of drink spiking – do not leave your drinks unattended or accept drinks from strangers.
Be wary of job offers that appear too good to be true. People have arrived in the Mekong region and have been illegally transported to neighbouring countries on the promise of high-paying jobs, which turn out to be scams.
There have been incidents of:
- passports being confiscated by scammers
- victims being held in poor living conditions
- coercion into undertaking wider online scamming activity
Transfers from airports and stations
Be cautious about offers of free bus transfers to hotels, unless organised in advance. These may be scams.
Laws and cultural differences
Personal id.
You must always carry photographic ID. The authorities will accept a printed copy of the photo page of your passport and visa.
Illegal drugs penalties
Penalties for possessing, distributing or manufacturing drugs are severe. You can get the death sentence if you’re found with even small amounts.
Illegal drugs are often tampered with or spiked and can be much stronger than in Europe. British nationals in Vietnam have suffered severe psychiatric problems because of drug use.
LGBT+ travellers
Vietnam is a generally tolerant and progressive place for LGBT+ travellers. There are no criminal penalties for same-sex sexual activity or changing gender. Same-sex marriage is not recognised in law.
Read more advice for LGBT+ travellers .
Respect local customs and dress in appropriate clothing when entering religious or cultural sites. This usually means covering your shoulders and knees. You’ll often see signs outside religious or cultural sites that tell you the dress code.
Money change counters
Only change money at official money exchange counters with a clear sign showing this status. Changing money elsewhere is illegal and you risk losing your money.
Some rice wines sold without recognised brand names can have very high and sometimes fatal levels of methanol.
Wildlife, animal products and souvenirs
It’s illegal to buy, sell, kill or collect protected wild animal or plants. If you’re caught buying or trafficking these items, you could get a fine or long prison sentence.
Restricted areas
There are restrictions on travel near military bases in Vietnam. Do not take photos near bases.
If you want to visit a village, commune or ward close to the border, you may need permission from the provincial police department. Contact the local authority for more information.
Legal system
People convicted of sex and drug offences can receive very long prison sentences or the death sentence. The Vietnamese legal system is not well developed, and the standard of prisons is very poor.
If you are under criminal investigation, you can be detained for long periods without evidence. There can be long delays before you can contact lawyers, British Embassy officials or family. Legal representation is far below UK standards.
Foreign nationals involved in traffic accidents have been stopped from leaving Vietnam until the police have completed their investigations. This process can take a long time, and foreign nationals have been asked to agree out of court financial settlements. FCDO advises you to get professional legal advice and representation if you are in this situation. See Getting help .
Internet access
There are sometimes restrictions on internet use, which can temporarily affect access to social media websites. Most social media sites are normally available.
Outdoor activities and adventure tourism
British nationals have died or been injured in Vietnam while engaged in adventure tourism in rural and mountainous areas.
Risks include:
- dangerous terrain
- remote areas that are difficult for rescue services to reach
- flooding, swollen rivers and landslides, especially during the rainy season
- lower safety standards than in the UK
To reduce your personal risk:
- follow safety guidelines
- stay on main routes
- take a reputable guide – in some places it is illegal to go without a guide
- use approved adventure tourism companies – check local authority websites
- check weather forecasts
- make sure your travel insurance covers your planned activity
Illegal tour guides have been known to offer tours and activities prohibited under local regulations.
Firearms activities
If you take part in leisure activities involving firearms, make sure a reputable guide supervises you. There is a risk of hearing loss.
Transport risks
Road travel.
If you are planning to drive in Vietnam, see information on driving abroad and driving rules in Vietnam .
You’ll need to have both the 1968 version of the international driving permit and your UK driving licence with you in the car. It is illegal to drive without third-party insurance.
Do not use your passport as a deposit for hiring vehicles or as a guarantee you will pay a fine for a traffic offence.
Drink-driving is a serious offence in Vietnam. If you are tested and found to have any alcohol in your system, you may get a fine and possible imprisonment.
Compliance with road laws is poor – keep your speed down and stay alert.
If you’re involved in an accident, you could face criminal charges and may need to pay compensation to injured people, even if the injuries are minor. Offer the police your full co-operation and inform the British Embassy in Hanoi or Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City .
Motorbike safety
Travelling by motorbike in Vietnam is much riskier than in the UK. Motorbike accidents are common and have killed and injured British nationals.
Do not hire a motorbike if you’re not an experienced rider. Always:
- check your motorbike thoroughly
- rent from a reputable organisation
- use a good helmet – it is illegal for drivers and passengers to ride without a helmet
Make sure your travel insurance covers your planned activity.
Metered taxis from larger firms are generally reliable. Where possible get hotels or restaurants to book you a reputable taxi. Always make sure the driver identifies themself before setting off. If you book taxis using the Grab app, which is similar to Uber – you can make sure the details of the vehicle and driver match those given by the company.
Buses and coaches
Bus and coach crashes are not uncommon and are more likely at night. Vehicles are often poorly maintained. Night bus drivers may become tired but continue driving, resulting in sometimes fatal crashes.
Check with your tour guide about the safety record and registration of boats, and the certification of staff. Make sure you get a full safety briefing and have a life jacket when joining any boat.
Consider safety standards carefully before taking an overnight boat trip on Halong Bay. Overcrowding and poor safety standards have led to accidents in past years. Some boats have sunk quickly and without warning.
Piracy in coastal areas of Vietnam is very rare. See piracy and armed robbery at sea for precautions you could take.
Landmines and unexploded weapons
Landmines and other unexploded weapons are a hazard in former battlefields. Areas of particular risk include central Vietnam and along the Laos border, formerly crossed by the Ho Chi Minh Trail. Mined areas are often unmarked.
Extreme weather and natural disasters
Find out what you can do to prepare for and respond to extreme weather and natural hazards .
Tropical cyclones
Tropical cyclones affect the eastern coastal regions of Vietnam, with a risk of:
- strong winds
- heavy rainfall and flooding
- disruption to transport
The season normally runs from May to November, but tropical cyclones can happen at other times. Monitor approaching storms on the National Centre for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting and Japan Meteorological Agency websites. Follow the advice of the local authorities, including any evacuation orders.
Vietnam has a tropical monsoon climate. There can be large amounts of rain in short periods of time. Localised flooding, flash floods and landslides are common. Take care if you’re trekking in rural and mountainous areas.
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Dial 115 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccine recommendations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest vaccine recommendations for Vietnam in TravelHealthPro’s Vietnam guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
See what health risks you’ll face in Vietnam , including:
- mosquito-borne diseases like Zika virus, dengue, malaria and Japanese encephalitis
- air pollution – see information on air quality on TravelHealthPro
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Vietnam. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
Some medicines can be hard to find in Vietnam and many are fake.
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
Vietnam has restrictions on medicines it classifies as ‘addictive’ or ‘psychotropic’. These include medicine used to treat of addiction, anxiety, depression, insomnia and other conditions.
It is illegal to have more than the amount prescribed by a doctor for 7 days (addictive medicine) or 10 days (psychotropic medicine). You should carry the prescription with your medication and a letter from your doctor stating how much of the medication you need during your trip.
The letter can be in English and should:
- include your name and age
- list the medicine name, volume and dosage
- include the doctor’s signature and address
If you’re unsure if your medication falls within these categories or you need to bring more medication than is usually allowed, contact the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK before travelling.
Healthcare in Vietnam
FCDO has a list of medical facilities in Vietnam where some staff will speak English.
There is also guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Vietnam .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) cannot provide tailored advice for individual trips. Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel.
Emergency services in Vietnam
Ambulance: 115
Police: 113
Contact your travel provider and insurer
Contact your travel provider and your insurer if you are involved in a serious incident or emergency abroad. They will tell you if they can help and what you need to do.
Refunds and changes to travel
For refunds or changes to travel, contact your travel provider. You may also be able to make a claim through insurance. However, insurers usually require you to talk to your travel provider first.
Find out more about changing or cancelling travel plans , including:
- where to get advice if you are in a dispute with a provider
- how to access previous versions of travel advice to support a claim
Support from FCDO
FCDO has guidance on staying safe and what to do if you need help or support abroad, including:
- finding English-speaking lawyers , funeral directors and translators and interpreters in Vietnam
- dealing with a death in Vietnam
- being arrested or imprisoned in Vietnam
- getting help if you’re a victim of crime
- what to do if you’re in hospital
- if you’re affected by a crisis such as a terrorist attack
Contacting FCDO
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this travel advice is updated.
You can also contact FCDO online .
Help abroad in an emergency
If you’re in Vietnam and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the British Embassy in Hanoi or the British Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City .
FCDO in London
You can call FCDO in London if you need urgent help because something has happened to a friend or relative abroad.
Telephone: 020 7008 5000 (24 hours)
Find out about call charges
Risk information for British companies
The Overseas Business Risk service offers information and advice for British companies operating in Vietnam on how to manage political, economic, and business security-related risks.

- GENERAL RULES
- REQUIRED DOCUMENTS
- APPLY IN PERSON AT THE EMBASSY OF VIET NAM
- APPLY BY POST
- APPLY BY EMAIL, COLLECT IN PERSON
- APPLY BY EMAIL, RECEIVE LOOSE-LEAF VISA BY POST
- PROCESSING TIME
- LEGALISATION
- CRIMINAL RECORD CERTIFICATE (Vietnamese Police check):
- VIETNAMESE PASSORT APPLICATION
- VIETNAMESE PASSPORT RENEWAL APPLICATION FOR VIETNAMESE ADOPTED CHILD LIVING IN THE UK OR IN THE REPUBLIC OF IRELAND
- BIRTH REGISTRATION
- MARRIAGE REGISTRATION
- LEGALISATION ON MARRIAGE PAPERWORK BETWEEN BRITISH/IRISH CITIZEN AND VIETNAMESE CITIZEN IN VIET NAM
- NOTARISATION AND SIGNATURE AUTHENTICATION
- VISA EXEMPTION CERTIFICATE
- LAISSER PASSER
- CERTIFICATE OF VIETNAMESE ORIGIN
- PERMIT FOR REPATRIATION OF DECEASED VIETNAMESE REMAINS OR BODIES TO VIET NAM
- About Vietnam
- BOOK APPOINTMENT

Book appointment/ Đặt lịch hẹn
Visa/ thị thực việt nam, legalisation/ hợp pháp hóa, police check/ criminal record, hộ chiếu/ passport, news/tin tức.

BANK HOLIDAY 2024
Date Day of the week Holiday 1 January Monday New Year Holiday 8 to 14 February Thursday to Wednesday Viet Nam New year Holiday 29 March Friday Good Friday 1 April Monday Easter... READ MORE

Vietnam – UK Relation 2021
1 year successfully READ MORE

Viet Nam to resume regular international passenger flights next year The Government has decided to resume regular international passenger flights on a pilot basis from January 1, 2022, in a bid to boost economic recovery.
The decision was announced Friday following a meeting chaired by Permanent Deputy Prime Minister Pham Binh Minh on Thursday to discuss a plan on resumption of regular international passenger flights proposed by the... READ MORE
Approved vaccines
https://www.gov.uk/guidance/countries-with-approved-covid-19-vaccination-programmes-and-proof-of-vaccination?utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=govuk-notifications&utm_source=284b62fe-1f4f-418b-83dd-cc4d76a316ea&utm_content=immediately READ MORE
Quarantine time for fully vaccinated visitors to Vietnam
Vietnam has decided to shorten quarantine time for fully vaccinated travellers with negative COVID-19 test results to 7 days of quarantine at an assigned facility followed by another seven days of medical surveillance... READ MORE
Patient 91: How Vietnam saved a British pilot and kept a clean Covid-19 sheet
By Oliver Barnes & Bui Thu BBC News “If I’d been almost anywhere else on the planet, I’d be dead. They would have flicked the switch after 30 days,” says Stephen Cameron from... READ MORE
Life after lockdown in Vietnam: This is what it’s like when an entire country reopens
Katie Lockhart • Updated 15th May 2020 Hanoi, Vietnam (CNN) — As the faint smell of smoke rose up from the sidewalk and into my bedroom, I jumped up and stepped out onto the balcony to... READ MORE

After aggressive mass testing, Vietnam says it contains coronavirus outbreak
Khanh Vu, Phuong Nguyen, James Pearson HANOI (Reuters) – Businessman Phan Quoc Viet was making his usual prayers at a pagoda in Tay Ninh, a province in southern Vietnam, when the government official’s call came.... READ MORE
- COUNTRY INFORMATION
- LATEST NEWS
- OUTBREAK SURVEILLANCE
- TOPICS IN BRIEF
- FACTSHEETS & RESOURCES
- WORLD OVERVIEW

Capital City: Hanoi
Official Languages: Vietnamese
Monetary Unit: dong (VND)
- General Information
- Vaccine Recommendations
- Other Risks
TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS ARE IN PLACE FOR THIS COUNTRY
There are entry requirements for anyone who plans to travel to England from this country. Please check here for further information. Advice may vary in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
The information on these pages should be used to research health risks and to inform the pre-travel consultation.
Due to COVID-19, travel advice is subject to rapid change. Countries may change entry requirements and close their borders at very short notice. Travellers must ensure they check current Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice in addition to the FCDO specific country page (where available) which provides additional information on travel restrictions and entry requirements in addition to safety and security advice.
Travellers should ideally arrange an appointment with their health professional at least four to six weeks before travel. However, even if time is short, an appointment is still worthwhile. This appointment provides an opportunity to assess health risks taking into account a number of factors including destination, medical history, and planned activities. For those with pre-existing health problems, an earlier appointment is recommended.
All travellers should ensure they have adequate travel health insurance .
A list of useful resources including advice on how to reduce the risk of certain health problems is available below.
- Food and water hygiene
- Insect and tick bite avoidance
- Personal safety
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Sun protection
Details of vaccination recommendations and requirements are provided below.
All travellers
Travellers should be up to date with routine vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK . These vaccinations include for example measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine and diphtheria-tetanus-polio vaccine.
Country-specific diphtheria recommendations are not provided here. Diphtheria tetanus and polio are combined in a single vaccine in the UK. Therefore, when a tetanus booster is recommended for travellers, diphtheria vaccine is also given. Should there be an outbreak of diphtheria in a country, diphtheria vaccination guidance will be provided.
Those who may be at increased risk of an infectious disease due to their work, lifestyle choice, or certain underlying health problems should be up to date with additional recommended vaccines. See the individual chapters of the 'Green Book' Immunisation against infectious disease for further details.
Certificate requirements
There are no certificate requirements under International Health Regulations.
Most travellers
The vaccines in this section are recommended for most travellers visiting this country. Information on these vaccines can be found by clicking on the blue arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral infection transmitted through contaminated food and water or by direct contact with an infectious person. Symptoms are often mild or absent in young children, but the disease can be more serious with advancing age. Recovery can vary from weeks to months. Following hepatitis A infection immunity is lifelong.
All travellers should take care with personal, food and water hygiene.
Hepatitis A vaccination
As hepatitis A vaccine is well tolerated and affords long-lasting protection, it is recommended for all previously unvaccinated travellers.
Hepatitis A in brief
Tetanus is caused by a toxin released from Clostridium tetani bacteria and occurs worldwide. Tetanus bacteria are present in soil and manure and may be introduced through open wounds such as a puncture wound, burn or scratch.
Travellers should thoroughly clean all wounds and seek medical attention for injuries such as animal bites/scratches, burns or wounds contaminated with soil.
Tetanus vaccination
- Travellers should have completed a tetanus vaccination course according to the UK schedule.
- If travelling to a country or area where medical facilities may be limited, a booster dose of a tetanus-containing vaccine is recommended if the last dose was more than ten years ago even if five doses of vaccine have been given previously.
Country-specific information on medical facilities may be found in the 'health' section of the FCDO foreign travel advice pages.
Tetanus in brief
Typhoid is a bacterial infection transmitted through contaminated food and water. Previous typhoid illness may only partially protect against re-infection.
Vaccination is recommended for most travellers, particularly travellers visiting friends and relatives, those in contact with an infected person, young children, frequent or long-stay travellers visiting areas where sanitation and food hygiene are likely to be poor, and laboratory personnel who may handle the bacteria for their work.
Typhoid vaccination
- Oral and injectable typhoid vaccinations are available.
Typhoid in brief
Some travellers.
The vaccines in this section are recommended for some travellers visiting this country. Information on when these vaccines should be considered can be found by clicking on the arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Cholera is a bacterial infection transmitted by contaminated food and water. Cholera can cause severe watery diarrhoea although mild infections are common. Most travellers are at low risk.
Cholera vaccination
This oral vaccine is recommended for those whose activities or medical history put them at increased risk. This includes:
- aid workers.
- those going to areas of cholera outbreaks who have limited access to safe water and medical care.
- those for whom vaccination is considered potentially beneficial.
Cholera in brief
Hepatitis b.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection; it is transmitted by exposure to infected blood or body fluids. This mostly occurs during sexual contact or as a result of blood-to-blood contact (for example from contaminated equipment during medical and dental procedures, tattooing or body piercing procedures, and sharing of intravenous needles). Mothers with the virus can also transmit the infection to their baby during childbirth.
Hepatitis B in Vietnam
2% or more of the population are known or thought to be persistently infected with the hepatitis B virus (intermediate/high prevalence).
Travellers should avoid contact with blood or body fluids. This includes:
- avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse.
- avoiding tattooing, piercing, public shaving, and acupuncture (unless sterile equipment is used).
- not sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- following universal precautions if working in a medical/dental/high risk setting.
A sterile medical equipment kit may be helpful when travelling to resource poor areas.
Hepatitis B vaccination
Vaccination could be considered for all travellers, and is recommended for those whose activities or medical history put them at increased risk including:
- those who may have unprotected sex.
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles through injecting drug use.
- those who may be exposed to blood or body fluids through their work (e.g. health workers).
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles as a result of having medical or dental care e.g. those with pre-existing medical conditions and those travelling for medical care abroad including those intending to receive renal dialysis overseas.
- long-stay travellers.
- those who are participating in contact sports.
- families adopting children from this country.
Hepatitis B in brief
Japanese encephalitis.
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito. These mosquitoes usually bite between dusk and dawn, mainly in rural areas; especially where there are rice fields, swamps and marshes. Mosquitoes become infected by biting JE infected animals (particularly pigs) or birds.
Travellers are at increased risk of infection when visiting rural areas. Short trips (usually less than a month) especially if only travelling to urban areas, are considered lower risk.
Japanese encephalitis in Vietnam
JE occurs in this country, with year-round transmission in the south and from May to October in the north. Cases may be reported outside these months in the north of the country.
All travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly between dusk and dawn.
Japanese encephalitis vaccination
- Vaccination is recommended for those whose activities put them at increased risk (see above).
- Vaccination could be considered for those on shorter trips if the risk is considered to be sufficient e.g. those spending time in areas where the mosquito breeds such as rice fields, marshlands, or pig farming areas.
Japanese encephalitis in brief
Rabies is a viral infection which is usually transmitted following contact with the saliva of an infected animal most often via a bite, scratch or lick to an open wound or mucous membrane (such as on the eye, nose or mouth). Although many different animals can transmit the virus, most cases follow a bite or scratch from an infected dog. In some parts of the world, bats are an important source of infection.
Rabies symptoms can take some time to develop, but when they do, the condition is almost always fatal.
The risk of exposure is increased by certain activities and length of stay (see below). Children are at increased risk as they are less likely to avoid contact with animals and to report a bite, scratch or lick.
Rabies in Vietnam
Rabies is considered a risk and has been reported in domestic animals in this country. Bats may also carry rabies-like viruses.
- Travellers should avoid contact with all animals. Rabies is preventable with prompt post-exposure treatment.
- Following a possible exposure, wounds should be thoroughly cleansed and an urgent local medical assessment sought, even if the wound appears trivial.
- Post-exposure treatment and advice should be in accordance with national guidelines.
Rabies vaccination
A full course of pre-exposure vaccines simplifies and shortens the course of post-exposure treatment and removes the need for rabies immunoglobulin which is in short supply world-wide.
Pre-exposure vaccinations are recommended for travellers whose activities put them at increased risk including:
- those at risk due to their work (e.g. laboratory staff working with the virus, those working with animals or health workers who may be caring for infected patients).
- those travelling to areas where access to post-exposure treatment and medical care is limited.
- those planning higher risk activities such as running or cycling.
- long-stay travellers (more than one month).
Rabies in brief
Tuberculosis.
TB is a bacterial infection most commonly affecting the lungs but can affect any part of the body. When a person with TB in their lungs or throat coughs or sneezes they could pass TB on to other people. TB is curable but can be serious if not treated.
The BCG vaccination helps to protect some people, particularly babies and young children who are at increased risk from TB.
Tuberculosis in Vietnam
This country has reported an annual TB incidence of greater than or equal to 40 cases per 100,000 population at least once in the last five years ( further details ).
Travellers should avoid close contact with individuals known to have infectious pulmonary (lung) or laryngeal (throat) TB.
Those at risk during their work (such as healthcare workers) should take appropriate infection control and prevention precautions.
Tuberculosis (BCG) vaccination
BCG vaccine is recommended for those at increased risk of developing severe disease and/or of exposure to TB infection. See UK Health Security Agency Immunisation against infectious disease, the 'Green Book '.
For travellers, BCG vaccine is recommended for:
- unvaccinated, children under 16 years of age, who are going to live for more than 3 months in this country. A tuberculin skin test is required prior to vaccination for all children from 6 years of age and may be recommended for some younger children.
- unvaccinated, tuberculin skin test-negative individuals at risk due to their work such as healthcare or laboratory workers who have direct contact with TB patients or potentially infectious clinical material and vets and abattoir workers who handle animal material, which could be infected with TB.
There are specific contraindications to BCG vaccine. Health professionals must be trained and assessed as competent to administer this vaccine intradermally.
Following administration, no further vaccines should be administered in the same limb for 3 months.
The BCG vaccine is given once only, booster doses are not recommended.
Tuberculosis in brief
Malaria is a serious illness caused by infection of red blood cells with a parasite called Plasmodium. The disease is transmitted by mosquitoes which predominantly feed between dusk and dawn.
Symptoms usually begin with a fever (high temperature) of 38°C (100°F) or more. Other symptoms may include feeling cold and shivery, headache, nausea, vomiting and aching muscles. Symptoms may appear between eight days and one year after the infected mosquito bite.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment is required as people with malaria can deteriorate quickly. Those at higher risk of malaria, or of severe complications from malaria, include pregnant women, infants and young children, the elderly, travellers who do not have a functioning spleen and those visiting friends and relatives.
Travellers should follow an ABCD guide to preventing malaria:
A wareness of the risk – Risk depends on the specific location, season of travel, length of stay, activities and type of accommodation.
B ite prevention – Travellers should take mosquito bite avoidance measures.
C hemoprophylaxis – Travellers should take antimalarials (malaria prevention tablets) if appropriate for the area (see below). No antimalarials are 100% effective but taking them in combination with mosquito bite avoidance measures will give substantial protection against malaria.
D iagnosis – Travellers who develop a fever of 38°C [100°F] or higher more than one week after being in a malaria risk area, or who develop any symptoms suggestive of malaria within a year of return should seek immediate medical care. Emergency standby treatment may be considered for those going to remote areas with limited access to medical attention.
- There is a low risk of malaria in the southern part of the country in the provinces of Tay Ninh, Lam Dong, Dak Lak, Gia Lai, and Kon Tum, and other rural areas of Vietnam: awareness of risk and bite avoidance recommended.
- There is no risk in large cities, including Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh (Saigon), the Red River delta, coastal areas north of Nha Trang and Phu Quoc Island: bite avoidance recommended.
Special risk groups
In low risk areas, antimalarials may be considered in exceptional circumstances for travellers who are at higher risk of malaria (such as long term travellers visiting friends and relatives), or of severe complications from malaria (such as the elderly [over 70 years], the immunosuppressed, those with complex co-morbidities, pregnant women, infants and young children). The final decision whether or not to advise antimalarials rests with the travel health advisor and the traveller after individual risk assessment.
Travellers with an absent or poorly functioning spleen should be dissuaded from travel to any area with risk of malaria. Where travel is essential awareness, rigorous bite avoidance and antimalarials should be advise, even for the low risk areaa.
For special risk groups, you may wish to seek specialist advice. For the low risk areas in this country/area atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline would be suitable options.
Antimalarial recommendations map

- Click on map to open in a new window
- Malaria in brief
- Malaria factsheet
- Children's antimalarial dose table
- Malaria prevention guidelines for travellers from the UK
There are some risks that are relevant to all travellers regardless of destination. These may for example include road traffic and other accidents, diseases transmitted by contaminated food and water, sexually transmitted infections, or health issues related to the heat or cold.
Some additional risks (which may be present in all or part of this country) are mentioned below and are presented alphabetically. Select risk to expand information.
There is a risk of altitude illness when travelling to destinations of 2,500 metres (8,200 feet) or higher. Important risk factors are the altitude gained, rate of ascent and sleeping altitude. Rapid ascent without a period of acclimatisation puts a traveller at higher risk.
There are three syndromes; acute mountain sickness (AMS), high-altitude cerebral oedema (HACE) and high-altitude pulmonary oedema (HAPE). HACE and HAPE require immediate descent and medical treatment.
Altitude illness in Vietnam
There is a point of elevation in this country higher than 2,500 metres. An example place of interest: Mt Fansipan 3,143m.
- Travellers should spend a few days at an altitude below 3,000m.
- Where possible travellers should avoid travel from altitudes less than 1,200m to altitudes greater than 3,500m in a single day.
- Ascent above 3,000m should be gradual. Travellers should avoid increasing sleeping elevation by more than 500m per day and ensure a rest day (at the same altitude) every three or four days.
- Acetazolamide can be used to assist with acclimatisation, but should not replace gradual ascent.
- Travellers who develop symptoms of AMS (headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and sleep disturbance) should avoid further ascent. In the absence of improvement or with progression of symptoms the first response should be to descend.
- Development of HACE or HAPE symptoms requires immediate descent and emergency medical treatment.
Altitude illness in brief
Biting insects or ticks.
Insect or tick bites can cause irritation and infections of the skin at the site of a bite. They can also spread certain diseases.
Diseases in South-eastern Asia
There is a risk of insect or tick-borne diseases in some areas of South-eastern Asia. This includes diseases such as chikungunya , leishmaniasis and scrub typhus .
- All travellers should avoid insect and tick bites day and night.
- There are no vaccinations (or medications) to prevent these diseases.
Further information about specific insect or tick-borne diseases for this country can be found, if appropriate on this page, in other sections of the country information pages and the insect and tick bite avoidance factsheet .
Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes which mainly feed during daytime hours. It causes a flu-like illness, which can occasionally develop into a more serious life-threatening illness. Severe dengue is rare in travellers.
The mosquitoes that spread dengue are more common in towns, cities and surrounding areas.
Dengue in Vietnam
There is a risk of dengue in this country.
- Travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly during daytime hours.
- A dengue vaccine is licensed in the UK for the prevention of dengue disease in individuals from 4 years of age. The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) and World Health Organization are in the process of reviewing the product information. Recommendations on the use of this vaccine will be published in due course.
Dengue in brief
Seasonal influenza is a viral infection of the respiratory tract and spreads easily from person to person via respiratory droplets when coughing and sneezing. Symptoms appear rapidly and include fever, muscle aches, headache, malaise (feeling unwell), cough, sore throat and a runny nose. In healthy individuals, symptoms improve without treatment within two to seven days. Severe illness is more common in those aged 65 years or over, those under 2 years of age, or those who have underlying medical conditions that increase their risk for complications of influenza.
Seasonal influenza in Vietnam
Seasonal influenza occurs throughout the world. In the northern hemisphere (including the UK), most influenza occurs from as early as October through to March. In the southern hemisphere, influenza mostly occurs between April and September. In the tropics, influenza can occur throughout the year.
All travellers should:
- Avoid close contact with symptomatic individuals
- Avoid crowded conditions where possible
- Wash their hands frequently
- Practise ‘cough hygiene’: sneezing or coughing into a tissue and promptly discarding it safely, and washing their hands
- Avoid travel if unwell with influenza-like symptoms
- A vaccine is available in certain circumstances (see below)*
*In the UK, seasonal influenza vaccine is offered routinely each year to those at higher risk of developing of severe disease following influenza infection, and certain additional groups such as healthcare workers and children as part of the UK national schedule (see information on vaccination ). For those who do not fall into these groups, vaccination may be available privately.
If individuals at higher risk of severe disease following influenza infection are travelling to a country when influenza is likely to be circulating they should ensure they received a flu vaccination in the previous 12 months.
The vaccine used in the UK protects against the strains predicted to occur during the winter months of the northern hemisphere. It is not possible to obtain vaccine for the southern hemisphere in the UK, but the vaccine used during the UK influenza season should still provide important protection against strains likely to occur during the southern hemisphere influenza season, and in the tropics.
Avian influenza
Avian influenza viruses can rarely infect and cause disease in humans. Such cases are usually associated with close exposure to infected bird or animal populations. Where appropriate, information on these will be available in the outbreaks and news sections of the relevant country pages. Seasonal influenza vaccines will not provide protection against avian influenza.

Avian influenza in brief
Outdoor air quality.
Poor air quality is a significant public health problem in many parts of the world. Exposure to high levels of air pollution over short time periods (e.g. minutes/hours/days) and longer time periods (e.g. years) is linked to many different acute and chronic health problems. These effects are mainly on the respiratory (lungs and airways) and cardiovascular (heart function and blood circulation) systems.
Current information on world air quality is available from the world air quality index project .
Travellers with health problems that might make them more vulnerable to the effects of air pollution who are travelling to areas of high pollution should:
- discuss their travel plans with their doctor, and carry adequate supplies of their regular medication.
- take sensible precautions to minimise their exposure to high levels of air pollution.
- check local air quality data and amend their activities accordingly.
- take notice of any health advisories published by the local Ministry of Health and Department for Environment, and follow the guidance provided.
It is unclear if face masks are beneficial at reducing exposure and may make breathing more difficult for those with pre-existing lung conditions. Those who choose to use one should make sure that the mask fits well and know how to wear it properly.
Outdoor air quality in brief
Zika virus (ZIKV) is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes which predominantly feed during daytime hours. A small number of cases of sexual transmission of ZIKV have also been reported. Most people infected with ZIKV have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are usually mild and short-lived. Serious complications and deaths are not common. However, ZIKV is a cause of Congenital Zika Syndrome (microcephaly and other congenital anomalies) and neurological complications such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Zika virus in Vietnam
There is a risk of Zika virus in this country. Details of specific affected areas within this country are not available, but information on current outbreaks where available will be reported on our outbreak surveillance database.
Pregnant women should discuss the suitability of travel and the potential risk that Zika virus may present with their health care provider.
- All travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly during daytime hours.
- There is no vaccination or medication to prevent Zika virus infection.
- Women should avoid becoming pregnant while travelling in this country, and for 2 months (8 weeks) after their last possible Zika virus exposure* (see below if male partner has travelled).
- If a woman develops symptoms compatible with Zika virus infection, it is recommended she avoids becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following recovery.
- Women who visited this country while pregnant, or who become pregnant within 2 months after their last possible Zika virus exposure*, should contact their GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if they have not been unwell.
Please note screening of returning travellers without Zika virus symptoms is not available on the NHS. Couples planning pregnancy in the very near future should consider whether they should avoid travel to a country or area with risk of Zika virus, rather than delay conception for the recommended period (see below) after travel. This particularly includes couples in assisted fertility programmes.
Prevention of sexual transmission
Couples should follow guidance on prevention of sexual transmission of Zika virus and avoid conception as follows:
- If both partners travelled, for 3 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
- Male traveller only, for 3 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
- Female traveller only, for 2 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
See further information for pregnant women, their partners and couples planning pregnancy .
*Last possible Zika virus exposure is defined as the later of either the date of leaving a country or area with risk for Zika virus transmission, or the date on which unprotected sexual contact with a potentially infectious partner took place.
See detailed guidance on factors to consider when assessing the risk of Zika virus.
Zika virus in brief
COVID-19 disease is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV2. The main symptoms of COVID-19 are a new continuous cough, a high temperature, and a loss of, or change in, normal sense of taste or smell. Symptoms range from mild to life-threatening. Older people and those with underlying health problems are more likely to develop severe disease.
COVID-19 is spread through close contact with people who have the virus. It is mainly transmitted from person to person by breathing in droplets produced when someone infected with the virus breathes, speaks, coughs or sneezes. It is also spread by touching the infected droplets on surfaces, then touching the eyes, nose or mouth.
COVID-19 vaccines provide high levels of protection against severe illness, hospitalisation, or dying from the virus. Vaccination against COVID-19 reduces, but does not eliminate the risk of infection, so social distancing and personal and respiratory hygiene remain important interventions, particularly during overseas travel.
Travellers should always check the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice and their country-specific pages for the latest COVID-19 travel advisories which may include information on travel restrictions, quarantine, COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements. This includes considering the recommendations and requirements for any transit countries.
Travellers should be aware that COVID-19 case numbers in individual countries/areas can increase rapidly, and healthcare capacity and country requirements can change at short notice.
COVID-19 in Vietnam
Most countries worldwide present a risk of exposure to COVID-19. The risk of COVID-19, public health policy, and travel advice or restrictions may change quickly, therefore travellers should ensure they have access to up to date information on COVID-19 and be prepared for rapid changes in guidance both before and during travel.
All travellers should check the FCDO travel advice and carefully consider their personal situation and risks of COVID-19 before travel to this country. This is particularly important in those at higher risk from COVID-19 who may wish to seek medical advice before travel.
Individuals entering or returning to the UK may be required to follow additional UK border measures .
If travelling to this country, travellers should:
- Consider the risk at all destinations including any transit countries, and the risk during travel itself.
- Check with the airline/tour operator about preventive measures in place to reduce risk during travel.
- Follow the latest guidance on social distancing and face coverings, including any local requirements and maintain good hand, respiratory, and personal hygiene at all times. This may be particularly important if staying with friends and family.
- Ensure they are up to date with their COVID-19 vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK vaccination programme.
See guidance on factors to consider when assessing the risk of COVID-19 for travellers .
If travellers develop COVID-19 symptoms while abroad, they should:
- Follow local guidelines on self-isolation, testing and avoiding travel.
- Contact their travel insurance provider.
- Seek medical advice if needed.
COVID-19 in brief

Lunar New Year: Travel advice
Celebrating the Lunar New Year abroad? Lunar New Year is a public holiday celebrated across several days in many countries worldwide

Changes to the Country Information pages: Zika
UK Health Security Agency and NaTHNaC have reviewed and updated country-specific Zika information and prevention advice

Malaria: a reminder for travellers over the winter holiday season
Advice for travellers and health professionals about malaria
Using information collated from a variety of sources, we regularly review and update information on overseas disease outbreaks and other health issues that may affect the UK traveller.
Please note that not all cases of disease or outbreaks are reported ; some diseases may only be reported if they occur outside of the usual recognised risk area or season, or they have been reported in greater than usual numbers.
Further information on the Outbreak Surveillance section.
Influenza A(H9N2) in Vietnam
As of 7 April 2024, the Vietnam Department of Information and Communications reported a confirmed human case of avian influenza A(H9N2) infection. This is the first confirmed human case of avian influenza A(H9N2) reported in Vietnam. To date, no further cases have been detected among close contacts.

Foreign travel advice

FEEDBACK SURVEY
Personal information:, successfully submitted .
UK Health Security Agency
Hospital for Tropical Diseases
Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine
London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust

Embassy of Vietnam in UK
Vietnam visa in United Kingdom
Complete Guide for UK Tourists and Business Travelers on Obtaining a Vietnam Visa
Table of Contents
For those from the UK intending to visit Vietnam, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the visa prerequisites and how to apply. This comprehensive guide offers all the essential details you need, guaranteeing a smooth visa process and enabling you to relish your Vietnam trip without any difficulties.

Vietnam waives visa requirement for UK citizens
UK citizens can now enjoy up to 15 days of visa-free travel to Vietnam starting from March 15, 2022, as part of the country’s visa exemption program that covers 13 nations, including the UK. But if your visit extends beyond 15 days, you need to secure a tourist or business visa.
Visa-Free Entry for UK Citizens on Short-Term Visits to Vietnam
UK nationals can enter Vietnam without a visa if they plan to stay for up to 15 days, provided that their passport is valid for at least six months from the arrival date. It is important to make sure that the passport is in good condition as any damage may lead to entry denial.

How to Get a Visa on Arrival for UK Citizens Traveling to Vietnam Beyond 15 Days
UK citizens can obtain a visa on arrival for trips exceeding 15 days in Vietnam. The application requires filling out an online form, and the visa will be stamped upon arrival at one of Vietnam’s designated visa on arrival airports.

Limits on Travel to Vietnam for Holders of British National Overseas Passports
It’s important to note that if you have a British National Overseas passport, you won’t be eligible for the visa exemption program. This means that regardless of how long you’ll be staying in Vietnam, you’ll need to apply for a visa.
Visa-Free Multiple Entries
UK citizens can now enter Vietnam multiple times without a visa and stay for up to 15 days each time, with no need for a 30-day interval between visits as before. The only requirement is that their passport remains valid.

How to Get Detailed Information about Visa Fees and Application Instructions
To acquire in-depth information on visa fees and application instructions, visit the embassy or consulate websites or approach trustworthy visa service providers. Accurate and current information is crucial for an effortless visa application process.

Visa Requirements and Application Process for UK Citizens Visiting Vietnam for Tourism or Business
If you’re a UK citizen intending to travel to Vietnam for tourism or business, here’s what you need to know about the visa requirements and application process for each category.
Visa-Free Travel to Vietnam for UK Tourists
In accordance with the travel guidelines provided by the UK government, individuals holding British citizenship can enter Vietnam without obtaining a visa for a maximum duration of 45 days. This visa exemption applies to purposes such as tourism, transit, and business activities that do not involve payment or voluntary work. As a result, UK citizens can conveniently experience Vietnam’s magnificent scenery, cultural heritage, and lively traditions without having to go through the visa application process.
UK Citizens Require Business Visa for Vietnam

To conduct business in Vietnam, a business visa is mandatory for UK citizens. This visa enables you to participate in multiple corporate events like meetings, conferences, trade shows, and develop business relationships.
Options for Acquiring a Vietnam Visa
UK citizens have two primary options for obtaining a visa to travel to Vietnam. These options include applying online for a visa on arrival or visiting the Vietnam embassy in person. Read on to find out more about each option.
Visa on Arrival
The visa on arrival is an ideal option for UK citizens traveling to Vietnam because it is simple and convenient. To apply, all you need to do is complete an online application form and get your visa stamped when you arrive at one of Vietnam’s visa on arrival airports.

To apply for a visa on arrival, you’ll need to provide basic personal information such as your name, passport details, and arrival date. It’s important that your British passport is valid for at least six months from your arrival date and has at least two blank pages.
Vietnam Embassy
Alternatively, you can choose to visit the Vietnam embassy to apply for your visa. The embassy will provide detailed instructions on the required documents and the application process. It is essential to accurately submit all necessary documents and follow the provided instructions to ensure a successful visa application.
Visa Costs and Timelines
The cost of tourist visas depend on your preferred processing time and arrival checkpoint. It’s crucial to consider the processing time while planning your Vietnam trip. Detailed information on fees and processing times can be obtained from the embassy or consulate.
For business visas, the fees only cover assistance for visa approval letter and not stamping fees at the embassy or airport. It’s important to budget wisely and ensure enough funds to cover all necessary fees and expenses.

Updates in Visa Regulations
It’s important to bear in mind that visa regulations and processes can vary over time. It’s essential to remain knowledgeable and stay current with the most recent information from trustworthy sources. This will prevent any unforeseen hurdles or difficulties during your visa application procedure.
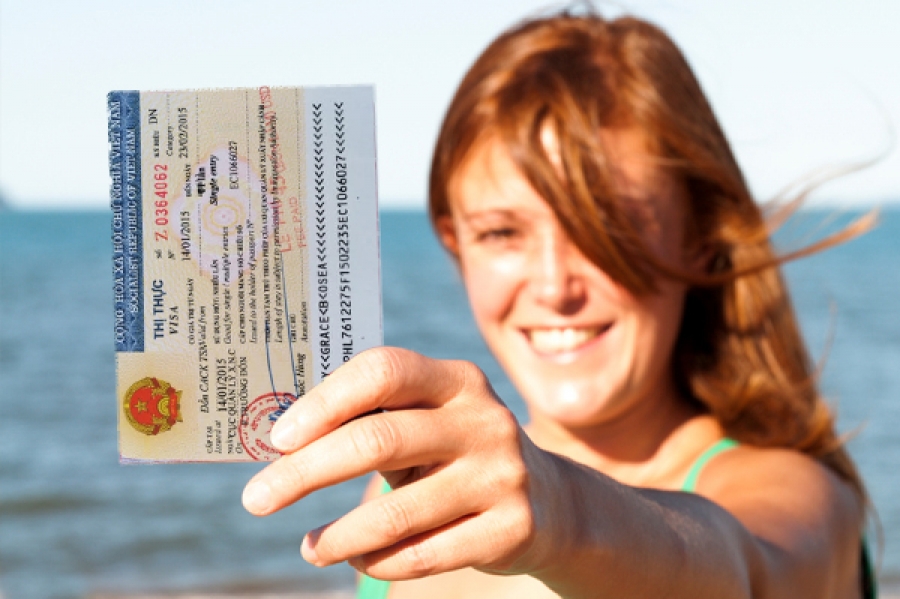

Having a Great Time in Vietnam
Now that the visa process is sorted, you can fully enjoy your trip to Vietnam without any worries. Experience the captivating culture and breathtaking scenery of this amazing country, from the lively streets of Hanoi to the tranquil vistas of Ha Long Bay.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: is a visa required for uk citizens to enter vietnam.
A: No, UK citizens can enter Vietnam without a visa for up to 15 days. However, if their stay exceeds 15 days, they must apply for a tourist or business visa.
Q: What is the maximum duration of stay in Vietnam for UK citizens without a visa?
A: UK citizens can stay in Vietnam for up to 15 days without a visa.
Q: Can UK citizens apply for a visa on arrival in Vietnam?
A: Yes, UK citizens can apply for a visa on arrival for stays longer than 15 days.
Q: Do UK citizens need a business visa for conducting business in Vietnam?
A: Yes, UK citizens require a business visa for conducting business in Vietnam.
Q: How can UK citizens obtain a visa for Vietnam?
A: UK citizens can apply for a visa on arrival or visit the Vietnam embassy to obtain a visa.
Q: Is it possible for UK citizens to enter Vietnam multiple times without a visa?
A: Yes, UK citizens can enter Vietnam multiple times without a visa, as long as each stay does not exceed 15 days and their passport remains valid.
If you’re a UK citizen planning a trip to Vietnam, it’s important to understand the visa requirements and application process. This guide provides all the essential information needed to secure the right visa for a hassle-free journey to Vietnam. Stay informed and keep up-to-date with any changes in visa regulations to avoid any unexpected issues. It’s now time to embark on an exciting Vietnamese adventure and make lasting memories in this enchanting country. Have a safe trip!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Live fully in Vietnam
Vietnam opens its door widely to welcome visitors all around the world! Starting from 15th August 2023, Vietnam extends e-visa validity to 90 days and unilateral visa exemption will be valid in 45 days! We are more than happy to welcome you all here and admire our stunning landscapes, free your soul on white sandy beaches, experience our unique and beautiful culture and meet the people in the most friendly country. Particularly, to indulge in our scrumptious cuisine at Michelin rated restaurants or to join us in outstanding mega culture, music, sports and tourism events! Let’s live to the fullest in Vietnam!

City Breaks
Can Tho: A glimpse of river and garden

Virtual travel to Trang An Landscape Complex

Go green in Co To

Local unpacked: One of a kind cuisine of Ha Giang karst plateau

Special daily tours at the Grand Prix of Binh Dinh 2024

10 Tourist spots not to be missed in Ho Chi Minh City

Ru Cha Mangrove Forest: A sleeping beauty of Hue

Lost in green wonderland in Tra Su Cajuput Forest

The infinity waters of Quang Lang Beach

Halong Bay - Cat Ba inter-provincial World Heritage Site: Trending destination in Vietnam

Nha Trang Best Beaches for a Sustainable Vacation

Explore the food of Hoi An

Comfort Meets Culture at Hanoi's Luxury Hotels

Outdoor & Recreational
Binh Dinh - a hot spot for festival goers in 2024

Enjoy the "Fast & Furious" F1H2O World Championship in Binh Dinh
Check out upcoming events in Vietnam
must-see sites
Take a 360-degree tour of some of the country's most compelling natural wonders and cultural attractions right here.

travel tips
Prepare for your trip with these practical articles

Vietnam through the lens of international news
Find out the reasons why Vietnam is worth to visit
TasteAtlas food rankings are based on the ratings of the TasteAtlas audience, with a series of mechanisms that recognize real users and that ignore bot, nationalist or local patriotic ratings, and give additional value to the ratings of users that the system recognizes as knowledgeable….
- TasteAtlas
Full article

Booking.com
Spring has finally arrived, bringing with it the perfect opportunity to venture out and explore the world.
- Booking.com

Travel Weekly
Visiting the South-East Asian country reminds Thompson Travel’s Sharon Thompson of the wonders of travel…
- Travel Weekly

Conde Nast Traveler
To get you started on your next fairy tale adventure, we’ve rounded up 50 of the most beautiful small towns in the world.
- Conde Nast Traveler
share your story
Tag your best #LiveFullyinVietnam moments on Instagram
SHARE YOUR STORY

Create an account
Already have an account? Click here to sign in
By clicking submit, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Sign in with your social accounts
Sign in with your email
Forgot password? Click here to get it back
Don't have an account? Sign up here
Forgot Password
The entered email has subscribed for Vietnam Tourism monthly newsletter

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Vietnam Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
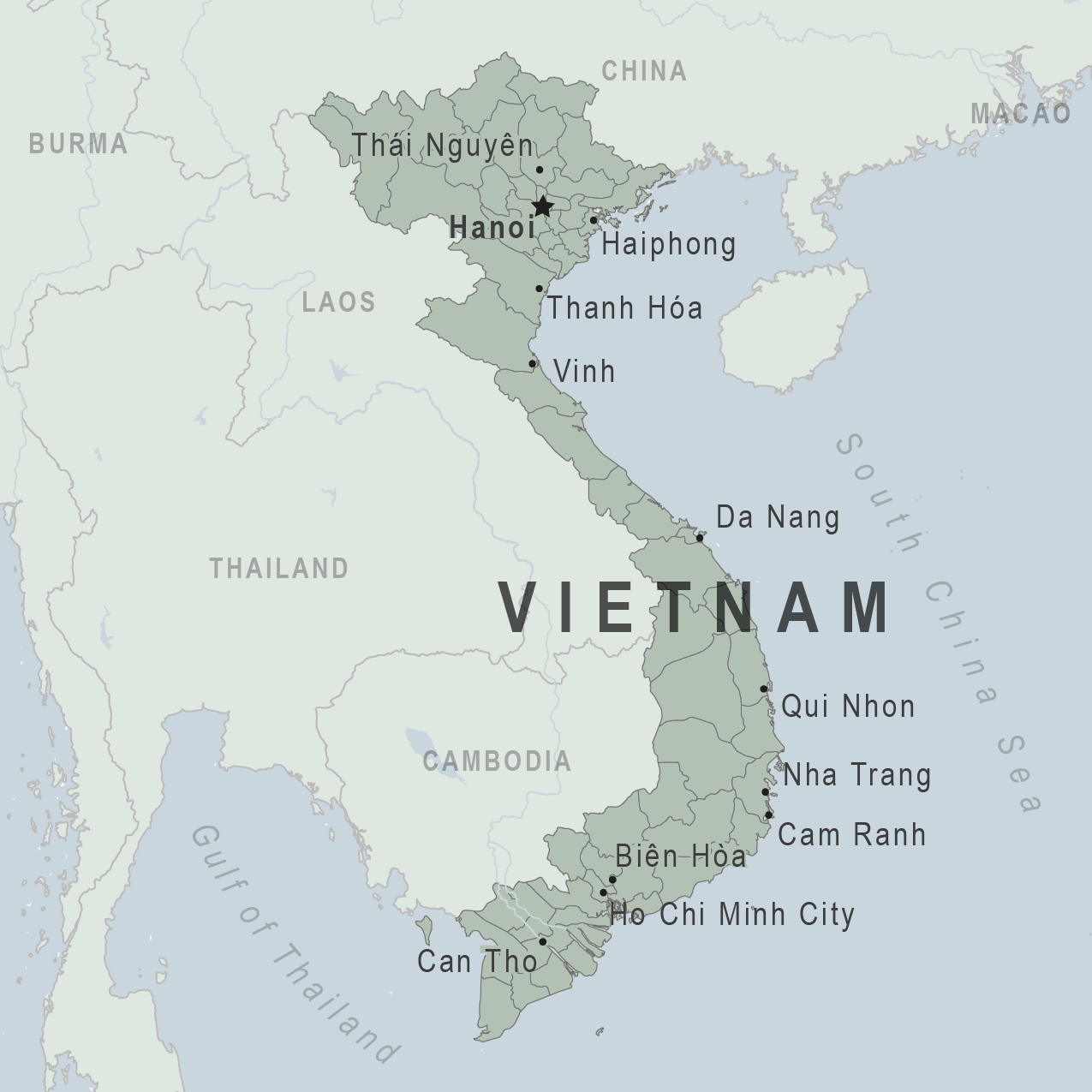
There are no notices currently in effect for Vietnam.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Vietnam.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Vietnam.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Vietnam take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Vietnam.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Vietnam. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Vietnam, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Vietnam.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Vietnam, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Vietnam. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Vietnam—such as dengue, Zika, and filariasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Vietnam include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Vietnam. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Vietnam’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Vietnam. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Vietnam may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Vietnam, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Vietnam, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Vietnam .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Vietnam, dial 115 for an ambulance, 114 for the fire department, and 113 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Vietnam before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Vietnam from the US Department of State
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Vietnam for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Travel vaccination advice
If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world.
Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever , typhoid and hepatitis A .
In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule protects you against a number of diseases, but does not cover all of the infectious diseases found overseas.
When should I start thinking about the vaccines I need?
If possible, see the GP or a private travel clinic at least 6 to 8 weeks before you're due to travel.
Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity.
And some vaccines involve a number of doses spread over several weeks or months.
You may be more at risk of some diseases, for example, if you're:
- travelling in rural areas
- backpacking
- staying in hostels or camping
- on a long trip rather than a package holiday
If you have a pre-existing health problem, this may make you more at risk of infection or complications from a travel-related illness.
Which travel vaccines do I need?
You can find out which vaccinations are necessary or recommended for the areas you'll be visiting on these websites:
- Travel Health Pro
- NHS Fit for Travel
Some countries require proof of vaccination (for example, for polio or yellow fever vaccination), which must be documented on an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP) before you enter or when you leave a country.
Saudi Arabia requires proof of vaccination against certain types of meningitis for visitors arriving for the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Even if an ICVP is not required, it's still a good idea to take a record of the vaccinations you have had with you.
Find out more about the vaccines available for travellers abroad
Where do I get my travel vaccines?
First, phone or visit the GP practice or practice nurse to find out whether your existing UK vaccinations are up-to-date.
If you have any records of your vaccinations, let the GP know what you have had previously.
The GP or practice nurse may be able to give you general advice about travel vaccinations and travel health, such as protecting yourself from malaria.
They can give you any missing doses of your UK vaccines if you need them.
Not all travel vaccinations are available free on the NHS, even if they're recommended for travel to a certain area.
If the GP practice can give you the travel vaccines you need but they are not available on the NHS, ask for:
- written information on what vaccines are needed
- the cost of each dose or course
- any other charges you may have to pay, such as for some certificates of vaccination
You can also get travel vaccines from:
- private travel vaccination clinics
- pharmacies offering travel healthcare services
Which travel vaccines are free?
The following travel vaccines are available free on the NHS from your GP surgery:
- polio (given as a combined diphtheria/tetanus/polio jab )
- hepatitis A
These vaccines are free because they protect against diseases thought to represent the greatest risk to public health if they were brought into the country.
Which travel vaccines will I have to pay for?
You'll have to pay for travel vaccinations against:
- hepatitis B
- Japanese encephalitis
- tick-borne encephalitis
- tuberculosis (TB)
- yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccines are only available from designated centres .
The cost of travel vaccines that are not available on the NHS will vary, depending on the vaccine and number of doses you need.
It's worth considering this when budgeting for your trip.
Other things to consider
There are other things to consider when planning your travel vaccinations, including:
- your age and health – you may be more vulnerable to infection than others; some vaccines cannot be given to people with certain medical conditions
- working as an aid worker – you may come into contact with more diseases in a refugee camp or helping after a natural disaster
- working in a medical setting – a doctor, nurse or another healthcare worker may require additional vaccinations
- contact with animals – you may be more at risk of getting diseases spread by animals, such as rabies
If you're only travelling to countries in northern and central Europe, North America or Australia, you're unlikely to need any vaccinations.
But it's important to check that you're up-to-date with routine vaccinations available on the NHS.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Speak to a GP before having any vaccinations if:
- you're pregnant
- you think you might be pregnant
- you're breastfeeding
In many cases, it's unlikely a vaccine given while you're pregnant or breastfeeding will cause problems for the baby.
But the GP will be able to give you further advice about this.
People with immune deficiencies
For some people travelling overseas, vaccination against certain diseases may not be advised.
This may be the case if:
- you have a condition that affects your body's immune system, such as HIV or AIDS
- you're receiving treatment that affects your immune system, such as chemotherapy
- you have recently had a bone marrow or organ transplant
A GP can give you further advice about this.
Non-travel vaccines
As well as getting any travel vaccinations you need, it's also a good opportunity to make sure your other vaccinations are up-to-date and have booster vaccines if necessary.
Although many routine NHS vaccinations are given during childhood, you can have some of them (such as the MMR vaccine ) as an adult if you missed getting vaccinated as a child.
There are also some extra NHS vaccinations for people at higher risk of certain illnesses, such as the flu vaccine , the hepatitis B vaccine and the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) .
Your GP can advise you about any NHS vaccinations you might need.
Find out about NHS vaccinations and when to have them
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2023 Next review due: 16 March 2026
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
beta This is a test version of the layout of this page. Take the survey to help us improve it
- Help and services around the world
UK help and services in Vietnam
Services if you're visiting, studying, working or living in Vietnam. Includes information about trading with and doing business in the UK and Vietnam.
Subscriptions
- Get emails for this topic UK help and services in Vietnam
Emergency help for British nationals
British consulate general ho chi minh city.
The British Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City represents the UK government in Vietnam.
British Embassy Hanoi
The British Embassy in Hanoi maintains and develops relations between the UK and Vietnam.
Get help if you're a victim of crime abroad
Contact the nearest British embassy, high commission, consulate or the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office in London to get help if you're the victim of crime abroad
If you’re affected by a crisis abroad
Advice to British people affected by crises abroad such as large-scale terrorist attacks, natural disasters and political unrest, and how the FCDO can help.
Support for British nationals abroad
This page lists guidance on how you can help yourself stay safe abroad, and the help the Foreign Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) can provide.
Vietnam – Prisoner Pack
Explanation of the legal and prison system to British Nationals
Vietnam: information for victims of rape and sexual assault
Information for British nationals who are victims of rape and sexual assault in Vietnam.
Passports and emergency travel documents
Apply for or renew a british passport if you're visiting the uk.
You can apply for or renew a British passport while you're visiting the UK - as long as you expect to be in the UK for long enough
Cancel a lost or stolen passport
What you need to do if your passport has been lost or stolen and you need to travel urgently.
Overseas British passport applications
Renew, replace or apply for an adult or child British passport if you’re living abroad or working overseas - forms, prices, how long it takes
Travel urgently from abroad without your UK passport
Apply for an emergency travel document if you're outside the UK and have not got a valid British passport - apply online, how to apply, fee, timings
Travelling to Vietnam
Getting married or registering a civil partnership abroad.
Requirements, paperwork and processes for weddings and civil partnerships overseas - registration, restrictions, fees
Reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad
How to minimise your risk, and what to do if there's a terrorist attack.
Vietnam travel advice
FCDO travel advice for Vietnam. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Coming to the UK
Check if you need a uk visa.
You may need a visa to come to the UK to visit, study or work.
Contact UK Visas and Immigration for help
How to contact UK Visas and Immigration (UKVI) for help with your application or immigration account, from inside and outside the UK.
Get your visa, immigration or citizenship documents back
Get your documents returned if you've made a UK visa, immigration or citizenship application but need them back urgently
Vietnam: tuberculosis test clinics for a UK visa
Where to get tested for tuberculosis (TB) in Vietnam for your UK visa application.
Living in Vietnam
Get your document legalised.
Use the online service to get a UK document legalised.
This guide sets out essential information for British nationals residing in Vietnam.
Professional services if you are abroad
Find English-speaking lawyers, doctors and medical providers, interpreters and translators, and funeral directors overseas.
UK benefits if you’re going or living abroad
Find out what benefits you might be able to receive while you’re abroad and how to export them from the UK or claim them while abroad
Vietnam – DHL Service Point
DHL Service Point
Vietnam: translators and interpreters
List of translators and interpreters for British nationals in Vietnam.
Voting if you move or live abroad
How to vote if you move or live abroad, including eligibility and registration
Tax, benefits, pensions and working abroad
Claiming benefits if you live, move or travel abroad.
Benefits you can claim if you go abroad and countries with social security arrangements with the UK
Moving or retiring abroad
What you need to know if you move or retire abroad - tax, pensions, voting and contacting your local council
National Insurance if you work abroad
Find out if you need to pay National Insurance in the UK or in the country you are visiting when you work abroad.
State Pension if you retire abroad
How to claim State Pension if you're overseas - payment, tax, change of circumstances - contact the International Pension Centre
Tax credits if you leave or move to the UK
Tax credits if you live abroad, go travelling, are a cross-border worker or subject to immigration control
Tax on foreign income
Find out whether you need to pay UK tax on foreign income - residence and ‘non-dom’ status, tax returns, claiming relief if you’re taxed twice (including certificates of residence)
Tax on your UK income if you live abroad
Find out whether you need to pay tax on your UK income while you're living abroad - non-resident landlord scheme, tax returns, claiming relief if you’re taxed twice, personal allowance of tax-free income, form R43
Birth, death and marriage abroad
Adoption in Vietnam for British nationals
Register a birth abroad
Parents must register the birth in the country where the child was born - find out if you can also register the birth in the UK.
Surrogacy overseas
Information for British nationals who are considering entering into surrogacy arrangements in foreign countries.
What to do after a British person dies in Vietnam
This guide gives advice about the death of a British person in Vietnam, including information on burial, cremation and repatriation.
What to do when someone dies: step by step
Check what to do after a death - how to register the death, notify government departments and deal with the estate.
News and events
Vietnam and the uk.
Updates, news and events from the UK government in Vietnam
Trade and invest
Department for business and trade vietnam.
DBT provides trade and investment services and practical support. We help UK companies succeed in Vietnam, and Vietnamese companies set up and invest in the UK
Overseas business risk for Vietnam
Information on how UK companies can control risks when doing business in Vietnam.
Set up a business
What you need to do to start a business: choose a legal structure, see if you need licences and insurance, learn about reliefs and benefits
British embassy or high commission
Vietnam: consular fees.
List of fees for consular information in Vietnam.
Vietnam: Notarial and documentary services
Documents, certificates, letters, and notes available at the British Embassy Hanoi and the British Consulate-General Ho Chi Minh City.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Basic Information
- Foreign Policy
- Legislation System
- Message from Ambassador
- Ambassador’s Biography
- Embassy's Staffs
- Working Time
- Notice from the Embassy
- Consular Procedure
- Recommendation
- Visa Exemption
- Consular Fees and Charges
- Embassy's News
- Senior Leaders Activity News
- Minister, Deputy Prime Minister Activities News
- Ministry Leaders Activity News
- Weekly News
- The milestone in Bilateral relations
- The agreements signed
- Chính sách của Việt Nam
- Quy định của nước sở tại đối với người nước ngoài
- Tạp chí Quê hương

The upcoming official visit to the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland by Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs Pham Binh Minh will create new momentum for the Vietnam-UK relations, now at their best development period, Vietnamese Ambassador to the UK Tran Ngoc An has affirmed.

In his interview granted to Vietnam News Agency on the threshold of the visit, Ambassador An stressed that Deputy PM Minh’s visit is the most important event among those held between the two countries to celebrate 45th anniversary of the diplomatic relations. During his stay, Deputy PM Minh will have meetings with representatives of the UK Government, Parliament and the royal family to bolster the strategic partnership between the two countries, he said, adding that this is an important period for both sides as the UK is leaving the European Union (EU) and advocating to broaden relations with countries outside Europe, while Vietnam is integrating deeply into the global economy with its increasing position in the international arena. Deputy PM Minh will chair a celebration to mark the 45 years of bilateral diplomatic establishment, which includes a stellar cultural programme “Vietnam Culture Day in the UK”, an exhibition displaying Vietnamese traditional costumes, and a photo exhibition highlighting Vietnam as an attraction of the world. Also, Minh will chair and attend a line-up of economic events to enhance two-way trade and investment, the diplomat added. Ambassador An said that since the two countries set up diplomatic relations in 1973, they have enjoyed positive achievements in their cooperative ties. In the field of politics, they have maintained high-level meetings and exchanges. The Vietnamese Party General Secretary, President, Prime Minister and Chairwoman of the National Assembly have already visited the UK. Meanwhile, the UK Prime Minister, parliamentary leaders, and members of the Royal family have visited the Southeast Asian country several times. In 2010, the two countries officially established the bilateral strategic partnership, paving the way for the formation of various cooperative mechanisms such as strategic dialogue, Joint Committee on Economic Cooperation, and working group on defence ties. They have served as a firm foundation to further the bilateral ties. On investment, the UK is now among the top 15 foreign investors in Vietnam, registering 4 billion USD in the country. Despite the complicated sitution in the world’s economy, two-way trade increased sharply to hit 6.1 billion USD in 2017, of which Vietnam exported 5.4 billion USD worth of products, up 10 percent from the previous year and tripling the figure recorded in 2010. In the field of education, there are some 12,000 Vietnamese students studying in the European country. Receiving training in the world’s leading education environment, they will make positive contributions to the socio-economic development in Vietnam when returning home. Regarding defence cooperation, the military attaché’s offices were set up in both nations. In addition, delegation exchange and experience sharing, especially in peacekeeping activities, have been maintained. Furthermore, people-to-people exchanges have been enhanced in recent years. UK citizens now have a deeper understanding of the Vietnamese culture thanks to an array of activities to introduce and popularise Vietnamese culture and tourism. Vietnamese traditional cuisines like “pho”, “bun cha”, and “nem cuon” have been favoured in the UK and Vietnamese restaurants are now mushrooming in London and other big cities. Ambassador An said that the two countries still have huge cooperative potential in the coming time. They see each other important to carry out their foreign policies. During Brexit, the UK prioritises relations with Asia-Pacfic in its “Global Britain” strategy. In the writing on the “All of Asia” policy, Minister of State for the Foreign and Commonwealth Office Mark Field affirmed that the UK is seeking ways to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and looking for opportunities to enhance connections with the ASEAN. Meanwhile, Vietnam has played an increasingly important role in cooperative frameworks and multilateral forums, including the CPTPP and the ASEAN. As the two countries have complementary economies, there is large room for them to foster trade and investment. Although Vietnam is the 25th largest partner of the UK, Vietnamese shipments to the country make up only 1 percent of its imports. In addition, the UK’s direct investment in Vietnam is still modest as it invests some 300 billion USD in foreign countries and becomes the 5th largest foreign investor in the world. The diplomat also relished his prospects for cooperation in other sectors like science-technology, defence and education. He said that increasing mutual understanding will open up new opportunities for collaborative projects in the time to come.

Other News
- Vietnamese businesses in UK boost cooperation with companies at home(Wednesday, February 1, 2023)
- Ambassador Nguyen Hoang Long called on FCDO Minister of State Nigel Adams(Monday, July 5, 2021)
- Legal documents for UKVFTA implementation to be released(Sunday, June 13, 2021)
- Vietnam proposes UK transfer COVID-19 vaccine production technology(Sunday, June 13, 2021)
- Long-term benefits from Vietnam-UK Free Trade Agreement(Sunday, June 13, 2021)
- Vietnam, UK issue joint declaration on strategic partnership(Monday, November 30, 2020)
- Vietnam, UK hold third defense policy dialogue(Monday, November 30, 2020)
- Top leader demans thorough preparations to ensure success of 13th National Party Congress(Monday, November 2, 2020)
- UK businesses seek cooperation opportunities in Viet Nam(Thursday, August 27, 2020)
- Vice Minister of Foreign Affairs To Anh Dung held virtual talks with the UK's Minister of State Nigel Adams(Monday, August 10, 2020) 1 2 3 4 Next »
- Copyright by Vietnam Ministry of Foreign Affairs Contact | Site map | Privacy | Q&A Embassy of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in England 12-14 Victoria Road, London W8 5RD Tel : +44-2079371912/2075652214/+44-2079375628 Fax : +44-207565385 Email: [email protected] Website: http://www.vietnamembassy-england.org/en/

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FCDO travel advice for Vietnam. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
To enter Vietnam, your passport must have: an 'expiry date' at least 6 months after the date you arrive. at least 2 blank pages. no damage - British nationals have been denied entry and exit ...
Vietnam travel advice. FCDO travel advice for Vietnam. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. Includes travel advice and how to get married abroad.
Vietnam's new visa policy effective from 15th August 2023 extends stay duration for 13 countries enjoying unilateral visa exemption from 15 days to 45 days, regardless of passport type and entry purpose. The 13 coutries include: Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the UK, Russia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland and Belarus.
Prior to travel, you should: Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return. Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination. Check if you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19.
Bars in Vietnam are . Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Vietnam such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Step 2: Click this link or access https://immigration.gov.vn/ and go to 'E-visa Issuance' then click on the link for 'Outside Vietnam foreigners'. Step 3: Upload your .jpg images (passport data page and passport photo) and fill out the required fields on the form completely. Submit your form. Step 4: Pay the e-Visa fee of 25 USD.
Currently, holidays to Vietnam are all but impossible from the UK, with the country only open to tourists booked onto a pilot programme of government-approved group tours. Visitors must also ...
Vietnam also allows passengers to apply for an electronic visa, or for short, an e-visa. Simply register for it online through the Vietnam Immigration website at xuatnhapcanh.gov.vn and receive an electronic visa document that permits entry into Vietnam. Generally, an e-visa for Vietnam is valid for a single entry and allows a stay of up to 30 ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
The UK government has confirmed it is monitoring a suspected Covid variant detected in Vietnam ahead of a decision on travel restrictions due later this week that could result in more destinations ...
Travel Insurance: If you decide to travel to Vietnam, conduct research on your destinations and obtain appropriate travel insurance. Your insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities, and expenses in case of an emergency. FCDO travel advice for Vietnam. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal ...
Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings.
Embassy of S.R. Vietnam in the UK 12-14 Victoria Road London W8 5RD Consular/Visa Section Opening hours: 09:30 - 12:30 (morning only), Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday (Appointment required) Email enquires: [email protected] (Recommended) Tel: 020 7937 1912 Fax: 020 7937 6108
Travellers should ideally arrange an appointment with their health professional at least four to six weeks before travel. However, even if time is short, an appointment is still worthwhile. This appointment provides an opportunity to assess health risks taking into account a number of factors including destination, medical history, and planned ...
Visa-Free Travel to Vietnam for UK Tourists. In accordance with the travel guidelines provided by the UK government, individuals holding British citizenship can enter Vietnam without obtaining a visa for a maximum duration of 45 days. This visa exemption applies to purposes such as tourism, transit, and business activities that do not involve ...
Live fully in Vietnam. Vietnam opens its door widely to welcome visitors all around the world! Starting from 15th August 2023, Vietnam extends e-visa validity to 90 days and unilateral visa exemption will be valid in 45 days! We are more than happy to welcome you all here and admire our stunning landscapes, free your soul on white sandy beaches ...
To call for emergency services while in Vietnam, dial 115 for an ambulance, 114 for the fire department, and 113 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip. Learn as much as you can about Vietnam before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Vietnam from the US Department of ...
Travel vaccination advice. If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever, typhoid and hepatitis A. In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule ...
Services if you're visiting, studying, working or living in Vietnam. Includes information about trading with and doing business in the UK and Vietnam. Emergency help for British nationals Get help ...
You don't need a visa to visit Vietnam, if you're staying for 45 days or less, but you must have a valid passport. For longer holidays, you'll need to get a visa before you travel. You can get this from the Vietnamese Embassy in London or apply for an e-visa online through the online portal. Alternatively, you can apply for a Visa ...
The upcoming official visit to the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland by Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs Pham Binh Minh will create new momentum for the Vietnam-UK relations, now at their best development period, Vietnamese Ambassador to the UK Tran Ngoc An has affirmed. In his interview granted to Vietnam News Agency on ...