Product Design Bundle and save
User Research New
Content Design
UX Design Fundamentals
Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
- UX training for teams
- Hire our alumni
- Student Stories
- State of UX Hiring Report 2024
- Our mission
- Advisory Council
Education for every phase of your UX career
Professional Diploma
Learn the full user experience (UX) process from research to interaction design to prototyping.
Combine the UX Diploma with the UI Certificate to pursue a career as a product designer.
Professional Certificates
Learn how to plan, execute, analyse and communicate user research effectively.
Master content design and UX writing principles, from tone and style to writing for interfaces.
Understand the fundamentals of UI elements and design systems, as well as the role of UI in UX.
Short Courses
Gain a solid foundation in the philosophy, principles and methods of user experience design.
Learn the essentials of software development so you can work more effectively with developers.
Give your team the skills, knowledge and mindset to create great digital products.
Join our hiring programme and access our list of certified professionals.
Learn about our mission to set the global standard in UX education.
Meet our leadership team with UX and education expertise.
Members of the council connect us to the wider UX industry.
Our team are available to answer any of your questions.
Fresh insights from experts, alumni and the wider design community.
Success stories from our course alumni building thriving careers.
Discover a wealth of UX expertise on our YouTube channel.
Latest industry insights. A practical guide to landing a job in UX.

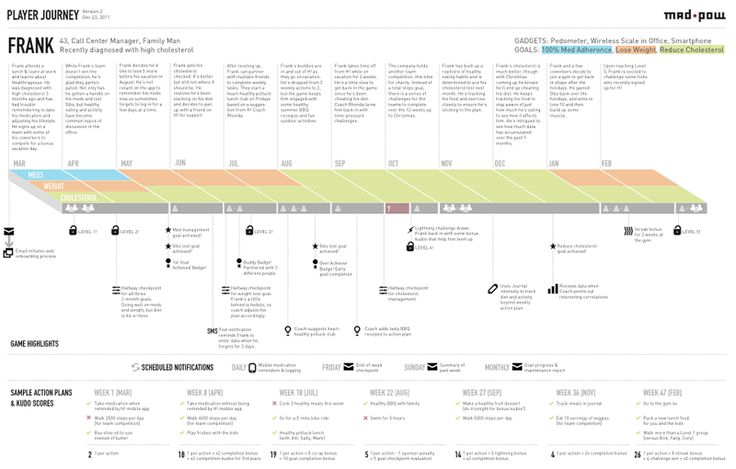
How to design a customer journey map (A step-by-step guide)
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how a user interacts with your product. Learn how to create a customer journey map in this practical step-by-step guide.
The State of UX Hiring Report 2024
Learn how to start your UX career with hard facts and practical advice from those who have gone before you. In this report, we look at UX hiring trends in 2024 to help you break into the industry.
Successful UX design is rooted in empathy. The best designers are able to step into their users’ shoes and imagine what they think, feel, and experience as they interact with a product or service.
One of the most effective ways to foster user empathy and consider different perspectives is to create customer journey maps—otherwise known as customer journey maps.
If you’re new to journey mapping, look no further than this guide. We’ll explain:
- What is a customer journey map?
Why create customer journey maps?
When to create customer journey maps, what are the elements of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map (step-by-step).
If you want to skip straight to the how-to guide, just use the clickable menu to jump ahead. Otherwise, let’s begin with a definition.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UX]
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (otherwise known as a user journey map) is a visual representation of how a user or customer interacts with your product. It maps out the steps they go through to complete a specific task or to achieve a particular goal—for example, purchasing a product from an e-commerce website or creating a profile on a dating app.
Where does their journey begin? What’s their first point of interaction with the product? What actions and steps do they take to reach their end goal? How do they feel at each stage?
You can answer all of those questions with a user journey map.
A user journey map template from Miro .
Creating customer journey maps helps to:
- Centre the end user and foster empathy. Creating a user/customer journey map requires you to step into the end user’s shoes and experience the product from their perspective. This reminds you to consider the user at all times and fosters empathy.
- Expose pain-points in the user experience. By viewing the product from the user’s perspective, you quickly become aware of pain-points or stumbling blocks within the user experience. Based on this insight, you can improve the product accordingly.
- Uncover design opportunities. User journey maps don’t just highlight pain-points; they can also inspire new ideas and opportunities. As you walk in your end user’s shoes, you might think “Ah! An [X] feature would be great here!”
- Get all key stakeholders aligned. User journey maps are both visual and concise, making them an effective communication tool. Anybody can look at a user journey map and instantly understand how the user interacts with the product. This helps to create a shared understanding of the user experience, building alignment among multiple stakeholders.
Ultimately, user journey maps are a great way to focus on the end user and understand how they experience your product. This helps you to create better user experiences that meet your users’ needs.
User journey maps can be useful at different stages of the product design process.
Perhaps you’ve got a fully-fledged product that you want to review and optimise, or completely redesign. You can create journey maps to visualise how your users currently interact with the product, helping you to identify pain-points and inform the next iteration of the product.
You can also create user journey maps at the ideation stage. Before developing new ideas, you might want to visualise them in action, mapping out potential user journeys to test their validity.
And, once you’ve created user journey maps, you can use them to guide you in the creation of wireframes and prototypes . Based on the steps mapped out in the user journey, you can see what touchpoints need to be included in the product and where.
No two user journey maps are the same—you can adapt the structure and content of your maps to suit your needs. But, as a rule, user journey maps should include the following:
- A user persona. Each user journey map represents the perspective of just one user persona. Ideally, you’ll base your journey maps on UX personas that have been created using real user research data.
- A specific scenario. This describes the goal or task the journey map is conveying—in other words, the scenario in which the user finds themselves. For example, finding a language exchange partner on an app or returning a pair of shoes to an e-commerce company.
- User expectations. The goal of a user journey map is to see things from your end user’s perspective, so it’s useful to define what their expectations are as they complete the task you’re depicting.
- High-level stages or phases. You’ll divide the user journey into all the broad, high-level stages a user goes through. Imagine you’re creating a user journey map for the task of booking a hotel via your website. The stages in the user’s journey might be: Discover (the user discovers your website), Research (the user browses different hotel options), Compare (the user weighs up different options), Purchase (the user books a hotel).
- Touchpoints. Within each high-level phase, you’ll note down all the touchpoints the user comes across and interacts with. For example: the website homepage, a customer service agent, the checkout page.
- Actions. For each stage, you’ll also map out the individual actions the user takes. This includes things like applying filters, filling out user details, and submitting payment information.
- Thoughts. What is the user thinking at each stage? What questions do they have? For example: “I wonder if I can get a student discount” or “Why can’t I filter by location?”
- Emotions. How does the user feel at each stage? What emotions do they go through? This includes things like frustration, confusion, uncertainty, excitement, and joy.
- Pain-points. A brief note on any hurdles and points of friction the user encounters at each stage.
- Opportunities. Based on everything you’ve captured in your user journey map so far, what opportunities for improvement have you uncovered? How can you act upon your insights and who is responsible for leading those changes? The “opportunities” section turns your user journey map into something actionable.
Here’s how to create a user journey map in 6 steps:
- Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
- Define your persona and scenario
- Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions
- Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
- Identify opportunities
- Define action points and next steps
Let’s take a closer look.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UI DESIGN]
1. Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
The easiest way to create a user journey map is to fill in a ready-made template. Tools like Miro , Lucidchart , and Canva all offer user/customer journey map templates that you can fill in directly or customise to make your own.
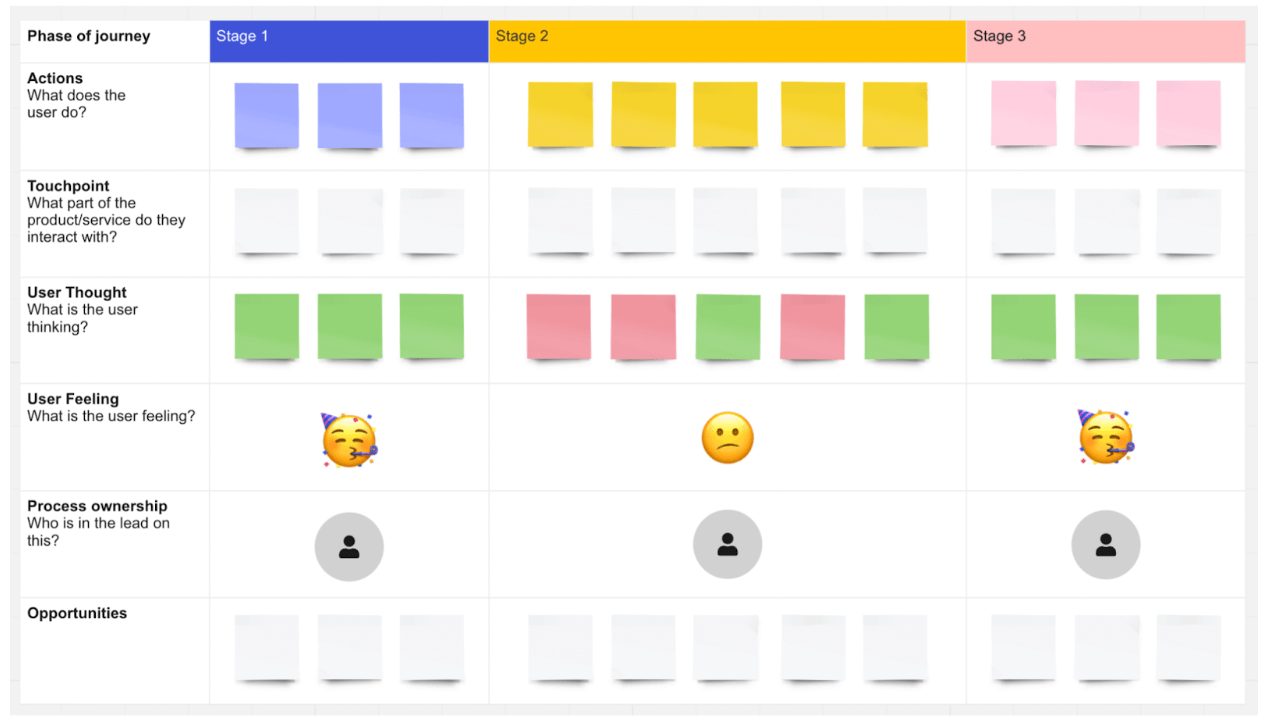
Here’s an example of a user journey map template from Canva:
2. Define your persona and scenario
Each user journey map you create should represent a specific user journey from the perspective of a specific user persona. So: determine which UX persona will feature in your journey map, and what scenario they’re in. In other words, what goal or task are they trying to complete?
Add details of your persona and scenario at the top of your user journey map.
3. Outline key stages, actions, and touchpoints
Now it’s time to flesh out the user journey itself. First, consider the user scenario you’re conveying and think about how you can divide it into high-level phases.
Within each phase, identify the actions the user takes and the touchpoints they interact with.
Take, for example, the scenario of signing up for a dating app. You might divide the process into the following key phases: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Service, and Advocacy .
Within the Awareness phase, possible user actions might be: Hears about the dating app from friends, Sees an Instagram advert for the app, Looks for blog articles and reviews online.
4. Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
Next, step even further into your user’s shoes to imagine what they may be thinking and feeling at each stage, as well as what pain-points might get in their way.
To continue with our dating app example, the user’s thoughts during the Awareness phase might be: “ I’ve never used online dating before but maybe I should give this app a try…”
As they’re new to online dating, they may be feeling both interested and hesitant.
While looking for blog articles and reviews, the user struggles to find anything helpful or credible. This can be added to your user journey map under “pain-points”.
5. Identify opportunities
Now it’s time to turn your user pain-points into opportunities. In our dating app example, we identified that the user wanted to learn more about the app before signing up but couldn’t find any useful articles or reviews online.
How could you turn this into an opportunity? You might start to feature more dating app success stories on the company blog.
Frame your opportunities as action points and state who will be responsible for implementing them.
Here we’ve started to fill out the user journey map template for our dating app scenario:
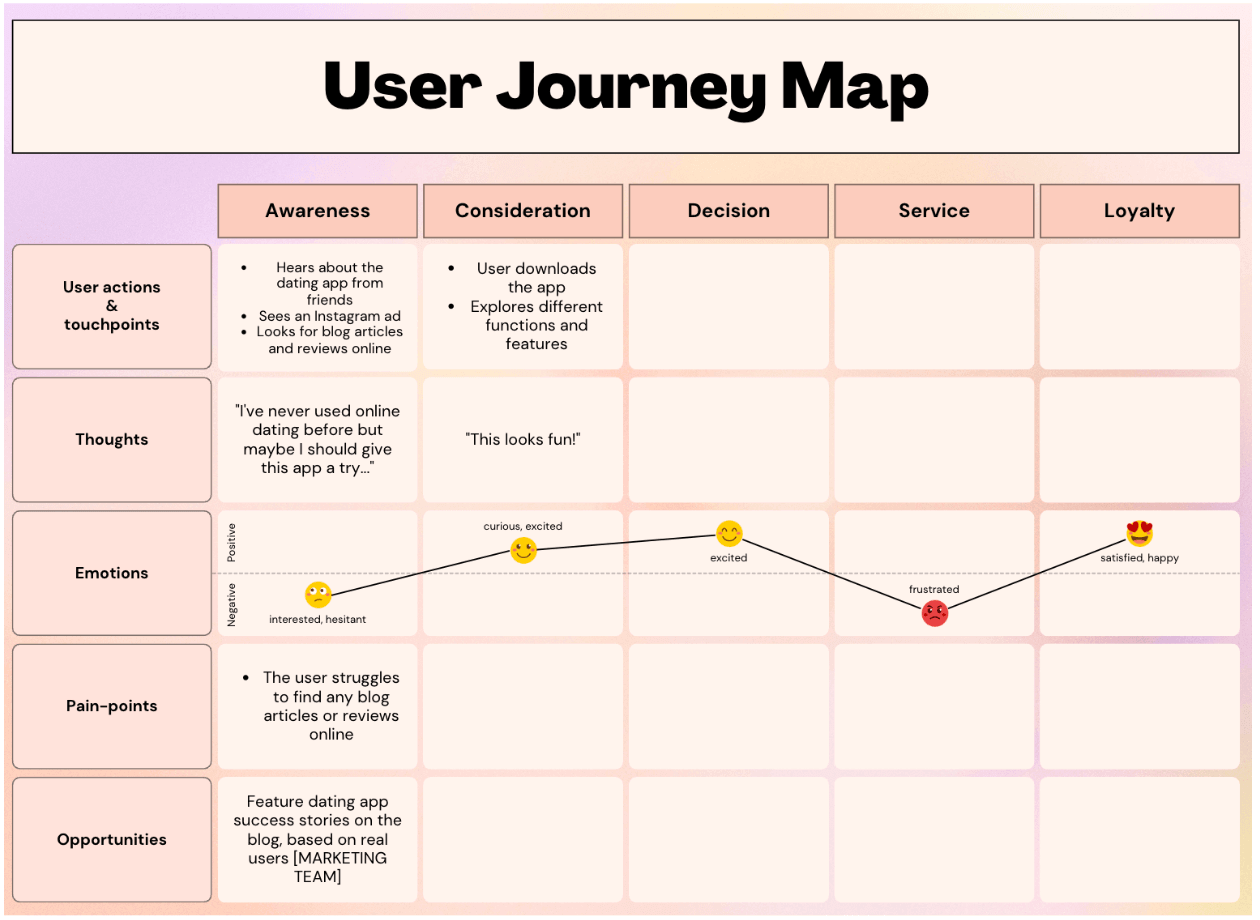
Repeat the process for each phase in the user journey until your map is complete.
6. Define action points and next steps
User journey maps are great for building empathy and getting you to see things from your user’s perspective. They’re also an excellent tool for communicating with stakeholders and creating a shared understanding around how different users experience your product.
Once your user journey map is complete, be sure to share it with all key stakeholders and talk them through the most relevant insights.
And, most importantly, turn those insights into clear action points. Which opportunities will you tap into and who will be involved? How will your user journey maps inform the evolution of your product? What are your next steps?
Customer journey maps in UX: the takeaway
That’s a wrap for user journey maps! With a user journey map template and our step-by-step guide, you can easily create your own maps and use them to inspire and inform your product design process.
For more how-to guides, check out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Storyboarding in UX
- How to Design Effective User Surveys for UX Research
- How to Conduct User Interviews
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the best UX insights and career advice direct to your inbox each month.
Thanks for subscribing to our newsletter
You'll now get the best career advice, industry insights and UX community content, direct to your inbox every month.
Upcoming courses
Professional diploma in ux design.
Learn the full UX process, from research to design to prototyping.
Professional Certificate in UI Design
Master key concepts and techniques of UI design.
Certificate in Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
Collaborate effectively with software developers.
Certificate in UX Design Fundamentals
Get a comprehensive introduction to UX design.
Professional Certificate in Content Design
Learn the skills you need to start a career in content design.
Professional Certificate in User Research
Master the research skills that make UX professionals so valuable.
Upcoming course
Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. Get the mindset, the skills and the confidence of UX designers.
You may also like

The ultimate guide to mobile app design: Follow these UI principles & best practices
The best online survey tools to use in 2024

What is colour theory? A complete introductory guide
Build your UX career with a globally recognised, industry-approved qualification. Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable.
- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
How to create an effective user journey map
No matter what you’re working on, the key to customer satisfaction and business growth is understanding your users. A user journey map helps you uncover pain points, explore the touchpoints from their perspective, and learn how to improve your product.
Imagine you just launched a new ecommerce platform. Shoppers fill their carts with products, but they abandon their carts before checkout. With a user journey map, you can pinpoint where the customer experience is going wrong, and how to enable more successful checkouts.
Read on to find out:
- What is a user journey map, and how it captures user flows and customer touchpoints
- Benefits of user journey mapping to refine UX design and reach business goals
- How to make user journey maps in five steps, using FigJam’s user journey map template
What is a user journey map?
Think about the path a user takes to explore your product or website. How would you design the best way to get there? User journey maps (or user experience maps) help team members and stakeholders align on user needs throughout the design process, starting with user research. As you trace users' steps through your user flows, notice: Where do users get lost, backtrack, or drop off?
User journey maps help you flag pain points and churn, so your team can see where the user experience may be confusing or frustrating for your audience. Then you can use your map to identify key customer touchpoints and find opportunities for optimization.
How to read a user journey map
Most user journey maps are flowcharts or grids showing the user experience from end to end. Consider this real-life journey map example of a freelancing app from Figma's design community. The journey starts with a buyer persona needing freelance services, and a freelancer looking for a gig. Ideally, the journey ends with service delivery and payment—but customer pain points could interrupt the flow.
Start your user journey map with FigJam
5 key user journey map phases.
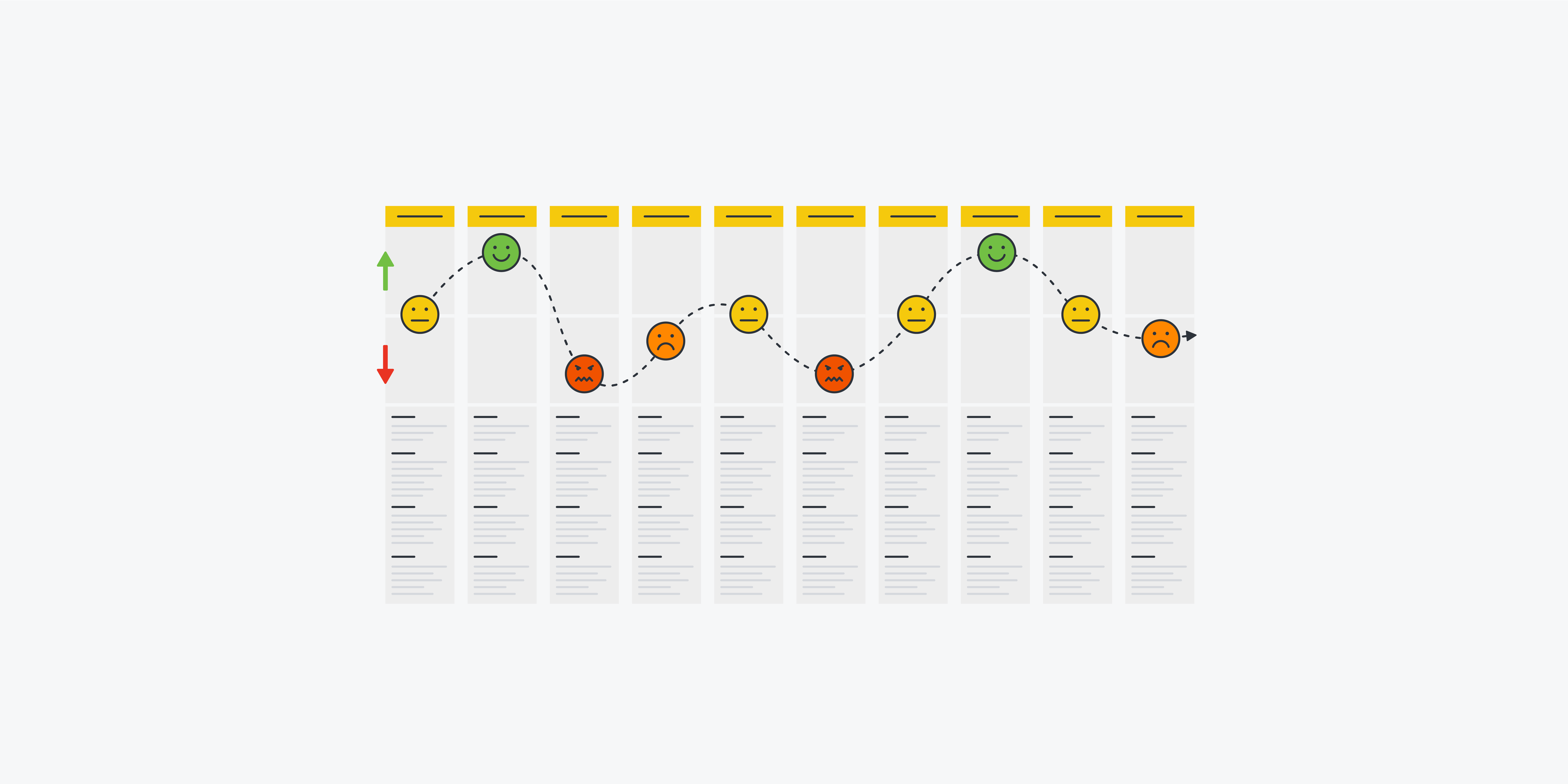
Take a look at another Figma community user journey template , which uses a simple grid. Columns capture the five key stages of the user journey: awareness, consideration, decision, purchase, and retention (see below). Rows show customer experiences across these stages—their thoughts, feelings, and pain points. These experiences are rated as good, neutral, and bad.
To see how this works, consider a practical example. Suppose a new pet parent wants to learn how to train their puppy and discovers your dog-training app. Here's how you might map out the five key user journey stages:
- Awareness. The user sees a puppy-training video on social media with a link to your product website. They're intrigued—a positive experience.
- Consideration. The user visits your product website to preview your app. If they can't find a video preview easily, this could be a neutral or negative experience.
- Decision. The user clicks on a link to the app store and reads reviews of your app and compares it to others. They might think your app reviews are good, but your price is high—a negative or neutral experience.
- Purchase. The user buys your app and completes the onboarding process. If this process is smooth, it's a positive experience. If not, the customer experience could turn negative at this point.
- Retention. The user receives follow-up emails featuring premium puppy-training services or special offers. Depending on their perception of these emails, the experience can range from good (helpful support) to bad (too much spam).
2 types of user journey maps—and when to use them
User journey maps are helpful across the product design and development process, especially at two crucial moments: during product development and for UX troubleshooting. These scenarios call for different user journey maps: current-state and future-state.
Current-state user journey maps
A current-state user journey map shows existing customer interactions with your product. It gives you a snapshot of what's happening, and pinpoints how to enhance the user experience.
Take the puppy training app, for example. A current-state customer journey map might reveal that users are abandoning their shopping carts before making in-app purchases. Look at it from your customers' point of view: Maybe they aren't convinced their credit cards will be secure or the shipping address workflow takes too long. These pain points show where you might tweak functionality to boost user experience and build customer loyalty.
Future-state user journey maps
A future-state user journey map is like a vision board : it shows the ideal customer journey, supported by exceptional customer experiences. Sketch out your best guesses about user behavior on an ideal journey, then put them to the test with usability testing. Once you've identified your north star, you can explore new product or site features that will optimize user experience.
How to make a user journey map in 5 steps
To start user journey mapping, follow this step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Define user personas and goals.
Gather user research and data like demographics, psychographics, and shopping behavior to create detailed customer personas representing your target audience. In your dog-training app example, one key demographic may be parents. What’s their goal? It isn't necessarily "hire a puppy trainer"—it could be "teach kids how to interact with a puppy."
Step 2: Identify customer touch points.
Locate the points along the user journey where the user encounters or interacts with your product. In the dog training app example, touchpoints might include social media videos, app website, app store category search (e.g., pets), app reviews, app store checkout, in-app onboarding, and app customer support.
Step 3: Visualize journey phases.
Create a visual representation of user journey phases across key touchpoints with user flow diagrams , flowcharts , or storyboards .
Step 4: Capture user actions and responses.
For each journey stage, capture the user story: at this juncture, what are they doing, thinking, and feeling ? This could be simple, such as: "Potential customer feels frustrated when the product image takes too long to load."
Step 5: Validate and iterate.
Finally, show your map to real users. Get honest feedback about what works and what doesn’t with user testing , website metrics , or surveys . To use the dog-training app example, you might ask users: Are they interested in subscribing to premium how-to video content by a professional dog trainer? Apply user feedback to refine your map and ensure it reflects customer needs.
Jumpstart your user journey map with FigJam
Lead your team's user journey mapping effort with FigJam, the online collaborative whiteboard for brainstorming, designing, and idea-sharing. Choose a user journey map template from Figma's design community as your guide. With Figma's drag-and-drop design features, you can quickly produce your own professional, presentation-ready user journey map.
Pro tip: Use a service blueprint template to capture behind-the-scenes processes that support the user journey, bridging the gap between user experience and service delivery.
Ready to improve UX with user journey mapping?
Journey mapping in UX design
Last updated
21 February 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Customers are essential to the success of a business. Without them, the company would cease to exist. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the stages customers go through when interacting with a brand. You can use a journey map to visualize this across all digital channels over time.
If you’re looking to create user-friendly, intuitive experiences for your customers, journey mapping is a key part of UX design . Find out everything you need to know about journey mapping in this guide.
- What are the four stages of journey mapping?
A journey map should accurately represent your user’s experience from when they first find you and start to interact with you, through to them making a purchase and becoming a loyal customer.
The stages of a journey map will therefore depend on your product. The four stages of a customer’s buying cycle are:
During this stage, customers are looking for solutions to a problem. They become aware of your brand, services, or products via advertisements or other marketing vehicles.
Social media is a powerful tool that companies use to boost awareness. During the awareness stage, the brand should share pertinent information, such as business goals, ethics, and values.
Consideration
At this stage, customers consider the brand against similar companies offering the same products and services.
You need to give potential customers a deeper understanding of what you’re offering and why your brand is a better choice. They may engage with the business by signing up for a newsletter or visiting a brick-and-mortar store.
Customers have decided what they want and make a purchase. They have gathered the information they need before committing to a purchase. They may find this information in email confirmations, FAQs on billing and shipping, and online ordering pages.
Customer loyalty
This is the last stage, after customers have made their purchase and are evaluating the overall experience. This phase is about creating loyal, returning clients by offering membership programs and future discounts.
- How to make a simple journey map
Each customer journey is unique, so journey maps vary depending on the scenarios experienced by customers. Although the maps vary widely, the same steps are involved in creating them.
Let’s look at a step-by-step approach to making a simple journey map.
Step 1: Scope definition
The first step is to clearly define your goals. What are you hoping to achieve from this journey map? Do you want to make a particular aspect of the purchasing cycle more user-friendly? Or are you trying to find out why potential customers don’t follow through with a purchase?
Setting a goal will provide guide rails around the particular customer path you’re trying to understand. This will drive UX designers throughout the journey.
Step 2: Create user personas
Next, get a grasp of who your customers are. Gather information to create different personas to improve your knowledge of the different segments of your target audience. This helps you to:
Define your target market
Create better products and services
Appeal to them through your marketing
Step 3: List channels and touchpoints
Touchpoints are points of interaction between the user and the product. The channels may be through social media platforms, the path a user would take through your product, and other supporting applications or communication necessary to complete their goal.
List all the channels and touchpoints in the journey scenarios. Identify the touchpoints with higher engagement and those that need to be optimized.
Step 4: Collect customer feedback
Gathering customer feedback helps gauge how your users feel about your product or service. Methods used to gather information include:
Questionnaires
Rating systems
Your aim is to see your product through the eyes of your customers.
Step 5: Define pain points and points of friction
Using the customer feedback you gathered in the previous stage, identify gaps in the user journey that make it difficult to move through stages. Identify when they happen and what triggers them.
This will help you to smooth out potential friction points in the customer journey.
Step 6: Improve and re-evaluate
The last step is to improve the overall experience of your customers. Once you have identified the pain points, opportunities, and goal metrics, brainstorm solutions to the identified flaws and implement necessary changes.
Regularly conduct further research and re-evaluate the customer journey.
- What are the elements of a journey map?
A journey map is made up of the following elements:
Persona (actor)
The persona is the one who experiences the journey; it may be a customer or a product user. Depending on the scenario, it could be a group or an individual.
The scenario is what the actor or persona is trying to achieve. A scenario describes the situation that the journey addresses. It primarily includes goals and expectations and can be real or imaginary.
Journey phase
Phases are the different stages of a journey, from awareness to purchasing and beyond. In each phase, try to visualize how you can meet the customer’s goals.
Thoughts and emotions
This refers to how the customer feels as they interact with your brand. Thoughts help the UX designer understand what the customer is experiencing, for example, relief, anxiousness, or frustration. Emotions allow the UX designer to focus on encouraging positive thoughts.
User actions
The action element details what the actor does in each phase to achieve their goal. It defines the actual steps taken by an actor throughout the journey.
Opportunities
This element offers the brand a chance to improve the customer's experience . They are insights gained from journey mapping and used to make informed decisions.
- Why are journey maps important?
Journey mapping brings the following benefits for a company.
Customer-centric philosophy
Using journey maps, UX designers can focus on how customers feel and think about the product being designed.
Journey maps help businesses understand their customers better, resulting in improved decision-making.
Broader business perspective
A journey map helps you to visualize situations experienced by a customer when interacting with your brand. The goal of a journey map is to remove obstacles and make the purchasing process intuitive and efficient.
Customer journey mapping helps a business owner gain an overview of their product or service from multiple viewpoints.
Improved customer experience
A journey map is the first step toward gaining a deeper understanding of customer engagement and fostering the flow of customer experience. It can help you to smooth out the customer experience and personalize it across all touchpoints.
Identification of opportunities
In complex business environments, gaps and breakdowns are common. Mapping out how a user interacts with your brand and/or product may reveal design flaws and areas that need change.
By charting the entire process, a journey map helps identify gaps and opportunities for improvement that will enhance customer experience.
Competitive advantage
Journey mapping helps a company eliminate design flaws and make its product stand out. Once a UX designer has improved customer experience, this becomes a differentiation factor among competitors in the market.
- How does a customer journey map help?
A detailed and well-researched journey map will help you to:
Build a customer-centric organization
Improve customer retention
Identify unmet opportunities that competitors may have missed
Understand the target audience
Align brand position with target market needs and expectations
Meet customer expectations
Understand different buyer personas
Optimize customer onboarding process
- How much does journey mapping cost?
The cost of journey mapping varies widely. The pricing depends on who’s doing it, how much research you want to do, and the complexity of the customer's journey.
- Designing journey maps
Journey maps are unique since they should represent whatever product or service they emulate. Variations of journey maps include:
Experience map
Empathy map
Service blueprint
You can use a third-party tool to build a well-designed journey map, such as:
Omnigraffle
However, there are no rules around what you use to build your journey map and can build it using a whiteboard, PDF format, and even Microsoft Paint. As long as it’s an accurate representation of the user’s journey, that’s what counts.
Experience maps
Experience maps are a zoom-out from journey maps. While journey maps represent a single persona’s behavior at each phase of the customer journey, experience maps can include multi-players that may interact with that user, additional products that customers typically use, or perhaps entirely different methods outside technology that users engage with to complete their goals.
Empathy maps
Empathy maps are used to understand customer personas . They do not follow a particular sequence of events along the journey. Empathy maps are divided into four parts and track what the customer does, thinks, says, and feels when using a product.
These can be helpful when defining who the persona is within your journey map.
Service blueprints
Service blueprints focus on how a brand delivers its products and services to customers rather than being customer-centric. In other words, they describe the behind-the-scenes details of the process.
They are mainly concerned with actions performed by every stakeholder in the purchase process. By focusing on service, gaps or friction points are identified and can be eliminated.
- Map your brand's path to success
Journey mapping offers many benefits to a company. Once your customer journey map is in place, you will fully understand your customers’ experience.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 26 January 2023
Last updated: 25 June 2023
Last updated: 31 January 2023
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 24 June 2023
Last updated: 29 May 2023
Last updated: 22 May 2023
Last updated: 19 May 2023
Last updated: 13 April 2023
Last updated: 27 March 2023
Last updated: 7 July 2023
Last updated: 3 June 2023
Last updated: 6 April 2023
Last updated: 11 May 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Customer Journey Maps
What are customer journey maps.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience and boost customer retention.
“ Data often fails to communicate the frustrations and experiences of customers. A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map.” — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert
In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
- Transcript loading…
Customer Journey Maps – Tell Customer Stories Over Time
Customer journey maps are research-based tools. They show common customer experiences over time To help brands learn more about their target audience.
Maps are incredibly effective communication tools. See how maps simplify complex spaces and create shared understanding.
Unlike navigation maps, customer journey maps have an extra dimension—time. Design teams examine tasks and questions (e.g., what-ifs) regarding how a design meets or fails to meet customers’ needs over time when encountering a product or service.
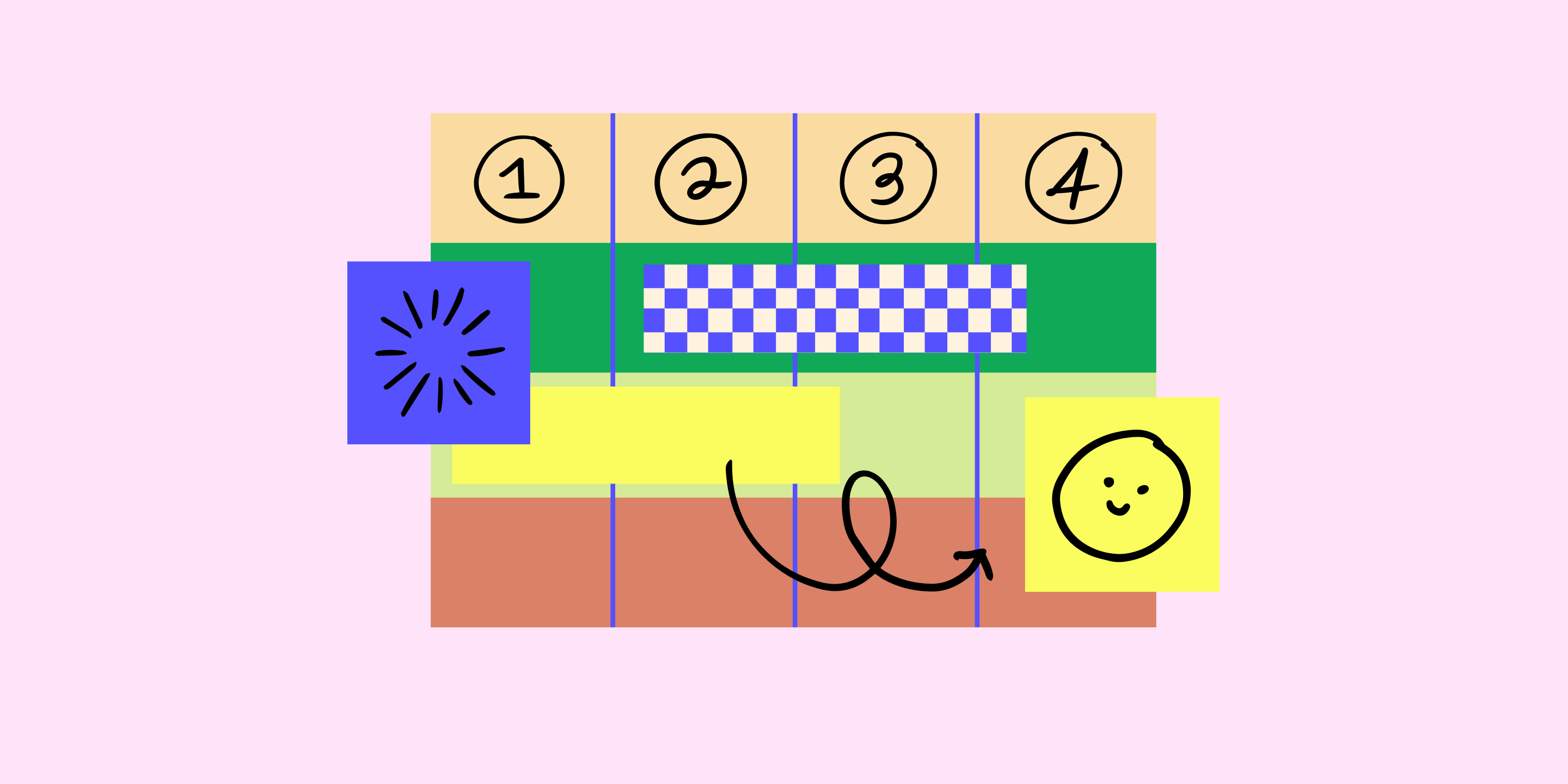
Customer journey maps should have comprehensive timelines that show the most essential sub-tasks and events. Over this timeline framework, you add insights into customers' thoughts and feelings when proceeding along the timeline. The map should include:
A timescale - A defined journey period (e.g., one week). This timeframe should include the entire journey, from awareness to conversion to retention.
Scenarios - The context and sequence of events where a user/customer must achieve a goal. An example could be a user who wants to buy a ticket on the phone. Scenarios are events from the first actions (recognizing a problem) to the last activities (e.g., subscription renewal).
Channels – Where do they perform actions (e.g., Facebook)?
Touchpoints – How does the customer interact with the product or service? What actions do they perform?
Thoughts and feelings – The customer's thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customer experience evolves over time. It allows you to identify possible problems and improve the design. This enables you to design products that are more likely to exceed customers’ expectations in the future state.

How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
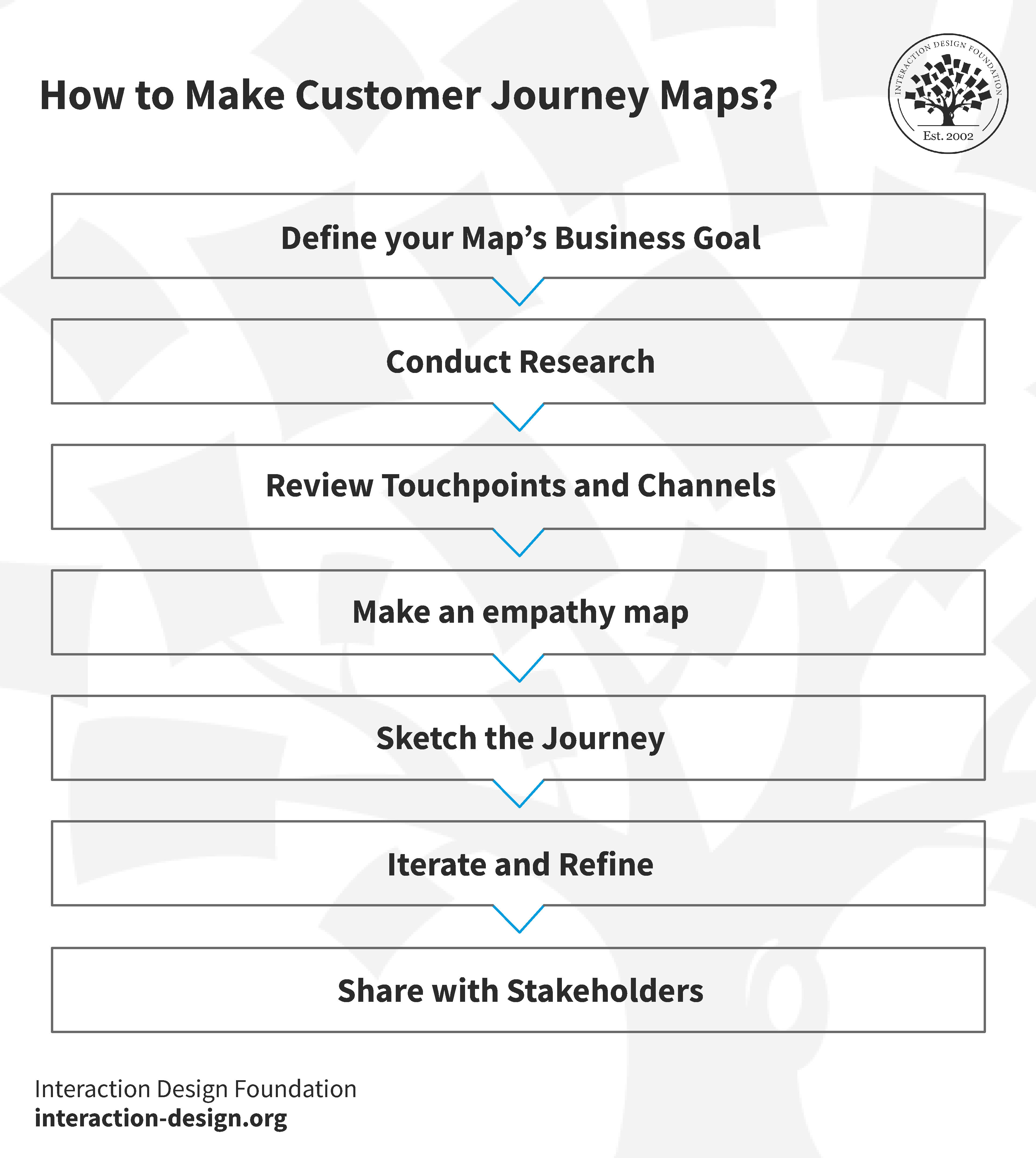
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.
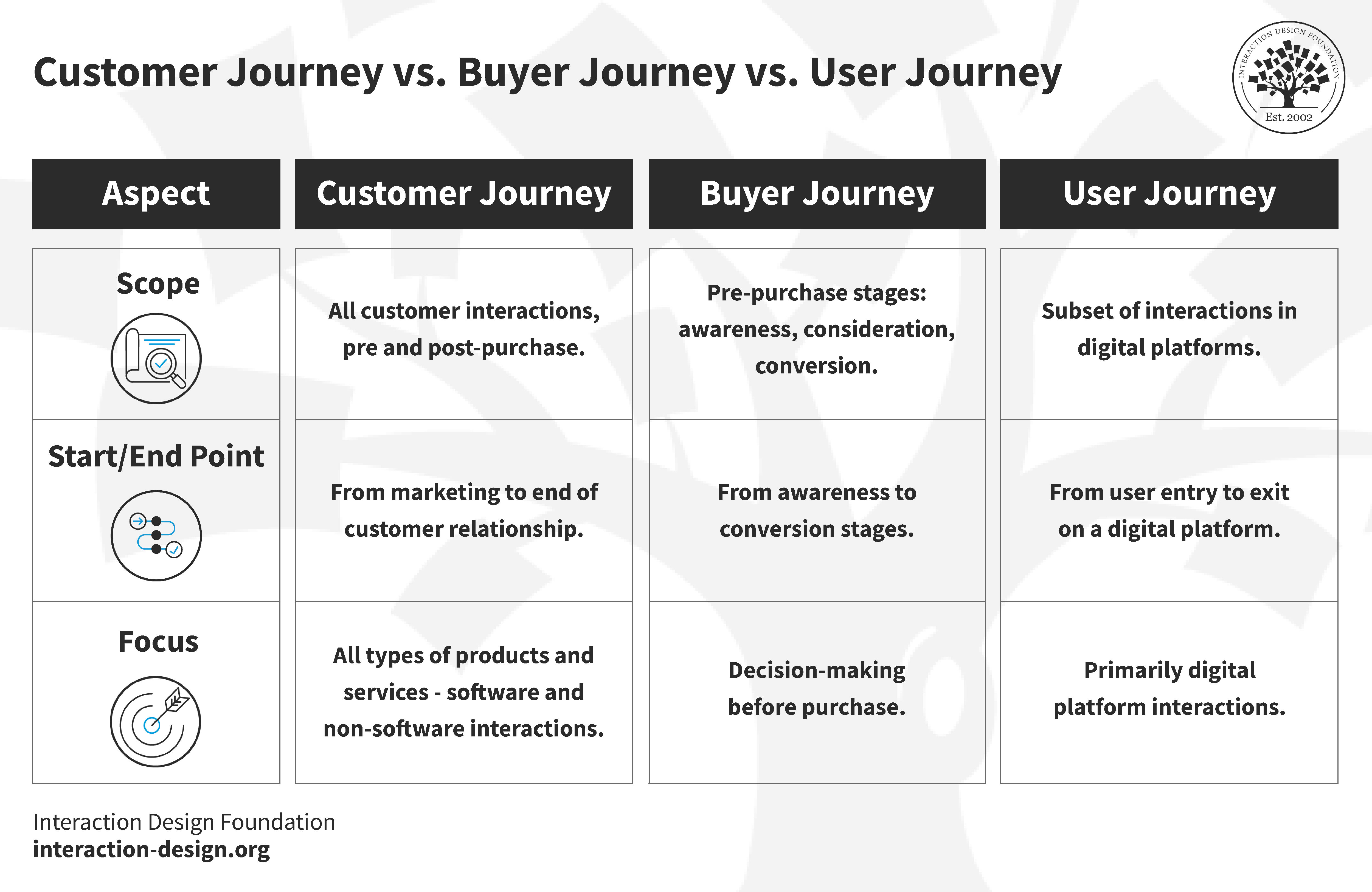
Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
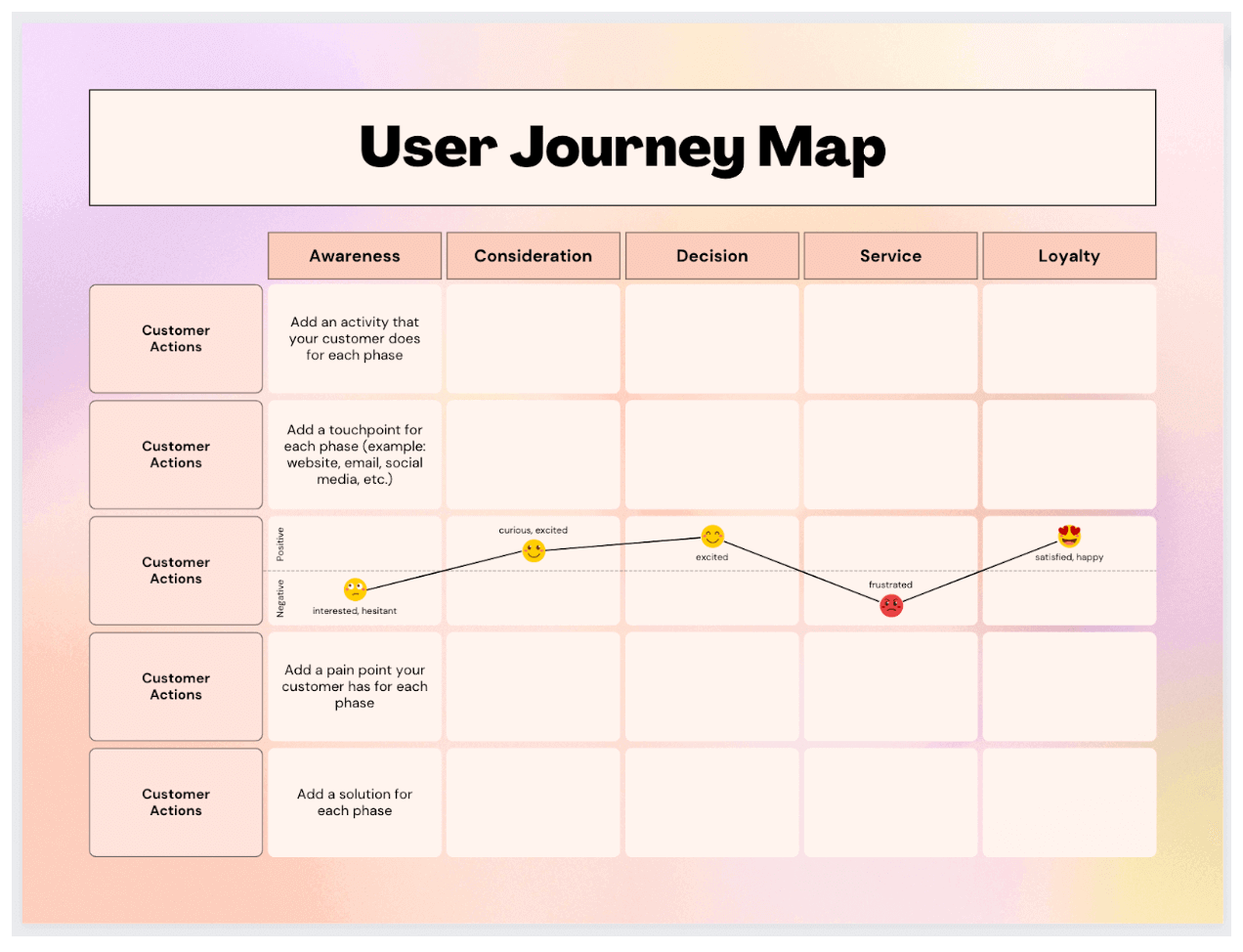
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.
Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 2 years ago
How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
- 11 mths ago
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
A Beginner’s Guide To User Journey Mapping
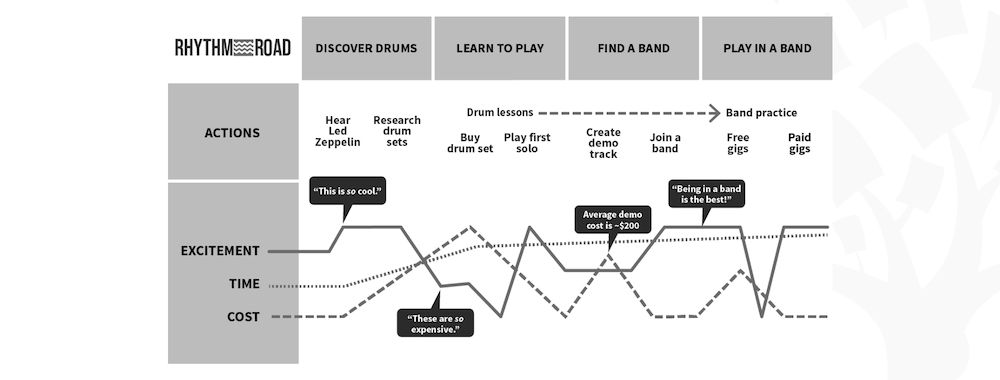
To design a great product, you need to understand what the user does with it. A user journey map will help you to answer that question for the product’s entire lifecycle.
“How do people actually use this product?” is a fundamental question that every product creator must answer. In order to do so, product designers need to understand the essence of the whole product experience from the user’s perspective. Fortunately, user journey mapping is an excellent exercise that can shed light on the ways in which the users interact with the product.
What Is a User Journey Map?
More From Nick Babich What Is Microcopy?
What Design Problems Does a User Journey Map Solve?
A user journey map is an excellent tool for UX designers because i t visualizes how a user interacts with a product and allows designers to see a product from a user’s point of view. This fosters a more user-centric approach to product design, which ultimately leads to a better user experience.
User journey maps help a product team to find the answer to the “What if?” questions. Also, a user journey map can be helpful when a company tracks quantitative key performance indicators . In this case, a user journey map can become a cornerstone for strategic recommendations.
The 8-Step Process of User Journey Mapping
Before creating a user journey map, review the goals of your business or service. This knowledge will help you align the business and user goals.
- Choose a scope.
- Create a user persona.
- Define the scenario and user expectations.
- Create a list of touchpoints.
- Take user intention into account.
- Sketch the journey.
- Consider a user’s emotional state during each step of the interaction.
- Validate and refine the user journey.
1. Choose a Scope
The scope of the user journey map can vary from a high-level map that shows end-to-end experience (e.g., creating a smart home in your house) to a more detailed map that focuses on one particular interaction (for instance, adding a new device to your smart home ecosystem).
2. Create a User Persona
Who is your user?
A user journey map is always focused on the experience of one main actor — a user persona who experiences the journey.
A user persona should always be based on information that you have about your target audience. That’s why you should always start with user research . Having solid information about your users will prevent you from making false assumptions.
Gather and analyze all available information about your target audience:
- Interview your real or potential users.
- Conduct contextual inquiry. This is an ethnographic field study that involves in-depth observation of people interacting with your product.
- Conduct and analyze the results of user surveys.
3. Define the Scenario and User Expectations
The scenario describes the situation that the journey map addresses. It can be real or anticipated. It’s also important to define what expectations a user persona has about the interaction. For example, a scenario could be ordering a taxi using a mobile app with the expectation of getting the car in five minutes or less.
4. Create a List of Touchpoints
Touchpoints are user actions and interactions with the product or business. You need to identify all the main touchpoints and all channels associated with each touchpoint. For example, for the touchpoint “Buy a gift,” the associated channels could be purchasing online or buying in the store.
5. Take User Intention Into Account
What motivates your user to interact with your product? Similarly, w hat problem are users looking to solve when they decide to use your product? Different user segments will have different reasons for adopting it.
Let’s take an e-commerce website. There is a big difference between a user who is just looking around and one who wants to accomplish a specific task like purchasing a particular product.
For each user journey, you need to understand:
- Motivation. Why are the users trying to do this action?
- Channels. Where the interaction takes place.
- Actions . The actual behaviors and steps the users take.
- Pain points . What are the challenges users are facing?
Also, ensure that the user is getting a consistent experience across all channels.
6. Sketch the Journey
Put together all the information you have and sketch a journey in the format of a step-by-step interaction. Each step demonstrates an experience that the persona has with a service/product or another person.
You can use a tool called a storyboard, which is a graphic representation of how a user does something, step by step. It can help you show how users can interact with a product. Using storyboards, you can visually depict what happens during each step.
7. Consider a User’s Emotional State During Each Step of the Interaction
What does a user feel when interacting with your product?
The products we design need to mirror the states of mind of our users. When we consider a user’s emotional state, this knowledge will help us to connect with them on a human level. That’s why it’s important to add an emotional lane to the user journey map. By visualizing the emotional ups and downs of the experience, you’ll find the areas that require refinement.
You can create an empathy map to better understand how the user feels. Try to mitigate the emotional downs and reinforce emotional ups with good design.
8. Validate and Refine the User Journey
Journey maps should result in truthful narratives, not fairy tales. Even when a user journey is based on research, you must validate it. Use the information from usability testing sessions and app analytics to be sure that your journey resembles a real use case.
Gather and analyze information about your users on a regular basis. For example, user feedback can be used to improve your understanding of the user journey.
More in Design + UX Hey Designers, Stop Using Users
Map the User Journey
Remember that the goal of making a user journey map is to create a shared vision within your product team and stakeholders. That’s why, once you create a user journey map, you should share it with your peers. Make it possible for everyone in your team to look at the entire experience from the user’s standpoint and draw on this information while crafting a product.
Recent Expert Contributors Articles

- How to Use This Site
- Usability Testing
- Domain Modeling
Taxonomy Design
- Wireframing
- Accessibility Evaluation
- Journey Mapping
- See All Methods A-Z
- Content Strategy
- Information Architecture
- Interaction Design
- Usability Evaluation
- User Research
- Visual Design

Photo by UX Indonesia via Unsplash
Journey Mapping Method
A journey map is a holistic, visual representation of a user’s experience with a product or service over time. Journey maps combine data and insight from other research and discovery methods to provide a detailed description from the user’s point of view of steps taken, decisions made, successes, pain points, and emotions felt.
Journey maps help designers understand the user’s motivations and needs at each step of a process, from the earliest earliest phases of researching a product or service all the way through adoption, providing crucial insight for designing solutions that better meet user and business needs. The journey map’s visual and storytelling elements also help it communicate research data and findings to broader audiences within an organization.
Preparation
Journey Mapping is often more effective when it is informed by these complementary methods.

Contextual Interviewing
Observation of users performing tasks in their own environment

Task Analysis
Observe users in action to understand how they perform tasks to achieve goals

Written descriptions of how users will perform tasks with your product or on your website

A specific user's context, motivations, and goals for visiting a website or app

Stakeholder Interviewing
Understanding the perspective and influence of those invested in a project's success

User Interviewing
Understand the tasks and motivations of the user group for whom you are designing
- Define business and user goals Clearly articulate the organizational goals for the product or service, the design and business goals for the mapping exercise, and the goals of the target user the map is to represent.
- Gather research data Effective journey maps are based on qualitative and quantitative data collected across a range of activities. Review and incorporate existing research as you create your journey map, and note where gaps in understanding indicate the need for additional research.
- Identify touchpoints and channels Touchpoints describe what users do and how they do it. Channels describe where the interaction takes place (e.g. website, call center, native app, or in-store).
- Create an Empathy Map Empathy maps describe what users do, think, feel, say, and hear in a given situation. They help you understand and articulate users’ emotional state, and provide the basis for illustrating the peaks and valleys of frustration, anxiety, happiness, etc.
- Sketch the journey Visualize the order in which users exhibit behaviors, use information, make decisions, and feel emotions. Group elements into phases related to the narrative of each user. Integrate touchpoints, channels, empathy insights, and other research to show the user’s course of motion across the timescale as a whole. Include the user’s feelings at each touchpoint.
- Review, refine, and revise Review your draft journey with team members and subject matter experts to gain new insight and integrate new perspectives. Use these to identify additional opportunities to make your journey map more accurate, more expressive of the data, and more useful for the design process. From time to time, evaluate your map to make sure it remains accurate. Revise as necessary to account for evolving research, product development, and user and business needs.
Journey Mapping typically produces insight and solutions focused on these areas:
User Preference
Elements, arrangements, or qualities of experience design that user state or show are valuable to them.
User Behavior
Information about how users currently use a site, service, or resource.
Journey Mapping Resources

10 most interesting examples of Customer Journey Maps
7 Interesting Real Life Customer Journey Map Examples

Customer journey maps for content: Untangle complex insights and create better experiences
144 Best Customer Journey Map Templates and Examples

Category Design
Creating structures and schemes that make the location and use of content clear

Persona Creation
Development of research-informed representations of target user goals, behaviors, and pain points
Style Tile Creation
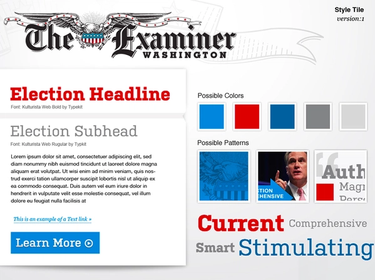
Communicate the use of fonts, colors, and interface elements in a design system

Define a system for labeling and classifying content to make it easier to find, understand, and use
Journey Mapping Method details last edited on Sunday, February 6, 2022

How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Customer Journey maps are a visual interpretation from an individual’s perspective of their relationship with an organization, service, product or brand.
This whiteboard animation (and article) shows you how to create a Customer Journey Map.
Despite best intentions and mountains of data, many organizations continue to offer lackluster experiences for their customers.
Many organizations function with an internal focus, and that becomes apparent when customers interact with their various products, services and employees. Every interaction a customer has with an organization has an effect on satisfaction, loyalty, and the bottom line. Plotting out a customer’s emotional landscape by way of a Customer Journey Map, or Experience Map, along their path sheds light on key opportunities for deepening those relationships.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A Customer Journey map is a visual or graphic interpretation of the overall story from an individual’s perspective of their relationship with an organization, service, product or brand, over time and across channels. Occasionally, a more narrative, text-based approach is needed to describe nuances and details associated with a customer experience. The story is told from the customer’s perspective, but also emphasizes the important intersections between user expectations and business requirements.
Inspired by user research , no two journey maps are alike, and regardless of format they allow organizations to consider interactions from their customers’ points of view, instead of taking an inside-out approach. They are one tool that can help organizations evolve from a transactional approach to one that focuses on long term relationships with customers built on respect, consistency and trust.
All organizations have business goals but leveraging customer journeys as a supporting component of an experience strategy keeps customers (or members, patients, employees, students, donors etc.) at the forefront when making design decisions. They can be used in both current state review and future state visioning to examine the present, highlight pain points and uncover the most significant opportunities for building a better experience for customers.
How Do We Use Them?
Customer engagement is not simply a series of interactions, or getting people to visit a website, “Like” something on FaceBook, or download a mobile app. Genuine engagement centers on compatibility, and identifying how and where individuals and organizations can exist harmoniously together. Giving thought to how your organization/product/service/brand fits into customers’ lives is crucial.
I also use journey maps to gain internal consensus on how customers should be treated across distinct channels. Holding collaborative workshops with cross-disciplinary teams mixing people who otherwise never communicate with each other can be extremely valuable in large organizations in particular.
Illustrating or describing how the customer experience could be brought to life across channels allows all stakeholders from all areas of the business to better understand the essence of the whole experience from the customer’s perspective. How do they want to be spoken to, what are they thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, and doing? Journey maps help us explore answers to the “what ifs” that arise during research and conceptual design.
What Components Does a Journey Map Include?
- Personas : the main characters that illustrate the needs, goals, thoughts, feelings, opinions, expectations, and pain points of the user;
- Timeline : a finite amount of time (e.g. 1 week or 1 year) or variable phases (e.g. awareness, decision-making, purchase, renewal);
- Emotion: peaks and valleys illustrating frustration, anxiety, happiness etc.;
- Touchpoints : customer actions and interactions with the organization. This is the WHAT the customer is doing; and
- Channels : where interaction takes place and the context of use (e.g. website, native app, call center, in-store). This is the WHERE they are interacting.
Nice-to-haves
- Moments of truth : A positive interaction that leaves a lasting impression, often planned for a touchpoint known to generate anxiety or frustration; and
- Supporting characters: peripheral individuals (caregivers, friends, colleagues) who may contribute to the experience.
The Process
1. review goals.
Consider organizational goals for the product or service at large, and specific goals for a customer journey mapping initiative.
2. Gather Research
Review all relevant user research, which includes both qualitative and quantitative findings to provide insights into the customer experience . If more research is needed, get those research activities in the books. Some of my favorite research methods include customer interviews, ethnography & contextual inquiry, customer surveys, customer support/complaint logs, web analytics, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
3. Touchpoint and Channel brainstorms
As a team, generate a list of the customer touchpoints and the channels on which those touchpoints occur today. Then brainstorm additional touchpoints and/or channels that can be incorporated in the future journeys you will be mapping. For example, the touchpoint could be “pay a bill”, and the channels associated with that touchpoint could be “pay online”, “pay via mail” or “pay in person”.
4. Empathy map
Empathy maps are a depiction of the various facets of a persona and his or her experiences in a given scenario. This exercise helps me organize my observations, build a deeper understanding of customers’ experiences, and draw out surprising insights into what customers need. Empathy maps also provide a foundation of material to fuel journey mapping. The goal is to get a well-rounded sense of how it feels to be that persona in this experience, specifically focusing on what they’re thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, saying and doing.
5. Brainstorm with lenses
The goal of lensed brainstorming is to generate as many ideas as possible in a short period of time. To gain focus as I generate ideas I use “lenses”—words representing key concepts, brand attributes or mindsets that help us look at a problem or scenario in a different way. For this exercise I recommend that the team agree on 3-5 lens words (for example: accessible, social, comforting), then set the clock for 2 minutes per lens word. Each person individually writes down as many ideas as they can think of in that time. After 2 minutes switch to the next lens word until all lens words have been used as idea inspiration. This ensures that every voice on the team is heard and generates a huge inventory of ideas.
6. Affinity diagram
This is a method to visually organize ideas and find cohesion in the team’s concepts. Affinity diagramming helps us shift from casting a wide net in exploring many possibilities, to gaining focus on the right solutions for this audience. All team members should put their ideas generated in the lensed brainstorming activity up on the wall. Have someone sort the ideas into categories and label them. As a group, begin to consider where you might combine, refine, and remove ideas to form a cohesive vision of the future customer experience.
7. Sketch the journey
Drumroll, please. This is the part you’ve been waiting for! It’s now time to put together all the pieces: timeline, touchpoints, channels, emotional highs and lows, and all the wonderful new ideas the team generated for how to improve the future customer journey. Get creative with how you lay it out—it doesn’t have to be a standard left to right timeline. It could be circular or helical. It could be one large map or it could be an interactive, clickable piece with embedded video. There are no templates, and there are infinite possibilities.
8. Refine and digitize
Journeys don’t always become a sophisticated deliverable—sometimes they begin and end as sticky notes on a wall or sketches on a whiteboard. But most of the time, when you go through the activities to arrive at a solid customer journey map, you want to polish it, leverage it in your work and share it with colleagues across the organization. If visual design isn’t your strong suit, consider collaborating closely with a visual designer who can transform the journey map sketch into an impressive artefact.
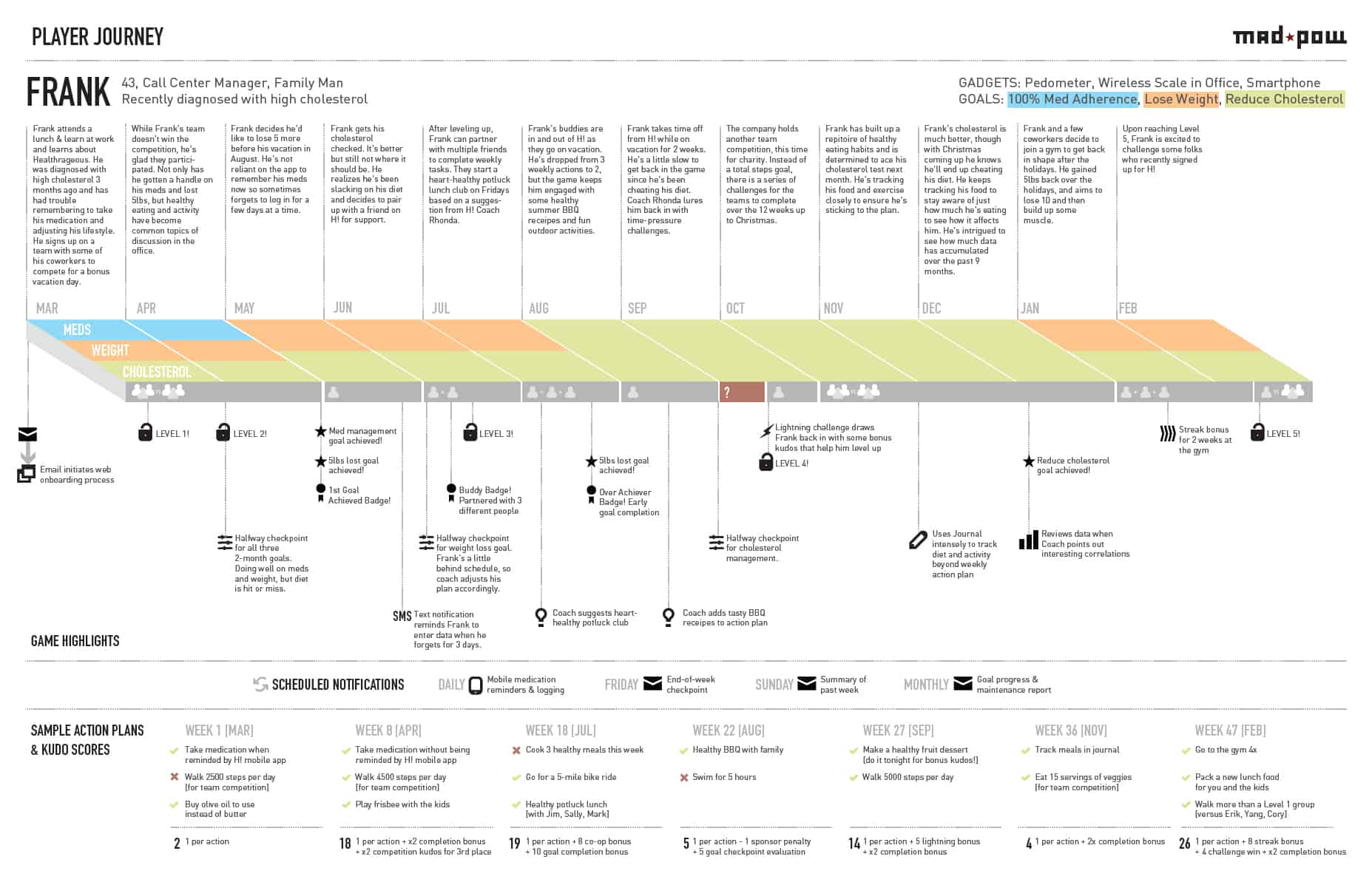
While journey maps are usually a tangible deliverable, like the one above, the process of journey mapping is what’s most important – it pushes us to think deeply about how we can use experience design to have a positive impact on our customers.
9. Share and use
It can be beneficial to maintain journey maps over time. For example, you could set a time each quarter or year to evaluate how your current customer experience matches your documented vision journeys. If your organization tracks quantitative KPIs, you can integrate these into a journey benchmarking process. Socializing journeys among stakeholders is critical in moving your organization toward action.
In addition to prioritization, the output of a journey map can serve as a backbone for strategic recommendations and more tactical initiatives.
For example, if you’re a mortgage company and you identify the closing process as a key area of frustration, anxiety and opportunity for engaging with the customer and designing for the “moment of truth”, then mark this as a high priority and get that on your strategic roadmap.
Schedule enough time to properly go through the recommended process. I’ve found that you can document a current state journey in about 3 hours, and a future state journey in about 5 hours. This makes for a full day to do both for one persona.
Make sure a good mix of people are involved in the journey map creation. It’s helpful to have stakeholder participants from many areas of the organization, as well as people of varying levels of seniority.
Once the journey maps are created, share them with zeal. Shout them from the rooftops and display them prominently in common areas.
Megan Grocki
Megan Grocki is an experience strategy director at Mad*Pow. With over 15 years of experience in research, experience design and strategy, she helps clients discover the expectations and behaviors of their audiences and identify opportunities for engagement. She has presented and led workshops at several UX, healthcare, and strategy industry events. In her spare time she is earning her master's degree in gastronomy with a concentration in food policy at Boston University. She hopes to leverage her design and strategy chops to educate the public about the connections between their health and what they eat, and use design to help affect changes in food policy at local, national and global levels.
Join the discussion Cancel reply
49 comments.
The post is incredibly good and very well explained. Well done Megan. Thanks UX Mastery for gathering this content and people.
Thanks Justin—I agree Megan did a great job explaining it, and we’re pretty proud of the resulting animation!
Keep an eye on the site as we tackle other UX techniques .
Megan – can you kindly post a better quality image to your final visual please – it certainly seems it will be worth reading your output. Good work!
That’s been done, Max.
Excellent Post Megan! Your process and explanations are easy to follow and very useful. I love the video too. I help people & groups as they through change and an early step in creating a compelling future is gaining a shared understanding of where we actually want to go. Techniques like the ones you’ve described here are so important to structuring the kind of dialogue needed to build that understanding! Thanks for sharing! -Steve
Great article, I agree with everything you’ve written. In my daily workflow, I use Mediatoolkit.com for media listening activities and I highly recommend it, because it enables me to be careful around the challenges you mentioned. :)
Great article Megan! As a Customer Journey Research provider from The Netherlands, it’s very interesting to read. The process and examples are well explained!
This is a really great article. It is well written and a step-by-step tool for mapping and exploring user journeys. The video is also excellent! Thanks!
Hey Megan!!
Just doing a little bit of research on customer journey maps for a talk and boom!! here you are!! This is very helpful information!!!
Great work. Thanks for sharing your methods.
Thanks for this article! However, several points are still unclear. For example – step 5) Brainstorm with Lenses. What exactly is the team brainstorming for? What ideas are we looking for? Shouldn’t the customer journey map be based on observing what frustrations and triumphs people have at each stage in the journey?
Similarly, I didn’t understand clearly how affinity diagramming fit into this process. Is it simply gathering and organizing all the data from research into potential steps in the customer journey?
Hope to hear from you soon! :) And thanks again!
Best wishes, Eureka UX Researcher at Piktochart
I had the same thought. I assume these are the steps for creating a future state journey map, not a current state.
Great post Megan! Thank you for the explanation and process mapping.
Thank you for your post and the video! We use it sometimes to explain our students in just several minutes how to build CJM. On step 4 we also try to identify mood (experience). And on step 10 we usually say “Iterate!” (: We also created a tool to create customer journey maps online – http://uxpressia.com .
Beautifully explained…Amazing how relevant this is for transporting your customer to a virtual world during a sales demo!
Hello Megan,
Very nice article & informative vide, ths for the share.
Regards, Ayman
Thanks for the great information. Very helpful and well-outlined. Much appreciated!
Love the intelligence and delivery. Off to put to good use hopefully! Thank you Megan.
Thank you for your thoughtful post. I’m finding that different groups in my company (engineers, sales, client services) all want and could benefit from user research assets such as personas and journey maps. However, they each prioritize different content. Do you happen to know of a tool that enables storing and maintaining a lot of content pieces (modules) about a persona and enables dynamic updating of “child” content? For example, if I tweaked the empathy map in the master, all the child artifacts that included the empathy map would be updated. I’d be happy to pay for a good solution, but have not found any. I also work on a mac… Thanks in advance for your help!
hi Megan thanks for your post being a student I have to create an assignment of a customer journey map of any service or any product can you tell me which software is to be used for this purpose.
Hello Megan for sharing extreamly good idea about customer journey map.Really Great Work.Keep it up
Thanks for brilliantly mapping the steps in visual form!
Excellent Megam, process mapping really well done.
Hey guys, what tool do you use Megan for the journey map? Can people recommend good free alternatives?
Great stuff… very helpful video.
1+1=3 Ger dig snabbt en bild av värdet i kundresan ur kundens perspektiv. vilka tjänster skall jag erbjuda med utgångspunkt från kundens resa
Well Done Megan! Great video.
One thing I’d maybe add for what it’s worth is the idea of interviewing Stakeholders as you begin the process. They can add some great ideas into what they perceive the customer pain points and relevant journeys to be. But more important than that, is that the Stakeholders will be more “bought-in” to your feedback when you present the final Journey Map product. That part is priceless.
Thank you for putting this together!
Hi, thanks for such an a valuable and insightful article. I’m just curious to understand more about affinity diagram. Could you elaborate more? From my understanding, I gathered that affinity diagraming is more of an activity than a documentation that requires a team discussion to gain consensus and categorize the deliverables from the preceding procedures into something more visual/documented? Could you elaborate more and point me in the right direction?
Trying to get in touch with Mad Pow Megan Grocki, does someone have her direct email address?
Thanks, Paul L
Some time has passed since we did that, but I think it’s still actual for the community. This year we’ve published a list of free customer journey maps templates here – https://uxpressia.com/templates . It is a pretty bunch of customer journey maps templates created for different business domains (including Healthcare, Travel, Banking, Telecom, etc.). All of them are based on the actual experience. You can download the template as PDF or start creating online map inside our tool based on that template.
All perfect and fine, but what I am always missing in discussions about user journeys is an overview of what we are ‘competing’ with. To achieve a touchpoint (meaning the client or user gives his or her attention to my app, or my service, or simply to me), what else is screaming for attention that the user then has to ignore.
I tried to discuss this here: http://www.expressiveproductdesign.com/competing-for-attention/
And did an attempt to create a template to help uncover the competition here: http://www.expressiveproductdesign.com/stickiness-creating-products-services-make-people-come-back/
Not sure if I am there yet. What do you think? Is ‘competition’ an issue in user journey mapping, and how do we best deal with this?
Great article!! In addition to all the pointers mentioned, would like to add the importance of CRM in regards to customer journey mapping. Traditionally retail stores, call centers, social media, and other channels were separately managed. However, now businesses cannot take the risk of handling these channels separately as it will result in a disjointed customer service.
Today the objective should be to have a broad single channel with multiple touch points. And that is only possible when all channels are merged.
Buisnesses who use a robust CRM software like ConvergeHub, Zoho or Infusionsoft are able to combine all communication channels to have a consolidated view of the customers and deliver consistent experience across all channels. So whether customers want to make a purchase, renew a service, or resolve a problem, they can do so in any of their preferred channels.
As the customers move across physical store, online e-commerce, social media and call centers, businesses can map the entire customer journey to provide a unified experience.
I dont see the highs and lows in the CJM?
This post illustrates well on this concept, thanks Megan, hope I have chance to translate the article into Chinese soon.
This is an awesome and very helpful post! Thanks for sharing these tidbits! I’d love to learn more.
This is immensely resourceful and precise. The nuances of user journey and the process explained in a lucid manner, keeping in mind the user journey of the reader. That’s a story within a story, using your technique to explain your technique. Thanks a ton, Megan. God bless!
Ditto. Very helpful, clear process to follow and great sample of the outcome. A watershed moment for me in documenting my own businesses CJM
Great post and video, thanks.
Wonderful post Megan
Great work, thank you very much!
Thanks for sharing, very useful post.
Thanks Kevin.
This is a really great article…concise with a great visual that really ties everything together well.
However, I struggle making these types of documents because of the abstraction. Frank isn’t real and the behavior pattern (the “journey”) has never happened. I know you pulled this from real data, but since I can’t tell what is real and what isn’t from this doc I am treating real behavior with equal weight to behavior you made up.
In fact searching for Healthrageous reveals a postmortem that admits they overbuilt and didn’t focus enough on market fit. This document fully embraces that admittedly flawed business approach…almost celebrates it. Do you think this document contributed to a false sense of security? Do you think it would have helped to surface more about what was real and what wasn’t, or is this document format more a symptom of this client’s approach than a cause?
Hi, I’am a trainee from Huawei Tunisia, i want to create a customer journey map and i’m looking for some examples of customer journey map for a telecom operator. Can you help me please with some design examples? I will be very grateful. Thank you.
This is a very informative document. I can’t wait to apply them. Thank you for sharing!
Thank you so much!!! Loved it:) Simple language & full of quality information:) Good job :)
Thank you so much its good
Hi, how to write the customer journey as a critical narrative. can u guide
Gorgeous 3-D Journey Map concept. Wish it was just a little less blurry!
Further reading

The Ethical Considerations, Trust, and Responsibility in Designing Voice UI
When it comes to creating Voice UI there’s a lot of conversation around voices, but very little around personality. How trustworthy should that...
Success in ResearchOps: An indicator of UX maturity
User research is not just an integrated part of business, but rather teams of people supporting the research process with the practice of ResearchOps...

How to Organize and Reuse Research Insights
Have you ever wondered what life would be like if we reused research insights? Lucky for you - it's easy! Zack Naylor from Aurelius teaches us how.

Follow @uxmastery

18 MIN READ
SHARE THIS POST
Product best practices
- Product Management
- UX research
User Journey Map Guide with Examples & FREE Templates
18 April, 2024

Senior UX Researcher

Customer journey mapping is also a popular workshop task to align user understanding within teams. If backed up by user data and research, they can be a high-level inventory that helps discover strategic oversights, knowledge gaps, and future opportunities.
Yet, if you ask two different people, you will likely get at least three different opinions as to what a user journey looks like and whether it is worth the hassle. Read on if you want to understand whether a UX journey map is what you currently need and how to create one.
You can get the templates here:
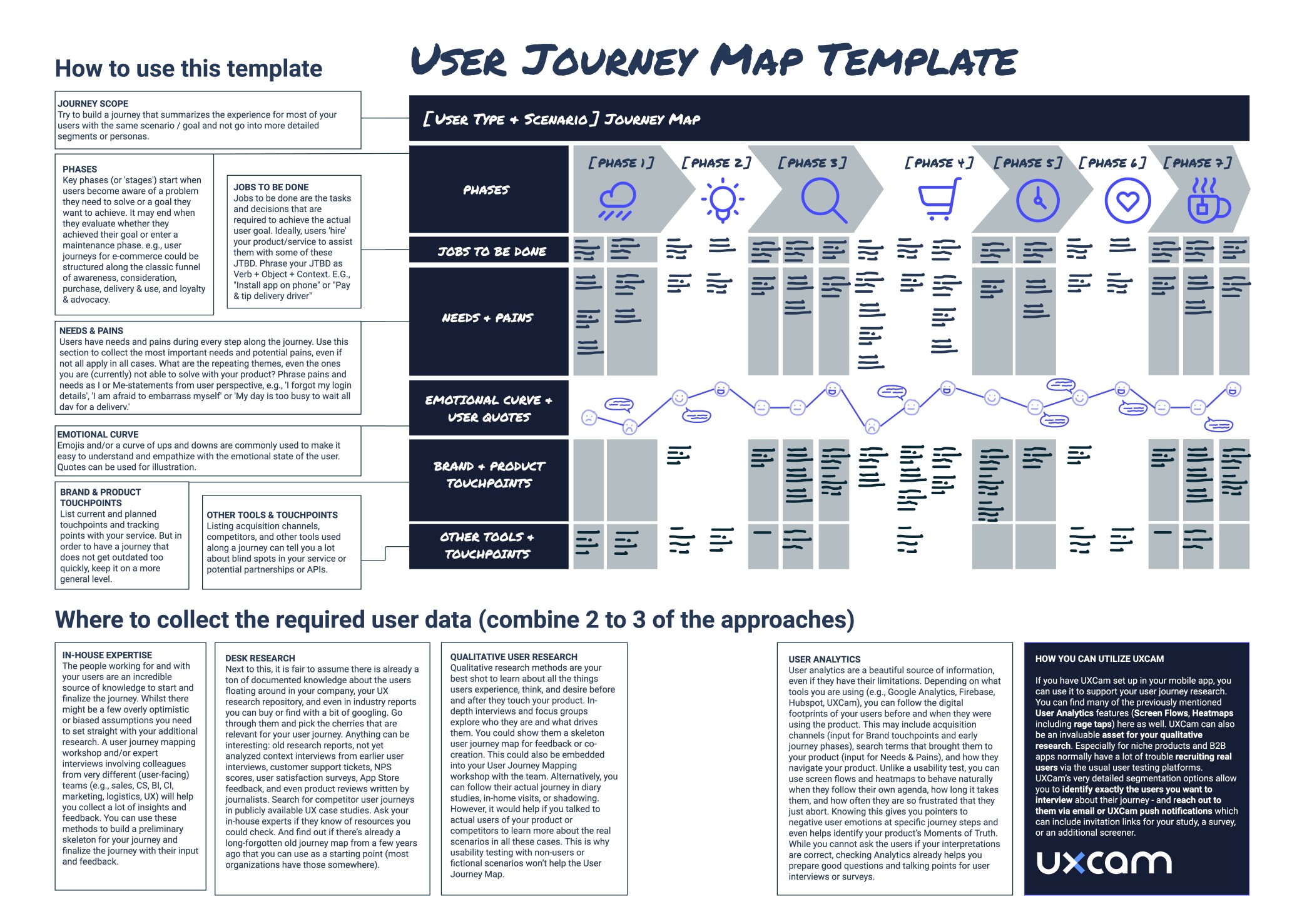
Click here to download a high-resolution PDF of this template.
What is user journey mapping?
Imagine your product is a supermarket and your user is the person wanting to refill their fridge. They need to:
Decide what to buy, and in what supermarket will they be able to find and afford it
Remember to bring their coupons
Park there
Find everything
Save the new coupons for the next shopping trip
Dive Deeper: Mobile Product Management Certification
If you want to learn more about how to optimize your user journeys, we recommend enrolling in our course "Mastering Mobile App Product Management" for free.
Unlock the secrets of user-centric design with our course
Gain practical skills in identifying user needs and crafting engaging, intuitive UX designs
Get 15+ templates and frameworks
Our modules, including "How to Map Out Your Discovery" and "User Research for Mobile Apps," ensure you create visually stunning and highly functional user experiences.
Enroll for free here.
Mobile App Product Management Certification
- Upskill for free
- Career growth
- Expert Instructors
- Practical Insights

3 ways to understand customer journey maps
Now, there are at least three ways to look at the customer journey.
1. Workflow maps for usability optimization
Some imagine a user journey map as a wireframe or detailed analysis of specific flows in their app . This could be, for example, a sign-up flow or the flow for inviting others to a document. In our supermarket example, it’s a closer look at what they do inside your supermarket, maybe even only in the frozen section. Or you could define what you want them to do in the frozen aisle.
.css-61w915{margin-right:8px;margin-top:8px;max-height:30px;}@media screen and (min-width: 768px){.css-61w915{margin-right:38px;max-height:unset;}} The focus here is on getting the details of the execution right, not how it fits into the bigger picture of what the user needs.
It is more or less a wireframe from a user perspective. Such a product-focused understanding is not what we want to discuss in this article, though many examples for the best user journey maps you might come across are exactly this. There are good reasons to do such an analysis as well, since it helps you smooth out usability for the people who have already found their way into your supermarket because of your excellent ice cream selection. Workflow maps won’t help you notice that your lack of parking spots is one of the reasons why you are missing out on potential customers in the first place. By only looking at what they do inside the supermarket, you might also miss out on an opportunity for user retention: You could help them get their ice cream home before it melts.
2. Holistic user journey maps for strategic insights
With a more holistic view of what people experience when trying to achieve a goal, product makers gain strategic insights on how their product fits into the big picture and what could be in the future. Because this journey document covers so much ground, it is usually a linear simplification of what all the steps would look like if they were completed. Going back to our supermarket example, it would start from the moment the person starts planning to fill the fridge and ends when the fridge is full again — even if the supermarket building is only relevant in a few phases of this journey. Creating this version of a user journey map requires quite some time and research effort. But it can be an invaluable tool for product and business strategy. It is an inventory of user needs that can help you discover knowledge gaps and future opportunities. Service blueprints are the most comprehensive version of a user journey map since they also lay out the behind-the-scenes of a service, usually called backstage. In our supermarket example, that could be:
the advertising efforts
logistics required to keep all shelves stocked
protocols the staffers follow when communicating with customers
3. Journey mapping workshops as an alignment method
In a user journey mapping workshop, stakeholders and team members share their knowledge and assumptions about the users. Some of these assumptions might need to be challenged — which is part of the process. The goal is not the perfect output, but rather to get everyone into one room and work out a common understanding of the users they are building products for. It forces everyone to organize their thoughts, spell out what they know and assumed was common knowledge — and ideally meet real users as part of the workshop. If done right, this establishes a more comprehensive understanding of what users go through and helps overcome the very superficial ideas one might have about the lives and needs of people outside their own social bubble.
Hence, such a workshop helps create aha moments and gives the consequences of great and poor product decisions a face. So at the end of the day, it is one of many methods to evangelize user-centricity in an organization.
What are the benefits of user experience (UX) mapping?
We already discussed the benefits and shortcomings of workflow maps, but what are the reasons you should consider a UX journey map and/or a journey mapping workshop ?
1. Switching perspectives
Empathy: Like any other UX method and user research output, user journey maps are supposed to foster empathy and help product makers put themselves into the shoes of a user. Awareness: It creates awareness of why users do all the things they do. And it challenges product makers to resist the temptation of building something because it’s feasible, not because it’s needed that way.
2. Aligned understanding
Given the team is involved in creating the user experience map (either as a workshop, in expert interviews, observing the user research, or at least as a results presentation), it forces a conversation and offers a shared mental model and terminology — the foundation for a shared vision.
3. Seeing the big picture
Imagine the vastly different perceptions Sales reps, Customer Support teams, C-level, and backend engineers might have since they all meet very different segments at very different stages of their journey. Day-to-day, it makes sense to be an expert in the stages of a user journey you are responsible for. A journey map helps to step back from this and see the bigger picture, where your work fits in, and where assumptions about the majority of users were wrong. It might even help define KPIs across teams that don’t cancel each other out.
4. Uncovering blind spots and opportunities
A user journey map gives you a structured and comprehensive overview of which user needs are already tackled by your product and which ones are either underserved or solved with other tools and touchpoints. Which moments of truth do not get enough attention yet? These are the opportunities and blind spots you can work on in the future.
When is customer journey mapping just a waste of time?
In all honesty, there are also moments when creating a user journey map or running a journey mapping workshop is destined to fail and should better be put on hold. It’s a lot of work, so don’t let this energy go to waste. User journey maps only make sense when there is an intention to collaboratively work on and with them. Here are some of the scenarios and indicators that it’s the wrong moment for a journey map:
No buy-in for the workshop: The requirements of a successful journey workshop are not met, e.g., there is not enough time (60 minutes over lunch won’t do the trick), only a few team members are willing to attend, and/or key stakeholders refuse to have their assumptions challenged.
Isolated creation: The whole creation process of the user journey map happens isolated from the team, e.g., it is outsourced to an agency or an intern. Nobody from the team observes or runs the user research, or is consulted for input or feedback on the first drafts. There is no event or presentation planned that walks the team through the output. Finally, a very detailed, 10-foot-long poster appears in a hallway, and none of the team members ever find time to read, process, or discuss it with each other.
UX theater: For one reason or another, there is no time/resources allocated to user research or reviewing existing insights whilst creating the map (usability tests with non-users do not count in this case, though). Such an approach, also known as, can do more harm than good since the resulting user journey may only reinforce wrong assumptions and wishful thinking about your users.
Unclear objectives: The user journey map is only created because it is on your UX design checklist, but the purpose is unclear. If you are unsure what you or your stakeholders want to achieve with this journey map, clarify expectations and desired output before investing more energy into this. E.g., there is a chance you were only meant to do a usability review of a bumpy app workflow.
Lack of follow-through: Creating a user journey map is just the start. Without a plan to implement changes based on insights gathered, the map is merely a paper exercise. This lack of action can result from limited resources, lack of authority, or inertia. It's vital to establish a process for turning insights from the map into design improvements or strategy adjustments. This includes assigning tasks, setting deadlines, and defining success metrics to ensure the map drives real change and doesn't end up forgotten.
Overcomplication: Sometimes, to capture every nuance and detail of the user experience, teams can create an overly complex user journey map. This can make the map difficult to understand and use, particularly for team members who weren't involved in its creation. A good user journey map should balance detail and clarity, providing insightful and actionable information without overwhelming its users.
Failure to update: User expectations, behaviors, and the digital landscape constantly evolve. A user journey map that remains static will quickly become outdated. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to ensure that the map reflects the current state of user experiences. This requires a commitment to ongoing user research and a willingness to adjust your understanding of the user's path as new information becomes available.
The good news is: UX maturity in an organization can change rapidly, so even if you run into one of the obstacles above, it is worth revisiting the idea in the future. Once you’re good to go, you can get started with the user journey map examples and templates below.
User journey mapping: examples, templates & tools
There is more than one way to do it right and design a great user journey map. Every organization and industry has its own templates, tools and approaches to what elements are most important to them. The following examples and template will give you an idea of what a user journey map can look like if you decide to create one yourself. Make it your own, and change up the sections and design so they make sense for your product and use cases.
User journey map template and checklist
To give you a first orientation, you can use this user journey template and check the two fictional examples below to see how you could adapt it for two very different industries: instant meal delivery and healthcare.
Click here to download a high-resolution PDF of the user journey map template.
While there is no official standard, most other user journey maps contain the following elements or variations of them:
Key phases (or ‘stages’) start when users become aware of a problem they need to solve or a goal they want to achieve and may end when they evaluate whether they achieved their goal or enter a maintenance phase. E.g., user journeys for e-commerce could be structured along the classic funnel of:
Consideration
Delivery & use
Loyalty & advocacy
2. Jobs to be done
Whilst some other user journey templates might call this section ‘steps’ or ‘tasks’, it can be very beneficial to structure the stages into ‘jobs to be done’ (JTBD) instead. This framework helps you distinguish better between the actual goal of a user vs. the tasks required to get there . For example, safe online payments are never a goal of a user, this is just one of many jobs on the long way to get new sneakers on their feet. Ideally, users ‘hire’ your product/service to assist them with some of the JTBD on their journey. Phrase your JTBD as verb + object + context . Examples:
Install app on phone
Tip delivery driver
Buy new shoes
Naturally, the stages closest to your current (and future) solution require a more detailed understanding, so you might want to investigate and document deeper what JTBDs happen there.
3. Needs and pains
Users have needs and pains every step along the journey. Use this section to collect the most important needs and potential pains, even if not all apply in all cases. Ask:
What are the repeating themes, even the ones you are (currently) not able to solve with your product?
Phrase pains and needs as I- or me-statements from the user perspective, e.g., ‘I forgot my login details, ‘I am afraid to embarrass myself’ or ‘My day is too busy to wait for a delivery.’
Which are the pains and needs that are so severe that, if not solved, they can become real deal-breakers for your product or service?
On the last point, such deal-breaker and dealmaker situations, or ‘ moments of truth ’, require particular attention in your product decisions and could be visually highlighted in your journey. In a meal delivery, the taste and temperature of the food are such a moment of truth that can spoil the whole experience with your otherwise fantastic service.
4. Emotional curve
An emotional curve visualizes how happy or frustrated users are at certain stages of their journey. Emojis are commonly used to make it easy to understand and empathize with the emotional state of the user across the whole journey. It can be a surprising realization that users are not delighted with your witty microcopy, but you already did a great job by not annoying them. It is also a good reminder that what might personally excite you is perceived as stressful or overwhelming by most other users. Strong user quotes can be used for illustration.
5. Brand and product touchpoints
Here, you can list current and planned touchpoints with your brand and product, as well as. Whilst the touchpoints when using your product might be obvious, others early and late in the journey are probably less obvious to you but critical for the user experience and decision to use or return to your product. This is why it is worthwhile to include them in your map. Make sure your journey does not get outdated too soon, and don’t list one-off marketing campaigns or very detailed aspects of current workflows — just what you got in general so there is no major revision needed for a couple of years.
6. Opportunities for improvement
As you map out your user journey, it is important to not only identify the current touchpoints and experiences but also opportunities for improvement. This could include potential areas where users may become frustrated or confused, as well as areas where they may be delighted or pleasantly surprised.
By identifying these opportunities, you can prioritize making meaningful improvements to the user experience and ultimately creating a more positive, long-lasting relationship with your users.
7. Other tools and touchpoints
This may seem the least interesting aspect of your journey or a user interview, but it can tell you a lot about blind spots in your service or potential partnerships or APIs to extend your service. E.g., Google Maps or WhatsApp are common workaround tools for missing or poor in-app solutions.
User journey map example 1: health industry
The following example is for a fictional platform listing therapists for people in need of mental health support, helping them find, contact, schedule, and pay for therapy sessions. As you can see, the very long journey with recurring steps (repeated therapy sessions) is cut short to avoid repetition.
At the same time, it generalizes very individual mental health experiences into a tangible summary. While it is fair to assume that the key phases happen in this chronological order, JTBD, timing, and the number of sessions are kept open so that it works for different types of patients.
You can also see how the journey covers several phases when the platform is not in active use. Yet, these phases are milestones in the patient’s road to recovery. Looking at a journey like this, you could, for example, realize that a ‘graduation’ feature could be beneficial for your users, even if it means they will stop using your platform because they are feeling better.
This user journey map is fictional but oriented on Johanne Miller’s UX case study Designing a mental healthcare platform .
User journey map example 2: delivery services
What the example above does not cover is the role of the therapist on the platform — most likely they are a second user type that has very different needs for the way they use the platform. This is why the second example shows the two parallel journeys of two different user roles and how they interact with each other.
Nowadays, internal staff such as delivery drivers have dedicated apps and ideally have a designated UX team looking out for their needs, too. Creating a frictionless and respectful user experience for ‘internal users’ is just as critical for the success of a business as it is to please customers.
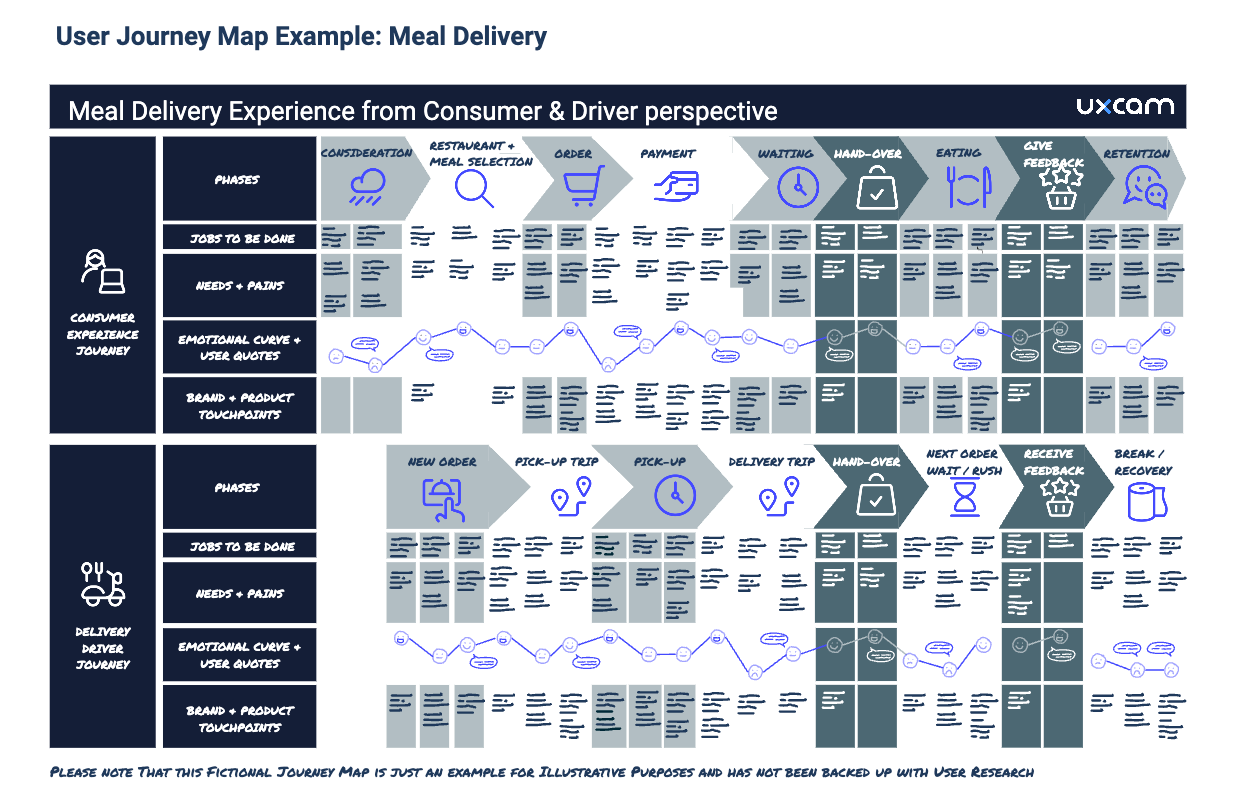
User journey map example: meal delivery. Please note that this fictional journey map is just an example for illustrative purposes and has not been backed up with user research.
For more inspiration, you can find collections with more real-life user journey examples and customer journey maps on UXeria , eleken.co & userinterviews.com , or check out free templates provided by the design tools listed below.
Free UX journey mapping tools with templates
No matter whether you’re a design buff or feel more comfortable in spreadsheets, there are many templates available for free(mium) tools you might be already using.
For example, there are good templates and tutorials available for Canva , Miro and even Google Sheets . If you are more comfortable with regular design software, you can use the templates available for Sketch or one of these two from the Figma (template 1 , template 2 ) community. There are also several dedicated journey map tools with free licenses or free trials, e.g., FlowMapp , Lucidchart and UXPressia , just to name a few.
Be aware that the first draft will require a lot of rearrangement and fiddling until you get to the final version. So it might help to pick where this feels easy for you.
How do I collect data for my app user journey?
User journey maps need to be rooted in reality and based on what users really need and do (not what we wish they did) to add value to the product and business strategy. Hence, user insights are an inevitable step in the creation process.
However, it’s a huge pile of information that needs to be puzzled together and usually, one source of information is not enough to cover the whole experience — every research method has its own blind spots. But if you combine at least two or three of the approaches below, you can create a solid app user journey .
1. In-house expertise
The people working for and with your users are an incredible source of knowledge to start and finalize the journey. Whilst there might be a few overly optimistic or biased assumptions you need to set straight with your additional research, a user journey mapping workshop and/or expert interviews involving colleagues from very different (user-facing) teams such as:
customer service
business intelligence
customer insights
will help you collect a lot of insights and feedback. You can use these methods to build a preliminary skeleton for your journey but also to finalize the journey with their input and feedback.
2. Desk research
Next to this, it is fair to assume there is already a ton of preexisting documented knowledge about the users simply floating around in your company. Your UX research repository and even industry reports you can buy or find with a bit of googling will help. Go through them and pick the cherries that are relevant for your user journey. Almost anything can be interesting:
Old research reports and not-yet-analyzed context interviews from earlier user interviews
NPS scores & user satisfaction surveys
App store feedback
Customer support tickets
Product reviews written by journalists
Competitor user journeys in publicly available UX case studies
Ask your in-house experts if they know of additional resources you could check. And find out if there’s already a long-forgotten old journey map from a few years ago that you can use as a starting point (most organizations have those somewhere).
3. Qualitative user research
Qualitative research methods are your best shot to learn about all the things users experience, think, and desire before and after they touch your product. In-depth interviews and focus groups explore who they are and what drives them. You could show them a skeleton user journey for feedback or co-creation .
This could also be embedded into your user journey mapping workshop with the team. Alternatively, you can follow their actual journey in diary studies , in-home visits or shadowing . However, in all these cases it is important that you talk to real users of your product or competitors to learn more about the real scenarios. This is why usability testing with non-users or fictional scenarios won’t help much for the user journey map.
4. Quantitative research
Once you know the rough cornerstones of your user journey map, surveys could be used to let users rate what needs and pains really matter to them. And what their mood is at certain phases of the journey. You can learn how they became aware of your product and ask them which of the motives you identified are common or exotic edge cases. Implementing micro-surveys such as NPS surveys , CES , and CSAT embedded into your product experience can give additional insights.
5. Customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey
Customer satisfaction surveys (or CSATs for short) are important tools that measure your customers' satisfaction with your product or service. It is usually measured through surveys or feedback forms, asking customers to rate their experience on a scale from 1 to 5. This metric can give valuable insights into the overall satisfaction of your customers and can help identify areas of improvement for your product.
CSAT surveys can be conducted at different customer journey stages, such as after purchase or using a specific feature. This allows you to gather feedback on different aspects of your product and make necessary changes to improve overall satisfaction.
The benefit of CSAT lies in understanding how satisfied customers are with your product and why. By including open-ended questions in the surveys, you can gather qualitative insights into what aspects of your product work well and what needs improvement.
5. User analytics
User analytics is a beautiful source of information, even if it has its limits. Depending on what tools you are using (e.g., Google Analytics, Firebase, Hubspot, UXCam), you can follow the digital footprints of your users before and when they were using the product. This may include acquisition channels (input for brand touchpoints and early journey phases), search terms that brought them to your product (input for needs and pains), and how they navigate your product.
Unlike a usability test, you can use screen flows and heatmaps to understand how your users behave naturally when they follow their own agenda at their own pace — and how often they are so frustrated that they just quit. Knowing this gives you pointers to negative user emotions at certain journey steps and even helps identify your product’s moments of truth. Whilst you cannot ask the users if your interpretations are correct, checking analytics already helps you prepare good questions and talking points for user interviews or surveys.
Curious to know how heatmaps will look in your app? Try UXCam for free — with 100,000 monthly sessions and unlimited features.
How can I utilize UXCam to collect App User Journey data?
If you have UXCam set up in your mobile app, you can use it to support your user journey research. You can find many of the previously mentioned user analytics features ( screen flows and heatmaps , including rage taps ) here as well.
UXCam can also be an invaluable asset for your qualitative research . Especially for niche products and B2B apps that normally have a lot of trouble recruiting real users via the usual user testing platforms.
UXCam’s detailed segmentation options allow you to identify exactly the users you want to interview about their journey — and reach out to them via either email or UXCam push notifications , which can include invitation links for your study, a survey or an additional screener.
Additionally, UXCam's session replay feature allows you to watch recordings of user sessions, providing valuable insights into how users interact with your app and where they may face challenges.
Where can I learn more?
Don’t feel ready to get started? Here are a few additional resources that can help you dive deeper into user journey mapping and create the version that is best for your project.
Creating user journey maps & service blueprints:
Mapping Experiences by Jim Kalbach
Journey Mapping 101
How to create customer journey maps
Customer Journey Stages for Product Managers
The Perfect Customer Journey Map
Planning and running user journey mapping workshops:
Journey mapping workshop
Jobs to be done:
The Theory of Jobs To Be Done
Moments of truth in customer journeys:
Journey mapping MoTs
What is a user journey map?
A user journey map is a visual representation of the process that a user goes through to accomplish a goal with your product, service, or app.
What is a user journey?
A user journey refers to the series of steps a user takes to accomplish a specific goal within a product, service, or website. It represents the user's experience from their point of view as they interact with the product or service, starting from the initial contact or discovery, moving through various touchpoints, and leading to a final outcome or goal.
How do I use a user journey map in UX?
User journey maps are an essential tool in the UX design process, used to understand and address the user's needs and pain points.
Related Articles
Best behavioral analytics tools to optimize mobile app UX
20+ powerful UX statistics to impress stakeholders
Mobile UX design: The complete expert guide
5 Best User Journey Mapping Tools
App user journey: Mapping from download to daily use
Your guide to the mobile app customer journey
Customer journey optimization: 6 Practical steps
Alice Ruddigkeit
Get the latest from uxcam.
Stay up-to-date with UXCam's latest features, insights, and industry news for an exceptional user experience.
Related articles
User journey map guide with examples & free templates.
Learn experience mapping basics and benefits using templates and examples with mixed-methods UX researcher Alice...

45 Mobile App Best Practices: The Ultimate List 2024
Proven best practices to improve user experience and performance of your mobile...

Jonas Kurzweg
Growth Lead
North Star Metric Examples from Tech Giants
Discover 9 North Star Metric examples to guide your business growth strategy, from user engagement to revenue, and align your team's...

Growth Manager
A comprehensive guide to effective customer journey mapping
A brand's user experience shapes its target audience's entire perception of your organization. Maximize audience engagement with customer journey mapping.

Discover key challenges today's marketing teams are facing, as well as opportunities for businesses in 2024.

Incorporating customer journey mapping into your web design process helps elevate consumer engagement to drive loyalty and sales.
Many in-house teams and web designers strive to better serve users by optimizing their customer experience (CX). Considering how your customers use your platform or service helps you see your website from a user perspective, letting you shape your design to better meet their needs. To achieve this, web designers can look to customer journey mapping.
A particularly handy tool for user experience (UX) design , this process helps teams understand who their users are and how to fulfill their expectations, guiding development decisions for improved audience engagement. Learn more about customer journey mapping and how you can implement it to enhance your CX.
User journey mapping: an overview
User journey mapping, also known as customer journey mapping (CJM), maps a website visitor's experience from their perspective. Presented through a visual diagram, the customer journey map charts the user’s path as they seek information or solutions, starting at the homepage and tracking their routes across other menus and links.
To create a customer journey map, you begin by researching who users are, what they want from your site, and how positive or negative their experiences have been.
There are two main purposes for mapping your customers’ journey.
1. Improve customer experience
This is the ultimate goal of CJM. Site navigation can be especially tricky to assess because you’re already familiar with the layout. A fresh perspective on your site often uncovers overlooked details such as navigation issues or broken links.
By conducting research on UX trends and visually mapping your results, you’ll identify any parts of your design that confuse or frustrate visitors. This process also reveals areas that work well, which you can repurpose elsewhere in the design.
2. Maintains ease-of-use as your site grows
A customer journey map can make even a simple site more straightforward to navigate. When your website or business grows, you may need to add content and features to accommodate the expansion. Implementing customer journey mapping ensures your website's fundamental flow remains intuitive and that new material and features are easily discoverable and usable.
Primary user journey map types
There are various ways to approach customer journey mapping based on the specific insights you’re seeking. The end result of each map will look similar, but the focus of each is different — which changes the information it offers. Here are three standard types of maps to get you started.
Current state
The current state map is the most common type. It evaluates your website’s present state to better understand visitors’ current experiences, helping identify improvement opportunities for its existing design.
Future state
A future state map explores a hypothetical "ideal" website, considering the visitor’s experience if every site component were optimized. This map is helpful when planning a total redesign or a specific change. When you collect user research and translate the results into your map, you can present a visual outline to your client or company for a straightforward explanation.
Persona-based
A persona-based map lays out the journey of a single designated type of user, or persona (which we will define below). This type of diagram is useful when optimizing your website for a specific sector of your audience with particular needs.

Learn best practices for integrating the workflows between design and development in this free webinar.
The 5-step customer journey mapping process
Once you’ve set clear goals for your map’s achievements, you can select the appropriate diagram type. To begin visualizing your user journey, follow this five-step process.
1. Define the map’s scope
Your map may focus on just one customer interaction or outcome, such as finding the newsletter sign-up sheet or making a payment, or it could cover the entire website’s navigation. A focused scope helps you troubleshoot a problem area or ensure an especially critical element functions properly. Alternatively, a larger-scope map provides a big-picture perspective of how the site works as a whole. Creating a comprehensive map is more complex, but high-level mapping helps comprehend the entire user experience from beginning to end.
2. Determine your user personas
A persona describes a particular type of visitor using your site. When imagining and defining these users, you can assign a name to each and include details about who they are, what they’re looking for, and why.
Focus on users who contribute most to your business goals, consulting your marketing or sales teams for insights. To define your customer personas, explore current user behavior through surveys, online reviews, and email list responsiveness.
For example, if you’re creating a website for a store that sells artisanal coffee-making tools, your personas could be:
- The gift giver. This user only knows a little about coffee but wants to select an impressive gift for someone else. They’ll need help with purchase decisions, so they might interact with an FAQ or chat feature before visiting the products page. They may also leave your site if overwhelmed by options, so it’s important to offer helpful information proactively. This will keep them engaged and more likely convert them to paying customers.
- The coffee nerd. This person is knowledgeable and always seeks the highest-quality tools, so easily accessible product details and customer reviews are important to them. To support their user experience and encourage them to purchase, ensure these elements are easily discoverable.
- The tourist. This user is on vacation and looking for a cute brick-and-mortar shop to visit. They aren't interested in your online store, but an appealing photo of your physical store with easily accessible hours and location information may convince them to come by in person.
These three types of users have very different needs and goals when visiting your website. To capture all of their business, create a map for each of them to ensure you accommodate their specific wants and circumstances.
3. Give the personas context
User context is the “when” and “how” of each persona visiting your site. A user will have a different experience loading your site on a mobile device than on a laptop. Additionally, someone in no rush may use your website differently than someone looking more urgently with a specific purpose.
Figure out when, how, and in what mindset your personas most commonly visit your site to map their experience accurately. This context has very concrete impacts on your finished design. If visitors tend to look for one specific page whenever in a hurry (like contact or location information), placing those details on the front page or prominently linking to it will smooth the user experience for those users.
Here’s an example of how to place a persona in context.
Persona: Jo is an apartment hunter in her early 20s and is still in college. She's looking for off-campus housing for herself and some roommates. The collective group values location and cost more than apartment features.
Context : Jo is in a hurry and trying to visit as many apartments as possible. She’s looking at property rental websites that clearly state apartment addresses in each listing.
Method : Jo is browsing the sites on her iPhone.
4. List persona touchpoints
Touchpoints mark when the user makes a purchase decision or interacts with your user interface (UI) . They include visitors' actions to move toward their goals and consider each associated emotion. The first touchpoint is how they reach your website — such as tapping a social media ad, clicking on a search result, or entering your URL directly.
First, list each action the visitor took and their corresponding emotional reactions. Subsequent touchpoints include instances when they navigate a menu, click a button, scroll through a gallery, or fill out a form. When you diagram the route through your site in an A-to-Z path, you can place yourself in the persona's mind to understand their reactions and choices.
A met expectation — for example, when clicking a "shop" button takes them to a product gallery — will result in a positive emotional reaction. An unmet expectation — when the “shop" link leads to an error page — will provoke an adverse reaction.
5. Map the customer journey
Illustrate the user journey by mapping these touchpoints on a visual timeline. This creates a narrative of users’ reactions across your entire service blueprint. To represent your users’ emotional states at each touchpoint, graph their correspondences like this:

The map helps you understand the customer experience as a whole.
For example, based on the diagram above, touchpoint 3 is the largest navigation challenge on the website. The graph also shows that the user's mood eventually rebounds after the initial setback. Improving the problem element in touchpoint 3 will have the biggest impact on elevating the overall user experience.
Customer journey mapping best practices
Now that you understand the mapping process, here are some best practices to implement when charting your customer journey.
- Set a clear objective for your map: Define your CX map’s primary goal, such as improving the purchase experience or increasing conversions for a specific product.
- Solicit customer feedback: Engage directly with customers through surveys or interviews so you can implement data-driven changes. Ask users about their journey pain points and invite both positive and negative feedback on the overall navigation.
- Specify customer journey maps for each persona: To specifically serve each customer persona, consider charting separate paths for each based on their behaviors and interests. This approach is more customer-centric, as not all user types interact with your website the same way.
- Reevaluate your map after company or website changes: As your business scales, your website must evolve — and so will your customer’s path. Review your map when making both large and small website adjustments to ensure you don’t introduce new user challenges. Navigational disruptions can frustrate visitors, causing would-be customers to leave your site and seek competitors .
Optimize your user journey map with Webflow
A user journey map is only as effective as the improvements it promotes. When redesigning your website based on insights your map provides, explore Webflow’s vast resource bank to streamline your design processes.
Webflow offers web design support with diverse guides , tutorials , and tools for straightforward web design. Visit Webflow today to learn how its site hosting , e-commerce , and collaboration resources support enhanced user experience for better engagement.
Webflow Enterprise gives your teams the power to build, ship, and manage sites collaboratively at scale.
Subscribe to Webflow Inspo
Get the best, coolest, and latest in design and no-code delivered to your inbox each week.
Related articles
What is customer experience? An essential guide
Learn why customer experiences are essential for your bottom line, and discover practical strategies to implement across your digital channels.

How to create marketing personas that start with empathy
Treating customers with respect earns you loyalty. Dig into marketing personas that reflect real people to gain the most valuable insight.
Elevate customer satisfaction with the power of AI personalization
Discover how different industries use AI personalization to improve customer experiences, and learn how to use hyper-personalization to maximize your marketing
How to implement and optimize effective customer-centric design
Implementing customer-centric design invites customers to collaborate with your brand and help shape truly unique products.

Multi-touch attribution models: A complete guide
Multi-touch attribution (MTA) enables you to assess multiple touchpoints to determine which ones are most critical in the path to purchase.

Keeping up with customer expectations in 2024
Tips for delighting your audience on the web in the new year
Get started for free
Try Webflow for as long as you like with our free Starter plan. Purchase a paid Site plan to publish, host, and unlock additional features.
Transforming the design process at
- Interactions
- Localization
- Figma to Webflow Labs
- DevLink Labs
- Feature index
- Accessibility
- Webflow vs WordPress
- Webflow vs Squarespace
- Webflow vs Shopify
- Webflow vs Contentful
- Webflow vs Sitecore
- Careers We're Hiring
- Webflow Shop
- Accessibility statement
- Terms of Service
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Cookie preferences
- Freelancers
- Global alliances
- Marketplace
- Libraries Beta
- Hire an Expert
- Made in Webflow
- Become an Expert
- Become a Template Designer
- Become an Affiliate
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Ux mapping methods compared: a cheat sheet.

November 5, 2017 2017-11-05
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
Designing and developing a product often involves a large team of people with different backgrounds and experiences who must be on the same page about the project goals, the user needs and behaviors, and even the component processes involved. This common understanding is often built with visualizations (commonly referred to as mappings). Mappings make sense of and describe various aspects and processes associated with a product.
In This Article:
Four types of mapping, empathy mapping, customer journey mapping, experience mapping, service blueprinting, three-step decision framework, use all four ux mapping methods.
This article gives an overview of four commonly used mappings, their defining characteristics, and when to use which:
- Empathy mapping
- Customer journey mapping
- Experience mapping
- Service blueprinting

Additionally, this article will outline the decisions that must be made before creating any of these mappings in a simple three-step approach framework.
Empathy maps help team members understand the user’s mindset.

Empathy map : A tool used to articulate what we know about a particular type of user. It externalizes user knowledge in order to 1) create a shared understanding, and 2) aid in decision making.
Characteristics:
- The map is split into 4 quadrants: Says, Thinks, Feels, Does.
- It shows user’s perspective regarding the tasks related to the product.
- It is not chronological or sequential.
- There is one empathy map for each persona or user type (1:1 mapping).
Why use it:
- To build empathy for your users
- To force alignment and understanding about a user type
When to use it:
- Beginning of any design process
- When categorizing research notes from a user interview
Customer journey maps focus on a specific customer’s interaction with a product or service.

Customer journey map : A visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal tied to a specific business or product. It’s used for understanding and addressing customer needs and pain points.
In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user goals and actions into a timeline skeleton. Next, the skeleton is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative. Finally, that narrative is condensed into a visualization used to communicate insights that will inform design processes.
- The map is tied to a specific product or service.
- It is split into 4 swim lanes: phases, actions, thoughts, mindsets/emotions.
- Including her mindset, thoughts, and emotions
- Leaving out most process details
- It is chronological.
- There is one map per persona/user type (1:1 mapping).
- To pinpoint specific customer journey touchpoints that cause pain or delight
- To break down silos to create one shared, organization-wide understanding of the customer journey
- To assign ownership of key touchpoints in the journey to internal departments
At any point in the design process, as a reference point amongst a team throughout a product design cycle
Experience maps generalize the concept of customer-journey maps across user types and products.

Experience map: A visualization of an entire end-to-end experience that a “generic” person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. This experience is agnostic of a specific business or product. It’s used for understanding a general human behavior (as opposed to a customer journey map, which is more specific and focused on related to a specific business).
- It is not tied to a specific product or service.
- It offers a general human perspective; it is not a specific to a particular user type or product/service.
- It depicts events in chronological order.
- To understand a general human behavior
- To create a baseline understanding of an experience that is product/service agnostic
- Before a customer journey map in order to gain understanding for a general human behavior
- When converging multiple experiences (tool and specific user agnostic) into one visualization
Service blueprints are counterparts to customer journey maps, focused on the employees.

Service blueprint : A visualization of the relationships between different service components — people, props (physical or digital evidence), and processes — that are directly tied to touchpoints in a specific customer journey.
Think of service blueprints as a part two to customer journey maps. Similar to customer journey maps, blueprints are instrumental in complex scenarios spanning many service-related offerings. Blueprinting is an ideal approach to experiences that are omnichannel, involve multiple touchpoints, or require a crossfunctional effort (that is, coordination of multiple departments).
- It is tied to a specific service.
- It is split into 4 swim lanes: customer actions, frontstage actions, backstage actions, and support processes.
- Focusing on the service provider and employees
- Leaving out most customer details
- It is chronological and hierarchical.
- To discover weaknesses in the organization
- To identify opportunities for optimization
- To bridge crossdepartment efforts
- To break down silos and create one shared, organization-wide understanding of how the service is provided
- After customer journey mapping
- Before making organizational or process changes
- When pinpointing a funnel or breakpoint internally
Before beginning any mapping effort (regardless of the type), 3 decisions must be made:
1. Current (as-is) vs. future (to-be)
This decision involves the actions and states depicted in the visualization: do they reflect the current state of the world or a desired state of the world?
- Current mappings are based on an actual “today” state of what you are mapping. This approach is ideal when the mapping goal is to identify and document existing problems and pain points. Use current state maps to help analyze research or align a team around a data-validated problem.
- Future mappings are based on an “ideal” state for a user type, experience, or a to-be service structure. Future state maps help reinvent and conceive how a user or experience would feel in the future. Use future state maps to set a benchmark or goal for the ideal form of your product or service.
2. Hypothesis vs. research
This decision depends on the type of input that you will use to build your mapping.
- Hypothesis mappings are based on an accumulation of existing understanding within a team or organization. This approach is a great way to merge multiple existing team views, create a research plan (based on the gaps that emerge from your hypothesis map), and make a first step towards a higher-fidelity, research-based map.
- Research mapping is based on data gathered specifically for building the map. This approach is best when there are time and resources dedicated to creating a research plan. While this method creates the best maps, it takes time and significant buy-in. Regardless of where you start, your maps should be iterative and constantly updated with new findings.
3. Low-fidelity vs. high-fidelity
This decision pertains to the quality of the final map visualization.
- Low-fidelity maps are unpolished and often created with sticky notes in a flexible, unrefined manner. These maps are best in an early part of the process. Low fidelity means little commitment or creation effort and empowers people to collaborate, revise, and update as needed. Use sticky notes (physically on the wall or digitally with tools like Mural.co) or collaborative excel sheets.
- High-fidelity maps are polished, created digitally, and look final. High fidelity maps are the best for creating an artifact that is going to be shared amongst many. High fidelity can be easier to read but less flexible because of the “finished” nature of the product. These maps are often created digitally and then dispersed.
All UX maps have two-fold benefits. First, the process of creating a map forces conversation and an aligned mental model. Second, the shared artifact resulting from the mapping can be used amongst your team, organization, or partners to communicate an understanding of your user or service. This artifact can also become the basis for decision making as the team moves forward.
Using one mapping method over another will not make or break a project. Ideally, a combination of all four will be used as needed at different points in your process to create an in-depth understanding of your users and organization.
Kyle, Beth. Pregnancy Experience Map. http://www.bethkyle.com/portfolio-item/pregnancy-experience-map/
Related Courses
Generating big ideas with design thinking.
Unearthing user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Interaction
Orchestrate people, props, and processes that are core to your digital experience
Journey Mapping to Understand Customer Needs
Capture and communicate UX insights across complex interactions
Related Topics
- Customer Journeys Customer Journeys
- Design Process
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YpC3R1zNdA
UX Mapping Methods: When to Use Which

The Role of Design
Don Norman · 5 min

Design Thinking Activities
Sarah Gibbons · 5 min

Design Thinking: Top 3 Challenges and Solutions
Related Articles:
Building Interactive UX Maps
Megan Brown · 6 min
User Journeys vs. User Flows
Kate Kaplan · 4 min
The 5 Steps to Service Blueprinting
Sarah Gibbons · 4 min
Service Design 101
Design Thinking Builds Strong Teams
Design Thinking: Study Guide
Kate Moran and Megan Brown · 4 min
New NPM integration: design with fully interactive components from top libraries!
UX Customer Journey — How to Map Out User Experience
Customer journey maps are effective visualizations that help organizations understand their customers and create better experiences. Product teams use these journey maps during the design process to solve usability issues, streamline user experiences, and identify opportunities that help the organization achieve its business goals.
Creating customer journey maps requires research, collaboration, the right tools, and an appropriate visualization format. Luckily, there are plenty of tools to streamline journey mapping, which we cover later in this article.
Build fully interactive prototypes of your user journeys that accurately represent the final product experience. Sign up for a free trial and enhance your customer experiences with UXPin.
Build advanced prototypes
Design better products with States, Variables, Auto Layout and more.
What is a UX Customer Journey?
A customer journey represents the steps customers go through when interacting with a product, service, or business process. Companies use journey maps to visualize this end-to-end process and identify customer needs across multiple touchpoints.
User journey map vs. customer journey map
While the theory and application are similar, there is a slight difference between a user journey map and a customer journey map:
- User journey map : A visual representation of the steps to complete a specific task or goal.
- Customer journey map : A broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints, including all the interactions with an organization.
Benefits of mapping the customer journey
Mapping customer journeys offer many benefits for organizations and teams, notably improving user experience and customer satisfaction by identifying pain points and opportunities.
Some key benefits of customer journey maps include:
- Enhanced customer understanding: helps organizations gain insights about their target audience’s needs, preferences, motivations, and pain points by visualizing the experience from the customer’s point of view.
- Pinpoint issues and opportunities: allows teams to identify which steps cause difficulty or frustration for customers. Conversely, the organization can find areas for improvement and innovation.
- Streamlined and consistent experiences: organizations can identify and fix inconsistencies and gaps across multiple touchpoints, creating a more cohesive and consistent user experience.
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty: by streamlining and optimizing product processes, organizations improve customer satisfaction leading to increased loyalty, recommendations, and growth.
- Informed decision-making: journey maps help teams across the organization make decisions about design, development, marketing, etc. Many organizations use these visualizations to prioritize features, updates, and investments.
- Cross-functional collaboration: customer journey maps allow organizations to visualize how customers pass through each department, creating opportunities for teams to collaborate and find ways to improve the customer experience at each touchpoint–UX design, marketing, customer support, social media, etc.
- Creating benchmarks and continuous evaluation: organizations can use customer journey maps to evaluate projects and how products evolve and improve with releases.
Customer Personas – The Foundation for Customer Journey Maps

A user persona (customer persona) is UX research artifact design teams use as a fictional representation of a user group, including their demographics, behaviors, goals, and pain points.
These user personas are the foundation for customer journey maps because they provide the framework for understanding how different types of users engage with the organization and its products.
For example, if a company is designing a fitness app, the research team might create personas for three primary user groups:
- Yoga practitioners
These three user personas will have different needs, priorities, goals, challenges, and ambitions. Their interactions with your brand and how they enter customer journeys will also differ.
Incorporating personas into the customer journey
User personas give designers a start and end goal for customer journey maps. They can use the persona’s behavioral patterns to highlight how these users interact with a product or service and tailor content that meets their needs.
Returning to our fitness app example above: Researchers learn that yoga users prefer to use the desktop application at home, while gym-goers use the mobile app in their local gym. The runners view their daily running program on a mobile device before their run and don’t view the app again until they return.
The customer journey maps for these three users will look completely different, each with varying steps, challenges, and goals.
This example demonstrates how customer journeys for each persona vary and the importance of separately acknowledging each group’s needs, behaviors, challenges, and goals.
Stages of a Customer Journey
There are several key stages of a customer journey:
- Awareness: the moment someone becomes aware of your brand through social media, paid ads, word-of-mouth, etc.
- Consideration: customers research your product and compare it to others by reading reviews, comparing prices, and evaluating features.
- Onboarding: once customers decide to use your product, they set up an account and learn to use its features . If your product uses a freemium model, these people may be users before converting to paying customers.
- Engagement: customers regularly use and engage with your product, its features, and its content. During engagement , they often upgrade to paid services and make purchases.
- Support: customers may require support during their journey. Organizations must answer questions (customer service, docs, etc.), identify ways to streamline experiences, and reduce support queries.
- Retention & loyalty: when customers have positive engagement and support experiences, they will continue using the product and recommend it to others.
Touchpoints and Channels
Touchpoints and channels are points of interaction between a brand and its customers.
Touchpoints
Touchpoints are the interaction points between a customer and a brand, including physical, digital, and emotional. Some touchpoint examples include paid ads, social media posts, customer service interactions, and product experiences.
Channels are the mediums or platforms delivering these touchpoints–for example, social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc.), email marketing, ad channels (Google Ads vs. Facebook Ads), digital products, and physical locations (stores, service centers, events, etc.).
Organizations map these touchpoints and channels to identify areas for improvement and optimize the customer experience.
Emotions, Motivations, and Pain Points
Understanding a user’s emotions, motivations, and pain points throughout the customer journey is crucial, as these elements drive user actions and decision-making.
Here is a rough outline of how these core user elements relate to each other:
- Emotions: The feelings people experience at each stage of the customer journey, including excitement, happiness, frustration, disappointment, and anger. Designers use empathy maps to visualize these emotions across the customer journey.
- Motivations: The reasons why people take action at different stages of the customer journey.
- Pain points: The challenges or obstacles customers experience during a customer journey.
By identifying these factors at each stage of the customer journey map, product teams can create solutions to reduce and mitigate problems while streamlining customer experiences.
Creating a Customer Journey Map
Select the appropriate format and tools for your journey map
The format and tools required for your journey map will depend on its complexity, level of detail, and available resources. Here are some tips:
- Consider your audience: who is the journey map for, and what are their needs? Do you need a high-level overview or a detailed step-by-step analysis?
- Choose a format: the level of detail will dictate the structure and medium of your journey map, including flowcharts, diagrams, infographics, and spreadsheets.
- Use tools: there are many tools for creating and sharing high-quality journey maps, including Lucidchart, UXPressia , Canva, Miro, Mural, and design tools.
- Find collaborators: identify teams, stakeholders , and departments that can offer insights and different perspectives about your customers to make journey maps as accurate and relevant as possible.
Collect and incorporate data from various sources
- List the touchpoints and channels customers will have with your brand for the specific journey, including website, social media channels, customer service, etc.
- Gather research data from customer surveys, user research, user interviews, analytics (product, social media, etc.), and other relevant sources.
- Analyze the data to identify patterns, trends, and behavior . The key is to find common customer pain points and friction across the journey.
- Create a visual representation of your customer journey, illustrating touchpoints and interactions and noting customer emotions, motivations, and pain points at each stage.
Visualize the customer journey in a clear and engaging way
Use your research to create a visualization of your customer journey. Start by sketching the journey and touchpoints or create a simple flow diagram mapping each step.
We recommend using customer journey map templates from Mural , UXPressia , or Miro to streamline the process and produce beautiful visualizations to share with your organization. You can even use a free whiteboard tool like Google Jamboard or create your journey map in a spreadsheet.
Recommended reading from UXPressia: Customer Journey Mapping Mistakes and How to Avoid Them .
Customer Journey Map Examples of Templates
Here are some customer journey map examples of templates that you may use at work or as an inspiration for your own visualizations.
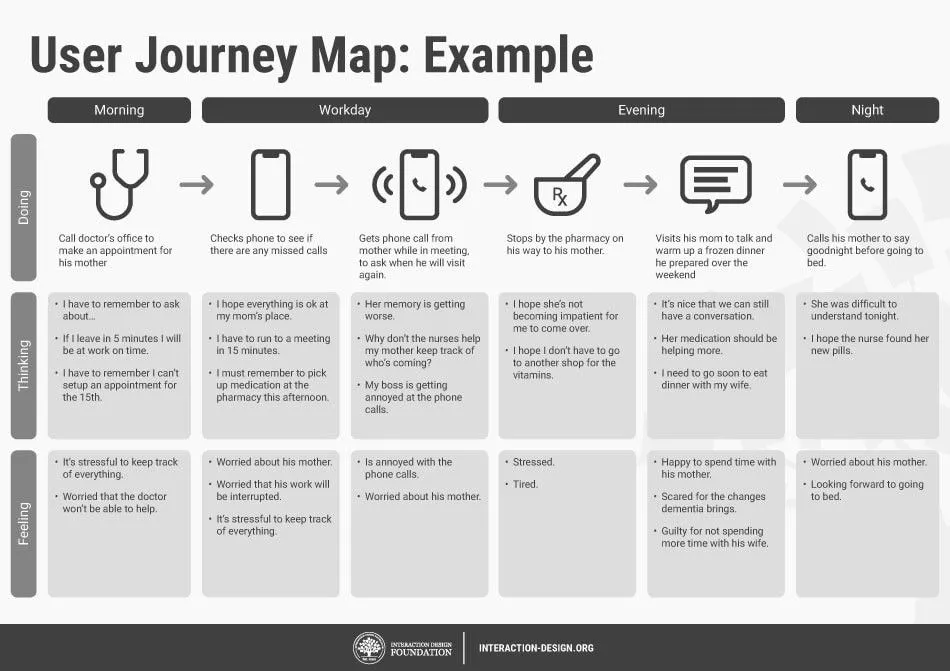
Design, Prototype, and Test Customer Experiences with UXPin
Prototyping and testing are crucial for iterating and evolving customer experiences. Designers must assess various user experiences within a customer journey to ensure they’re free of roadblocks, usability issues, and friction.
Product design teams can use UXPin’s advanced features to build prototypes that accurately replicate the final product experience. These interactive prototypes give designers meaningful, actionable feedback from usability participants and stakeholders to iterate and improve. Create beautiful, intuitive product experiences your customers will love with UXPin. Sign up for a free trial .
Build prototypes that are as interactive as the end product. Try UXPin
by UXPin on 17th April, 2023
UXPin is a web-based design collaboration tool. We’re pleased to share our knowledge here.
UXPin is a product design platform used by the best designers on the planet. Let your team easily design, collaborate, and present from low-fidelity wireframes to fully-interactive prototypes.
No credit card required.
These e-Books might interest you

Design Systems & DesignOps in the Enterprise
Spot opportunities and challenges for increasing the impact of design systems and DesignOps in enterprises.

DesignOps Pillar: How We Work Together
Get tips on hiring, onboarding, and structuring a design team with insights from DesignOps leaders.
We use cookies to improve performance and enhance your experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- What is Customer Experience?
- UX Journey Map
See how XM for Customer Frontlines works
What is ux journey mapping.
12 min read What is a user journey map, and how can it help your business to improve its outcomes? Create your own user journey map and understand customer journey mapping differences with our full guide.
What is user journey mapping?
A user journey map is a visual representation of what a user must do to achieve a goal, and outlines the experience they have with your brand. Their goal might be to complete a purchase, find information, or sign up to a service. Whatever the user’s goal is, a journey map can help businesses to figure out where there are pain points and improve the user or customer experience.
A journey map is best used for outlining complex journeys that involve either multiple events, a particular process with several stages, or involve more than one channel. User journey maps can help to clarify these complicated journeys and ensure that the process is smooth and fulfilling for everyone.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to customer journey mapping
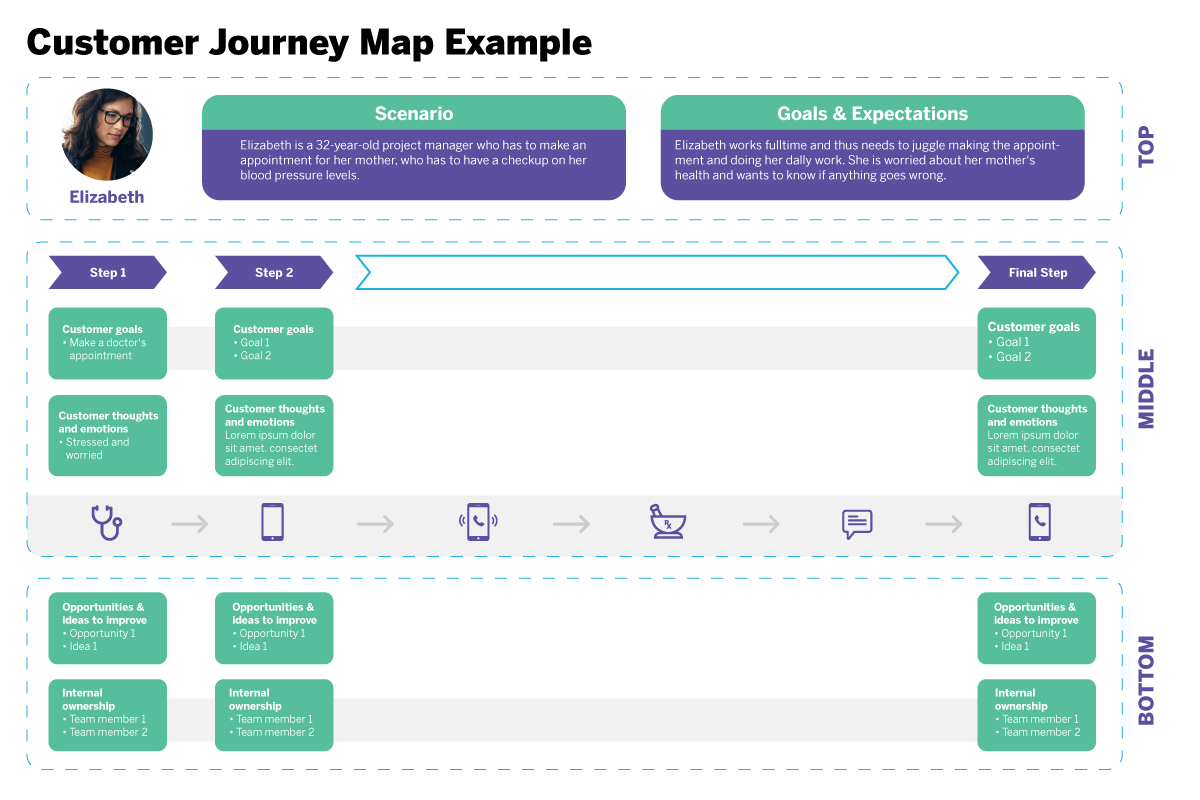
A user journey map / UX journey map vs a customer journey map
Sometimes, the phrases “user journey mapping” or “UX journey mapping are used interchangeably with “customer journey mapping”. In most cases, this is accurate – the users of your website are your customers, so creating a customer journey map will effectively be a UX journey map. However, this doesn’t cover all scenarios. For example:
Customer journey maps don’t cover all users
Customer journey maps are useful for understanding the customer experience you offer, but what if your users aren’t customers? Internal and external stakeholders, researchers, employees, and more might need to find information on your website, even though they’re not customers.
Customer journey mapping is usually tied to a financial goal
Customer journey mapping usually has a financial goal, with a monetary transaction at the end of it (even if the initial goal isn’t, such as a free sign up to a service). A user journey map doesn’t necessarily tie into financial goals – it might be to provide information, for example.
UX journey maps are usually for UX design thinking
A customer journey map is a tool that can be used for many different areas of business – sales journeys, marketing journeys and more can be mapped out. However, a UX journey map is usually used for the UX design process, and might involve more technical information such as website usage data.
Why is a UX journey map important for business?
Getting the complete picture and a deep understanding of your user or customer journey allows your business to understand where problems lie and where positive action can be taken.
Defining your users’ needs, issues, and the scale of their interactions with your brand gives you the ability to fix pain points and develop new pathways for users that you hadn’t thought of before.
For example, perhaps your business has taken a desktop-first approach, offering a great experience for desktop users at the expense of creating a mobile-responsive design. By creating a user journey map, you might see that your users are actually coming in via mobile searches – and with 58.33% of global users choosing mobile , this is quite likely. Your UX journey map gives you a better idea of how to win over your mobile users and provide them with a better user experience.
Why user experience matters
Creating a user experience that meets and exceeds expectations allows you to:
- Create positive feelings and a stronger connection with your users. Fully connected users are on average 52% more valuable than users that are highly satisfied. By offering a positive, connective experience, you can reap the benefits.
- Develop loyal users who return time and time again. With 88% of online users being less likely to return to a website after a bad user experience, it’s important to cultivate loyalty by understanding where your user journeys are failing to impress.
- Invest in your business with a proven ROI. According to Forrester, every dollar invested in UX brings $100 in return on average, an ROI of 9,900%.
- Stand out from the competition. Your journey map might not be too different from a competitor’s – but what will make you stand out is the exceeding of the usual expectations at each stage of the user or customer experience.
Building out a journey map or multiple journey maps for your users allows you to create a deeper relationship with your audience, enabling them to have an intuitive, cohesive experience with your brand.
Components of a thorough user journey map
There are several key elements of a user journey map that are vital for creating an effective service blueprint. You can get started with our basic customer journey map template here , or read on for a more in-depth approach.
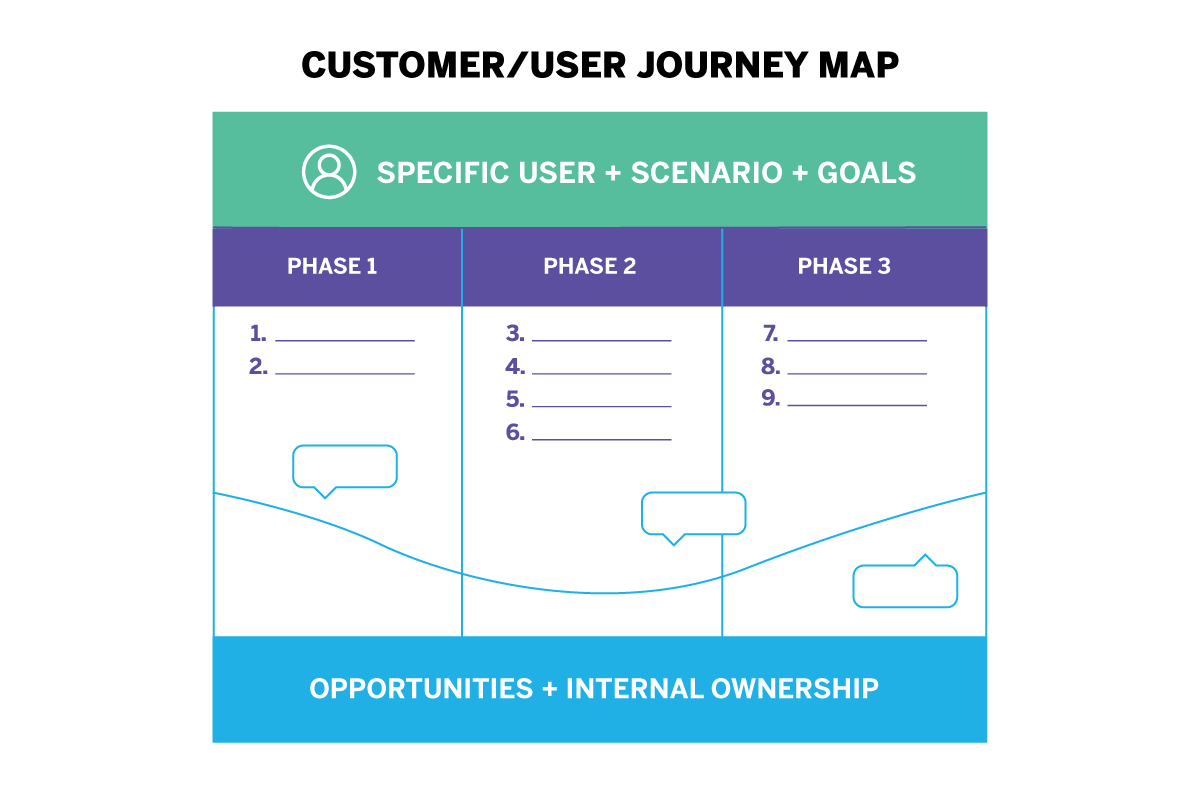
1. The specific user
You will likely create a variety of user journey maps. Each one will require you to focus on a specific user and their journey through the assets you’ve created.
Your specific user for each journey map will usually tie into a customer persona. Your user persona should be based on data you’ve collected about your business, such as who is buying your products, has a stake in your business, or is employed by you.
For example, you might have a user who is a senior team member in your business, and a user who is a new employee – both might need different journey maps.
2. The scenario and the goals
On journey maps, the scenario is the situation that the user finds themselves in, with a specific goal in mind. For example, say your user is a customer – the scenario might be that they’re buying a product, with the goal of completing a transaction.
You don’t have to create a user journey map for an existing scenario or goal – perhaps you’re looking to map out a process that’s in the works for a future product launch.
3. User journey stages or phases
Your user journey map is now broken down into stages or phases. This is the high-level view of your user’s scenario, broken down into individual interactions or customer touch points.
For example, if you were selling a product to a customer to fix a particular problem, your stages might be the following:
4. Actions, attitudes and emotions
Within each user journey stage, you will need to map out the actions a user will take; their mindset or attitude toward this journey stage; and the user’s emotional state.
For example, for the “Discovery” phase in the product sale example above, you might note:
- Actions : Use online search engine to find information, visit website, read blog article
- Attitude: Searching for help for a problem
- Emotions: Frustrated with the problem they’re trying to solve, happy at potentially finding a solution
5. Opportunities
When you’ve mapped out the above on your user journey map or customer journey map, you’ll start to see where you have the opportunity to create change. For example, perhaps you’ve seen that you lose lots of users at the Purchase stage. Is there a problem with your purchase system? What incentive could you offer to get users over the hurdle?
Ask yourself:
- What can you do with the knowledge you’ve gained from this journey map?
- What are the main opportunities that should be tackled first for the best ROI?
6. Internal ownership
Once you’ve identified the opportunities, you can then assign internal ownership. Without assigning specific actions and responsibilities, improving your customer experience or user experience can easily fall under the radar.
Your customer journeys or user journeys outlined in your journey map might touch upon multiple parts of your organization. For example, the customer journey outlined in this example involves product design, marketing, sales and frontline customer service departments. Each area of your business will need to take action for the best user or customer experience.
7. Measurement
To understand how your user journey has improved, you’ll need to determine the metrics each improvement will be judged against. This might be customer satisfaction (CSAT) , sales numbers, Net Promoter Scores (NPS ), or positive user reviews – whichever you feel best represents an improvement for your users’ experience. It’s best to create KPIs to track over time to see how your actions contribute towards tangible change in the user experience.
How to build a user journey map
Now you understand how to create a customer journey map or user journey map, how do you gather all the data you need to flesh it out?
The main sources of useful information will be:
- User/ customer research , such as market research
- Unsolicited user data, such as web traffic numbers or social media listening data
- Solicited user data, such as data from user interviews or customer surveys
- Operational data, such as financial transaction data
Qualitative UX research
Qualitative user research helps you to understand the “why” behind user’s actions. How was your customer feeling in the moment when they interacted with you? Which emotion drove them to move into the next phase of your user journey map?
This type of user research involves collecting non-numerical data, such as opinions or feelings. To do this, you might decide to:
- Host user interviews/customer interviews to discover pain points and understand the drivers behind users and customers’ experience
- Perform user research through surveys to gather information on experiences at all user and customer touchpoints
- Conduct research to understand why specific demographics might act in a specific way during their user journey
- Observe users in action, either in person or through screen recordings, to get contextual information on what happens during the journey
- Create an empathy map, outlining what a user says, thinks, does and feels, for each stage of the user or customer journey
Quantitative UX research
Quantitative user research is a more structured approach to gathering user information for your journey map. Rather than the “why” behind your user or customer’s experience, it illustrates the “what.” What are your users doing? How often are they doing it? How much do they spend on it?
- Get insights from internal data to understand actions, such as what happens during user pain points or how often your customers return for another purchase
- Test the usability and accessibility of your website to understand if there are technical drivers behind actions
- Use user research methods such as mouse heatmaps, funnel analysis, analytics and more to understand user behavior
With all this information, you can then create user personas to help kickstart your user journey mapping and UX design process.
Create effective UX journey maps with Qualtrics
Get a deeper understanding of your users and build better customer experiences with user journey maps, enabled by Qualtrics. Build multiple in-depth user journey maps, populated with your organization’s collated data and third-party inputs, for better UX design and customer experience.
With Qualtrics CustomerXM™ , you’ll be able to:
- Outline individual user and customer journeys with input from across your business
- Automatically surface emotions, drivers and sentiments in unsolicited and solicited data with iQ™
- Deliver insights and actions automatically to key parties within your organization to enable positive change
- Create UX designs that meet and exceed user expectations
Related resources
User Experience
What is Interaction Design? 20 min read
User experience 20 min read, user experience surveys 9 min read, ux research tools 8 min read, user analytics 11 min read, rage clicks 11 min read, user experience analytics 10 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

7 Simple Steps to Build a Customer Journey Map

As you get your start in the world of UX, one important tool you’ll need in your skillset is the customer journey map . Creating journey maps can seem intimidating and you may not know where to start. We’ve broken down how to create effective and accurate customer journey maps using seven simple steps.
Research has shown that companies who take the time to design positive, meaningful experiences for their customers are more likely to gain loyal patrons and increase their bottom line. Many brands are looking for innovative ways to solve their customers’ needs in a way that encourages them to continue interacting with the company over time.
A great way to understand if your brand is providing smooth and worthwhile experiences that meet the expectations of your customers is to create a customer journey map.
This guide will give you a template to use as you create your first customer journey map and outline these seven steps to follow:
- Set a clear objective for the map
- Define your personas and highlight target customers
- Define stages and identify goals for each
- List out touchpoints
- Gather data and customer feedback
- Determine pain points and points of friction
- Identify areas for improvement
Before we jump in, note that we’ll be using our downloadable customer journey map template below to walk you through creating an awesome customer journey map. You’ll want to customize your map to the needs of your brand but our template is a great place to start getting your ideas out. Ready to learn how to create a stellar customer journey map? Let’s get started.

Note that if you’d like a set of inclusive images to use in conjunction with this template, have a look at the images we suggest using with our user persona template (you can catch the full guide here: 5 Steps to build your first user persona ).
1. Set a clear objective for your customer journey map
One of the best things you can do before diving into your customer journey map is to have a clear idea of what you and your team wish to accomplish by creating one. What sort of information are you hoping to gather and how will you use it? What insights do you hope to gain? Setting these goals early on can help ensure your efforts are not wasted and you are accurately portraying the customer journey.

2. Define your personas and highlight target customers
Much of the information you’ll use to create a customer journey map will come from your customer personas . Since a single organization can have many different customer profiles, you’ll need to decide whether you want your map to reflect multiple different buyer’s personas in one, the majority or most prevalent persona, or if you’ll create an individual map for each target customer.
To create accurate personas, you’ll have to gather feedback directly from your customers as well as data from customer analytics. Here are some great ways to gather valuable data when defining your customer personas:
- Conduct consumer surveys and questionnaires
- In-person interviews with customers
- Run user testing with your product
- Interview employees with customer-facing positions
- Run a Google Analytics report
- Gather analytics from your website and social media
Be sure to focus on people that actually have interest in using your services or have used your product before. You’ll also want to ensure you’re asking questions that get to the info you’re after without bias or influencing your customers’ answers. Here are some good questions to seek answers for:
- What problem drove the customer to your company?
- How did they find your website or company?
- Was the site or app easy to navigate?
- What competitors did they research?
- What differentiated your brand from the others? What made them decide to (or not to) choose your product?
- What do they hope to achieve when interacting with your company?
- How often do they interact with your brand or product and for how long each time?
- Have they ever contacted support? What was the experience like?
- What do they enjoy about your company? What do they find frustrating?
- Are there areas they think could be improved? If so, what and how?
Once you have your persona(s) defined, you’ll be ready to identify the stages they move through when interacting with your brand.
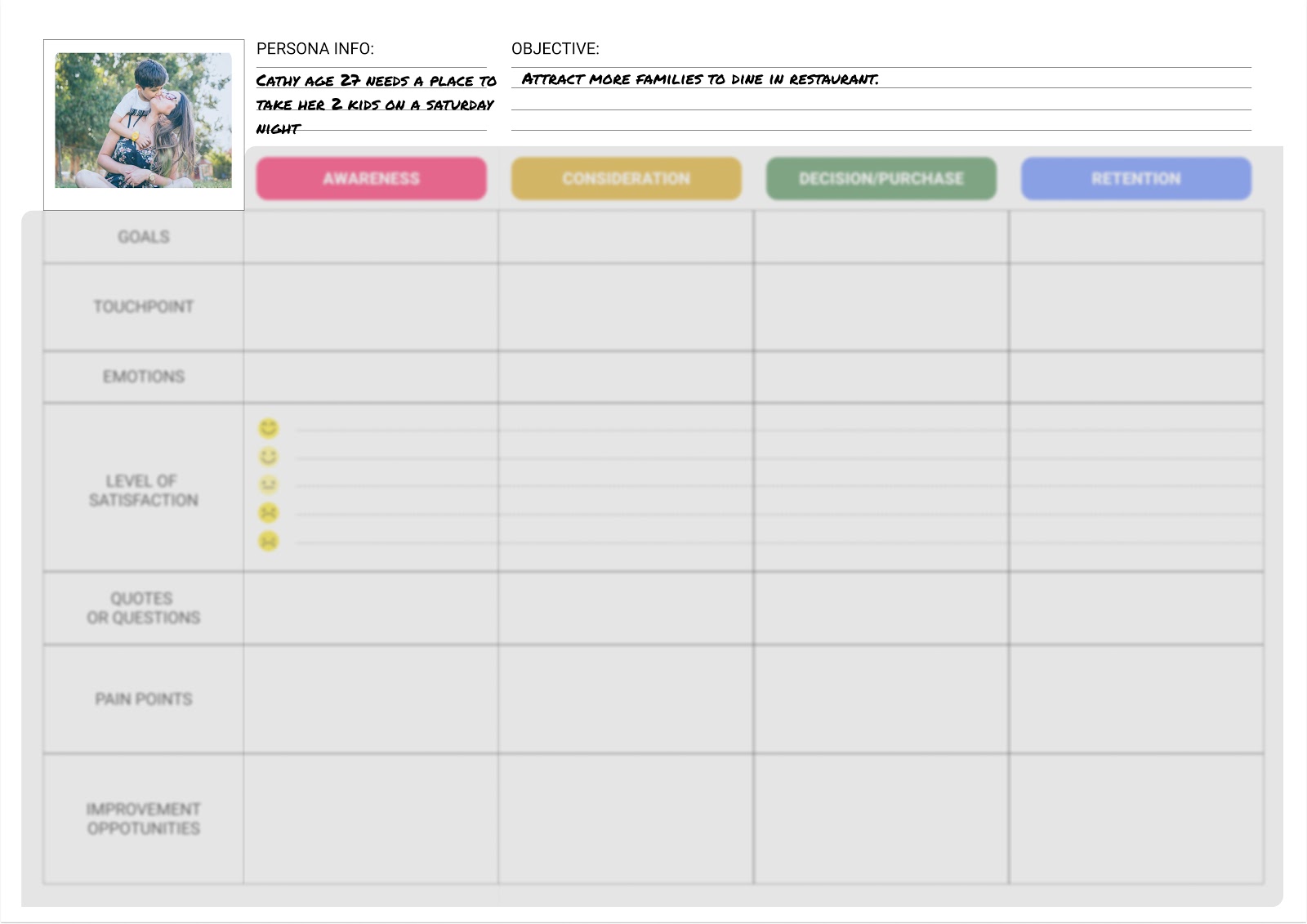
3. Define stages and identify goals for each
A customer journey map (or buyer’s journey, as it’s often called) can have many unique stages. The stages you define for your map depend largely upon the goal you are trying to achieve and what you want it to show. However, a typical customer journey has four distinct stages: the awareness stage, the consideration stage, the purchase (or decision) stage, and retention.
Awareness stage : Your customer has identified a problem that needs solving and has just encountered your product or brand for the first time. This phase encompasses why they are searching for a product, their motivations for buying and the first moment they become aware of your brand.
Consideration stage : Your customer is considering what you have to offer and actively researching your brand as well as competitor products. This is where customers are encountering homepages, browsing product descriptions and pricing, visiting About Pages, Contact pages, help centers and FAQs, as well as searching through online reviews.
Decision stage: Your customer has gathered enough information to commit to a purchase. This phase often includes in-person purchasing experiences, online ordering pages, email confirmations, and FAQs on shipping and billing expectations.
Retention: Your customer has made an initial purchase and is evaluating their overall experience. This phase is all about creating loyal, returning customers and usually evaluates the quality of your company’s customer support services, delivery and return options, as well as future discount or membership programs.
These are the most common customer journey stages, but the stages you define for your map will depend on what you’re using it for. For instance, if you want to see how customers interact with your product from early morning to late night you can create a “day in the life” journey map. Another interesting option may be focusing on the journey your customer takes when noticing an issue, contacting customer service, and receiving help.
4. List out touchpoints
Now that you have the stages of your customer journey map defined, you can list each touchpoint the customer will have within each stage.
A touchpoint is each time your customer interacts with some aspect of your brand, whether it be your company website, an advertisement, an online review, purchasing and using your services, or contacting customer support.
Brainstorm all the different ways your customer can interact with your brand and note what actions they take for each one. Be sure to think outside the box! Things like “word of mouth” or an email confirmation can be touchpoints as well.
This example shows one or two touchpoints per stage, however, your customers will most likely have many different touchpoints within each phase of a journey map:
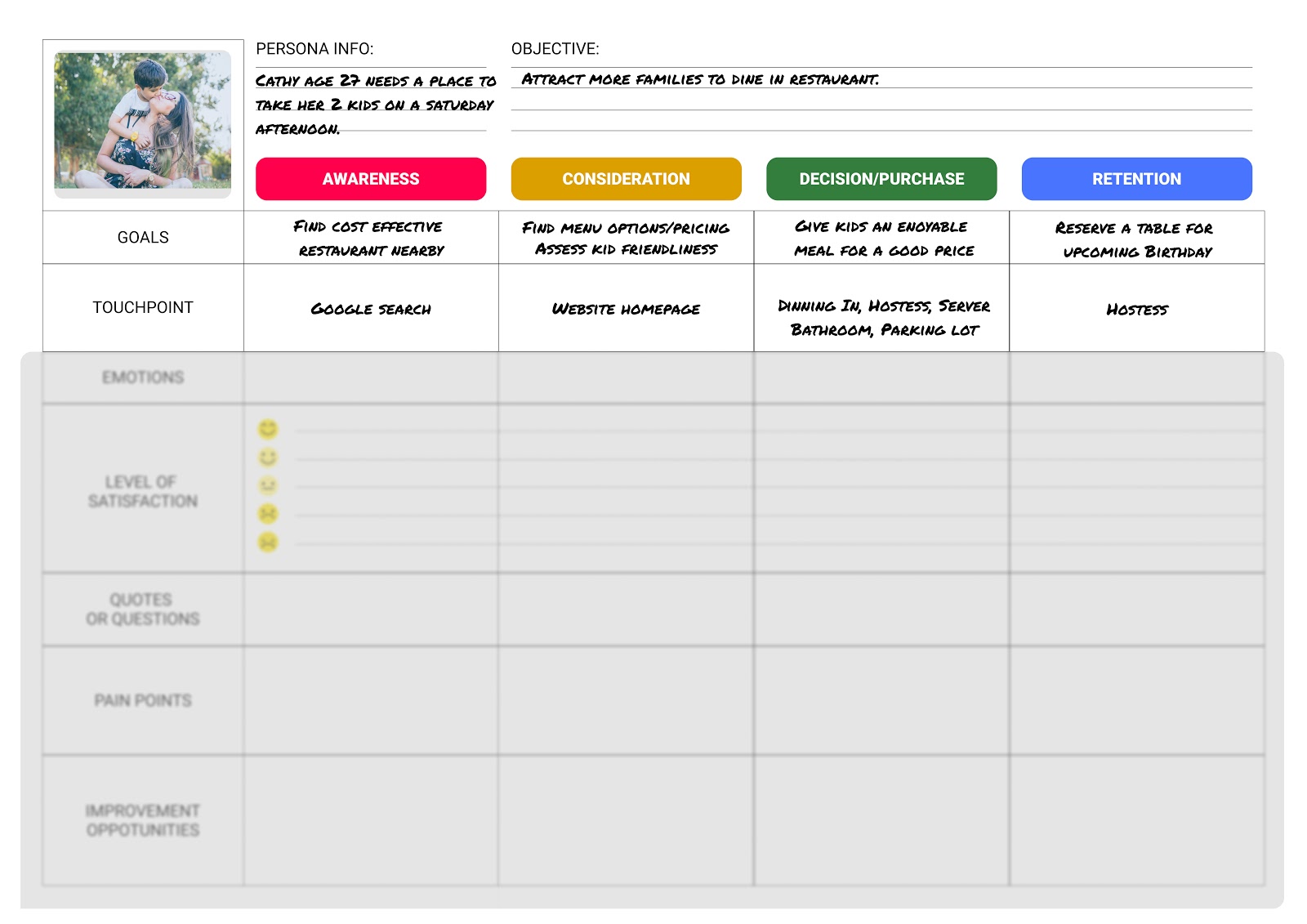
5. Gather data and customer feedback
At this point in the creation of your map, you should have a pretty good idea of how your customers move through your brand. The next step is to gauge what your customers are thinking and feeling as they move from touchpoint-to-touchpoint and stage-to-stage. You’ll want to take the customer journey yourself so you can see what your customers are experiencing first hand. However, it’s most important to gather feedback from actual customers to include in your map.
There are many different ways to map the emotions, thoughts, and motivations your customer has when interacting with your brand. You can include sections for quotes from in-person interviews and online reviews or include a section to list stats from surveys and questionnaires. You can also use emojis or pictures to relate feedback from user testing or even use rating systems and color codes that represent customers’ emotions at each stage.
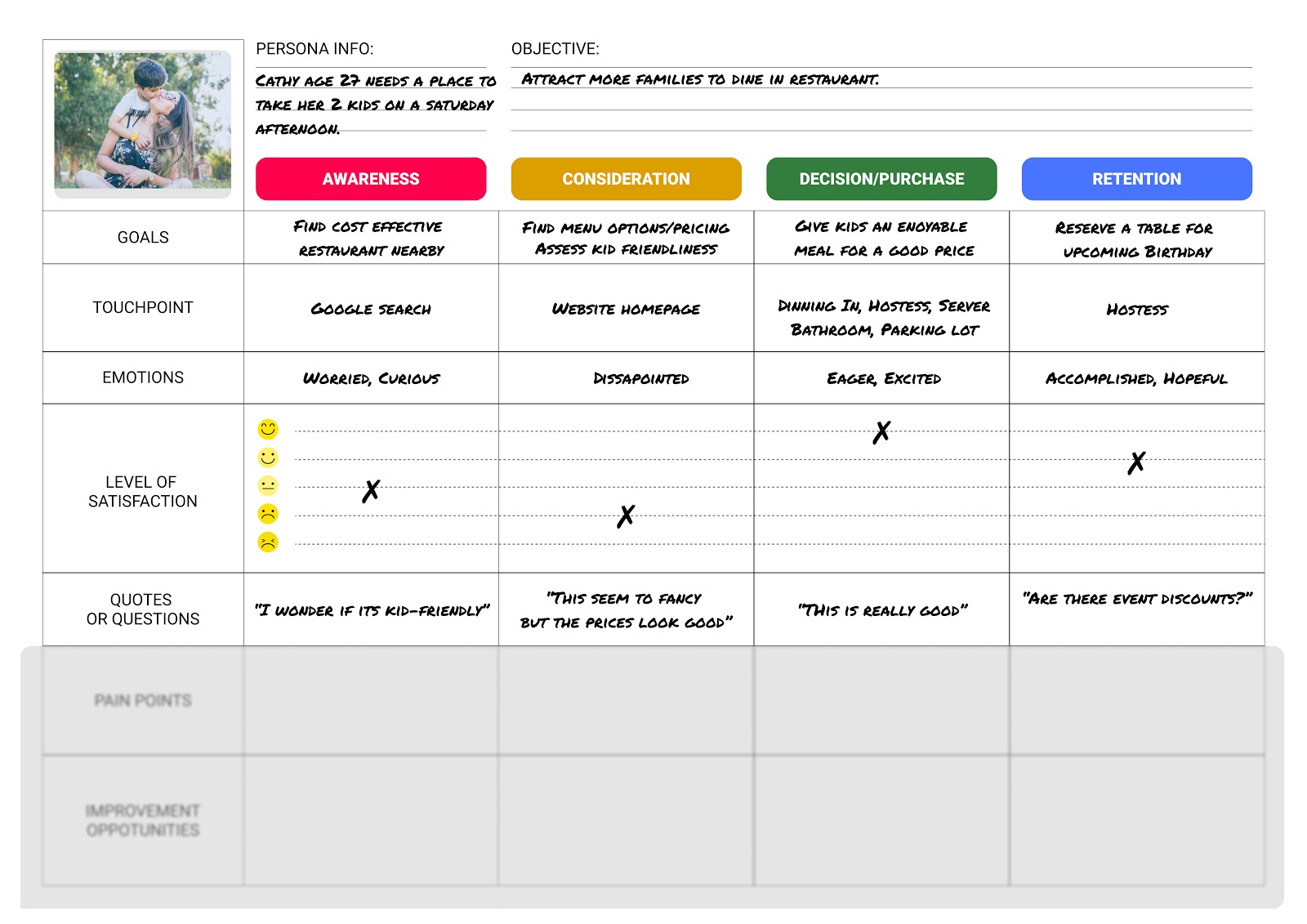
6. Determine pain points and points of friction
Once you’ve mapped the data from customer feedback, you’ll be able to more clearly see any potential areas of friction of hang-ups your customers might be experiencing.
Where are your customers expressing frustration? Are there gaps within the journey or difficulties when moving between stages?
Pay attention to when pain points manifest, what triggers them, how your customers react, and what departments within your company are involved. Chances are there will be customer pain points throughout your map in each different stage.
Try to highlight the most prevalent or problematic points of friction that, when solved, will have the greatest impact on the overall customer journey.
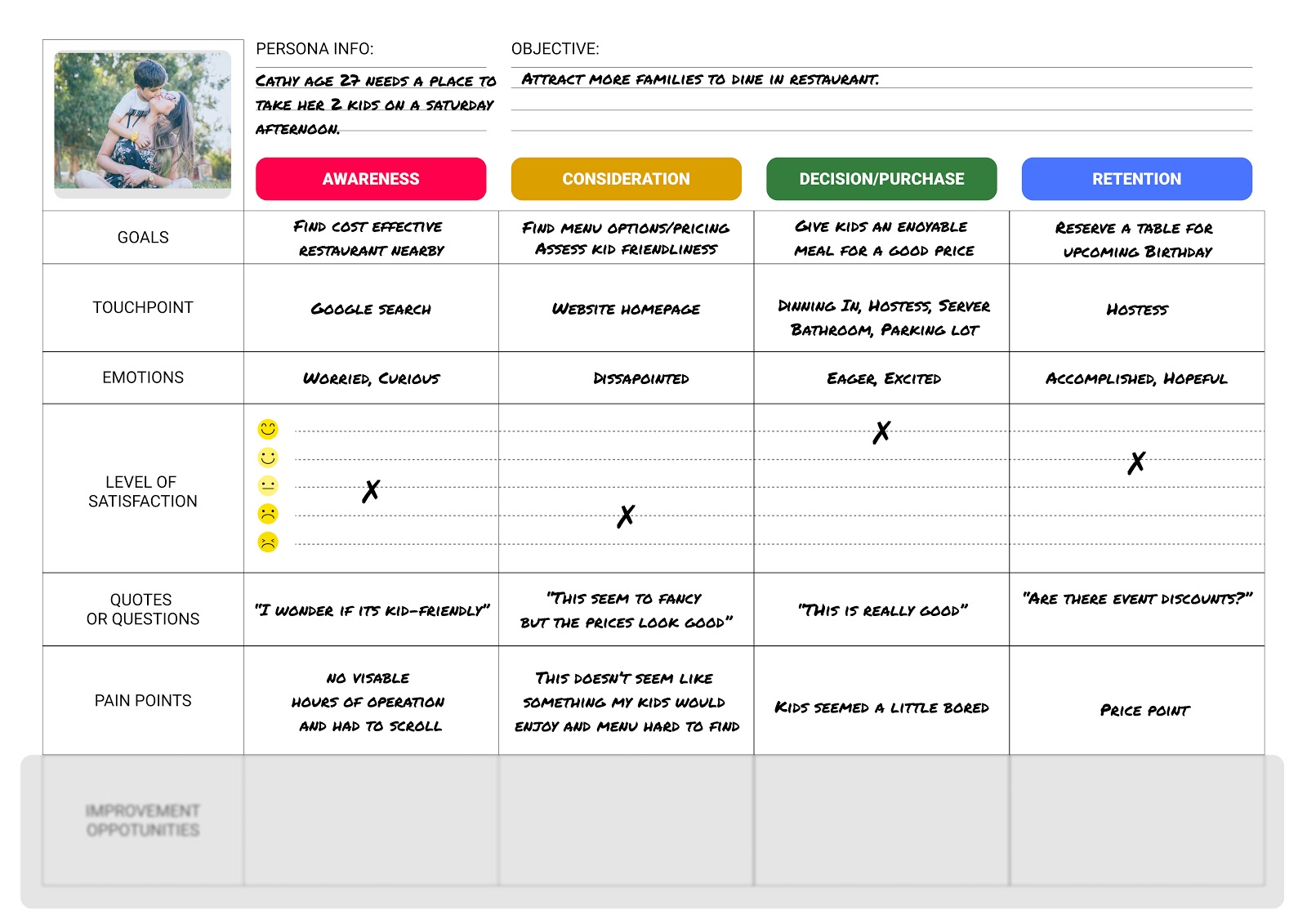
7. Identify areas for improvement
Identifying what areas of the customer journey need tweaking is the first step to improving your customer’s overall experience. The next thing to do is to brainstorm solutions or remedies for each pain point. Having a section of your map that addresses suggested solutions or opportunities to improve is paramount to getting the most out of your map. Once you’ve brainstormed different ways to alleviate your customer’s frustrations, you can implement the necessary changes, conduct further research, and evaluate the customer journey again.
Having trouble coming up with solutions for your customers’ pain points? Try creating a separate map of an ideal customer journey within your company and compare and contrast to their actual journey. Viewing the maps side-by-side may shine a light on what can be done to improve your customers attitude towards your brand.
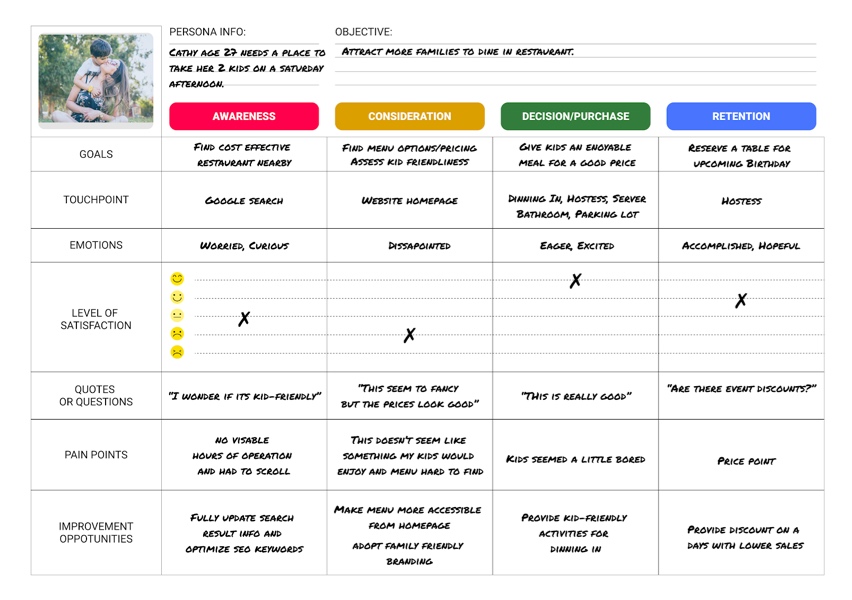
Key takeaways
As your company or brand evolves, the customer experience will change —and so will your journey map. It is rare for a customer journey map to stay static for very long as your brand constantly strives to design better experiences for your customers. Customer journey maps are regularly revisited and revised as improvement initiatives within the company are implemented. Be sure to use all the resources available to you when creating and revising your journey maps. Most importantly, keep your customer in mind from beginning to end.
To learn more about customer journey maps, UX design, and how to create better experiences for users, check out these articles:
- What is a customer journey map and why is it important?
- What is the UX design process? A complete, actionable guide
- What are user flows in UX design?
- Storytelling for UX Design Teams

- Demo Videos
- Interactive Product Tours
- Request Demo
Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) for UX Designer
A customer journey is the set of interactions a customer has with your business to complete a task such as evaluating, onboarding, getting support, or renewing a product or service. A customer journey map is a visualization of an individual’s relationships with a product/brand over time and across different channels. It helps businesses better understand the customer experience including all the journey steps and touchpoints along the way to achieving their goals. By exposing the gaps between the user’s expectations and perceptions at key steps in the journey with associated departments and stakeholders.
Why Customer Journey Map (CJM)?
Customers are increasingly empowered by competition, digital channels and easy access to information such as, their devices become more integrated and connected to your business and systems via the Web, self-service and mobile apps. The customer’s buying cycle starts long before they visit the website – and the service and support experience continues long after they place their order.
This digital disruption is making customer experience a priority and shifting business focus from traditional systems of record to dynamic systems of engagement. Companies that fail to take the full buying cycle into account commonly under-deliver on customer expectations. Thus, the businesses force to reinvent themselves to increase customer value and deliver great experiences by re-factoring systems and processes to consistently support customers on these new touchpoints.
Customer journey maps can be useful beyond the UX design and marketing teams. They can help facilitate a common business understanding of how every customer should be treated across all sales, logistics, distribution, care, etc. channels. This in turn can help break down “organizational silos” and start a process of wider customer-focused communication in a business and consequently, a CJM helps us to achieve the following:
- It fosters a more user-centric approach to product design, which ultimately leads to better user experience design.
- It serves as a corrective lens, providing an outside-in perspective and helping multiple teams within the organization understand the big picture from the customer’s perspective and create a shared understanding of the experience.
- It creates alignment across your business and help drive customer-centric change from product teams and business unit leads to IT operations and then out to marketing, sales and service.
- These business silos (isolated departments or business units) are usually hindered by poor exchange of information, bad assumptions, and lack of common standards and duplication of effort.
What is CJM?
Customer journey map illustrates the relationship of a customer with a business over a period of time using storytelling technique and visual cues. Story are being told from the perspective of customer, which provides insights of the total experience from the customers, helping your get a better understanding and addresses customers’ needs and pain points as they experience your product or service. It is an excellent tool for UX designers to visualize how a user interacts with a product and allows designers to see a product from a user’s point of view.
Different parts of the organization such as marketing, sales, support and collections often only understand their portion of the user’s end-to-end journey. They naturally gravitate towards supporting their own touchpoints, which then creates organizational silos.
Customer Journey maps are a common approach used to design customer-centric processes for multi-channel customer engagement. The ultimate purpose of the exercise is to find flaws, weaknesses and opportunities for improvement in the current process. They often serve as:
- The foundation for UX optimization programs, identifying new ways to help your customers reach their goals while still delivering on the company’s objectives.
- customer interviews
- observation
- web analytics
So how do you virtualize the outside-in scenario to see the full picture including customer perceptions, mobile and social media engagement? The short answer is by creating journey maps which visually document a customer persona’s needs, perceptions and the touchpoints encountered for each step towards the customer’s journey goal.
Inside-out to Outside in Approach
The Inside-Out approach is guided by the belief that the inner strengths and capabilities of the organization will make the organization prevail. The Outside-In approach is instead guided by the belief that customer value creation, customer orientation and customer experiences are the keys to success.
Taking a journey-focused, outside-in approach to continuous UX optimization helps put the customer at the center of your business strategy, which in turn drives loyalty and revenue. Companies with a mature approach to customer experience take an iterative, disciplined approach to continuous improvement, with the ongoing assessment and optimization of customer journeys as a core practice.
Pain Points and Touch Points in CJM
A pain point describes a moment in a customer’s experience that causes frustration, emotional discomfort, irritation or hassle which are the critical touchpoints encountered along his / her customer journey. Every badly managed touchpoint that is not designed in keeping with the brand leaves the customer with a negative experience; so it becomes a pain point which means that the overall customer experience turns negative.
There many different types of pain points, but generally speaking, there are four typical types of pain points, all of which can be broken down into many smaller categories. These are the four main types and an example of a struggle associated with the problem.
- Financial – Your prospect is spending too much money on their current solution and wants to spend less.
- Productivity – Your prospect is spending too much time and energy on completing a task and they would prefer to complete it with greater efficiency.
- Process – Your prospect has a certain process that needs to be more effective to accomplish specific goals (either in a business or personal setting).
- Support – Your prospect isn’t receiving the sort of support that they need at a particular stage in the customer journey or conversion funnel.
Solution for Pain Points
Once you figure out the pain point(s) of your ideal customer, you can start thinking about how to position your company or product as a solution to your prospects’ problems.
Regardless of what’s causing the pain, you now have a pain point you can counter in your marketing. Remember our list of pain points from earlier in this post? Let’s take a look at the pain points we identified, and see how we could address them in our marketing:
- Financial – Emphasize lower price point (if applicable), highlight the average savings of your client base, use language that reiterates better ROI
- Productivity – Highlight reductions in wasted time experienced by current customers, emphasize ease-of-use features (such as at-a-glance overviews or a centralized dashboard)
- Processes – Mention current/planned integrations with existing products/services (i.e. Slack’s integration with Dropbox and Salesforce), highlight how your product/service can make typically difficult/time-intensive tasks easier
- Support – Help the prospect feel like a partner by highlighting your after-market support, use connecting language (“us,” “we” etc.) in your copy
How to Creating CJM in 8 Steps
Journey maps can take a wide variety of forms. The end goal, however, is always the same: find and resolve the pain points of your customers.
Step 1. Define your persona
Personas and journey maps are both important strategic tools that help provide an in-depth understanding of who your customers are, what they need, and how they interact with your business across all touch points. But more importantly, for sharing customer insights across the organization. Much of the information for creating a journey map comes from your personas (e.g., their goals, motivations, key tasks they want to accomplish, and current pain points), which is why it’s best to create the personas first.
The first thing you need to decide is whose journey you are going to map such as, a specific customer type (persona), a potential (target) customer, or a segment of customers, depending on the purpose of your journey mapping initiative. Once you’ve created distinct personas, you can use them to create customer journey maps that describe each persona’s experience at various touch points during their lifecycle with your company.
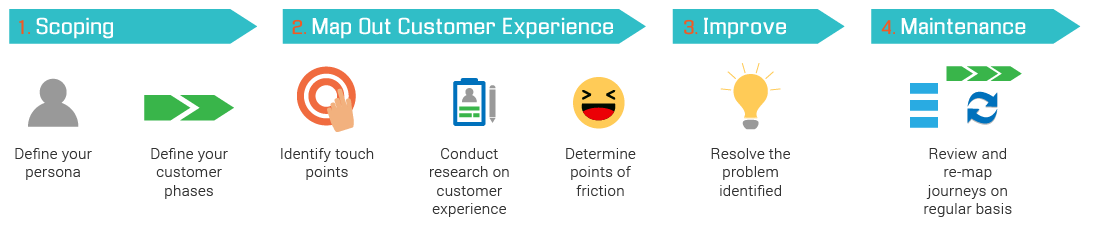
Step 2. Define your customer phases
Journey maps are typically organized by customer stages (sometimes referred to as phases). Each stage represents a major goal your customer is trying to achieve in their overall journey. You should build a customer journey map with stages that represent your customer’s goal-oriented journey, not your internal process steps.
So once you’ve defined your persona, you have to identify the stages of the customer’s journey. What process does it take to start from consideration all the way through buying your product or services? Based on the persona define the stages that your customer experiences with you over time. Define how, when and where they: discover your company, research your products or services, choose you over competitors, purchase from you, and maintain a relationship with you.
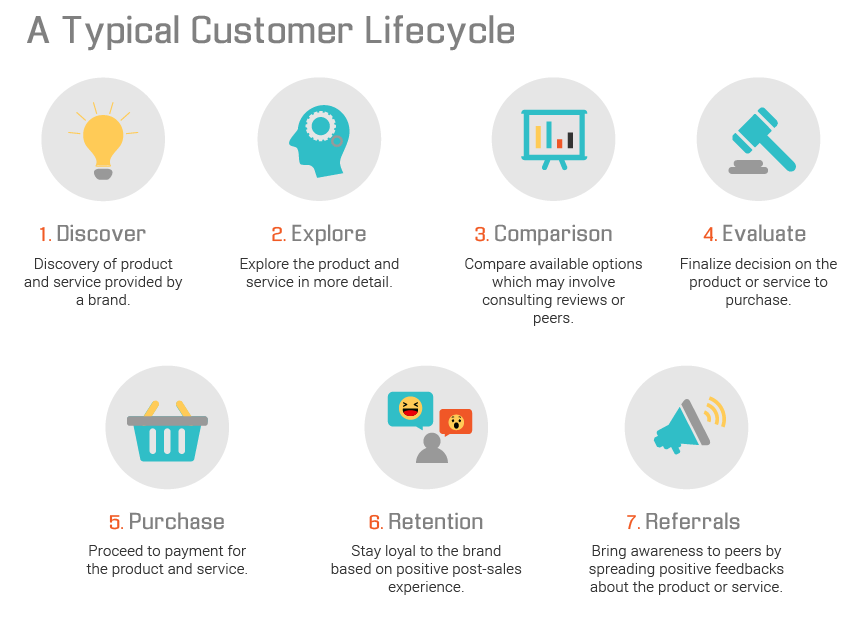
Step 3. Describe the Touchpoints Your Customer Uses to Interact with Your Organization
Customer touchpoints are your brand’s points of customer contact, from start to finish. For example, customers may find your business online or in an ad, see ratings and reviews, visit your website, shop at your retail store or contact your customer service. This seems like a long list, but these are just a few of your touchpoints! Identifying your touchpoints is an important step towards creating a customer journey map and making sure your customers are satisfied every step of the way.
Step 4. Conduct research
While you may need to offer some incentives for participation, most people are happy to help if they believe you are genuinely interested in their experience and will use their feedback to improve things for others.
- For each stage of the journey, try to identify:
- What were their goals, what did they want to achieve
- What did they expect the process would be like
- The steps and touchpoints they used to complete the stage
- How did they feel emotionally during each touchpoint experience and why
- Other thoughts they had during the stage
- How long did it take to complete
Step 5. Determine points of friction
Once you have understood your persona’s goals and written down their touchpoints, it’s time to look at the big picture – the totality of their experience with your company. Every business will look through the lens of their customer personas differently. Walking through each of the journey map stages with your team will help you identify any points of friction within the customer experience.
Of course, every business is different and YOU will know your customers best. There are a few example questions below to get you started:
- Where could friction appear in this particular touchpoint?
- Are people abandoning purchases because of this?
- Are customers not aware of this solution that you’ve already provided? If so, why not?
Step 6. Resolve
Journey maps aren’t meant to be purely illustrative. A typical exercise should identify a few quick fixes, including opportunities to boost enjoyment and improve the journey. And, of course, most firms discover the process helps drive broader customer experience improvements as customer needs are better understood and met. In brief, mapping the journey should help lead to specific actions that improve the experience and drive the ROI. Treat your map as a living document to be revisited regularly and updated as required and remember to share it with any relevant stakeholders
Search for CJM Design Software?
Visual Paradigm’s online Customer Journey Mapping tool helps you streamline the UX initiatives and automate the entire information acquisition process:
- Provide a bird’s eye view of the entire customer journey.
- Bring teams together to resolve specific customers’ hurdles while understanding the core customer journey paths.
- Increase customer conversion rates by minimizing negative customer experiences, through identification of key steps and decision points.
- Improve customer retention, by understanding how they transit through. For example, ensure all the information is available and accessible to all the stakeholders during each stage of a procurement cycle.
- Businesses can zoom-in on a single customer journey in a specific channel.
- Understanding the required metrics to identify customer’s progress and fall out points, providing opportunities to bring customers back on board.
- Allow businesses to prioritize actions in their customer experience strategy
- Reveal the gaps between various channels and departments
Turn every software project into a successful one.
We use cookies to offer you a better experience. By visiting our website, you agree to the use of cookies as described in our Cookie Policy .
© 2024 by Visual Paradigm. All rights reserved.
- Privacy statement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of a Journey Map. Definition: A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user actions into a timeline. Next, the timeline is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative.
The main job of a UX designer is to make products intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. By creating a user journey map, you're thinking about a product from a potential customer's point of view. This can help in several ways. User journey maps foster a user-centric mentality. You'll focus on how a user might think and feel while ...
Here's how to create a user journey map in 6 steps: Choose a user journey map template (or create your own) Define your persona and scenario. Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions. Fill in the user's thoughts, emotions, and pain-points. Identify opportunities.
With a user journey map, you can pinpoint where the customer experience is going wrong, and how to enable more successful checkouts. Read on to find out: What is a user journey map, and how it captures user flows and customer touchpoints; Benefits of user journey mapping to refine UX design and reach business goals
A journey map helps UX designers identify stress points and missing connections in the product to eliminate inefficiency. Journey mapping makes products functional, intuitive, and easy to use. If you're looking to create user-friendly, intuitive experiences for your customers, journey mapping is a key part of UX design.
Where journey mapping focuses on exposing the end-to-end of your customer's front stage experience, blueprinting focuses on exposing the surface-to-core of the business that makes up the backstage and behind the scenes of how you deliver and operate, and ties that to the customer's experience. More on this you can find in "The difference ...
A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map." — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert. In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
A user journey map is an excellent tool for UX designers because i t visualizes how a user interacts with a product and allows designers to see a product from a user's point of view. This fosters a more user-centric approach to product design, which ultimately leads to a better user experience. User journey maps help a product team to find ...
Steps. Define business and user goals Clearly articulate the organizational goals for the product or service, the design and business goals for the mapping exercise, and the goals of the target user the map is to represent.; Gather research data Effective journey maps are based on qualitative and quantitative data collected across a range of activities. . Review and incorporate existing ...
1. Review Goals. Consider organizational goals for the product or service at large, and specific goals for a customer journey mapping initiative. 2. Gather Research. Review all relevant user research, which includes both qualitative and quantitative findings to provide insights into the customer experience.
The user journey map, also known as customer journey map or user experience journey map is a way to visually structure your knowledge of potential users and how they experience a service.. Customer journey mapping is also a popular workshop task to align user understanding within teams. If backed up by user data and research, they can be a high-level inventory that helps discover strategic ...
The Journey Map, helps teams understand and visualize the end-to-end experience of a user as they interact with a product or service. They provide a comprehensive view of the user's interactions, emotions, and touchpoints throughout their journey. These maps are a versatile tool in UX design that aids in understanding, visualizing, and ...
User journey mapping is a valuable tool in UX design, helping designers understand the needs, goals, and pain points of users, identify opportunities for improvement, and align stakeholders. By following the steps outlined in this article, designers can create effective user journey maps that inform design decisions and improve the user experience.
2. Senior Designer Bundle: Become a design leader with systems to help you build a meaningful career & grow your designers. Join 500+ aspiring leaders. 3. UX Portfolio Critique: Get a 20-minute video review of your portfolio. A checklist of actionable things to fix, in less than 48 hours. Get a personalised portfolio critique here.
A particularly handy tool for user experience (UX) design, this process helps teams understand who their users are and how to fulfill their expectations, guiding development decisions for improved audience engagement. Learn more about customer journey mapping and how you can implement it to enhance your CX. User journey mapping: an overview
UX Mapping Methods Compared: A Cheat Sheet. Sarah Gibbons. November 5, 2017. Summary: Empathy maps, customer journey maps, experience maps, and service blueprints depict different processes and have different goals, yet they all build common ground within an organization. Designing and developing a product often involves a large team of people ...
A good UX journey map has everything we covered so far. But a truly great one grows and evolves over time based on data. ... Design better products with user journey maps. Customer journey maps are proven visual tools that provide teams with incredible insights into the minds of their users as they interact with their offerings.
Emotions: The feelings people experience at each stage of the customer journey, including excitement, happiness, frustration, disappointment, and anger. Designers use empathy maps to visualize these emotions across the customer journey. Motivations: The reasons why people take action at different stages of the customer journey.
UX journey maps are usually for UX design thinking. A customer journey map is a tool that can be used for many different areas of business - sales journeys, marketing journeys and more can be mapped out. However, a UX journey map is usually used for the UX design process, and might involve more technical information such as website usage data.
A customer journey is the experience an established or prospective customer has with your company when trying to accomplish a certain goal. The customer journey takes into account every point of contact a customer has with a business, not just their interaction with a single product. For instance, say someone wants to find a way to learn French ...
This guide will give you a template to use as you create your first customer journey map and outline these seven steps to follow: Set a clear objective for the map. Define your personas and highlight target customers. Define stages and identify goals for each. List out touchpoints. Gather data and customer feedback.
Customer journey maps can be useful beyond the UX design and marketing teams. They can help facilitate a common business understanding of how every customer should be treated across all sales, logistics, distribution, care, etc. channels. This in turn can help break down "organizational silos" and start a process of wider customer-focused ...
Not a whole lot. Sometimes, user journey maps refer to specific maps UX designers make during the design process to understand potential points of friction in the customer journey. But typically, the difference is semantic: The terms "user journey map" and "customer journey map" are largely interchangeable and can depend on the context ...
Geographic data analysis: AI can be used to analyze large geographic data sets to identify patterns, trends and relationships. Data visualization: AI can be used to create visually appealing and informative maps that communicate complex ideas clearly and concisely. Interactive maps: AI can be used to create interactive maps that allow users to explore data and perform queries in real time.