Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
The interstellar vagabond continues to explore the cosmos along with its twin, Voyager 1.


Voyager 2 as the backup
Jupiter and saturn flyby, uranus and neptune flyby, voyager 2's interstellar adventure, voyager 2's legacy, additional information.
Voyager 2, was the first of two twin probes NASA sent to investigate the outer planets of our solar system.
The probe was launched aboard a Titan IIIE-Centaur from Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 41 (previously Launch Complex 41) on Aug. 20, 1977, its twin spacecraft Voyager 1 was launched about two weeks later on Sept. 5. NASA planned for the Voyager spacecraft to take advantage of an alignment of the outer planets that takes place only every 176 years. The alignment would allow both probes to swing from one planet to the next, with a gravity boost to help them along the way.
While Voyager 1 focused on Jupiter and Saturn , Voyager 2 visited both those planets and also ventured to Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2's mission to those last two planets would be humanity's only visit in the 20th century.
Related: Celebrate 45 years of Voyager with these amazing images of our solar system (gallery)
Voyager 2 is now traveling through interstellar space. As of early November 2018, NASA announced that Voyager 2 had crossed the outer edge of our solar system ( Voyager 1 crossed the boundary into interstellar space in 2012. ) Voyager 2 is now approximately 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) away from Earth and counting!

Although there was not enough money in Voyager 2's budget to guarantee it would still work when flying past Uranus and Neptune, its trajectory was designed to go past those planets anyway. If the spacecraft were still working after Saturn, NASA could try to take pictures of the other planets.
Voyager 2 was ready as a backup for Voyager 1. If Voyager 1 failed when taking pictures of Jupiter and Saturn, NASA was prepared to alter Voyager 2's path to follow Voyager 1's trajectory. It would cut off the Uranus and Neptune option, but still, preserve the possibility of capturing images.
The backup plan was never executed, though, because Voyager 1 went on to make many discoveries at Jupiter and Saturn, working well enough for NASA to carry out its original plans for Voyager 2.

Voyager 2 reached Jupiter in 1979, two years after launching from Cape Canaveral. Since Voyager 1 had just gone through the system four months earlier, Voyager 2's arrival allowed NASA to take valuable comparison shots of Jupiter and its moons. It captured changes in the Great Red Spot and also resolved some of the moon's surfaces in greater detail.
Voyager 2 took pictures of many of Jupiter's satellites. Among its most spectacular findings were pictures from the icy moon Europa . Voyager 2 snapped detailed photos of the icy moon's cracks from 128,000 miles (205,996 km) away and revealed no change in elevation anywhere on the moon's surface.
Proving that moons are abundant around the outer planets, Voyager 2 happened to image Adrastea, a small moon of Jupiter, only months after Voyager 1 found two other Jupiter moons, Thebe and Metis. Adrastea is exceptionally small, only about 19 miles (30.5 kilometers) in diameter at the smallest estimate.

Next in line was Saturn. Voyager 2 became the third spacecraft to visit Saturn when it arrived at its closest point to the ringed planet on Aug. 26, 1981, and took hundreds of pictures of the planet, its moons and its rings . Suspecting that Saturn might be circled by many ringlets, scientists conducted an experiment. They watched the star Delta Scorpii for nearly two and a half hours as it passed through the plane of the rings. As expected, the star's flickering light revealed ringlets as small as 330 feet (100 meters) in diameter.

Voyager 2's made its closest approach to Uranus on Jan. 24, 1986, becoming the first spacecraft to visit the ice giant. The probe made several observations of the planet, noting that the south pole was facing the sun and that its atmosphere is about 85% hydrogen and 15% helium.
Additionally, Voyager 2 discovered rings around Uranus, 10 new moons and a magnetic field that, oddly, was 55 degrees off the planet's axis. Astronomers are still puzzling over Uranus' orientation today.
Voyager 2's pictures of the moon Miranda revealed it to be perhaps the strangest moon in the solar system. Its jumbled-up surface appears as though it was pushed together and broken apart several times.
The spacecraft then made it to Neptune , reaching the closest point on Aug. 25, 1989. It skimmed about 3,000 miles from the top of the planet's atmosphere and spotted five new moons as well as four rings around the planet. Remarkably, Voyager 2 is currently the only human-made object to have flown by the intriguing ice giant, according to NASA .
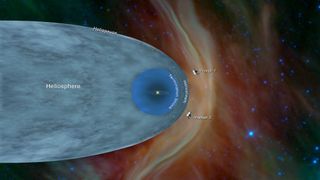
On November 5, 2018, Voyager 2 crossed the heliopause — the boundary between the heliosphere and interstellar space. At this stage, the probe was 119 astronomical units from the sun. (One AU is the average Earth-sun distance, which is about 93 million miles, or 150 million kilometers.) Voyager 1 made the crossing at nearly the same distance, 121.6 AU.
According to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) , Voyager 2 has enough fuel to keep its instruments running until at least 2025. By then, the spacecraft will be approximately 11.4 billion miles (18.4 billion kilometers) away from the sun.
But Voyager 2 is destined to roam the Milky Way long after its instruments have stopped working.
In about 40,000 years Voyager 2 will pass 1.7 light-years (9.7 trillion miles) from the star Ross 248, according to NASA JPL. The cosmic vagabond will continue its journey through interstellar space and pass 4.3 light-years, (25 trillion miles) from Sirius in about 296,000 years.
Voyager 2's observations paved the way for later missions. The Cassini spacecraft, which was at Saturn between 2004 and 2017, tracked down evidence of liquid water at the planet's icy moons several decades after the Voyagers initially revealed the possible presence of water. Cassini also mapped the moon, Titan , after the Voyagers took pictures of its thick atmosphere.
Voyager 2's images of Uranus and Neptune also serve as a baseline for current observations of those giant planets. In 2014, astronomers were surprised to see giant storms on Uranus — a big change from when Voyager 2 flew by the planet in 1986.
To see where Voyager 2 is now you can check out the mission status with resources from NASA . Learn more about the iconic spacecraft with the National Air and Space Museum .
Bibliography
NASA. In depth: Voyager 2. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www.solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/voyager-2/in-depth/
NASA. Voyager - mission status. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www.voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/status/
NASA. Voyager - the interstellar mission. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www. voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/interstellar-mission
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
- Daisy Dobrijevic Reference Editor
Building rockets and looking for life on Venus: Q&A with Rocket Lab's Peter Beck
SpaceX launches 23 Starlink satellites, aces 300th rocket landing (photos, video)
Watch 2 cosmonauts conduct spacewalk outside the ISS today
Most Popular
- 2 Watch China launch 3 astronauts to Tiangong space station today
- 3 Buried in the Cat's Paw Nebula lies one of the largest space molecules ever seen
- 4 Netflix releases official trailer for Jennifer Lopez mech combat sci-fi film 'Atlas' (video)
- 5 Ancient rocks hold proof of Earth's magnetic field. Here's why that's puzzling
Voyager Mission Status Report
Voyager status report.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

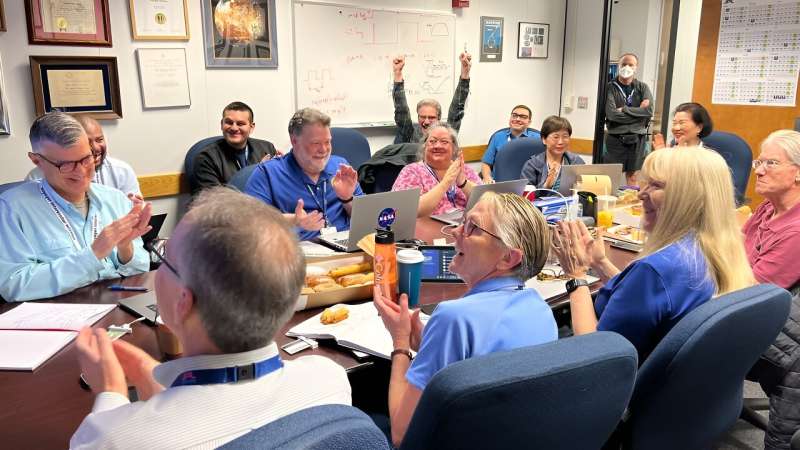
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
share this!
April 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth

For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft's three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory—including some of the FDS computer's software code—isn't working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.

The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft's engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22.5 hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification had worked: For the first time in five months, they were able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Provided by NASA
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Managing meandering waterways in a changing world
10 hours ago

New dataset sheds light on relationship of far-red sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence to canopy-level photosynthesis

How much trust do people have in different types of scientists?
12 hours ago

Scientists say voluntary corporate emissions targets not enough to create real climate action

Barley plants fine-tune their root microbial communities through sugary secretions

A shortcut for drug discovery: Novel method predicts on a large scale how small molecules interact with proteins

Yeast study offers possible answer to why some species are generalists and others specialists

Cichlid fishes' curiosity promotes biodiversity: How exploratory behavior aids in ecological adaptation

Climate change could become the main driver of biodiversity decline by mid-century, analysis suggests

First-of-its-kind study shows that conservation actions are effective at halting and reversing biodiversity loss
Relevant physicsforums posts, our beautiful universe - photos and videos.
3 hours ago
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
9 hours ago
'Devil' comet visible tonight 21.04.24
Waves in space.
13 hours ago
Documenting the setup of my new telescope
Apr 24, 2024
What did I capture?
Apr 23, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

NASA's Voyager team focuses on software patch, thrusters
Oct 20, 2023

NASA's Voyager will do more science with new power strategy
Apr 27, 2023

Engineers investigating NASA's Voyager 1 telemetry data
May 18, 2022
Recommended for you

Japan's moon lander wasn't built to survive a weekslong lunar night. It's still going after 3

Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms, study finds
Apr 22, 2024

'Tube map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory
Apr 17, 2024

NASA's Ingenuity Mars helicopter team says goodbye—for now

NASA confirms mystery object that crashed through roof of Florida home came from space station
Apr 16, 2024

NASA is seeking a faster, cheaper way to bring Mars samples to Earth
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Voyager 1 Sends Clear Data to NASA for the First Time in Five Months
The farthest spacecraft from Earth had been transmitting nonsense since November, but after an engineering tweak, it finally beamed back a report on its health and status
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan
Daily Correspondent
:focal(2016x1133:2017x1134)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/32/30/3230d19e-cc50-4905-840c-7f3afeb2a0c3/e1-pia26275-voyager-copy-16.jpg)
For the first time in five months, NASA has received usable data from Voyager 1, the farthest spacecraft from Earth.
The aging probe, which has traveled more than 15 billion miles into space, stopped transmitting science and engineering data on November 14. Instead, it sent NASA a nonsensical stream of repetitive binary code . For months, the agency’s engineers undertook a slow process of trial and error, giving the spacecraft various commands and waiting to see how it responded. Thanks to some creative thinking, the team identified a broken chip on the spacecraft and relocated some of the code that was stored there, according to the agency .
NASA is now receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. The next step is to get the spacecraft to start sending science data again.
“Today was a great day for Voyager 1,” Linda Spilker , a Voyager project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), said in a statement over the weekend, per CNN ’s Ashley Strickland. “We’re back in communication with the spacecraft. And we look forward to getting science data back.”
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
Voyager 1 and its companion, Voyager 2, separately launched from Earth in 1977. Between the two of them, the probes have studied all four giant planets in the outer solar system—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune—along with 48 of their moons and the planets’ magnetic fields. The spacecraft observed Saturn’s rings in detail and discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io .
Originally designed for a five-year mission within our solar system, both probes are still operational and chugging along through space, far beyond Pluto’s orbit. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to reach interstellar space, the area between stars. The probe is now about eight times farther from the sun than Uranus is on average.
Over the decades, the Voyager spacecraft have transmitted data collected on their travels back to NASA scientists. But in November, Voyager 1 started sending gibberish .
Engineers determined Voyager 1’s issue was with one of three onboard computers, called the flight data system (FDS), NASA said in a December blog post . While the spacecraft was still receiving and executing commands from Earth, the FDS was not communicating properly with a subsystem called the telemetry modulation unit (TMU). The FDS collects science and engineering data and combines it into a package that the TMU transmits back to Earth.
Since Voyager 1 is so far away, testing solutions to its technical issues requires time—it takes 22.5 hours for commands to reach the probe and another 22.5 hours for Voyager 1’s response to come back.
On March 1, engineers sent a command that coaxed Voyager 1 into sending a readout of the FDS memory, NASA said in a March 13 blog post . From that readout, the team confirmed a small part—about 3 percent—of the system’s memory had been corrupted, NASA said in an April 4 update .
The core of the problem turned out to be a faulty chip hosting some software code and part of the FDS memory. NASA doesn’t know what caused the chip to stop working—it could be that a high-energy particle from space collided with it, or the chip might have just run out of steam after almost 50 years spent hurtling through the cosmos.
“It’s the most serious issue we’ve had since I’ve been the project manager, and it’s scary because you lose communication with the spacecraft,” Suzanne Dodd , Voyager project manager at JPL, told Scientific American ’s Nadia Drake in March.
To receive usable data again, the engineers needed to move the affected code somewhere else that wasn’t broken. But no single location in the FDS memory was large enough to hold all of the code, so the engineers divided it into chunks and stored it in multiple places, per NASA .
The team started with moving the code responsible for sending Voyager’s status reports, sending it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. They received confirmation that the strategy worked on April 20, when the first data on the spacecraft’s health since November arrived on Earth.
In the next several weeks, the team will relocate the parts of the FDS software that can start returning science data.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan | | READ MORE
Will Sullivan is a science writer based in Washington, D.C. His work has appeared in Inside Science and NOVA Next .

Quick Facts
Voyager 1 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.5 AU per year
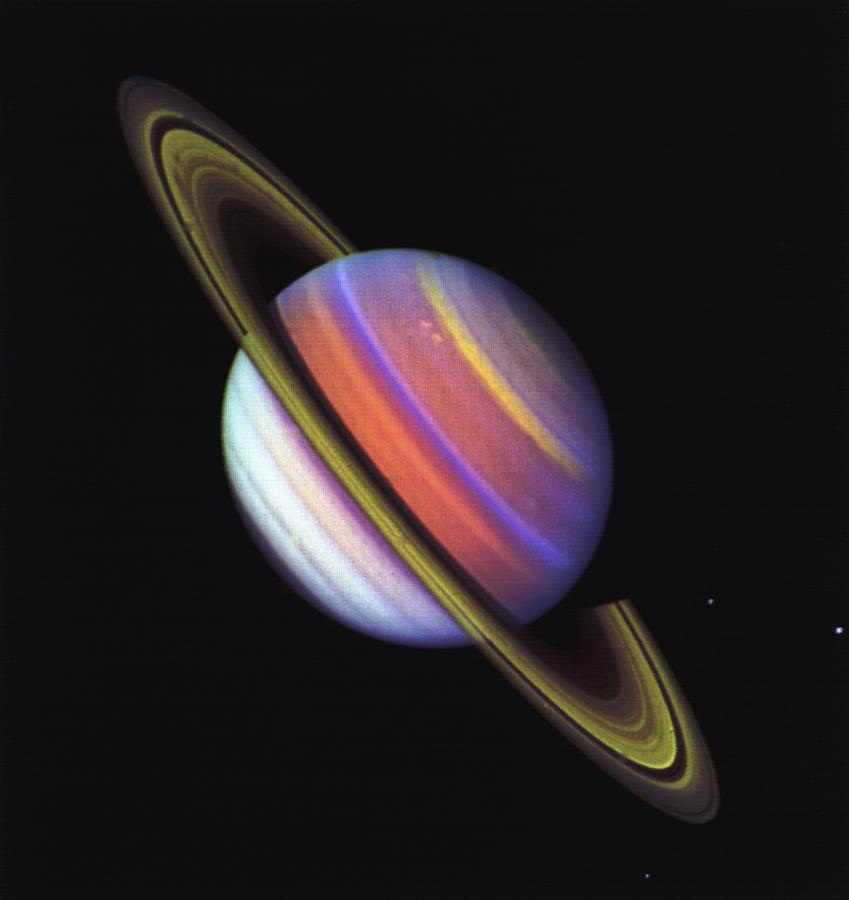

Voyager 2 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.1 AU per year
Five spacecraft - Voyagers 1 and 2; Pioneers 10 and 11; and New Horizons are on an interstellar trajectory.
Voyager's computers procees about 8,000 instructions per section. A modern smartphone yields more than 14 billion instructions per second.

Can the Voyager imaging cameras be turned back on?
It is possible for the cameras to be turned on, but it is not a priority for Voyager's Interstellar Mission. After Voyager 1 took its last image (the "Solar System Family Portrait" in 1990), the cameras were turned off to save power and memory for the instruments expected to detect the new charged particle environment of interstellar space. Mission managers removed the software from both spacecraft that controls the camera. The computers on the ground that understand the software and analyze the images do not exist anymore. The cameras and their heaters have also been exposed for years to the very cold conditions at the deep reaches of our solar system. Even if mission managers recreated the computers on the ground, reloaded the software onto the spacecraft and were able to turn the cameras back on, it is not clear that they would work.
In addition, it is very dark where the Voyagers are now. While you could still see some brighter stars and some of the planets with the cameras, you can actually see these stars and planets better with amateur telescopes on Earth.
What instruments on the spacecraft are still working and what have been turned off?
View an updated list of the status o/f Voyager instruments: Mission Status .
How long can Voyager 1 and 2 continue to function?
Editor's note: Both Voyagers were still functioning in January 2024.
The radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) on each spacecraft puts out 4 watts less each year. Because of this diminishing electrical power, the Voyager team has had to prioritize which instruments to keep on and which to turn off. Heaters and other systems have also been turned off one by one as part of power management.
The Voyager team has chosen to keep operating the instruments that are the most likely to send back key data about the heliosphere and interstellar space -- the fields and particles instruments. Engineers expect to begin turning off fields and particles science instruments one by one, starting in 2020 for Voyager 2. Voyager 2 will have to start turning science instruments off sooner because it is currently operating one more instrument than Voyager 1. Engineers expect each spacecraft to continue operating at least one science instrument until around 2025.
Even if science data won't likely be collected after 2025, engineering data could continue to be returned for several more years. The two Voyager spacecraft could remain in the range of the Deep Space Network through about 2036, depending on how much power the spacecraft still have to transmit a signal back to Earth.
Where are Voyager 1 and 2 today?
Where is Voyager 1 going? When will it get there? How about Voyager 2?
Voyager 1 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.5 AU per year, 35 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the north, in the general direction of the solar apex (the direction of the sun's motion relative to nearby stars). Voyager 1 will leave the solar system aiming toward the constellation Ophiuchus. In the year 40,272 AD (more than 38,200 years from now), Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of an obscure star in the constellation Ursa Minor (the Little Bear or Little Dipper) called AC+79 3888.
Voyager 2 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.1 AU per year, 48 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the south toward the constellations of Sagittarius and Pavo. In about 40,000 years, Voyager 2 will come within about 1.7 light years of a star called Ross 248, a small star in the constellation of Andromeda..
Where do we consider our solar system to end; Pluto's orbit? Solar apex?
The solar system may be broadly defined as consisting of all those objects that are ultimately governed by the gravitational field of the sun. In addition to the planets, moons, asteroids and dust of the planetary system, it includes the distant bodies of the Kuiper Belt and Oort cloud, the last extending perhaps as far as 50,000 astronomical units (1 AU = about 93 million miles). The gravitational influence of the sun may extend as far as 2 light years. (From "Solar System", James H. Shirley, in Encyclopedia of Planetary Science).
That said, Pluto (and sometimes Neptune) is the most distant planet in our planetary system. The Voyagers passed the orbit of Neptune (which was furthest at the time) in August 1989. Neither flew by Pluto, which was elsewhere in its orbit at the time.
Another concept is the heliosphere, which is a bubble around the sun created by the outward flow of the solar wind from the sun and the opposing inward flow of the interstellar wind. That heliosphere is the region influenced by the dynamic properties of the sun that are carried in the solar wind - such as magnetic fields, energetic particles, solar wind plasma, etc. Voyager 1, which is traveling up away from the plane of the planets, passed out of the heliosphere into interstellar space, beyond the bubble of the solar wind, on Aug. 25, 2012. Voyager 2, which is traveling below the plane of the planets, is expected to enter interstellar space in the coming years.
Have any human-made objects ever exited the solar system?
Sometimes, it is written that Voyager and Pioneers 10 and 11 have exited the solar system. Though all of these spacecraft have gone beyond all the planets of the solar system, they have not exited the solar system, based on the scientific definition. To leave the solar system, they need to pass beyond the Oort Cloud. Voyager 1 was the first-ever object to reach interstellar space on August 25, 2012 when it passed beyond the sun’s realm of plasma influence (the heliosphere) and it is the most distant human-made object. But it will take about 300 years for Voyager 1 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly about 30,000 years to fly beyond it. Voyager 2 has not yet reached interstellar space or exited the heliosphere (bubble of solar plasma). Pioneer 10 and 11 are no longer transmitting science data back to Earth.
Are the distance counters rolling backwards?
Often they are, and it's actually not an error. This is caused by the fact that Earth moves around the sun more quickly than either Voyager spacecraft is departing from Earth. So, at certain times of the year, the distance between Earth and each Voyager actually decreases.
Did either of the Voyagers visit Pluto? Why didn't the Voyagers fly by Pluto?
Both Voyagers flew beyond the orbit of Pluto/Neptune in 1989, but neither flew by Pluto, which was elsewhere in its orbit at the time. It was never planned that the Voyagers would visit Pluto.
The original mission of Voyager was to explore Jupiter and Saturn. Two spacecraft were sent on slightly different paths, first to Jupiter and then, with gravity assists, on to Saturn. Voyager 1 could have been aimed on to Pluto, but exploration of Titan and the rings of Saturn was a primary scientific objective. This caused the trajectory to be diverted upward out of the ecliptic plane such that no further planetary encounters were possible for Voyager 1. Once Voyager 1 had successfully gathered data at Titan, Voyager 2 was allowed to go on to Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2, theoretically, could have been aimed for Pluto, but the aim point would have been inside the planet of Neptune - not very practical. NASA's New Horizons spacecraft visited Pluto in July 2015.
When we send spacecraft through the asteroid belt to the outer planets, how do we navigate the craft through the belt?
Pioneers 10 and 11 had preceded the Voyagers to Jupiter and the asteroid belt was a major concern for them. By the 1960's more than 3000 minor planets had been discovered and their orbits well determined. Even 50,000 minor bodies spread over the volume of space occupied by the asteroid belt would produce little direct danger, although a chance collision with an uncatalogued object was possible.
"While the largest of the asteroids were known and their orbits charted, many of the asteroids moved in unknown orbits. Although the risk of a spacecraft colliding with a charted asteroid was negligible, there was no way to estimate how many particles the size of a grain of sand might be present in the asteroid belt to collide with the spacecraft and seriously damage it". (From Pioneer, First to Jupiter, Saturn and Beyond, NASA SP-446, 1980) Only by going there could the danger be properly assessed - and Pioneer was first.
I was reading Dr. Carl Sagan's biography recently and found that he persuaded NASA administrators to turn one of the Voyager space probes around in order to take a last image of the solar system. Is this true? Do the craft send back any images of where they are?
I think you are referring to the series of photos taken by Voyager 1 on Valentine's Day 1990. These were the final images taken by either of the Voyager spacecraft.
On Feb. 14, 1990, after the spacecraft had passed the orbits of Neptune and Pluto, the cameras of Voyager 1 pointed back toward the sun and took a series of pictures of the sun and the planets, making the first ever 'portrait' of our solar system as seen from the outside.
I can not locate a copy of the Murmurs of Earth CD. Would you know of a vendor that might sell copies of it?
There was a book and CDROM published by Warner New Media in 1992. The book was a reprint of the Carl Sagan, et al, "Murmurs of Earth" that was originally published in 1978.
Carl Sagan and his colleagues did the assemblage of the information on the Voyager Golden Phonograph Record. Most of the material they used was copyrighted by the creators/owners and Sagan had to get copyright releases in order to assemble the original record. Subsequently, Warner Multimedia was able to obtain copyright releases for the 1992 version of "Murmurs of Earth", by Carl Sagan, et al and included all the sounds and songs on the CDROM set that accompanied the Warner New Media release of the book. We have included on the Voyager web site only that information for which we were able to get release, that's why everything, especially the music and the photos, is not there.
Unfortunately, the book and CDROM are no longer being published and are hard to find as a set. Your best bet to find one quickly may be in a public or university library or at a used bookstore. You might try used bookstores on line at http://www.bookfinder.com/ and search on: Author: Carl Sagan Title: Murmurs of Earth
You can find many instances where the book is for sale at prices around $40 US or less (most less than $20), but few (if any) include the CDROM. Look for availability of 1992 or later versions.
If there is intelligent life in our universe and they were not a peace loving species, wouldn't the information on the Voyager be enough to destroy human kind?
We have received almost nothing but praise for the inclusion of the Golden Phonograph Record on Voyager. We have also received lots of compliments on the contents, however, that praise rightly belongs to Carl Sagan and his colleagues who chose, assembled and got permission to use the material.
There were a few detractors, even as Sagan was formulating the disk.
In the Sagan, et al book, "Murmurs of Earth, the Voyager Interstellar Record", while describing some of his earlier work in sending messages from the Arecibo radar, spoke of two protests to that effort. Excerpts from that passage follow:
"One was from a few scientists who worried that we hadn't corrected for the speed of Earth in space in launching the message. ...............The other protest was a serious one, made by Sir Martin Ryle, a Nobel laureate and the Astronomer Royal of England. He wrote with great anxiety that he felt it was very hazardous to reveal our existence and location to the galaxy. For all we know, any creatures out there were malevolent or hungry, and once they knew of us, the might come to attack or eat us...........Many other less knowledgeable people had the same concerns.
"The fact is, for better or for worse, we have already announced our presence and location to the universe, and continue to do so every day. There is a sphere of radio transmission about thirty light years thick expanding outward at the speed of light, announcing to every star it envelops that the earth is full of people. Our television programs flood space with signals detectable at enormous distances by instruments not much greater than our own. It is a sobering thought that the first news of us may be the outcome of the Super Bowl.
"........... Whether or not Sir Martin Ryle is justified in his anxieties about revealing the location of our civilization is of course a debatable subject. Even so, it is too late to worry about it, so we might as well try to be friendly".
What were the most important discoveries of the Voyager space probes?
There are so many. Voyager is probably the most scientifically productive mission ever. It was only the second mission to visit Jupiter and Saturn and the only one to visit Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 1 and 2 obtained the first detailed profiles of the atmospheres of Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and improved our understanding of the characteristics of the atmosphere of Jupiter. The Voyager spacecraft revealed the enormous amount of detail in the rings of Saturn, discovered the rings of Jupiter and provided the first detailed images of the rings of Uranus and Neptune. Voyager imaged Earth's moon and discovered twenty-three new moons at the outer planets. Voyager made significant improvements in the measurements of the magnetospheres at Jupiter and Saturn and provided the first measurements of the magnetospheres at Uranus and Neptune. The significance of the Voyager is the vast amount of new knowledge about our outer solar system it provided and the interest in further exploration it generated. That interest has resulted in the Galileo mission to Jupiter and the Cassini mission to Saturn as well as the discovery of three new satellites at Saturn using Earth-based instruments.
Discovery of active volcanism on Io, a satellite of Jupiter, was probably the greatest surprise. It was the first time active volcanoes had been seen on another body in the solar system. It appears that activity on Io affects the entire Jovian system.
How big is Voyager? How much does it weigh?
The Voyager spacecraft weight, including hydrazine, at launch was 815 kg or about 1797 pounds. It was almost the weight and size of a sub-compact car. The current approximate weight of Voyager 1 is 733 kg and Voyager 2 is 735 kg. The difference is in the amount of hydrazine remaining. Hydrazine is being used to control the spacecrafts' attitude.
The spacecraft, without the various booms could fit inside a cube that is about 4 meters on each side. The approximate measurements of the different structures follow:
- The high gain antenna is 3.7 meters across (diameter).
- The magnetometer boom is 13 meters long
- The two Planetary Radio Astronomy and Plasma Wave antenna are 10 meters long.
- The Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator boom is 3.7 meters long
- The science instrument boom (near top of picture) is 3 meters long.
- The Bus Housing Electronics is about 1.8 meters in diameter.
The spacecraft height - from the top of the reflector structure in the middle of the high gain antenna to the bottom of the triangular feet below the bus housing electronics - is about 3.8 meters
The launch vehicle was a Titan III E/ Centaur rocket, which stands nearly 50 m (164 ft) high and weighs almost 635,000 kg (1.4 million lb).
Is it true that a sketch by Da Vinci is included in the "Message to the Universe" of Voyagers 1 and 2?
There are messages on the Voyagers in the form of a phonograph record and drawings on the cover that protects the record. However, Leonardo Da Vinci's Vitruvian Man was not part of the Voyager Golden Phonograph Record, the Voyager cover, or the Pioneer plaque. Read more about the golden record .
What kind of computers are used on the Voyager spacecraft?
There are three different computer types on the Voyager spacecraft and there are two of each kind. Total number of words among the six computers is about 32K.
- Computer Command System (CCS) - 18-bit word, interrupt type processors (2) with 4096 words each of plated wire, non-volatile memory.
- Flight Data System (FDS) - 16-bit word machine (2) with modular memories and 8198 words each
- Attitude and Articulation Control System (AACS) - 18-bit word machines (2) with 4096 words each.
According to my calculations, that's a total of about 68KB, or small potatoes compared to today's microprocessors. We probably could perform all functions with one of today's boards and still have room for solid state data storage and much more fault detection software. We would still need a second unit for redundancy. Today's microprocessors are also much faster than the chips used on Voyager and a comparative system would use less electrical power. On the other hand, software might be more complicated as opposed to that used in an interrupt type system, but it would be much more capable and more flexible.
Let's look closer at the CCS. The CCS has two main functions: to carry out instructions from the ground to operate the spacecraft, and to be alert for a problem or malfunction and respond to it. Two identical 4096- word memories contain both fixed routines (about 2800 words) and a variable section (about 1290 words) for changing science sequences. The CCS issues commands to the AACS for movement of the scan platform or spacecraft maneuvers; to the FDS for changes in instrument configurations or telemetry rates and to numerous other subsystems within the spacecraft for specific actions. Fault-protection algorithms are also stored in the CCS, occupying roughly 10 percent of the CCS memory.
The main functions of the FDS are to collect data from, and controls the operations of, the scientific instruments; and to format engineering and science data for on-board storage and/or real-time transmission. The FDS also keeps the spacecraft "time" and provides frequency references to the instruments and other spacecraft subsystems.
The Voyager spacecraft computers are interrupt driven computer, similar to processors used in general purpose computers with a few special instructions for increased efficiency. The programming is a form of assembly language.
There is no clock chip, as such, in the spacecraft. The "clock" is really a counter, based on one of several electronically generated frequencies. These frequencies, based on a reference, generated by a very stable oscillator, are converted and fed to different locations in the spacecraft as synchronization signals, timers, counters, etc. The "clock" signal is part of the information telemetered to the ground and it is with ground software that we convert to day of year, time of day Greenwich Mean Time.
Voyager was built in-house at JPL; the computers were manufactured by General Electric to JPL specifications.
How fast are the Voyager computers?
Not very fast compared to today’s standards. The master clock runs at 4 MHz but the CPU’s clock runs at only 250 KHz. A typical instruction takes 80 microseconds, that is about 8,000 instructions per second. To put this in perspective, a 2013 top-of-the-line smartphone runs at 1.5 GHz with four or more processors yielding over 14 billion instructions per second.
What is the "direction" (constellation and/or star) both Voyager 1 & 2 and the Pioneers are "aimed" for, at present.
- Pioneer 10 is headed towards the constellation of Taurus (The Bull). It will take Pioneer over 2 million years to pass by one of the stars in the constellation.
- Pioneer 11 is headed toward the constellation of Aquila (The Eagle), Northwest of the constellation of Sagittarius. Pioneer 11 may pass near one of the stars in the constellation in about 4 million years.
- Voyager 1 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.5 AU per year, 35 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the north, in the general direction of the Solar Apex (the direction of the Sun's motion relative to nearby stars). Voyager 1 will leave the solar system aiming toward the constellation Ophiuchus. In the year 40,272 AD, Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of an obscure star in the constellation Ursa Minor (the Little Bear or Little Dipper) called AC+79 3888.
- Voyager 2 is also escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.1 AU per year, 48 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the south toward the constellations of Sagitarrius and Pavo. In about 40,000 years, Voyager 2 will come within about 1.7 light years of a star called Ross 248, a small star in the constellation of Andromeda.
Where can I find pictures of what the Voyager spacecraft took?
You can view pictures from Voyager and other missions at several locations:
- NSSDC Planetary Image Catalog http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/imgcat
- Planetary Photojournal http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/
- NSSDC Photo Gallery http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/photo_gallery
Is there some sort of plate with pictograms on the Voyager 1 spacecraft? Also is it similar to the Pioneer spacecraft plaque?
You asked about the Voyager plate. I'm assuming you mean the engravings on the aluminum record cover on each of the two Voyagers. You can see the record cover installed on the spacecraft bus . Also, from Carl Sagan's book, "Murmurs of Earth", here is a description of the cover engravings:
"In the upper left-hand corner is an easily recognized drawing of the phonograph record and the stylus carried with it. The stylus is in the correct position to play the record from the beginning. Written around it in binary arithmetic is the correct time of one rotation of the record, 3.6 seconds, expressed in time units of 0,70 billionths of a second, the time period associated with a fundamental transition of the hydrogen atom. The drawing indicates that the record should be played from the outside in. Below this drawing is a side view of the record and stylus, with a binary number giving the time to play one side of the record - about an hour.
"The information in the upper right-hand portion of the cover is designed to show how pictures are to be constructed from the recorded signals. The top drawing shows the typical signal that occurs at the start of a picture. The picture is made from this signal, which traces the picture as a series of vertical lines, similar to ordinary television (in which the picture is a series of horizontal lines). Picture lines 1, 2 and 3 are noted in binary numbers, and the duration of one of the "picture lines," about 8 milliseconds, is noted. The drawing immediately below shows how these lines are to be drawn vertically, with staggered "interlace" to give the correct picture rendition. Immediately below this is a drawing of an entire picture raster, showing that there are 512 vertical lines in a complete picture. Immediately below this is a replica of the first picture on the record to permit the recipients to verify that they are decoding the signals correctly. A circle was used in this picture to insure that the recipients use the correct ratio of horizontal to vertical height in picture reconstruction.
"The drawing in the lower left-hand corner of the cover is the pulsar map previously sent as part of the plaques on Pioneers 10 and 11. It shows the location of the solar system with respect to 14 pulsars, whose precise periods are given. The drawing containing two circles in the lower right-hand corner is a drawing of the hydrogen atom in its two lowest states, with a connecting line and digit 1 to indicate that the time interval associated with the transition from one state to the other is to be used as the fundamental time scale, both for the time given on the cover and in the decoded pictures.
"Electroplated onto the record's cover is an ultra-pure source of uranium-238 with a radioactivity of about 0.00026 microcuries. The steady decay of the uranium source into its daughter isotopes makes it a kind of radioactive clock. Half of the uranium-238 will decay in 4.51 billion years. Thus, by examining this two-centimeter diameter area on the record plate and measuring the amount of daughter elements to the remaining uranium-238, an extraterrestrial recipient of the Voyager spacecraft could calculate the time elapsed since a spot of uranium was placed aboard the spacecraft. This should be a check on the epoch of launch, which is also described by the pulsar map on the record cover."
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe
Engineers spent months working to repair link with Earth’s most distant spacecraft, says space agency
Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday , JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X . “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries , including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.

Cosmic cleaners: the scientists scouring English cathedral roofs for space dust

Russia acknowledges continuing air leak from its segment of space station

Uncontrolled European satellite falls to Earth after 30 years in orbit

Cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko sets world record for most time spent in space

‘Old smokers’: astronomers discover giant ancient stars in Milky Way

Nasa postpones plans to send humans to moon

What happened to the Peregrine lander and what does it mean for moon missions?

Peregrine 1 has ‘no chance’ of landing on moon due to fuel leak
Most viewed.
Voyager 2 Enters Final Planetary Encounter

NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatoryphase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system.
Voyager mission controllers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., will now be tracking the spacecraft around the clock as Voyager begins taking systematic images of Neptune and sending back about 50 pictures day.
"Now that we've entered the observatory phase we'll be taking about six images every three hours to study changes in the atmosphere from rotation to rotation," said Dr. Ellis Miner, Voyager deputy project scientist.
Signals from Voyager 2 marking the beginning of the observatory phase were received at 3:40 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time. This official start of the Neptune encounter places Voyager at the top of the priority list of spacecraft being tracked by the NASA/JPL Deep Space Network. Before today, Voyager had to compete with other projects for DSN coverage. During the observatory phase, the spacecraft will be monitored at regular intervals by more than one antenna at each of the DSN sites in California, Spain and Australia.
In addition to taking images of the planet, Voyager 2 will also be making systematic ultraviolet observations of Neptune looking for any auroral activity and escaping gases. Calibrations of the spacecraft's instruments will also be done in preparation for critical near-encounter observations.
In observations of Neptune made by Voyager 2 in late 1988 and January of 1989, scientists saw bright spot in the southern hemisphere of the planet. Since January, that spot has dimmed and larger dark area has been seen in the images. Recently, the bright spot has begun to brighten again and other spots are becoming apparent. Neptune's atmosphere has also revealed regions of dark banding near its southern pole and similar banding has been seen north of the planet's equator.
Voyager's observatory phase ends and its far encounter phase starts on Aug. 6, 1989.
The near-encounter phase of the mission includes Voyager's closest approach to Neptune at 9 p.m. Pacific Daylight Time on Aug. 24, 1989, when the spacecraft passes just 4,850 kilometers (3,000 miles) from the planet's cloud tops. Five hours later, the spacecraft will fly about 39,000 kilometers (24,000 miles) from the planet's major moon Triton.
Voyager 2 is now 117 million kilometers (73 million miles) from Neptune. The Neptune flyby will be Voyager 2's fourth and final planetary encounter before the spacecraft heads out of the solar system to explore interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 and its twin Voyager 1 have encountered Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 went on to fly by Uranus in January 1986 while Voyager 1 continues its trek out of the solar system.
Now 4.271 billion kilometers (2.654 billion miles) from Earth, Voyager 2 is so far away that data radioed at the speed of light (186,000 miles per second) take nearly four hours to reach Earth. Voyager's images are being recorded on the spacecraft's tape recorders and will be played back to Earth beginning Tuesday morning.
The Voyager project is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications.
After months of silence, Voyager 1 has returned NASA’s calls

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end.
Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has diligently sent regular updates to Earth on the health of its systems and data collected from its onboard instruments.
But in November, the craft went quiet.
Voyager 1 is now some 15 billion miles away from Earth. Somewhere in the cold interstellar space between our sun and the closest stars, its flight data system stopped communicating with the part of the probe that allows it to send signals back to Earth. Engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge could tell that Voyager 1 was getting its messages, but nothing was coming back.
“We’re to the point where the hardware is starting to age,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager mission. “It’s like working on an antique car, from 15 billion miles away.”
Week after week, engineers sent troubleshooting commands to the spacecraft, each time patiently waiting the 45 hours it takes to get a response here on Earth — 22.5 hours traveling at the speed of light to reach the probe, and 22.5 hours back.

Science & Medicine
This space artist created the Golden Record and changed the way we see the universe
Space artist Jon Lomberg has produced work that attempts to visualize what we can’t truly see, and to communicate with creatures we can’t yet imagine.
July 26, 2023
By March, the team had figured out that a memory chip that stored some of the flight data system’s software code had failed, turning the craft’s outgoing communications into gibberish.
A long-distance repair wasn’t possible. There wasn’t enough space anywhere in the system to shift the code in its entirety. So after manually reviewing the code line by line, engineers broke it up and tucked the pieces into the available slots of memory.
They sent a command to Voyager on Thursday. In the early morning hours Saturday, the team gathered around a conference table at JPL: laptops open, coffee and boxes of doughnuts in reach.
At 6:41 a.m., data from the craft showed up on their screens. The fix had worked .
“We went from very quiet and just waiting patiently to cheers and high-fives and big smiles and sighs of relief,” Spilker said. “I’m very happy to once again have a meaningful conversation with Voyager 1.”
Voyager 1 is one of two identical space probes. Voyager 2, launched two weeks before Voyager 1, is now about 13 billion miles from Earth, the two crafts’ trajectories having diverged somewhere around Saturn. (Voyager 2 continued its weekly communications uninterrupted during Voyager 1’s outage.)

Space shuttle Endeavour is lifted into the sky, takes final position as star of new museum wing
A shrink-wrapped Endeavour was hoisted and then carefully placed in its final location Tuesday at the still-under-construction Samuel Oschin Air and Space Center.
Jan. 30, 2024
They are the farthest-flung human-made objects in the universe, having traveled farther from their home planet than anything else this species has built. The task of keeping communications going grows harder with each passing day. Every 24 hours, Voyager 1 travels 912,000 miles farther away from us. As that distance grows, the signal becomes slower and weaker.
When the probe visited Jupiter in 1979, it was sending back data at a rate of 115.2 kilobits per second, Spilker said. Today, 45 years and more than 14 billion miles later, data come back at a rate of 40 bits per second.
The team is cautiously optimistic that the probes will stay in contact for three more years, long enough to celebrate the mission’s 50th anniversary in 2027, Spilker said. They could conceivably last until the 2030s.
The conversation can’t last forever. Microscopic bits of silica keep clogging up the thrusters that keep the probes’ antennas pointed toward Earth, which could end communications. The power is running low. Eventually, the day will come when both Voyagers stop transmitting data to Earth, and the first part of their mission ends.
But on the day each craft goes quiet, they begin a new era, one that could potentially last far longer. Each probe is equipped with a metallic album cover containing a Golden Record , a gold-plated copper disk inscribed with sounds and images meant to describe the species that built the Voyagers and the planet they came from.
Erosion in space is negligible; the images could be readable for another billion years or more. Should any other intelligent life form encounter one of the Voyager probes and have a means of retrieving the data from the record, they will at the very least have a chance to figure out who sent them — even if our species is by that time long gone.

JPL tries to keep Voyager space probes from disconnecting the world’s longest phone call
Keeping in touch with NASA’s two aging Voyager spacecraft is getting harder to do as they get farther away and their power sources dwindle.
Sept. 3, 2022
More to Read
Too expensive, too slow: NASA asks for help with JPL’s Mars Sample Return mission
April 15, 2024

NASA’s attempt to bring home part of Mars is unprecedented. The mission’s problems are not
March 25, 2024
Budget deal for NASA offers glimmer of hope for JPL’s Mars Sample Return mission
March 6, 2024

Corinne Purtill is a science and medicine reporter for the Los Angeles Times. Her writing on science and human behavior has appeared in the New Yorker, the New York Times, Time Magazine, the BBC, Quartz and elsewhere. Before joining The Times, she worked as the senior London correspondent for GlobalPost (now PRI) and as a reporter and assignment editor at the Cambodia Daily in Phnom Penh. She is a native of Southern California and a graduate of Stanford University.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Kern County supervisor investigated for allegedly sexually assaulting his child
April 25, 2024

Oceanside Pier fire now contained, officials say

When was the last time the No. 1 overall NFL draft pick came from USC?

San Bernardino County teacher arrested after allegations of inappropriate conduct with 16-year-old girl

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
mission Mission Status. Voyager 1 Voyager 2; Launch Date: ... Note: Because Earth moves around the Sun faster than Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 is traveling from Earth, the one-way light time between Earth and each spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of the year. Cosmic Ray Data:
NASA's Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space. On Dec. 10, 2018, the spacecraft joined its twin - Voyager 1 - as the only human-made objects to enter the space between the stars. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range. Voyager 2 discovered a 14th moon at ...
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. Missions. Search All NASA Missions; ... Mission Status. Voyager 1. Voyager 2. Launch Date. Monday, Sep 5, 1977 12:56:00 UTC. Saturday Aug 20, 1977 14:29:00 UTC. Mission Elapsed Time. 46 years, six months.
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have ever visited Uranus and Neptune, and has made its way to interstellar space, where its twin, Voyager 1, has resided since 2012. The spacecraft's launch date was Aug. 20, 1977 and its current status is current, meaning it is operating as normal.
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-45-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the Sun than Pluto. ... Status. Learn about Voyagers' mission status: where they are in the space, the time required to communicate ...
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech. UPDATE, Aug. 4, 2023: NASA has reestablished full communications with Voyager 2. The agency's Deep Space Network facility in Canberra, Australia, sent the equivalent of an interstellar "shout" more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) to Voyager 2, instructing the spacecraft to reorient itself and ...
News updates on Voyager 2's encounter with Neptune will be available to the public during late August on special telephone numbers from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Frequently updated reports on the spacecraft mission can be heard August 19-31 by phoning (900) 590-1234. Cost for each call on this 900 number is 45 cents for the first minute ...
NASA Mission Update: Voyager 2 Communications Pause. Article. 5 Min Read. NASA's Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy. Article. 7 Min Read. NASA Missions Study What May Be a 1-In-10,000-Year Gamma-ray Burst. Multimedia Go To Galleries Go To Galleries Keep Exploring
Its primary mission was to study the outer solar system, and already, Voyager 2 has proved its status as a planetary pioneer. Equipped with several imaging instruments, the spacecraft is credited ...
Voyager 2 is currently unable to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth due to a carrier signal issue. The spacecraft is operating normally and on its expected trajectory, and the mission team is working to reestablish full communications with the spacecraft.
Voyager 2. Heliocentric positions of the five interstellar probes (squares) and other bodies (circles) until 2020, with launch and flyby dates. Markers denote positions on 1 January of each year, with every fifth year labelled. Plot 1 is viewed from the north ecliptic pole, to scale. Plots 2 to 4 are third-angle projections at 20% scale.
In about 40,000 years Voyager 2 will pass 1.7 light-years (9.7 trillion miles) from the star Ross 248, according to NASA JPL. The cosmic vagabond will continue its journey through interstellar ...
The Voyager primary mission was completed in 1989, with the close flyby of Neptune by Voyager 2. The Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) is a mission extension, ... Voyager Mission status (updated in real time) Voyager Spacecraft Lifetime; NASA Facts - Voyager Mission to the Outer Planets; Voyager 1 and 2 atlas of six Saturnian satellites, 1984;
The mission team expects Voyager 2 to remain on its planned trajectory during the quiet period. Voyager 1, which is almost 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, continues to operate normally. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a ...
VOYAGER MISSION STATUS. August 1, 1994. Both the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are healthy and they are continuing to take data on fields and particles in interplanetary space. The Voyager 2 spacecraft used two of its scientific instruments to look at the impacts of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 fragments as they impacted Jupiter July 16-22.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 2's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 2 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
VOYAGER STATUS REPORT. July 1, 1994. Both the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are healthy and they continue to collect fields and particles data in their quests to detect the heliopause, the outer edge of the sun's energy influence. In addition, both spacecraft are using the ultraviolet spectrometers to look back at our Sun and study solar activities.
Engineers for NASA's Voyager mission are taking steps to help make sure both spacecraft, launched in 1977, continue to explore interstellar space for years to come. ... A critical system aboard the probe was sending garbled data about its status. Engineers have fixed the issue but are still seeking the root cause. ... the Voyager 2 spacecraft ...
For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1, which along with its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space, has not been able to send readable data about its health or scientific mission since Nov ...
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system.
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and ...
Voyager 2 is also escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.3 AU per year, 48 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the south. To check Voyager 1 and 2's current distance from the sun, visit the mission status page. Passage through the termination shock ended the termination shock phase and began the heliosheath exploration phase.
Members of the Voyager 1 flight team celebrate after receiving health and status data from the spacecraft. Next, engineers need to enable the probe to start sending science data again.
The current approximate weight of Voyager 1 is 733 kg and Voyager 2 is 735 kg. The difference is in the amount of hydrazine remaining. Hydrazine is being used to control the spacecrafts' attitude. The spacecraft, without the various booms could fit inside a cube that is about 4 meters on each side.
In an update released on Monday, JPL announced the mission team had managed "after some inventive sleuthing" to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1's engineering ...
The Voyager project is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications. 818-354-5011. 1989-1246. NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatoryphase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system.
For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end. Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA's Voyager 1 ...
pdt: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 0 utc: apr 25 apr 26 utc: 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7