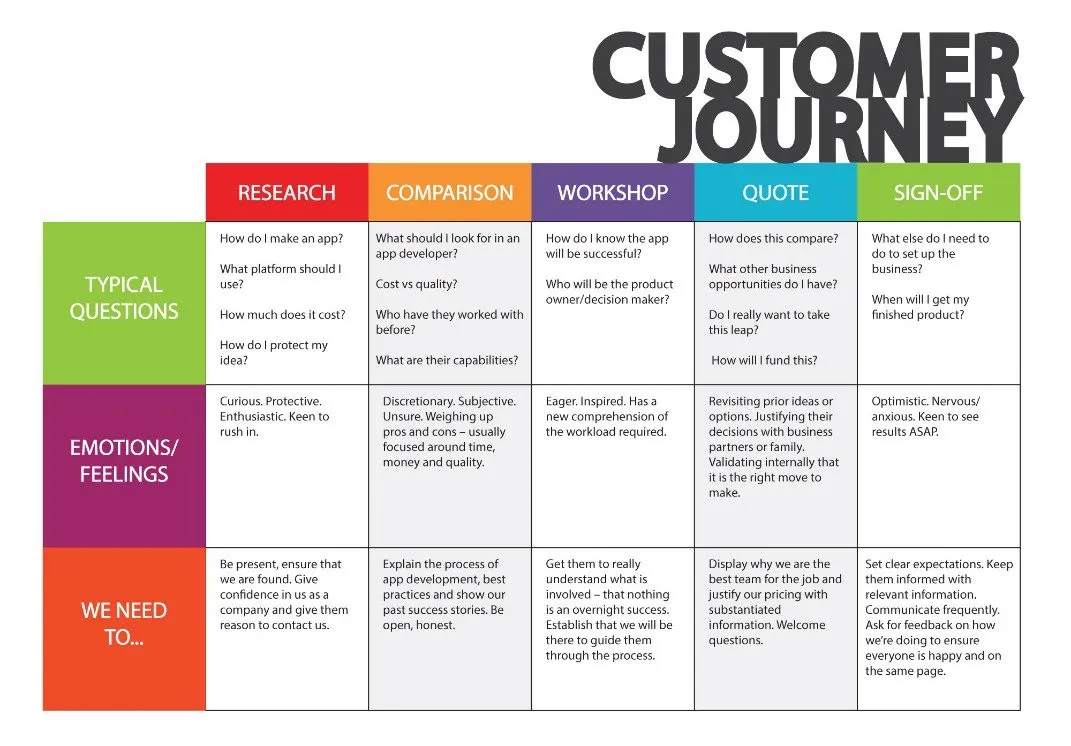
The customer journey — definition, stages, and benefits

Businesses need to understand their customers to increase engagement, sales, and retention. But building an understanding with your customers isn’t easy.
The customer journey is the road a person takes to convert, but this journey isn’t always obvious to business owners. Understanding every step of that journey is key to business success. After reading this article, you’ll understand the customer journey better and how to use it to improve the customer experience while achieving your business goals.
This post will discuss:
- What a customer journey is

Customer journey stages
Benefits of knowing the customer journey.
- What a customer journey map is
How to create a customer journey map
Use the customer journey map to optimize the customer experience, what is a customer journey.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers’ experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint.
Giving customers a positive customer experience is important for getting customers to trust a business, so optimizing the customer journey has never mattered more. By mastering the customer journey, you can design customer experiences that will lead to better customer relationships, loyalty, and long-term retention .
Customer journey vs. the buyer journey
The stages of the customer’s journey are different from the stages of the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey follows the customer experience from initial awareness of a brand to buying a product. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase and follows how customers interact with your product and how they share it with others.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around.
Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey:

1. Awareness
In the awareness phase, your target audience is just becoming aware of your brand and products. They need information or a solution to a problem, so they search for that information via social media and search engines.
For example, if someone searches on Google for pens for left-handed people, their customer journey begins when they’re first aware of your brand’s left-handed pen.
At this stage, potential customers learn about your business via web content, social media, influencers, and even their friends and family. However, this isn’t the time for hard sells. Customers are simply gathering information at this stage, so you should focus first on answering their questions and building trust.
2. Consideration
In the consideration phase, customers begin to consider your brand as a solution to their problem. They’re comparing your products to other businesses and alternative solutions, so you need to give these shoppers a reason to stick around.
Consideration-stage customers want to see product features that lean heavily toward solving problems and content that doesn’t necessarily push a sale. At this stage, businesses need to position their solution as a better alternative. For example, a nutrition coaching app might create content explaining the differences between using the app and working with an in-person nutritionist — while subtly promoting the benefits of choosing the app.
3. Purchase
The purchase stage is also called the decision stage because at this stage customers are ready to make a buying decision. Keep in mind that their decision might be to go with a competing solution, so purchase-stage buyers won’t always convert to your brand.
As a business, it’s your job to persuade shoppers at this stage to buy from you. Provide information on pricing, share comparison guides to showcase why you’re the superior option, and set up abandoned cart email sequences.
4. Retention
The customer journey doesn’t end once a shopper makes their first purchase. Once you’ve converted a customer, you need to focus on keeping them around and driving repeat business. Sourcing new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing clients, so this strategy can help you cut down on marketing costs and increase profits.
The key to the retention stage is to maintain positive, engaging relationships between your brand and its customers. Try strategies like regular email outreach, coupons and sales, or exclusive communities to encourage customer loyalty.
5. Advocacy
In the advocacy stage, customers are so delighted with your products and services that they spread the word to their friends and family. This goes a step beyond retention because the customer is actively encouraging other people to make purchases.
Customer journeys don’t have a distinct end because brands should always aim to please even their most loyal customers. In the advocacy stage of the customer journey, you can offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs, and special deals for your most active customers to encourage further advocacy.
Being aware of the customer journey helps shed more light on your target audience’s expectations and needs. In fact, 80% of companies compete primarily on customer experience. This means optimizing the customer journey will not only encourage your current customers to remain loyal but will also make you more competitive in acquiring new business.
More specifically, acknowledging the customer journey can help you:

- Understand customer behavior. Classifying every action your customers take will help you figure out why they do what they do. When you understand a shopper’s “why,” you’re better positioned to support their needs.
- Identify touchpoints to reach the customer. Many businesses invest in multichannel marketing, but not all of these touchpoints are valuable. By focusing on the customer journey, you’ll learn which of these channels are the most effective for generating sales. This helps businesses save time and money by focusing on only the most effective channels.
- Analyze the stumbling blocks in products or services. If leads frequently bail before buying, that could be a sign that something is wrong with your product or buying experience. Being conscious of the customer journey can help you fix issues with your products or services before they become a more expensive problem.
- Support your marketing efforts. Marketing requires a deep familiarity with your target audience. Documenting the customer journey makes it easier for your marketing team to meet shoppers’ expectations and solve their pain points.
- Increase customer engagement. Seeing the customer journey helps your business target the most relevant audience for your product or service. Plus, it improves the customer experience and increases engagement. In fact, 29.6% of customers will refuse to embrace branded digital channels if they have a poor experience, so increasing positive customer touchpoints has never been more important.
- Achieve more conversions. Mapping your customers’ journey can help you increase conversions by tailoring and personalizing your approach and messages to give your audience exactly what they want.
- Generate more ROI. You need to see a tangible return on your marketing efforts. Fortunately, investing in the customer journey improves ROI across the board. For example, brands with a good customer experience can increase revenue by 2–7% .
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Today, 94% of customers say a positive experience motivates them to make future purchases. Optimizing the customer journey helps you meet shopper expectations, which increases satisfaction and loyalty.

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every step your customer takes from being a lead to eventually becoming an advocate for your brand. The goal of customer journey mapping is to simplify the complex process of how customers interact with your brand at every stage of their journey.
Businesses shouldn’t use a rigid, one-size-fits-all customer journey map. Instead, they should plan flexible, individual types of customer journeys — whether they’re based on a certain demographic or on individual customer personas. To design the most effective customer journey map, your brand needs to understand a customer’s:
- Actions. Learn which actions your customer takes at every stage. Look for common patterns. For example, you might see that consideration-stage shoppers commonly look for reviews.
- Motivations. Customer intent matters. A person’s motivations change at every stage of the customer journey, and your map needs to account for that. Include visual representation of the shopper’s motivations at each stage. At the awareness stage, their motivation might be to gather information to solve their problem. At the purchase stage, it might be to get the lowest price possible.
- Questions. Brands can take customers’ common questions at every stage of the customer journey and reverse-engineer them into useful content. For example, shoppers at the consideration stage might ask, “What’s the difference between a DIY car wash and hiring a professional detailer?” You can offer content that answers their question while subtly promoting your car detailing business.
- Pain points. Everybody has a problem that they’re trying to solve, whether by just gathering intel or by purchasing products. Recognizing your leads’ pain points will help you craft proactive, helpful marketing campaigns that solve their biggest problems.
Customer journey touchpoints
Every stage of the customer journey should also include touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are the series of interactions with your brand — such as an ad on Facebook, an email, or a website chatbot — that occur at the various stages of the customer journey across multiple channels. A customer’s actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will differ at each stage and at each touchpoint.
For example, a customer searching for a fishing rod and reading posts about how they’re made will have very different motivations and questions from when later comparing specs and trying to stay within budget. Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.

It might sound like more work, but mapping the entire customer journey helps businesses create a better customer experience throughout the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with your brand.
Before jumping into the steps of how to create the customer journey map, first be clear that your customer journey map needs to illustrate the following:
- Customer journey stages. Ensure that your customer journey map includes every stage of the customer journey. Don’t just focus on the stages approaching the purchase — focus on the retention and advocacy stages as well.
- Touchpoints. Log the most common touchpoints customers have at every stage. For example, awareness-stage touchpoints might include your blog, social media, or search engines. Consideration-stage touchpoints could include reviews or demo videos on YouTube. You don’t need to list all potential touchpoints. Only list the most common or relevant touchpoints at each stage.
- The full customer experience. Customers’ actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will change at every stage — and every touchpoint — during the customer journey. Ensure your customer journey map touches on the full experience for each touchpoint.
- Your brand’s solutions. Finally, the customer journey map needs to include a branded solution for each stage and touchpoint. This doesn’t necessarily mean paid products. For example, awareness-stage buyers aren’t ready to make a purchase, so your brand’s solution at this stage might be a piece of gated content. With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process.
1. Create buyer personas
A buyer persona is a fictitious representation of your target audience. It’s a helpful internal tool that businesses use to better understand their audience’s background, assumptions, pain points, and needs. Each persona differs in terms of actions, motivations, questions, and pain points, which is why businesses need to create buyer personas before they map the customer journey.
To create a buyer persona, you will need to:
- Gather and analyze customer data. Collect information on your customers through analytics, surveys, and market research.
- Segment customers into specific buying groups. Categorize customers into buying groups based on shared characteristics — such as demographics or location. This will give you multiple customer segments to choose from.
- Build the personas. Select the segment you want to target and build a persona for that segment. At a minimum, the buyer persona needs to define the customers’ basic traits, such as their personal background, as well as their motivations and pain points.

For example, ClearVoice created a buyer persona called “John The Marketing Manager.” The in-depth persona details the target customer’s pain points, pet peeves, and potential reactions to help ClearVoice marketers create more customer-focused experiences.
2. List the touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you’ve created your buyer personas, you need to sketch out each of the five stages of the customer journey and then list all of the potential touchpoints each buyer persona has with your brand at every one of these five stages. This includes listing the most common marketing channels where customers can interact with you. Remember, touchpoints differ by stage, so it’s critical to list which touchpoints happen at every stage so you can optimize your approach for every buyer persona.
Every customer’s experience is different, but these touchpoints most commonly line up with each stage of the customer journey:
- Awareness. Advertising, social media, company blog, referrals from friends and family, how-to videos, streaming ads, and brand activation events.
- Consideration. Email, sales calls, SMS, landing pages, and reviews.
- Purchase. Live chat, chatbots, cart abandonment emails, retargeting ads, and product print inserts.
- Retention. Thank you emails, product walkthroughs, sales follow-ups, and online communities.
- Advocacy. Surveys, loyalty programs, and in-person events.
Leave no stone unturned. Logging the most relevant touchpoints at each stage eliminates blind spots and ensures your brand is there for its customers, wherever they choose to connect with you.
3. Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now that you’ve defined each touchpoint at every stage of the customer journey, it’s time to detail the exact experience you need to create for each touchpoint. Every touchpoint needs to consider the customer’s:
- Actions. Describe how the customer got to this touchpoint and what they’re going to do now that they’re here.
- Motivations. Specify how the customer feels at this moment. Are they frustrated, confused, curious, or excited? Explain why they feel this way.
- Questions. Every customer has questions. Anticipate the questions someone at this stage and touchpoint would have — and how your brand can answer those questions.
- Pain points. Define the problem the customer has — and how you can solve that problem at this stage. For example, imagine you sell women’s dress shoes. You’re focusing on the buyer persona of a 36-year-old Canadian woman who works in human resources. Her touchpoints might include clicking on your Facebook ad, exploring your online shop, but then abandoning her cart. After receiving a coupon from you, she finally buys. Later, she decides to exchange the shoes for a different color. After the exchange, she leaves a review. Note how she acts at each of these touchpoints and detail her likely pain points, motivations, and questions, for each scenario. Note on the map where you intend to respond to the customer’s motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions. If you can create custom-tailored solutions for every stage of the funnel, that’s even better.
A positive customer experience is the direct result of offering customers personalized, relevant, or meaningful content and other brand interactions. By mapping your customers’ motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions, you’ll find opportunities to improve the customer experience. When you truly address their deepest needs, you’ll increase engagement and generate more positive reviews.
Follow these strategies to improve the customer experience with your customer journey map:
- Prioritize objectives. Identify the stages of the customer journey where your brand has the strongest presence and take advantage of those points. For example, if leads at the consideration stage frequently subscribe to your YouTube channel, that gives you more opportunities to connect with loyal followers.
- Use an omnichannel approach to engage customers. Omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather information and create a more holistic view of the customer journey. This allows you to personalize the customer experience on another level entirely. Use an omnichannel analytics solution that allows you to capture and analyze the true cross-channel experience.
- Personalize interactions at every stage. The goal of mapping the customer journey is to create more personalized, helpful experiences for your audience at every stage and touchpoint. For example, with the right data you can personalize the retail shopping experience and customer’s website experience.
- Cultivate a mutually trusting relationship. When consumer trust is low, brands have to work even harder to earn their customers’ trust. Back up your marketing promises with good customer service, personalized incentives, and loyalty programs.
Getting started with customer journeys
Customer journeys are complicated in an omnichannel environment, but mapping these journeys can help businesses better understand their customers. Customer journey maps help you deliver the exact experience your customers expect from your business while increasing engagement and sales.
When you’re ready to get started, trace the interactions your customers have at each stage of their journey with your brand. Adobe Customer Journey Analytics — a service built on Adobe Experience Platform — can break down, filter, and query years’ worth of data and combine it from every channel into a single interface. Real-time, omnichannel analysis and visualization let companies make better decisions with a holistic view of their business and the context behind every customer action.
Learn more about Customer Journey Analytics by watching the overview video .
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/introducing-adobes-customer-journey-maturity-model
https://business.adobe.com/blog/how-to/create-customer-journey-maps
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-customer-journey-map

- Get Out Of Dark
- Creating CJM
- Improving CX
- Expert advice
- Online Marketing
- Marketing OPS
- Consultants

1998: From contact centers to corporate missions
Fast forward to 1998, and the concept wasn’t just for frustrated callers anymore. OxfordSM, a consulting firm, applied journey mapping to help Eurostar, a high-speed rail service, define its brand and mission. This move marked a shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive experience design. Suddenly, businesses saw the power of understanding the entire customer journey, not just isolated touchpoints.
2000s: The digital wave and the rise of personas
The turn of the millennium brought the digital revolution, and customer journeys became increasingly complex. Websites, email, and eventually social media became additional touchpoints, each demanding attention. To navigate this new landscape, personas emerged – fictional representations of ideal customers – helping businesses personalize the journey and cater to specific needs.

2010s: Big data, analytics, and the quantified customer
The 2010s saw an explosion of customer data . Businesses could now track behavior, analyze sentiment, and measure every click and swipe. This led to a more data-driven approach to journey mapping, with heatmaps, A/B testing, and complex analytics informing design decisions.
Today: The age of experience and the evolving journey
Today, customer journey mapping is no longer just a tool; it’s a mindset. Businesses understand that the journey is an ongoing conversation, not a linear path. They actively listen to feedback, iterate based on insights, and strive to create seamless, emotional experiences across all touchpoints.
The Future: What Lies Ahead for the Journey?
As technology continues to evolve, so too will customer journey mapping. Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the ever-changing digital landscape will present new challenges and opportunities. But one thing remains constant: the need to understand and empathize with customers , creating journeys that are not just efficient, but truly delightful.
So, the next time you map a customer journey, remember, you’re not just creating a diagram; you’re contributing to a rich history of understanding and serving customers better. And who knows, maybe your map will be the one that shapes the future of customer experience!
- Online marketing
Do you want to create an interactive and easy-to-use customer journey map with powerful touchpoints, personas, automatic KPI import & monitoring, and much more?
Related articles, 8 ways companies disappoint customers (and how to avoid it), 7 steps to becoming a lovebrand, 6 ways how to decrease cart abandonment in your online store, 6 cool ways ai can change customer journey mapping in the future.
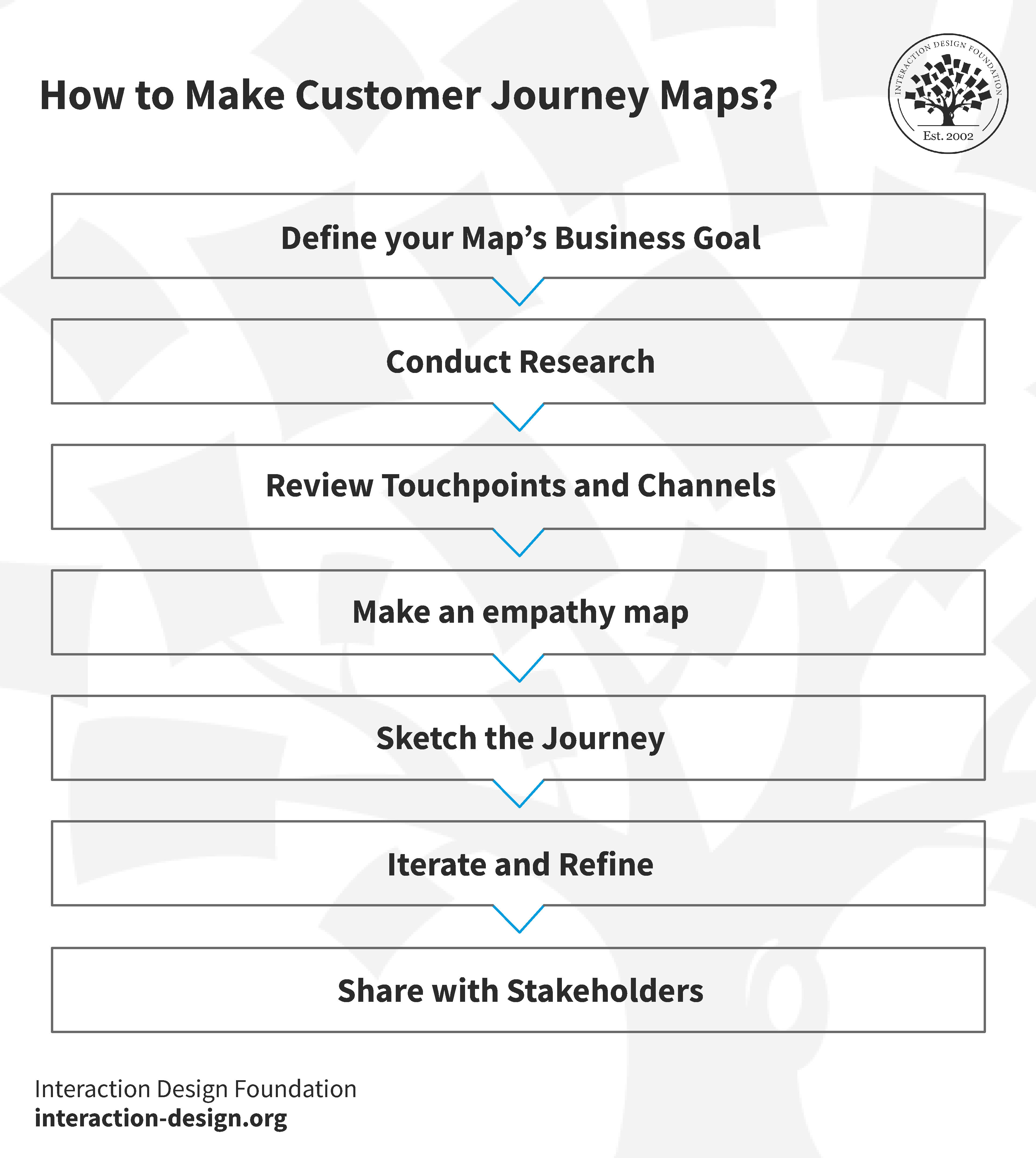
How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.
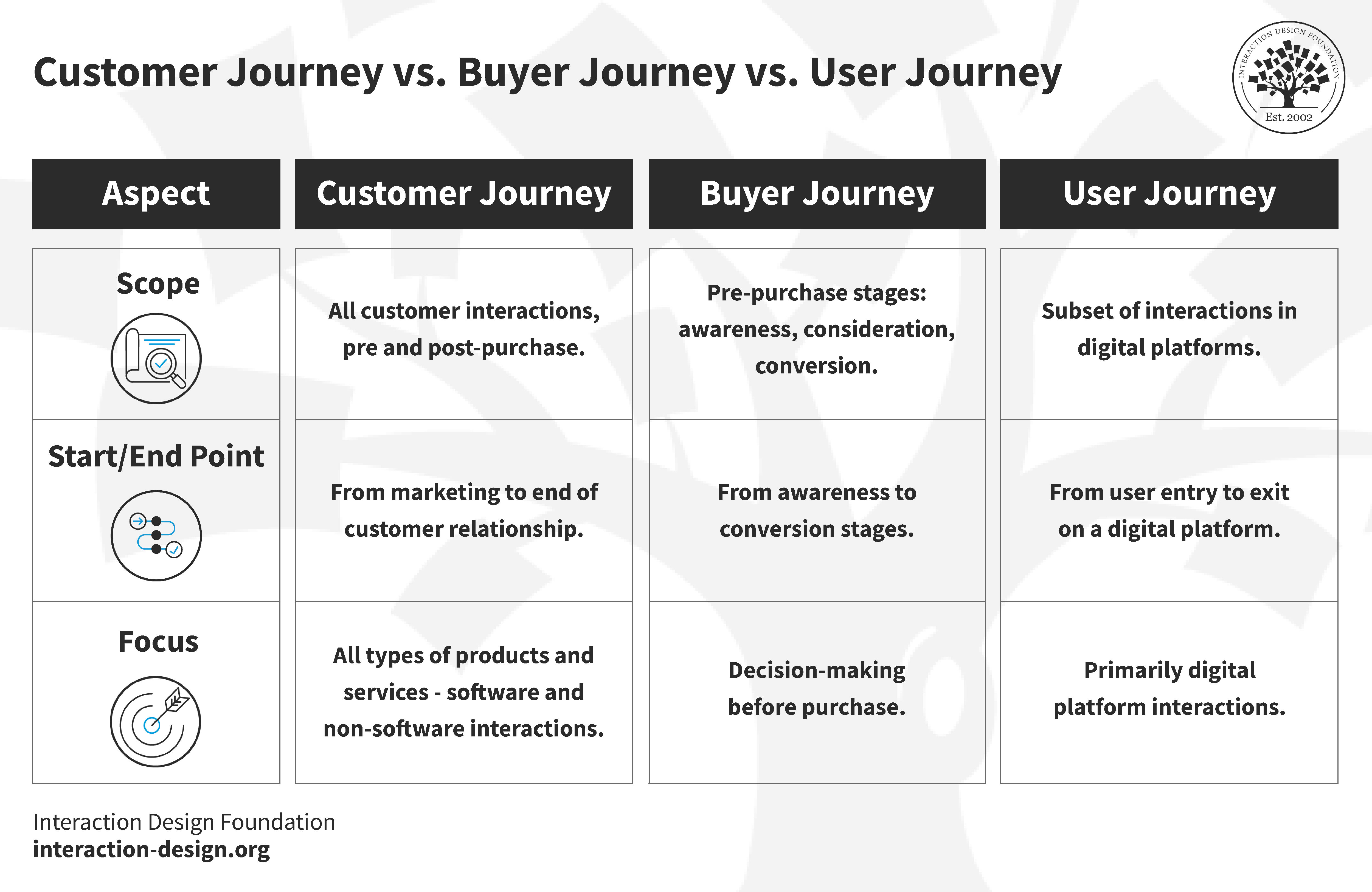
Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.
Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
- 11 mths ago
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
- 2 years ago
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Customer Journey
- 1 Definition
- 2 Customer journey models
- 3 Mapping the customer journey
- 4 How does understanding your customer journeys benefit your marketing?
- 5 Possible problems when mapping the customer journey
- 6 Related links
- 7 Similar articles
The term “customer journey” describes the experiences a customer makes between the first contact with a brand and their final purchase decision. This model assumes that a customer rarely decides spontaneously, but rather gets in touch with a brand, a product, or a service at different points during their journey, called touchpoints . These can be at least partially influenced by a company. By optimizing these touchpoints you can positively affect customer experience and direct them towards a purchase decision. In online business, companies benefit from the fact that most of the digital customer journey can be monitored.
Customer journey models
There are several models in the marketing field that aim to map and analyze customer journeys. One of them is called “ AIDA ” and has been used in sales psychology for more than a hundred years. AIDA defines four steps for the customer journey, starting with “Attention”. In the second stage (“Interest”) customers have an initial buying interest in a product which is reinforced by “Desire”. At last, “Action” is the moment when a business transaction takes place. In many cases, the steps of this AIDA model are supplemented by touchpoints such as “consideration”, i.e. product comparison, or the decisive trigger for action (“intent to purchase”).
Each touchpoint along the customer journey can be analyzed and optimized. For example, attention can be created through advertising for a product whereas interest can arise through in-depth product information on specialist portals. The actual purchase can be pushed by providing an online experience that is convenient, fast and secure. Therefore, each customer touchpoint can be considered a “ moment of truth ” as for each stage, there is a chance that customers jump off. Ideally, these moments of truth will encourage potential customers in their decision-making process during their customer journey, so that they are satisfied and become regular customers or even recommend your offers to others.
While you can control the customer journey and touchpoints on your website, other moments of truth are outside of your direct influence. A critical media report or negative experiences of other customers are factors that can severely disrupt the AIDA approach at an early stage. For this reason, you should concentrate on analyzing the collected data during the customer journey and draw conclusions in order to increase conversions.
Mapping the customer journey
To fully understand the journey of your customers, you can create a customer journey map that allows you to visualize the process. This is more than just illustrating when and where interactions between your company and customers take place. As you also have to consider a customer’s feelings and emotions, a customer journey map should include all of their experiences at each touchpoint. Such a map can help to research where your company is doing good and where you need to improve.
How does understanding your customer journeys benefit your marketing?
Analyzing and understanding your customers' journeys can have a positive effect in many ways. For example, if you notice that customers often cancel during the order or payment process, there is obviously a need for optimization at this touchpoint. Then you have to find out whether this is due to hidden additional costs, complicated navigation, or other details and correct it accordingly. The same applies to other touchpoints such as online ads not leading to clicks or an unfulfilled demand for information of potential customers. Enterprises track customer journeys to ensure they know what is happening to their target audience and where customers are hesitating or dropping out before reaching their primary goal - making a purchase.
Another benefit of analyzing the customer journey in depth is that you can take advantage of positive side effects. At which point in the decision-making process are customers willing to share their email address and subscribe to a newsletter? When do they expect personal service? Which advertising measures are effective?
Cookies and other tools for tracking the digital customer journey can help to transparently capture and evaluate touchpoints. However, marketing is finding its limits here.
Possible problems when mapping the customer journey
There are three major problems that can occur when trying to map your customer’s journeys. First, touchpoints outside the internet are difficult to map reliably. Touchpoints like the first moment of truth cannot be captured by the instruments of online mapping. Did it take place through newspaper advertisements or private recommendations? Do retailers present the product in an appealing way? This information would, however, be helpful in measuring the success of strategies regarding the customer journey.
The second major challenge in digitally tracking the customer journey is that internet users are increasingly suspicious of cookies and other tracking mechanisms. Web browsers such as Apple's Safari and Google's Chrome suppress many cookies that allowed you to track customer journeys across multiple websites in the past. EU regulations for the protection of personal data and the use of ad and script blockers are additional factors that make the mapping of customers’ behavior difficult or even impossible. While most marketers would like to completely track customer journeys from start to finish, many consumers are sensitized and actively protect themselves against such measures.
The third problem is that more and more purchasing processes and touchpoints take place in social networks or on other platforms, which share their customer journey information only partially or not at all. Facebook, as an example, only shares a small amount of what it knows about its users with other companies. Thus, the customer journey only becomes partially transparent.
Related links
- https://blog.hubspot.com/service/customer-journey-map
- https://www.superoffice.com/blog/customer-journey/
Similar articles
- Conversion Rate
- Online Marketing
Navigation menu
Check Site now for free
- Imprint Privacy
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
The definitive 8-step customer journey mapping process
In business, as in life, it's the customer's journey that makes the company's destination worth all the trouble. No customer wants to jump through several different hoops to get to your product: they want it fast and they want it now.
Following certain customer journey mapping stages helps you improve your user's experience (UX) to create a product they love interacting with, ensures you stay ahead of key workflow tasks, and keeps stakeholders aligned. But a misaligned map can derail your plans—leading to dissatisfied users who don’t stick around long enough to convert or become loyal customers.
Last updated
Reading time.

This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Learn how customers interact with your product and website
Hotjar's Observe and Ask tools let you go ‘behind the scenes’ to understand your users’ product experiences and improve their customer journey.
An 8-step process for effective customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visualization of every point of interaction a user has with your company and product.
Mapping out the customer journey gives you insights into your buyers’ behavior to help you make changes that improve your website and the user flow between touchpoints. This helps you increase online sales and turn users into loyal customers and brand advocates.
Follow these eight proven steps to understand—and enhance—the customer experience.
Note: every business is distinct, so be sure to adapt these steps to your particular user and business needs.
1. Define your purpose
The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won’t know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
To define your purpose, consider your company’s mission statement and incorporate your specific user pain points as much as possible.
Make your purpose specific to your company’s needs and goals—for example, the purpose of an ecommerce brand looking to help users navigate several different products and make multiple purchases will differ from that of a SaaS company selling subscriptions for one core product.
2. Make sure your team is aligned and roles are clear
Cross-functional collaboration is essential when mapping out your brand's or product’s user journey. Get insights from different teams within your organization to find out exactly how users engage with key touchpoints to derive a holistic sense of the user experience (UX), which will help you improve every aspect of the customer experience.
Lisa Schuck , marketing lead at Airship , emphasizes the importance of keeping “anybody that has a touchpoint with a customer” involved. She advises teams to “figure out how to align your external marketing and sales with your internal operations and service.”
Although sales, product, and marketing departments are often the key players in customer journey mapping, also involve your operations and design teams that are responsible for creating the user flow.
If you have a SaaS company, for example, marketing creatives, sales teams, product owners and designers, and your customer experience department all need to participate in the process. Clearly define who’s responsible for different aspects of the map, and regularly check in to make sure your final map isn’t missing any important perspectives.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Highlights feature to collect and organize key product experience (PX) insights and data on user behavior from teams across your organization to help you build your customer journey map. Then use Hotjar’s Slack integration to quickly share learnings with your relevant stakeholders to get buy-in and ensure everyone is aligned.
Hotjar’s Slack integration Slack lets teams discuss insights in the moment, so they’re up to date with critical issues
3. Create user personas
Once you’ve defined your purpose and involved all relevant stakeholders, it’s time to design your user personas . Use resources like UXPressia and HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool to help you design various product personas .
Create a range of user personas to understand what each type of buyer needs to curate a journey that’s easy and enjoyable for every customer. This is an important early step in the customer journey mapping process—because if you don’t understand your users, you won’t be able to fully comprehend how they interact with your brand to better it.
Create user personas for all your product’s possible buyers—for example, to map out a B2B customer journey for a company in the hospitality business means developing personas for a range of different customers, from large chain hotel managers to small vacation rental owners.
4. Understand your user goals
Once you’ve designed your user personas, it’s time to define their jobs to be done . What do your users hope to accomplish when they search for your product or service? What do they want to do when they click on your website? Address and answer these questions to build a deep understanding of your users’ goals and pain points to inform your customer journey.
In a SaaS customer journey , perhaps users are looking for helpful comparisons of product features on your website, or want to easily sign up for a trial account in the hopes that your product will solve their problems. But you won’t know until you ask .
Once you have users or test users, get direct insights from them with Hotjar's Feedback tools and Surveys to ask buyers exactly what their goals are as they browse different pages of your website or interact with product features.
Since user goals are at the center of your customer journey map, define them early on—but keep speaking to your users throughout the entire process to make sure you’re up to date with their needs.
5. Identify customer touchpoints
After you understand your users and what their goals are, it’s time to identify the ways they interact with your company and your product.
"Touchpoints are the moments the customer interacts with your brand, be it through social media channels, your product, or customer support. The quality of these experiences affects the overall customer experience, which is why it’s important to be aware of them. Consider what happens before, during, and after a customer makes a purchase or uses your product."
Key customer journey touchpoints for a website or product include your homepage, landing pages, product pages, CTA buttons, sign-up forms, social media accounts, and paid ads.
Collaboration is key to identifying touchpoints throughout the entire customer journey. Include insights from different teams and stakeholders —your marketing and sales teams will have a strong understanding of the touchpoints involved pre-purchase, while the customer experience department can shed light on post-purchase touchpoints.
Post-purchase touchpoints can help turn users into loyal customers and even advocates for your brand.
In the words of Lisa Schuck, "When you create a raving fan, or a brand advocate, who goes out and tells the world how wonderful you are, you get social credibility and validity. It’s becoming more and more important to have advocates."
Pro tip : speak with your users regularly to get direct voice-of-the-customer (VoC) insights on what they love and what frustrates them on their journey. Place Hotjar Feedback widgets and Surveys at key website touchpoints like your homepage and landing pages to get valuable user insights on what you can improve. Use Hotjar’s survey templates to get inspiration for your survey questions.
An example of an on-site Hotjar Survey
6. Map out the customer journey
Once your user and product research are complete and all roles are distributed, it’s time to map out the full customer journey.
First, map out an overarching customer journey by putting your key touchpoints in order and identifying how your various user personas interact with them. Then, home in on the details, looking at how customers engage with specific aspects of your website, product, or social media accounts.
Breaking down the mapping process into smaller phases will ensure you don’t miss any key interactions.
Here’s how an ecommerce brand could lay out general touchpoints, then narrow each down into more specific actions:
Pro tip : it’s helpful to think of the user journey in terms of different functions when mapping it out, like:
Connect: how are buyers connecting with your brand?
Attract: how are you convincing them to convert?
Serve: how are you serving customers when they want to purchase?
Retain: how are you promoting brand advocacy and customer retention ?
7. Test the customer journey
Once you’ve mapped out the customer journey, it’s time to take it for a spin. You can’t understand how your users move through customer touchpoints unless you test out the user flow yourself.
Start with an informational Google search, then visit your website, check out your social media pages, and simulate the purchase process. This will help you get a better sense of how users interact with each touchpoint and how easy it is to move between them.
Be sure to try out the journey from the standpoint of every relevant user persona. For an enterprise software company, this could mean looking at how decision-makers move through the user flow vs. the employees who’ll use your software day to day.
By walking through the customer journey yourself, you can identify issues and difficulties that users may have to address them proactively.
Try out the user flow with test users to get a realistic perspective of the user experience. Be sure to use focus groups that represent every one of your user personas.
8. Use continuous research to refine your map
Continuously map out, analyze, and evaluate the customer journey by observing users and getting their feedback. Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings help you understand how your users are experiencing the customer journey on your website: create heatmaps to see whether users are clicking on CTAs or key buttons, and watch recordings to find out how they navigate once they reach your homepage.
Then, use Google Analytics to get an overview of your website traffic and understand how customers from different channels move through the user journey.
Finally, once you have these combined user insights, use them to make changes on your website and create a user journey that is more intuitive and enjoyable.
Pitfalls to avoid during the customer journey mapping stages
Jamie Irwin , director & search marketing expert at Straight Up Search , says companies should avoid these three common mistakes when mapping out the customer journey:
Don't map out the entire customer journey at once
Don't forget about the ‘hidden journeys’
Don't make assumptions about customer behavior
To sidestep these common pitfalls:
Start by mapping out the overall journey, and only drill down into more detail once you have a broader, higher-level overview of the customer journey
Factor in every way that customers interact with your brand, even the ones you don’t have as much visibility on, like ‘dark social’ communications about your brand shared in private channels. Talk to your users to find out what they’ve heard about your brand outside of public channels , and use sticky share buttons to keep track of when your content’s shared through email or social media messengers.
Take a data-informed approach: don’t assume you already know your users —test out your hypotheses with real users and qualitative and quantitative data.
Follow proven steps to successfully map out the customer journey
Take the time to understand your business goals and users, involve the right teams, and test frequently to consistently improve your customer journey and make the decisions that will help you map out an experience that will get you happy and loyal customers.
FAQs about customer journey mapping stages
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping helps you visualize how users interact with your business and product, from the moment they find it until long after they make their first purchase.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into the buyer's journey to create a more enjoyable, streamlined, and intuitive experience for your customers.
What are the benefits of following a customer journey mapping process?
The main benefits of a customer journey mapping process are: :
Building on tried-and-tested processes
Not missing any key steps
Considering all buyer personas
Keeping all relevant stakeholders involved
Creating a valuable customer journey map
Improving user experience
What happens if you don’t follow key steps in customer journey mapping?
If you don’t follow key steps when mapping out the customer journey, your map likely won’t give you the insights you need to enhance the experience users have with your most important touchpoints —like your homepage, landing pages, CTAs, and product pages.
This can result in high bounce rates, low conversion, and unsatisfied users who fail to become loyal customers.
CJM benefits
Previous chapter
CJM touchpoints
Next chapter
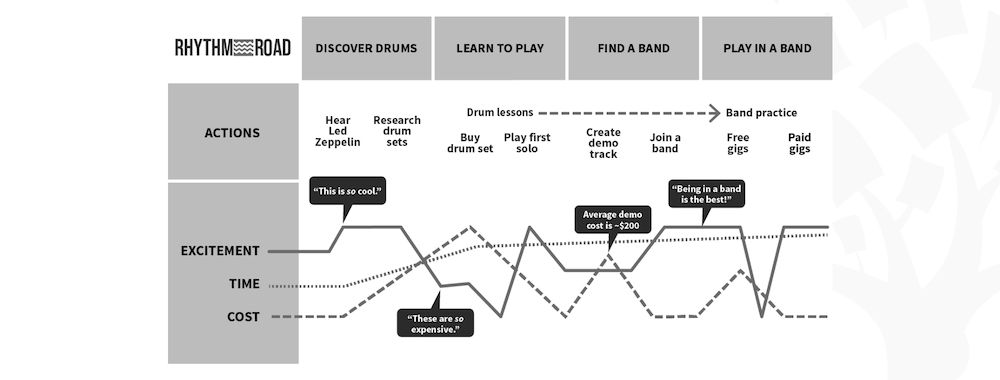
What is Customer Journey?

If earlier, before the advent of digital technologies, it seemed that it was enough to advertise your product to potential clients directly, and they would immediately turn into buyers. But with excessive online channels, where they can learn about alternative products and choose the right offers quicker, brands no longer control the entire flow of information the clients receive to make their final decision. This means a more intricate customer journey or user path. What’s that?
What is a customer journey?
What is a customer journey? The customer journey or client path is the path that a client goes through: from the emergence of a need for a product or service to the moment of purchase or becoming a fan of the brand. In customer journey marketing it’s often reflected in a customer journey map.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
Over time, marketers have come to the conclusion that there is another way to fight competitors, in addition to price or quality. And that’s customer journey mapping. You need to find out how the clients live before and after the purchase, and then use this knowledge to keep them.
Customer journey mapping is important because it is a way to a strategic approach for a better understanding of customer expectations. Customer journey mapping is crucial for optimizing that customer experience. Client journey is just as important for small and medium-sized enterprises as it is for larger corporations.

The Customer Journey Mapping Process
How to create a customer journey map? This is the most often a really full-fledged map of the customer journey, and quite confusing. A customer can learn about a brand through word of mouth, google it, go to the store to feel the product, etc. But in the end, they order what they want online because it’s cheaper. So, everything is complicated.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
A journey map traditionally lays out every touch point which customers may go through the bran. It’s from how they come across the idea of using this or that product, hear about it through the grapevine, find it on social media or brand ads, to their direct interactions with your company product, website, brand customer service, sales or support team. It further includes all the actions your customer takes to complete an objective across the sales funnel . Before you create a journey map, consider its components.
Customer stages
To organise effective user journey marketing, one of the first steps of creating a practical customer journey map will be to define the stages in the customer journey as per your business goals and the funnel you have.
Buyer personas
After that user research, you may pass over to creating your buyer personas based on the user data from the path and their experience. A buyer persona will be an average composite representation of a market segment. When you point out it, you know your target audience better.
Customer touchpoints
Another part of your customer experience journey mapping is defining customer touchpoints. But what is a customer touchpoint?
A customer touch point is any direct or indirect contact a customer has with a brand. Customer touch points can occur within and outside of a brand’s control and may happen before, during or after the purchase of a brand’s product or service. (Techtarget)
Finally, what is a customer journey map without your users’ feelings and emotions spotted? To be exact, you may include an emotional journey map which will be associated with the indication of various emotional statuses when users pass through each stage of their experience.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
It’s worth starting with defining the portrait of the client (buyer personas) and describing its main parameters. After that, it is worth describing all the situations that are triggers for the emergence of a need. From any need, you can describe the whole range of tasks that our persona wants to solve. Next comes the stage of finding a solution, in which it is important to describe as fully as possible all the possible ways and actions that your customers will take.
Based on the work done you may create a mapping with all the team members on the project in about seven easy steps:
- Step 1: Create buyer personas.
- Step 2: Select your target customers.
- Step 3: Enlist customer touchpoints.
- Step 4: Identify their actions and emotions.
- Step5: Analyse your available resources.
- Step 6: Create a map of appropriate type.
- Step 7: Analyze the customer journey and find the insights.
You may come up with the different types of user journey to depict your customer success story and analyse the progress.
Types of Customer Journey Maps
Here you will basically find four major types of web customer journey. You can design them to understand various scenarios your customer may encounter in the purchasing story:
- Current state ,
- Future state,
- Day in the Life ,
- and Service Blueprint .
There is no need to chart all four of them, but it may be helpful to understand each of the types depending on your marketing goals.
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
Understanding the customer journey is a great way to improve your marketing and achieve business goals successfully, as well as analyze possible pros and cons of your flaws if any. Feel free to apply the best possible practices to pave that way.
- Focus on the customers, not your company.
- Divide, but don’t forget to conquer.
- Enlist multiple failure warnings.
- Refresh every 3-7 years.
- Focus gaps & pain points of real customers.
- Organize workshops, not just create reports.
Not just real actions, but emotions should be considered to achieve customer satisfaction. When you have a basic understanding of your product, you know who your target audience is and what channels of interaction you use (or plan to use) with it. Try to model every possible way that a persona needs your product. The deeper you dig into the prerequisites and triggers of the need, the better.
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
Structurally, customer journey meaning CJM allows you to conduct analytics on your market, study competitors, determine target indicators, find your weaknesses, get closer to your target audience, measure customer loyalty and optimal LTV , upgrade your product and team.
It is also a methodology that helps you understand the journey a user takes while interacting with your product: what they do like, what can help them, what annoys them, etc. Thanks to CJM, you may come up with new ideas for product development and significantly improve user satisfaction. Using this methodology in the case of a new product launch, will allow foreseeing problem areas and safeguarding so as not to get dramatically mistaken.
CJM can be used by different types of companies – both those for which a digital product generates additional revenue and app-based companies for which a digital product is the basis of their business. Also, this methodology can help at different stages of product existence.
Customer Journey Mapping Examples
Here you may discover the quality customer journey map examples created by various companies for different projects.
How can I optimise my customer journey map?
To optimize your maps, you may apply the best practices, and examples, as well as use the tools for marketing success. Every time you organize your work in a complex, set clear objectives for the Highlight your target customer personas, and enlist touch points. Try to distinguish the elements you need your map to show you and include the resources you lack or have to satisfy all the process demands. Apply modern marketing optimization tools to speed up your work.
It is important to correctly understand the customer journey definition and how to use this method productively. We have a persona, the prerequisites for the emergence of a need (interest) in our product, an understanding: what action scenarios are there, what channels of interaction are available to you, your resources, and the expectations the client has, what emotions formed on each of stages, etc. Also, apply optimization tools that are important to track and better measure the effectiveness of your marketing success, as well as create objective user journeys in future.

You seem to enjoy the article!
I mean... Just saying. If you like what you just read, it's probably a sign that Creabl and you are meant for each other. Don't be shy, have a look around! It's free, you know ;)
Customer journey stages

Key Takeaways:
- There are five stages to the customer journey: awareness, consideration, purchase/decision, loyalty, and advocacy.
- While the high-level stages are the same, there are nuances among the B2C and B2B customer journey stages.
- Not every customer journey is linear; the stages for each customer may not fall in the same order.
Table of Contents
No matter the type of business, each customer takes a journey with a brand. During this journey, customers progress from hearing about a business or service to engaging the business and then (ideally) sharing their positive experiences with friends and colleagues. In short, the customer journey is how customers go from being a target audience to loyal fans.
Before improving or optimizing the customer journey , it’s critical to first understand the customer journey stages.
What are the stages of the customer journey?
There are five main stages of the customer journey. Each stage represents customer touchpoints between clients and a company. In many cases, organizations outline these stages on a customer journey map.
It’s important to note that not every customer journey is linear and follows these stages in this order. But in general, companies look at the five customer journey stages as:
1. Awareness - This is when a potential customer becomes aware of your company and services. They could become passively aware, such as by seeing an advertisement, or they may become aware proactively, such as by searching for companies in your area that offer the services you do.
2. Consideration - At the consideration stage, the potential customer is now aware of your company and that you offer services that could fit their needs. During this stage, prospective customers weigh their options and evaluate your services against your competition. They may be completing activities such as checking online reviews or inquiring with trusted friends or colleagues to learn what others say about your brand. In doing so, they seek a clear answer on whether to purchase from your brand.
3. First purchase/decision - A potential customer reaches this stage when they have all the information they need to decide whether your company can meet their needs within their determined budget and scope. The individual or purchasing team goes from being a potential customer to a customer. Depending on the perceived importance of the purchase — as well as the personality of the buyer — it may take a long time to reach this phase.
4. Retention/loyalty: - The retention phase focuses on keeping your customers happy and engaged. As your customers use your product or service, they make repeat purchases and continue to buy again from your company. During this stage, you are also focused on providing excellent customer service.
5. Advocacy - In this stage, customers to whom you have delivered value that exceeded their expectations are doing their own marketing work for your company. They voluntarily talk about your business and encourage their colleagues and friends to try your services for themselves. Customers who share positive reviews about your company show that you deliver on brand promises you’ve made. Not all customers will reach this stage, but your goal should be to plan programs that ensure many of your customers will become loyal advocates for your brand.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map visually represents the entire customer journey or lifecycle. It covers all five customer journey stages and the different interactions or touchpoints across channels, including social media, in-store, website, or email. Journey maps may also include information about customer or buyer personas .
For example, a customer’s first touchpoint with your organization may be a paid search ad, which is the starting point on their customer journey map. The map then charts all of that user’s interactions and may have branching points for choices they could make.
Customer journey mapping is valuable for any organization looking to improve customer experience, customer retention, and loyalty.
Stage 1: Awareness stage
The awareness stage is a potential customer’s first impression of your brand, so it is worth a significant investment. They may encounter your brand passively by viewing an online or in-person advertisement. Or, they may have actively discovered your brand while researching a problem using a search engine.
You should aim to educate prospective customers about your brand and offerings through ads, social media accounts, your website, and other high-level touchpoints (also known as “top of the funnel” touchpoints).
This customer journey stage aims to meet the right customers at the right time. It’s all about getting your brand name in front of your ideal customers, even if they don’t know they need your service.
Using analytics platforms has greatly improved marketers’ efforts to reach their target audience effectively. Examples of these platforms include Brandwatch Consumer Intelligence , Dstillery , Audiense , and Adverity . These platforms can provide rich data about potential customers, such as location, age, choice of device, and conversion rates. Choose an analytics platform that fits your marketing practices and goals.
Best practices for the awareness stage
- Target the channels your prospects use most - Using data from a consumer analytics platform, develop strategies that keep your brand front and center on the channels your customers use most. For example, if your potential audience is more senior and primarily on Facebook and Instagram, skip advertising on TikTok.
- Focus on education - Create content — such as infographics and blog posts — that help educate consumers about why they need a product or service like yours.
- Skip the hard sell - Avoid coming on too strong with sales tactics. Give your customer the content and space to learn about your product and brand.
Awareness stage content examples
The type of awareness phase content you develop will depend on your audience and whether you’re in the B2B or B2C space. In some cases, social media ads may be the right fit. Other companies may have more success with downloadable content like eBooks.
Once potential customers see your brand, keep them engaged with easy-to-digest information about your services and offerings. Awareness stage content can include:
- Infographics
- Free courses
- Social media posts/ads
- General eBooks related to your product category or industry
- General videos related to your product category or industry
- Paid search ads
- General whitepapers related to your product category or industry
- How-to articles and guides
Stage 2: Consideration stage
In this stage, a potential customer is now aware of your brand and is researching whether your company or product is what they need. This customer journey stage aims to move the customer to further engage with your brand and closer to a purchase or decision.
During the consideration phase, you must ensure your offering stands out among the competition. A customer in the consideration phase may spend time on your website, review your social media pages, engaging with your sales team, and seek out what others say about your brand. This can include Google, G2, Capterra, Yelp, or Facebook reviews. They may also ask experienced friends, colleagues, or family members for recommendations.
Many items are outside your control during this phase: your potential customer’s needs and budget, your competitors, online review websites, and individuals who have prior experience with your brand or your competitor.
Best practices for the consideration stage
While there are some factors you cannot control during the consideration phase, you have many opportunities to portray your brand as the best choice for prospective customers.
- Take ownership of reviews - Responding to past negative reviews or past customer service complaints can show that your company is moving in a positive direction. Addressing significant issues from past reviews shows potential customers that your team takes customer service seriously.
- Highlight your differentiators and value - Consumers in this phase are likely comparing your brand to others. Make sure your brand’s key differentiators are featured throughout your consideration phase content. Review your website’s product and service pages to ensure they are easy to understand and highlight your product’s value.
- Build trust - A consumer is more likely to select a credible, trustworthy brand. Remember this as you’re developing content. Use customer quotes to boost credibility and avoid making unsubstantiated claims about your product or brand.
- Consider using third-party research - C onsider bringing in an expert third party to review your brand’s web presence — including properties you own and control and those you don’t. During this exercise, your marketing team can partner with other key business units to identify positive changes you can make to ensure your brand stacks up well against your competition during the consideration phase.
Consideration stage content examples
Consideration phase content should highlight how your offering is the right choice. In some cases, content can overlap in other stages of the customer journey, such as the awareness phase.
Some types of marketing content that can be helpful during the consideration phase include:
- Case studies and customer testimonials
- Product comparison guides and charts
- Product-focused videos
- Product-focused white papers
- Retargeting ads on social media that target prospects who have been on your website
Stage 3: First purchase/decision stage
By now, the customer has gathered all the information they need about your brand — such as case studies or online reviews — and is ready to purchase. At this stage, they decide between your brand or product and your competition. This phase is significant because it demonstrates that the customer has confidence in your brand and may lead to a purchase or sale.
The main players during this stage are the customer and your sales team. Your customer service or implementation teams may also be involved if the purchase includes an integration or installation process.
Best practices for the purchase/decision stage
- Eliminate purchase barriers - Take the necessary steps to make the buying process as smooth as possible. If your company uses an online storefront, ensure your checkout process is straightforward. Consider providing resources to help them with financing, if needed. And if there is an integration or installation involved, get your customer success or implementation team involved as soon as possible.
- Provide incentives - Look for ways to move a deal or a purchase across the finish line. Discounts, coupons, or add-ons are some ways you can motivate customers to purchase.
- Offer references - If appropriate, offer to connect prospects to existing customers. Having conversations with individuals who are happy with your product or service may help convince the consumer to move forward with your brand.
- Collaborate with sales - Touch base with your sales contacts regularly to find ways to improve the purchasing process.
Purchase/decision phase content examples
Once a customer is ready to make a purchase, they likely understand the value of your product. They may, however, require additional resources to convince internal stakeholders or blockers. Content types you may want to create for this stage of the customer journey include:
- Free consultations
- Product sign-up pages
- Pricing pages
- Limited time product promotions or coupons – “Sign up within 48 hours and save 25%!”
- Influencer videos
Stage 4: Retention/Loyalty stage
The overarching goal of this phase is to keep your customers happy, so they become loyal, lifelong customers.
59% of U.S. customers say that once they’ve found a brand they love, they are loyal for life. However, just because a customer has made an initial purchase with your company doesn’t mean your work is finished. Your team still has opportunities to educate the customer on the value of your brand, paving the way for additional purchases, upsells, or contract renewals.
Retaining customers is crucial, as selling to or retaining an existing customer is much more cost-effective than acquiring a new one. Optimove estimates that it costs businesses five times as much to market to a new customer than a current customer.
What’s more, keeping repeat customers happy makes your job easier. Semrush found that your chances of selling to an existing happy customer are between 60 and 70%. Your chances of selling to a new customer are between 5 and 20%.
There are many players in the retention phase including:
- Your customer
- Your marketing teams who can help to keep your brand top-of-mind for your customer
- Your customer service team, who is responsible for quickly and effectively remediating any issues that arise
- Your analytics teams, who can provide insight on customer data
- Your product team, who is responsible for providing suggestions on which new products or additional offerings may be relevant to specific customers or developing new features for users
- Your sales teams, who can individually reach out to target customers with personalized offers and upsells
Best practices for the retention stage
- Leverate your customer data - Now that your customer has purchased from you, you have valuable data about them. Use this data to send them regular, personalized communications with opportunities for upselling them with premium offers or cross-selling for related product purchases.
- Make it easy to contact your team - Ensure your company is easy to contact — especially if a customer has encountered an issue. Provide your phone number or support email in a prominent location on your website and in all of your email communications. And consider adding a chatbot to your website if you have a team to support it.
- Maintain regular communication with your customers - Keep customers in the loop with regular newsletters and updates about your products and company.
- Collaborate with customer success - While you may have collaborated closely with the sales team up to this point, now is the time to work closely with your customer success (CS) team. Collaborate to identify ways to improve the customer experience through content and communication.
- Establish a seamless onboarding process - Work together with your CS colleagues to develop an onboarding journey that helps customers fully understand how to use your product or service.
- Create a knowledgebase or FAQ - This resource can help customers find answers to questions and troubleshoot issues without needing employee resources.
Retention stage content examples
One key aspect of the retention phase is to provide best-in-breed customer service. If a customer runs into an issue with your service, your customer service team should work diligently and quickly to solve the issue so that the customer maintains a positive image of your brand.
Another aspect of this customer journey stage is proactively following up with customers. This involves sales teams reaching out to customers individually to ensure all is well with their services and to provide support when needed. Proactive communication also involves marketing teams sending out meaningful, relevant emails that may include:
- Information on the latest product offerings
- Suggestions for cross-sell/upsell
- Personalized offers based on prior purchases
- Rewards for loyalty
Other retention phase content examples may include:
- SMS texts or push notifications
- Customer newsletters
- FAQ/knowledgebase documents or webpages
Stage 5: Advocacy stage
The advocacy stage aims to enable your most loyal customers to recommend and advocate for your brand.
Customers can become vocal supporters of your brand when they have positive and meaningful experiences with your products or services. This support can drive significant results for your organization, with 81% of U.S. and U.K. customers stating that they trust product recommendations from family and friends over brand messaging.
You should aim for all customers to reach the advocacy stage. When you understand the needs of your customers and meet or exceed customer expectations through high-quality products and services, as well as exceptional customer service, they become loyal and are more likely to tell others about their experiences with your brand.
The advocacy phase involves your customers, your brand, their contacts, and how they share information about your brand with the people they know. For example, a loyal customer may share your Instagram profile with a friend looking for a service you provide. Another loyal customer may forward a relevant product marketing email to a colleague who has never heard of your brand. When the customer journey comes full circle in this manner, the new contact (potential customer) enters the first stage of the customer journey — the awareness phase.
Best practices for the advocacy stage
- Simplify referrals - Make it easy for your loyal customers to refer their friends, colleagues, and family to you. Encourage social media shares and provide intuitive ways for customers to tell friends about a product or service.
- Provide referral incentives - Encourage advocacy by incentivizing referrals with discounts, coupons, or loyalty points.
- Look to competitor referral programs - Consider researching what your competitors offer for loyalty programs and referral rewards.
- Give opportunities for feedback - Periodically survey your customers and conduct NPS, or customer satisfaction, surveys to identify potential advocates for case studies or testimonials. These ratings will also highlight key areas for improvement.
- Acknowledge customer feedback - If a survey reveals a consistent complaint or issue with your product or service, address it with your customers by highlighting fixes in newsletters or social media posts.
Advocacy stage content examples
- Highly personalized offers and incentives sent via SMS text or email
- Social media giveaways
- Customer profiles or features on social media or email newsletters
Do customer journey stages differ from B2B vs. B2C?
The five high-level journey stages are the same for B2B and B2C businesses. However, the specific actions and best practices may vary from stage to stage. For example, in a B2C industry, there is typically only a single decision-maker, and the dollar amount strongly influences the length of the consideration phase. With B2B, there are often multiple decision-makers or account contacts. Depending on the client and business, these may include legal, security, and other teams.
B2B vs. B2C customer journey stages
While the high-level stages are the same, there are nuances among the B2C and B2B customer journey stages. Some differences may include:
- Email marketing is targeted to different decision-maker types for B2B - Email marketing for B2B vs. B2C audiences will speak to the differing values and goals of the different decision-makers at each business type. For example, B2B decision-makers may value security, cost savings, marketing segmentation, and solving concrete business problems. Consider creating specific email marketing campaigns to speak to these considerations.
- Social media marketing is more relevant for B2C - In general, social media marketing is more relevant to B2C industries than to B2B, though it can play a role in both. Specifically, marketing for a B2C audience during the awareness and consideration phases should focus more on social media.
- Referrals are very important for all industry types - Referrals are necessary across virtually all B2B and B2C industries. However, loyalty and referral programs will look different across B2B vs. B2C and between different industry verticals.
- Adjust marketing materials for industry type - Be nimble and poised to adjust your marketing content for B2B vs. B2C. For instance, more formal marketing materials such as eBooks and white papers are more impactful for B2B industries. On the other hand, free courses or coupons may be more critical for B2C.
- Initial touchpoints will differ - Conferences or industry conventions are important customer touchpoints for B2B, especially for the awareness and consideration phases. In the B2C world, the early touchpoints may be social media ads or paid search campaigns or out-of-home ads like billboards.
More from the University
Customer journey, customer journey orchestration, looking for guidance on your data warehouse.
Supercharge your favorite marketing and sales tools with intelligent customer audiences built in BigQuery, Snowflake, or Redshift.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Stages
See how XM for Customer Frontlines works
The complete guide to customer journey stages.
12 min read If you want to turn a potential customer into a lifetime one, you’ll need to get to know every step of the entire customer journey. Here’s why the secret to customer retention lies in knowing how to fine-tune your sales funnel…
What is the customer journey?
What do we actually mean when we talk about the customer journey? Well, the simplest way to think about it is by comparing it to any other journey: a destination in mind, a starting point, and steps to take along the way.
In this case, the destination is not only to make a purchase but to have a great experience with your product or service – sometimes by interacting with aftersale customer support channels – and become a loyal customer who buys again.
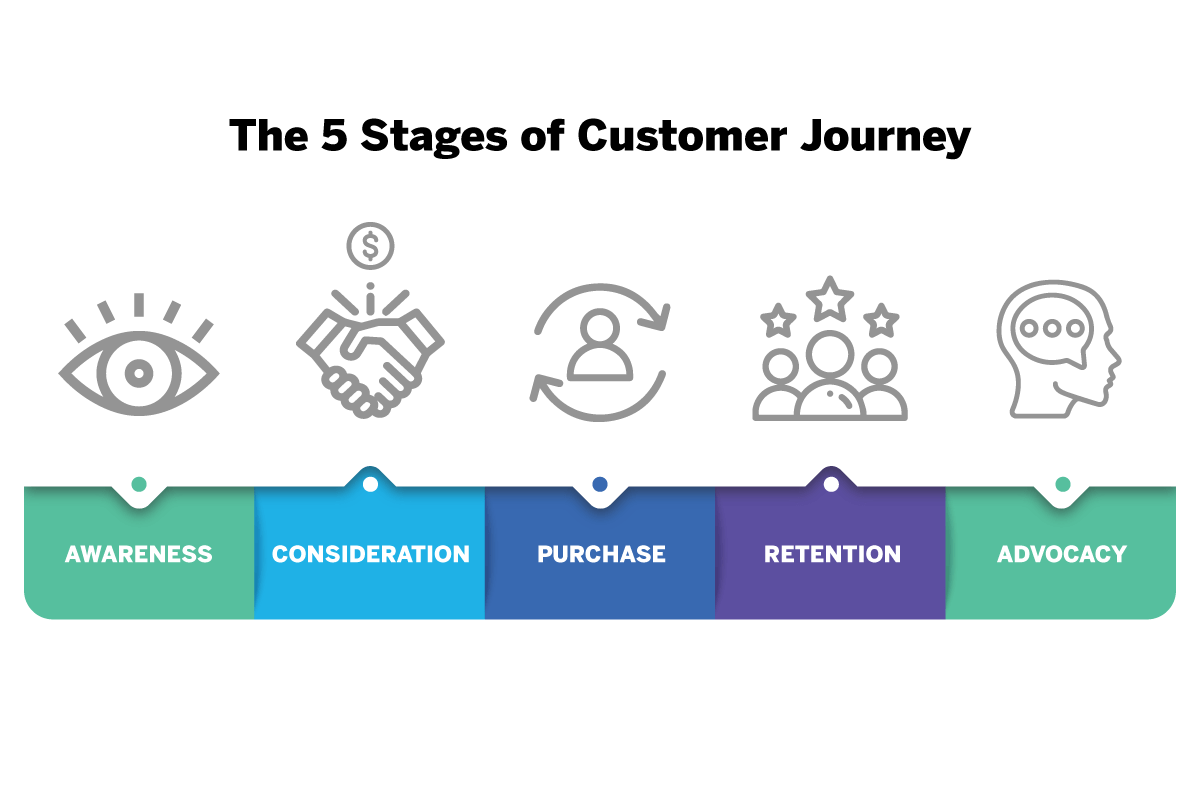
And, just like how you can’t arrive at your vacation resort before you’ve done you’ve found out about it, the customer journey starts with steps to do with discovery, research, understanding, and comparison, before moving on to the buying process.
“Maximizing satisfaction with customer journeys has the potential not only to increase customer satisfaction by 20% but also lift revenue up by 15% while lowering the cost of serving customers by as much as 20%”
– McKinsey, The Three Cs of Customer Satisfaction
In short, the customer journey is the path taken by your target audience toward becoming loyal customers. So it’s really important to understand – both in terms of what each step entails and how you can improve each one to provide a maximally impressive and enjoyable experience.
Every customer journey will be different, after all, so getting to grips with the nuances of each customer journey stage is key to removing obstacles from in front of your potential and existing customers’ feet.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management & Improvement
What are the essential customer journey stages?
While many companies will put their own spin on the exact naming of the customer journey stages, the most widely-recognized naming convention is as follows:
- Consideration
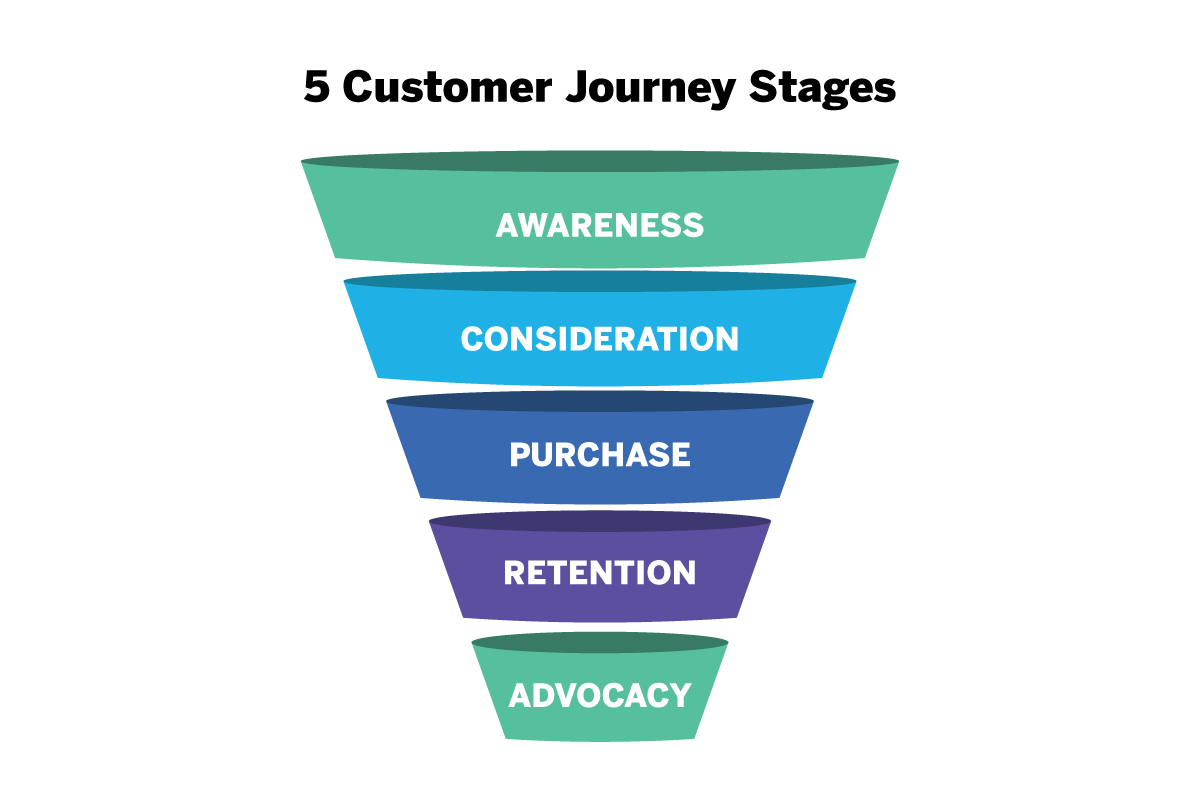
These steps are often then sub-categorized into three parts:
- Sale/Purchase
It’s important to understand every part of the puzzle, so let’s look at each sub-category and stage in turn, from the awareness and consideration stage, right through to advocacy:
Customer journey: Pre-sale
In the pre-sale phase, potential customers learn about products, evaluate their needs, make comparisons, and soak up information.
Awareness stage
In the awareness stage, your potential customer becomes aware of a company, product, or service. This might be passive – in that they’re served an ad online, on TV, or when out and about – or active in that they have a need and are searching for a solution. For example, if a customer needs car insurance, they’ll begin searching for providers.
Consideration stage
In the consideration stage, the customer has been made aware of several possible solutions for their particular need and starts doing research to compare them. That might mean looking at reviews or what others are saying on social media, as well as absorbing info on product specs and features on companies’ own channels. They’re receptive to information that can help them make the best decision.
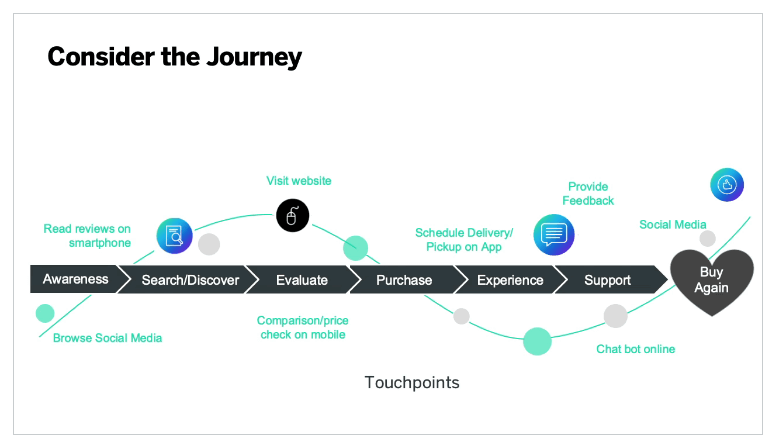
Customer journey: Sale
The sale phase is short but pivotal: it’s when the crucial decision on which option to go with has been made.
Decision stage
The customer has all the information they need on the various options available to them, and they make a purchase. This can be something that’s taken a long time to decide upon, like buying a new computer, or it can be as quick as quickly scouring the different kinds of bread available in the supermarket before picking the one they want.
Customer journey: Post-sale
Post-sale is a really important part of the puzzle because it’s where loyal customers , who come back time and again, are won or lost.
Retention stage
The retention stage of the customer journey is where you do whatever you can to help leave a lasting, positive impression on the customer, and entice them to purchase more. That means offering best-in-class customer support if they have any issues, but it also means being proactive with follow-up communications that offer personalized offers, information on new products, and rewards for loyalty.
Advocacy stage
If you nail the retention phase, you’ll have yourself a customer who not only wants to keep buying from you but will also advocate on your behalf. Here, the customer will become one of the most powerful tools in your arsenal, in that they’ll actively recommend you to their friends, family, followers, and colleagues.
What’s the difference between the customer journey and the buyer’s journey?
Great question; the two are similar, but not exactly the same. The buyer’s journey is a shorter, three-step process that describes the steps taken to make a purchase. So that’s awareness , consideration, and decision . That’s where things stop, however. The buyer’s journey doesn’t take into account the strategies you’ll use to keep the customer after a purchase has been made.
Why are the customer journey stages important?
The short answer? The customer journey is what shapes your entire business. It’s the method by which you attract and inform customers, how you convince them to purchase from you, and what you do to ensure they’re left feeling positive about every interaction.
Why this matters is that the journey is, in a way, cyclical. Customers who’ve had a smooth ride all the way through their individual journeys are more likely to stay with you, and that can have a massive effect on your operational metrics.
It’s up to five times more expensive to attract a new customer than it is to keep an existing customer, but even besides that: satisfied customers become loyal customers , and customer loyalty reduces churn at the same time as increasing profits .
So companies looking to really make an impact on the market need to think beyond simply attracting potential customers with impressive marketing, and more about the journey as a whole – where the retention and advocacy stages are equally important.
After all, 81% of US and UK consumers trust product advice from friends and family over brand messaging, and 59% of American consumers say that once they’re loyal to a brand, they’re loyal to it for life.
Importantly, to understand the customer journey as a whole is to understand its individual stages, recognize what works, and find things that could be improved to make it a more seamless experience. Because when you do that, you’ll be improving every part of your business proposition that matters.
How can you improve each customer journey stage?
Ok, so this whole customer journey thing is pretty important. Understanding the customer journey phases and how they relate to the overall customer experience is how you encourage customers to stick around and spread the news via word of mouth.
But how do you ensure every part of the journey is performing as it should? Here are some practical strategies to help each customer journey stage sing…
1. Perform customer journey mapping
A customer journey map takes all of the established customer journey stages and attempts to plot how actual target audience personas might travel along them. That means using a mix of data and intuition to map out a range of journeys that utilize a range of touch points along the way.
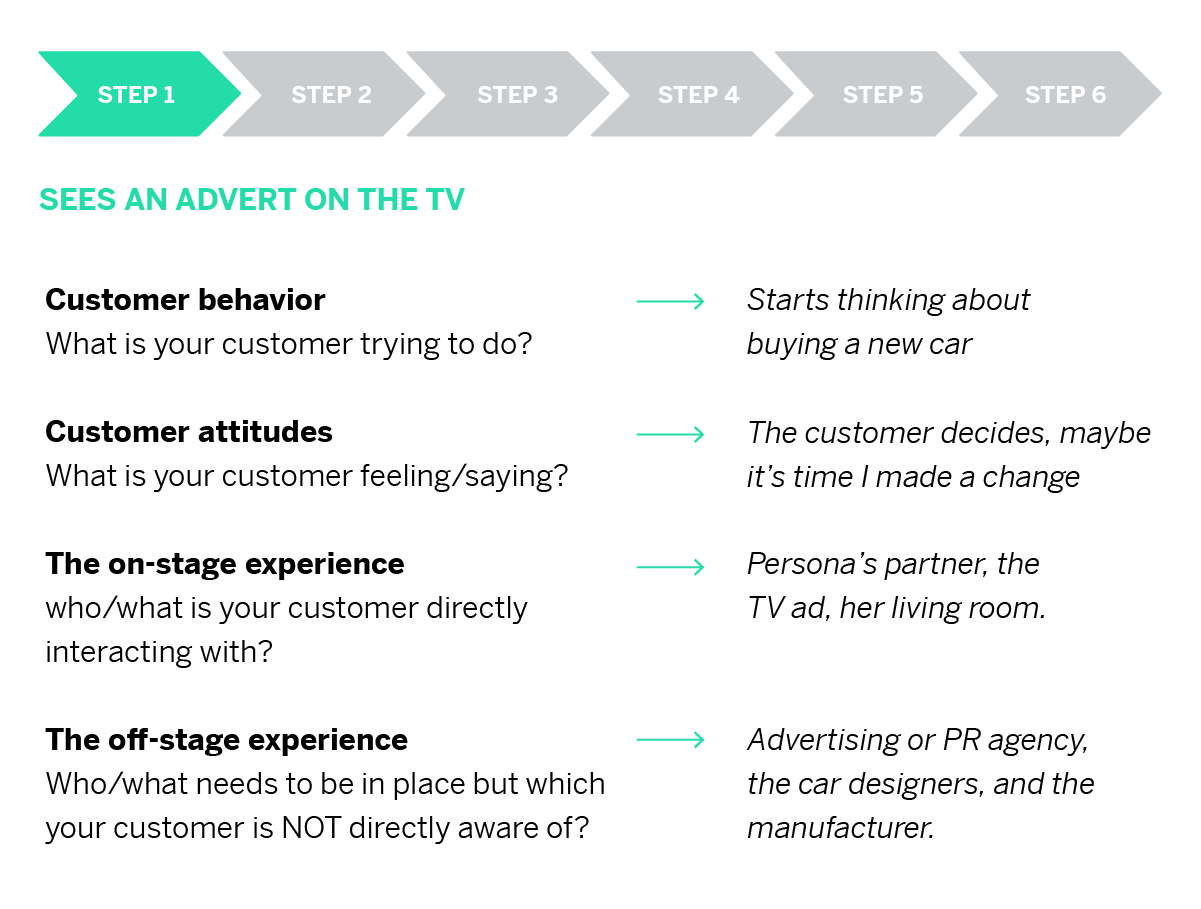
One customer journey map, for example, might start with a TV ad, then utilize social media and third-party review sites during the consideration stage, before purchasing online and then contacting customer support about you your delivery service. And then, finally, that customer may be served a discount code for a future purchase. That’s just one example.
Customer journey mapping is really about building a myriad of those journeys that are informed by everything you know about how customers interact with you – and then using those maps to discover weaker areas of the journey.
2. Listen like you mean it
The key to building better customer journeys is listening to what customers are saying. Getting feedbac k from every stage of the journey allows you to build a strong, all-encompassing view of what’s happening from those that are experiencing it.
Maybe there’s an issue with the customer sign-up experience, for example. Or maybe the number advertised to contact for a demo doesn’t work. Or maybe you have a customer service agent in need of coaching, who only makes the issue worse. By listening, you’ll understand your customers’ issues and be able to fix them at the source. That customer service agent, for example, may just feel disempowered and unsupported, and in need of the right tools to help them perform better. Fixing that will help to optimize a key stage in the customer journey.
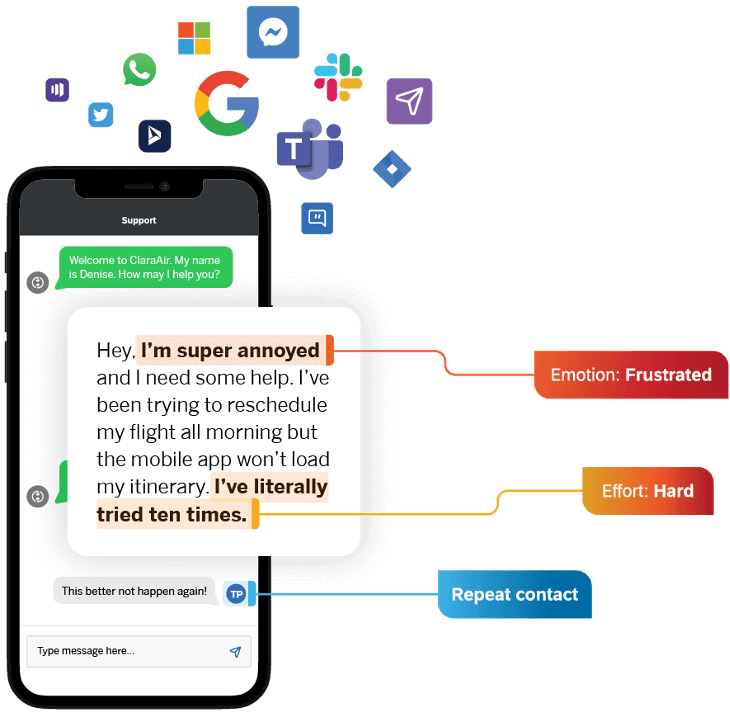
The key is to listen at every stage, and we can do that by employing the right technology at the right customer journey stages.
Customer surveys, for instance, can help you understand what went wrong from the people who’re willing to provide that feedback, but conversational analytics and AI solutions can automatically build insights out of all the structured and unstructured conversational data your customers are creating every time they reach out, or tweet, or leave a review on a third party website.
3. Get personal
The other side of the ‘listening’ equation is that it’s worth remembering that each and every customer’s journey is different – so treating them with a blanket approach won’t necessarily make anything better for them.
The trick instead is to use the tools available to you to build out a personalized view of every customer journey, customer journey stage, and customer engagemen t, and find common solutions.
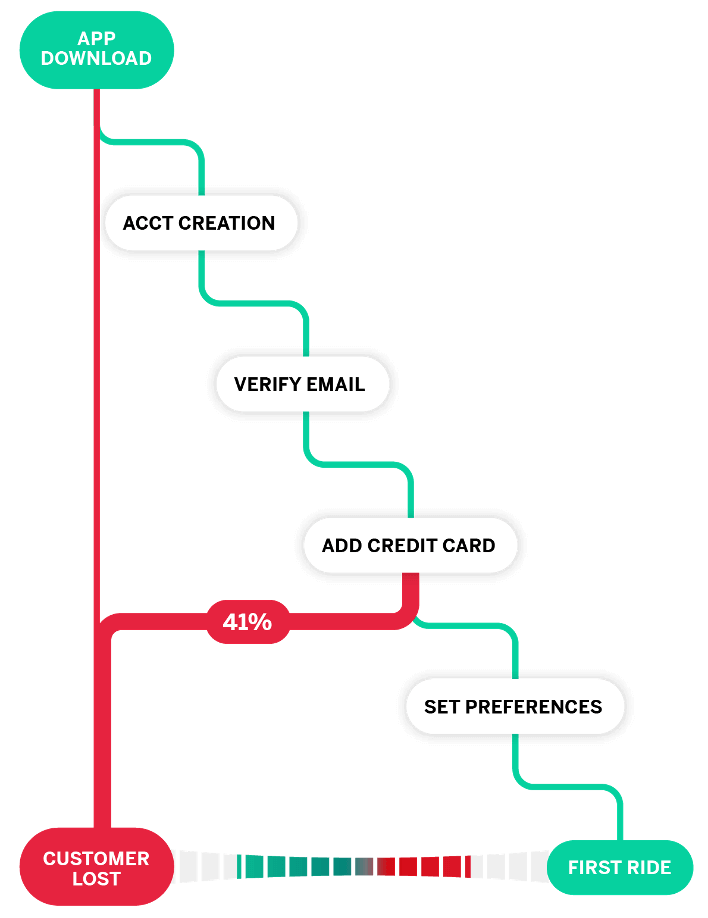
Qualtrics Experience iD , for example, is an intelligent system that builds customer profiles that are unique to them and can identify through AI, natural language processing , and past interactions what’s not working – and what needs fixing.
On an individual basis, that will help turn each customer into an advocate. But as a whole, you’ll learn about experience gaps that are common to many journeys.
Listening to and understanding the customer experience at each customer journey stage is key to ensuring customers are satisfied and remain loyal on a huge scale.
It’s how you create 1:1 experiences, because, while an issue for one person might be an issue for many others, by fixing it quickly you can minimize the impact it might have on future customers who’re right at the start of their journey.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management Improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
Buyer's Journey 16 min read
Customer journey analytics 13 min read, how to create a customer journey map 22 min read, b2b customer journey 13 min read, customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
The 9 Customer Journey Stages and Why They Are Important

In broad strokes, the customer journey is all the steps a person takes to become a customer. This path encompasses everything from realizing they have a problem that needs solving to buying and using your product to solve that problem.
Knowing this customer journey is vital because it allows you to focus your marketing efforts on different stages of that journey. It's similar to the sales funnel but more variable; everyone takes their unique path through your customer journey. Each step of the customer journey can be categorized within the sales funnel, but each customer has their way of making it through those stages.
Think about this: when you call a business, you must go through a phone tree to be directed to the right place. Or, you have to explain yourself to a receptionist, who has to figure out who to send you to. Or, you talk to a CS rep in a call center, get transferred up the chain three times, and still don't know if you'll ever get your issue solved.
If the business knew your stage in the journey, they could ensure that the people you contact the first time are the right people to talk to.
The Phases of the Customer Journey
When you define a customer journey, you'll find a bunch of guides and think pieces with different outlines for the customer journey. Some list four phases, some five, some six, and even more. What's going on?
The barest minimum customer journey has three stages: before the sale, during the sale, and after the sale. Sounds simple, right? It's a straightforward definition, but where do you draw the lines?

You can get quite granular with this. For example, here's a nine-stage example:
- Someone who isn't a customer and isn't even aware of your business yet discovers a problem they need to solve. This example can be anything from too much static in their laundry to a newfound dietary restriction to a business problem.
- The non-customer, aware that they have a problem, starts to look into possible solutions. Along the way, they discover you as one potential solution to their problem.
- This non-customer isn't sure they want to go with you to solve their problem. After all, if there's a company that might fix their issue, there's probably more than one. So, they carefully analyze your company to see your selling point and how well you can solve their problem.
- Still in the research phase, the non-customer looks at competitors and other potential solutions to their problem. They may not have even decided between buying an eCommerce product or rigging something DIY yet, but this is exploring their options. They may be signed up to your mailing list or become a fan on social media, but they are not yet a customer.
- The customer, through their research, has made two decisions. The first is to buy a competitor's solution, and the second is to buy your solution. They are now a customer.
- You don't take money, ship a product, and wash your hands of the transaction, do you? Of course not. In this stage, you engage with the customer – passively and actively – to onboard them into using your product. This process can involve anything from an instruction booklet in your product to a drip campaign offering usage tips.
- The usage stage is where the customer decides whether or not the investment was a good one. This time is also when they may reach out for support or leave a review. We've all had times when we make a purchase, but it takes weeks or months to get around to actually using it.
- This step is the ongoing relationship you have with an existing customer. Depending on your business, the relationship can be an ongoing subscription (or an increased service plan), or it can be a repeat purchase of a consumable, or it can be purchasing add-ons and extras (lenses and cases for a camera, for example.)
- Fully satisfied with both your product and your support, this customer is now loyal; they recommend you to their friends and strangers online, they advocate for you, and if you offer it and they're in the proper position, they may sign up to promote you via an affiliate program or referral system.
Several of these can be condensed, you may skip some, and some have dramatically more extended amounts of time a customer spends in them than others. That's what makes the customer journey so tricky, after all.
The Customer Journey in the Context of Content Marketing
All digital marketing is interconnected, but let's be honest; I'm not a PPC management agency or a technical SEO specialist; I'm a content marketer. I know enough to talk authoritatively about other forms of marketing, but I specialize in blogging and how blog content can engage potential customers. So, let's look at the customer journey stages in content marketing.
I've written before about why it's essential to know the user intent behind a keyword , so you know what type of content you should be writing. For example, if someone is searching for "red shoes," they're probably less interested in learning the history of how red shoes are viewed in various cultures and more interested in finding pages where they can buy red shoes.
Knowing the stage of the customer journey is similarly important. Giving visitors a user guide for a product they haven't even decided to buy will not work for you. Similarly, forwarding customers to a sales-focused landing page when they've already purchased your product is considered poor support.
Let's look at those nine journey stages and what content might be relevant to them.
1. Challenge
Challenge is the stage where a user learns they have a problem that may be solvable. This step is also a prime opportunity for content marketing .

Blog content written in this stage focuses on defining the user's pain point. It's about educating users on the issue, its challenges, the repercussions of not solving it, and how you may solve it. It uses keywords usually not used within the industry because a user might not know enough about the industry to use those terms.
To use content marketing as an example , I might produce content aimed at people who have no idea why a blog is helpful, explaining the basics of SEO and Google's algorithms and how content marketing interacts with them.
2. Discovery
At this point, the customer may have been on your blog before reading about their problem, or maybe they've only seen a reference to you on social media or elsewhere. The discovery stage is where they learn about your brand and that you aren't just educating them about the problem; you're offering a solution.

Content marketing here takes two forms. The first is landing pages. Landing pages aren't considered blog posts, but they can have some similarities, as they're both longer-form content. This content is still educational, but instead of educating the user on their problem, you're educating them about how your product can solve it.
You won't always get a sale from this content directly. Users may be too unaware of their options to pull the trigger, so they're likely to research alternatives.
3. Consideration
The consideration stage is where the user researches you in more detail. Blog posts don't necessarily come into play as much here, but technical writing, landing pages, features pages, pricing pages, reputation management, and other forms of marketing very much do.

This step is also where the user may decide between different solutions, like a DIY option versus a product they can use versus a service they can hire. For example, someone who needs photography for an event might research the pros and cons of cell phone pictures versus buying a camera versus hiring a photographer.
4. Comparison
Similar to consideration (and often considered part of it), the comparison phase is where the user performs similar research into your competitors.
We create blog content that converts - not just for ourselves, but for our clients, too.
We pick blog topics like hedge funds pick stocks. Then, we create articles that are 10x better to earn the top spot.
Content marketing has two ingredients - content and marketing. We've earned our black belts in both.

This step is where comparison pages come into play. Blog posts can also do a lot of heavy lifting here. You can write lists of the top companies offering a service (with your position at the top), you can write about how to solve various problems authoritatively, and so on. You want a whole ecosystem of content that positions you as a reliable authority.
5. Purchase
The actual act of making the purchase doesn't have anything to do with content marketing.

The user decides, they go to your website to buy or sign up, and that's that. The purchase decision step is a critical stage to analyze, which is why it gets a unique entry, but that's more about the analytics and the KPIs you harvest than the content you produce.
6. Adoption
Once a user has made a purchase, you want to onboard them. Depending on the product you're selling , this can occur in various ways.
Content marketing involves creating usage guides, tips and tricks blog posts, drip campaigns offering resources, an internal knowledge base, and other content types. This step is also where customer support can come into play, with a staff that can help assist users with configuration, onboarding, setup, and so on.
Content marketing doesn't necessarily play a significant role in usage, but it can be relevant if you write content about how to use your product for specific purposes.

Your onboarding may cover primary uses, but you can cover more advanced or unusual benefits in other forms of content.
Support, again, isn't necessarily the realm of content marketing. However, it's usually a good idea for your support to have at least a self-help option, like a knowledge base or a blog category dedicated to solving issues and fixing problems.

That way, when the user has a problem, they can find resources on your site to use and have the option to contact you for more support if necessary. Being available for your customer's needs is critical for retention and a positive customer experience. This stage also involves listening closely to customer feedback and improving product functionality.
9. Advocacy
For customers that had a positive user experience, advocacy is a natural next stage. After all, we all have to navigate the world of commercialized everything around us, and recommendations from people we trust are among the most powerful ways to spread a product.

Through affiliate marketing and referral guides, customer loyalty programs, and more, content marketing can work here. However, some of this content marketing won't be yours, it will be the advocate's, so you may want to create style guides, brand reference guides, or media packs to help them out.
Customer Journey Glossary
You've likely heard some of these phases before, and others may be brand new to you.
Here are a few terms and phases we've left out from this list to define and demystify them:
- Retention stage: This is a common phase in a customer journey. Customer retention is along the lines of Phase #7, "Support"; after a customer has made a purchase, you provide support to ensure they're happy and remain a customer with your company.
- Decision stage: This is identical to Phase #5, "Purchase." When the customer decides to purchase, they are now a customer and have entered a new phase in the customer journey.
- First impression stage: This stage is identical to Phase #2, "Discovery." The visitor discovers your brand, product, or website for the first time and is aware of you.
- Awareness stage: The awareness stage of the journey is also identical to phase #2, "Discovery," just with a different name.
- Customer Journey Map: Also called a customer journey roadmap, this is an illustration of each of your customer journey phases. This chart can help train and educate the members of your team to help them understand how a new visitor becomes a customer and all of the steps in between.
- Touchpoints: Touchpoints are moments in time when visitors or customers might interact with your brand, and they can be from users who are at different stages of the customer journey. This may be a YouTube ad that they watched, an email they received, a word-of-mouth recommendation, or even a "Thank you for your order" email after deciding to purchase.
As you can see, there are a few different nicknames for some of these stages, but the definition remains the same.
Putting the Pieces Together
The stage of the user journey is just one aspect of content marketing. User intent, keywords, and the buyer persona are also relevant.
I always say that writing a blog post is just about the easiest part . A successful blog requires a ton of groundwork, both in one-time or annual research and in topic-specific, keyword-specific, and persona-specific definitions.
That's about all the help I can give you in generic terms. The trouble with this is that it heavily depends on your business, niche, and target audience. I have done a ton of research into my niche and industry, product, keywords, metrics, and all the rest, but it would only be helpful to my direct competitors if I shared it. Your job is to define all of it for yourself. Or, of course, hire me to handle your content marketing strategy for you and have me do it—your choice.
James Parsons is the founder and CEO of Content Powered, a premier content marketing agency that leverages nearly two decades of his experience in content marketing to drive business growth. Renowned for founding and scaling multi-million dollar eCommerce businesses through strategic content marketing, James has become a trusted voice in the industry, sharing his insights in Search Engine Watch, Search Engine Journal, Forbes, Entrepreneur, Inc, and other leading publications. His background encompasses key roles across various agencies, contributing to the content strategies of major brands like eBay and Expedia. James's expertise spans SEO, conversion rate optimization, and effective content strategies, making him a pivotal figure in the industry.
Join Thousands of Marketers and Get Free Tips Weekly!
Related Posts

Blog Sales Funnels: How Do They Work and Are They Worth It?

18 Methods to Find Buyer Intent Keywords For Your Business

How to Build an Effective SaaS Marketing Content Strategy
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Name (required)
Email (will not be published) (required)
Your Comment
Let’s Grow Your Business
Want some free consulting? Let’s hop on a call and talk about what we can do to help.
Customer experience
Interaction between an organization and a customer / from wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, dear wikiwand ai, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:.
Can you list the top facts and stats about Customer experience?
Summarize this article for a 10 year old
Customer experience is the totality of cognitive , affective , sensory , and behavioral customer responses during all stages of the consumption process including pre-purchase, consumption, and post-purchase stages. [1] [2] [3]
Different dimensions of customer experience include senses, emotions, feelings , perceptions , cognitive evaluations, involvement, memories , as well as spiritual components, and behavioral intentions . [4] [1] [5] The pre-consumption anticipation experience can be described as the amount of pleasure or displeasure received from savoring future events, while the remembered experience is related to a recollection of memories about previous events and experiences of a product or service. [6] [7] [8]
What is CX?

You might have an intuitive sense of what separates good CX, or customer experience, from bad. Imagine, say, you want a latte. When you visit the coffee shop, are staff members attentive? If you are a regular, do they greet you by your name? Was the store designed intuitively? Do they take your order promptly and hand you your cup with a smile? If you have a problem, is it promptly resolved, or is someone sent to help you? Do they proactively reach out to understand your overall experience?
All of those questions touch on elements of customer experience. The four components of CX are brand, product, price, and service.
Basically, CX refers to everything an organization does to deliver superior experiences, value, and growth for customers. And it’s crucial in an age when how a business delivers for its customers is just as important as—if not more important than—the products and services it provides. In a digital world, where customers review and share their experiences with a company in public forums, it has become vital for companies to connect with customers across their journeys at an emotional level. Not only is customer experience the right thing to do for customers but it also results in 3x returns to shareholders .
The COVID-19 pandemic was a test of how to connect with customers in times of crisis . And many did surprisingly well in providing good CX, for instance, by swiftly reorienting their efforts to meet customers’ primary needs with respect to safety, security, and everyday convenience. Take, for example, e-commerce companies and food delivery services that developed methods of contactless delivery to keep customers and drivers safe as the virus spread.
This article offers a brief overview of customer experience-related topics and answers questions such as:
What are customer journeys?
How to measure customer experience, what is the consumer decision journey, what is customer care, how to improve customer experience.
A customer journey describes the customer’s end-to-end experience, as opposed to their satisfaction at various individual transactions or touchpoints. These can include many things that occur before, during, or after the customer experiences a given product or service. Examples of customer journeys include bringing a new customer on board, resolving a technical issue, or upgrading a product.
Consider onboarding a new customer. At one company , this process took about three months and on average entailed nine phone calls, a technician visit, and interactions via both the web and mail. While there was a 90 percent chance, at any given touchpoint, of the interaction going well, average customer satisfaction fell nearly 40 percent over the course of the journey. More important than solving issues at the level of individual touchpoints was to reimagine the approach to service operations around the most crucial CX journeys.
Attending to full customer journeys instead of touchpoints can drive stronger business outcomes. For instance, a McKinsey survey found that customer satisfaction with health insurance is 73 percent more likely when the entire journey works well than when only touchpoints do. Looking to the hospitality industry, customers of hotels that get the entire customer journey right may be 61 percent more willing to recommend those hotels than customers of hotels that just focus on touchpoints.
If your company is looking to reinvigorate its customer experience, three efforts can help you move from touchpoints to journeys :
- Observe. Put yourself in your customers’ shoes: What do they see? This can help organize and mobilize employees around customer needs. In addition to identifying and understanding the customer’s journey, you’ll need to quantify what matters to customers and define a clear aspiration and common purpose.
- Shape. When you design customer experiences, interactions must be reshaped into different sequences. Even if your effort starts small, it can swiftly become much larger and entail the digitization of processes, the reorientation of company culture, and nimble refinements in the field.
- Perform. Making the transition to prioritize journeys can be a journey in itself that takes years and requires deep engagement from everyone in the company, from corporate leaders right down to the front line.
Learn more about our Growth, Marketing & Sales and Operations practices.
You might have a hard time imagining how you measure something as ephemeral as the magic your company creates for customers. But it can be done. Best practice calls for three guiding principles to help optimize customer-experience measurement :
- Measure the customer experience at the journey level, rather than at the level of touchpoints or overall satisfaction.
- Invest in hardwired technology that captures feedback on a daily basis from multiple channels, integrating survey results and other data into comprehensive dashboards.
- Cultivate a mindset of continuous improvement at all levels.
Depending on the level of CX adoption within an organization, consider the power of predicting CX , which can help you stay ahead of customer churn and dissatisfaction. Why? Survey-based systems alone don’t necessarily meet the needs of today’s companies; they’re limited, reactive, ambiguous, and unfocused. Predictive customer insight may unlock more powerful insights to improve customer experiences.
The consumer decision journey (CDJ) is a reconceptualization of the traditional marketing funnel. In this approach, the way customers make decisions is framed as a circular process involving four phases where customers can be gained or lost:
- initial consideration
- active evaluation, or the process of researching potential purchases
- closure, when consumers buy brands
- postpurchase, when consumers experience those brands
And conceptions of the consumer decision journey continue to evolve , especially in light of the new technologies and capabilities available to consumers. Today, it is important for brands not only to react to customers but also to actively shape their decision journeys. This may mean compressing or even eliminating the consideration and evaluation phases to drive competitive advantage . To foster an accelerated customer loyalty journey , four distinct but interconnected capabilities are crucial:
- Automation can be used to streamline the customer journey (for example, being able to snap a photo of a check and deposit it via your bank’s app rather than physically visiting a bank branch).
- Proactive personalization uses a customer’s information to instantly customize CX.
- Contextual interaction uses knowledge about where a customer is in a journey to deliver them to the next set of interactions.
- Journey innovation finds new sources of value, such as new services, for both the customer and the brand. This involves companies mining their data and insights about customers to figure out what other services they might appreciate. The best companies also design customer decision journeys that allow open-ended testing and frequent prototyping of new services or features.
Learn more about our Growth, Marketing & Sales practice.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
Customer care generally happens within contact-center operations. These are sometimes referred to as call centers, and people working at these organizations support customers throughout their journeys with a company’s products or services—no matter where customers need help (in-store, online, via mobile apps, etcetera). This is as all part of providing an omnichannel customer experience. Contact centers play an important role in customer care, and a forward-looking vision for these centers could entail hyperpersonalization to meet customers’ expectations in a way that’s both strategic and experience oriented.
How has COVID-19 changed customer experience?
COVID-19 changed customer experience in several ways. Many companies needed to shift the ways they worked with customers, for example, by providing alternative digital experiences when it was not safe for physical stores to be open. More broadly, how your company interacted with customers throughout the pandemic may have triggered an immediate and lingering effect on customers’ sense of trust and loyalty. In times of crisis, meeting customer needs with empathy, care, concern, and connection is important. It can help frame short-term responses, build longer-term resilience, and prepare for success after a crisis passes by keeping a pulse on how preferences are changing in real time. And it’s worth noting that more than three-quarters of consumers changed their buying habits during the pandemic—and in addition to value and convenience, purpose also drives shopping decisions.
What does digital customer experience mean?
Digital customer experience refers to elements of the experience that happen online or with the support of digital and analytics. This can facilitate interactions that are holistic, predictive, prioritized, and focused on value.
Consider the example of a leading airline that built a machine-learning system to track and prioritize customers who might choose a different carrier because they experienced multiple flight delays or other issues. The system, built in three months, drove an 800 percent increase in customer satisfaction and also reduced churn for priority customers by 60 percent.
When it comes to digital customer experience, companies are increasingly aiming to transition to predictive insights that could represent the future of CX . Some CX leaders are pushing on predictive CX platforms, which consist of three key elements:
- a customer-level data lake, with customer, financial, and operational data to develop a rigorous understanding of customer experiences
- predictive customer scores using analytics that track what’s influencing customer satisfaction and business performance
- an action and insight engine that’s shared with a broad set of employees, via tools such as customer-relationship-management platforms, through an API layer
These platforms can play a powerful role in linking CX to value and building clear business cases to improve CX. Of course, companies must stay attuned to customers and the privacy imperative . And it will also be crucial to build security into the digital customer experience .
Learn more about our Growth, Marketing & Sales , Digital McKinsey , and Risk & Resilience practices.
What about customer experience and loyalty?
If you offer a good CX, chances are your customers will be loyal to you or your brand. But that doesn’t happen without real effort. “Consumers are changing, and consumer trends are driving this,” says former McKinsey partner Jess Huang on the new generation of customer loyalty programs . “With the move to digital over the last ten years, consumers are spending more and more time on their phones and various digital channels. This makes it much easier to access the consumer, but there is also a lot more noise. Brands are trying to figure out the right way to break through that noise and develop a relationship with the consumer.”
Loyalty programs are vital to doing so, but two-thirds of them fail to deliver. Focusing on eight elements can help your loyalty programs perform better:
- Don’t be afraid to offer customers incentives to redeem their loyalty points.
- Consider the customer segments where there’s “breakage” (people whose points expire), and think about potential opportunities for improvement.
- Enlist strategic partners to enhance offers and rewards.
- Offer points-plus-cash options.
- Measure success based on engagement, not just accruals.
- Segment customers into groups you can handle.
- Personalize test-and-learn across customer segments.
- Create a standard P&L to accurately measure the incremental impact of loyalty programs.
Is customer experience the same in B2B and B2C contexts?
Much of CX in B2B isn’t the same as in B2C. Here’s why :
- relationships often go deeper in B2B
- longer, more complex B2B journeys involve more individuals
- customization is more widespread in B2B than B2C
- the stakes are usually higher in B2B deals, as individual B2B customer relationships are often worth millions of dollars
Nevertheless, more B2B customers say they would like a better customer experience—one that is more like those of B2C customers. And in complex B2B sectors like industrial services—think aftermarket service contracts for jet engines, industrial robots, or utility-transmission equipment— better customer experience is increasingly critical for growth . In a survey of 1,000 B2B decision makers, lack of speed in interactions with their suppliers emerged as the number-one “pain point” and was mentioned twice as often as price.
Keeping a finger on the B2B pulse can help you understand and respond to emerging B2B customer needs , especially in light of the shift to omnichannel . Adjusting your approach for the mix of traditional, remote, and self-service sales channels is increasingly important—and 94 percent of B2B decision makers say new omnichannel sales model are as effective or more effective than prepandemic sales models. For even more, here’s a case study of how a B2B organization in China became more customer-centric.
How do different industries approach customer experience?
Because customer needs and expectations vary by context, different industries may approach CX in different ways. Here are just a few examples of how industries grapple with the issues:
- Automotive. Car companies are putting customer experience in the driver’s seat —whereas manufacturers once competed on their engineering capabilities, CX is now a true differentiator, and customer-centric innovation is crucial.
- Travel. The COVID-19 pandemic turned travel upside down, and travelers’ customer experience is emerging as a challenge during the recovery. Doing better could entail aiming higher on experience, understanding customers more deeply, and moving faster operationally.
- Retail. Retail and consumer CX likely needs to account for a variety of omnichannel operational considerations . Retailers also need to stay attuned to the rise of the inclusive consumer and make adjustments to serve their needs. And preparing for the future of shopping , where technology is everywhere, will also be important.
- Banking. CX transformation in banking can pay off by delighting customers and, in turn, delivering revenue and cost improvements for banks themselves. And in regions like Asia–Pacific, digital innovation in banking offers some insight on whether or how banks should rethink customer engagement . Keeping up with customer trends can also unearth new opportunities, for instance, as we’ve seen with buy now, pay later financing models. Fintech players may be on the vanguard when it comes to taking the friction out of financial services for customers.
- Insurance. Many insurers have invested heavily in digitizing customer journeys and processes to improve the experience. A user-first, omnichannel approach could rely on the availability of online purchasing capabilities, the ease of navigating online journeys, and seamless integration of sales support and advice. The rise of insurtechs has also helped the industry address some customer pain points.
- Healthcare. In coming months and years, “Care at Home” could reshape the way health systems deliver patient-centered care . The rise of telehealth could also affect CX in healthcare . Focusing on whole-person care could improve outcomes for patients with behavioral-health conditions. Monitoring healthcare consumer insights will remain important, and providing compassionate, personalized care can benefit both patients and healthcare organizations.
- Utilities. Transforming CX in utilities helps customers and can allow utilities themselves to drive out costs. Self-service and digital channels are crucial in this context.
- Government. Prioritizing and improving customer experience in government can offer big benefits for customers. It can also give employees greater purpose—and improve agencies’ reputations.
- Service businesses. Are customers of industrial-services businesses happy? The bar is rising, but for industrial OEM customer experience , organizations will need to better understand what customers want and need.
What are the differences between customer experience and employee experience?
While the design thinking that transformed customer experience is now also transforming employee experience (EX) , there are some differences between the two:
- A customer journey is often a lot quicker than an employee journey. It might take months or even up to a year for employers to hire a new employee. That’s a lot longer than most customer journeys.
- Many employers’ interactions with their employees continue to be top-down instead of being a constant, two-way iterative process—as successful customer journeys have become. For instance, while many companies are exploring hybrid work options, others are considering a full return to the office, even though many of their employees would prefer to continue working from home.
But happy employees are crucial to providing good CX—meaning that CX and EX are related. In that regard, improving employee experience in service of building a customer-centric culture can have a powerful effect. Just consider how much mindsets matter here: some employees, for instance, might think, “I’m not involved in asking for customer feedback.” But in a customer-centric culture, reframing that so employees feel empowered to create opportunities to ask for customer feedback can pay dividends.
Learn more about our Growth, Marketing & Sales , People & Organizational Performance , and Operations practices.
Three building blocks are essential in transforming or improving customer experience throughout your organization:
- Build aspiration and purpose. A clearly defined CX aspiration should deliver on your company’s purpose and brand promise. Have you developed a customer-centric vision and aspiration, linked it to value, and translated it into a concrete road map?
- Transform the business. Here’s where you discover customer needs, design solutions, and deliver impact, whether that’s via customer journeys, products, services, or business models.
- Enable the transformation. After introducing a new experience for customers, your company needs to consider how to sustain its efforts. This involves transforming employee mindsets; building capabilities; stepping up on technology, data, and analytics; establishing cross-functional governance and an agile operating model; and deploying systems to measure and manage performance.
Improving customer experience can make a big difference. In over a decade of helping more than 900 companies design and implement enterprise-wide CX programs, approaches that rest on these building blocks have delivered 15 to 20 percent boosts in sales conversion rates, 20 to 50 percent reductions in service costs, and 10 to 20 percent improvement in customer satisfaction.
It’s also important to stay attuned to customer experience pitfalls so your organization can avoid them. These include failing to link CX to value, taking a narrow view of CX, and applying limited creativity; don’t miss the examples of how other organizations have sidestepped these issues in transforming CX.
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Customer Experience collection. Learn more about the Marketing & Sales , Operations , and McKinsey Digital Practices, and check out customer experience–related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ Six customer experience pitfalls to avoid ,” March 17, 2022, Itai Miller, Kevin Neher , Rens van den Broek, and Tom Wintering
- “ Next in loyalty: Eight levers to turn customers into fans ,” October 12, 2021, José Carluccio, Oren Eizenman, and Phyllis Rothschild
- “ This time it’s personal: Shaping the ‘new possible’ through employee experience ,” September 30, 2021, Jonathan Emmett, Asmus Komm , Stefan Moritz , and Friederike Schultz
- “ How to boost growth in industrial services: Better customer experience ,” July 28, 2021, Hugues Lavandier , Senthil Muthiah, Kevin Neher , Stephanie Trottier, and Hyo Yeon
- “ Prediction: The future of CX ,” February 24, 2021, Rachel Diebner, David Malfara, Kevin Neher , Mike Thompson, and Maxence Vancauwenberghe
- “ The three building blocks of successful customer-experience transformations ,” October 27, 2020, Victoria Bough , Ralph Breuer , Nicolas Maechler , and Kelly Ungerman
- “ The human touch at the center of customer-experience excellence ,” October 8, 2020, Alex Camp, Harald Fanderl , Nimish Jain , Bob Sternfels , and Ryter von Difloe
- “ The CEO guide to customer experience ,” McKinsey Quarterly , August 17, 2016, includes interviews with Alfonso Pulido , Ron Ritter, and Ewan Duncan
- “ The consumer decision journey ,” McKinsey Quarterly , June 1, 2009, David Court, Dave Elzinga, Susan Mulder, and Ole Jørgen Vetvik

Want to know more about CX?
Related articles.

Six customer experience pitfalls to avoid

Next in loyalty: Eight levers to turn customers into fans

Prediction: The future of CX

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Customer journey mapping is a design tool used to track customers' movements through different touchpoints with the business in question. It maps out the first encounters people may have with the brand and shows the different routes people can take through the different channels or marketing (e.g. online, television, magazine, newspaper). ...
Customer Journey. A customer journey is a tool that helps marketers understand the series of connected experiences that customers desire and needs — whether that be completing a desired task or traversing the end-to-end journey from prospect to customer to loyal advocate.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers' experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint. ...
The customer journey is a comprehensive mapping of the steps a consumer takes from their initial awareness of a brand to the eventual purchase of a product or service, and their experiences beyond this point. This journey encompasses a multitude of interactions with a brand, including initial research, contemplation of options, and post ...
1985: Ron Zemke and Don Peppers initiate customer journey mapping to address service issues at a telephone company, focusing on emotions and pain points. 1998: OxfordSM uses journey mapping to help Eurostar define its brand and mission, marking a shift to proactive experience design. 2000s: With the digital revolution, personas emerge to ...
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain ...
The customer journey map is a tool to visualize the experience of interacting with your brand from the customer's point of view. This map is critical because it forces you to look at how your ...
Definition. The term "customer journey" describes the experiences a customer makes between the first contact with a brand and their final purchase decision. This model assumes that a customer rarely decides spontaneously, but rather gets in touch with a brand, a product, or a service at different points during their journey, called touchpoints.
The customer journey, or customer lifecycle, describes the varying steps a customer goes through when interacting with a company, from the first touchpoint to the last. Discovering a product or service, researching it, purchasing, engaging with a brand on social media, using the product, and seeking support are all examples of interactions ...
1. Define your purpose. The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won't know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
The customer journey or client path is the path that a client goes through: from the emergence of a need for a product or service to the moment of purchase or becoming a fan of the brand. In customer journey marketing it's often reflected in a customer journey map.
3. Master the digital-first journey, but don't stop there We analyzed different types of customer journeys: those that are completely online, those that start online and finish in a branch, those that start in a branch and finish online, and those that take place fully in a branch. We found that digital-first journeys led to higher customer-
Step 1 gets you into action on your top-priority journeys. Step 2 takes you two levels deeper, even as it extends your understanding of all the journeys by linking the voice of the customer (VOC) to the drivers of performance. Here, precise research design makes the difference between "interesting" insights and those that actually drive ...
Customer journey mapping is valuable for any organization looking to improve customer experience, customer retention, and loyalty. Stage 1: Awareness stage. The awareness stage is a potential customer's first impression of your brand, so it is worth a significant investment. They may encounter your brand passively by viewing an online or in ...
Customer Journey ( ugs. zu dt.: Die Reise des Kunden) ist ein Begriff aus dem Marketing und bezeichnet den Weg, bzw. die einzelnen Zyklen, die ein potenzieller Kunde durchläuft, bevor er sich für den Kauf eines Produktes entscheidet. Aus Sicht des Marketing bezeichnet die Customer Journey alle Berührungspunkte ( Touchpoints) - sowohl ...
One customer journey map, for example, might start with a TV ad, then utilize social media and third-party review sites during the consideration stage, before purchasing online and then contacting customer support about you your delivery service. And then, finally, that customer may be served a discount code for a future purchase.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
Decision stage: This is identical to Phase #5, "Purchase." When the customer decides to purchase, they are now a customer and have entered a new phase in the customer journey. First impression stage: This stage is identical to Phase #2, "Discovery." The visitor discovers your brand, product, or website for the first time and is aware of you.
Customer experience is the totality of cognitive, affective, sensory, and behavioral customer responses during all stages of the consumption process including pre-purchase, consumption, and post-purchase stages.
Value streams are not customer journey maps. While both value streams and journey maps take the perspective of the external stakeholder, they seek to describe different sets of information. Customer journey maps typically seek to describe the emotions, intent, and individual interactions with a customer. Alignment to agile methodologies
A customer journey is often a lot quicker than an employee journey. It might take months or even up to a year for employers to hire a new employee. That's a lot longer than most customer journeys. Many employers' interactions with their employees continue to be top-down instead of being a constant, two-way iterative process—as successful ...