UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Un standards for measuring tourism, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin

Glossary of tourism terms
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which involve tourism expenditure.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y Z
Activity/activities : In tourism statistics, the term activities represent the actions and behaviors of people in preparation for and during a trip in their capacity as consumers ( IRTS 2008, 1.2 ).
Activity (principal): The principal activity of a producer unit is the activity whose value added exceeds that of any other activity carried out within the same unit ( SNA 2008, 5.8 ).
Activity (productive): The (productive) activity carried out by a statistical unit is the type of production in which it engages. It has to be understood as a process, i.e. the combination of actions that result in a certain set of products. The classification of productive activities is determined by their principal output.
Administrative data : Administrative data is the set of units and data derived from an administrative source. This is a data holding information collected and maintained for the purpose of implementing one or more administrative regulations.
Adventure tourism : Adventure tourism is a type of tourism which usually takes place in destinations with specific geographic features and landscape and tends to be associated with a physical activity, cultural exchange, interaction and engagement with nature. This experience may involve some kind of real or perceived risk and may require significant physical and/or mental effort. Adventure tourism generally includes outdoor activities such as mountaineering, trekking, bungee jumping, rock climbing, rafting, canoeing, kayaking, canyoning, mountain biking, bush walking, scuba diving. Likewise, some indoor adventure tourism activities may also be practiced.
Aggregated data : The result of transforming unit level data into quantitative measures for a set of characteristics of a population.
Aggregation : A process that transforms microdata into aggregate-level information by using an aggregation function such as count, sum average, standard deviation, etc.
Analytical unit : Entity created by statisticians, by splitting or combining observation units with the help of estimations and imputations.
Balance of payments : The balance of payments is a statistical statement that summarizes transactions between residents and non-residents during a period. It consists of the goods and services account, the primary income account, the secondary income account, the capital account, and the financial account ( BPM6, 2.12 ).
Bias : An effect which deprives a statistical result of representativeness by systematically distorting it, as distinct from a random error which may distort on any one occasion but balances out on the average.
Business and professional purpose (of a tourism trip): The business and professional purpose of a tourism trip includes the activities of the self-employed and employees, as long as they do not correspond to an implicit or explicit employer-employee relationship with a resident producer in the country or place visited, those of investors, businessmen, etc. ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Business tourism : Business tourism is a type of tourism activity in which visitors travel for a specific professional and/or business purpose to a place outside their workplace and residence with the aim of attending a meeting, an activity or an event. The key components of business tourism are meetings, incentives, conventions and exhibitions. The term "meetings industry" within the context of business tourism recognizes the industrial nature of such activities. Business tourism can be combined with any other tourism type during the same trip.
Business visitor : A business visitor is a visitor whose main purpose for a tourism trip corresponds to the business and professional category of purpose ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Central Product Classification : The Central Product Classification (CPC) constitutes a complete product classification covering goods and services. It is intended to serve as an international standard for assembling and tabulating all kinds of data requiring product detail, including industrial production, national accounts, service industries, domestic and foreign commodity trade, international trade in services, balance of payments, consumption and price statistics. Other basic aims are to provide a framework for international comparison and promote harmonization of various types of statistics dealing with goods and services.
Census : A census is the complete enumeration of a population or groups at a point in time with respect to well defined characteristics: for example, Population, Production, Traffic on particular roads.
Coastal, maritime and inland water tourism : Coastal tourism refers to land-based tourism activities such as swimming, surfing, sunbathing and other coastal leisure, recreation and sports activities which take place on the shore of a sea, lake or river. Proximity to the coast is also a condition for services and facilities that support coastal tourism. Maritime tourism refers to sea-based activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports and includes their respective land-based services and infrastructure. Inland water tourism refers to tourism activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports which take place in aquatic- influenced environments located within land boundaries and include lakes, rivers, ponds, streams, groundwater, springs, cave waters and others traditionally grouped as inland wetlands.
Coherence : Adequacy of statistics to be combined in different ways and for various uses.
Competitiveness of a tourism destination : The competitiveness of a tourism destination is the ability of the destination to use its natural, cultural, human, man-made and capital resources efficiently to develop and deliver quality, innovative, ethical and attractive tourism products and services in order to achieve a sustainable growth within its overall vision and strategic goals, increase the added value of the tourism sector, improve and diversify its market components and optimize its attractiveness and benefits both for visitors and the local community in a sustainable perspective.
Consistency : Logical and numerical coherence.
Country of reference : The country of reference refers to the country for which the measurement is done. ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Country of residence : The country of residence of a household is determined according to the centre of predominant economic interest of its members. If a person resides (or intends to reside) for more than one year in a given country and has there his/her centre of economic interest (for example, where the predominant amount of time is spent), he/she is considered as a resident of this country.
Country-specific tourism characteristic products and activities : To be determined by each country by applying the criteria of IRTS 2008, 5.10 in their own context; for these products, the activities producing them will be considered as tourism characteristic, and the industries in which the principal activity is tourism-characteristic will be called tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 5.16 ).
Cultural tourism : Cultural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions.
Data checking : Activity whereby the correctness conditions of the data are verified. It also includes the specification of the type of error or of the condition not met, and the qualification of the data and their division into "error-free data" and "erroneous data".
Data collection : Systematic process of gathering data for official statistics.
Data compilation : Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules.
Data confrontation : The process of comparing data that has generally been derived from different surveys or other sources, especially those of different frequencies, in order to assess and possibly improve their coherency, and identify the reasons for any differences.
Data processing : Data processing is the operation performed on data by the organization, institute, agency, etc., responsible for undertaking the collection, tabulation, manipulation and preparation of data and metadata output.
Data reconciliation : The process of adjusting data derived from two different sources to remove, or at least reduce, the impact of differences identified.
Destination (main destination of a trip): The main destination of a tourism trip is defined as the place visited that is central to the decision to take the trip. See also purpose of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.31 ).
Destination management / marketing organization (DMO) : A destination management/marketing organization (DMO) is the leading organizational entity which may encompass the various authorities, stakeholders and professionals and facilitates tourism sector partnerships towards a collective destination vision. The governance structures of DMOs vary from a single public authority to a public/ private partnership model with the key role of initiating, coordinating and managing certain activities such as implementation of tourism policies, strategic planning, product development, promotion and marketing and convention bureau activities. The functions of the DMOs may vary from national to regional and local levels depending on the current and potential needs as well as on the decentralization level of public administration. Not every tourism destination has a DMO.
Documentation: Processes and procedures for imputation, weighting, confidentiality and suppression rules, outlier treatment and data capture should be fully documented by the survey provider. Such documentation should be made available to at least the body financing the survey.
Domestic tourism : Domestic tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor within the country of reference, either as part of a domestic tourism trip or part of an outbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Domestic tourism consumption : Domestic tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Domestic tourism expenditure : Domestic tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor within the economy of reference, (IRTS 2008, 4.15(a)).
Domestic tourism trip : A domestic tourism trip is one with a main destination within the country of residence of the visitor (IRTS 2008, 2.32).
Domestic visitor : As a visitor travels within his/her country of residence, he/she is a domestic visitor and his/her activities are part of domestic tourism.
Durable consumer goods : Durable consumer goods are goods that may be used repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more, assuming a normal or average rate of physical usage. When acquired by producers, these are considered to be capital goods used for production processes, as is the case of vehicles, computers, etc. When acquired by households, they are considered to be consumer durable goods ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.39 ). This definition is identical to the definition of SNA 2008, 9.42 : A consumer durable is a goodthat may be used for purposes of consumption repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more.
Dwellings : Each household has a principal dwelling (sometimes also designated as main or primary home), usually defined with reference to time spent there, whose location defines the country of residence and place of usual residence of this household and of all its members. All other dwellings (owned or leased by the household) are considered secondary dwellings ( IRTS 2008, 2.26 ).
Ecotourism : Ecotourism is a type of nature-based tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to observe, learn, discover, experience and appreciate biological and cultural diversity with a responsible attitude to protect the integrity of the ecosystem and enhance the well-being of the local community. Ecotourism increases awareness towards the conservation of biodiversity, natural environment and cultural assets both among locals and the visitors and requires special management processes to minimize the negative impact on the ecosystem.
Economic analysis : Tourism generates directly and indirectly an increase in economic activity in the places visited (and beyond), mainly due to demand for goods and services thatneed to be produced and provided. In the economic analysis of tourism, one may distinguish between tourism's 'economic contribution' which refers to the direct effect of tourism and is measurable by means of the TSA, and tourism's 'economic impact' which is a much broader concept encapsulating the direct, indirect and induced effects of tourism and which must be estimated by applying models. Economic impact studies aim to quantify economic benefits, that is, the net increase in the wealth of residents resulting from tourism, measured in monetary terms, over and above the levels that would prevail in its absence.
Economic territory : The term "economic territory" is a geographical reference and points to the country for which the measurement is done (country of reference) ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Economically active population : The economically active population or labour force comprises all persons of either sex who furnish the supply of labour for the production of goods and services as defined by the system of national accounts during a specified time-reference period (ILO, Thirteenth ICLS, 6.18).
Economy (of reference): "Economy" (or "economy of reference") is an economic reference defined in the same way as in the balance of payments and in the system of national accounts: it refers to the economic agents that are resident in the country of reference ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Education tourism : Education tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation the tourist's engagement and experience in learning, self-improvement, intellectual growth and skills development. Education Tourism represents a broad range of products and services related to academic studies, skill enhancement holidays, school trips, sports training, career development courses and language courses, among others.
Employees : Employees are all those workers who hold the type of job defined as "paid employment" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employer-employee relationship : An employer-employee relationship exists when there is an agreement, which may be formal or informal, between an entity and an individual, normally entered into voluntarily by both parties, whereby the individual works for the entity in return for remuneration in cash or in kind ( BPM6, 11.11 ).
Employers : Employers are those workers who, working on their own account with one or more partners, hold the type of job defined as a "self-employment job" and, in this capacity, on a continuous basis (including the reference period) have engaged one or more persons to work for them in their business as "employee(s)" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employment : Persons in employment are all persons above a specified age who, during a specified brief period, either one week or one day, were in paid employment or self-employment (OECD GST, p. 170).
Employment in tourism industries : Employment in tourism industries may be measured as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in any of their jobs, as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in their main job, or as a count of the jobs in tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 7.9 ).
Enterprise : An enterprise is an institutional unit engaged in production of goods and/or services. It may be a corporation, a non-profit institution, or an unincorporated enterprise. Corporate enterprises and non-profit institutions are complete institutional units. An unincorporated enterprise, however, refers to an institutional unit —a household or government unit —only in its capacity as a producer of goods and services (OECD BD4, p. 232)
Establishment : An establishment is an enterprise, or part of an enterprise, that is situated in a single location and in which only a single productive activity is carried out or in which the principal productive activity accounts for most of the value added ( SNA 2008, 5.14 ).
Estimation : Estimation is concerned with inference about the numerical value of unknown population values from incomplete data such as a sample. If a single figure is calculated for each unknown parameter the process is called "point estimation". If an interval is calculated within which the parameter is likely, in some sense, to lie, the process is called "interval estimation".
Exports of goods and services : Exports of goods and services consist of sales, barter, or gifts or grants, of goods and services from residents to non-residents (OECD GST, p. 194)
Frame : A list, map or other specification of the units which define a population to be completely enumerated or sampled.
Forms of tourism : There are three basic forms of tourism: domestic tourism, inbound tourism, and outbound tourism. These can be combined in various ways to derive the following additional forms of tourism: internal tourism, national tourism and international tourism.
Gastronomy tourism : Gastronomy tourism is a type of tourism activity which is characterized by the visitor's experience linked with food and related products and activities while travelling. Along with authentic, traditional, and/or innovative culinary experiences, Gastronomy Tourism may also involve other related activities such as visiting the local producers, participating in food festivals and attending cooking classes. Eno-tourism (wine tourism), as a sub-type of gastronomy tourism, refers to tourism whose purpose is visiting vineyards, wineries, tasting, consuming and/or purchasing wine, often at or near the source.
Goods : Goods are physical, produced objects for which a demand exists, over which ownership rights can be established and whose ownership can be transferred from one institutional unit to another by engaging in transactions on markets ( SNA 2008, p. 623 ).
Gross fixed capital formation : Gross fixed capital formation is defined as the value of institutional units' acquisitions less disposals of fixed assets. Fixed assets are produced assets (such as machinery, equipment, buildings or other structures) that are used repeatedly or continuously in production over several accounting periods (more than one year) ( SNA 2008, 1.52 ).
Gross margin : The gross margin of a provider of reservation services is the difference between the value at which the intermediated service is sold and the value accrued to the provider of reservation services for this intermediated service.
Gross value added : Gross value added is the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 3.32 ).
Gross value added of tourism industries : Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI) is the total gross value added of all establishments belonging to tourism industries, regardless of whether all their output is provided to visitors and the degree of specialization of their production process ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.86 ).
Grossing up : Activity aimed at transforming, based on statistical methodology, micro-data from samples into aggregate-level information representative of the target population.
Health tourism : Health tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation, the contribution to physical, mental and/or spiritual health through medical and wellness-based activities which increase the capacity of individuals to satisfy their own needs and function better as individuals in their environment and society. Health tourism is the umbrella term for the subtypes wellness tourism and medical tourism.
Imputation : Procedure for entering a value for a specific data item where the response is missing or unusable.
Inbound tourism : Inbound tourism comprises the activities of a non-resident visitor within the country of reference on an inbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Inbound tourism consumption : Inbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Inbound tourism expenditure : Inbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(b) ).
Innovation in tourism : Innovation in tourism is the introduction of a new or improved component which intends to bring tangible and intangible benefits to tourism stakeholders and the local community, improve the value of the tourism experience and the core competencies of the tourism sector and hence enhance tourism competitiveness and /or sustainability. Innovation in tourism may cover potential areas, such as tourism destinations, tourism products, technology, processes, organizations and business models, skills, architecture, services, tools and/or practices for management, marketing, communication, operation, quality assurance and pricing.
Institutional sector : An aggregation of institutional units on the basis of the type of producer and depending on their principal activity and function, which are considered to be indicative of their economic behaviour.
Institutional unit : The elementary economic decision-making centre characterised by uniformity of behaviour and decision-making autonomy in the exercise of its principal function.
Intermediate consumption : Intermediate consumption consists of the value of the goods and services consumed as inputs by a process of production, excluding fixed assets whose consumption is recorded as consumption of fixed capital ( SNA 2008, 6.213 ).
Internal tourism : Internal tourism comprises domestic tourism and inbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident and non-resident visitors within the country of reference as part of domestic or international tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(a) ).
Internal tourism consumption : Internal tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of both resident and non-resident visitors within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and inbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Internal tourism expenditure : Internal tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of visitors, both resident and non-resident, within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and inbound tourism expenditure. It includes acquisition of goods and services imported into the country of reference and sold to visitors. This indicator provides the most comprehensive measurement of tourism expenditure in the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(a) ).
International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities : The International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) consists of a coherent and consistent classification structure of economic activities based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, principles and classification rules. It provides a comprehensive framework within which economic data can be collected and reported in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking. The classification structure represents a standard format to organize detailed information about the state of an economy according to economic principles and perceptions (ISIC, Rev.4, 1).
International tourism : International tourism comprises inbound tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips and the activities of non-resident visitors within the country of reference on inbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(c) ).
International visitor : An international traveller qualifies as an international visitor with respect to the country of reference if: (a) he/she is on a tourism trip and (b) he/she is a non-resident travelling in the country of reference or a resident travelling outside of it ( IRTS 2008, 2.42 ).
Job : The agreement between an employee and the employer defines a job and each self-employed person has a job ( SNA 2008, 19.30 ).
Measurement error : Error in reading, calculating or recording numerical value.
Medical tourism : Medical tourism is a type of tourism activity which involves the use of evidence-based medical healing resources and services (both invasive and non-invasive). This may include diagnosis, treatment, cure, prevention and rehabilitation.
Meetings industry : To highlight purposes relevant to the meetings industry, if a trip's main purpose is business/professional, it can be further subdivided into "attending meetings, conferences or congresses, trade fairs and exhibitions" and "other business and professional purposes". The term meetings industry is preferred by the International Congress and Convention Association (ICCA), Meeting Professionals International (MPI) and Reed Travel over the acronym MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions) which does not recognize the industrial nature of such activities.
Metadata : Data that defines and describes other data and processes.
MICE : See meetings industry.
Microdata : Non-aggregated observations, or measurements of characteristics of individual units.
Mirror statistics : Mirror statistics are used to conduct bilateral comparisons of two basic measures of a trade flow and are a traditional tool for detecting the causes of asymmetries in statistics (OECD GST, p. 335).
Mountain tourism : Mountain tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in a defined and limited geographical space such as hills or mountains with distinctive characteristics and attributes that are inherent to a specific landscape, topography, climate, biodiversity (flora and fauna) and local community. It encompasses a broad range of outdoor leisure and sports activities.
National tourism : National tourism comprises domestic tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors within and outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(b) ).
National tourism consumption : National tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of resident visitors, within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and outbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
National tourism expenditure : National tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of resident visitors within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and outbound tourism expenditure ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(b) ).
Nationality : The concept of "country of residence" of a traveller is different from that of his/her nationality or citizenship ( IRTS 2008, 2.19 ).
Non-monetary indicators : Data measured in physical or other non-monetary units should not be considered a secondary part of a satellite account. They are essential components, both for the information they provide directly and in order to analyse the monetary data adequately ( SNA 2008, 29.84 ).
Observation unit : entity on which information is received and statistics are compiled.
Outbound tourism : Outbound tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor outside the country of reference, either as part of an outbound tourism trip or as part of a domestic tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39(c) ).
Outbound tourism consumption : Outbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Outbound tourism expenditure : Outbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(c) ).
Output : Output is defined as the goods and services produced by an establishment, a) excluding the value of any goods and services used in an activity for which the establishment does not assume the risk of using the products in production, and b) excluding the value of goods and services consumed by the same establishment except for goods and services used for capital formation (fixed capital or changes in inventories) or own final consumption ( SNA 2008, 6.89 ).
Output (main): The main output of a (productive) activity should be determined by reference to the value added of the goods sold or services rendered (ISIC rev.4, 114).
Pilot survey : The aim of a pilot survey is to test the questionnaire (pertinence of the questions, understanding of questions by those being interviewed, duration of the interview) and to check various potential sources for sampling and non-sampling errors: for instance, the place in which the surveys are carried out and the method used, the identification of any omitted answers and the reason for the omission, problems of communicating in various languages, translation, the mechanics of data collection, the organization of field work, etc.
Place of usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides, and is defined by the location of his/her principal dwelling (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.20 to 2.24).
Probability sample : A sample selected by a method based on the theory of probability (random process), that is, by a method involving knowledge of the likelihood of any unit being selected.
Production account : The production account records the activity of producing goods and services as defined within the SNA. Its balancing item, gross value added, is defined as the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption and is a measure of the contribution to GDP made by an individual producer, industry or sector. Gross value added is the source from which the primary incomes of the SNA are generated and is therefore carried forward into the primary distribution of income account. Value added and GDP may also be measured net by deducting consumption of fixed capital, a figure representing the decline in value during the period of the fixed capital used in a production process ( SNA 2008, 1.17 ).
Production : Economic production may be defined as an activity carried out under the control and responsibility of an institutional unit that uses inputs of labour, capital, and goods and services to produce outputs of goods or services ( SNA 2008, 6.24. ).
Purpose of a tourism trip (main): The main purpose of a tourism trip is defined as the purpose in the absence of which the trip would not have taken place ( IRTS 2008, 3.10. ). Classification of tourism trips according to the main purpose refers to nine categories: this typology allows the identification of different subsets of visitors (business visitors, transit visitors, etc.) See also destination of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 3.14 ).
Quality of a tourism destination : Quality of a tourism destination is the result of a process which implies the satisfaction of all tourism product and service needs, requirements and expectations of the consumer at an acceptable price, in conformity with mutually accepted contractual conditions and the implicit underlying factors such as safety and security, hygiene, accessibility, communication, infrastructure and public amenities and services. It also involves aspects of ethics, transparency and respect towards the human, natural and cultural environment. Quality, as one of the key drivers of tourism competitiveness, is also a professional tool for organizational, operational and perception purposes for tourism suppliers.
Questionnaire and Questionnaire design : Questionnaire is a group or sequence of questions designed to elicit information on a subject, or sequence of subjects, from a reporting unit or from another producer of official statistics. Questionnaire design is the design (text, order, and conditions for skipping) of the questions used to obtain the data needed for the survey.
Reference period : The period of time or point in time to which the measured observation is intended to refer.
Relevance : The degree to which statistics meet current and potential users' needs.
Reliability : Closeness of the initial estimated value to the subsequent estimated value.
Reporting unit : Unit that supplies the data for a given survey instance, like a questionnaire or interview. Reporting units may, or may not, be the same as the observation unit.
Residents/non-residents : The residents of a country are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located in its economic territory. For a country, the non-residents are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located outside its economic territory.
Response and non-response : Response and non-response to various elements of a survey entail potential errors.
Response error : Response errors may be defined as those arising from the interviewing process. Such errors may be due to a number of circumstances, such as inadequate concepts or questions; inadequate training; interviewer failures; respondent failures.
Rural tourism : Rural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing. Rural tourism activities take place in non-urban (rural) areas with the following characteristics:
- Low population density;
- Landscape and land-use dominated by agriculture and forestry; and
- Traditional social structure and lifestyle
Same-day visitor (or excursionist): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Sample : A subset of a frame where elements are selected based on a process with a known probability of selection.
Sample survey : A survey which is carried out using a sampling method.
Sampling error : That part of the difference between a population value and an estimate thereof, derived from a random sample, which is due to the fact that only a subset of the population is enumerated.
Satellite accounts : There are two types of satellite accounts, serving two different functions. The first type, sometimes called an internal satellite, takes the full set of accounting rules and conventions of the SNA but focuses on a particular aspect of interest by moving away from the standard classifications and hierarchies. Examples are tourism, coffee production and environmental protection expenditure. The second type, called an external satellite, may add non-economic data or vary some of the accounting conventions or both. It is a particularly suitable way to explore new areas in a research context. An example may be the role of volunteer labour in the economy ( SNA 2008, 29.85 ).
SDMX, Statistical Data and Metadata Exchange : Set of technical standards and content-oriented guidelines, together with an IT architecture and tools, to be used for the efficient exchange and sharing of statistical data and metadata (SDMX).
Seasonal adjustment : Seasonal adjustment is a statistical technique to remove the effects of seasonal calendar influences on a series. Seasonal effects usually reflect the influence of the seasons themselves, either directly or through production series related to them, or social conventions. Other types of calendar variation occur as a result of influences such as number of days in the calendar period, the accounting or recording practices adopted or the incidence of moving holidays.
Self-employment job : Self-employment jobs are those jobs where remuneration is directly dependent upon the profits (or the potential of profits) derived from the goods or services produced.
Self-employed with paid employees : Self-employed with paid employees are classified as employers.
Self-employed without employees : Self-employed without employees are classified as own-account workers.
Services : Services are the result of a production activity that changes the conditions of the consuming units, or facilitates the exchange of products or financial assets. They cannot be traded separately from their production. By the time their production is completed, they must have been provided to the consumers ( SNA 2008, 6.17 ).
Social transfers in kind : A special case of transfers in kind is that of social transfers in kind. These consist of goods and services provided by general government and non-profit institutions serving households (NPISHs) that are delivered to individual households. Health and education services are the prime examples. Rather than provide a specified amount of money to be used to purchase medical and educational services, the services are often provided in kind to make sure that the need for the services is met. (Sometimes the recipient purchases the service and is reimbursed by the insurance or assistance scheme. Such a transaction is still treated as being in kind because the recipient is merely acting as the agent of the insurance scheme) (SNA 2008, 3.83).
Sports tourism : Sports tourism is a type of tourism activity which refers to the travel experience of the tourist who either observes as a spectator or actively participates in a sporting event generally involving commercial and non-commercial activities of a competitive nature.
Standard classification : Classifications that follow prescribed rules and are generally recommended and accepted.
Statistical error : The unknown difference between the retained value and the true value.
Statistical indicator : A data element that represents statistical data for a specified time, place, and other characteristics, and is corrected for at least one dimension (usually size) to allow for meaningful comparisons.
Statistical metadata : Data about statistical data.
Statistical unit : Entity about which information is sought and about which statistics are compiled. Statistical units may be identifiable legal or physical entities or statistical constructs.
Survey : An investigation about the characteristics of a given population by means of collecting data from a sample of that population and estimating their characteristics through the systematic use of statistical methodology.
System of National Accounts : The System of National Accounts (SNA) is the internationally agreed standard set of recommendations on how to compile measures of economic activity in accordance with strict accounting conventions based on economic principles. The recommendations are expressed in terms of a set of concepts, definitions, classifications and accounting rules that comprise the internationally agreed standard for measuring indicators of economic performance. The accounting framework of the SNA allows economic data to be compiled and presented in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking ( SNA 2008, 1.1 ).
Total tourism internal demand : Total tourism internal demand, is the sum of internal tourism consumption, tourism gross fixed capital formation and tourism collective consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.114 ). It does not include outbound tourism consumption.
Tourism : Tourism refers to the activity of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ).
Tourism characteristic activities : Tourism characteristic activities are the activities that typically produce tourism characteristic products. As the industrial origin of a product (the ISIC industry that produces it) is not a criterion for the aggregation of products within a similar CPC category, there is no strict one-to-one relationship between products and the industries producing them as their principal outputs ( IRTS 2008, 5.11 ).
Tourism characteristic products : Tourism characteristic products are those that satisfy one or both of the following criteria: a) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share total tourism expenditure (share-of-expenditure/demand condition); b) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share of the supply of the product in the economy (share-of-supply condition). This criterion implies that the supply of a tourism characteristic product would cease to exist in meaningful quantity in the absence of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 5.10 ).
Tourism connected products : Their significance within tourism analysis for the economy of reference is recognized although their link to tourism is very limited worldwide. Consequently, lists of such products will be country-specific ( IRTS 2008, 5.12 ).
Tourism consumption : Tourism consumption has the same formal definition as tourism expenditure. Nevertheless, the concept of tourism consumption used in the Tourism Satellite Account goes beyond that of tourism expenditure. Besides the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips, which corresponds to monetary transactions (the focus of tourism expenditure), it also includes services associated with vacation accommodation on own account, tourism social transfers in kind and other imputed consumption. These transactions need to be estimated using sources different from information collected directly from the visitors, such as reports on home exchanges, estimations of rents associated with vacation homes, calculations of financial intermediation services indirectly measured (FISIM), etc. ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.25 ).
Tourism destination : A tourism destination is a physical space with or without administrative and/or analytical boundaries in which a visitor can spend an overnight. It is the cluster (co-location) of products and services, and of activities and experiences along the tourism value chain and a basic unit of analysis of tourism. A destination incorporates various stakeholders and can network to form larger destinations. It is also intangible with its image and identity which may influence its market competitiveness.
Tourism direct gross domestic product : Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP) is the sum of the part of gross value added (at basic prices) generated by all industries in response to internal tourism consumption plus the amount of net taxes on products and imports included within the value of this expenditure at purchasers' prices ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.96 ).
Tourism direct gross value added : Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA) is the part of gross value added generated by tourism industries and other industries of the economy that directly serve visitors in response to internal tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.88 ).
Tourism expenditure : Tourism expenditure refers to the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables, for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips. It includes expenditures by visitors themselves, as well as expenses that are paid for or reimbursed by others ( IRTS 2008, 4.2 ).
Tourism industries : The tourism industries comprise all establishments for which the principal activity is a tourism characteristic activity. Tourism industries (also referred to as tourism activities) are the activities that typically producetourism characteristic products. The term tourism industries is equivalent to tourism characteristic activities and the two terms are sometimes used synonymously in the IRTS 2008, 5.10, 5.11 and figure 5.1 .
Tourism product : A tourism product is a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the potential customers. A tourism product is priced and sold through distribution channels and it has a life-cycle.
Tourism ratio : For each variable of supply in the Tourism Satellite Account, the tourism ratiois the ratio between the total value of tourism share and total value of the corresponding variable in the Tourism Satellite Account expressed in percentage form ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.56 ). (See also Tourism share).
Tourism Satellite Account : The Tourism Satellite Account is the second international standard on tourism statistics (Tourism Satellite Account: Recommended Methodological Framework 2008 –TSA:RMF 2008) that has been developed in order to present economic data relative to tourism within a framework of internal and external consistency with the rest of the statistical system through its link to the System of National Accounts. It is the basic reconciliation framework of tourism statistics. As a statistical tool for the economic accounting of tourism, the TSA can be seen as a set of 10 summary tables, each with their underlying data and representing a different aspect of the economic data relative to tourism: inbound, domestic tourism and outbound tourism expenditure, internal tourism expenditure, production accounts of tourism industries, the Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) attributable to tourism demand, employment, investment, government consumption, and non-monetary indicators.
Tourism Satellite Account aggregates : The compilation of the following aggregates, which represent a set of relevant indicators of the size of tourism in an economy is recommended ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.81 ):
- Internal tourism expenditure;
- Internal tourism consumption;
- Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI);
- Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA);
- Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP).
Tourism sector : The tourism sector, as contemplated in the TSA, is the cluster of production units in different industries that provide consumption goods and services demanded by visitors. Such industries are called tourism industries because visitor acquisition represents such a significant share of their supply that, in the absence of visitors, their production of these would cease to exist in meaningful quantity.
Tourism share : Tourism share is the share of the corresponding fraction of internal tourism consumption in each component of supply ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.51 ). For each industry, the tourism share of output (in value), is the sum of the tourism share corresponding to each product component of its output ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.55 ). (See also Tourism ratio ).
Tourism single-purpose consumer durable goods : Tourism single-purpose consumer durables is a specific category of consumer durable goods that include durable goods that are used exclusively, or almost exclusively, by individuals while on tourism trips ( TSA:RMF 2008 , 2.41 and Annex 5 ).
Tourism trip : Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.29 ).
Tourist (or overnight visitor): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Tourism value chain : The tourism value chain is the sequence of primary and support activities which are strategically fundamental for the performance of the tourism sector. Linked processes such as policy making and integrated planning, product development and packaging, promotion and marketing, distribution and sales and destination operations and services are the key primary activities of the tourism value chain. Support activities involve transport and infrastructure, human resource development, technology and systems development and other complementary goods and services which may not be related to core tourism businesses but have a high impact on the value of tourism.
Travel / traveller : Travel refers to the activity of travellers. A traveller is someone who moves between different geographic locations, for any purpose and any duration ( IRTS 2008, 2.4 ). The visitor is a particular type of traveller and consequently tourism is a subset of travel.
Travel group : A travel group is made up of individuals or travel parties travelling together: examples are people travelling on the same package tour or youngsters attending a summer camp ( IRTS 2008, 3.5 ).
Travel item (in balance of payments): Travel is an item of the goods and services account of the balance of payments: travel credits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from an economy by non-residents during visits to that economy. Travel debits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from other economies by residents during visits to other economies ( BPM6, 10.86 ).
Travel party : A travel party is defined as visitors travelling together on a trip and whose expenditures are pooled ( IRTS 2008, 3.2 ).
Trip : A trip refers to the travel by a person from the time of departure from his/her usual residence until he/she returns: it thus refers to a round trip. Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips.
Urban/city tourism : Urban/city tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by non-agricultural based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social and natural experiences and products for leisure and business.
Usual environment: The usual environment of an individual, a key concept in tourism, is defined as the geographical area (though not necessarily a contiguous one) within which an individual conducts his/her regular life routines ( IRTS 2008, 2.21 ).
Usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.16 to 2.18).
Vacation home : A vacation home (sometimes also designated as a holiday home) is a secondary dwelling that is visited by the members of the household mostly for purposes of recreation, vacation or any other form of leisure ( IRTS 2008, 2.27 ).
Valuables : Valuables are produced goods of considerable value that are not used primarily for purposes of production or consumption but are held as stores of value over time ( SNA 2008, 10.13 ).
Visit : A trip is made up of visits to different places.The term "tourism visit" refers to a stay in a place visited during a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.7 and 2.33 ).
Visitor : A visitor is a traveller taking a trip to a main destination outside his/her usual environment, for less than a year, for any main purpose (business, leisure or other personal purpose) other than to be employed by a resident entity in the country or place visited ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ). A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Wellness tourism : Wellness tourism is a type of tourism activity which aims to improve and balance all of the main domains of human life including physical, mental, emotional, occupational, intellectual and spiritual. The primary motivation for the wellness tourist is to engage in preventive, proactive, lifestyle-enhancing activities such as fitness, healthy eating, relaxation, pampering and healing treatments.

- The Tourism Academy Learning Management System (LMS)
- Platform Functionality - Instructors
- Marketing Your Course
- Course Creator Tools
- Selling Courses
- Tourism Essentials
- Tools for Academy Administrators
- Business Class Podcast
- Knowledge Base
Do you have a glossary of travel, tourism & hospitality terms?
Every industry has its own jargon and lingo. tourism is no different. here's a great list of tourism terms that you should know..
The list has been compiled by the world-class team of strategists, consultants, educators and established tourism experts at the nonprofit Tourism Academy . Our team offers relationship powered professional development, trade marketing, tourism development and consulting solutions.
Glossary of Tourism Terms

adventure travel: a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion
affinity group : a group of people linked by a common interest or purpose. See also pre- formed group.
agent : one who acts or has the power to act as the representative of another. A person whose job it is to arrange travel for end clients (individuals, groups, corporations), confirming travel components and simplifying the planning process for customers, providing consultation services and travel packages.
American Bus Association (ABA) : A trade organization consisting of member bus lines throughout the country. www.buses.org
American National Standards Institute (ANSI): A private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. www.ansi.org
American Society of Travel Agents (ASTA): The oldest and largest travel agent organization in the world with travel agents being the primary members. Other companies providing travel industry products and services can be associate members. www.astanet.com
Application Programming Interface ( API) : a code that allows two software programs to communicate with each other.
attrition : Shortfall of sleeping room block pick-up or food-and-beverage projections from numbers agreed to in a contract. Penalties for attrition may be outlined in a contract’s attrition clause.
Average Daily Rate (ADR) : a statistical unit that represents the average rental income per paid occupied room in a given time period.
back of house : a business term that refers to parts of a business operation that customers do not see. This may refer to mechanical rooms, accounting offices, kitchens, and those persons who are engaged in those areas.
block : a group of rooms, tickets, seats or space reserved for a specific customer - usually for a set period of time. Room blocks are commonly reserved for conventions, meetings or groups in general. Room blocks may also be allocated to high volume buyers (wholesale, receptive, tour) who intend to sell them as tour components on an ongoing basis. A room block is usually under a firm agreement and is for a set period of time.
Brand USA : A public/private partnership to promote inbound tourism to the United States and communicate US entry/exit policies. Also known as the Corporation for Travel Promotion. www.thebrandusa.com
bulk pricing : the practice of offering exceptionally low, typically non-commissionable rates to high volume buyers who purchase a specified number of units to resell at a mark up.
campaign : A specific, defined series of activities used in marketing a new or changed product or service, or in using new marketing channels and methods.
Certified Tour Professional (CTP) : A designation administered by the National Tour Foundation and conferred upon tour professionals who complete prescribed evaluation requirements.
certificate: an official document attesting to a fact such as a level of achievement in a course of study or training.
certification: the action or process of providing someone or something with an official document attesting to a status or level of achievement. See also: American National Standards Institute
certified: officially recognized as possessing certain qualifications or meeting certain standards.
Certified Travel Counselor (CTC) : A designation conferred upon travel professionals who have completed a travel management program offered by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents.
Certified Meeting Planner (CMP) : A designation conferred upon convention and meeting management professionals who have completed an application and written exam offered by the Events Industry Council.
channel manager : a system or platform that coordinates the distribution of product details, inventory and pricing in real time across multiple sales “channels”
charter : to hire for exclusive use any aircraft, motorcoach, cruise ship or other vehicle
class of service : a parameter used to differentiate the types of accommodation offered by travel suppliers, often denoted by fare code on air tickets. Classes may reflect differences in space, comfort, amenities and cabin service. Ex: First Class, Business Class, Coach Class or please hold this chicken until we land.
commercial rate : A special rate given by a hotel or rental car, motor coach, bus or passenger transport company to an organization based on either the volume of business done or the type of accommodation or rental car. Also referred to as a corporate rate.
commission : The varying amount paid by suppliers to travel agents for the sale of travel products and services.
commissioned tours : A tour available for sale through retail and wholesale travel agencies, which provides for a payment of an agreed upon sales commission either to the retail or wholesale seller.
complementary : goods or services that add to the value of another good or service. Ex: peanut butter complements jelly
complimentary (comp) : Service, space or item given at no charge.
complimentary (comp) ratio : The number of rooms, tickets, meals or service items provided at no cost based on the number of occupied rooms.
- The industry standard is one complimentary room per 20-50 rooms occupied per day.
- The industry standard for ticketed attractions and restaurants is one complimentary admission/meal per 10-20 paid.
complimentary registration : Waiver of registration fees.
concierge : a hotel employee whose job is to assist guests by arranging tours, local transportation, making reservations for theater or restaurants, etc.
Convention & Visitors Bureau (CVB) : A nonprofit organization supported by bed taxes, government budget allocations, private memberships or a combination of these. A CVB promotes tourism, encourages groups to hold meetings and trade shows in its city, and assists groups before and during meetings.
consolidator : a person or company which forms groups to travel using group rates on to increase sales, earn override commissions or reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
consortium : a loosely knit group of independently owned and managed companies such as travel agencies, tour operators, hotels, or other suppliers, with a joint marketing distribution process
convention and visitors bureau (CVB) : a nonprofit local organizations charged with representing (and promoting) a specific destination. CVBs are funded by transient room taxes, government budget allocations, private membership dues, sponsorship sales and program participation fees, or a combination of these mechanisms. See also: destination marketing organization
co-op marketing: outreach activities that help multiple suppliers reach the target audience by sharing costs, resources and tactics.
course: a series of lessons or modules to teach the skills and knowledge for a particular job or activity.
destination : a place where travelers might visit. This may be any neighborhood, city, region or country that can be marketing as a single entity for tourists.
destination management company (DMC) : Company or professional individual engaged in organizing tours, meetings of all types and their related activities. Also referred to as a ground operator.
destination marketing organization (DMO) : A nonprofit marketing organization for a city, state, province, region or area whose primary purpose is the promotion of the destination. See also: convention & visitors bureau
direct spend : the value of goods and services purchased by tourists (e.g., attraction ticket, hotel room rate and meals)
double double : refers to a room containing two separate double beds, capable of sleeping up to four guests comfortably, sometimes referred to as a “quad”
double occupancy rate : the price per person for a room that will be shared between two people
dynamic pricing : the practice of varying the price for a product or service to reflect changing market conditions, in particular the charging of a higher price during times of greater demand. This is the opposite of static pricing.
educational travel : a type of niche tourism, built around learning objectives, often to the benefit of students and/or those who share a common interest, hobby or profession
emerging market : A group of customers who do not provide as much business as the target markets, but show interest in the destination.
escort : a person employed or contracted by a seller of packaged travel product who accompanies tour participants from point to point often acting as a the tour operator liaison and onsite problem solver.
escorted tour : a packaged, pre-planned itinerary that includes the services of a tour manager or tour escort who accompanies participants for the full duration of the tour
escrow : a legal concept and financial instrument whereby assets are held by a third party on behalf of two other parties that are in the process of completing a transaction. In many places, agents and tour operators are required by law to maintain customer deposits and pre-payments in escrow until the time of service.
excursion : a trip made for leisure, education or physical purposes. It is often an adjunct to a longer journey, cruise or visit to a place.
familiarization tour (FAM) : A program designed to acquaint participants with specific destinations or services. Offered in groups and on an individual basis.
folio : an itemized record of guest charges and credits, often referred to as a guest bill or statement.
frequent independent travel (FIT) : A custom-designed, pre-paid travel package with many individualized arrangements. An FIT operator specializes in preparing FITs documents at the request of retail travel agents. FITs usually receive travel vouchers to present to onsite services as verification or pre-payment. Also known as foreign individual/independent travel or frequent individual travel.
front office : a business term that refers to a company’s departments that come in direct contact with customers.
gateway : a city, airport, port or area where visitors arrive. International gateway refers to places where foreign visitors may first enter a country.
ground operator : a company or individual providing local accommodations, transfers, ticketing and related services. See also: receptive operator
group booking : Reservation for a block of rooms for a single group.
group tour : A prearranged, prepaid travel program for a group usually including transportation, accommodations, attraction admissions and meals. Also referred to as a package tour.
guaranteed departure : a tour that will definitely operate on the day it is scheduled and will not be cancelled.
Horizontal Market : audiences for products or services that are not easily distinguished by consumer characteristics. Examples of horizontal markets include those for computer security, legal or accounting services.
Hospitality Sales and Marketing Association International (HSMAI): A trade association for hotel sales, marketing and revenue management professionals.
hotel classifications : Classification of a hotel by its amenities, facilities, service and cost. Qualifications and terms may vary by country.
- limited service or economy is generally a reasonably priced, generally providing a bed, telephone, TV, shower and free parking. They often do not have room service or a restaurant.
- full service may refer to a property of any price category that offers some meeting space and features a restaurant onsite
- moderate medium-priced property with services and amenities such as a restaurant and possibly conference rooms.
- upper moderate is a property that offers special services such as a first-rate restaurant, banquet and conference rooms, valet service, room service, cable TV, and a host of other amenities.
- luxury or deluxe is a top-grade hotel or resort offering the highest service and the maximum variety of amenities. All rooms have a private bath, and all the usual public rooms and services are provided.
- boutique is loosely used to describe properties that have typically between 10 and 100 rooms and often contain luxury facilities in unique or intimate settings with full service accommodations.
hub and spoke : a style of tour that has guests staying in a single location with excursions to nearby destinations
incentive tour : travel experience offered to stimulate employee productivity or as a reward for sales agents
incidentals : items not included in the package price
inclusive : referring to a package or product price that includes all of the varying components, taxes and gratuities for a flat rate. An inclusive tour may include transportation, lodging, transfers, etc. for a set price. An inclusive meal might include food, drink, tax and gratuity.
independent tour : a style of travel packaging that allows visitors to move about without the accompaniment of a tour manager or escort
indirect spend : the value of all goods and services used to produce tourism output. (e.g., toiletries for hotel guests, ingredients for meals and plastic used in souvenirs)
International Inbound Travel Association (IITA) : A trade association of inbound receptive tour operators and suppliers from the US. Formerly RSAA Receptive Services Association of America.
incentive travel : A travel reward given by companies to employees to stimulate productivity. Also known as an incentive trip.
inclusive tour : A specific package in which all components of the package are part of the price. Generally, an inclusive package includes transportation, lodging, meals, gratuities and taxes, and some form of sightseeing or rental car. The terms and conditions of a tour contract should specify exactly what is covered. Also referred to as an all-expense tour and an all-inclusive tour.
inclusive rate : The rate charged to an operator that includes all service, tax, gratuities and additional fees.
IPW : A computerized scheduled appointment show for international tour operators always held in the United States and sponsored by U.S. Travel Association. Formerly known as Pow Wow.
itinerary : a schedule of travel components put together by an agent or operator.
leg : a portion of a journey between two scheduled stops.
lesson: an amount of teaching given at one time; a period of learning or teaching.
market segment : a group of consumers or buyer types that share one or more common characteristics, lumped together for sales or marketing purposes.
markup : the difference between the cost of a good or service and its selling price.
meet and greet : Pre-purchased service for meeting and greeting a client upon arrival in a city, usually at the airport, and assisting the client with entrance formalities, baggage and transportation.
microlearning : a tool for training, teaching and development that delivers content in small, very specific bursts.
module: each of a set of standardized parts or independent units that can be used to construct a more complex structure such as an item of furniture or a building. multiple lessons may be combined to create a module.
motor coach : A large, comfortable, well-powered bus that can transport groups and their luggage over long distances. Motor coaches are normally able to accommodate 46 to 54 passengers.
motor coach tour operator : A company that creates tours in which group members are transported via motor coach to their destination, itinerary activities and back.
mystery tour : a short journey, usually in a bus, that people make for pleasure without knowing where they are going.
NAJ : Producers of the RTO (receptive tour operator) summit and similar small trade show formats with a regional focus. Also referred to as North American Journeys
net rate : A wholesale rate for groups (usually 10-15 people) which an operator may add a mark up.
NTA (formerly National Tour Association) : A trade association of North American motor coach tour operators. www.ntaonline.com
occupancy : the percentage of available rooms in use during a given period.
online travel agent (OTA) : a travel website that specialized in the sale of travel products to consumers
outbound operator (or outbound tour) : A company or tour that takes groups from a given city or country to another city or country.
Ontario Motor Coach Association (OMCA) : A trade association of motorcoach operators based in and around Ontario province.
package : Travel arrangements with two or more components offered for one price, inclusive of all taxes. Also refers to a single-fee booth package offered by show management.
packager : An individual or organization that coordinates and promotes the development of a package tour and establishes operating procedures and guidelines for that tour.
performance tour operator : A tour operator company that focuses on planning trips for groups that must perform while traveling like school bands, choral groups, etc.
plus plus : a term used to describe a product price that does not include taxes, gratuities and/or service charges. Ex: The meal is $15 plus tax and gratuity OR $15++.
pre- and post-trip tours : Optional extension or side trip package offered before or after a meeting, gathering or convention.
pre-formed group : a group that contacts the tour operator to plan travel exclusively for the group members.
rack rate : the normal rate of a product or service, before any discounts, commissions or net price arrangements
receptive operator : A tour operator who provides local services, transfers, sightseeing, guides, etc. Many large receptive operators develop packages and sell them through wholesale tour operators in foreign countries. Also referred to as a ground operator, an inbound tour operator, a land operator, an RTO and a receiving agent.
retail tour : A tour put together by a tour operator and sold to individuals.
request for proposal (RFP) : A document that stipulates what services the organization wants from an outside contractor and requests a bid to perform such services.
retailer : one who sells directly to the consumer. See also: travel agent
return on investment (ROI) : Net profit divided by net worth. A financial ratio indicating the degree of profitability.
revenue per available room (RevPAR) : A measure used by hotels that divides revenue for a given time period by the number of available rooms for the same time period.
sales mission : Intense selling effort in a particular locality; calling upon qualify leads. Usually performed by a group of people who may or may not all be in a sales capacity but have an interest in meeting with the same buyers.
Seasons (from a buyer/operator perspective):
- looking The time of year when tour operators are looking at for new activities & vendors to include in future trips. Also known as product or catalog development season.
- selling The time of year when tour operators are focused on reaching out to their customers, promoting future trips and selling packaged travel programs.
- booking The time of year when tour operators are booking and confirming tour components they plan to utilize.
- travel The time of year when the majority of the tour operators’ customers are traveling.
Seasons (from a supplier perspective):
- off-season The time of year when tourist traffic, and often rates, are at their lowest because of decreased demand. Also referred to as low season, off-peak or value season.
- peak season The time of year when demand and price is at a premium. Also known as high season.
- shoulder season The season between peak season and off-season when demand is average and the travel product will not produce the highest price but does not need a deep discount to generate traffic.
series : describing a piece of business or scheduled itinerary that takes place on a regular frequency
site inspection : Personal, careful survey of property, facility or area.
Skål is a professional, fraternal organization of tourism leaders around the world, promoting global tourism and friendship.
SMERF : Meetings acronym for a category of meeting market segments including social, military, educational, religious and fraternal type groups. These organizations often are looking for value when selecting a meeting destination.
supplier : The actual provider of a travel product such as the hotel, attraction, restaurant, airline or car rental agency; not the travel agent or tour operator selling the product.
STAR (STR) Report : a tool used to measure hotel performance against competitive aggregates and within local markets. Data is collected and distributed by strglobal
static pricing : the practice of maintaining the same price for a product or service at all times regardless of changing market conditions, trends and demand. This is the opposite of dynamic pricing.
Student Youth Travel Association (SYTA) : a trade association representing tour operator companies that specialize in student travel. www.syta.com
tariff : a schedule of rates for a good or services provided by a supplier
tiered pricing : A pricing structure that offers a variety of price points for different customer types. For more or suggested rates by buyer type.
tour operator : A person or company that negotiates discount rates, packages travel products, prints brochures, and markets these travel products through travel agents or to the general public.
tour vouchers : Documents issued by tour operators to be exchanged for accommodations, meals, sightseeing, admission tickets and other services. Also referred to as coupons and tour orders.
tourism : travel for business or pleasure; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. Tourism may be international, or within the traveler’s country.
tourism ambassador: an individual possessing the knowledge, skill and training to represent a destination, assist tourists and create better visitor experiences.
Tourism Cares : A charitable organization that focuses on helping preserve the travel experience for future travelers. www.tourismcares.org
trade association : Group of persons employed in a particular trade.
trade publication : A magazine or newsletter that targets a specific industry.
trade show : Exhibit of products and services that is targeted to a specific clientele and not open to the public.
travel agent (or travel agency) : Person or firm qualified to advise and arrange for travel needs such as hotel rooms, meals, transportation, tours and other travel elements. Represents all travel suppliers worldwide. Also referred to as a retailer.
Travel Alliance Partners (TAP) : A member-owned organization of tour operators that work together to develop unique itineraries within their respective regions, cross-promote products offered by other members and leverage their collective buying power. www.tapintotravel.com
travel receipt : purchase of travel and tourism related goods and services by visitors. These goods and services include food, lodging, recreation, gifts, entertainment, local transportation and other items incidental to travel.
United Motor Coach Association (UMA) : North America's largest association for operators of motorcoach companies providing charter, tour and regular route services. www.uma.org
United States Tour Operators Association (USTOA) : A nationwide organization of tour operators offering protection for travelers purchasing member travel products by way of a multi-million-dollar bond. www.ustoa.com
Upsell : sales technique where a seller induces the customer to purchase more expensive items, upgrades or other add-ons in an attempt to make a more profitable sale
U.S. Travel Association : The national, nonprofit association representing all components of the U.S. travel industry. (formerly known as TIA - Travel Industry Association of America) www.ustravel.org
Vertical Market : used to identify areas where vendors offer goods & services specific to a group of customers with specialized needs. Examples may include customers identified by their areas of origin, age range(s) or interest types.
Visa : a conditional authorization granted by a country to a foreigner, allowing them to enter, remain within, or to leave that country.
voluntourism : the act or practice of doing volunteer or charitable work as needed in the communities where one is vacationing
voucher : documents or digital codes issued to consumers by tour operators that may be exchanged for tour components
walk-through : Review of meeting details, or inspection of function room or trade show floor prior to event.
webinar : Short for web-based seminar, a presentation, lecture, workshop or seminar that is transmitted over the web. A key feature of the webinar is its interactive elements – the ability to give, receive and discuss information. Contrast with webcast in which the data transmission is one way and does not allow interaction between the presenter and the audience.
wholesaler : A company that creates and markets inclusive tours and FITs for sale through travel agents. Often used interchangeably with “tour operator,” but several distinctions should be drawn: a wholesaler presumably sells nothing at retail, a tour operator does both; a wholesaler does not always create his or her own products, a tour operator virtually always does; and a wholesaler is less inclined than a tour operator to perform local services.
World Tourism Organization (WTO) : An organization created to promote and develop tourism in the interest of the economic, social and cultural progress of all nations. www.world-tourism.org
About the Author
Stephen Ekstrom is the Chief Strategist at The Tourism Academy | tourismacademy.org, featured speaker at numerous tourism industry conferences, travel writer and host of the Business Class podcast.
Break the Ice Media & Travel Alliance Partners have merged to offer you more as Travel Alliance Partnership.
Travel and Tourism Terms, Acronyms & Abbreviations
Every industry has its language; can you talk tourism.
We abbreviate words or phrases to save time, effort or space. This is great, but if you don’t know what the acronym or abbreviation stands for, it may feel like people are speaking a different language. For those of us in the tourism industry, like many others, we use a wide array of abbreviations and/or acronyms. Below are 21 travel and tourism terms used frequently.
Jump to a section: A-D F-G I-N M-T

Travel and Tourism Terms
Accessible: Usable by all people . Whether a hotel, restaurant, or attraction can by enjoyed by people of all ages and abilities, regardless of physical or other limitations.
Assets: The attractions, hotels and restaurants within a given region . Assets are what that area has to offer guests who visit.
Buyers: Travel Trade professionals who sell to consumers . They are tour operators, receptive operators, travel agents and OTAs (online travel agents). They look for destinations and attractions to package and sell to their customers.
CVB : Convention and Visitors Bureau. Primarily the same thing as a DMO or TPA (see below).
DMO: Destination Marketing Organization. A destination marketing organization is an entity that promotes a town, city, region, or country to increase visitation. It promotes the development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing, and services. The primary goals of a DMO are to create and implement strategic marketing plans around tourism, to bring local tourism businesses together and to help them work collectively. This transforms a set of attractions, activities and services into a cohesive and compelling travel experience. For example, Break the Ice Media works with several DMOs, including Cayuga County Office of Tourism , Genesee County Office of Tourism and Visit Syracuse .
Implement strategic marketing plans
FAM : Familiarization Tour . FAMs are marketing initiatives, inviting either media or travel trade professionals to tour a region or destination . Experiencing it helps them write about it or sell it as a product to their customers. The activities on a FAM are typically shorter than what the actual visitor experiences. They provide a sampling of what is offered.
FIT: Foreign Independent Traveler . An international family or small group travelling to the USA. They arrive by airplane and usually rent cars for transportation.
Fly drive: A v acation package that includes air transportation and a rental car . Many international tourists (FITs) prefer to buy these types of packages to explore a destination.
Front-line staff: People who interact with and give service to customers, guests and visitors. For example, front desk staff at a hotel or a cashier at an attraction.
Group Leader: The p erson who accompanies and/or leads the people on a group tour . They work for the Group Tour Operator who sells the tour.
Group Tour Operator: A person who puts together vacation packages for groups . They sell these packages as products to consumers. They also fit into the category of Buyers.
Tourism generated by visitors from foreign countries
Inbound operators: Agencies that specialize in providing tour packages to international travelers visiting the United States. Also known as Receptive Operators. Travel agents from foreign countries will work with an inbound receptive operator to find a travel package that suits their customers. A couple of examples are TourMappers and ATI , who we’ve worked with.
Inbound Tourism: Tourism generated by visitors from foreign countries . This does not include domestic travel like visitors from drive markets and in-state visitors.
Itinerary: The planned route for a trip. This is what travel trade professionals sell to their customers. It’s a pre-planned experience with where to go, when, and what to expect when you get there.
Motorcoach: Large passenger bus. This is the vehicle most often used for people travelling with group travel tours.
Net Rate: Hotel room inventory sold via a third-party distributor at prices subject to commission. The Net Rate is the price for a hotel room without the commission of the third-party distributor. These distributors could be a travel agent, receptive operator or online travel agent. (See also, Rack Rate)
Create Itineraries for Foreign Independent Travelers
Partners: The people who own or manage the assets of a region. These partners work closely with their region’s DMO and benefit from tourism dollars spent at their establishments.
Rack Rate: Standard daily rate established for hotel rooms. This rate is typically public, printed on hotel brochures and listed on websites.
Suppliers: Tourism or Travel professionals who sell to businesses aka Buyers . They sell B2B (that means business to business). They work with tourism companies to promote their attraction or destination.
TPA: Tourism Promotion Agency. This is basically the same thing as a DMO. A government agency that promotes tourism in a specific county or region within a state.
Travel Advisor: Someone who assists consumers in booking trips. Previously called travel agents, travel advisors do more than book travel for people. The term agent switched to advisor to demonstrate how these professionals coordinate trips and help groups, families or individuals plan and book their travel.
Rhonda Carges
Related Posts
Collaboration Drives Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism has growing importance in the world of travel and tourism. As destinations grow in popularity, they need to collaborate closely with residents, local…
Marketing for Group Travel: Building Solid Relationships with Tour Operators
Group travel is a significant segment of the tourism market, and if you want to see those buses pulling up to the curb and filling…
- Collaboration (51)
- Content Development (6)
- Facebook Advertising (4)
- Industry News (1)
- Destination Leadership (30)
- Crisis Communications (1)
- Influencer Marketing (7)
- Travel PR (32)
- Strategic Planning (7)
- Destination Marketing (137)
- Group Travel (27)
- Virtual Events (140)
Collaboration Toolkit

Our first research study confirmed that collaboration is a constant in the travel, tourism and hospitality industry. It is not a matter of if, but when and how, organizations will collaborate together. Our latest study reveals how organizations are putting collaboration into operation and how they are setting up systems and processes so that collaboration becomes a strategic part of the organization.
" * " indicates required fields
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
90 English Tourism Vocabulary Words and Phrases [With Sample Dialogues]
English is the most common language used in the international tourism industry.
People who work in the tourism industry use it to communicate with tourists from all over the world.
If you work in tourism or hope to find a job in the industry, it helps to know the right words and phrases for this type of work.
Interacting with Customers
Greeting customers, asking customers questions , responding to questions, checking for understanding, common scenarios in tourism english, giving recommendations, giving directions , making friendly small talk, jobs in hospitality and tourism, jobs at hotels and resorts, bar and restaurant staff, jobs at travel and tourism companies, more tourism vocabulary in english, how to learn english tourism vocabulary, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)

You always want to welcome customers or guests with a friendly, professional greeting :
- Good morning (before 12 p.m.)
- Good afternoon (between 12 p.m. and 5 p.m.)
- Good evening (after 5 p.m.)
- Welcome to… [company name] . My name is… [your name] .
Be sure to always use a respectful term to refer to your customers:
- Miss — Young women (under age 30)
- Ma’am — Mature women (over age 30)
- Sir — Men of all ages
For example, using these terms you can now greet customers in a very respectful way:
- Good morning, miss .
- Good afternoon, sir .
If you are working at a hotel, restaurant or tour agency, you can greet a customer and then ask them this question:
Do you have a reservation with us?
To answer the phone, you only need one simple phrase:
Hello, you’ve reached [company name]. This is [your name]. How may I help you?
If you are working with customers in a hotel, before they go to their rooms you can say one of these phrases:
- We hope you enjoy your stay!
- Please let us know if you have any questions or comments during your stay.
You will want to make sure your customers are safe and happy while they are with you. You can do this by asking friendly and polite questions, such as:
- How are you doing this morning? (or afternoon/evening)
- Have you been having a good time?
- Is there anything else we can do to make your experience more enjoyable?
Customers will have many questions, and sometimes you will not know the answer. You may need to ask a coworker or supervisor. When this happens, you can use the following phrases:
- I will get that information for you right away.
- That’s a great question! I will check with my supervisor and let you know.
As a guide, host or receptionist, you will need to double-check for understanding. These phrases are simple and quick ways to make sure you have understood the guest or customer:
- I heard you ask (about flights) . Is that correct?
- So, you said (you wanted to visit the ruins) , right?
- Okay, I understand that (your flight leaves at 3 PM) . Is that correct?
To ask for clarification
Your guest may use vocabulary that you are unfamiliar with. Likewise, they might have an accent that is difficult for you to understand. Here are some polite ways to ask them to repeat or clarify what they said:
- I’m sorry, I didn’t quite understand that. Can you say that again?
- Pardon my English, but I didn’t understand that. Can you say that again?
- I’m sorry, I didn’t catch that. Can you describe what you mean?
To invite your guests to ask questions
You can make all of your guests feel welcome by encouraging them to ask questions:
- Does anyone have any questions?
- Yes, sir? / Yes, ma’am? Do you have a question?
- Please feel free to raise your hand any time if you have a question.
- So, any questions?
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!

When working in tourism, you might need to give directions to tourists, share recommendations for a good restaurant or attraction or make friendly conversation.
In these scenarios, you will play the part of the “guide,” but it could be any job where you interact with tourists. Practice these dialogues so you feel confident using these words and phrases in your interactions.
- For (authentic cuisine, family activities, etc.), I recommend…
- My favorite place is…
- Personally, I suggest…
Tourist: Excuse me, do you know a good place for ice cream?
Guide: Oh, yes. For really good ice cream, I recommend Maria’s. It’s located about six blocks from here, and it’s my favorite place. Personally, I suggest the chocolate cherry flavor. I think your family will like it.
Tourist: Great, thanks!
If you work in tourism, you will need to give directions to visitors. Here are some key phrases you might use to explain how to get somewhere:
- Go straight
- Stop at the…
- Continue until…
- Take the subway (or bus, train, etc.)
- Follow the signs for…
- At the traffic light
- At the next street (or light, block, etc.)
- In five blocks
- Near the hotel (or beach, station, etc.)
- On the main plaza
See this post for more words and phrases for giving directions:
Asking for and giving directions in English is a helpful skill, and this guide will show you the important vocabulary you need to know, with audio pronunciation included!…
Tourist: Can you tell me how to get to the theater?
Guide: Sure! The theater is near the train station. You need to go straight down this street for one block. At the next street, turn left. Continue until you see a sign for the theater, in about five blocks. If you’re lost, you can follow the signs for the train station. Does that make sense?
Tourist: Yes, thank you!
Here’s a helpful video to practice basic phrases for giving directions:
Here are some phrases that you can use when you want to make friendly conversation with a guest or visitor:
- So, are you enjoying your time in (Paris) so far?
- Tell me, what is your favorite part of the city so far?
- What do you think of the (architecture, food, beach, festival, etc.) ?

This vocabulary will help you a lot when you are working in the tourism industry or searching for jobs.
- Bellhop / baggage handler — the person who will open the front door for guests and carry their bags to their rooms
- Concierge / receptionist — the person at the front desk who welcomes the guests, gives out room keys, helps guests make reservations and takes payments for reservations
- Maid / housekeeper — the person who cleans the hotel rooms ( see English vocabulary for housekeeping here )
- Janitor — the person responsible for cleaning everything outside of hotel rooms, such as the lobby and other common areas
- Groundskeeper — the person who takes care of all the plants outside the hotel
- Maintenance worker — the person who fixes anything that stops working in the hotel
- Manager / supervisor — the person who makes sure everything goes well at the hotel, hires employees, teaches new employees how to do their jobs and makes sure that guests are happy
- Event planner — the person who makes sure the hotel is ready for big events such as business conventions (meetings) or weddings
Here are a couple of vocabulary guides for working in hotels:
Practicing English for receptionists can help you greet and assist hotel guests with ease. By studying the right phrases, you can prepare yourself to handle common…
Knowing hotel vocabulary in English is essential if you want to work in the hospitality industry. Check out our list of 100+ vocabulary words and phrases on everything…
These jobs might exist at a hotel if it has a bar and/or restaurant.
- Bartender — the person who makes and serves drinks at the bar
- Host / hostess — the person who stands at the entrance to the restaurant and welcomes guests, brings them to a table and takes reservations on the phone and in person
- Server / waiter / waitress — the person who serves customers who are eating at the restaurant (“waiter” refers to a male, “waitress” refers to a female and “server” can refer to any gender)
- Busboy / busser — the person who makes sure that tables are clean and ready for customers
- Chef / cook — the person who prepares food at the restaurant
If you work or want to work in a bar or restaurant, check out this vocabulary guide next:
Click here to learn English for restaurant staff! Here, we have information about six essential restaurant positions, the common phrases used by each one and study…
There are entire companies that exist just to help travelers book their trips. If you work for one of these companies, you will either work in an office or outside the office helping travelers enjoy their time in your city or country.
- Secretary / administrative assistant — someone who takes care of the whole office by organizing paperwork, making and receiving phone calls, organizing the office schedule and taking reservations for tours and trips
- Travel agent — someone who helps people find the most affordable flights, hotels, etc. and helps them buy tickets and make reservations before they travel
- Tour guide — someone who goes out with tourists and takes them on adventures to explore towns, cities, farms, mountains, jungles and more
- Taxi driver / private driver — someone who drives tourists in a taxi or private car between different places, and sometimes on a tour around the area
- Shuttle driver — someone who drives a large vehicle (usually a small bus or large van) to transport groups of people between places, such as from the hotel to some popular tourist destinations or between the hotel and the airport
- Airline agent — someone who works at the desk of an airline (a company that owns airplanes and provides transportation services with them)
- Flight attendant — someone who takes care of passengers on airplanes by serving food and drinks and giving safety instructions ( see English vocabulary for flight attendants here )
- Cruise attendant — someone who takes care of people on boats and ships by doing the same things as flight attendants, providing services like food and drinks and giving safety instructions
- Translator — someone who translates between different languages in writing, such as for tourism guides or flyers
- Interpreter — someone who translates between two languages by listening and speaking, often to help tourists and visitors understand and speak with local people
- Recreational guide — someone who goes with tourists to do activities like yoga, surfing, cycling, running, hiking and climbing mountains
Here is a list of common tourism-related English words. You might be asked questions with these words or you might need to use them yourself. Make sure you’re familiar with them and can use them in full sentences.
- Tourist – someone who travels to different places for enjoyment or to see new things
- Attractions — places of interest that are often visited by tourists, such as museums or amusement parks
- Landmark – a special or famous place that people can easily recognize, often used for giving directions
- Destination – a place to which people travel for leisure, business or other purposes
- Guide – a person who helps tourists by showing them around and giving them information about a place
- Guidebook – a book that provides information for travelers about a particular destination, including attractions, hotels and restaurants
- Souvenir – a small item that people buy to remember a place they visited, like a keychain or a postcard
- Itinerary – a plan or schedule that shows the activities or places someone will visit during their trip
- Accommodation – a place where travelers can stay overnight, such as a hotel, hostel or campground
- Transportation – the way people travel from one place to another, such as by car, bus, train or airplane
- Passport – a document issued by a government that proves a person’s identity and nationality, allowing them to travel internationally
- Visa – a stamp or document given by a country’s government that allows someone to enter or stay in that country for a certain period of time, usually for tourism, work, or study
- Business district — also called the financial district, this is the center of the city where many offices, banks and companies are located
- Entertainment district — a part of a city where there are lots of restaurants, bars, theaters and other fun places
- Dining district — an area within a city with a lot of restaurants
- Custom — a traditional way of doing something that is common in a particular culture or society
- Highlight — the most interesting or exciting part of something, often the main attraction
- Scenery — the natural features of an area, such as mountains, rivers or forests, that people find beautiful to look at
- Surroundings — the area or environment around a particular place, including nearby buildings, landscapes and neighborhoods
- Depart — to leave from a place, especially when traveling
- Arrive — to reach or get to a place or destination, especially when traveling
- Recommend — to suggest or advise someone to do something because you think they will enjoy it
- Read the “English for International Tourism” textbooks. They are available in low-intermediate , intermediate and high-intermediate levels. As long as you have a foundation in English, this series is perfect for learning how to communicate with coworkers and tourists in different tourism-related scenarios. Here are some more English for Tourism books we recommend.
- Take an English for Tourism course. You can find some great courses on Udemy, such as this English for Business and Tourism course aimed at low-intermediate to intermediate students. Or take lessons with a tutor who specializes in tourism on Preply .
- Complete tourism English courses on Memrise. Focus on Memrise English courses for tourism. These lessons feature English vocabulary words and phrases that anyone in the tourism industry would use in their daily activities. Try spending at least 30 minutes a day using Memrise to brush up on your tourism vocabulary—you’ll notice a difference!
- Follow travel vloggers on YouTube. Look for channels or specific videos about the place where you will be working. Engage in discussions in the comments as well! Not only will that make using YouTube more fun , but it will also require you to learn and use new words during your chats back and forth with others.
- Participate in discussions on travel forums. Travel forums allow you to use your new tourism vocabulary with native speakers and practice written English . On TripAdvisor , you can talk with English speakers about traveling, hotels, restaurants, transportation and more. The /r/travel subreddit is a great place to talk about everything related to tourism.
- Give yourself daily homework. A great place to start is the tourism section of ESL Conversation Questions . You’ll find a variety of tourism-related topics that you can discuss with your friends and coworkers. If you’re a hospitality professional, check out Oxford University Press’ free online workbook series, English for Careers .
Bookmark this page so you can come back and view this tourism vocabulary whenever you have some free time.
Soon you will be able to communicate with any tourist who crosses your path!
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
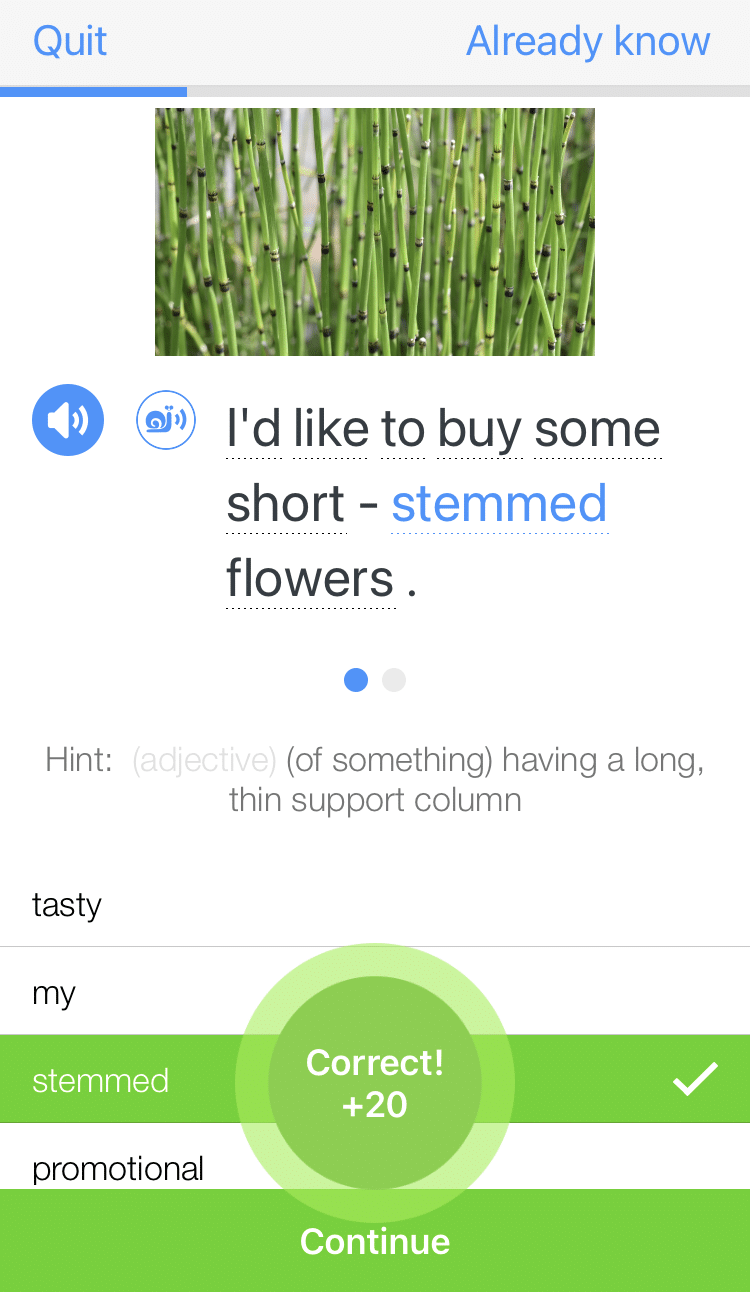
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

_edited.png)
Travel Glossary: 100+ Terms, Acronyms & Definitions You Need To Know
This travel glossary contains more than 100 of the most common terms and acronyms you are likely to hear in the travel industry.
The travel niche has its own terms, abbreviations, and definitions.
As it can get complicated to understand them all, we created this complete travel glossary.
You can either click on:
- A letter
- Ctrl + f to use the search function
Note that we are still working on this glossary and we’ll update it frequently.

Abbreviation for American Airlines.
A Broken Backpack
A travel blog about long-term travel, adventure travel, budget travel, and more. You’re currently reading abrokenbackpack.com. At first, our blog was targeting backpackers and long-term travelers. Over the years, we have expanded our content with more travel tips for everyone.
Abbreviation for Air Canada.
Usually, an option that can come with an extra cost. Examples: optional luggage, optional meal.
Abbreviation for Air France.
Abbreviation for Air India.
Airalo is an online eSIM store that allows you to purchase eSIMs (digital SIM cards) in 190+ countries and regions around the world at affordable prices. Learn more about eSIM cards for travel .
An organization that provides air transportation.
A set of buildings, facilities and runways that are made for take-off, landing, and plane maintenance.
Airport codes
A combination of 3 letters is used to identify a specific airport. Examples: YUL identifies the airport in Montreal city.
Airport tax
Costs that an airline has to pay for departure and arrival in airports. These can vary from one airport to another and are usually included in a flight ticket price.
Practice in which you can order individual items from a menu instead of a set meal.
All-inclusive
A vacation that includes all the essentials (usually accommodation, food, and drinks). We commonly refer to an all-inclusive holiday or an all-inclusive resort.
An association or union between countries or airlines. Examples: Star alliance is an airline association regrouping several major airlines that collaborate to offer more flight connections and smooth stopovers.
Abbreviation for Aeromexico Cargo.
Abbreviation for Alaska Airlines.
Abbreviation for Royal Air Maroc.
Availability
The number of hotel rooms, or seats remaining.
Abbreviation for Finnair.
Abbreviation for Alitalia.
A bag that you use to carry things on your back. Usually large enough to carry all your things when you travel. Synonyms include “packsack” or “rucksack”.
A traveler or hiker who carries their belongings in a backpack.
Backpacking
A travel style that includes travels or hikes with a large backpack. Commonly, backpacking is a way to travel on a budget. The traveler may hike and camp outside for multiple days, or stay in hostels during their travels.
The basic cost of an airline ticket. Usually, this fare doesn’t include extra fees, taxes, or surcharges.
A bed and breakfast (often shortened to B&B) is a small hotel that offers overnight accommodation and breakfast.
Black Friday
A Friday at the end of November when you’ll find crazy travel deals on airfares, hotels, Amazon, etc. You can stay up to date with Black Friday deals here .
Step in which passengers are getting into the airplane. Usually, the airport staff calls passengers divided into different zones to board the plane.
Boarding pass
A paper ticket or a mobile ticket issues after check-in that allows you to board the plane.
Booking.com
An accommodation travel booking website with worldwide coverage comparing hotels, hostels, apartments and car rentals. You can book your hotels easily on Booking.com .
Booking number
Also known as a reservation number – a unique code including letters and numbers that confirm your reservation.
Bucket list
A travel expression used to define a set of destinations to visit or things to do in a country.
A bus travel booking website with worldwide coverage comparing bus route fares. You can purchase bus tickets on Busbud .
Business-class
A section that is usually between the first class and the economy class. The business class provides more amenities and services than the economy class. You can find a business class on planes or trains.
A cabin in a plane is the space inside the plane where passengers sit. A cabin in a ship is a room where a passenger sleeps.
Van that was designed for sleeping and road-tripping. Some campers prefer to sleep inside a van than in a tent. Also known as a camper van.
An activity that involves sleeping in a tent.
A captain in a plane is the pilot.
Carry-on baggage
A piece of luggage that you can bring along on the plane cabin. Usually, you’ll put this luggage in the overhead compartment or under the seat in front of you.
Checked luggage
A bigger piece of luggage that you don’t have access to during the flight. Usually, you’ll drop off your luggage at the airline counter before you go through security and customs.
A confirmation of your presence on a flight, train, or bus. Usually, you can check-in online or directly at the airport, bus station, or train station. Once the check-in is completed, you’ll get a boarding pass which can be issued electronically or on paper.
It can also be used in hotels. In this situation, the client goes to the hotel reception, presents identification documents, and receives a key to their hotel room.
A client leaves a hotel by bringing back the key on time at the hotel reception and paying for any remaining fees.
It’s a synonym of a bus.
A hotel staff member who helps guests organize transportation, reservations, or any special requests.
Connecting flight
A flight that includes a stopover and as a result, the passenger must change aircraft.
Culture is a shared system of symbols and meanings that allow people to communicate and interact with one another. It includes the customs, traditions, and values that are passed down from generation to generation.
Custom Tour
A custom tour is a personalized experience that is tailored to your specific needs. A custom tour can be created for any location, and can be customized to include any number of activities or attractions.
Cyber Monday
A Monday at the end of November or early December when you’ll find crazy travel deals on airfares, hotels, Amazon, etc. You can stay up to date with Cyber Monday deals here .
Direct flight
A flight that goes from an origin to a destination without stops, or connections.
A deck is a floor on a ship. Some cruise ships can have multiple decks.
Destination
The final stop on a travel itinerary.
Type of rooms where you’ll find several beds or bunk beds. Usually popular in hostels because of their cheap rates.
Double room
A hotel room that had two double beds and that can accommodate between 2 and 4 people.
Exemption from import taxes. For example, in an airport, there’s a duty-free shop area where you won’t need to pay import taxes on products.
Early check-in
Early check-in is when you check in to your hotel before the check-in time.
Economy class
A section of the plane, bus, or train, with basic services and lower fares.
Electronic boarding pass
A virtual boarding pass that is usually on a mobile phone.
Another word for expatriate. A person who lives in a different country temporarily or permanently.
First class
The class with the most services – usually comes with more space, better meals, and premium services.
A fjord is a long and narrow inlet of the sea, usually flanked by steep cliffs.
Frequent flyer program
An airline loyalty program that allows you to collect points and transform them into vouchers or rewards.
G-Adventure
Adventure travel company that organizes small-group tours, expeditions and safaris around the world.
Area and door where passengers board their flight from or deplane at their arrival.
An establishment that provides accommodations to travelers.
Holafly is a website that allows you to purchase eSIM for your travels. You can read our complete Holafly review to learn more about it.
A budget accommodation offering shared dorms and private rooms. Very popular amongst budget travelers, backpackers and young travelers.
A popular airport where many airlines organize connecting flights to smaller destinations.
Immigration
An area where a traveler must present travel documents like their passport or visa in order to enter the country.
A plan, or route designed for a trip, usually in chronological order.
A feeling of tiredness felt by a person after flying across different time zones.
King-size bed
The biggest bed size there is.
A period of time between transportation connections, or stopover.
One part of a journey. For example, one flight out of a 3-flight route.
A small house or a part inside a large house where travelers sleep. Usually, it’s a synonym for guest houses or hotels.
The hotel is located next to the main roads and that is made for road trippers.
A vehicle that is designed for mobile living accommodation. For example, RVs, campervans, campers.
A traveler or passenger that doesn’t show up for a flight, hotel, or reservation without canceling the booking.
Point of departure.
Overbooking
A popular practice in which airlines sell more seats that they have available to compensate for no-shows. Unfortunately, this practice can create problems if all the passengers show up.
A document issued by a government that includes information about the identity, nationality, and visa of a traveler.
A word used as a synonym for passenger, mostly used in the travel and the tourism industry.
When staying in a hotel, a traveler can request a quiet room. Usually, this room is isolated or is in a quieter area.
Reservation
Action taken to book a flight, activity, or hotel room.
An area designed for massage, hot springs, steam baths, or saunas.
A building or area inside an airport. For example, an airport can be divided into multiple terminals so that passengers can know where their departure or arrival gate is located.
Moving to a better class of service, or accommodation.
A stamp or a sticker in a passport allowing you to enter a country for a specific amount of time.
Documents you can use to exchange for goods, accommodation, or services. Usually, the payments for these good, and services has already been made.
Synonym of travel in the French language.
A list of potential travelers that are not confirmed yet.
A software designed for digital nomads and online entrepreneurs who have a business in Estonia.
An expression used amongst young people that means You Only Live Once.
An establishment that displays, studies, and rescues wild animals.
MY TOP RECOMMENDATIONS
BOOK HOTEL ON BOOKING.COM
BOOK HOSTEL ON HOSTELWORLD
GET YOUR TRAVEL INSURANCE
LEARN HOW TO START A TRAVEL BLOG
LEARN HOW TO VOLUNTEER ABROAD


- Travel Terms Glossary
We have provided a glossary for your use. The travel industry is replete with jargon and acronyms and we hope you find this glossary/dictionary of travel terms useful when you run across a term you are not familiar with. We encourage our clients to submit any words or concepts they would like defined or clarified to us on the Contact Us page and we will be happy to reply by email with a definition and include the term or clarification in our glossary/dictionary of travel terms for other clients benefit as well.
A la carte – referring to meals, an indication that each dish is priced separately; also that a choice of meals may be vailable, such as on a tour.
A la Carte Bar – Also known as a “Cash Bar,” a bar located within one’s hotel room that is pre-stocked with an assortment of snacks and beverages.
ABC – a reference to the Caribbean islands of Aruba, Bonaire, and Curacao, in the Netherlands Antilles, just off the northern coast of South America (Venezuela). Fabulous for diving, snorkeling and all manner of watersports.
Abeam – A directional term, used on ships and aircraft, which describes something off to the side of the vessel, such as the wings.
Accessible Tourism – Travel that ensures that there is high availability in destinations, accommodations, attractions, products, and services to all people.
Accessible Travel – Travel that ensures that there is high availability in destinations, accommodations, attractions, products, and services to all people.
Actual Time of Arrival – Literally, the actual time of arrival. As opposed to the ETA (Estimated Time of Arrival).
Add-on – an option, usually at extra cost, added to travel arrangements.
Adjoining rooms – Two hotel or accommodation rooms that have a door connecting them from the inside, allowing the guests to combine the two rooms into one larger room.
Adoption Rate – the percentage of tickets issued through an online booking system compared to the traditional booking channel of agent-assisted reservations.
ADT – Atlantic Daylight Time; Alaska Daylight Time. Advance Purchase Fare – airfare that requires the traveler to purchase the ticket a minimum number of days prior to departure.
Advance Purchase Requirement – APR, or Advance Purchase Requirement, is the requirement that a ticket must be purchased a minimum number of days before the flight departs.
Adventure tour – A tour designed around an adventurous activity such as rafting, hiking, or mountain climbing.
Adventure travel – adventure travel is category of travel involving exploration or travel with perceived (and possibly actual) risk, and potentially requiring specialized skills and physical exertion.
Adventure Traveler – Adventure travelers travel to destinations with the specific purpose of active physical participation and exploration of new experiences.
Affinity Card – These are credit or debit cards issued by a banking institution in partnership and co-branded with a particular frequent traveler program.
Affinity group – A group of people that share a common hobby, interest, or activity, or that are united through regular participation in shared outings. Also see preformed group.
Aft – toward the rear of a ship.
After-departure charge – Charges that do not appear on the guest’s bill at checkout such as telephone or dining charges.
Agent – A person who has the power to act as the representative for another person. Most frequently in travel, a specific kind of agent such as a travel agent.
AIO variables – Activities, interests, and opinions-used to measure and categorize customer lifestyles.
Air mile – a distance of approx. 6076 feet.
Air Traffic Control – Usually refers to the control tower at the airport, but may also be a control center somewhere else in charge of controlling a large area of sky.
Air Travel Card – a credit card sponsored by the airlines, for the purchase of air travel only.
Air Travel – air travel is the action or process of making a journey by aircraft.
Air/sea – a term referring to tickets, trips, fares, etc. that include both air and land-based travel arrangements, such as a cruise package with air included.
Aircraft – Generally speaking, any machine capable of flight. However, in the travel industry, these often mean airplanes.
Airline Alliance – These are agreements of cooperation between groups of airlines. Alliances offer airlines more flexibility and larger networks.
Airline fare – Price charged for an airline ticket. Several types of fares exist and can change with market conditions.
Airlines Reporting Corporation (ARC) – An organization that provides a method of approving authorized agency locations for the sale of transportation and cost-effective procedures for processing records and funds of such sales to carrier customers.
Airport access fee – a fee paid by the car rental companies to the airport authority, for the use of shuttle vehicles, etc. – usually passed on to the consumer.
Airport transfer – a transport service to/from an airport to hotel, etc., normally prepaid as part of a package tour, but available separately as well.
Air-Sea – A cruise or travel package in which one or more transportation elements are provided by air and one or more by sea. The package is usually combined with local lodging.
All Inclusive – sold for one price that includes charges and fees that are often added separately.
All-inclusive package – A tour package in which most travel elements are purchased for set price. Also called an all-expense package.
Alternative Tourism – Travel that is not conventional in nature, though that is hard to define. It can be a niche kind of tourism.
Alternative Travel – Travel that is not conventional in nature, though that is hard to define. It can be a niche kind of tourism.
Alumni tour – A tour created for customers who have previously traveled with a tour operator. Also called a reunion tour.
Ambassador – The head of a state’s diplomatic mission in another state, usually with offices inside the main embassy.
Amenities – a desirable or useful feature or facility of a building or place
Amenity package – A cluster of special features, such as complimentary shore excursions, bar or boutique credit, or wine at dinner offered to clients on a given tour or cruise, usually as a bonus or extra feature. Usually used to induce clients to book through a particular travel agency or organization.
Amenity – The facilities and features of a property, usually cruise ship, airline or destination accommodation.
American plan – a hotel’s meal plan that usually includes all three meals each day.
AMEX – American Express (AX).
Amidships – toward the middle of a ship – usually the most stable part of the vessel.
Anniversary travel – a type of milestone travel celebrating a date that is remembered or celebrated because a special or notable event occurred on that date in a previous year, such as a wedding anniversary.
Antebellum – describes a building and/or period of time prior to the Civil War, such as an antebellum mansion on a cotton plantation in the southern US.
APEX – an airline term meaning “advance purchase excursion fare” – normally the least expensive fares.
Apron – The area surrounding the gate areas of a terminal, generally used for parking and maintenance of planes.
ARC – Airline Reporting Corporation- the agency that regulates ticket sales and reports to the airlines for travel agencies.
Archipelago – An archipelago is a grouping of islands, essentially. Indonesia and Japan are both archipelago countries.
ARTA – Association of Retail Travel Agents – professional trade group of travel agents only.
ASC Fee – Administrative Service Charge. Usually it’s the same as the change fee, or the fee to exchange the ticket for future travel.
AST – Atlantic (or Alaska) Standard Time.
ASTA – American Society of Travel Agents – trade group consisting of travel agencies, travel agents, and allied members (suppliers, etc.).
ATO – Airline Ticket Office – becoming rarer these days, as carriers continue to reduce customer service.
Attractions – An item or specific interest to travelers, such as natural wonders, manmade facilities and structures, entertainment, and activities.
Autobahn – high-speed equivalent to the US interstate highway system, in Germany and a few other European countries.
Availability – The total number of seats allowed to be sold at a particular rate.
Average room rate – The total guest room revenue for a given period divided by the number of rooms occupied for the same period.
B&B – A bed and breakfast home or guest house that a proprietor has converted into accommodation(s) for the public. Each room becomes a separate unit for rent and typically breakfast and/or other meals are served as part of the fare.
Babymoon – A relaxing and romantic vacation or getaway taken by parents-to-be before their baby is born.
Back to back – A term used to describe tours operating on a consistent, continuing basis. For instance, a motor coach arriving in a city from a cross-country tour may conclude the first tour upon arrival, then transport a second group back along the same route to the origination city of the first tour.
Back-to-back ticket(ing) – an against-the-rules practice whereby an air ticket is issued round-trip with only one portion to be used. Another is then issued roundtrip, again with only one portion to be used. In effect, this amounts to using one ticket for the outbound part of a trip, and the other for the return. The normal Saturday night stay requirement is then avoided – useful only when two roundtrip tickets are less than the cost of a single ticket with no Saturday night stayover.
Baggage Allowance – The amount of baggage a passenger may transport without having to pay extra charges, determined by carrier.
Baggage handler – See porter.
Baggage master – The person who controls baggage handling on a ship.
Balcony – sometimes called a verandah – an outside “porch ” that is usually private, just outside your ship’s cabin. Great for relaxing and port arrivals!
Barge cruising – pleasure cruising along a canal system, such as in upstate New York or in Europe, in converted barges or new ships that resemble them.
Base fare – the basic price of an airline ticket, before ANY taxes, surcharges, airport fees, etc.
Base – Flight crew term for their home airport; where the flights originate from and terminate at.
Beam – a ship’s width at its widest point; determines whether or not a vessel can pass through the Panama Canal.
Bed and breakfast (B&B) – Overnight accommodations usually in a private home or boarding house, often with a full American-style or Continental breakfast included in one rate.
Bell captain – The person in charge of luggage at a hotel.
Bellboy – Also called “Bellboy” or “Bellman,” a person that is hired by the hotel to assist guests, such as with luggage, running errands, etc.
Bellman – a person who carries one’s luggage to a hotel room.
Benelux – term for the countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
Berth – usually refers to the bed in a ship’s cabin; also the space at which a ship is docked.
Bespoke tour – a tour that is customized, personalized and tailor-made for the traveler.
Biking Trips and tours – Bicycle trips and touring means self-contained cycling trips or pleasure, adventure and autonomy rather than sport, commuting or exercise. Touring can range from single to multi-day trips, getaways or vacations.
Birthday travel – a type of milestone travel celebrating a birthday, quite often marking decade birthday milestones such as 40 th , 50 th , 60 th , 70 th etc. birthdays.
Blackout dates – Specific dates in which special fares or promotions do not apply. Typically exist around holidays or special events.
Block – A number of rooms, seats, or space reserved in advance, usually by wholesalers, tour operators, or receptive operators who intend to sell them as components of tour packages.
Blocked space – seats, rooms, and/or cabins held on airlines, in hotels, or aboard ships. Usually held speculatively and made available at reduced rates.
Boarding pass – a receipt with a seat number, now issued only at check-in at the airport. A ticket is not valid unless a boarding pass has been issued. A Boarding Pass is not a ticket, but allows you to board a plane or ship or other mode of transportation.
Boarding Pass – Bonded – protected or guaranteed by a bond, usually referring to the protection of passenger’s funds.
Booking form – A document which purchasers of tours must complete to give the operator full particulars about who is buying the tour. It states exactly what is being purchased (including options) and must be signed as acknowledgment that the liability clause has been read and understood.
Boutique Hotel – A boutique hotel is a type of hotel, usually smaller and more intimate than a chain hotel, which conforms to a niche.
Bow – Bow is a directional term. Front of a ship or the nose of an aircraft; specifically, the foremost point of the hull of the craft.
Breakage – Expenses budgeted for a tour but not used or expended, thus resulting in additional profit to the tour operator. Examples include meals budgeted but not consumed, currency fluctuations in favor of the tour operator, or the tour selling to much larger numbers of passengers than expected.
Break-even point (BEP) – The point at which revenues and expenses are the same. For example, the BEP is the number of products (or seats, cabins, tickets, etc.) that must be sold for a company to break even. The BEP is calculated as fixed costs divided by the selling price less variable costs. See reasonable number.
Break-even pricing – Pricing a product based on a forecast of the break-even point and the cost of achieving the break-even point.
Bridge – the navigational center of a ship.
Bucket list destinations – Bucket list travel is a list of destinations a person wants to travel to and experience before reaching a certain age or dying.
Bulk contract – An agreement whereby an airline sells large blocks of seats at a discount for resale by a third party.
Bulk fare – A reduced fare for purchases of a large number of tickets.
Bulkhead Seat – Seats located directly behind a bulkhead wall separator. As these seats don’t have the benefit of a seatback in front of them.
Bulkhead – A partitioning wall, usually referring to one within the cabin of an aircraft, or perhaps on another mode of transportation.
Bumping – the airline practice of denying boarding to confirmed passengers who hold tickets on a specific flight, due to an oversold condition. The carrier will ask for volunteers to take later flights, and will normally provide some sort of compensation in the form of vouchers or tickets for future travel. Rules for when compensation must be provided are complicated; ask the ticket agent for a copy of that carrier’s rules, as each has their own set of guidelines.
Business class – While amenities vary based on the airline, business class generally falls between first class and coach.
Cabin – the passenger area on an aircraft; the stateroom aboard a cruise ship.
Cabin Crew – The collective group of flight attendants and the purser as a whole. The cabin crew is responsible primarily for handling the duties within the cabin.
Cabin steward – the person responsible for maintaining/cleaning the cabins aboard ship.
Cabin-(Aircraft) – The section of the aircraft in which passengers travel.
Cabin – A sleeping room on a ship.
Cancellation penalty – the monetary penalty due when travel plans are cancelled, usually after final payment has been made.
Cape – A small version of a peninsula, usually long and narrow, that juts far out into a body of water.
Captain – (Aircraft-The captain is the pilot in command (PIC), which is the person in the cockpit sitting on the left with 4 stripes on their shoulder.
Card mill – a “business “that sells potentially fake travel agent ID cards, usually in a sort of pyramid scheme, whereby the buyer intends only to partake of any legitimate agent benefits.
Carrier – generic term for any company that transports passengers and/or freight.
Carry-on – currently, there are no uniformly enforced airline restrictions concerning carry-on luggage.
Cashless cruising – a term that applies to the system of onboard payment used for most all cruises; the final bill for any such purchases is presented against a credit card or cash deposit given upon check-in. The final statement itemizes the purchases of all passengers in a cabin, such as drinks, shore tours, etc.
Casual research – A form of marketing research that is used to test cause-and-effect relationships between a marketing program and customers.
Cay – pronounced “key” – term for a small island, used primarily in the Caribbean, such as Princess Cay.
Celebrity Travel – celebrity and high net worth travel is an ultra-luxurious travel category describing the highly demanding travel requirements of celebrity and high net worth travelers characterized by the ultra-luxurious travel modalities and destinations with attention to privacy, security and confidentiality.
Certified Tour Professional (CTP) – A designation conferred upon tour professionals who have completed a prescribed course of academic study, professional service, tour employment, and evaluation requirements. The CTP program is administered by the National Tour Association (Lexington, KY) and is open to individuals employed in any segment of the tourism industry.
Certified Travel Associate – (CTA) – a travel professional certified by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents, who has passed a series of rigorous tests, assuring the traveling public of professional competence.
Certified Travel Counselor (CTC) – A designation attesting to professional competence as a travel agent. It is conferred upon travel professionals with five or more years of industry experience who compete a two-year graduate-level travel management program administered by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents (Wellesley, MA).
Certified Travel Industry Specialist (CTIS) – A designation conferred upon American Bus Association member company employees who successfully complete five correspondence courses (three) required and two electives and written evaluation of eight marketplace seminars.
Chain-ratio method – A method for forecasting market demand by multiplying a base market figure by a series of consumption constraints.
Chamber of commerce – A DMO that operates at the local level and is comprised of businesses that are not necessarily associated with the tourism industry.
Chancery – The physical building that houses an embassy and its diplomatic delegation.
Change of equipment – when a flight, with a single flight number, lands and changes the type of airplane used before continuing on to its destination. Sometimes referred to as a change of gauge.
Charter service – The transportation of preformed groups (organized by someone other than the carrier), which have the exclusive use of the vehicle.
Charter – To hire the exclusive use of any aircraft, motorcoach, or other vehicle.
Chauffer driven tours – a chauffeur tour is a tour driven by a chauffeur employed to drive a passenger motor vehicle, especially a luxury vehicle such as a large sedan or limousine.
Chunnel – slang for the tunnel beneath the English Channel, from England to France, through which the Eurostar train passes.
Circle itinerary – A travel routing design that overnights in different locations and returns to the point of departure without retracing the travel route.
Circle trip – any trip that involves more than a single destination, but which returns to the initial point of departure.
City guide – A tour guide who points out and comments on the highlights of a city, usually from a motor coach or van.
City Pair – The departure and destination points of an air or rail journey.
City tour – A sightseeing trip through a city, usually lasting a half day or a full day, during which a guide points out the city’s highlights.
Class of Service – The inventory in which a passenger is booked according to the fare purchased. (E.g. a full fare coach class cabin is usually Y class of service)
CLIA – Cruise Lines International Association, located in New York City, NY.
Client list – A printout of the names of all tour participants.
Client mix – Objectives set by companies to achieve percentages of customers from different market segments.
Closed-end question – A question for which the answers are provided for the respondent, who chooses only from those answers.
Closeout – Finalization of a tour, cruise, or similar group travel project after which time no further clients are accepted. Any unsold air or hotel space is released, and final lists and payments are sent to all suppliers.
Coach – the “economy ” section of an aircraft, which may have literally scores of different fares for the same flight.
Collision damage waiver-(CDW) – Optional insurance provided by car rental companies that eliminates all responsibility of the driver in case of an accident. Car rental insurance covering any damage to a rental vehicle (CDW) many credit card companies cover their clients in this area if they use that card to pay for the rental. Check with you credit card company to see if you are covered and to what extent.
Commission – Money paid to a travel agency or ARC number by suppliers for generating bookings.
Commission cap – The limit placed on commissions paid to travel agents for the sale of air tickets, regardless of their price; designed to allow airlines to increase their profits at the expense of their primary distribution system – the travel agents.
Commissionable tour – A tour available through retail and wholesale travel agencies which provides for a payment of an agreed-upon sales commission to the retailer or wholesale seller.
Common carrier – Any person or organization that offers transportation for a fee.
Commuter – term referring to the small, regional airlines, sometimes called puddle-jumpers.
Comp policy – Arrangements for free tickets, rooms, meals, etc.
Complimentaries (comps) – Items provided free of charge, such as rooms, meals, tickets, airfare, gifts, souvenirs, etc.
Computerized reservation system (CRS) – An automated system used by travel agents that contains pricing, availability and product descriptions for hotels, car rentals, cruises, and air transportation.
Concierge – a hotel employee who provides additional advice, recommendations, and other services to guests, such as restaurant reservations. An employee of the hotel whose primary task is to serve as the liaison between the hotel and non-hotel attractions, facilities, services, and the guest.
Concierge Level – special service level normally offered at higher grade hotels that provide the guest additional amenities and information, typically at a higher rate.
Conditions – The section or clause of a transportation or tour contract that specifies what is not offered and that may spell out the circumstances under which the contract may be invalidated (in whole or in part).
Configuration – The interior arrangement of a vehicle, particularly an airplane. The same airplane, for example, may be configured for 190 coach-class passengers, or it may hold 12 first-class passengers and 170 coach passengers, or any other combination within its capacity.
Confirmed reservation – An oral or written statement by a supplier that he has received and will honor a reservation. Oral confirmation have virtually no legal weight. Even written or faxed confirmations have specified or implied limitations. For example, a hotel is usually not obliged to honor a reservation if a guest arrives after 6 p.m., unless late arrival has been guaranteed.
Confluence – A confluence, also known as a conflux, is the meeting point of two flowing bodies of water, such as streams or rivers; the place where they come together.
Conflux – A confluence, also known as a conflux, is the meeting point of two flowing bodies of water, such as streams or rivers; the place where they come together.
Connecting Flight – A flight that makes a stop at an intermediate point where travelers must change planes in order to connect to another flight to reach their destination. (I.e. San Francisco to Chicago and Chicago to New York).
Connecting room – Two rooms that are connected to each other by a door.
Consolidation – Cancellation by a charter tour operator of one more flights associated with a specific charter departure or departure period, with the transfer of passengers to another charter flight or flights to depart on or near the same day. Also, selling the same tour with identical departure dates through a number of wholesalers, cooperatives, or other outlets in order to increase sales and reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
Consolidator – A wholesaler who purchases airline tickets in bulk and re-sells them to individuals and travel agencies at a discounted rate. These fares tend to have complex restrictions, but can be cheaper than buying direct from the airline. Consolidator fares are found to have the most savings on international flights.
Consortium – A collection of organizations made up of independently owned and managed agencies who band together to increase their buying power.
Consulate – Essentially a satellite office of the embassy, but its roles are limited in scope.
Consul – Head diplomat of the consulate.
Consumer protection plan – A plan offered by a company and/or association that protects the customer’s deposits and payments from loss in the event of company bankruptcy.
Consumer – The actual user of a product or service. See also customer.
Consumption constraints – Issues that limit the number of people in a market who will purchase a product.
Continental breakfast – At a minimum, a beverage (coffee, tea, or milk) and rolls and toast, with fruit juice sometimes included.
Continent – Large landmasses that the world is divided into, by convention, although it is generally-accepted that there are seven.
Contract – A legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties.
Control Tower – Often referred to as simply the tower, the people in the Control Tower oversee aircraft movements at the airport, including ground traffic.
Convenience sample – A collection of research subjects who are the easiest for the researcher to select.
Convention and Visitors Bureau (CVB) – A nonprofit DMO that operates at the county and city level. A CVB typically encourages groups to hold meetings, conventions, and trade shows in its city.
Co-op tour – Selling a tour through a number of wholesalers, cooperatives, or other outlets in order to increase sales and reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
Cooperative (co-op) advertising – An agreement between two parties to share the cost of placing an advertisement.
Corporate agency – A travel agency that usually caters to medium-large sized businesses.
Corporate Rate – a hotel rate that is designed to appeal to the needs of the business traveler. It is not necessarily a discounted rate or the minimum rate offered by the hotel. Corporate rates normally guarantee the best available room at a fixed cost for a specific period of time, typically outlined in a contract between the hotel and company.
Corporate Travel – Corporate Travel is travel arranged by a business for business purposes. A division or department of a travel agency devoted to such travel.
Costing – The process of itemizing and calculating all the costs the tour operator will pay on a given tour.
Cost-plus pricing – See markup pricing.
Couchette – the sleeping compartment of a train that can contain up to 6 beds.
Coupon – See voucher.
Cruise Tour – A land and sea vacation, which combines a cruise with a multi-night land tour to inland destinations that the ship can’t reach.
Cruise – A cruise is a voyage on a ship or boat taken for pleasure or as a vacation and usually docking at several port destinations.
CST – Central Standard Time.
CTA – Certified Travel Associate.
CTC – Certified Travel Counselor – the ultimate in travel professionals, CTC certification can be compared to the “Master’s Degree “of the industry.
Cuisin e – a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes associated with a specific culture or geographic region.
Culinary Tourism – Culinary tourism is defined as the pursuit of unique and memorable eating and drinking experiences. By combining travel with these edible experiences, culinary tourism offers both locals and tourists alike an authentic taste of a specific culture or geographic region.
Cultural Tourism – Cultural tourism is the category or tourism concerned with a country or region’s culture, specifically the lifestyle of the people in those geographical areas, the history of those people, their art, architecture, religion(s), and other elements that helped shape their way of life.
Cultural Travel – This is travel with regard to a region’s culture and history.
Culture – Similar shared traits or characteristics unique to an ethnic group, region, or nation.
Custom tour – A travel package created specifically for a preformed group or niche market.
Customer – The buyer of a product or service. See consumer.
Customized tours – a customized tour is a tour category where an independent travel plan is designed and arranged just for the traveler’s needs, goals and desires. This type of travel includes private airport/hotel transfers, hotels, internal airfare, trains, cruises, performances, events, activities and privately guided tours.
Customs – The common term for U.S. Customs Service, the federal agency charged with collecting duty on specified items imported into the country. The agency also restricts the entry of forbidden items.
CVB – Convention and Visitor’s Bureau (generic term).
Database – A computerized, organized collection of individual customer information.
Day rate – Also called a day room. A reduced rate granted for the use of a guest room during the daytime, not overnight occupancy. Usually provided on a tour when a very late-night departure is scheduled.
Day tour – An escorted or unescorted tour that lasts less than 24 hours and usually departs and returns on the same day. See sightseeing tour.
Deadheading – Making a trip or a segment of a trip without passengers, such as driving an empty motor coach somewhere.
Debark – to get off an airplane or passenger ship.
Deck – the floor area of a ship. Some cruise liners have as many as 11 to 14 decks or more.
Deck plan – the drawing representing the location of the decks, public rooms, cabins, etc. of a cruise ship.
Demand generators – Strategies and programs developed by DMOs and suppliers to generate destination demand. Examples include festivals, events, cultural tours, and consumer promotion.
Demands – A consumer’s wants backed by the ability to purchase.
Demographics – Population measures, such as age, gender, income, education, race/ethnicity, religion, marital status, household size, and occupation.
Denied-boarding compensation – that payment and/or voucher given those bumped from a flight; may be somewhat negotiable – always ask! See “bumping”.
Department of State – the US government agency that, among other things, issues cautions and warnings concerning travel to many points worldwide. Connect to the Department of State for the latest updates for the areas you are interested in.
Departure point – The location or destination from which a tour officially begins.
Departure tax – Fee collected from a traveler by the host country at the time of departure.
Deplane -To disembark, or get off, a plane.
Deposit policy – A specified amount or a percentage of the total bill due on a specified date prior to arrival.
Deposit – An advance payment required to obtain and confirm space.
Descriptive research – a form of marketing research that is used to provide detailed answers about customer markets.
Destination alliance – A DMO that operates as a for-profit association of select suppliers who form a paid-membership network to promote their services to travelers.
Destination management company (DMC) – A for-profit company that operates similar to a CVB by providing planning and execution services for the convention and meeting market.
Destination marketing organization (DMO) – An organization that promotes a location (city, region, state province, country) as a travel destination.
Destination Weddings – a destination wedding a category of travel where couples celebrate their marriage at a destination of their choosing away from home.
Destination – The geographic place to which a traveler is going.
Dine-around-plan – A meal plan, usually prepaid, that allows one to dine at various restaurants in an area.
Direct access – Refers to a travel agent’s ability to get directly into an airlines database to get true last-seat availability and correct pricing – a big difference between internet fare ” quotes ” and an agent’s CRS ( Computer Reservations System ).
Direct Flight – A flight that goes from a traveler’s origin to their final destination with one or more intermediate stops. No change in aircraft occurs. (I.e. San Francisco to New York with a stop in Chicago)
Direct marketing – Sales and marketing communication that feature direct interaction between a company and its customers without any distribution intermediaries.
Disaster Tourism – Travel when tourists go to an area that may be or may have been affected by natural disasters, civil strife, or warfare.
Disclaimer – a legal document that advises clients that a travel agent acts only as a middleman in the sale of travel products; any liability ultimately lies with the supplier, i.e. airline, hotel, car rental company, tour operator, railway, etc.
DMC – Destination Management Company
Docent – A tour guide who works free of charge at a museum.
Domestic fare – a fare charged for travel within a country.
Double booking – a not-nice practice of holding reservations to the same destination for the same times/days, on the same carriers but through different travel agencies, when only one reservation will ultimately be used.
Double Double – A room with two double beds.
Double occupancy – the way in which almost all cruise fares and tour packages are quoted, that is, based on two people traveling together. Most hotel rooms are quoted based on two adults to a room.
Double-occupancy rate – The price per person for a room to be shared with another person; the rate most frequently quoted in tour brochures.
Double-room rate – The full price of a room for two people (twice the double-occupancy rate.)
Downgrade – To move to a lesser level of accommodations or a lower class of service.
Driver guided tours – A driver guided tour is a tour guided by an individual that operates a vehicle while providing commentary in a front-line position who leads participants (individual or groups) on tours, ensures that itineraries are followed, provides commentary in an informative and entertaining manner, and creates positive experiences for tour participants.
Driver-guide – A tour guide who does double duty by driving a vehicle while narrating.
Drop-off charge – the fee added to a car rental when the vehicle is returned to a city other than where it was originally rented. In some states, there is no drop off fee most of the time, such as in Florida.
Duty-free imports – Item amounts and categories specified by a government that are fee of tax or duty charges when brought into the country.
Early Check-In – A perk that allows a guest to check in at an earlier time than the standard check-in time.
Eco/Sustainable Tourism – Eco or Sustainable Tourism is tourism directed toward exotic, often threatened, natural environments, especially to support conservation efforts and observe wildlife.
Eco-Conscious Travel – Though often interchangeable, being “eco-conscious” literally means that one is simply aware of their environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Travel – Though often interchangeable, being “eco-conscious” literally means that one is simply aware of their environmental impact.
Economic impact study – Research into the dollars generated by an industry and how these dollars impact the economy through direct spending and the indirect impact of additional job creation and the generation of income and tax revenue.
Ecotour – A tour designed to focus on preserving the environment, or to environmentally sensitive areas.
Ecotourism – Tourism directed at exotic and/or endangered destinations while fostering an environmental understanding and conservation.
Educational tour – A tour designed around an educational activity, such as studying art.
Elder hostel – hostel catering to seniors – see “hostel”.
Electronic ticket – a “paperless” airline ticket allowing one to check-in and fly with just proper photo ID. What may look like a ticket is actually just a paper passenger receipt. E-tickets cannot be lost, or used by anyone else, so they are safer than standard paper tickets, which may soon become extinct. One drawback is that e-tickets on one carrier cannot be honored by another, so in a cancelled-flight snafu, the original carrier must print hard copy tickets before another airline can accept them. This presents major paperwork problems for the affected carrier.
Embark – to board a plane or cruise ship.
End suite – in the hotel industry, indicates that a certain feature(s) is directly in the room, or adjacent to that room.
English breakfast – basic meal of cereal, juice, eggs, meats, and other beverages. Common with most hotels in the UK/Great Britain.
Environmental scanning – The process of monitoring important forces in the business environment for trends and changes that may impact a company.
Errors and Omissions Insurance – Insurance coverage equivalent to malpractice insurance, protecting an agent’s or operator’s staff if an act of negligence, an error, or an omission occurs that causes a client great hardship or expense.
Escort – See tour director.
Escorted group tour – A group tour that features a tour director who travels with the group throughout the trip to provide sightseeing commentary and coordinate all group movement and activities.
Escrow accounts – Funds placed in the custody of licensed financial institutions for safekeeping. Many contracts in travel require that agents and tour operators maintain customers’ deposits and prepayments in escrow accounts.
ES T – Eastern Standard Time.
Estimated Time of Arrival – Literally, the estimated time of the transport’s arrival. As opposed to the ATA (Actual Time of Arrival), the ETA is the time that the flight or transport arrives.
Estuary – A body of water connecting a flowing river and a larger body, such as a sea or ocean. Because it is the transition point.
ETA – estimated time of arrival.
ETD – estimated time of departure.
Ethnicity – A term that groups people together with a similar cultural identity; unlike terms such as nationality, ethnicity is more ambiguous.
Ethno-Tourism – Focusing on exploration of indigenous populations and their respective culture and traditions.
E-Ticket – Regarding transportation, especially on airlines, an electronic ticket, or e-ticket, is the digital version of a paper ticket, issued via email.
Eurailpass – a special fare ticket that allows either unlimited train travel, or travel for a certain number of days/weeks, in many European countries (except in Britain, where the Britrailpass offers similar travel in England, Scotland, and Wales).
European pla n – a rate at a hotel that includes no meals.
Exchange order – See voucher.
Exclusive fare – Discounted airfares offered by travel consolidators.
Excursion – a side trip from a main destination, usually at added cost and optional.
Excursion Fare – special airline fares with restrictions such as minimum and maximum stays.
Exotic Travel – Exotic travel refers to a category of travel that is strikingly, excitingly and mysteriously different or unusual. Exotic travel is travel that is completely different than what a traveler is accustomed to and is highly subjective in nature.
Experiential Travel – Experiential travel is also known as immersion travel and is a form of tourism in which people focus on experiencing a country, city or particular place by connecting to its history, people and culture.
Exploratory research – A form of marketing research that’s used to obtain preliminary information and clues. It is most often used when the marketing problem is ambiguous.
Extension – A fully arranged sub-tour offered optionally at extra cost to buyers of a tour or cruise.
Extensions may occur before, during, or after the basic travel program.
FAM (familiarization) tour – A free or reduced-rate trip offered to travel professionals to acquaint them with what a destination, attraction, or supplier has to offer.
Familiarity Tour – A familiarity tour as used in the travel industry it is a tour of a travel destination, travel accommodation, travel activity or travel mode (airline, cruise, ground transportation) to familiarize a travel advisor and provide knowledge and direct experience with the product or service so they can better serve their clients.
Family plan – offered by most hotels, allow children to stay in the same room as parents, at no additional charge. Age requirements vary between hotels.
Family Vacation – a family vacation is a travel category referring to travel involving family members. It is also commonly referred to as multi-generational travel.
Familymoon – A neologism term used to describe a type of honeymoon a newlywed couple can make along with their children from previous relationships.
Fare Aggregator – Fare aggregators’ redirect the users to an airline, cruise, hotel, or car rental site or online travel agent for the final purchase of a ticket. Aggregators’ business models include getting feeds from major OTAs, then displaying to the users all of the results on one screen. The OTA then fulfills the ticket. Aggregators generate revenues through advertising and charging OTAs for referring clients.
Fare Basis – the letters and numbers assigned to a specific fare like an identification number.
Fare basis (code) – The code that determines the price of an airline ticket.
Final Boarding Call – Last call to board before the jet bridge closes and the flight departs, leaving late passengers stranded.
First class – The class which offers the most premium service. Enhanced seating, meal selection, and drink offerings staples of this services.
First Officer – Pilot who is second in command. The pilot in the cockpit sitting on the right with 3 stripes.
Fishing Trips and tours – a fishing trip or fishing tour is a travel tour category where groups of fisherman are provided guided tours and typically lodging with the overall purpose of catching fish.
FIT – foreign independent tour – actually used generically now for a travel package put together by a travel agent from separate components such as car, hotel and airfare, adjusted exactly as the traveler wishes. May include city tours, theater tickets, and other “independent ” options, and may also include custom mapping/routing to accomplish the client’s goals. It now is more commonly used as an acronym for Flexible Independent Travel. It describes a type of travel or tourism that does not incorporate a packaged tour but is nonetheless customized by a travel-selling professional.
Fjord – a narrow inlet from the ocean, usually bounded by cliffs, and with spectacular scenery. Most are located in Alaska, Norway, and New Zealand.
Flight Attendant – Commonly referred to as stewards/stewardesses and air hosts/hostesses, flight attendants are available to ensure the safety and comfort of the passengers of an aircraft.
Flight Crew – Sometimes called the aircrew, the flight crew consists of everyone hired by the airlines on a flight, including pilots, pursers, and flight attendants.
Fly/drive tour – An F.I.T. package that always includes air travel and a rental car and sometimes other travel components.
Fly-drive package – a travel package featuring airfare, rental car, and perhaps hotels. Usually less expensive than booking each separately.
Folio – An itemized record of a guest’s charges and credits which is maintained in the front office until departure. Also referred to as a guest bill or guest statement.
Fore – Directional term. Towards the front of the craft, lengthwise, such as the bow of a ship or the nose of a plane. Opposite of aft.
Frequent Flier Program – A program that a traveler can enroll in that earns them rewards such as free flights on a particular airline for being a loyal customer of that airline.
Frequent Flier – One who flies frequently.
Frequent Independent travel (F.I.T.) – A custom-designed, prepaid travel package with many
Full house – A hotel with all guest rooms occupied.
Full service hotel – a hotel with restaurant facilities.
Function room – A special room that is used primarily for private parties, banquets, and meetings. Also called banquet rooms.
Funnel flight – a flight, such as on a regional or commuter carrier that “feeds “larger planes which continue on to other destinations. Also, the use of a single flight number for an itinerary that really involves a connection with two separate flight numbers, thus making the itinerary appear to be a direct flight with a change of aircraft as opposed to a connection. Just call it a connection and be done with it.
Fuselage – The aircraft’s main body section, the cylindrical, central piece that contains the cabin and holds the crew and cargo.
Galley – The kitchen/kitchenette area of a plane or train or ship. On a plane, the galley may be a small affair with a simple arrangement and a few carts.
Gate-Airport – The specific area in an airport where passengers board a plane for a flight. Gates are located in concourses.
Gateway – City, airport, or area from which a flight or tour departs.
GDS – Global Distribution Systems – A system containing information about availability, prices, and related services for Airlines, Car Companies, Hotel Companies, Rail Companies, etc. and through which reservations can be made and tickets can be issued. A GDS also makes some or all of these functions available to subscribing travel agents, booking engines, and airlines. The GDS leaders are Amadeus, Apollo/Galileo/Worldspan, Sabre.
Geotourism – this is “tourism that sustains or enhances the distinctive geographical character of a place.
Global distribution system (GDS) – An international computer reservation system that accesses many databases of suppliers, airlines, etc. in different countries, such as Sabre.
Graduation travel – graduation travel is a milestone category of travel which refers to travel celebrating a graduation typically from high school or college.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) – solar based time in Greenwich, England, fun which time in all other time zones in the world is based.
Gross Registered Tonnage (GRT) – a measurement of the enclosed space in a ship. Cruise ships in the 70,000 ton range are considered “superliners”.
Ground operator – See receptive operator.
Group – several persons, usually 10 or more, traveling together. Group travel is often available at discounted rates.
Group leader – An individual who has been given the responsibility of coordinating tour and travel arrangements for a group. The group leader may act as a liaison to a tour operator or may develop a tour independently (and sometimes serve as the tour director).
Group Rate – A negotiated rate on travel, perhaps a stay or vacation plan, that incentivizes for a large crowd or group that books together.
Group tour – A travel package for an assembly of travelers that has a common itinerary, travel date, and transportation. Group tours are usually prearranged, prepaid, and include transportation, lodging, dining, and attraction admissions. See also escorted group tour.
Group Travel – group travel refers to a category of travel with a group arranged by an outside company or organization or travel with a group of friends and family that you have organized yourself. Some groups are small, private and escorted, while others large.
GST – Goods and Services Tax, such as levied in Canadian Provinces.
Guaranteed share – a cruise term that promises that a companion will be found for a single passenger, at a special rate. That rate will be honored even if the cruise line is unable to find a cabin mate. The rate is usually the going double-rate at that time, and is much less than the single person rate for that cabin.
Guaranteed tour – A tour guaranteed to operate unless canceled before an established cutoff date (usually 60 days prior to departure).
Guest account – See folio.
Guest houses – a guest house is a private house offering accommodations to paying guests.
Guest ranch – a guest ranch, also known as a dude ranch, is a type of ranch oriented towards visitors or tourism. It is considered a form of agritourism.
Guide or guide service – A person or company qualified to conduct tours of specific localities or attractions.
Guided tour – A local sightseeing trip conducted by a guide.
Half pension – a hotel rate that includes breakfast and one other meal, usually dinner. Sometimes called Modified American Plan (MAP) or demi-pension.
Hard-copy – a printed version of a document, such as an airline ticket or hotel voucher.
Head tax – Fee charged for arriving and departing passengers in some foreign countries.
Hidden-city ticketing – another airline no-no; buying a ticket from A to C with a stop in B. The passenger gets off at B, which was the intended destination anyway. The ticket is purchased because the fare from A to C is LESS than A to B.
High season – the time of year when a destination gets the greatest crowds, and thus can increase hotel and rental car rates, etc. As an example, summertime is high season for travel to Europe (just check the airfares!).
High season – See peak season.
Hiking Trips and tours – a hiking trip or hiking tour is a category of travel vacation or getaway where the traveler is walking or hiking as the major mode of transportation.
Honeymoon Travel – Honeymoon travel is a category of travel where a newly married couple travels while celebrating their marriage.
Hosted group tour – A group tour that features a representative (the host) of the tour operator, destination, or other tour provider, who interacts with the group only for a few hours a day to provide information and arrange for transportation. The host usually does not accompany the group as it travels.
Hostel – an inexpensive accommodation, usually dormitory style, popular with the student crowd – thus the term “youth hostel”.
Hotel – a hotel is an establishment providing accommodations, meals, and other services for travelers and tourists.
House – A synonym used for hotel.
Hub – an airport or city in which an airline has a major presence and many flights to other destinations. As an example, Delta has a hub in Atlanta. Many carriers use the hub-and-spoke system to maximize profits by keeping the aircraft in the air as much as possible. Flights to the hub are many, and from there flights too many other destinations are scheduled.
Hub-and-spoke itinerary – A travel routing design that uses a central destination as the departure and return point for day trips to outlying destinations and attractions.
Hurricane season – in the Caribbean primarily, and the Southeastern US, a period from June through October during which such storms are likely to occur.
IATA – International airline industry trade group, headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland.
IATAN – International Airlines Travel Agent Network – administers the IATAN card, the only widely accepted form of legitimate travel agent identification.
In season – meaning only available at certain times of the year.
In transit – en route; in the process of traveling.
Inbound operator – A receptive operator that usually serves groups arriving from another country.
Inbound tour – A tour for groups of travelers whose trip originates in another location, usually another country.
Incentive or incentive commission – See override.
Incentive tour – A trip offered as a prize, particularly to stimulate the productivity of employees or sales agents.
Incentive trave l – travel as a reward for an employee’s outstanding performance.
Incidental Charge – Items and services billed to a room after their use, such as movies, phone calls, etc.
Incidentals – Charges incurred by the participants of a tour, but which are not included in the tour price.
Inclusive tour – a package tour that bundles transportation, accommodations, transfers, sightseeing, possibly some meals, etc.
Inclusive tour – See all-inclusive package.
Independent tour – A travel package in which a tour operator is involved only with the planning, marketing, and selling of the package, but is not involved with the passengers while the tour is in progress.
In-flight Service – Entertainment (movies, television, etc.), meals, beverages and other items made available during a flight for the convenience of the passenger.
Inside cabin – a stateroom aboard ship that has no window. Sometimes smaller, but at times the same size as an outside cabin.
Intercontinental – Having to do with two continents. In travel, transit from one continent to another. Not to be confused with transcontinental.
interline connection – a flight on one airline that connects to a flight on another carrier – these tickets are usually more expensive than flying all on one carrier but may be the only way to get to a destination in some cases.
Intermodal tour – A tour that uses several forms of transportation, such as a plane, motorcoach, cruise ship, and train.
International Air Transport Association – International airline industry trade group, headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland.
International Date Line – at 180 degrees longitude, the date on one side of this imaginary line, running from the north to the South Pole, is different from the other. The line runs through the Pacific Ocean, and because of it, it is possible to leave one destination on one day, and arrive in another the day before
International Rate Desk – Utilizes all available resources to ensure the lowest fare for your selected itinerary, including splitting tickets, consolidator fares, and available discounts.
Involvement device – An element of direct mail that gets the reader involved in the process of evaluating and/or responding to the solicitation.
Itinerary – A list of a tour’s or entire trip’s schedule and major travel elements.
Jet Bridge – An enclosed, movable connector which extends from a terminal gate to a plane, allowing passengers to board and disembark without having to go outside.
Jet lag – an upset of one’s biological clock, due to travel across many time zones; not all folks are affected by it.
Jones Act – a law dating back to 1886, that forbids foreign-flagged ships from carrying passengers between US ports with no foreign port stops in-between.
Judgment sample – A sample based on the researcher’s choice of subjects for a study.
Jump Seat – A flight term referring to an auxiliary (extra) seat for persons who are not operating the aircraft, such as the cabin crew or perhaps a trainee.
Kilometer – a measure of distance used in almost all other countries, at about 5/8 mile.
King room – a hotel room with a king bed.
Knot – a nautical measure of speed equaling approx. 1.5 mph. A ship traveling at 15 knots is traveling at about 22 mph.
Kph – kilometers-per-hour – land speed measurement in most other countries. 60 kph equals approx. 36 miles-per-hour.
Land arrangements – all the details of a land portion of a trip (hotel, car, tours, sightseeing, etc.).
Land Destinations – A land destination or travel destination is a place to which one is journeying, typically for its inherent or exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure, adventure and amusement.
Land operator – See receptive operator.
Land Transfers – travel by train, bus, limo or taxi to and from an accommodation, plane or cruise ship.
Land-only – a rate that does NOT include airfare; usually includes most other land-based charges such as accommodations, transfers, taxes, and perhaps other optional items like theme park tickets, rental care, etc.
Last-seat availability – the ability of a travel agent to get, literally, the ” last seat ” for you on a particular flight, either at a certain fare or actually the last remaining seat on an aircraft. See “direct access”.
Late booking fee – a fee due if travel arrangement are made at the last minute. Normally covers express delivery of documents and other last-minute arrangements that may have to be made by a tour operator.
Late Checkout – A more exclusive perk for some guests that allow a few extra hours to check out from the normal hours.
Latitude – imaginary horizontal lines of angular distance, measured in degrees north or south of the equator.
Layover – a period of time spent during a trip, sometimes overnight, while waiting for a transportation connection – usually a change of planes.
Layover – The period of time spent between connecting flights.
LDW – loss damage waiver – additional insurance pertaining to car rentals, covering theft and vandalism in addition to accident damage.
Lead-in price – the lowest available price for a travel product, often pertaining to cabins on a cruise ship. Usually, there are only a few staterooms available on board each cruise liner in this category, but often better accommodations are only slightly higher in price. Rock-bottom price shoppers normally insist on these rates, though they sell out quickly.
Leeward – the side of a ship or an island that is located opposite from the direction of the prevailing wind -the “Leeward Islands” in the Caribbean for example.
Leg – Portion of a journey between two scheduled stops.
Leisure travel – Usually signifies traveling for relaxation, vacation, or to visit friends/family. Travel for pleasure as opposed to business.
Letter of agreement – A letter from the buyer to the supplier accepting the terms of the proposal. This may also be the supplier’s first proposal that has been initialed by the buyer.
Lido deck – usually the deck on a cruise ship that surrounds the pool area.
Limited service hotel – a hotel property without a restaurant.
List broker – A seller of mail lists for direct marketing.
Load factor – The number of passengers traveling on a vehicle, vessel, or aircraft compared to the number of available seats or cabins.
Locater map – A map of an area or a city, showing locations of attractions and hotels.
Lodging – Any establishment that provides shelter and overnight accommodations to travelers.
Logistics – Management of the details of an operation.
Low season – the period when a destination experiences its lowest prices and the fewest number of guests.
Low season – See off peak.
Lower (bed) – in a cruise stateroom, the bed(s) on the floor as opposed to the higher bunks (uppers), if any. On many ships, two lowers can be arranged to make a king or queen bed.
Lowest available fare – the current, lowest airfare available for purchase right then.
Lowest available fare – The most inexpensive flight currently available.
Lowest fare – the lowest published airfare between two cities; may not have seats available at that fare, as the airlines usually have a limited number of those seats on any given flight.
Luxury class – the most expensive, high-class accommodations or category of fare.
Luxury Cruise – Luxury cruises are the most comfortable and convenient way to see the world. Ships are usually smaller in size so the ratio of crew and staff to guests is generally higher than other cruise ships offering that premium service and attention to detail to be expected of exquisite vacations.
Luxury Ocean Cruise – a luxury ocean cruise is an ocean cruise on a luxury cruise ship or luxury cruise liner or passenger ship used for pleasure voyages, where the voyage itself and the ship’s amenities are a part of the experience, as well as the different destinations along the way.
Luxury River Cruise – a luxury river cruise is a river cruise on a luxury cruise ship or luxury passenger ship used for pleasure voyages, where the voyage itself and the ship’s amenities are a part of the experience, as well as the different destinations along the way.
Luxury travel – while luxury travel is completely subjective to the traveler, it can be loosely defined at travel that constitutes the state of great comfort and extravagant living.
Luxury vacations – a luxury vacation is a vacation that encompasses a state of great comfort and extravagant living.
Macro-environment – The broad forces in society and the business world that impact most companies.
Management Company – A firm that owns several lodging properties.
Manifest – Final official listing of all passengers and/or cargo aboard a transportation vehicle or vessel.
Market demand – The amount of a specific product or service that may be purchased during a certain period of time in a particular geographic area.
Market forecast – The realistic demand within a given time period for the products produced by all companies within a certain industry or product category.
Market – All existing and potential customers for a product or service.
Marketing mix – The 4 Ps of marketing- product, price, promotion, place (distribution).
Marketing plan – A written report that details marketing objectives for a product or service, and recommends strategies for achieving these objectives.
Marketing research – The function that links the consumer, customer, and public to the marketer through the systematic gathering and analyzing of information.
Markup pricing – Pricing a product by adding a standard markup to costs. Also called cost-plus pricing.
Markup – A percentage added to the cost of a product to achieve a selling price.
Master account – The guest account for a particular group or function that will be paid by the sponsoring organization. See folio.
Maximum stay – The longest period of time a traveler can stay at a particular destination and still qualify for the promotion or discounted fare.
Media – Communications channel such as broadcast (radio, TV), print (newspapers, magazines, direct mail), outdoor (billboards), and multimedia (Internet).
Meet-and-greet service – A pre-purchased service for meeting and greeting clients upon arrival in a city, usually at the airport, pier, or rail station, and assisting clients with entrance formalities, collecting baggage, and obtaining transportation.
Meeting/conference tour – A tour designed around a specific meeting or conference for the participants.
Microenvironment – Those forces close to a company that impact operations and marketing programs.
Midships – Directional term. Amidships, sometimes termed midships, is the center of the vessel or aircraft.
Minimum connect time – defined as the minimum time necessary between connecting flights – 30 minutes domestically, usually – ideally, at least an hour. The shortest time required in order to successfully transfer to a connecting flight. It is recommended to select a connecting flight that exceeds the minimum connection time.
Mission statement – The concise description of what an organization is, its purpose, and what it intends to accomplish.
Modified American plan (MAP) – meal plan that includes two daily meals, usually breakfast and dinner.
Motorcoach tour operators – Tour operators that own their own motorcoaches.
Motorcoach Tour – A tour that features the motorcoach as the form of transportation to and from destinations.
Motorcoach – A large, comfortable bus that can transport travelers and their luggage long distances.
MST – Mountain Standard Time.
Multi-day tour – A travel package of two or more days. Most multi-day tours are escorted, all-inclusive packages.
Multigenerational Travel – multigenerational travel is a travel category referring to travel with parents, siblings, kids, grandkids, and assorted family members with the goal to broaden horizons, provide opportunities to reconnect and provide an enriching assortment of shared experiences.
Murder-mystery tour – A tour that features a staged “murder” and involves travelers in solving the crime.
Mystery tour – A journey to unpublicized destinations in which tour takers aren’t told where they will be going until en route or upon arrival.
NACTA – National Association of Career Travel Agents – trade group representing primarily independent and home-based agents, now part of ASTA.
National tourism organization (NTO) – A federal-government-level DMO that promotes country as a travel destination.
Nautical Mile – Unit of length that is about one minute of arc of latitude along any meridian, but is approximately one minute of arc of longitude. Air-Sea distance measurement of approx. 1.1 statute miles.
Negotiated Rate – A discounted rate offered to a company based on the volume of business you agree to provide the selected vendor.
Net fare, net rate – Implies the commission has already been added to the price of the fare.
Net wholesale rate – A rate usually slightly lower than the wholesale rate, applicable to groups of individuals when a hotel is specifically mentioned in a tour brochure. The rate is marked up by wholesale sellers of tours to cover distribution and promotion costs.
Niche market – A highly specialized segment of the travel market, such as an affinity group with a unique special interest.
No show – a passenger who doesn’t show for a flight, hotel, or rental car booking. A guest with confirmed reservations who does not arrive and whose reservation was not canceled.
Non Stop Flight – Do not land in between your departure and arrival destinations. (I.e. San Francisco to New York)
Non-Changeable Ticket – A ticket that cannot be exchanged for a different route or flight once it’s been purchased.
Non-refundable – a fare that cannot be refunded either in cash or via a credit card credit; very seldom is there an exception.
Non-Refundable Ticket – A ticket that cannot be returned for cash or credit once it’s been purchased, but may be changeable for a fee.
Nonstop – A flight that travels directly to its destination without connections or layovers.
Non-transferable – A ticket that can only be used by the person who was originally scheduled to fly at the time of purchase.
NTSB – National Transportation Safety Board; investigates accidents and other incidents related to public transportation.
Objective and task method – A process for creating a promotion budget that sets objectives first, then defines the tasks needed to achieve those objectives, and then commits funds necessary to perform the tasks.
Occupancy rate – the percent of hotel rooms expected to be filled during a specific time period.
Occupancy – The percentage of available rooms occupied for a given period. It is computed by dividing the number of rooms occupied for a period by the number of rooms available for the same period.
Ocean view cabin – a cabin aboard a cruise ship with a window, such as a porthole or picture-window, and perhaps a balcony/verandah.
OCV – ocean view, usually in reference to a hotel room.
Offline connection – a change of aircraft also involving a change of carriers.
Off-peak – A less expensive time to travel as result of lower consumer volume during these periods.
On-site guide – A tour guide who conducts tours of one or several hours’ duration at a specific building, attraction, or site.
Onsite – An on-site is an expert travel provider that lives in the country they serve and has firsthand knowledge and long-standing relationships with all aspect of travel in their country.
Open jaw – a trip in during which there is no travel by air between two cities, such as a flight to Washington DC, then travel by rental car to Charlotte, NC, then a return by air from Charlotte back to the original departure city.
Open return – an air ticket with no return date specified. Rarely done these days, usually quite expensive and not allowed on most discounted fares.
Open-end question – A question that allows the respondent to provide a free-response answer.
Open-jaw itinerary – A travel routing design that departs from one location and returns to another. For example, travelers may fly into one city and depart from another one. Or a traveler may purchase round-trip transportation from the point of origin to one destination, at which another form of transportation is used to reach a second destination, where the traveler resumes the initial form of transportation to return to the point of origin.
Operations – Performing the practical work of operating a tour or travel program.
Operator – a company providing transportation or travel related services (airline, cruise line, railway, hotel, car Rental Company, etc.).
Operator – See Tour Operator.
Option date – drop dead date on which a reservation must be deposited or cancellation will result.
Optionals – Optional tour features that are not included in the base tour price, such as sightseeing excursions or special activities.
OTA – Online travel agencies, examples include Priceline, Expedia and Orbitz
Outbound – the departure leg of a journey.
Outbound operator – A company that takes groups from a given city or country to another city or country.
Outbound tour – A tour that takes travelers out of the area, usually from a domestic city to another country.
Outside cabin – see “ocean view ” cabin.
Outside salesperson – job description of a travel agency employee who sells travel but is not based primarily in the agency location most of the time.
Overbook – Accepting reservations for more space than is available.
Overbooking – the practice of selling more airline seats than are available on a specific flight, to make up for no-shows. Usually backfires on the carrier and at times can create much consumer ill-will. Requires passengers to be “bumped” – not always voluntarily. To some extent, happens in the hotel industry as well.
Overhead – Those fixed costs involved in regular operations, such as rent, insurance, management salaries, and utilities.
Override – A commission over and above the normal base commission percentage.
Packaged travel – A package in combination of two or more types of tour components into a product which is produced, assembled, promoted and sold as a package by a tour operator for an all-inclusive price.
Passenger facility charge (PFC) – a fee for the use of many airports, added in to the cost of an air ticket – another name for an additional tax on travelers.
Passenger name record (PNR) – The official name of one’s reservation in a computer reservation system (CRS).
Passenger vessel – Ships, yachts, ferries, boats, etc.
Passport/visa service – a service that will take your passport and hand carry, if necessary, to the appropriate embassy in order to expedite a visa. Can be expensive if you have waited until the last minute to obtain a travel visa.
Patronage Program – A program that rewards the customer for loyalty and repeat purchase, such as frequent-flyer programs.
Peak season – A destination’s high season when demand is strong. Also called the high season.
Peninsula – A piece of land that is connected to a mainland or larger piece of land on only one side, while the other sides are surrounded by water.
Per Diem – “by the day;” in the cruise industry, the per-day cost of a cruise, per person.
Per-capita costs – Per-person costs.
Per-capita tour – See scheduled tour.
Perceived value – The ratio of perceived benefits to perceived price.
Personal effects coverage – Additional car rental insurance covering loss of personal property from the rented vehicle.
Point-to-point – refers to the fares between two cities; the service between two cities without additional segments or any continuation.
Port – the place where a ship docks; a place visited by cruise ship; the left side of a vessel.
Port charges/taxes – fees levied by local authorities upon the cruise lines for each passenger visiting a port of call, normally added to the total cruise fare.
Port of Debarkation – Port of Debarkation is the geographic point where personnel arrive on a cruise vessel
Port of Embarkation – Port of Embarkation is the geographic point where personnel depart on a cruise vessel
Port of entry – Destination providing customs and immigration services.
Port-Directional – When facing forward, the side of the ship or aircraft that is on the left.
Porter – A person who handles luggage at an airport, train station, etc.; also called skycap or baggage handler.
Porthole – usually a round, sealed window in a shipboard stateroom.
Posada – a small country hotel (Spanish).
Positioning strategy – The development of a clear, unique, and attractive image for a company and/or product in the minds of target customers.
Positive space – space aboard a ship or aircraft that can be confirmed ahead of time.
Post-Cruise Vacation – a post-cruise vacation is a vacation or getaway prior to a cruise in the town or region of the port of debarkation of the cruise.
PPDO – per person, double occupancy. Most tours and cruises are quoted this way; the average cost to stay in a particular location per day.
Pre- and post-trip tour – An optional extension or side trip package before and/or after a meeting, gathering, or convention.
Pre-Cruise Vacation – a vacation or getaway prior to a cruise in the town or region of the port of embarkation of the cruise.
Pre-deduct commission – When a distributor such as a travel agent takes up front the commission on a sale and sends the supplier the balance of the sales price.
Preferred Supplier – The selection of specific supplier(s) for priority promotion to customers and/or integration in travel packages in exchange for reduced rates and/or higher commission.
Preferred Vendor – The vendor(s) a company specifies as their first choice for travelers.
Preformed group – A pre-existing collection of travelers, such as affinity groups and travel clubs, whose members share a common interest or organizational affiliation.
Prepaid ticket advice – a form used when purchasing an air ticket to be picked up and used by someone else at another airport. E-tickets have reduced the need for this greatly.
Primary research – The collection of data specifically to solve the marketing problem at hand.
Prix fixe – meals offered at a fixed price, usually fairly low, consisting of several courses with no substitutions allowed. Common in Europe.
Profit margin – A dollar value that represents the markup of a product’s price over its costs.
Promotion mix – Promotion tools including advertising, direct marketing, sales promotion, and public relations.
Promotional group tour – A travel package composed of tour elements that match the specific needs and wants of niche customers who aren’t part of an organized or preformed group.
Promotional partnership – The combination of two or more companies to offer special incentives to customers.
Prop – referring to propeller-driven aircraft.
Property – A specific lodging structure, such as a hotel, and the ground on which it is built.
Property – A general term that may be used by a place of accommodation that denotes the facility.
Protection overbooking – The practice of blocking space that will likely be in excess of what will actually be needed.
Pseudo-agent – someone claiming to be a travel agent who really isn’t. They often produce bogus ID cards, and can disappear when problems arise!
PST – Pacific Standard Time.
Psychographics – Measures of a person’s lifestyle. See also AIO variables.
Public relations (PR) – A management function that determines the attitudes and opinions of an organization’s publics, identifies its policies with the interests of its publics, and formulates and executes a program of action to earn public understanding and goodwill.
Public tours – See scheduled tour.
Published fare – an airfare that is listed in the carrier’s tariff.
Pull strategy – A marketing approach that creates demand at the customer level by generating awareness, interest, and desire so customers pull a product through a distribution channel by demanding it.
Purser – aboard ship, the person responsible for providing a wide array of services such as information, making change, stamps, etc. Found at the purser’s desk.
Purser-(Airline) – On a flight, the purser is the head flight attendant, responsible for overseeing the attendants and making sure travelers’ needs are met.
Push strategy – A marketing approach that creates demand at the distributor level by providing resellers with an incentive to push (sell) a product to end consumers.
Quad – a room suitable for four persons.
Quay – a pier – pronounced the same as “key”.
Query – The process of sorting and retrieving information from a database.
Quid – a monetary term for a British pound sterling.
Quota sample – A research sample that involves forming groups based on certain characteristics. A random sample can then be selected form the quota segments.
Rack rate – The published (brochure) rate for a travel component. The price of a hotel prior to discount.
Rate desk – the office of an air carrier that calculates fares for passengers and travel agents.
Reach – The measure of how many people in a market will be exposed to a certain advertisement via a specific medium.
Reasonable number – A forecast of the break-even point for a tour.
Rebate (ing) – the practice of returning part of an agency’s commission on a scale back to the client in the form of a rebate or “discount.” The trade-off is usually little or no personal/customer service. This is practiced often by “800 ” number travel sellers and others who deal in huge volume.
Receptive operator – A local tour company that specializes in services for incoming visitors, often for tour operator groups.
Reconfirm – to double-check a reservation.
Record locator – The number assigned to a reservation in the airlines number. This number is unique, as it will never be assigned again.
Record locator – the number assigned to one’s reservation in an airline’s computer system.
Red-eye flight – An overnight flight that leaves at night and arrives early the next morning.
Referral agent/agency – an ” agent ” that refers business to a travel agency in return for a commission or fee – often as part of a card mill operation
Registry – the formal registration of a ship’s ownership, and the country it is registered in (such as Panama, Liberia, Norway, etc.).
Reissue – the generation of a new ticket that is exchanged for another, due to a change of plans, dates, flights, etc. May involve additional fare, penalties and fees.
Relationship marketing – The process of building and nurturing ongoing, solid relationship with customers.
Repositionin g – the moving of a cruise ship to another home port for all of part of a season, such as the repositioning of ships to Alaska for the summer. Often these cruises are excellent bargains, but will involve one-way airfare home from the port of debarkation.
Res – short for “reservation”.
Research constraints – Those issues, such as cost and timing that will limit the scope of marketing research.
Reseller – See retailer and wholesaler.
Reservation fee – A customer payment for a certain percentage of the travel package price that’s made immediately after booking.
Responsible Tourism – Travel that extends beyond being merely environmentally responsible, to being culturally-conscious and economically-aware, locally.
Retail price – The actual price a customer pays for a travel element or tour.
Retail tour – See scheduled tour.
Retailer – A middleman, such as a travel agent, who sells directly to the customer.
Retirement travel – retirement travel is a category of travel referring to when a traveler is has retired from a career and commences to travel. Travel done after retirement age.
Rollaway – a cot or other bedding that can be added to a hotel room to accommodate another guest. There is often an extra charge for this.
Romantic Destinations – romance destination and romance travel is a category of travel that involves travel involving a feeling of excitement and mystery associated with love and often refers to travel associated with a wedding, honeymoon, wedding anniversary, babymoon or another type of romantic getaway.
Room Night – In the hotel (hospitality) industry, a room night, room/night occupancy, is a measure of occupancy where a room is the unit of measure.
Room Occupancy – In the hotel (hospitality) industry, a room night, room/night occupancy, is a measure of occupancy where a room is the unit of measure.
Room rates – The various rates used by lodging properties to price rooms. These include- day rate (usually one half the regular rate for a room used by a guest during the day up to 5 p.m.-sometimes called a use rate), flat rate (a specific room rate for a group agreed upon by the hotel and group in advance), group rate (same as flat rate), net group rate ( a wholesale rate for group business to which an operator may add a markup if desired), net wholesale rate ( a rate usually lower than the group rate and applicable to groups or individuals when a hotel is specifically mentioned in a tour folder), and published rate ( a full rate available to or advertised to the public-also called the rack rate.)
Rooming list – A printout of the names of all tour participants that also lists special lodging requests and provides a spot for the hotel or cruise ship to fill in the passenger’s room number.
Round trip – A flight to a single destination and a return.
Run-of-house (ROH) – refers to a hotel room, the type of which is assigned at the discretion of the hotel shortly before you arrive. Usually, the rates are lower.
Run-of-ship – cabin is assigned at the last moment, giving the cruise line the ability to shift accommodations as needed. Usually, you are guaranteed a minimum category of cabin, and sometimes get an upgraded stateroom at no additional cost. Most upgrades are from inside-to-inside cabins, or from outside-to-outside but occasionally an inside-to-ocean view upgrade will occur. It is not always worth the gamble though.
Run-of-the-house rate – A flat rate for which a lodging property agrees to offer any of its available rooms to a group. Final assignment of the rooms is at the discretion of lodging management.
Sabre® – A computerized travel reservation system.
Safaris – Today the negative hunting connotations of the word ‘safari’ are being rapidly replaced by more modern associations with socially and environmentally responsible travel. Safari travel typically implies that the journey will include game viewing and some time spent in wilderness areas (game reserves and national parks). A traditional is usually focused on seeing wildlife, but safaris are definitely not limited to game viewing. Safaris are now for admiring wildlife and birds in the wild, along with a host of other adventures. Safaris have largely developed into vacation trips that actually benefit the wildlife by supporting local conservation efforts and wildlife sanctuaries. As opposed to hunting the animals, visitors get to encounter them and help make a difference in protecting the species. Safari companies either actively contribute towards conservation projects or help generate tourism revenue which is used to manage wildlife projects and game reserves. The modern safari is also a socially responsible journey designed to interact ethically with local communities and have a positive impact on local economies. The cultural interactions offered by reputable safari operators do not exploit local people. The local communities benefit from sustainable tourism through employment and financial gains from selling goods and services.
Sales margin – A term used by resellers to describe profit as a percentage of sales revenue.
Sample – The portion of a population chosen to represent the population being studied for research.
Saturday night stay – A requirement by the airlines that your travel must involve a Saturday night stay over in order to obtain our lowest fare.
Saturday night stay – In order to receive a specialty fare, a Saturday stay over is sometimes required.
Scandals tour – A light-hearted history tour that shows locations where interesting scandals took place.
Scheduled carrier – An airline that offers regularly scheduled flights between destinations.
Scheduled flights – Air flights that are publicly scheduled and promoted by major airlines.
Scheduled tour – A tour that’s set in a tour operator’s regular schedule of tour departures and that’s often sold to the general public. Also called public tour or retail tour.
Sea bands – a product resembling a bracelet that is worn on the wrists and operates via acupressure.
Wearers claim that seasickness can be avoided by their use, thus eliminating the need for drugs such as Dramamine, etc.
Sea legs – the ability to move around on a ship without losing balance and without sea sickness.
Secondary information – Research data that was collected by another company or person and usually for a purpose that’s different than the research objectives and tasks at hand.
Sectioning system (GPS) – system of satellites that allows miniature radio receivers on earth to pinpoint one’s location within a few feet. Most cruise ships make use of this system to navigate the world’s oceans.
Segment – a “leg” or part of a journey, usually in reference to an air itinerary. One take-off and landing during air travel constitutes a “segment”.
Segment – One leg or portion of a trip. The segment begins when you board the plane and ends when you de-board the plane. (I.e. A connecting flight from San Francisco to New York through Chicago equals 2 segments)
Self-drive – a rental car (British term).
Service non comprise – in French, meaning “service not included”.
Shells – Preprinted brochures with photos, illustrations, and graphics but no text; also called slicks.
Shore excursio n – tours that are purchased as an option when visiting ports of call while on a cruise; can sometimes be bought before you cruise.
Shore excursion – A land tour, usually available at ports of call, sold by cruise lines or tour operators to cruise passengers.
Shoulder season – a period of time between high and low seasons, where prices at a destination are between their highest and lowest, and the crowds are thinner.
Shoulder season – Those periods between the peak and off season when destination demand is moderate.
Sightseeing companies – Organizations that provide local guided tours.
Sightseeing guide – See driver/guide.
Sightseeing tour – Short excursions of usually a few hours that focus on sightseeing and/or attraction visits.
Simple random sample – A sample that draws a group of respondents randomly from all members of the population.
Single Room – A room that is only guaranteed to comfortably accommodate one guest. May also be called a “Standard Room.”
Single Supplement – An additional charge added to a solo traveler, when prices were originally quoted for dual occupancy.
Sleeper – the sleeping compartment aboard a train.
Soft adventure – an outdoor travel experience that is not especially physically demanding, such as a canyon horseback trail ride or a hot-air balloon flight.
Sommelier – A wine professional, usually hired by the most upscale restaurants and establishments, on staff to primarily suggest wine and food pairing to patrons.
Spa – a resort area centered around a mineral springs, hot springs and the like, typically where one can find massage, hydrotherapy, exercise, steam baths, etc.
Special event tour – A travel package that features major happenings, such as concerts or sporting events, as the reason for the journey.
Special fare – Any fare that deviates from normal pricing (typically discounted).
Special interest tour – a tour catering to the needs of a specific interest, such as bird-watching, whale-watching, river rafting, mountain biking, rain forest exploration among many others.
Split itinerary – An itinerary in which part of the group does one thing while the other part does something else.
Split Ticket – Issuing multiple tickets for one round-trip journey. This is done to reduce the total cost of the entire reservation.
Sports Tourism – sports tourism refers to travel which involves either observing or participating in a sporting event staying apart from their usual environment.
Stabilizer – a device on most all cruise vessels, to reduce pitch and roll when at sea – the movement that can cause seasickness. Stabilizers are often pulled in at night in order to allow faster speeds when traveling between ports of call.
Standby – Referring to a passenger who does not have a confirmed seat on the intended flight.
Star Service – a critical guide describing in detail many hotel and cruise ship properties. Can be subjective, as it is based on someone’s opinion, but provides a travel agent with a non-commercial point-of-view.
Starboard – the right side of a ship.
Stateroom – A private cabin or compartment with sleeping accommodations on a ship or train.
Step-on guide – A tour guide who boards a motorcoach to give detailed, expert commentary about the city or area being visited.
Stern – the rear of a ship.
Stopover – a planned stayover in a city for a day or more, while enrooted to another destination. Sometimes adds significantly to the cost of an air ticket.
Strategic plan – A report that describes a company’s mission statement, goals, objectives and strategic actions.
Student visa – permission to enter a country, issued to a student, normally for the purpose of attending school in that country.
Subcontractor – A local operator who provides services for a wholesaler.
Suite – a hotel accommodation with more than one room, or sometimes a single room with distinct sleeping and living areas and often a kitchenette. A suite in a hotel or other public accommodation denotes a class of accommodations with more space and amenities than a typical accommodation room. Luxury or upscale accommodations often have a scaled range of suites progressively increasing in size, luxury and amenities starting with a junior suite and culminating in the largest and most luxurious suite which is often called a presidential or royal suite.
Supplier – any company that supplies travel and/or related services to the traveling public. The actual producer and seller of travel components.
Surface – travel over land that does not involve an aircraft.
SWOT analysis – A summary of a company’s strengths and weaknesses, and the environmental opportunities and threats that will most influence it.
T&E – Travel and Entertainment expenses.
Target market – The group of customers who will be the focus of a company’s marketing efforts.
Tariff – a schedule of prices/fares.
Telemarketing – Direct marketing via the telephone.
Tender – a small boat or ferry that carries passengers from an anchored cruise ship to the pier at a port of call. Many ships are too large for existing port facilities at some destinations, and so they anchor just off shore and “tender “their passengers in for their visit.
Terminal – A building where clients report for trips via train, plane, etc.; also called a depot or a station.
TGV – the term applied to the French high-speed train system.
Theme cruise – a cruise devoted to a specific interest, such as big bands, country western, Star Trek, exercise and weight-loss, cooking and cuisine, and many more. There is usually a theme cruise to suit just about any interest.
Theme tour – A tour that’s designed around a concept of specific interest to the tour takers, such as history or sports.
Through passenger – a passenger who is not disembarking at a particular stop while enrooted to the final destination.
Ticket stock – Blank airline tickets.
Tickler system – A method for monitoring reservations and payments that’s arranged by date and points out late payments so customers can be contacted.
Tiered override pla n – When commissions rise proportionately with a corresponding increase in sales.
Tiered pricing – When suppliers offer different prices to receptive operators, tour operators, and group leaders, so each party can earn a profit by marking up the supplier’s price while still offering a fair price to customers.
Tour broker – See tour operator.
Tour catalog – A publication by tour wholesalers listing their tour offerings. Catalogs are distributed to retail agents who make them available to their customers. Bookings by retail agents are commissionable.
Tour Company – A tour company or tour operator typically combines tour and travel components to create a packaged vacation. They advertise and produce brochures to promote their products, vacation and itineraries.
Tour conductor – the person who accompanies and is in charge of a tour, often on a motor coach tour. See tour director.
Tour departure – The date of the start by any individual or group of a tour program or, by extension, the entire operation of that single tour.
Tour director – Also called tour manager, tour conductor, and tour escort. The person who is responsible for a group on tour and for most aspects of a tour’s execution.
Tour escort – See tour director.
Tour guide – A person qualified (and often certified) to conduct tours of specific locations or attractions.
See also step-on guide, city guide, on-site guide, and docent.
Tour manager – See tour director.
Tour manual – A compendium of facts about a destination, tour procedures, forms, and other information that a tour operator gives to its tour directors.
Tour menu – A menu that limits group clients to two or three choices.
Tour operator – A person or company that contracts with suppliers to create and/or market a tour and/or subcontract their performance.
Tour order – A voucher given to the purchaser of a tour package that identifies the tour, the seller, and the fact that the tour is prepaid. The purchaser then uses this form as proof of payment and receives vouchers for meals, porterage, transfers, entrance fees, and other expenses. See also voucher.
Tour planner – A person who researches destinations and suppliers, negotiates contracts, and creates itineraries for travel packages.
Tour rate – See group rate.
Tour series – Multiple departures to the same destination throughout the year.
Tour – A prearranged, prepaid journey to one or more destinations that generally returns to the point of origin, is usually arranged with an itinerary of leisure activities, and includes at least two travel elements.
Tourism – The business of providing marketing services and facilities for leisure travelers.
Tourist card – a card issued to a visitor in lieu of a visa, usually for a short duration visit.
Tourist – This is the majority of adult travelers, when not vacationing. Tourists may be couples, families, or just a person or two who visit locations.
Tours – a tour is a journey for pleasure which includes the visiting of a number of places in sequence, especially with an organized group often led by a guide.
Tracking study – A survey of customers before and after implementing a promotion campaign to assess changes in consumer behavior.
Trans-canal – passing through the Panama Canal.
Transcon – Having to do with crossing a continent. For example, travel of this sort would be from one end of a continent to another.
Transcontinental – Having to do with crossing a continent. For example, travel of this sort would be from one end of a continent to another.
Transfer – Local transportation and porterage from one carrier terminal to another, from a terminal to a hotel, or from a hotel to an attraction.
Transient Occupancy Tax – Also known as a Bed Tax, it is a City or County tax added to the price of the room.
Transient – A person who stays in a place for just a short while; not a permanent resident, such as a visitor or tourist.
Transit visa – A visa allowing the holder to stop over in a country or make a travel connection or a brief visit.
Transportation – Any method of moving travelers from one point in a journey to another, such as air, ship, rail, and motor coach travel.
Travel advisor – a travel advisor simplifies the time-consuming and complicated process of planning travel for their customers in addition to providing consultation services and entire travel packages. They may book flights, cruises, rental cars and hotels, as well as resort stays and events. Agents cater to a wide demographic, serving both individuals and corporations. They may also concentrate in a special segment of travel; many advisors specialize in leisure, business or group travel, or destination-specific journeys.
Travel advisory – a travel warning issued by the US Department of State, indicating a special caution should be taken in a country due to political unrest, natural disaster, or other special situation. These can be obtained from any good travel agent, on any area you are considering visiting.
Travel agency – Usually used in the travel industry to refer to an ARC-appointed storefront retailer.
Travel agent – A person or firm qualified to arrange for lodging, meals, transportation, cruises, tours, and other travel elements, typically on a commission basis. A travel agent simplifies the time-consuming and complicated process of planning travel for their customers in addition to providing consultation services and entire travel packages. They may book flights, cruises, rental cars and hotels, as well as resort stays and events. Agents cater to a wide demographic, serving both individuals and corporations. They may also concentrate in a special segment of travel; many agents specialize in leisure, business or group travel, or destination-specific journeys.
Travel component – Transportation, lodging, dining, attractions, entertainment, guide services, and other travel elements offered as part of a travel package.
Travel Destination – a place to which one is journeying.
Travel Experience – A travel experience or experiential travel (also known as immersion travel) as it is commonly referred to, is a form of tourism in which people focus on experiencing a country, city or particular place by connecting to its history, people and culture.
Travel Institute – the primary educational and certification arm of the travel industry. Was formerly the “Institute of Certified Travel Agents” (ICTA), located in Wellesley, Mass.
Travel Insurance – Travel insurance is insurance that is intended to cover medical expenses, trip cancellation, lost luggage, flight accident and other losses incurred while traveling, either internationally or within one’s own country.
Travel Itinerary – a travel itinerary is a travel plan or organization of your travel and involves all of the details, times and dates concerning things like airline, cruises and train transportation confirmations, hotel, villa and accommodation reservations, rental car information, restaurant reservations and much more.
Travel Policy – A fluid internal document, pertinent to the company’s culture that outlines the guidelines for business travel and expenses within a company.
Travel rewards – Travel reward programs are often referred to as a loyalty rewards program, and they are generally a campaign devised to generate repeat customers for a particular company by offering a point gratification system for the customers’ business. They are also meant to provide customers with a “thank you” for their loyalty to a company’s product or service. That benefit is typically some sort of discount on certain items or services. Travel specialist – a travel specialist is a travel agent or travel advisor that concentrates in a special segment of travel; many travel agents or travel advisors specialize in leisure, group or business travel, or destination specific travel.
Travel Tours – a travel tour is a journey for pleasure which includes the visiting of a number of places in sequence, especially with an organized group often led by a guide.
Traveler – One who travels.
Travelogues – Many travel websites are online travelogues or travel journals, usually created by individual travelers and hosted by companies that generally provide their information to consumers for free. These companies generate revenue through advertising or by providing services to other businesses. This medium produces a wide variety of styles, often incorporating graphics, photography, maps, and other unique content.
Trip director – An escort for an incentive company. Larger companies reserve this title for the person who directs all personnel and activities for a particular incentive trip.
Trundle Bed – Bed that stores itself under another bed, usually on casters. Often found in smaller hotel rooms or in cramped transport accommodations.
Turn – Airline parlance. A flight that leaves base and returns back to base in the same day. Also known as a turnaround.
Turnaway – A potential reservation that couldn’t be satisfied because the tour (or hotel, ship, etc.) was fully booked.
Twenty-four hour time – used extensively in Europe and other countries, 1pm becomes 1300 hours, 4pm is 1500 hours, etc., up to 2359 ( 1159pm ). Midnight is then considered 2400 or “zero ” hours. 1-20am is then 0120 or “one hour, twenty minutes “and so on. Most schedules and timetables in the majority of other countries are listed in the 24-hour format.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites – a UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place (such as a building, city, complex, desert, forest, island, lake, monument, or mountain) that is listed by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) as being of special cultural or physical significance.
Unlimited mileage – No mileage restriction when renting a car.
Unrestricted fare – an airfare that has no special advance purchase, Saturday stay or certain days to travel requirements, and is usually refundable. Many full coach and most first-class fares are unrestricted. An airfare with no limitations. It is typically refundable and has no blackout days.
Upgrade – To move to a better accommodation or class of service.
USTOA – United States Tour Operators Association – a trade association which requires its members to be very financially stable and to have a million dollars or more in funds set aside for consumer protection against defaults. Visit www.ustoa.com for more information.
Value added tax (VAT) – a tax on goods in Europe, which under certain circumstances can be refunded.
Value season – similar to shoulder or low season, when pricing is lower. See off season.
Value – The relationship between the benefits associated with a product or service and the costs of obtaining the product or service. See also perceived value.
Value-added tax (VAT) – A type of tax system which adds a fixed percentage of taxation on products and services at each step of production or service delivery.
Value-based pricing – Pricing a product based on buyer perceptions of value rather than actual product costs.
Variable costs – Costs that change with sales or production levels.
Variance report – A summary of how much a company has gone above or below budget.
Verandah – a roofed-porch, such as connected to a cruise ship stateroom.
VIA rail – the Canadian railway system.
Villas – a large and luxurious country residence. A villa is a fancy vacation home. The word has been around ever since ancient Roman times to mean “country house for the elite.” In Italian, villa means “country house or farm.” Most villas include a large amount of land and often barns, garages, or other outbuildings as well.
VIP experiences – a VIP Experience is the most exclusive way to go behind the scenes or experience a travel destination, accommodation or mode of transportation.
Visa – usually a stamp in a passport allowing entry into a country for a specific purpose and a finite amount of time.
Visa service – a service that can expedite the processing of a visa, sometimes even at the last minute. A fee is charged that varies, depending on the nature of the service needed. Visas are usually stamped into the pages of a valid passport and are issued for varying reasons and periods of time. Not all countries require them, especially for United States Citizens.
Volume incentive – See override.
Volume purchase – The purchase of large quantities of a product or service.
Voucher – Documents that are exchanged for goods and service to substantiate payment that will be or already has been made.
Voyage – a voyage is a long journey involving travel by sea or in space.
Waitlist – A list of clients awaiting transportation or accommodations at times when they are not available. Waitlisted clients are confirmed as a result of subsequent cancellations.
Waiver – a written acknowledgement that a passenger has declined something, such as insurance coverage for a trip, for example. Also, the formal acknowledgement of the waiving or dismissal of a requirement, such as a waiver of a penalty for late booking, etc.
Waiver – A written acknowledgement that a passenger has declined something.
Walk-up – one who purchases an air ticket at the last moment, usually at the airport ticket counter.
Wants – Ways in which a person satisfies a basic need.
Wellness Travel – wellness travel is a category of travel for the purpose of promoting health and well-being through physical, psychological, or spiritual activities
Wet bar – the area of a hotel room that has a bar or other counter space with running water, used for the preparation of drinks.
Wholesale – Sale of travel products through an intermediary in exchange for a commission or fee generally at reduced tariffs.
Word-of-mouth promotion – Personal communication about a product or service from one customer to another.
World Travel Guide – a yearly publication that provides detailed information on most every country in the world, with entries on currency, transportation, climate, visa and passport requirements, sightseeing opportunities, etc. A primary book of knowledge for the professional travel agent.
Yield management – Calculating and analyzing the profits earned per customer.

World Travel Agency, LLC is owned and operated by Michael and Cheryl LaBaw. We are a husband and wife team dedicated to working together with our clients to insure they travel well. World Travel Agency, LLC is an independent affiliate of Andavo Travel, a Virtuoso® Member. Travel should be more than just a journey, it should be a series of unforgettable experiences. We work hard to ensure our clients’ trips are always stimulating, authentic and – above all else – fun... READ MORE

- Recent Blog Posts
- Luxury Ocean Cruise
- Luxury River Cruises
- Land Destinations
- Group Travel
- Corporate Travel
- Family Vacation
- Adventure Travel
- Celebrity Travel
- Travel Experience
- Wellness Travel
- Romantic Destinations
- Destination Weddings
- Value of an Adviser
- Mission Statement
- Publications
- Travel Photos
- Travel Videos
- Distinctive Travel Offers
- Travel Tips & Ideas
- Subscriber Services
- For Authors
- Publications
- Archaeology
- Art & Architecture
- Bilingual dictionaries
- Classical studies
- Encyclopedias
- English Dictionaries and Thesauri
- Language reference
- Linguistics
- Media studies
- Medicine and health
- Names studies
- Performing arts
- Science and technology
- Social sciences
- Society and culture
- Overview Pages
- Subject Reference
- English Dictionaries
- Bilingual Dictionaries
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search

A Dictionary of Travel and Tourism
Allan beaver.
Over 6,500 entries
Provides over 6,500 definitions of travel and tourism terminology, including the operating language of the travel industry, acronyms of organizations, associations, and trade bodies, IT terms, and brand names. Completely up to date, this dictionary covers the implications of web technology and social media on the travel and tourism industry, as well as new products and services, such as e-tickets, home-based travel agents, awareness amongst consumers and within the industry of terror-threatened travel, recent changes in legislation, and environmental concerns.
Useful appendices include the World Tourism Organization Global Code of Ethics for Tourism , the recommended tourism syllabus content for Higher Education courses worldwide, and a list of the EC Neutral Computerized Reservation System Rules . Providing a wealth of information on one of the fastest-growing global industries of the 21st century, this dictionary is the ideal point of reference for students taking travel, tourism, and hospitality courses, as well as professionals working within these areas.
Bibliographic Information
Affiliations are at time of print publication..
Allan Beaver is an expert in the fields of travel and tourism, and is Visiting Professor at Bournemouth University and Director of Beaver Travel . Previous publications include Mind Your Own Travel Business (1993), Travel Agency Layout, Equipment and Design (1989), and Air Fares Guide (1995).
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
- All Contents
Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription.
Please subscribe or login to access full text content.
If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code.
For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us .
AACC International
Front matter, publishing information, general links for this work, introduction, recommended tourism syllabus content for higher education courses, ec computer reservation system rules, acknowledgements.
- Oxford University Press
PRINTED FROM OXFORD REFERENCE (www.oxfordreference.com). (c) Copyright Oxford University Press, 2023. All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice ).
date: 30 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.159]
- 81.177.182.159
Character limit 500 /500

- Service Providers + Destinations
- Content Creators
- Collaborations + Partnerships
- What is Rooted?
- Rooted’s Founder

Guide: 70+ Sustainable Tourism Terms
Enter your email below to be added to the newsletter and receive instant access to the resource!
Any conversation about sustainability is filled with jargon … and that’s especially true in the travel and tourism industry. It’s time to demystify all that terminology! This guide is a go-to resource to help make sense of 70+ common words and phrases related to sustainable tourism. (Yes, even that murky term “sustainable tourism” is defined!) This A-to-Z collection touches on topics related to the environment, tourism supply chain, consumer behavior, and more.
Highlights of this free terminology guide include:
- 70+ relevant words and phrases clearly defined
- Tips for talking about sustainable tourism in an accessible way
- Updated regularly to incorporate industry terminology
Other Resources
The Resource Hub is a list of internal and external resources, carefully curated to make sure you have the very best, most comprehensive information at your fingertips, regardless of your role.
Page [tcb_pagination_current_page] of [tcb_pagination_total_pages]

Travel Keywords: Ultimate List Of Ideas For Tour Operators
Every time your ideal customer goes online to research their next trip, they type travel keywords into the search engine. If you don’t know what these keywords are, it’s very difficult to know how to optimize your content for SEO.
SEO is the biggest driver of organic traffic to your website. When you use the right keywords in your content, you can potentially get greater visibility online.
Although the travel industry is a competitive space to be in, with basic SEO knowledge and keyword research, you can set your website up to attract more visitors.
Here, we’ll quickly walk you through how to identify your ideal keywords. Plus, we’ve included a list of general keyword ideas to point you in the direction of getting started.

How To Pinpoint Your Ideal Travel Keywords
When identifying travel keywords for your web content, there are three points to think about:
- Search Volume : The number of times users search a keyword in a month. The higher the search volume, the more web traffic you can potentially get from the keyword.
- Difficulty : Generally speaking, keywords with a higher search volume and commercial intent are more difficult to rank for. And if you’re competing against loads of high-authority websites for a specific keyword, this will also make it more challenging to rank for.
- Search inten t: When people enter keywords into the search bar, does the content in the results give them the information they are looking for? Offer the information that the person wants, and the keywords will bring you relevant traffic, not just a lot of traffic.
Our guides on how to do keyword research and local keyword research have more tips and insights on the subject.
Tools For Finding Travel Keywords
There are plenty of awesome SEO tools to help you find relevant and up-to-date keywords for your tour operator business. These tools are easy to use and offer some fantastic insights to improve your online visibility.
For a free tool, you can try Wordstream . You can check what keywords your competitors are ranking for, get ideas for the travel industry, and narrow down the results to be relevant for your state or country.

Another free option is Keywordtool.io . This generates hundreds of long-tail keywords, questions, and related prepositions based on the search term you enter. Long-tails can be useful as they often have a more focused search intent and lower difficulty.
There is also Ubersuggest , which provides a certain amount of daily free insights. Enter a domain or keyword, and the tool will bring all sorts of data, including keyword and content ideas.
For a paid keyword that gives greater insight, Ahrefs is a winner. Get a deeper look into keywords, backlinks, competitor analysis, content gaps, and more.

Travel Keyword Ideas For Your Business
To rank on the search engines, you need to start with a keyword.
We did a bit of research using the tools mentioned above to give you general ideas on what travelers are typing into search engines right now.
Keywords can be written into your website content so that you begin to rank for them in the SERPS. Include the terms naturally and optimally in your landing pages, blog posts, tour descriptions, website copy, product write-ups, social copy, adverts, and more.
Also, keep in mind that keywords are in a constant state of flux based on current market trends and conditions. For example, search volumes on travel insurance and travel restrictions are likely to currently be higher than they have ever been because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
High-Volume Travel Keywords
Here is a list of high-volume keywords related to travel in general. This is what people are searching for right now on the topic of travel and tourism.
Keywords That Travelers Might Use To Find Your Business
This list of general keywords includes a few terms that travelers might use to find you online.
Keywords To Describe Tours & Types Of Travel
These keywords are some of the popular tour and trip types that travelers are currently searching on the internet.
Final Thoughts
While these are pretty general keywords, they do at least provide a base from which you can brainstorm ideas for your travel business.
Because travel is a hot topic online, the competition on the SERPs is pretty high. Taking a data-informed approach to optimizing your content will better position your website for ranking.
Remember, ranking content on search engines is not a quick fix and doesn’t happen overnight. So, it’s a good idea to include other types of marketing in your overall strategy to grow your travel business.
To get more content like this sent directly to your inbox, sign up below for WeTravel’s newsletter.
New resources, straight to your inbox
We’re committed to your privacy. WeTravel uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe at any time.
About the author

Related Posts
Customer success story – happy gringo, customer success story – nepal eco adventure, customer success story – one yoga.
How to Find the Best Tourism Keywords by Geography
By Kyla Steeves
Share this article:
- Facebook icon
- LinkedIn icon
- Twitter icon

When it comes to marketing your tours or activities, one of the most important facets is search engine optimization (SEO). As the biggest driver for organic traffic, SEO can help you rank for popular travel and tourism keywords in your destination — whether in Google Search, Google Maps, or other online directories — to capture interested travelers and locals alike.
While travel related keywords are very common, what makes them highly valuable is the intention behind them. Typically, the traveler has an end goal; they already know what they want to do, they’re just looking to book with the right tour operator.
For example, let’s say someone wants to go wine tasting in Italy for a bachelorette trip. Instead of entering “best bachelorette party ideas for big groups” into Google, they might try something like, “wine tour Venice Italy.” Understand the difference?
You see, they’re primed to book already. After weeks of travel planning, they’ve had time to look up ideas, and now, just need to find a winery tour operator to host the party. But sometimes, people make last-minute travel plans while in-destination; it’s almost instinctive. “What do you want to do today? Go kayaking? Gotcha. Looking up a place to rent kayaks right now.”
And more often than not, they will go with a business in Google’s local snack pack (see image below) or the first page of results. Usually, that’s because they like what they see right away, are in a hurry, assume the best choices are in the top positions, or the reason is a combination of all three.
When done right, SEO can help you snag those higher rankings and increase your chances of capturing high-converting leads at such a crucial time. There are lots of advanced travel SEO tactics, but we’re going to start by going over finding the best tourism keywords, as they should become the basis for all of your optimization efforts.
What are tourism keywords?
Tourism keywords are the search terms or phrases people use to find things to do in your destination. They normally contain a niche descriptor and a geographical modifier, following a structure that tends to look like this:
Niche descriptor + Geographical modifier = tourism keyword
whale watching tour + Victoria BC = whale watching tour Victoria BC
In terms of SEO, you can add relevant travel and tourism keywords to your website content, Tripadvisor listing, and even your YouTube channel, to tell search engines (mostly Google) and other directories that your business offers what the searcher is specifically looking for.
But of course, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all for travel keywords. Every searcher is unique, and so is their go-to phrasing, which means there could be hundreds of variations for the same search intent.
For example, someone might replace the location with term near me instead :
escape rooms + near me = escape rooms near me
Another searcher might throw in modifiers like best, top, cheapest :
best + mountain bike rentals + Virgin Utah = best mountain bike rentals Virgin Utah
And finally, someone might switch up the order altogether:
surfing + Bondi Beach + lessons = surfing Bondi Beach lessons
So, how do you know what travel and tourism keywords to use? Which ones are the most popular to get the most clicks? And what competition will you face — do you even have a chance at ranking for them? That’s where local keyword research comes into play.
How to find keywords for tourism website
Without taking the time to research the top travel keywords for your destination, you’re essentially taking a shot in the dark for SEO. If you wouldn’t do that in an axe throwing competition, why would you do that for something that matters as much as your brand’s online visibility?
That said, doing a keyword search by city is a simple process — involving nothing more than brainstorming with online keyword tools — and doesn’t take too long once you get it down pat. The objective is to generate an extensive list of all potential keywords so that you can quickly compare for best use cases. Here are the steps:
1. Create a travel keywords list
First things first, you will want to create a spreadsheet for your keyword ideas to live. That way, you can quickly refer to it whenever you publish new content, like a blog post or web page. Just remember to keep it updated, considering keyword trends change all the time. We’ll get to that soon.
For the most part, your keyword spreadsheet will only need three columns: local keyword, search volume , and competition. But since many keywords, local included, are long-tail keywords — highly specific phrases of three words or more — it’s a good idea to set it up like below to get a better understanding of the structure commonly used:
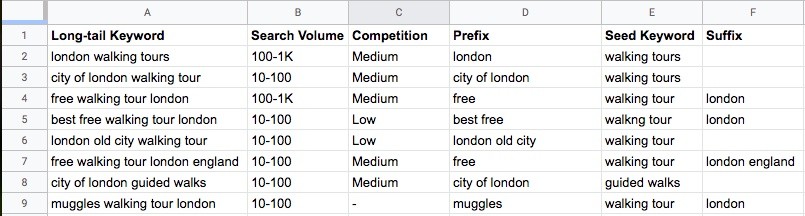
Long-tail keyword: the full keyword, with or without a geo modifier (location)
Search volume: the average monthly searches for a specific keyword
Competition: the level of competition between advertisers bidding on the keyword — like online travel agents (OTAs)
Prefix: the word(s) that come before the seed keyword
Seed keyword: the industry-related keyword, or better put, the keyword that describes your product — such as bus tour, kayak rentals, lake cabins, or aerial ropes course
Suffix: the word(s) that come after the seed keyword
2. Brainstorm with Google and other keyword tools
One of the best places to begin your local keyword research is Google itself. You might have noticed already that Google will autocomplete your search as soon as you type, make predictions in a dropdown menu, and provide a list of related searches at the bottom of the search engine results page (SERP).
Well, you can actually use these suggestions as a jumping-off point because Google comes up with them based on related and popular keywords for a better search experience. So if you start by entering a few search terms you would use yourself to find your offerings (not brand specific), you will end up finding relevant keywords to add to your spreadsheet.
On top of that, you can find out what queries your guests already use to discover your business with Google Search Console . As long as you have a Google Account, you can enter your domain, then click on Google Search Results under Performance and see what queries get the most clicks and impressions. You can also filter the results on a per-page basis by clicking +New , then Page , and pasting your page URL.
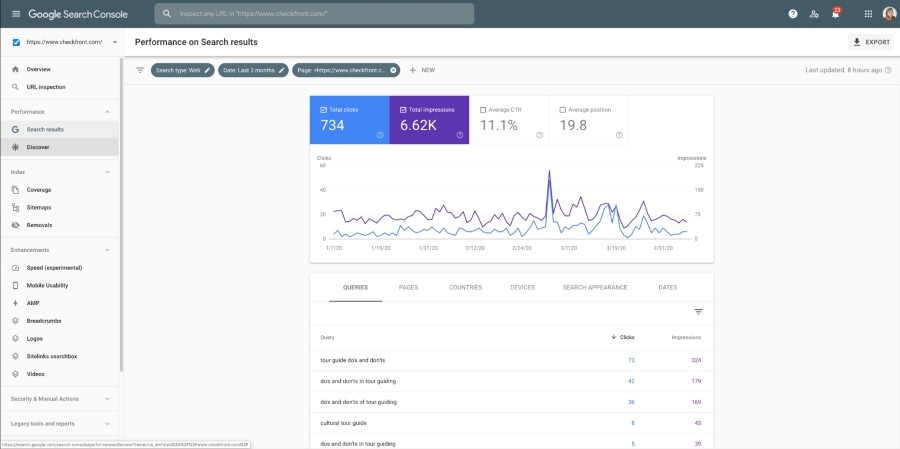
Once you have a list going, you can then turn to an online keyword tool for more insight. There are many options available that come with powerful features and databases — like Ahrefs Keyword Explorer or SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool . However, Google Ads Keyword Planner is free and does a good enough job.
Here’s how to use Google Keyword Planner
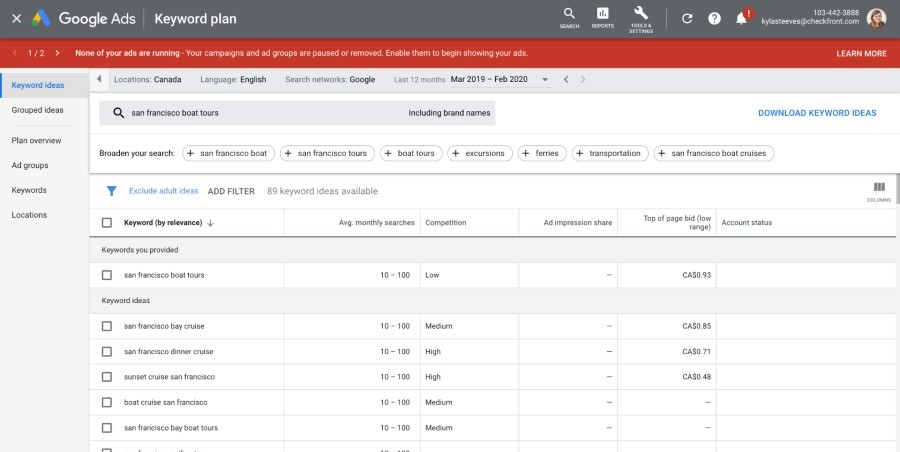
- Access Google Keyword Planner by clicking on Go to Keyword Planner
- Follow the prompts to set up a Google AdWords account. Don’t worry, you won’t have to run an advertising campaign to use the keyword tool.
- Select the box with Discover new keywords
- Copy and paste your keywords separately into the search bar and click Get results. You can broaden the search by using multiple seed keywords, separated by commas.
- Record the average monthly searches and competition for the keyword in your spreadsheet
- Scroll through the keyword ideas and add any more to your list that also apply to your business
Now, if you run your tourism operation in a location that doesn’t have a high population, you might not see any results because there just isn’t enough data available. If that’s the case, try replacing your geo modifier with another city nearby, and then make the switch back in your spreadsheet.
For example, nothing much comes up in Keyword Planner for Half Moon Bay boat tours, even though there are over 7 million results in Google Search. But if we use San Francisco instead, which is 29.4 miles away, we get 89 keyword recommendations that we can adapt for Half Moon Bay keywords.
3. Choose the top keywords for tourism
After you feel like your keyword list is long enough, you can go ahead and choose your top picks. And the easiest way to do this is by sorting the search volume column from lowest to highest.
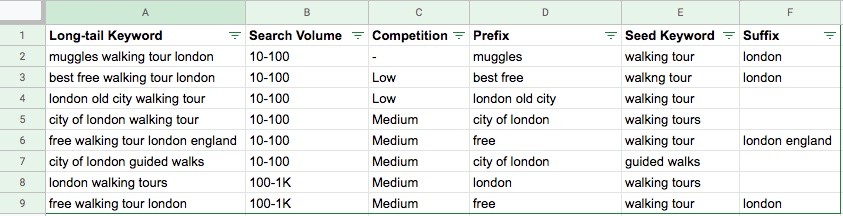
But wait, shouldn’t it be the other way around? Don’t you want to target travel related keywords with the highest search volume? Normally, yes. However, as a small business, you have a better chance of ranking for low volume keywords — around the 10-100 range.
That’s because high volume keywords are highly competitive. It only makes sense; popular keywords attract more competition because they drive more search traffic. And unfortunately, larger companies tend to earn these rankings because they’ve already built the SEO-strength for an extra boost.
Keep in mind though, while low volume keywords get less search traffic, they usually have higher conversion value because they are more specific. So targeting them is actually a strategic move on your part, and as you improve your SEO overall, you can eventually go after the higher volume keywords, too.
Also, Google Trends is another useful and free tool for choosing the best keywords. You can compare up to 5 similar keywords and their popularity overtime, so that you know which ones to focus on more. Note: If you don’t see anything come up, try filtering the results by your country instead of worldwide.
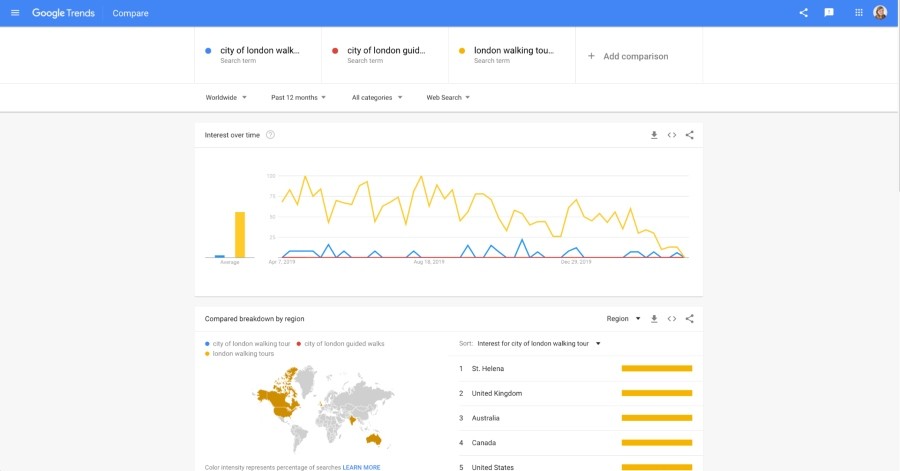
4. Repeat the process for each tour
If you have multiple products, you will want to find travel related keywords for all of them. For example, let’s say you offer a city bike tour, but also a brewery bike tour. Although both fall in the same category and have the same seed keyword (bike tour), a person looking to book a city bike tour nearby won’t use the same search term as they would for the latter.
Just add a new sheet in your keyword spreadsheet for each of your products and repeat the above steps. The same goes for if you have multiple locations — but for better organization, you may want an entirely new spreadsheet for each site and its products.
Where to put travel and tourism keywords
For the best SEO practice, you should have a different keyword theme for each page on your website. Since your homepage will likely rank best for your brand name, you can optimize your booking page(s) with your travel keywords. Besides, that’s where it makes the most sense to direct traffic, considering most local searches have a transactional intention.
Again, if you have multiple locations, categories, and products, you should consider having a separate booking page for each. That way, you can really target those tourism keywords by giving Google and other search engines a clear idea of what every booking page is specifically about.
With the previous example, you would optimize your category booking page with the local seed keyword, bike tour Dublin, and then list all of your bike tours with call-to-action buttons to their separate booking page. Doing this will also improve your internal linking structure for better overall SEO. From there, every product booking page could then target long-tail keywords.
Here all the places to put travel and tourism keywords on your booking page(s):
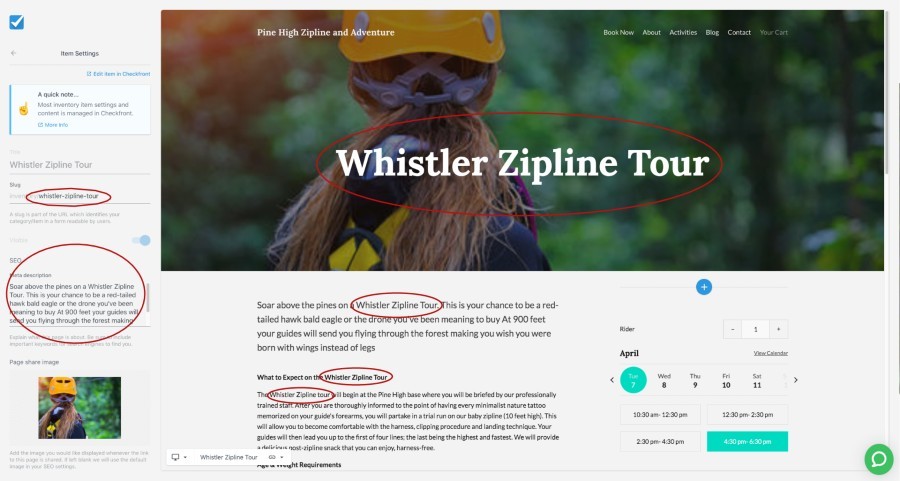
- Page title: also known as a title tag, it’s an HTML element that specifies the title of your booking page, which appears in the search results and the browser window
- Meta-description: a snippet of around 160 characters that also displays in the SERPs and describes what your booking page is about
- Heading: the main title at the start of your booking page with the H1 tag
- Sub-headings: the section headings of your booking page with an H2, H3, or H4 tag — the best places for your keyword synonyms
- Body text: the main content of your booking page, usually where you have paragraph sections
- Item name: the name of one of your products in tours, activities, accommodation or rentals
- Item description: the description for tours and travel , which includes essential details
- URL slug: the part of the URL that comes after your primary domain that identifies your booking page — like pinehighzipline.com/zipline-tours
- Image alt-text: a description of the image that gets read-aloud for the visually impaired with screen readers or appears when the picture doesn’t load. It should be short, but descriptive
- Image filename: a sneaky place to optimize your content, which can also help your image appear in Google Images, like saving an image as london-ghost-walking-tour.jpg rather than IMG-12.jpg.
It’s easy to get carried away when adding keywords to travel websites. What you want to avoid is keyword stuffing, which is an old blackhat SEO tactic that Google penalizes today. Instead, you should focus on working your travel and tourism keywords naturally into your page content and switching up your keyword usage with the various synonyms in your local keyword list.
Understandably, it might feel unnatural to put your location everywhere, especially in the headings, sub-headings, and item names. And that’s alright; you don’t have to, seeing as you can also put your NAP on every page for optimal SEO.
Don’t forget about your NAP
Your NAP is your business info, which includes your Name, Address, and Phone Number. On your website, the best place for your NAP is in the footer. You should put your NAP somewhere on every page, but if you have multiple locations, make sure to assign the appropriate address for that specific booking page.
One of the most common SEO problems is neglecting to keep your NAP consistent and up-to-date across the board, from your website to your Google My Business listing, even on your Facebook Business Page. Maintaining consistency in your citations signals to Google that you are a legitimate business and care about giving your guests accurate information.
Other places for tourism keywords
Tourism keywords don’t just belong on your website. As I mentioned earlier, you can optimize your local listings and social media profiles with them as well. But we’ll get to that more in the second chapter of the Local Marketing Guide for Experience Providers. Get your free copy below!
Ready to target travelers who are nearby?

Get 52 pages of local marketing tips
And learn all about what you can do to stand out in your community and local search results.
Related Articles

How to write ATV tour descriptions that drive bookings (with examples)
Learn how to write ATV rental descriptions with SEO-ready language that help you sell more bookings
- Marketing Strategies

Easy & effective pricing tactics for activity and rental operators
Ever wondered why at the movie theatre you’re likely to opt for a Large Popcorn instead of a Small or…
Search Blog
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Get tips and strategies to grow your business and impress your guests.
Blog Categories
- Booking Management
- Business Tips
- Guest Experience
- Operator Highlights

100 Comprehensive Travel Keywords During Your Keyword Research?

SEO is the biggest driver of organic traffic to your website. When you use the right keywords in your content, you can get greater online visibility.
Understanding the best Keyword for travel is essential in creating successful and effective travel blog posts.
Although the travel industry is a competitive space, with basic SEO knowledge and keyword research, you can set your website up to attract more visitors.
However, with so many other tasks involved in running a travel blog, finding the time for keyword research can be challenging.
This leads to the question: when should you do keyword research? This blog post will discuss the best timing for keyword research, how it can benefit your travel blog, and the best keywords for a travel blog.
So, if you’re a travel blogger looking to improve your SEO game, keep reading to learn more about the importance of keyword research for travel bloggers.
the Importance of having the best Travel Keywords
Keyword research plays a crucial role in the success of travel blogging. It is a vital tool for understanding what people are searching for in relation to your travel niche and allows you to create content that is not only informative and engaging but also optimized for search engines.
Incorporating relevant travel keywords into your blog posts increases the chances of your content being discovered, more organic traffic, and, ultimately, increased page views.
One of the critical benefits of keyword research for travel bloggers is the ability to tap into the mindset of your audience.
You can tailor your content to address their needs, preferences, and interests by understanding the specific search terms they are using.
This helps you to create more relevant and targeted blog posts that resonate with your readers, making them more likely to stay on your site, engage with your content, and even convert into loyal followers.
Another important aspect of travel keyword research is its impact on search engine optimization (SEO).
By incorporating keywords into your blog posts, you signal to Google what your content is about, helping them to index and rank your site more accurately.
This increases the likelihood of your blog appearing higher in Google search results (SERPs), making it more visible and driving organic traffic to your site.
Overall, keyword research is a fundamental aspect of travel blogging that should not be overlooked.
By dedicating time and effort to keyword research , you can ensure that your blog effectively reaches and engages with your intended audience, helping you grow your blog and achieve your blogging goals.

Optimal Times to Conduct Travel Keyword Research
To maximize the effectiveness of your keyword research for travel blogs, it’s essential to consider the optimal times to conduct keyword research.
While keyword research can be done at any time, specific periods can provide better results and help you stay ahead of the competition.
One of the best times to conduct keyword research is during the initial stages of planning your blog post.
By identifying relevant keywords early on, you can ensure that your future blog posts are strategically optimized from the start.
This allows you to align your content creation process with the keywords most likely to drive organic traffic to your site.
Another opportune time to research keywords for travel is when you’re brainstorming new blog post ideas.
By conducting keyword research during this phase, you can uncover popular search terms related to your travel niche and use them as inspiration for your content.
This ensures your blog posts are interesting, informative, and highly relevant to those Googling-specific travel keyphrases.
In addition, it’s beneficial to revisit and update your keyword research periodically.
Trends and search behaviors can change over time, so by regularly conducting keyword research, you can stay up-to-date with the latest keywords that resonate with your audience.
This will help you consistently optimize your blog content and maintain its visibility in search engine results.
By strategically timing your keyword research, you can ensure that your travel blog stays relevant, attracts more readers, and continues to grow in popularity.
Strategies to Effectively Implement Keywords for Travel
To effectively carry out keyword research for your travel blog, here are some strategies to consider:
1. Use keyword research tools
There are various keyword research tools available that can help you identify relevant and popular keywords for your travel niche.
These tools provide insights into search volume, competition, and related keywords, allowing you to make informed decisions about which keywords to target.
2. Analyze your competition
Take a look at what keywords your competitors are ranking for. This can give you valuable insights into which keywords are driving traffic to their blogs and help you identify any gaps or opportunities that you can capitalize on.
3. Focus on long-tail keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific keyword phrases that often have lower search volume but higher intent.
By targeting long-tail keywords, you can attract a more targeted audience and increase your chances of ranking higher in search engine results.
4. Consider user intent
When conducting keyword research, it’s important to consider the intent behind the search query. Are users looking for information, inspiration, or to book a trip?
By understanding the intent, you can tailor your content to meet their needs and increase the chances of converting them into readers or customers.
5. Monitor and track keyword performance
Once you have incorporated keywords into your blog posts, monitoring their performance is important.
Use analytics tools to track the organic traffic, engagement, and conversions generated by specific keywords.
This will help you identify which keywords are bringing the most value to your blog and make adjustments as needed.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively carry out keyword research for your travel blog and improve its visibility, attract more readers, and achieve your blogging goals.
Remember, keyword research is an ongoing process, so it’s essential to regularly review and update your keywords to stay ahead of the competition.
- Use the target or main keyword within the first 100 words of your page.
- Don’t add an outgoing link with your keyword ad anchor text.
- Aim to use each keyword two times naturally.

Tips for Incorporating Keywords into Your Travel Blog Posts
In order to effectively incorporate keywords into your travel blog posts, consider the following tips:
1. Utilize keywords naturally
While it’s essential to include your chosen keywords throughout your content, it’s crucial to do so in a natural and organic way.
Avoid keyword stuffing or forcing keywords into your writing. Instead, focus on creating high-quality, informative content that naturally incorporates your keywords.
2. Include keywords in your title and headings
One of the most impactful places to include keywords is in your blog post titles and headings. This not only helps search engines understand the relevance of your content but also catches the attention of readers searching for specific terms.
3. Optimize your meta tags
Meta tags, including your meta title and meta description, play a significant role in search engine optimization. Incorporate your target keywords into these tags to improve your blog post’s visibility in search engine results.
4. Create unique and engaging content
While incorporating keywords is important, it’s equally crucial to create unique and engaging content that appeals to your audience.
Your blog posts should provide valuable information and insight into your travel niche, encouraging readers to stay on your site and explore more of your content.
5. Don’t forget about image optimization
Images can also contribute to your blog’s visibility in search engine results. Optimize your image alt text and file names with relevant keywords to increase the chances of your images being discovered.
How To Pinpoint Your Ideal Travel Keywords
When identifying travel keywords for your web content, there are three points to think about:
- Search Volume : The number of times users search a keyword in a month. The higher the search volume, the more web traffic you can get from the keyword.
- Difficulty : Generally speaking, keywords with a higher search volume and commercial intent are more challenging to rank for. And if you’re competing against loads of high-authority websites for a specific keyword, it will also be more challenging to rank for.
- Search inten t: When people enter keywords into the search bar, does the content in the results give them the information they are looking for? Offer the information that the person wants, and the keywords will bring you relevant traffic, not just a lot of traffic.
High-Volume Travel Keywords
Below you will find a list of some of the most popular keywords in the travel niche along with their global monthly search volume on Google.
If your website or business focuses on travel, these keywords can be helpful for content ideas and increasing your SEO presence.
Remember, keyword research is an ongoing process, so regularly revisit and update your keywords to stay ahead of the competition and ensure continued success.
Final Thoughts
While these are pretty general keywords, they do at least provide a base from which you can brainstorm ideas for your travel business.
Because travel is a hot topic online, the competition on the SERPs is pretty high. Taking a data-informed approach to optimizing your content will better position your website for ranking.
Remember, ranking content on search engines is not a quick fix and doesn’t happen overnight. So, it’s a good idea to include other types of marketing in your overall strategy to grow your travel business.
Learn how to do keyword research with Me
You’ve learned the basics about how to do keyword research, but if you’re looking to take your keyword research skills to the next level, I am here to help to schedule a SEO Strategy Call today
One Comment
- Pingback: Stay22 is the Best Hotel Affiliate Program for 2024!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Most Important Keywords for the Travel & Tourism Industry
For Candidates

By our guest blogger, CareerTuners
Is your resume getting noticed? Recruiters and employers in the travel & tourism industry rely heavily on Application Tracking System (ATS) software to analyze resumes and shortlist applicants. One critical way to optimize your resume for ATS is to add keywords.
Keywords are nouns or noun phrases that ATS algorithms “catch.” They help indicate to employers that the candidate has skills that match the job requirements. Common keywords include job titles, terms, tools, technologies, degrees, licenses, certifications, training, patents, publications, and locations.
There are two types of keywords. Hard keywords are those that can be quantified or that someone can take a test for, for example, the names of marketing analytics programs. They are the most important with respect to ranking in ATS. In contrast, soft keywords are abstract skills that are hard to test for, but are critical to succeeding at your job, e.g., strong interpersonal skills.
Below are some important keywords for travel & tourism management positions, in bold .
Feel free to copy and paste these terms to your resume if they match your skill set.
However, merely mentioning these keywords in your resume is not enough. You must also write powerful accomplishments that highlight these skills. After each keyword are the most critical questions you should ask yourself before incorporating it into your resume:
Program Development
- Travel Planning: Did you develop any backup/contingency plans for program bottlenecks, such as cancelled flights, overbooked hotels, and stranded clients?
- Itinerary Management: How did you make itinerary management an efficient and cost-effective process? Did you introduce any software solutions to automate routine tasks?
- Reservation Management : What steps did you take to ensure quick and accurate price calculations? Did you increase reservations by developing attractive travel and tourism packages?
Travel & Tourism Industry Partnerships
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: How did you overcome language and cultural barriers when developing business partnerships in other countries?
- Vendor Management: How did you address vendor delays and inefficiencies?
- Community Outreach: What challenges did you address in collaborating with hotels, airlines, and tourist attractions to create value-adding deals?
- Airline Experience: How did you build strategic partnerships with various airlines to get special discounts and deals?
Operations Management
- Safety Management: What steps did you take to ensure program and client safety in foreign locations?
- Data Entry: Did you eliminate errors and redundancies in the data entry process by introducing automation?
- Budget Optimization & Cost Control: What steps did you take to eliminate multivendor costs?
- Industry & Competitor Analysis: What steps did you take to stay abreast of competitor launches?
- Invoicing: What steps did you to take to ensure hassle-free billing?
- Customer Relationship Management: What steps did you take to standardize customer service? Did you develop templates for frequently asked questions?
Sales & Marketing
- Sales Experience: By how much did you increase revenue and sales from upselling and cross-selling travel services?
- Commission Sales: What steps did you take to sustain sales during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- New Business Development: Did you identify and tap new customer and market segments?
- Customer Acquisition & Retention: Did you develop any loyalty or reward programs to generate repeat business?
In addition to these, consider carefully going over the job listing you are interested in for keywords. Which ones are you familiar with? Weave these keywords into your resume.
By asking yourself these questions, you will be able to uncover accomplishments that highlight your strategic leadership skills. This will not only optimize your resume for ATS-compatibility but also set you apart from other applicants.
Click here to view all industry articles created by CareerTuners.
At CareerTuners, we help ambitious professionals land their dream jobs by providing professional, Applicant-Tracking-System-compatible resume writing services. Some of our other services include cover letter writing, LinkedIn profile development, interview coaching, and resume distribution. To check out our free resources and blog, please visit careertuners.com .
Bristol Associates, Inc. is an executive search firm with over 50 years of excellence in recruiting nationwide. Bristol specializes in recruiting for the Casino Gaming; Facilities and Concessions; Food and Beverage Manufacturing; Hospital and Healthcare; Hotels and Resorts; Nonprofit; Restaurant; and Travel, Tourism, and Attractions industries.
If you’re interested in working with Bristol Associates, click here if you’re an employer or here if you’re a candidate.
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter here .
Get The Newsletter
Receive exclusive career opportunities, hiring best practices, and more straight to your inbox.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Tourism industries (also referred to as tourism activities) are the activities that typically producetourism characteristic products. The term tourism industries is equivalent to tourism characteristic activities and the two terms are sometimes used synonymously in the IRTS 2008, 5.10, 5.11 and figure 5.1.
Glossary of Tourism Terms. Add-on: a product or service not included in the list or package price. See also: Upsell. adventure travel: a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion. affinity group: a group of people linked by ...
TPA: Tourism Promotion Agency. This is basically the same thing as a DMO. A government agency that promotes tourism in a specific county or region within a state. Travel Advisor: Someone who assists consumers in booking trips. Previously called travel agents, travel advisors do more than book travel for people.
The Tourism Academy released an update to the official glossary of tourism terms.New additions this year include phrases like certified, cross-sell, tourism ambassador and more. The tourism glossary now includes over 200 terms, phrases and popular acronyms that are unique to the tour and travel industry. Available online or as a PDF download, the tourism industry terms and glossary are free to ...
90 English Tourism Vocabulary Words and Phrases [With Sample Dialogues] English is the most common language used in the international tourism industry. People who work in the tourism industry use it to communicate with tourists from all over the world. If you work in tourism or hope to find a job in the industry, it helps to know the right ...
A company that creates and/or markets packaged tours and/or performs tour services. Tourism: Is defined as: "The activities of persons traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes.".
A company that creates and/or markets packaged tours and/or performs tour services. Tourism: Is defined as: "The activities of persons traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes.".
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Tourism: The Key Concepts offers a comprehensive collection of the most frequently used and studied concepts in the subject of tourism. Within the text key terms, concepts, typologies and frameworks are examined in the context of the broader social sciences, blending together theory and practice to explore the scope of the subject. Terms covered include: Ethical Tourism LGBT Tourism ...
tour manual: (1) a summary of facts about a company s rules, regulations, and official procedures; (2) a compendium of facts about a destination, including its attractions, accommodations, geography, and special events, used by destination marketing organizations to attract tour operators and visitors and their area.
This travel glossary contains more than 100 of the most common terms and acronyms you are likely to hear in the travel industry. The travel niche has its own terms, abbreviations, and definitions. As it can get complicated to understand them all, we created this complete travel glossary. You can either click on: Note that we are still working ...
Air Travel - air travel is the action or process of making a journey by aircraft. Air/sea - a term referring to tickets, trips, fares, etc. that include both air and land-based travel arrangements, such as a cruise package with air included. Aircraft - Generally speaking, any machine capable of flight.
eISBN: 9780191733987. Allan Beaver, author. Allan Beaver is an expert in the fields of travel and tourism, and is Visiting Professor at Bournemouth University and Director of Beaver Travel. Previous publications include Mind Your Own Travel Business (1993), Travel Agency Layout, Equipment and Design (1989), and Air Fares Guide (1995).
It's time to demystify all that terminology! This guide is a go-to resource to help make sense of 70+ common words and phrases related to sustainable tourism. (Yes, even that murky term "sustainable tourism" is defined!) This A-to-Z collection touches on topics related to the environment, tourism supply chain, consumer behavior, and more.
Travel Vocabulary Words for ESL Beginners. Airport. a complex of runways and buildings for the take-off, landing, and maintenance of civil aircraft, with facilities for passengers. Check-in. the action of registering one's presence, typically as a passenger at an airport. Fly. travel through the air; be airborne.
Terms in this set (100) Domestic tourism. Taking holidays and trips within your own country. outbound tourism. Travelling to a different country for a visit or holiday. inbound tourism. Visitors from overseas coming into the country. Lesiure travel. Travelling to relax and enjoy yourself.
Organisations that provide supporting services for tourists or travellers. Sustainability. The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Domestic, Outbound, Inbound and more.
When identifying travel keywords for your web content, there are three points to think about: Search Volume: The number of times users search a keyword in a month. The higher the search volume, the more web traffic you can potentially get from the keyword. Difficulty: Generally speaking, keywords with a higher search volume and commercial ...
See also: Upsell. adventure travel: a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion. affinity group: a group of people linked by a common interest or purpose. See also pre- formed group.
Here's how to use Google Keyword Planner. Access Google Keyword Planner by clicking on Go to Keyword Planner. Follow the prompts to set up a Google AdWords account. Don't worry, you won't have to run an advertising campaign to use the keyword tool. Select the box with Discover new keywords. Copy and paste your keywords separately into the ...
Use keyword research tools. There are various keyword research tools available that can help you identify relevant and popular keywords for your travel niche. These tools provide insights into search volume, competition, and related keywords, allowing you to make informed decisions about which keywords to target. 2. Analyze your competition.
One critical way to optimize your resume for ATS is to add keywords. Keywords are nouns or noun phrases that ATS algorithms "catch.". They help indicate to employers that the candidate has skills that match the job requirements. Common keywords include job titles, terms, tools, technologies, degrees, licenses, certifications, training ...
Study Flashcards On GCSE Geography Tourism Key Terms at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want! ... (approx. 200 words) Tourism can be known as a person's pursuit to travel and s... The Importance Of Community Tourism . Tourism, according to United Nation World Tourism ...
Sex tourism on its own is very complex and has been defined as tourism for which the main motivation or at least part of the main aim of the trip is to consummate or engage in commercial sexual relations, usually by people from rich countries to developing countries (Omondi, 2003; Ryan and Hall, 2001).Kong (2009) also acknowledges the difficulty in defining sex tourism emanating from its ...