An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Get Vaccinated Before You Travel
It’s important to plan ahead to get the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit.

Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by:
- Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip
- Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines
- Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family’s travel plans
Avoid getting sick or coming back home and spreading the disease to others.
Vaccinate at least a month before you travel
See your doctor when you start to plan your trip abroad. It’s important to do this well in advance.
- Your body needs time to build up immunity.
- You may need several weeks to get all the doses of the vaccine.
- Your primary doctor may not stock travel vaccines. Visit a travel medical clinic .
- You’ll need time to prepare for your pre-travel appointment .
- If the country you visit requires a yellow fever vaccine , only a limited number of clinics have the vaccine and will probably be some distance from where you live. You must get it at least 10 days before travel.
Find out which vaccines are recommended or required for the countries you plan to visit .
TIP : Save time by getting routine vaccines during the same doctor visit. Use the Vaccine Self-Assessment Tool and discuss the results with your doctor. It tells you which U.S. recommended vaccines you (19 years and older) or your child (birth – 18 years) might need.
Last-minute travelers
When traveling to another country be aware your doctor may not carry a travel vaccine and you may have to visit a medical clinic.
Many travel vaccines require multiple shots or take time to become fully effective. But some multiple-dose vaccines (like hepatitis A) can still give you partial protection after just one dose. Some can also be given on an “accelerated schedule,” meaning doses are given in a shorter period of time.
- Discover and learn about specific diseases that can affect you while traveling
- What to do if you get sick after traveling
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
About Us | Contact Us | Newsroom
Immunization for Travelers

If you plan to travel outside the United States, you may need vaccines to protect yourself against diseases that aren't common in the United States. For more information, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Travelers' Health website .
Check with your local pharmacy to ask if they offer travel vaccines. Your local health department may give travel vaccines or refer you to local travel vaccination clinics.
Yellow fever vaccine is only available at a yellow fever vaccine clinic , so call ahead (well in advance of travel) and book your appointment. You can protect yourself from yellow fever by getting vaccinated at least 10 days before travel and taking steps to prevent mosquito bites .
For current health issues at destinations that may impact you, visit the CDC Travel Notices webpage . For questions not answered on the CDC's website or our department website, call 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636) TTY 888-232-6348 . English and Spanish are available.
Health Issues
Yellow fever.
Find a location near you that gives yellow fever vaccine on CDC's Travelers' Health Yellow Fever Vaccination Clinics webpage .
Yellow fever vaccine is recommended for people age 9 months and older who are traveling to or living in areas at risk for yellow fever in South America and Africa . Some countries require travelers to show proof of yellow fever vaccination. Proof of vaccination is not valid until 10 days after you get the vaccine. Plan to get the vaccine early if you need it. A single dose provides lifelong protection for most people. For more information, go to the CDC's Travelers' Health Yellow Fever webpage .
- Yellow Fever Vaccine (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Yellow Fever information
- Frequently Asked Questions About Yellow Fever (CDC)
Travelers going to certain parts of Africa and Asia may be at risk for polio. Everyone should be up to date with their routine polio vaccination series . Travelers to certain countries also need a one-time adult polio vaccine booster dose. See individual destination pages for vaccine recommendation information.
For more information, go to the CDC's Travelers' Health Polio webpage .
Measles is highly contagious. Most measles outbreaks in the United States happen because infected travelers bring it back from other parts of the world. There are currently large outbreaks of measles in many countries.
Before international travel, make sure the following people are immunized against measles:
- Babies 6 months through 11 months of age should have 1 dose of measles vaccine.
- Children 12 months of age or older should have 2 doses separated by at least 28 days.
- Unvaccinated adolescents and adults should get 2 doses separated by at least 28 days.
For more information, go to the CDC's Travelers' Health Measles webpage .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is very common in many other countries outside of the United States. Travelers going to Central or South America, Mexico, Asia (except Japan), Africa, and Eastern Europe should get the hepatitis A vaccine.
If you are traveling:
- Start the hepatitis A vaccine series early for the best protection.
- Babies age 6 months and older should get the hepatitis A vaccine before travel outside of the U.S.
For more information on hepatitis A for travelers, go to the CDC's Travelers' Health Hepatitis A webpage . For more information on vaccines needed for your destination, see the CDC's Travelers' Health website .
Meningococcal Disease
Travelers going to Saudi Arabia to take part in Hajj or Umrah are required to get the meningococcal conjugate vaccine . The meningococcal vaccine is good for about five years. Consider other recommended vaccines if you are going on Hajj or Umrah, and traveling to other destinations.
Going For Hajj or Umrah? (PDF) flyer covers vaccination requirements, how to find a travel clinic, and a chart explaining 10 different vaccines and the 14 diseases they prevent. If you are planning to go on Hajj or Umrah, this flyer has important health information for you.
Travel agencies, clinics giving vaccines, mosques, and other agencies and organizations can share this flyer from the Department of Health to Washington residents planning a pilgrimage or travel to Saudi Arabia. Here is a version of the flyer that can be sent to a print shop to make copies.
- Care-a-Van Mobile Health Services
- Disability Organizations
- Drug User Health
- Food Safety
- Healthy Aging
- Healthy Home
- Illness and Disease
- Immunization
- Infants and Children
- Injury and Violence Prevention
- Men's Health
- Nutrition and Physical Activity
- Oral Health
- Poisoning and Drug Overdose
- Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Adolescents & Young Adults
- Women's Health
- Air Quality
- Climate and Health
- Contaminants
- Drinking Water
- Essentials for Childhood Initiative
- Health Equity
- Healthy Communities Washington
- Wastewater Management
- Water Recreation
- Worksite Wellness
- Facilities - New, Renew or Update
- File Complaint About Provider or Facility
- Healthcare Enforcement and Licensing Management System (HELMS)
- Healthcare Professional Credentialing Requirements
- Medical Commission
- Board of Nursing
- Professions - New, Renew or Update
- Provider Credential Search
- Veterans, Service Members and their Families
- Vital Records
- Data Guidelines
- Data Systems
- Data Topics A-Z
- Diseases and Chronic Conditions
- Environmental Health
- Health Behaviors
- Health Statistics
- Healthcare in Washington
- Injury Violence and Poisoning
- State Health Assessment
- Washington Tracking Network (WTN)
- Bioterrorism and Terrorism
- Emergency Information for Specific Groups
- Get Ready for an Emergency
- Severe Weather and Natural Disasters
- Emergency Contacts and Numbers
- Clinical Laboratory Reporting
- Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Systems
- Emergency Preparedness
- Healthcare Professions and Facilities
- Lactation and Infant Feeding-Friendly Environments
- Notifiable Conditions
- Public Health Laboratories
- Public Health System Resources and Services
- Rural Health
- Tribal Public Health and Relations
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Vietnam Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
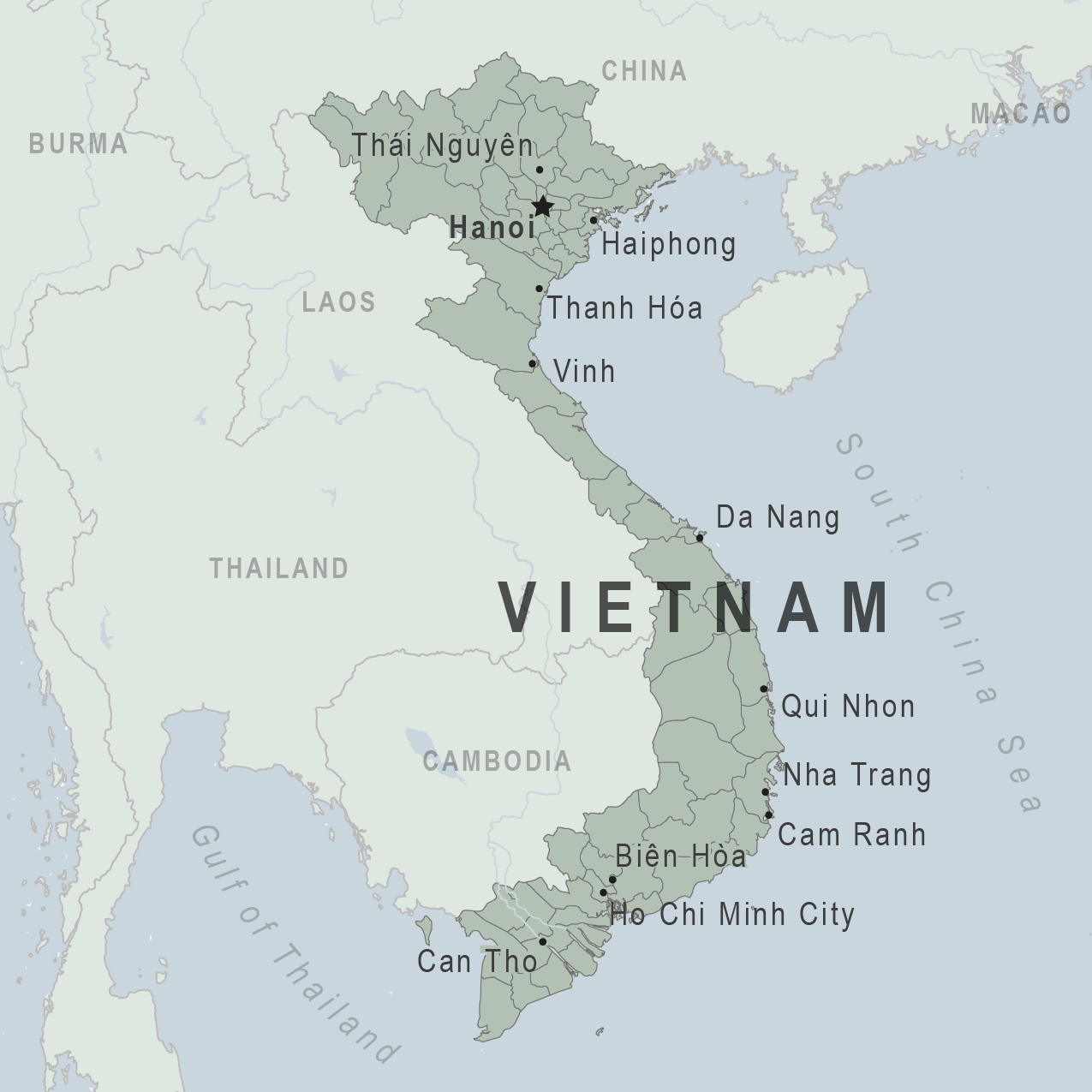
There are no notices currently in effect for Vietnam.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine

Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Vietnam.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Vietnam.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Vietnam take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Vietnam.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Vietnam. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Vietnam, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Vietnam.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Vietnam, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Vietnam. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Vietnam—such as dengue, Zika, and filariasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Vietnam include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Vietnam. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Vietnam’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Vietnam. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Vietnam may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Vietnam, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Vietnam, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Vietnam .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Vietnam, dial 115 for an ambulance, 114 for the fire department, and 113 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Vietnam before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Vietnam from the US Department of State
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Vietnam for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

US State Department Issues Updated Travel Guidance for Israel, the West Bank and Gaza
T he U.S. State Department has issued an updated travel advisory for Israel, the West Bank and Gaza amid the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas.
As of Thursday, Americans are advised to reconsider travel to Israel and the West Bank due to terrorism and civil unrest and avoid travel to Gaza entirely due to terrorism and armed conflict.
"The security situation remains unpredictable, and U.S. citizens are reminded to remain vigilant and take appropriate steps to increase their security awareness as security incidents, including mortar and rocket fire, often take place without warning," the State Department says of the current situation in the Middle East .
U.S. government employees in Israel under Chief of Mission security responsibility are restricted from personal travel within seven miles of the Gaza demarcation line; the cities of Ashdod and Ashkelon; within 2.5 miles of the Lebanese and Syrian borders and within 1.5 miles of the Israel-Egypt border.
It's been more than six months since Hamas launched a surprise attack on southern Israel, prompting heightened travel advisories from the U.S. State Department in Israel, the West Bank and Gaza in addition to a worldwide caution for all Americans traveling abroad.
"Due to increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests, the Department of State advises U.S. citizens overseas to exercise increased caution," officials warned last fall.
Travelers who do visit Israel, the West Bank or Gaza this spring are advised to avoid demonstrations or crowds, maintain a high level of situational awareness, exercise caution, check the most recent Embassy alerts, obtain travel medical insurance and enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive fast alerts and make it easier to be located in the event of an emergency.
After suspending operations last fall, major U.S. airlines are resuming service to Israel. United Airlines restarted service between Newark and Tel Aviv last month and Delta Air Lines will follow suit with service from New York's JFK to Tel Aviv on June 7.

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 31, 2023
Tanzania - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Tanzania due to crime, terrorism, and targeting of LGBTI persons . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Reconsider Travel To:
- Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania due to the threat of terrorism.
Country Summary : Violent crime, such as assault, sexual assault, robberies, mugging, and carjacking, is common. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious crime.
Terrorist groups could attack in Tanzania with little or no warning, targeting embassies, police stations, mosques, and other places frequented by Westerners. Please see the additional information below regarding the increased threat of terrorism in Mtwara Region.
Members of the LGBTI community have been arrested, targeted, harassed, and/or charged with unrelated offenses. Individuals detained under suspicion of same-sex sexual conduct could be subject to forced anal examinations.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Tanzania.
If you decide to travel to Tanzania:
- Always carry a copy of your U.S. passport and visa and keep original documents in a secure location.
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not leave your food or drink unattended.
- Stay alert in all locations, especially those frequented by Westerners.
- Avoid public displays of affection particularly between same-sex couples.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter.
- Review the Country Security Report for Tanzania.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania – Level 3: Reconsider Travel There have been reports of violence in Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania. Increased activity by extremists along the southern border has led to attacks against both government and civilian targets.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Yellow fever required if traveling from a yellow fever endemic country
Travelers are required to declare international currency valuing more than $10,000 on both entrance and exit from Tanzania. Non-residents (except Kenyans and Ugandans) may not import or export Tanzanian Shillings (TZS)
Non-residents (except Kenyans and Ugandans) may not import or export Tanzanian Shillings (TZS)
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy dar es salaam.
686 Old Bagamoyo Road, Msasani Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Telephone: +(255) 22-229-4000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(255) 22-229-4000, dial '1' for an emergency operator Fax: +(255) 22-229-4721 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visas are required for U.S. citizens traveling to Tanzania.
Foreign nationals may apply for a visa online in advance of travel. Applicants may complete the e-visa application form and make payment online with a credit card or bank transfer at www.immigration.go.tz . If the e-visa is approved, the applicant will receive a “grant notice” via email. Present a copy of the grant notice to the Immigration Officer on arrival at the airport in Tanzania.
U.S. citizens may also obtain a tourist visa upon arrival at the airport in Tanzania. The cost is $100 USD. Be prepared to pay in cash in case connectivity issues make electronic transactions impossible.
A passport valid for a minimum of six months beyond visa issuance and/or date of entry, and at least one blank visa page, is required. Visitors who enter on visas must present a roundtrip ticket and demonstrate they have sufficient funds for their stay.
Be prepared to show your passport and explain your visa status when entering or departing Zanzibar or when traveling around the mainland.
Volunteer activity – even if the traveler is paying for the opportunity – is prohibited on a tourist visa. If you plan to engage in business or commercial transactions in Tanzania, please consult with the Embassy of Tanzania in Washington, D.C. before applying for a visa.
Visit the Embassy of Tanzania website for the most current visa information. Read the page on visas and immigration to ensure you will have the correct status during your visit to Tanzania.
For information on obtaining a residence permit, please see the Tanzanian Immigration Department's Ministry for Home Affairs website or contact them by phone: Dar es Salaam: +255 (0) 22 2850575/6 Zanzibar: +255 (0) 24 223 9148
Yellow fever vaccination is required for all travelers arriving from, or having transited through, countries where yellow fever is endemic. Direct arrivals from non-endemic countries, including all countries in Europe and North America, are usually not required to show a yellow fever vaccination certificate. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) provides additional information about recommended vaccines and medications for travelers going to Tanzania. The CDC notes there are reports that unless a traveler has a medical exemption letter from a physician, some immigration officials require evidence of the vaccine for entry in Tanzania – particularly entry via Zanzibar – from all travelers. Travelers with neither the shot nor an exemption letter are usually allowed entry and directed to a health officer to obtain the vaccine. The CDC recommends that travelers staying for an extended time or those who will be heavily exposed to mosquitoes consider obtaining the vaccination before visiting Tanzania.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Tanzania.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Currency Restrictions: Travelers are required to declare international currency valuing more than $10,000 on both entrance and exit from Tanzania. Non-residents (except Kenyans and Ugandans) may not import or export Tanzanian Shillings (TZS.)
Safety and Security
Terrorist incidents, including the 1998 bombings of the U.S. Embassies in Dar es Salaam and Nairobi, as well as occasional attacks by extremists on police stations and mosques, among other targets, highlight the threat posed by terrorism in East Africa and underscore the capacity of terrorist groups to carry out such attacks against Westerners.
U.S. citizens should exercise caution when traveling between Julius Nyerere International Airport and Dar es Salaam, as there have been incidents of robberies while cars are stopped at traffic lights and kidnappings. Drivers should lock their doors and keep windows up at all times.
Crime: U.S. citizens are urged to exercise caution and stay current with media coverage of local events. Report crimes to the closest police station and request a copy of the report to use for any insurance claims.
Muggings, Robberies, and Assaults:
Robberies are common in Tanzania. U.S citizens become victims when they hail taxis at airports, bus stations, hotels, or on the street. Victims are held until they provide passwords for credit/debit cards and are driven around town to deplete their accounts at all available ATMs. Victims are usually released hours later. A number of people have been victimized en route to the airport. To minimize risk, travelers should use marked or known modes of transport. They should also consider leaving ATM cards at home and traveling to Tanzania with a minimal number of credit cards.
- Stay alert when walking on beaches, footpaths, and roads; especially on Zanzibar, in Dar es Salaam, and Arusha.
- Avoid carrying a bag, wearing flashy jewelry, or using personal electronics while in public.
- If you must carry a bag, hold it by the handle loosely so you can let go quickly and not be injured if someone in a passing vehicle attempts to grab it. Do not put the strap across your chest as you can be dragged and badly injured.
- While on safari, visiting parks, hiking, or mountain climbing, remain alert to your surroundings and report anything unusual to your tour guide, park ranger, or the police.
- If someone attempts to rob you, hand over all your valuables immediately, comply with the demands, and do not make eye contact with the aggressors.
ATM/Bank Fraud: To reduce your vulnerability:
- Minimize the amount of cash you carry.
- Avoid using stand-alone ATMs.
- Monitor your account balance regularly and immediately report unusual activity.
- Avoid using debit cards if possible.
- If you will be spending time outside of the large cities, have sufficient cash or traveler’s checks for your trip.
Reputable financial institutions will require the bearer of a traveler’s check to present the original receipt for the checks and proof of identity before completing a transaction.
If a public official attempts to solicit the payment of a fine from you, ask to travel to the nearest police station to file a report regarding the incident. Obtain a receipt and a written report of any such transactions. If your passport is seized, ask for a receipt, note the officer’s name, location, and contact details and report it immediately to the U.S. Embassy.
Home Invasions: U.S. citizens residing in Arusha and Dar es Salaam frequently report crimes targeting the homes of expatriates. Armed home invasions usually involve some violence and some victims have been seriously injured.
- If you live in Tanzania, ensure that your home has a safe haven, a secure area with reinforced barriers, where you can retreat and remain safe if intruders enter.
- A professional security company with 24-hour guards and roving patrols as well as the use of house alarms can help mitigate risks.
Carjackings: To avoid carjackings:
- Drive with doors locked and windows rolled up.
- Do not stop in unpopulated areas.
- Travel in convoys if possible.
- Be wary of drivers of stopped cars flagging motorists down for assistance.
Dar es Salaam: Exercise caution in the Coco Beach area of Touré Drive, the scenic beachfront road leading from the Sea Cliff Hotel into town, on Msasani Peninsula. This road is a concern any time of day or night, whether you are on foot or in a vehicle. There are regular reports of muggings, pick-pockets, and thefts from cars.
Walking or jogging on the streets at any time can be hazardous because motorists can be careless, pathways abruptly end, and there are frequently no shoulders.
Zanzibar: Beware of pickpocketing, assaults, and bag snatching in Zanzibar. Wear modest dress and keep a low profile, especially on Friday afternoons, the traditional time to attend mosque.
Arusha: In Arusha, the high number of foreign tourists attracts pickpockets and bag snatchers. You are strongly discouraged from walking around at dusk or at night, and encouraged to avoid the section of Arusha on the far side of the Themi River at all times when on foot. Many muggings have occurred near the clock tower in the center of town.
Tanga: Criminals use the Amboni Caves north of Tanga City to hide from authorities. Police and military raid the cave system to apprehend criminals. Additionally, armed robberies in the shopping establishments of the Mzizima Ward of Tanga Rural District are common.
Mwanza: Violence and attacks by armed groups in and around the city of Mwanza have increased. You should remain alert and avoid large gatherings when travelling to Mwanza.
Pwani coastal region: Following an uptick in violence in April 2017, Tanzanian authorities have increased their security presence in the Pwani coastal region, about 100km south of Dar es Salaam. Additional checkpoints are in place, particularly on highways and in towns.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
VICTIMS OF CRIME:
U.S. citizen victims of crime should report crimes to the local police at 111 and contact the U.S. Embassy at 255 22 229 4122 and at 255 22 229 4000, dial ‘1’ for an emergency operator.
Sexual Assault: Sexual assault is a risk for U.S. citizens, especially for women travelers. Victims of sexual assault should see a doctor immediately to ask about the availability of post-exposure HIV prophylaxis or other necessary medical care. They should also report crimes to local police at 111 and may contact the U.S. Embassy at 255 22 229 4122 and at 255 22 229 4000, dial ‘1’ for an emergency operator.
- Avoid drinks given to you by strangers and do not leave your drink unattended
- Avoid walking after sunset, especially alone
- Be careful about sharing travel plans as well as personal and social media information
Some police stations in Dar es Salaam (such as Oysterbay and Selander Bridge) offer a special desk for tourists to report crimes. However, they have limited daytime hours. In general, police stations may not have an English speaker available or be staffed to make a written report even during opening hours.
Local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- help you find appropriate medical care
- assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- provide a list of local attorneys
- provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not consistently occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities and to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned.
Penalties for possession or sale of illegal drugs of any kind are severe in Tanzania, with a minimum sentence of seven years imprisonment for simple possession and 30 years to life for more serious charges.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately.
Photography: Photographing military installations is forbidden. Individuals have been detained and/or had their cameras and film confiscated for taking pictures of hospitals, schools, bridges, industrial sites, and airports. Sites where photography is prohibited are not always marked.
Animal products: In Tanzania, it is illegal to export an animal or animal part (including live or dead animal parts, such as skins, bones, teeth, and feathers) without export certification from the Tanzanian government. It is also illegal to export any such products received as a gift or exchange without the correct documentation. The penalties can range from a fine and/or two to five years imprisonment. Additionally, it is illegal to gather, collect, or remove flora or fauna, including seashells and ebony or mpingo wood. Penalties include a fine and/or imprisonment of up to two years.
Safaris: Remember that the animals you encounter on safaris are wild. Their reflexes and reaction times are quicker than those of trained guides. Critically review and assess the protection measures offered by safari companies. Stay in vehicles or protected enclosures when in game parks.
If you have chronic health problems, consider the risks before joining an extended trip in the African wilderness where emergency medical help is not readily available.
- Know the signs of altitude sickness.
- Heed the advice of the professionals organizing the ascent.
- Don't try to save money by selecting a tour guide who offers a faster ascent - your body needs adequate time to acclimate to the altitude.
- If you experience altitude sickness, descend immediately and seek medical help.
What to Wear: While visiting Tanzania, you should dress modestly (upper arms and legs covered and no exposed midriffs) outside of the hotel or resort and when arriving and departing from Zanzibar.
Ramadan: During the holy month of Ramadan, when Muslims fast during daylight hours, avoid eating, drinking, smoking, or chewing gum in public except in hotels or restaurants.
Scams: U.S. citizens have been victims of scams involving the alleged sale of gold, diamonds, gemstones, minerals, and other natural resources. You should be very cautious of seemingly lucrative business opportunities offered by agents based in, or with ties to, Tanzania and neighboring countries.
There are also scams involving offers to arrange volunteer visas and safari excursions. Vet anyone offering to provide you such a service and check their references carefully.
Faith-Based Travelers: See our following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Rights: Tanzania’s penal code criminalizes consensual same-sex sexual activity on the mainland and on Zanzibar. Those arrested and charged for consensual same-sex sexual conduct may be sentenced up to thirty years in prison. Authorities use the penal code to intimidate and arrest individuals on the basis of their real or perceived sexual orientation or gender identity. Individuals detained under suspicion of same-sex sexual conduct may be subject to or threatened with forced anal examinations. Members of the LGBTI community may be denied entry to Tanzania by immigration authorities (including on Zanzibar) or once admitted may be targeted, harassed, and/or charged with unrelated offenses. Public displays of affection between persons of the same sex may be met with harassment or violence. Non-governmental organizations that support the LGBTI community and their staff may also be targeted, harassed, or have staff members detained by local authorities.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance: Individuals with disabilities may find accessibility and accommodation challenging to find in Tanzania. Sidewalks are nearly non-existent and there are frequent power outages. The Tanzanian constitution prohibits discrimination against persons with disabilities.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Hire only legitimate tour guides, preferably arranged by a known travel agency or hotel. Be wary of offers of sightseeing from new contacts and avoid being alone with strangers who propose special, customized sightseeing trips. Practice common sense and remain vigilant regarding your surroundings.
If you are the victim of sexual assault, see your doctor immediately to ask about the availability of post-exposure HIV prophylaxis or seek medical care outside of Tanzania if needed. Feminine hygiene products can be difficult to obtain, particularly outside of large cities.
See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare does not apply overseas.
Click here to access the list of medical facilities in Tanzania from the Embassy website.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
- Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Although Tanzania typically only requires yellow fever shots for those traveling from an endemic country, there are occasional reports of officials requiring yellow fever shots from all foreign travelers.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Road travel in Tanzania can be extremely dangerous, especially at night. Traffic in Tanzania moves on the left. Drivers and pedestrians alike must maintain vigilance. Although a number of inter-city highways are periodically repaved and maintained, maintenance schedules are erratic and even good roads may deteriorate quickly due to weather conditions.
During the rainy seasons (late March to mid-June and mid-November to mid-December), many roads in Tanzania, both urban and rural, are passable only with four-wheel-drive vehicles.
Traffic Laws: Tanzanian law requires all motor vehicle operators to be in possession of a valid driver’s license. Persons staying in Tanzania for fewer than six months may use a valid U.S. driver’s license after validation by local traffic authorities, or an international driver’s license. Persons intending to remain in Tanzania for more than six months are required to obtain a Tanzanian driver’s license. All vehicles are required to carry third-party liability insurance and to post the decal in the front window.
Public Transportation: Use taxis or hire a driver from a reputable source. When traveling by taxi:
- Do not ride in a taxi hailed by someone you do not know.
- Ask the hotel or restaurant to recommend a driver. Before entering the vehicle, ask the driver to see their credentials, take a picture of the taxi license plates, and send the photo to a friend.
- Make sure the child locks are not engaged and the door can be opened from the inside.
- After entering, lock the doors and roll up the windows. If the driver unlocks the doors or rolls down the windows, exit immediately.
- Do not ride in taxis already carrying a passenger. If a taxi stops to allow another person to enter, exit immediately.
Travelers should also avoid using dala-dala microbuses and bajaji, three-wheeled taxis.
Ferries traveling between the mainland and Zanzibar may be unsafe. When traveling by ferry:
- Travel on a high-speed ferry.
- Purchase your tickets inside the ferry terminal, from a travel agency, or online in advance, not from vendors outside.
- Tickets should include your name, date of travel, and class of travel.
- Travel during daylight with good visibility, fair weather, and calm water.
- Avoid overcrowded vessels or those which lack sufficient life vests, easy access to exits, and a functioning communications system.
- Become familiar with emergency procedures on board, especially the locations of life jackets and emergency exits.
- Beware of pickpockets aboard the ferry, and be wary even of uniformed personnel who seek to assist you.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Motorcycles: Riding motorcycles is not advisable and is restricted in some areas.
Aviation Safety Oversight: As there is no direct commercial air service to the United States by carriers registered in Tanzania, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has not assessed the government of Tanzania's Civil Aviation Authority for compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards. Further information may be found on the FAA's safety assessment page.
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Tanzania should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts at www.marad.dot.gov/msci . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website and the NGA broadcast warnings website (select “broadcast warnings”).
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Tanzania . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Adoption Notices
Travel advisory levels, assistance for u.s. citizens, tanzania map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Rotavirus. Rubella. Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids. Varicella. In order to assist the panel physican, and to avoid delays in the processing of an immigrant visa, all immigrant visa applicants should have their vaccination records available for the panel physician's review at the time of the immigrant medical examination.
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Here is a list of possible vaccines that you may need to get for the first time or boosters before you travel. COVID-19. Chickenpox. Cholera. Flu (Influenza) Hepatitis A. Hepatitis B. Japanese encephalitis.
These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. ... Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver's License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers ...
U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories. COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
Call your doctor or local health department to see if they can provide pre-travel advice, vaccines, and medicines. List of health departments. Travel Medicine Clinics. If you want to see a travel medicine specialist, the International Society of Travel Medicine (ISTM) can help you find a clinic.
Your local health department may give travel vaccines or refer you to local travel vaccination clinics. Yellow fever vaccine is only available at a yellow fever vaccine clinic, so call ahead (well in advance of travel) and book your appointment. You can protect yourself from yellow fever by getting vaccinated at least 10 days before travel and ...
Review the state.gov Travel Advisory for Chile; Check with airlines and transit/destination countries for how COVID testing and vaccine requirements might impact travel; Assistance: U.S. Embassy Santiago, Chile. Phone number: +56 2 2330 3716 (8:30 A.M. to 5:00 P.M) and +56 2 2330 3000 (After business hours) Email address: [email protected]
Credit: WTHR. Dr. Christopher Belcher details the health benefits of scheduling a travel medicine appointment. Staying up-to-date on regular vaccines and taking preventive measures against malaria and Salmonella exposure are crucial steps. Though vaccinations like the typhoid shot may cause momentary discomfort, they offer vital protection ...
Consider vaccination for travelers. ... You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety. Hide. Prevent bug bites. Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Vietnam. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine.
Special Representative for Commercial and Business Affairs Morgenthau's Travel to Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. April 5, 2024. Remarks. Secretary Antony J. Blinken Remarks to the Press. Antony J. Blinken April 5, 2024 Brussels Melsbroek Airport Brussels, Belgium. Media Note. Joint Statement on the U.S.-Spain Central America Working Group.
The U.S. State Department has issued an updated travel advisory for Israel, the West Bank and Gaza amid the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas. As of Thursday, Americans are advised to ...
TOURIST VISA REQUIRED: Yes. VACCINATIONS: Yellow fever required if traveling from a yellow fever endemic country. CURRENCY RESTRICTIONS FOR ENTRY: Travelers are required to declare international currency valuing more than $10,000 on both entrance and exit from Tanzania. Non-residents (except Kenyans and Ugandans) may not import or export ...
Pet Travel. Take a Pet From the United States to Another Country (Export) Bring a Pet From Another Country into the United States (Import) Take a Pet From One U.S. State or Territory to Another (Interstate) USDA-Accredited Veterinarians: Certifying Pets for International Travel; Traveling With Food or Agricultural Products
The United States led an international and coordinated effort to accelerate access to safe and effective vaccines to meet global needs. Between May 2021 and February 2024, the United States donated more than 692 million vaccine doses to 117 countries and economies, in partnership with COVAX, Caricom, AVAT, and bilaterally. We donated hundreds of millions […]
Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken will attend the G7 Foreign Ministers Meeting in Capri, Italy from April 16-19. This meeting will bring together the Foreign Ministers of Italy, Canada, France, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union to discuss common efforts to shape a free, secure, and prosperous world. The Secretary looks forward to discussions ...