
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Chapter 16 Hospitality and Tourism
Learning objectives.
- Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance.
- Understand the economic, social, and environmental benefits and costs of tourism.
- Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition.
- Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined.
- Examine the different categories of food service operations.
- Understand the different types of events, meetings, and conventions.

The tourism industry is often cited as the largest industry in the world, contributing 10 percent of the world’s GDP. In 2016 there were over 1.2 billion international tourists: that’s a substantial economic impact and movement of goods and services! [1] Tourism is also considered an export and is unique in that the consumers come to the product where it is consumed on-site. Before we dig any deeper, let’s explore what the term “tourism” means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
A social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure. [2]
In other words, tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure). It is important to understand the various groups and constituencies involved in this movement. Of course it includes the tourist, but also the vast array of businesses providing goods and services for the tourist, the government and political structure of a destination, and the local residents of the destination community itself. Each of these components are necessary parts of a successful tourism destination and operate within private and public sectors, the built environment, and the natural environment. All these come together to create the processes, activities, and outcomes of tourism.
If it all seems a little overwhelming, it might be helpful to break tourism down into broad industry groups, each of which will be covered in this chapter:
Accommodation and Lodging
- Food and Beverage Services (F & B)
Recreation and Entertainment
- Convention & Event Management
Travel Services
- Private Clubs
Benefits and Costs of Tourism
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations. Some impacts gain more attention than others. It is also important to recognize that different groups and constituencies are impacted differently.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The tourism industry has a huge economic impact that continues to expand to new markets and destinations. According to the UNWTO, in 2016 “The total export value from international tourism amounted to US$ 1.5 trillion.” [3] Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned (2016 vs 2015) are Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Americas Europe. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report. As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 20 3 0 Vision report predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.8 billion by 2030. [4] Figure 16.2 provides additional information about the impact of tourism worldwide.

Positive impacts from this economic boom include robust foreign exchange, increases in income, and GDP growth. Tourism can also offer diverse employment opportunities, can be developed with local products, and is often compatible with other economic activities within a destination. Tourism often injects money into the community that leads to secondary economic development as well. For example, successful resorts may create the need for a commercial laundry facility or a pet boarding business.
However, there are also negative impacts. Property values may increase to the point of unaffordability for local residents, and the seasonality of the tourism industry may create a feast-or-famine economy. As with any economy, if too many resources are focused on just one industry, communities may be vulnerable to any unexpected economic, social, or environmental changes. One example is the New Jersey shore after the devastation of Hurricane Sandy in 2012. The tourism industry was severely impacted, leaving no economic fallback for local residents.
Social Impacts of Tourism
In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts, culture, heritage and tradition, celebration of indigenous communities, and community pride. Tourism also has the potential to break down language, socio-cultural, religious, and political barriers. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents and promotes a positive image of the destination.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme, negative social impacts of tourism can include: change or loss of indigenous identity and values; culture clashes; changes in family structure; conflict within the community for the tourism dollar; and ethical issues, including an increase in sex tourism, crime, gambling, and/or the exploitation of child workers. [5]
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. In some destinations, there is a great appreciation of the environmental resources as the source of the tourism industry, and as such there are environmental protection policies and plans in place. Tourism has helped to save many delicate ecosystems and their flora and fauna. Preservation of these important resources benefits not only the tourist but also the local residents as well.
Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can still have severe negative economic impacts. According to The United Nations Environment Programme, these can include the depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.), pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering), and physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity, and spread of disease). [6]
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach beyond local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is often identified as a major contributor to climate change.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate.
The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves.” [7] Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry.

The pineapple has long been the symbol of hospitality. The Caribs, indigenous people of the Lower Antilles in the Caribbean, first used it as such a symbol. The Spaniards knew they were welcome if a pineapple was placed at the entrance to the village. This symbolism spread across Europe and North America where it became the custom to carve the shape of a pineapple into the columns at the entrance of the plantation. [8] Charles Carter added a three and a half foot wooden pineapple to the peak of the roof at Shirley Plantation, the first plantation in Virginia. [9] It is now common to see the image of the pineapple as a sign of welcome, warmth and hospitality.
The types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business—whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground—are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation and lodging . Figure 16.4 summarizes the various groupings within the industry.
Hotel Types
Hotels are typically referred to by hotel type or other classifications. Hotel type is determined primarily by how it will function and what amenities will be included within the property. Size, location, service levels and type of business or targeted market segments are additional classifications. Industry also classifies hotels by chain scale … separating hotels into categories determined by their average daily rates. Various ownership structures and brand affiliations also differentiate hotels.
Classifications
Hotels may be classified on a number of different variables. Type of Hotel : There are numerous classifications by hotel type including all-inclusive hotels, all-suite properties, B&B/Inns, boutique, convention/conference centers, condo hotels, resort, extended stay, full service, casino, limited service and timeshare properties. Size and Complexity: A hotel can be classified by the number of guest rooms it has; hotel sizes can range from a small boutique hotel with fewer than 50 rooms to a large resort hotel with more than 1,000 rooms. The complexity of the hotel is determined by the volume and number of additional revenue generating functions such as the square feet of available conference space, number of F&B operations and additional services and amenities like pools, fitness centers, spas, golf, etc. Location: The location of a hotel can also determine the type of guest served. An airport hotel may be very different from a city-center property in an urban environment, or a remote island resort or a small quaint bed and breakfast located on top of a mountain. Hotels that specialize in conferences, may locate near entertainment destinations like Las Vegas or Disney theme parks to provide pre-post conference activities for attendees. Service Level: The level of service provided is also a key variable, ranging from an inexpensive budget or economy hotel, (Limited or Focused Service Hotels) which may have limited services and amenities, to upscale and luxury hotels (Full Service Hotels) with many services and a wide range of amenities. Market Segmentation: Figure 16.5 on the next page outlines the characteristics of specific hotel types that have evolved to match the needs of a particular traveler segment. As illustrated, hotels adapt and diversify depending on the markets they desire and need to drive occupancy levels and generate revenues. Some hotels will specialize in a specific market segment, but in today’s competitive environment, most hotels will target a combination of these segments.
There are several other industry related organizations, such as Forbes and AAA which provide Consumer Ratings for individual hotels … another form of classifying a property. Forbes has traditionally awarded one to five “Stars” and AAA, one to five “Diamond” ratings. Additionally, many social media applications like Trip Advisor offer hotel property ratings to consumers.
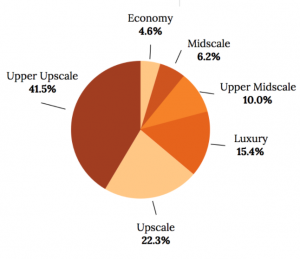
Chain Scale: Smith Travel Research (STR) is an organization that provides the lodging industry with global data benchmarking, analytics and marketplace insights. STR classifies the lodging industry into six chain scale segments according to their respective brand Average Daily Rate (ADR). The six segments are defined as Luxury ; Upper Upscale ; Upscale ; Mid-Scale with F&B ( Upper Mid-Scale ); Mid-Scale without F&B ( Mid-Scale ) and Economy . Through STR’s 30—plus years of service to the hospitality industry—they have developed vital benchmarking performance solutions, established market trend transparency and provided data used by the investment community to support hotel development projects. Their core product, the STAR report, provides hotel owners and operators with comparative performance data between their property and a defined set of market competitors and allows you to follow trends in hotel occupancy, average daily rate (ADR) and revenue per available room (RevPar). Developers, investors, industry analysts, hotel brands and management companies all utilize STR data when determine what type of hotel to build and what location would provide maximum opportunity for success.
The type of ownership, brand affiliation and management are also very important variables in the classification of hotels. Owners may manage their own hotels independently but in today’s competitive environment, they would likely sign a Franchise Agreement with a nationally recognized brand as well as a Management Contract with a hotel management company to manage the property. A hotel chain such as Marriott, Hilton, Hyatt or IHG (Intercontinental Hotel Group) is comprised of multiple brands: Marriott, following their recent merger with Starwood currently has 30 different hotel brands, with each name representing a different level of price, service or targeted market segments.
Branding Decision
Selecting a brand affiliation is one of the most significant decisions hotel owners must make. [10] The brand affiliation selected will largely determine the cost of hotel development or conversion of an existing property to meet the standards of the new brand. The affiliation will also determine a number of things about the ongoing operation including the level of services and amenities offered, cost of operation, marketing opportunities or restrictions, and the competitive position in the marketplace. For these reasons, owners typically consider several branding options before choosing to operate independently or to adopt a brand affiliation.
Franchise Agreements
Another managerial and ownership structure is franchising. A hotel franchise enables individuals or investment companies (the franchisee) to build or purchase a hotel and then buy or lease a brand name to become part of a chain of hotels using the franchisor’s hotel brand, image, loyalty program, goodwill, procedures, cost controls, marketing, and reservations systems. [11]
A franchisee becomes part of a network of properties that use a central reservations system with access to electronic distribution channels, regional and national marketing programs, central purchasing, revenue management support, and brand operating standards. A franchisee also receives training, support, and advice from the franchisor and must adhere to regular inspections, audits, and reporting requirements.
Selecting a franchise structure may reduce investment risk by enabling the franchisee to associate with an established hotel company. Franchise fees can be substantial, and a franchisee must be willing to adhere to the contractual obligations with the franchisor. [12] Franchise fees typically include an initial fee paid with the franchise application and continuing fees paid during the term of the agreement. These fees are usually a percentage of revenue but can be set at a fixed fee. The total percentage of sales ranges significantly for hotels from 3.3–14.7 percent with a median of 11.8 percent. [13]

Management Contracts
It is common for ownership to utilize a management contract , which is a service offered by a management company to manage a hotel or resort for its owners. Owners have two main options for the structure of a management contract. One is to enter into a management agreement with an independent third-party hotel management company to manage the hotel. There are hundreds of these companies, but some of the large organizations include Aimbridge, Benchmark Hospitality, Crescent Hotels, Interstate Hotels, and White Lodging. A slightly different option is for owners to select a single company to provide both the brand and the expertise to manage the property. Marriott, Hilton, and Hyatt, are companies that provide this second option to owners.

Food and Beverage Services

The food and beverage sector is commonly known to industry professionals by its initials F&B. The F&B sector grew from simple origins to meet the basic needs for food and beverage services to increasing demand for unique experiences and broader options. As the interests of the public became more diverse, so too did the offerings of the F&B sector. The increasing awareness and demand for organic, sustainable, local or craft options as well as special dietary needs in food and beverage continue to challenge this industry. In addition, in order to better attract and serve a diverse array of diners, the F&B industry now consists of a variety of segments. The following is a discussion of each.
Quick-Service Restaurants
Formerly known as fast-food restaurants, examples of quick-service restaurants , or QSRs, include Chick-fil-A, Subway, and Pizza Hut. This prominent portion of the food sector generally caters to both residents and visitors, and it is represented in areas that are conveniently accessed by both. Brands, chains, and franchises dominate the QSR landscape. While the sector has made steps to move away from the traditional “fast-food” image and style of service, it is still dominated by both fast food and food fast; in other words, food that is purchased and prepared quickly, and generally consumed quickly as well.

Fast-Casual Restaurants
Fast-Casual restaurants focus on higher quality ingredients than QSR’s and provide made-to-order food in an environment that does not include table service. Customers usually queue and order at a counter. The seating area is more upscale and comfortable. Examples would include Chipotle Mexican Grill, Panera and Jason’s Deli.

Full-Service Restaurants
Full-service restaurants are perhaps the most fluid of the F&B operation types, adjusting and changing to the demands of the marketplace. Consumer expectations are higher here than with QSRs. [14] The menus offered are varied, but in general reflect the image of the restaurant or consumer’s desired experience. Major segments include fine dining, family/casual, ethnic, and upscale casual. Fine dining restaurants are characterized by highly trained chefs preparing complex food items, exquisitely presented. Meals are brought to the table by experienced servers with sound food and beverage knowledge in an upscale atmosphere with table linens, fine china, crystal stemware, and silver-plate cutlery. The table is often embellished with fresh flowers and candles. In these businesses, the average check, which is the total sales divided by number of guests served, is quite high (often reviewed with the cost symbols of three or four dollar signs: $$$ or $$$$.) Examples include the Inn at Little Washington, Ruth’s Chris Steakhouse and Capitol Grille.

Casual restaurants serve moderately-priced to upscale food in a more casual atmosphere. Casual dining comprises a market segment between fast casual establishments and fine dining restaurants. Casual dining restaurants often have a full bar with separate bar staff, a larger beer menu and a limited wine menu. This segment is full of chains such as Chili’s, Outback, Red Robin and Cracker Barrel as well as many independent restaurants in regional or local markets.
Family restaurants offer affordable menu items that span a variety of customer tastes. They also have the operational flexibility in menu and restaurant layout to welcome large groups of diners. An analysis of menus in family/casual restaurants reveals a high degree of operational techniques such as menu item cross-utilization, where a few key ingredients are repurposed in several ways. Both chain and independent restaurant operators flourish in this sector. Examples of chains in this category would be Golden Corral, Cici’s Pizza and Ponderosa Steakhouse.
Ethnic restaurants typically reflect the owner’s cultural identity, Vietnamese, Cuban, Thai, etc. The growth and changing nature of this sector reflects the acceptance of various ethnic foods within our communities. Ethnic restaurants generally evolve along two routes: toward remaining authentic to the cuisine of the country of origin or toward larger market acceptance through modifying menu items. [15] Examples would be P.F. Chang’s, Tara Thai or Pei Wei.
Bars, Wineries, and Craft Distilling
The beverage industry continues to evolve as well with a strong focus on local craft beers, wines, cider and distilling. Wineries exist in almost every state, with over 250 in Virginia as of 2015. [16] Wine, bourbon, cider trails and brew pub crawls, etc. are used to generate awareness and create experiences for customers. Wineries often use event space or festivals to take advantage of the beauty of the winery and supplement their revenues.
Institutional Food Service
Institutional f ood s ervice is large scale and often connected to governmental (National Parks) or corporate level organizations. Often run under a predetermined contract, the institutional F&B sector includes:
- Educational institutions
- Prisons and other detention facilities
- Corporate staff cafeterias
- National Park restaurants and concessions
- Cruise ships
- Airports and other transportation terminals and operations
Examples of companies who focus on Institutional Food Service are Compass, Sodexho, Aramark.
Accommodation Food Service
This sector includes hotel restaurants and bars, room service, and self-serve dining operations (such as a breakfast room). Hotel restaurants are usually open to the public and reliant on this public patronage in addition to business from hotel guests. Collaborations between hotel and restaurant chains have seen reliable pairings such as the combination of Shula’s Steakhouse and Marriott Hotels.
Restaurant Industry Profitability and Cost Control
According to the National Restaurant Association, QSRs have the highest pre-tax profit margin at 6.3 percent, while full-service restaurants have a margin of 4.7 percent. There will be significant variances from these percentages at individual locations, even within the same brand. [17]
A number of costs influence the profitability of an F&B operation. Some of the key operating expenses (as a percentage of revenue) are detailed in Figure 16.16, above, where food cost and salaries & wages are the two major expenses, each accounting for approximately a third of the total. Other expenses include rental and leasing of venue, utilities, advertising, and depreciation of assets. These percentages represent averages, and will vary greatly by sector and location.
Cost control and containment is essential for all F&B businesses. Demanding particular attention are the labor, food, and beverage costs, also known as the operator’s primary costs. In addition to these big ticket items, there is the cost of reusable operating supplies such as cutlery, glassware, china, and linen in full-service restaurants.
Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one’s spare time [19] and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however, is more challenging.
Let’s start by exploring some recreation-based terms that are common in the tourism industry. Outdoor recreation can be defined as “outdoor activities that take place in a natural setting, as opposed to a highly cultivated or managed landscape such as a playing field or golf course.” [20] This term is typically applied to outdoor activities in which individuals engage close to their community. When these activities are further away, and people must travel some distance to participate in them, they are often described as “adventure tourism”. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), adventure tourism is “a trip that includes at least two of the following three elements: physical activity, natural environment, and cultural immersion.” [21]

Ultimately, categorization is based on a combination of several factors, including manner of engagement in the activity (risk exposure, experience requirement, group or solo activity), the distance travelled to access the activity, and the type of environment (proximity to nature, level of challenge involved) in which the activity occurs.
A 2013 adventure tourism market study discovered that people who travel for adventure experiences tend to be well-educated, with 48 percent holding a four-year degree or higher credential. They value natural beauty and rank this factor highest when choosing a destination. The most cited reasons for their travel are “relaxation, exploring new places, time with family, and learning about different cultures.” [22]
Globally, it is estimated that the continents of Europe, North America, and South America account for 70 percent of adventure tourism, or US$263 billion in adventure travel spending. [23]
Entertainment
Entertainment is a very broad category which overlaps with many of the areas discussed elsewhere in this chapter, like hotels and accommodation. Two major types of entertainment that we’ll discuss here are gaming and theme parks.
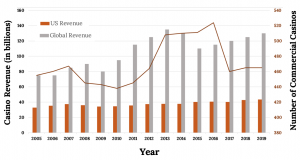
Gaming has grown significantly in the United States and globally. The number of casinos in the United States has been growing since 2010, and in 2013, there were over 500 commercial casinos, as shown in Figure 16.16. Casinos are found all over the United States in major cities, riverboats, and on Native American lands. However, US casino revenue has been relatively flat, while global gaming revenues have been on the increase, largely due to Asian market growth. Most casinos involve other facets of the Hospitality industry such as lodging, F&B, golf, entertainment, spas, etc., but they also have the added challenges of casino operations.
Theme Parks
Theme parks have a long history dating back to the 1500’s in Europe, and have evolved ever since. Today, it is hard not to compare any amusement park destination to Disneyland and Disney World. Opened in 1955 in sunny California, Disneyland set the standard for theme parks. Theme parks outside of California and Florida are often highly seasonable operations challenged with significant staffing and training requirements each year.

Convention and Event Management
A convention is a large meeting of people with similar interests who meet for a period of at least a few days to discuss their field. An event is a gathering at a given place and time, usually of some importance, often celebrating or commemorating a special occasion.
Both conventions and events can be extremely complex projects, which is why, over time, the role of meeting planners has taken on greater importance. The development of education, training programs, and professional designations such as CMPs (Certified Meeting Planners), CSEP (Certified Special Events Professional), and CMM (Certificate in Meeting Management) has led to increased credibility in this business and demonstrates the importance of the sector to the economy.
Meeting planners may be independent contractors hired to facilitate the planning process, work directly for the company full time to coordinate their meeting, or work for hotels, conference centers and event venues directly.
- The various tasks involved in meeting and event planning include:
- Conceptualizing/theming
- Site inspection & selection
- Logistics and planning
- Human resource management
- Marketing and public relations
- Budgeting and financial management
- Sponsorship procurement
- Management and evaluation
Event Categories
Mega-events.
A m ega-event is a large scale, highly prestigious event such as the Olympic Games, the FIFA World Cup, or a global economic summit. These events typically gain tremendous media coverage and have major economic impacts on the host location, both positive and negative. High levels of tourism (1 million visitors) associated with a mega-event brings revenue, but the revenue may be outweighed by substantial capital and social costs incurred by the host. The events are often awarded to host destinations through a bidding process and gain tremendous media coverage.

Special Events
A special event is a one-time or infrequent specific ritual, presentation, performance, or celebration. Special events are planned and created to mark a special occasion, such as a presidential inauguration or the Queen of England’s 90 th birthday. Like mega-events, there may be significant media coverage and economic impact for the host city or destination.
Hallmark Events
A hallmark event is a unique event that is often identified with the location where it is held, like Carnival in Rio de Janeiro or Oktoberfest in Munich. Hallmark events contribute significant economic benefits and even can create a competitive advantage for the host city or destination that attracts tourists.

A festival is a themed public celebration that conveys, through a kaleidoscope of activities, certain meaning to participants and spectators. Festivals are often celebrations of community or culture and feature music, dance, or dramatic performances. Examples include Lollapalooza, the Cannes Film Festival, and Junkanoo in the Bahamas.
Local Community Events
A local community event is generated by and for locals; although it may attract tourists, its main audience is the local community. The community may experience measurable economic impacts, as might happen at The Steppin’ Out Street Fair in Blacksburg (think hotel stays and eating out). Fundraisers and community picnics are also examples in this category.
Meetings and Conventions
The tourism industry also has a long history of creating, hosting, and promoting meetings and conventions that draw business travelers. In fact, Convention and Visitor Bureau’s (CVB’s) work hard to attract these meetings and conventions to their city to drive economic benefit for hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, etc.
There are several types of such events
Conventions generally have very large attendance, and are held on a regular schedule but in different locations. They also often require a bidding process. Political conventions are one such example.
Association M eetings or C onferences are held regionally and nationally for hundreds of associations or events focused on specific themes. Examples would be the National Restaurant Association Annual Convention, ComicCon, or the National Auto Show.
Corporate M eetings will vary significantly in size and purpose and include regional or national sales meetings, shareholder meetings, training sessions, or celebrations. The location will vary depending on the nature of the meeting. They may be held at an airport property, a traditional corporate meeting facility or even an upscale resort.
Trade S hows and T rade F airs can be stand-alone events, or adjoin a convention or conference.
S eminars , W orkshops , and R etreats are examples of smaller-scale events.
As meeting planners have become more creative, meeting and convention delegates have been more demanding about meeting sites. No longer are hotel meeting rooms and convention centers the only type of location used; non-traditional venues have adapted and become competitive in offering services for meeting planners. These include architectural spaces such as airplane hangars, warehouses, or rooftops and experiential venues such as aquariums, museums, and galleries. [24]
Transportation and travel services are another large element of the tourism industry. This area includes cruise ships, airlines, rail, car rentals, and even ride sharing such as Uber and Lyft. Each of these segments is impacted significantly by fuel costs, safety issues, load factors and government regulation.
If you’ve ever been on a cruise, you are in good company. According to CLIA (Cruise Lines International Association), 23 million passengers were expected to go on a cruise worldwide on 62 member lines in 2015. [25] The industry employs over 900,000 people. [26]
Over 55 percent of the world’s cruise passengers are from North America, and the leading destinations (based on ship deployments), according to CLIA are: [27]
- The Caribbean (36 percent)
- The Mediterranean (20 percent)
- Northern Europe (11 percent)
- Australia/New Zealand (6 percent)
- Alaska (6 percent)
- Asia (5 percent)
- South America (3 percent)

The t ravel services sector is made up of a complex web of relationships between a variety of suppliers, tourism products, destination marketing organizations, tour operators, and travel agents, among many others. Under the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), the travel services industry group includes “establishments primarily engaged in travel arrangement and reservation services. Examples … are tourist and travel agencies; travel tour operators and wholesale operators; convention and visitors’ bureaus; airline, bus, railroad and steamship ticket offices; sports and theatrical ticket offices; and airline, hotel and restaurant reservation offices.” [28] Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveler (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travelers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveler and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies. [29] Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
Online Travel Agencies (OTAs)
Online travel agents (OTAs) are companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include Booking.com, Expedia.com, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs are gaining popularity with the travelling public; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion [30] and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013. [31] Over 40 percent of US travelers booked flights online in 2014. [32]
Tour Operators
A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveler. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies. [33] Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveler could by purchasing individually.
Destination Marketing Organizations (DMOs)
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” [34] .
Country Clubs
Country c lubs are another part of the Hospitality industry with a very different service strategy focusing on serving members who will develop relationships with the staff compared to a more transactional service interaction in lodging, restaurants or airlines.
Country clubs do not focus as strongly on profit as they do on maximizing member satisfaction, retention and growth while maintaining an attractive fee structure. Country (or city) clubs, will typically have restaurant and bar operations, catered events and other amenities such as golf, tennis, pool, fitness facilities, etc. Depending on the type of club, family and youth events are important to maintain and grow membership.
Strong customer service, culinary, event management and general management skills are necessary to be successful in clubs.

Chapter Video
As in any other fast-moving industry, the landscape in Hospitality and Tourism is always changing. This video explores 10 of the more important current trends impacting the industry.
(Copyrighted material)
Key Takeaways
- The Tourism industry is the largest industry in the world with significant benefit and costs to a region. The global competition for the tourism dollar is significant within the US and between countries.
- Hotels vary significantly in size, quality, purpose, chain affiliation, and ownership. The complexity of the operation and leadership vary as well.
- Food and Beverage is made up of a wide variety of restaurant types from QSR, Fast Casual, Fine Dining and Ethnic. Institutional food service in business , hospitals, education, parks and concessions are a significant part of the Food and Beverage industry.
- The evolution of tastes and consumer expectations in food and beverage continue to provide opportunity and challenges in the industry for ethnic sustainable, organic, local, craft, and other unique experiences.
Portions of this chapter were adapted from Westcott, Morgan (Ed) Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC. CC BY 4.0 https://opentextbc.ca/introtourism . Available for free at: http://open.bccampus.ca
Image Credits: Chapter 16
Figure 16.1: Siebe Warmoeskerken (2018). Unsplash. Public Domain. Retrieved from: https://unsplash.com/photos/mxNrtFzOd-I
Figure 16.2: Data retrieved from: https://wttc.org/Research/Economic-Impact ; World map retrieved from: Max Naylor (2006). “BlankMap-World-Continents-Coloured.” Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 3.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:BlankMap-World-Continents-Coloured.PNG
Figure 16.3: Rodhullandemu (2012). “The Pineapple Hotel, Park Road, Liverpool.” CC BY-SA 3.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pineapple,_Park_Road,_Liverpool.jpg
Figure 16.6: Stephen J. Skripak. “Example of a Hotel Market Segmentation by STR’s Chain Scale.” CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16.7: Christina Hsu (2009). “San Diego City and Bay at Night.” Flickr. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://flic.kr/p/6KZ5Cv
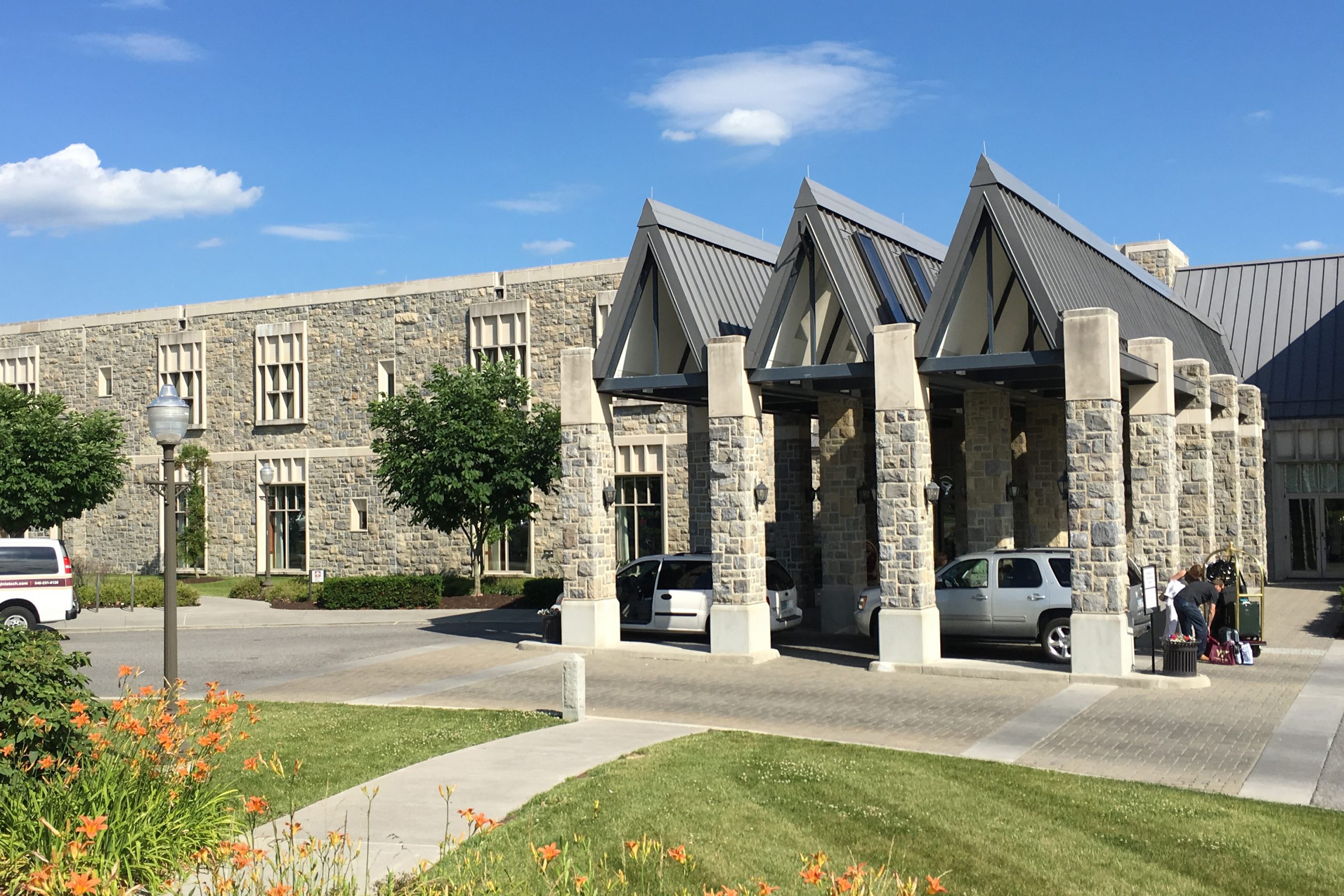
Figure 16.8: Anastasia Cortes (2016). “The Inn at Virginia Tech.” Public Domain. Provided by the author.
Figure 16.9: Dale Cruse (2014). “New Zealand langoustines at Troquet.” Flickr. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dalecruse/8551895022/
Figure 16.10: Imzadi1979 (2012). “An Axample of a Typical American Logo Sign.” Wikipedia. Public Domain. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logo_sign#/media/File:Logo_Sign.svg
Figure 16.11: Mike Mozart (2014). “Panera Bread.” Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Panera_Bread_(13883443466).jpg
Figure 16.12: Michael Rys. “Le Procope.” Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Inside_Le_Procope.jpg#mw-jump-to-license
Figure 16.13: Stephen J. Skripak. “The Restaurant Industry Career Path.” CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16.14: Table adapted from National Restaurant Association (2014). 2013 -2014 Restaurant Operations Report .
Figure 16.15: JohnSM (2013). “Rafting in Turkey.” Pixabay. Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/raftingturkey-travel-1125213/
Figure 16.16: UNLV Center for Gaming Research. “US and Global Casino Revenues (2005-2019).” (2005-2015) Data Retrieved from: https://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_annual_revenues.pdf ; (2016) Data Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20170301070205/http://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_monthly.pdf ; 2017 Data Retrieved from: https://www.americangaming.org/resources/state-of-the-states-2018-the-aga-survey-of-the-commercial-casino-industry/ ; 2018 Data Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20190201140714/https://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_monthly.pdf ; 2019 Data Retrieved from: https://abcnews.go.com/Entertainment/wireStory/us-commercial-casinos-won-436-billion-2019-37-71069042; Global Revenue Data Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/271577/global-casino-gaming-market-revenue/ ; Number of Commercial Casinos Data Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/187972/number-of-us-commercial-casinos-since-2005/
Figure 16.17: Josh Hallett (2009). “The ‘Big Bang’ at Wishes – Magic Kingdom – Walt Disney World.” Flickr. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/hyku/3830182777
Figure 16.18: Peter23 (2011). “Beijing National Stadium.” Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 3.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Beijing_national_stadium.jpg
Figure 16.19: Skeeze (2014). “Mardi Gras in New Orleans.” Pixabay. Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/photos/mardi-gras-new-orleans-festival-1176483/
Figure 16.20: Peter Hansen (2017). “Cruise Ship Photo.” Unsplash. Public Domain. Retrieved from: https://unsplash.com/photos/MeGmdPNe36w
Figure 16.21: Dan Perry (2006). “Riviera Country Club in Pacific Palisades, California.” Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Riviera_Country_Club,_Golf_Course_in_Pacific_Palisades,_California_(168828797).jpg
Video Credits: Chapter 16
Sisyanti, Ling Ling, Wasim Amsal, Ella Qiu, and Rebecca Catherine Stephany (2015, February 6). “10 trends in Hospitality and Tourism Industry.” YouTube. Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SJ8Momwv7Qk
- World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015). “Why Tourism?” Retrieved from: http://www2.unwto.org/content/why-tourism ↵
- United Nations Statistics Division (2010, December). “Tourism as an Internationally Traded Service and Beyond.” Newsletter of the Interagency Task Force on Statistics of International Trade in Services. No. 6. p. 1. Retrieved from: http://unstats.un.org/unsd/tradeserv/tfsits/newsletter/TFSITS_newsletter_6.pdf ↵
- World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015). “Exports from International Tourism Rise 4% in 2015.” Retrieved from: http://media.unwto.org/press-release/2016-05-03/exports-international-tourism-rise-4-2015 ↵
- Association of Bhutanese Tour Operators (2010). “UNWTO Tourism Vision 2020 Forecast Released.” Retrieved from: http://www.abto.org.bt/2010/06/unwto-tourism-2020-vision-forecast-released/ ↵
- United Nations Environment Programme (2016). “Negative Socio-Cultural Impacts from Tourism.” Retrieved from: http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/Socio-CulturalImpacts/NegativeSocio-CulturalImpactsFromTourism/tabid/78781/Default.aspx ↵
- United Nations Environment Programme (2016). “Tourism’s Three Main Impact Areas.” Retrieved from: http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/TheTourismandEnvironmentProgramme/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/EnvironmentalImpacts/TourismsThreeMainImpactAreas/tabid/78776/Default.aspx ↵
- Discover Hospitality (2015). “What is Hospitality?” Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20150814071021/http://discoverhospitality.com.au/what-is-hospitality ↵
- L. P. Coyle (1982). “Pineapple” in World Encyclopedia of Food . New York: Facts on File. p. 517. ↵
- Colonial Williamsburg Foundation (2016). “The Pineapple in Colonial Williamsburg.” Retrieved from: http://www.history.org/almanack/life/christmas/dec_pineapple.cfm ↵
- C. Crandell, K. Dickinson, and G. I. Kanter (2004). "Negotiating the hotel management contract" In Hotel Asset Management: Principles & Practices . East Lansing, MI: University of Denver and American Hotel & Lodging Educational Institute. ↵
- S. Rushmore (2005). “What Does a Hotel Franchise Cost?” Canadian Lodging Outlook. Retrieved from: www.hotel-online.com/News/PR2005_4th/Oct05_FranchiseCost.html ↵
- Ibid.; N. Migdal (n.d.). “Franchise Agreements vs. Management Agreements: Which One Do I Choose?” Hotel Business Review. Retrieved from: hotelexecutive.com/business_review/2101/test-franchise-agreements-vs-management-agreements-which-one-do-i-choose ↵
- Stephen Rushmore Jr., Erin S. Bagley (2014). “2014 United States Hotel Franchise Fee Guide.” HVS. Retrieved from: http://www.hvs.com/article/7097/2014-united-states-hotel-franchise-fee-guide/ ↵
- H. G. Parsa, K. R. Lord, S. Putrevu, and J. Kreeger (2015). “Corporate Social and Environmental Responsibility in Services; Will Consumers Pay for It?” Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. Vol. 22. pp. 250-260. ↵
- A. H. Mak, M. Lumbers, A. Eves, and R. C. Change (2012). “Factors Influencing Tourist Food Consumption.” International Journal of Hospitality Management. Vol. 31. No. 3. pp. 928-936. ↵
- Virginia Wine Association (2016). “Virginia Wineries.” Virginia Wines. Retrieved from: https://www.virginiawine.org/wineries/ ↵
- American Restaurant Association and Deloitte Development LLC (2013). 2013-2014 Restaurant Operations Report . Washington, D.C.: National Restaurant Association. p. 7. ↵
- Table adapted from National Restaurant Association (2014). 2013-2014 Restaurant Operations Report . Washington, D.C.: National Restaurant Association. ↵
- J. Tribe (2011). The Economics of Recreation, Leisure, and Tourism , 4th ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier. ↵
- Tourism BC (2013). “2009/2010 Outdoor Recreation Study.” Destination British Columbia. Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/Outdoor-Recreation-Study-2009-2010,-January-2013/Outdoor-Recreation-for-Distribution-14Jan13-FINAL-DRAFT-(2).pdf.aspx ↵
- United Nations World Tourism Organization (2014). Global Report on Adventure Tourism . UNWTO and the Adventure Tourism Trade Association. p. 12. Retrieved from: http://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/pdf/final_1global_report_on_adventure_tourism.pdf ↵
- Ibid., p. 15. ↵
- George Washington University (2013). “Adventure Tourism Market Study 2013.” The Adventure Travel Trade Association. p. 2. Retrieved from: http://files.adventuretravel.biz/docs/research/adventure-tourism-market-study-2013-web.pdf ↵
- K. Colston (2014, April 24). "Non-Traditional Event Venues – Endless Entertainment." Retrieved from: http://helloendless.com/non-traditional-event-venues/ ↵
- CLIA (2016). CLIA 2015 Annual Report: One Voice: Advancing Our Industry Together . Cruise Lines International Association. p. 10. Retrieved from: http://www.cruising.org/docs/default-source/market-research/clia_2015_annualreport_web.pdf?sfvrsn=0 ↵
- Ibid. ↵
- CLIA (2015). CLIA 2015 Cruise Industry Outlook: Cruising to New Horizons and Offering Travelers More . Cruise Lines International Association. p. 28. Retrieved from: http://www.cruising.org/docs/default-source/research/2015-cruise-industry-outlook.pdf ↵
- Government of Canada (2014). “NAICS 2007: 5615 Travel Arrangement and Reservation Services.” Statistics Canada. Retrieved from: http://stds.statcan.gc.ca/naics-scian/2007/cs-rc-eng.asp?criteria=5615 ↵
- C. Goeldner and B. Ritchie (2003). Tourism: Principles, Practices, Philosophies , 9th ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ↵
- R. Carey, K. Kang, and M. Zea (2012). "The Trouble With Travel Distribution." McKinsey & Company. Retrieved from: www.mckinsey.com/insights/travel_transportation/the_trouble_with_travel_distribution ↵
- The Economist (2014). “Sun, Sea and Surfing: The Market for Booking Travel Online Is Rapidly Consolidating.” Economist. Retrieved from http://www.economist.com/news/business/21604598-market-booking-travel-online-rapidly-consolidating-sun-sea-and-surfing ↵
- The Trefis Team (2015). “An Update on the Online Travel Agencies.” Forbes. Retrieved from: http://www.forbes.com/sites/greatspeculations/2015/09/30/an-update-on-the-online-travel-agencies/#60c1ed4d3e0b ↵
- The Destination Marketing Association International (2014). “The value of DMOs.” Retrieved from: http://www.destinationmarketing.org/value-dmos ↵
Chapter 16 Hospitality and Tourism Copyright © 2020 by Stephen J. Skripak and Ron Poff is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Components of tourism: Structure of the tourism industry
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
The travel and tourism industry is argued by many as being the largest industry in the world. It is, therefore, no surprise that the structure of the tourism industry is quite complex, involving many components of tourism.
With many different types of tourism and types of businesses operating within the tourism industry, from private companies to charities and NGOs, the structure of the tourism industry is made up of many different segments and components.
In this article I will provide you with an overview of the structure of the tourism industry, outlining the types of organisations and stakeholders in tourism that are involved.
Structure of the tourism industry
Components of tourism, international organisations, national tourist boards, regional tourist boards, tourist information centres, travel by air, travel by road, travel by train, travel by water, hotels chains, hostels and budget accommodation, holiday parks and campsites, accommodation innovations, world travel market, football world cup, glastonbury, holi festival, day of the dead, natural attractions, built attractions, tour operators, travel agents, ancillary services, components of tourism | structure of the tourism industry, structure of the tourism industry | components of tourism: further reading.
The importance of tourism is demonstrated when you can see how big the industry is!
The structure of the industry is made up of several components of tourism and involves many different stakeholders. These components are all interrelated in one way of another. The components of tourism make up the entire tourism system.

There are several integral components of tourism. Without these components, the tourism industry would struggle to function. I have explained what this means below, but before you read on, take a look at this short video that I made (and if you like what you see, don’t forget to subscribe to my YouTube channel)!
This was demonstrated, for example, during the Coronavirus pandemic, which halted air travel around the world. Travel services are a vital component of tourism and without these services being operational, the tourism industry struggled to survive!
There are six major components of tourism, each with their own sub-components. These are: tourist boards, travel services, accommodation services, conferences and events, attractions and tourism services.

Below, I will explain what each of the components offer to the tourism industry and provide some relevant examples.
Components of tourism: Tourist boards
A tourist board is an essential component of tourism and an integral part of the structure of the tourism industry.
A tourism board is responsible for the promotion of tourism in a particular area. This could be a city, a region, a country or a group of countries.
A tourism board is usually Government funded and is usually a public travel and tourism organisation (although this is not always the case).
A tourism board is also often referred to as a Destination Marketing Organisation (DMO).
Most tourist boards focus on promoting tourism in a particular area, city or country. There are, however, some organisations which aim to promote tourism across more than one country.
Whilst these organisation often have many functions other than tourism, they will also play a role in the promotion of tourism in particular parts of the world. This could include the European Union , the ASEAN network or organisations such as the United Nations.
A national tourist board is a national organisation whose aim is to promote tourism across the country.
There are usually several management bodies that are involved with a national tourist board. They are essential stakeholders who determine many aspects of tourism in the country, such as budgets, taxation and regulations.
Said management bodies include the parliament, the tourist board, an auditing committee and the Prime Minister, President or Head of State.
The national tourist board is funded from tourist taxes, membership fees, Government funding and other sources.
Examples of national tourist boards (often most commonly referred to by their ‘campaign title’ as opposed to the Government title) include Visit Britain , Incredible India and Amazing Thailand .
A regional tourist board is a tourist board that focusses on a particular region of a country. They are often a sub-division of a country’s national tourist board.
Regional tourism boards are often funded and operated in the same way as national tourist boards.
Examples of successful regional tourism boards include: Visit Cornwall in the UK, Kerala Tourism in India, Visite Montreal in Canada and Cape Town Tourism in South Africa.
A tourist information centre is the place where tourists can go for advice and help with regards to all matters related to tourism in the area.
In the tourist information centre (TIC) you will find staff who are knowledgeable about the local area. There will often be a range of printed and digital information for you, including leaflets, maps, coupons and guidebooks. Sometimes there will be virtual tourism facilities.
Tourist information centres have been an important component of tourism throughout the history of travel and tourism , however, they are coming under increasing pressure as a result of information that is available online. This has resulted in fewer people visiting TICs in person.
Most major tourist areas will have a tourist information centre. These are usually centrally located.
Tourist information centres are funded by the local Government.
Other posts that you might be interested in: – What is tourism? A definition of tourism – The history of tourism – Stakeholders in tourism – Dark tourism explained – What is ABTA and how does it work? – The economic impacts of tourism
Components of tourism:Transport services
The relationship between transport and tourism is strong.
According to the most commonly accepted definitions of tourism, a person must travel away from their home environment for at least one night in order to be a tourist (although I would argue that this definition needs updating given that it doesn’t account for novel forms of tourism such as a staycation or virtual tourism ).
Based on this fact, therefore, transport is an integral component of tourism. Without transport, people cannot reach their intended destination.
There are a range of different transport types. The most common and popular methods of transport that make up the structure of the tourism industry, however, are: air, road, train and water .

Travel by air has grown exponentially in the past few decades. With the introduction of low cost airlines and deregulation, the competitive market has been a tourist’s paradise.
New routes opening up has introduced tourists to areas that they may never have been able to reach before and low prices have resulted in more of us taking more trips abroad using air travel as our means of transportation.
Travel by air is an essential component of tourism and this was demonstrated during the Coronavirus epidemic. During this time most air traffic was halted, which had a devastating impact of the tourism industry world-wide.
Travel by road is also a core component of tourism, particularly for domestic tourism .
Travel by road is more popular in some countries than others. This largely depends on accessibility options (i.e. what is accessible by road), distances required and road conditions.
In destinations where travel by road is popular, there are often many car hire or rental companies.
Travel by train is very popular in destinations that have good rail networks in infrastructure.
In some parts of the world, such as China and Japan, there are world-class high-speed railways that can be more efficient than flying.
In other parts of the world, the rail journey is part of the tourism experience. A good example of this is the Siberian Railway.
In Europe you can buy an affordable interrail pass , which allows you to travel throughout Europe using the rail system.

Travel by water is also an important component of tourism.
The structure of the tourism industry includes cruises, ferries and leisure boats, among other types of travel by water.
Travel by water can vary considerably in price and can include anything from a round the world cruise to a short long tail ride in Thailand .
Components of tourism: Accommodation services
Accommodation services make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Whilst accommodation services were traditionally focussed mainly around the hotel industry, nowadays accommodation options for tourists are much more varied. This adds an additional layer of complexity to the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many hotel chains that operate throughout the tourism industry and that are a key component of tourism.
Multinational corporations have expanded throughout the tourism industry with key players being hotel chains such as Marriott, Radisson, Hilton, Travel Lodge and Holiday Inn.
However, hotel chains such as these have come under increased scrutiny as a result of the economic leakage in tourism that they cause.
Hostels and budget accommodation options are popular with budget travellers and backpackers.
There are a range of hostels found throughout the world. These are particularly popular in destinations where accommodation is expensive, such as London, New York and Singapore.
The Youth Hostel Association (YHA) and Hostelling International are popular hostel providers that are found across the UK and overseas.
Billy Butlin changed the face of the British holiday market with the introduction of his seaside holiday parks back in 1936.
Since this time, other similar chains have expanded throughout the UK and the rest of the world.
Camping is also an important component of tourism. There are camp sites situated throughout the world ranging from safari camps to glamping (glamorous camping).
Homestays have become an increasingly prominent component of tourism.
Whilst bed and breakfast accommodation has been around for a very long time, nowadays there are many more options that are grounded on the concept of a homestay.
The sharing economy has seen the growth and introduction of many types of accommodations into the travel and tourism sector that did not exist before.
The most popular of these is Airbnb, where people rent out a room or an entire property to tourists. You can read more about how Airbnb works here .
In recent years consumers have been demanding new and unusual experiences more than ever. In response to this, we have seen many accommodation innovations emerge throughout the world.
From staying in an ice hotel in Finland, to sleeping in a hammock in Borneo to a night in a haunted castle in Wales, there are many different types of accommodation options that can make your holiday a little bit more exciting!
Components of tourism: Conferences and events
Conferences and events make up a significant part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Conferences, which often come under business tourism , come in all shapes and sizes around the world.
From a small academic gathering to a large-scale summit involving national leaders from around the world, conferences are an important component of tourism.
Likewise, the event sector is also a significant part of the tourism industry.
There are millions of events that take place around the world each year that vary in size and function. Many of these form an integral part of the tourism industry.
Examples of major conferences and events around the world
There are many major conferences and events that take place around the world every year. Here are a few of my favourites:
The World Travel Market (WTM) is held in London each November. This is a large event that is held at the Excel venue.
WTM provides travel industry experts with the opportunity to showcase their work, learn more about the industry and to network.
ITB is the world’s leading international travel trade show. It is held in Berlin each year.
Similar to the WTM, this large-scale event enables industry professionals to network and undertake continuous professional development.
The vast majority of people are familiar with the Football World Cup.
The Football World Cup is held every four years in a different location.
The Football World Cup attracts millions of tourists from all over the world. The event also acts as a stimuli for tourism as the nation will often use the opportunity of hosting the event as a chance to market tourism in the area to those who are tuning in from their TVs from around the world.
Sports tourism , which includes events such as the Football World Cup, contributes significantly to the overall tourism industry.
Glastonbury is a popular British music festival. It takes place each summer in Somerset.
Glastonbury is a five-day festival of contemporary performing arts. In addition to music, the festival hosts dance, comedy, theatre, circus, cabaret, and other arts to entertain visitors.
Glastonbury attracts many domestic tourists as well as international tourists.
San Fermin is a festival that is held in Pamplona, Spain each July.
San Fermin, also known as the ‘Running of the Bulls’ is a historically-rooted festival that lasts five days. It involves dancing, eating and drinking, games and the famous bull races and fights.
San Fermin has been subject to a lot of controversy in recent years, with many people protesting that it is a cruel form of animal tourism .

Holi Festival is known as the ‘festival of spring’, the ‘festival of colours’ or the ‘festival of love’.
Holi Festival is celebrated in India each year during the month of March.
Holi Festival is famous for the way in which coloured paints are used and often thrown onto people’s faces and clothes.
This is a Hindu festival that signifies the victory of good over evil.
The Day of the Dead festival, locally referred to as ‘Dia de los Muertos’, is a festival that is celebrated in November each year in Mexico.
This day is a celebration of the deceased, whereby it is believed that the alive and the dead are reunited. On this day many people will create offerings for the deceased.
Many people choose to dress up as skeletons and in halloween-type outfits and they celebrate with food, drink and music.
Components of tourism: Attractions
An essential component of the tourism industry are the tourist attractions.
There are a multitude of different tourist attractions around the world.
Some are built, some are natural. Some are paid, some are free. Some are famous, others are not. Some are large and some are small.
Natural attractions are just as it says on the tin – natural. In other words, they are attractions that have not been made by man.
Natural attractions are found all over the world and vary in size and scope. There is even a definitive list of the seven natural wonders of the world .
I have visited many natural attractions around the world, here is a list of some of my favourites:
- Drakansburg Mountains, South Africa
- Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
- Mount Toubkal, Morocco
- Sahara Desert, Morocco
- Red Sea, Egypt
- Dead Sea, Israel
- Sierra Nevada, Spain
- Chicken Island, Thailand
- Niagara Falls, USA
- Rocky Mountains, Canada
- Pammukale Thermal Pools, Turkey
- Iceland (the island is filled with wonderful natural attractions!)
- Amazon Rainforest , Ecuador
- Cenotes, Mexico
- Iguazu Falls, Brazil
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia
- Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Waterways of Kerela, India
- Mount Hallasan, South Korea
Built attractions also make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many built attractions throughout the world. Some attractions are built for the purpose of tourism, such as theme parks or museums. Other attractions are built for other purposes but then become tourist attractions, such as the Empire State Building or the Sydney Opera House.
I have visited many built attractions throughout the world. Here are some of my favourites:
- Robin Island, South Africa
- The Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
- La Sagrada Familia, Spain
- The Eiffel Tower, France
- The United States Capitol Building, USA
- Statue of Liberty, New York
- Petronas Towers, Malaysia
- Marina Sands Bay Hotel, Singapore
- Angkor Wat, Cambodia
- Taj Mahal, India
- Sydney Harbour Bridge, Australia
- Houses of Parliament, UK
- Sheikh Zayed Mosque, UAE
Components of tourism: Tourism services
Tourism services are an essential component of tourism. Without many tourism services, the tourism industry would fail to adequately function.
Below I will explain the three major tourism services that make up the structure of the tourism industry.
A tour operator is the individual or organisation who puts together a trip.
Typically, a tour operator would package together essential elements including accommodation, transport and transfer. They would then sell this package to the tourists.
However, tour operators are becoming fewer in recent years. Consumers are now far more Internet savvy and are more capable of researching the individual elements of their holiday and booking this independently. This is known as dynamic packaging .
Traditionally, a travel agent would sell the product that the tour operator has produced i.e. the package holiday.
While travel agents have and continue to sell individual holiday components, they have historically been most commonly used by tourists who wish to book a package holiday.
In today’s society, there is far less scope for travel agents than there used to be. A few years ago it would be easy to finish school and to get a job in a travel agent selling holidays. Now, however, people are more likely to set up their own travel agent business online or to be employed by an online retailer.
Many high street stores have now closed as there is little demand these days for holidays to be booked in this way. Instead, many people are selling holidays and travel services via their blogs or websites.
The travel agent does still exist, but he has changed the way he looks.
Ancillary services are another core component of tourism.
Ancillary basically means ‘extra’ or ‘additional’. An ancillary service in the context of tourism, therefore, is any product or service that is additional to the core elements of accommodation, transport and transfer.
Here are some examples of ancillary products:
- Attraction tickets
- Meal tickets
- Extra luggage
- Currency exchange
- Airport parking
As you can see, the tourism industry is large and complex, but understanding the different components of tourism isn’t too difficult.
All of the components of tourism are interconnected in one way or another and many rely on one another to be successful.
Want to learn more about the structure of tourism? I have listed some recommended texts below.
- An Introduction to Tourism : a comprehensive and authoritative introduction to all facets of tourism including: the history of tourism; factors influencing the tourism industry; tourism in developing countries; sustainable tourism; forecasting future trends.
- The Business of Tourism Management : an introduction to key aspects of tourism, and to the practice of managing a tourism business.
- Tourism Management: An Introduction : gives its reader a strong understanding of the dimensions of tourism, the industries of which it is comprised, the issues that affect its success, and the management of its impact on destination economies, environments and communities.
Liked this article? Click to share!
Please wait while your request is being verified...

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

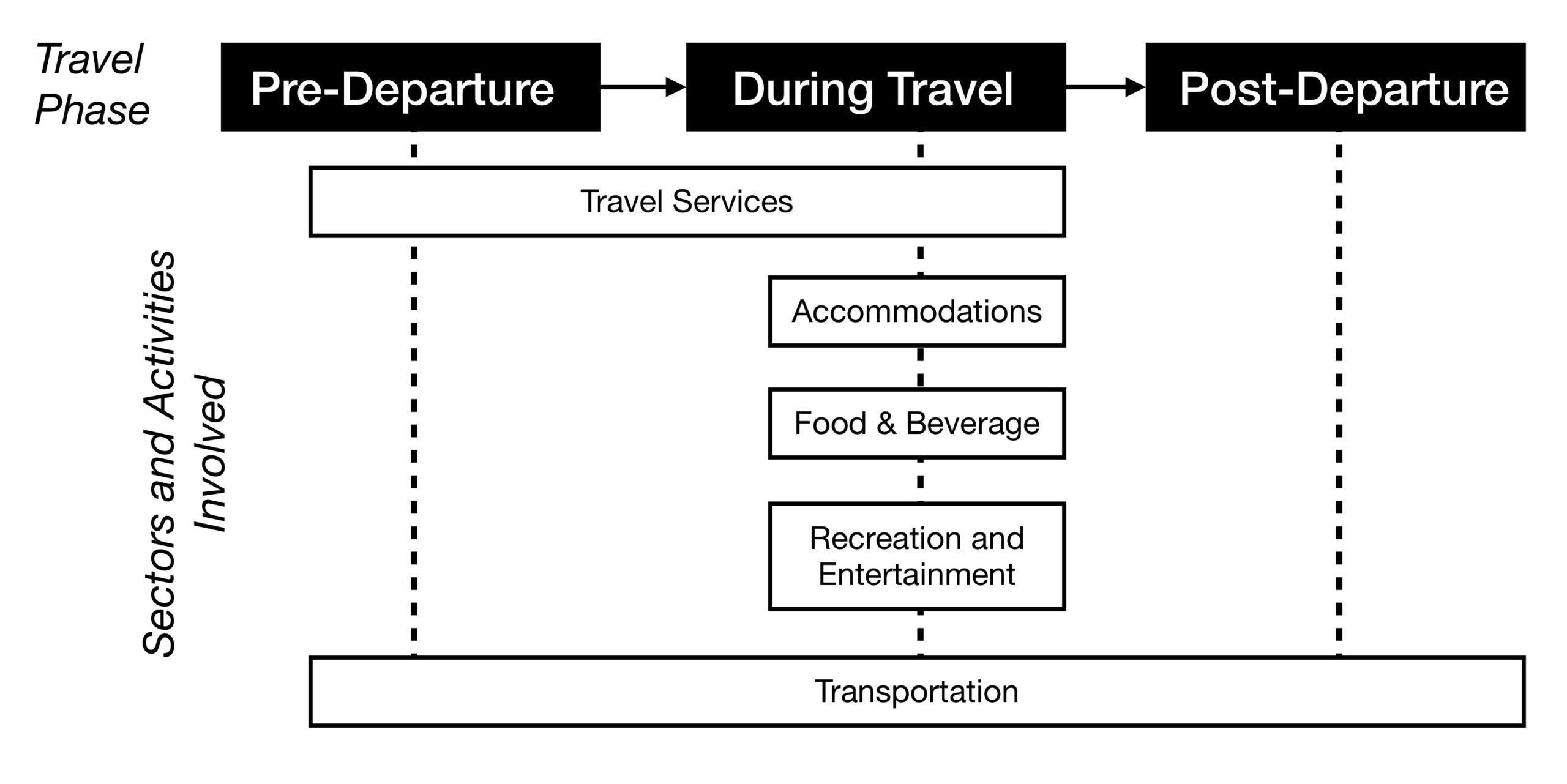
It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- What is tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are thriving industries encompassing many sectors, including hotels, restaurants, travel, events, and entertainment.
It’s an exciting and dynamic area, constantly evolving and adapting to changing customer demands and trends.
The tourism and hospitality industry offers a diverse range of career opportunities that cater to various interests, skills, and qualifications, with positions available from entry-level to executive management.
The booming tourism and hospitality industry also offers job security and career growth potential in many hospitality-related occupations.
What is tourism?
Tourism is traveling for leisure, pleasure, or business purposes and visiting various destinations, such as cities, countries, natural attractions, historical sites, and cultural events, to experience new cultures, activities, and environments.
Tourism can take many forms, including domestic, or traveling within your country, and international tourism, or visiting foreign countries.
It can also involve sightseeing, adventure tourism , eco-tourism, cultural tourism, and business tourism, and it’s a huge contributor to the global economy, generating jobs and income in many countries.
It involves many businesses, including airlines, hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, tour operators, and transportation companies.
What is hospitality?
Hospitality includes a range of businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, bars, resorts, cruise ships, theme parks, and other service-oriented businesses that provide accommodations, food, and beverages.
Hospitality is all about creating a welcoming and comfortable environment for guests and meeting their needs.
Quality hospitality means providing excellent customer service, anticipating guests’ needs, and ensuring comfort and satisfaction. The hospitality industry is essential to tourism as both industries often work closely together.
What is the difference between tourism and hospitality?
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries.
Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including transportation, accommodation, and attractions.
Transform your outlook for a successful career as a leader in hospitality management
This inspiring Bachelor’s in hospitality management gives you the knowledge, skills, and practical experience to take charge and run a business

Is tourism and hospitality a good career choice?
So, why work in hospitality and tourism? The tourism and hospitality industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world, providing a colossal number of job opportunities.
Between 2021 and 2031, employment in the hospitality and tourism industry is projected to expand faster than any other job sector, creating about 1.3 million new positions .
A tourism and hospitality career can be a highly rewarding choice for anyone who enjoys working with people, has a strong service-oriented mindset, and is looking for a dynamic and exciting career with growth potential.
Growth and job opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Tourism and hospitality offers significant growth and job opportunities worldwide. The industry’s increasing demand for personnel contributes to economic and employment growth, particularly in developing countries.
The industry employs millions globally, from entry-level to high-level management positions, including hotel managers, chefs, tour operators, travel agents, and executives.
It provides diverse opportunities with great career progression and skill development potential.
Career paths in tourism and hospitality

There are many career opportunities in tourism management and hospitality. With a degree in hospitality management, as well as relevant experience, you can pursue satisfying and fulfilling hospitality and tourism careers in these fields.
Hotel manager
Hotel managers oversee hotel operations. They manage staff, supervise customer service, and ensure the facility runs smoothly.
Tour manager
Tour managers organize and lead group tours. They work for tour companies, travel agencies, or independently. Tour managers coordinate a group’s transportation, accommodations, and activities, ensuring the trip runs to schedule.
Restaurant manager
Restaurant managers supervise the daily operations of a restaurant. They manage staff, ensure the kitchen runs smoothly, and monitor customer service.
Resort manager
Resort managers supervise and manage the operations of a resort. From managing staff to overseeing customer service, they ensure the entire operation delivers excellence.
Entertainment manager
Entertainment managers organize and oversee entertainment at venues like hotels or resorts. They book performers, oversee sound and lighting, and ensure guests have a great experience.

Event planner
Event planners organize and coordinate events, such as weddings, conferences, and trade shows. They work for event planning companies, hotels, or independently.
vent planners coordinate all aspects of the event, from the venue to catering and decor.
Travel consultant
Travel consultants help customers plan and book travel arrangements, such as flights, hotels, and rental cars. They work for travel agencies or independently. Travel consultants must know travel destinations and provide superb customer service.
What skills and qualifications are needed for a career in tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are rewarding industries with growing job opportunities. Necessary qualifications include excellent skills in communication, customer service, leadership, problem-solving, and organization along with relevant education and training.
Essential skills for success in tourism and hospitality
A career in the tourism and hospitality industry requires a combination of soft and technical skills and relevant qualifications. Here are some of the essential key skills needed for a successful career.
- Communication skills : Effective communication is necessary for the tourism and hospitality industry in dealing with all kinds of people.
- Customer service : Providing excellent customer service is critical to the success of any tourism or hospitality business . This requires patience, empathy, and the ability to meet customers’ needs.
- Flexibility and adaptability : The industry is constantly changing, and employees must be able to adapt to new situations, be flexible with their work schedules, and handle unexpected events.
- Time management : Time management is crucial to ensure guest satisfaction and smooth operations.
- Cultural awareness : Understanding and respecting cultural differences is essential in the tourism and hospitality industry, as you’ll interact with people from different cultures.
- Teamwork : Working collaboratively with colleagues is essential, as employees must work together to ensure guests have a positive experience.
- Problem-solving : Inevitably, problems will arise, and employees must be able to identify, analyze, and resolve them efficiently.
- Technical skills : With the increasing use of technology, employees must possess the necessary technical skills to operate systems, such as booking software, point-of-sale systems, and social media platforms.
Revenue management : Revenue management skills are crucial in effectively managing pricing, inventory, and data analysis to maximize revenue and profitability
Master fundamental hospitality and tourism secrets for a high-flying career at a world-leading hospitality brand
With this Master’s degree, you’ll discover the skills to manage a world-class hospitality and tourism business.

Education and training opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Education and training are vital for a hospitality and tourism career. You can ensure you are prepared for a career in the industry with a Bachelor’s in hospitality management and Master’s in hospitality programs from Glion.
These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of the guest experience, including service delivery and business operations, while developing essential skills such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving. You’ll gain the knowledge and qualifications you need for a successful, dynamic, and rewarding hospitality and tourism career.
Preparing for a career in tourism and hospitality
To prepare for a career in tourism and hospitality management, you should focus on researching the industry and gaining relevant education and training, such as a hospitality degree . For instance, Glion’s programs emphasize guest experience and hospitality management, providing students with an outstanding education that launches them into leading industry roles.
It would help if you also worked on building your communication, customer service, and problem-solving skills while gaining practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in the industry. Meanwhile, attending industry events, job fairs, and conferences, staying up-to-date on industry trends, and networking to establish professional connections will also be extremely valuable.
Finding jobs in tourism and hospitality
To find jobs in tourism and hospitality, candidates can search online job boards, and company career pages, attend career fairs, network with industry professionals, and utilize the services of recruitment agencies. Hospitality and tourism graduates can also leverage valuable alumni networks and industry connections made during internships or industry projects.
Networking and building connections in the industry
Networking and building connections in the hospitality and tourism industry provide opportunities to learn about job openings, meet potential employers, and gain industry insights. It can also help you expand your knowledge and skills, build your personal brand, and establish yourself as a valuable industry professional.
You can start networking by attending industry events, joining professional organizations, connecting with professionals on social media, and through career services at Glion.
Tips for success in tourism and hospitality

Here are tips for career success in the tourism and hospitality industry.
- Gain relevant education and training : Pursue a hospitality or tourism management degree from Glion to gain fundamental knowledge and practical skills.
- Build your network : Attend industry events, connect with colleagues and professionals on LinkedIn, and join relevant associations to build your network and increase your exposure to potential job opportunities.
- Gain practical experience : Look for internships, part-time jobs, or volunteering opportunities to gain practical experience and develop relevant skills.
- Develop your soft skills : Work on essential interpersonal skills like communication, empathy, and problem-solving.
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends : Follow industry news and trends and proactively learn new skills and technologies relevant to tourism and hospitality.
- Be flexible and adaptable : The tourism and hospitality industry constantly evolves, so be open to change and to adapting to new situations and challenges.
- Strive for excellent guest service : Focus on delivering exceptional guest experiences as guest satisfaction is critical for success.
Tourism and hospitality offer many fantastic opportunities to create memorable guest experiences , work in diverse and multicultural environments, and develop transferable skills.
If you’re ready to embark on your career in tourism and hospitality, Glion has world-leading bachelor’s and master’s programs to set you up for success.
Photo credits Main image: Maskot/Maskot via Getty Images

LISTENING TO LEADERS

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED

GLION SPIRIT

WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview

The Economics of Tourism Destinations pp 269–309 Cite as
The Supply of Tourism Services: Hospitality, Transport, Attractions
- Guido Candela 3 &
- Paolo Figini 3
- First Online: 01 January 2012
3786 Accesses
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Business and Economics ((STBE))
In this chapter, where we continue from Chap. 7 the investigation of the different types of tourism firms, we study the companies that supply tourism services included in the matrix of the tourism product. These services are also included in the package holiday produced by the tour operator: the hospitality firms supply accommodation services of different variety and quality (see Sect. 9.2); transport firms supply different types of travel (see Sect. 9.3); and museums, amusement parks, and other firms supply leisure or cultural attractions (see Sect. 9.4).
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Lundberg et al. ( 1995 ) include restaurants, bars, and other catering services in the list of tourism companies. Since restaurants also serve non-tourist customers, these authors call “tourism restaurants” those that mainly serve customers who live at least 50 miles away from the business. Because this classification seems too rough and little operational, we decided to not explicitly consider restaurants in our investigation, even if they provide an important contribution to the composition of the tourism product.
We refer to the literature on hotel management for the investigation of specific management issues (see for example Hayes and Ninemeier 2006 , Rutherford and O’Fallon 2006 ).
The marginal cost of production is given instead by the change in costs due to a one-unit increase in the number of stays. In our case, with constant returns we have dTC/d N H = dVC/d N H = c .
Although the calculations of ( 9.3 ) and ( 9.5 ) have been presented in terms of overnight stays (per person or per bed place), they can be similarly computed “per room”, according to the commercial practice in use.
Other useful indicators for the hotel management are the breakdown of variable costs (such as the share of labor costs on total cost, the share of spending for drinks on the total cost for the breakfast, etc.) and the ratio between liquid and financial assets.
We define as theme cruises those cruises offering a set of activities to be carried on board or at ports around a theme that usually characterizes the entire trip: for example, culture (art, folklore, and language courses), entertainment (music, dance, film and theater), fashion (with fashion shows on board).
To be more precise, the size of the aircraft to be used is not exogenously given, but is a very important strategic decision that the firm has to take. To keep things simple we assume that the firm has already chosen in a previous stage of the decision process the size N of the vector.
Arvanitis, P., & Zenelis, P. (2008). Africa. In A. Graham, A. Papatheodorou, & P. Forsyth (Eds.), Aviation and tourism: implications for leisure travel . Aldershot: Ashgate.
Google Scholar
Bowdin, G., Allen, J., O’Toole, W., Harris, R., & McDonnell, I. (2010). Events Management . Abingdon: Routledge.
Boyd, A. (1998). Airline Alliance Revenue Management. OR/MS Today , 25 October.
Candela, G., & Figini, P. (2005). Economia dei sistemi turistici . Milan: McGraw-Hill.
Candela, G., & Scorcu, A. E. (2004). Economia delle arti . Bologna: Zanichelli.
Cavour, C.B. (1939). Discorsi parlamentari , vol. VIII. In A. Omodeo (Ed.) Firenze: La Nuova Italia.
Cooper, C. P., Fletcher, J., Gilbert, D., Shephard, R., & Wanhill, S. (1998). Tourism. Principles and practice (2nd ed.). New York: Longman.
Cooper, C. P., Fletcher, J., Gilbert, D., Shephard, R., & Wanhill, S. (2008). Tourism. Principles and practice (4th ed.). New York: Longman.
Cross, R. G. (1997). Revenue management: hard-core tactics for market domination . New York: Broadway Books.
Dewailly, J. M., & Flament, E. (1995). Géographie du tourisme et des loisirs . Sedes: CDU.
Doganis, R. (2005). The Airline Business . London: Routledge.
Dowling, R. K. (2006). Cruise ship tourism . Wallingford: CABI.
Book Google Scholar
Field, D., & Pilling, M. (2003). Privatised airports blasted. Airline Business, 19 , 10.
Gil Molto, M.J., & Piga, C. (2007). Entry and exit in a liberalised market. Rivista di Politica Economica , 3–38.
Graham, A. (2008). Managing airports: an international perspective . Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Hayes, D. K., & Ninemeier, J. D. (2006). Hotel operations management . New York: Prentice Hall.
Henscher, D., & Brewer, A. (2001). Transport: an economics and management perspective . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Iatrou, K., & Oretti, M. (2007). Airline choices for the future: from alliances to mergers . Aldershot: Ashgate.
Ingold, A., McMahon-Beattie, I., & Yeoman, I. (2000). Yield management . London: Thomson.
Kimes, S. E. (2000). A strategic approach to yield management: strategies for the service industries. In A. Ingold, U. McMahon-Beattie, & I. Yeoman (Eds.), Yield management: strategies for the service industries . London: Thomson.
Kotler, P., Bowens, J. T., & Makens, J. C. (2009). Marketing for hospitality and tourism . New York: Prentice Hall.
Law, R. (2000). Back propagation learning in improving the accuracy of neural network based tourism demand forecasting. Tourism Management, 21 , 331–340.
Article Google Scholar
Lundberg, D. E., Krishnamoorthy, M., & Stavenga, M. H. (1995). Tourism economics . New York: Wiley.
Mallen, C., & Adams, L. J. (2008). Sport, recreation and tourism event management . Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Mathisen, T. A., & Solvoll, G. (2007). Competitive tendering and structural changes: an example from the bus industry. Journal of Transport Policy, 15 , 1–11.
Mintel (2007). European cruises. Travel and Tourism Analyst , August
Motta, M. (2004). Competition policy . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Murthy, B., & Dev, C. S. (1992). Average daily rate. In A. Khan, M. D. Olsen, & T. Var (Eds.), NVR’s encyclopedia of hospitality and tourism . New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
O’Connor, W. E. (2000). An introduction to airline economics . Westport, CT: Praeger.
Pak, K., & Piersma, N. (2002). Airline revenue management: an overview of OR techniques 1982–2001. ERIM Report Series, 12 . Rotterdam: Erasmus University.
Papatheodorou, A. (2003b). Corporate strategies of British tour operators in the Mediterranean region: an economic geography approach. Tourism Geographies, 5 , 280–304.
Papatheodorou, A. (2006). The cruise industry. An industrial organization perspective. In R. Dowling (Ed.), Cruise ship tourism . Wallingford: CABI.
Papatheodorou, A. (2008). The impact of civil aviation regimes on leisure travel. In A. Graham, A. Papatheodorou, & P. Forsyth (Eds.), Aviation and tourism: implications for leisure travel . Aldershot: Ashgate.
Papatheodorou, A., & Platis, N. (2007). Airline deregulation, competitive environment and safety. Rivista di Politica Economica, I–II , 221–242.
Pasqualoni, P. (2008). La gestione delle prenotazioni delle compagnie aeree Un esperimento sulla tratta Parigi – New York . Bologna: University of Bologna. Mimeo.
Ropero, A. (2011). Dynamic pricing policies of hotel establishments in an online travel agency. Tourism Economics, 17 , 1087–1102.
Rutherford, D. G., & O’Fallon, M. J. (2006). Hotel management and operations . New York: Wiley & Sons.
Schwartz, Z., Stewart, W., & Backlund, E. A. (2012). Visitation at capacity-constrained tourism destinations: exploring revenue management at a national park. Tourism Management, 33 , 500–508.
Shaw, M. (1992). Hotel pricing. In A. Khan, M. D. Olsen, & T. Var (Eds.), VNR’s encyclopedia of hospitality and tourism . New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Shy, O. (2008). How to price. A guide to pricing techniques and yield management . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Stabler, M. J., Papatheodorou, A., & Sinclair, M. T. (2010). The economics of tourism (2nd ed.). London: Routledge.
Talluri, K. T., & van Ryzin, G. (2005). The theory and practice of revenue management . Heidelberg: Springer.
Vila, N., & Corcoles, M. (2011). Yield management and airline strategic groups. Tourism Economics, 17 , 261–278.
Wensveen, J. G. (2007). Air transportation: a management perspective . Aldershot: Ashgate.
White, P. R. (2008). Public transport: its planning, management and operations . London: Routledge.
Zenelis P, Papatheodorou A (2008). Low cost carriers’ penetration: a comparative case study of Greece and Spain. Mimeo
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy
Guido Candela & Paolo Figini
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Candela, G., Figini, P. (2012). The Supply of Tourism Services: Hospitality, Transport, Attractions. In: The Economics of Tourism Destinations. Springer Texts in Business and Economics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20874-4_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20874-4_9
Published : 23 May 2012
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-642-20873-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-642-20874-4
eBook Packages : Business and Economics Economics and Finance (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
16 Chapter 16 Hospitality & Tourism
Richard Parsons; Stephen Skripak; Anastasia Cortes; Anita Walz; and Gary Walton
Learning Objectives
- Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance.
- Understand the economic, social and environmental benefits and costs of tourism.
- Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition.
- Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined.
- Examine the different categories of food service operations.
- Understand the different types of events, meetings and conventions.

The tourism industry is often cited as the largest industry in the world, contributing 10% of the world’s GDP. In 2016 there were over 1.2 billion international tourists: that’s a substantial economic impact and movement of goods and services! 1 Tourism is also considered an export and is unique in that the consumers come to the product where it is consumed on-site. Before we dig any deeper, let’s explore what the term “tourism” means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
A social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure. 2
In other words, tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure). It is important to understand the various groups and constituencies involved in this movement. Of course it includes the tourist, but also the vast array of businesses providing goods and services for the tourist, the government and political structure of a destination, and the local residents of the destination community itself. Each of these components are necessary parts of a successful tourism destination and operate within private and public sectors, the built environment, and the natural environment. All these come together to create the processes, activities, and outcomes of tourism.
If it all seems a little overwhelming, it might be helpful to break tourism down into broad industry groups, each of which will be covered in this chapter:
Accommodation and Lodging
- Food and Beverage Services (F & B)
Recreation and Entertainment
- Convention & Event Management
Travel Services
- Private Clubs
Benefits and Costs of Tourism
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations. Some impacts gain more attention than others. It is also important to recognize that different groups and constituencies are impacted differently.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The tourism industry has a huge economic impact that continues to expand to new markets and destinations. According to the UNWTO, in 2016 “The total export value from international tourism amounted to US$ 1.5 trillion.” 3 Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned (2016 vs 2015) are Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Americas Europe. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report. As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 20 3 0 Vision report predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.8 billion by 2030. 4 Figure 16.2 provides additional information about the impact of tourism worldwide.

Positive impacts from this economic boom include robust foreign exchange, increases in income, and GDP growth. Tourism can also offer diverse employment opportunities, can be developed with local products, and is often compatible with other economic activities within a destination. Tourism often injects money into the community that leads to secondary economic development as well. For example, successful resorts may create the need for a commercial laundry facility or a pet boarding business.
However, there are also negative impacts. Property values may increase to the point of unaffordability for local residents, and the seasonality of the tourism industry may create a feast-or-famine economy. As with any economy, if too many resources are focused on just one industry, communities may be vulnerable to any unexpected economic, social, or environmental changes. One example is the New Jersey shore after the devastation of Hurricane Sandy in 2012. The tourism industry was severely impacted, leaving no economic fallback for local residents.
Social Impacts of Tourism
In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts, culture, heritage and tradition, celebration of indigenous communities, and community pride. Tourism also has the potential to break down language, socio-cultural, religious, and political barriers. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents and promotes a positive image of the destination.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme, negative social impacts of tourism can include: change or loss of indigenous identity and values; culture clashes; changes in family structure; conflict within the community for the tourism dollar; and ethical issues, including an increase in sex tourism, crime, gambling, and/or the exploitation of child workers. 5
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. In some destinations, there is a great appreciation of the environmental resources as the source of the tourism industry, and as such there are environmental protection policies and plans in place. Tourism has helped to save many delicate ecosystems and their flora and fauna. Preservation of these important resources benefits not only the tourist but also the local residents as well.
Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can still have severe negative economic impacts. According to The United Nations Environment Programme, these can include the depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.), pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering), and physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity, and spread of disease). 6
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach beyond local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is often identified as a major contributor to climate change.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate.
The original version of this chapter contained H5P content. This content is not supported in cloned books. You may want to remove or replace this section.
The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves.” 7 Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry.

The pineapple has long been the symbol of hospitality. The Caribs, indigenous people of the Lower Antilles in the Caribbean, first used it as such a symbol. The Spaniards knew they were welcome if a pineapple was placed at the entrance to the village. This symbolism spread across Europe and North America where it became the custom to carve the shape of a pineapple into the columns at the entrance of the plantation. 8 Charles Carter added a three and a half foot wooden pineapple to the peak of the roof at Shirley Plantation, the first plantation in Virginia. 9 It is now common to see the image of the pineapple as a sign of welcome, warmth and hospitality.
The types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business — whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground — are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation and lodging . Figure 16.4 summarizes the various groupings within the industry.
Hotel Types
Hotels are typically referred to by hotel type or other classifications. Hotel type is determined primarily by how it will function and what amenities will be included within the property. Size, location, service levels and type of business or targeted market segments are additional classifications. Industry also classifies hotels by chain scale…separating hotels into categories determined by their average daily rates. Various ownership structures and brand affiliations also differentiate hotels.
Classifications
Hotels may be classified on a number of different variables. Type of Hotel : There are numerous classifications by hotel type including all-inclusive hotels, all-suite properties, B&B/Inns, boutique, convention/conference centers, condo hotels, resort, extended stay, full service, casino, limited service and timeshare properties. Size and Complexity: A hotel can be classified by the number of guest rooms it has; hotel sizes can range from a small boutique hotel with fewer than 50 rooms to a large resort hotel with more than 1,000 rooms. The complexity of the hotel is determined by the volume and number of additional revenue generating functions such as the square feet of available conference space, number of F&B operations and additional services and amenities like pools, fitness centers, spas, golf, etc. Location: The location of a hotel can also determine the type of guest served. An airport hotel may be very different from a city-center property in an urban environment, or a remote island resort or a small quaint bed and breakfast located on top of a mountain. Hotels that specialize in conferences, may locate near entertainment destinations like Las Vegas or Disney theme parks to provide pre-post conference activities for attendees. Service Level: The level of service provided is also a key variable, ranging from an inexpensive budget or economy hotel, (Limited or Focused Service Hotels) which may have limited services and amenities, to upscale and luxury hotels (Full Service Hotels) with many services and a wide range of amenities. Market Segmentation: Figure 16.5 on the next page outlines the characteristics of specific hotel types that have evolved to match the needs of a particular traveler segment. As illustrated, hotels adapt and diversify depending on the markets they desire and need to drive occupancy levels and generate revenues. Some hotels will specialize in a specific market segment, but in today’s competitive environment, most hotels will target a combination of these segments.
There are several other industry related organizations, such as Forbes and AAA which provide Consumer Ratings for individual hotels….another form of classifying a property. Forbes has traditionally awarded 1 to 5 “Stars” and AAA, 1 to 5 “Diamond” ratings. Additionally, many social media applications like Trip Advisor offer hotel property ratings to consumers.
Chain Scale: Smith Travel Research (STR) is an organization that provides the lodging industry with global data benchmarking, analytics and marketplace insights. STR classifies the lodging industry into six chain scale segments according to their respective brand Average Daily Rate (ADR). The six segments are defined as Luxury ; Upper Upscale ; Upscale ; Mid-Scale with F&B ( Upper Mid-Scale ); Mid-Scale without F&B ( Mid-Scale ) and Economy . Through STR’s 30 –plus years of service to the hospitality industry, they have developed vital benchmarking performance solutions, established market trend transparency and provided data used by the investment community to support hotel development projects. Their core product, the STAR report, provides hotel owners and operators with comparative performance data between their property and a defined set of market competitors and allows you to follow trends in hotel occupancy, average daily rate (ADR) and revenue per available room (RevPar). Developers, investors, industry analysts, hotel brands and management companies all utilize STR data when determine what type of hotel to build and what location would provide maximum opportunity for success.

The type of ownership, brand affiliation and management are also very important variables in the classification of hotels. Owners may manage their own hotels independently but in today’s competitive environment, they would likely sign a Franchise Agreement with a nationally recognized brand as well as a Management Contract with a hotel management company to manage the property. A hotel chain such as Marriott, Hilton, Hyatt or IHG (Intercontinental Hotel Group) is comprised of multiple brands: Marriott, following their recent merger with Starwood currently has 30 different hotel brands, with each name representing a different level of price, service or targeted market segments.
Branding Decision
Selecting a brand affiliation is one of the most significant decisions hotel owners must make. 10 The brand affiliation selected will largely determine the cost of hotel development or conversion of an existing property to meet the standards of the new brand. The affiliation will also determine a number of things about the ongoing operation including the level of services and amenities offered, cost of operation, marketing opportunities or restrictions, and the competitive position in the marketplace. For these reasons, owners typically consider several branding options before choosing to operate independently or to adopt a brand affiliation.
Franchise Agreements
Another managerial and ownership structure is franchising. A hotel franchise enables individuals or investment companies (the franchisee) to build or purchase a hotel and then buy or lease a brand name to become part of a chain of hotels using the franchisor’s hotel brand, image, loyalty program, goodwill, procedures, cost controls, marketing, and reservations systems. 11
A franchisee becomes part of a network of properties that use a central reservations system with access to electronic distribution channels, regional and national marketing programs, central purchasing, revenue management support, and brand operating standards. A franchisee also receives training, support, and advice from the franchisor and must adhere to regular inspections, audits, and reporting requirements.
Selecting a franchise structure may reduce investment risk by enabling the franchisee to associate with an established hotel company. Franchise fees can be substantial, and a franchisee must be willing to adhere to the contractual obligations with the franchisor. 12 Franchise fees typically include an initial fee paid with the franchise application and continuing fees paid during the term of the agreement. These fees are usually a percentage of revenue but can be set at a fixed fee. The total percentage of sales ranges significantly for hotels from 3.3% – 14.7% with a median of 11.8%. 13

Management Contracts
It is common for ownership to utilize a management contract , which is a service offered by a management company to manage a hotel or resort for its owners. Owners have two main options for the structure of a management contract. One is to enter into a management agreement with an independent third-party hotel management company to manage the hotel. There are hundreds of these companies, but some of the large organizations include Aimbridge, Benchmark Hospitality, Crescent Hotels, Interstate Hotels, and White Lodging. A slightly different option is for owners to select a single company to provide both the brand and the expertise to manage the property. Marriott, Hilton, and Hyatt, are companies that provide this second option to owners.

Food and Beverage Services

The food and beverage sector is commonly known to industry professionals by its initials F&B. The F&B sector grew from simple origins to meet the basic needs for food and beverage services to increasing demand for unique experiences and broader options. As the interests of the public became more diverse, so too did the offerings of the F&B sector. The increasing awareness and demand for organic, sustainable, local or craft options as well as special dietary needs in food and beverage continue to challenge this industry. In addition, in order to better attract and serve a diverse array of diners, the F&B industry now consists of a variety of segments. The following is a discussion of each.
Quick Service Restaurants
Formerly known as fast-food restaurants, examples of quick-service restaurants , or QSRs, include Chick-fil-A, Subway, and Pizza Hut. This prominent portion of the food sector generally caters to both residents and visitors, and it is represented in areas that are conveniently accessed by both. Brands, chains, and franchises dominate the QSR landscape. While the sector has made steps to move away from the traditional “fast-food” image and style of service, it is still dominated by both fast food and food fast; in other words, food that is purchased and prepared quickly, and generally consumed quickly as well.

Fast Casual Restaurants
Fast Casual restaurants focus on higher quality ingredients than QSR’s and provide made-to-order food in an environment that does not include table service. Customers usually queue and order at a counter. The seating area is more upscale and comfortable. Examples would include Chipotle Mexican Grill, Panera and Jason’s Deli.

Full-Service Restaurants
Full-service restaurants are perhaps the most fluid of the F&B operation types, adjusting and changing to the demands of the marketplace. Consumer expectations are higher here than with QSRs. 14 The menus offered are varied, but in general reflect the image of the restaurant or consumer’s desired experience. Major segments include fine dining, family/casual, ethnic, and upscale casual. Fine dining restaurants are characterized by highly trained chefs preparing complex food items, exquisitely presented. Meals are brought to the table by experienced servers with sound food and beverage knowledge in an upscale atmosphere with table linens, fine china, crystal stemware, and silver-plate cutlery. The table is often embellished with fresh flowers and candles. In these businesses, the average check, which is the total sales divided by number of guests served, is quite high (often reviewed with the cost symbols of three or four dollar signs: $$ \$\$\$ or \$\$\$\$ $$.) Examples include the Inn at Little Washington, Ruth’s Chris Steakhouse and Capitol Grille.

Casual restaurants serve moderately-priced to upscale food in a more casual atmosphere. Casual dining comprises a market segment between fast casual establishments and fine dining restaurants. Casual dining restaurants often have a full bar with separate bar staff, a larger beer menu and a limited wine menu. This segment is full of chains such as Chili’s, Outback, Red Robin and Cracker Barrel as well as many independent restaurants in regional or local markets.
Family restaurants offer affordable menu items that span a variety of customer tastes. They also have the operational flexibility in menu and restaurant layout to welcome large groups of diners. An analysis of menus in family/casual restaurants reveals a high degree of operational techniques such as menu item cross-utilization, where a few key ingredients are repurposed in several ways. Both chain and independent restaurant operators flourish in this sector. Examples of chains in this category would be Golden Corral, Cici’s Pizza and Ponderosa Steakhouse.
Ethnic restaurants typically reflect the owner’s cultural identity, Vietnamese, Cuban, Thai, etc. The growth and changing nature of this sector reflects the acceptance of various ethnic foods within our communities. Ethnic restaurants generally evolve along two routes: toward remaining authentic to the cuisine of the country of origin or toward larger market acceptance through modifying menu items. 15 Examples would be P.F. Chang’s, Tara Thai or Pei Wei.
Bars, Wineries, and Craft Distilling
The beverage industry continues to evolve as well with a strong focus on local craft beers, wines, cider and distilling. Wineries exist in almost every state, with over 250 in Virginia as of 2015. 16 Wine, bourbon, cider trails and brew pub crawls, etc. are used to generate awareness and create experiences for customers. Wineries often use event space or festivals to take advantage of the beauty of the winery and supplement their revenues.
Institutional Food Service
Institutional f ood s ervice is large scale and often connected to governmental (National Parks) or corporate level organizations. Often run under a predetermined contract, the institutional F&B sector includes:
- Educational institutions
- Prisons and other detention facilities
- Corporate staff cafeterias
- National Park restaurants and concessions
- Cruise ships
- Airports and other transportation terminals and operations
Examples of companies who focus on Institutional Food Service are Compass, Sodexho, Aramark.

Accommodation Food Service
This sector includes hotel restaurants and bars, room service, and self-serve dining operations (such as a breakfast room). Hotel restaurants are usually open to the public and reliant on this public patronage in addition to business from hotel guests. Collaborations between hotel and restaurant chains have seen reliable pairings such as the combination of Shula’s Steakhouse and Marriott Hotels.
Restaurant Industry Profitability and Cost Control
According to the National Restaurant Association, QSRs have the highest pre-tax profit margin at 6.3%, while full-service restaurants have a margin of 4.7%. There will be significant variances from these percentages at individual locations, even within the same brand. 17
A number of costs influence the profitability of an F&B operation. Some of the key operating expenses (as a percentage of revenue) are detailed in Figure 16.16, above, where food cost and salaries & wages are the two major expenses, each accounting for approximately a third of the total. Other expenses include rental and leasing of venue, utilities, advertising, and depreciation of assets. These percentages represent averages, and will vary greatly by sector and location.
Cost control and containment is essential for all F&B businesses. Demanding particular attention are the labor, food, and beverage costs, also known as the operator’s primary costs. In addition to these big ticket items, there is the cost of reusable operating supplies such as cutlery, glassware, china, and linen in full-service restaurants.
Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one’s spare time 19 and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however, is more challenging.
Let’s start by exploring some recreation-based terms that are common in the tourism industry. Outdoor recreation can be defined as “outdoor activities that take place in a natural setting, as opposed to a highly cultivated or managed landscape such as a playing field or golf course.” 20 This term is typically applied to outdoor activities in which individuals engage close to their community. When these activities are further away, and people must travel some distance to participate in them, they are often described as “adventure tourism”. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), adventure tourism is “a trip that includes at least two of the following three elements: physical activity, natural environment, and cultural immersion.” 21

Ultimately, categorization is based on a combination of several factors, including manner of engagement in the activity (risk exposure, experience requirement, group or solo activity), the distance travelled to access the activity, and the type of environment (proximity to nature, level of challenge involved) in which the activity occurs.
A 2013 adventure tourism market study discovered that people who travel for adventure experiences tend to be well-educated, with 48% holding a four-year degree or higher credential. They value natural beauty and rank this factor highest when choosing a destination. The most cited reasons for their travel are “relaxation, exploring new places, time with family, and learning about different cultures.” 22
Globally, it is estimated that the continents of Europe, North America, and South America account for 70% of adventure tourism, or US$263 billion in adventure travel spending. 23
Entertainment
Entertainment is a very broad category which overlaps with many of the areas discussed elsewhere in this chapter, like hotels and accommodation. Two major types of entertainment that we’ll discuss here are gaming and theme parks.
Gaming has grown significantly in the U.S. and globally. The number of casinos in the U.S. has been growing since 2010, and in 2013, there were over 500 commercial casinos, as shown in Figure 16.16. Casinos are found all over the U.S. in major cities, riverboats, and on Native American lands. However, U.S. casino revenue has been relatively flat, while global gaming revenues have been on the increase, largely due to Asian market growth. Most casinos involve other facets of the Hospitality industry such as lodging, F&B, golf, entertainment, spas, etc., but they also have the added challenges of casino operations.

Theme Parks
Theme parks have a long history dating back to the 1500’s in Europe, and have evolved ever since. Today, it is hard not to compare any amusement park destination to Disneyland and Disney World. Opened in 1955 in sunny California, Disneyland set the standard for theme parks. Theme parks outside of California and Florida are often highly seasonable operations challenged with significant staffing and training requirements each year.

Convention and Event Management
A convention is a large meeting of people with similar interests who meet for a period of at least a few days to discuss their field. An event is a gathering at a given place and time, usually of some importance, often celebrating or commemorating a special occasion.
Both conventions and events can be extremely complex projects, which is why, over time, the role of meeting planners has taken on greater importance. The development of education, training programs, and professional designations such as CMPs (Certified Meeting Planners), CSEP (Certified Special Events Professional), and CMM (Certificate in Meeting Management) has led to increased credibility in this business and demonstrates the importance of the sector to the economy.
Meeting planners may be independent contractors hired to facilitate the planning process, work directly for the company full time to coordinate their meeting, or work for hotels, conference centers and event venues directly.
- The various tasks involved in meeting and event planning include:
- Conceptualizing/theming
- Site inspection & selection
- Logistics and planning
- Human resource management
- Marketing and public relations
- Budgeting and financial management
- Sponsorship procurement
- Management and evaluation
Event Categories
Mega events.
A m ega-event is a large scale, highly prestigious event such as the Olympic Games, the FIFA World Cup, or a global economic summit. These events typically gain tremendous media coverage and have major economic impacts on the host location, both positive and negative. High levels of tourism (1 million+ visitors) associated with a mega-event brings revenue, but the revenue may be outweighed by substantial capital and social costs incurred by the host. The events are often awarded to host destinations through a bidding process and gain tremendous media coverage.

Special Events
A special event is a one-time or infrequent specific ritual, presentation, performance, or celebration. Special events are planned and created to mark a special occasion, such as a presidential inauguration or the Queen of England’s 90 th birthday. Like mega-events, there may be significant media coverage and economic impact for the host city or destination.
Hallmark Event
A hallmark event is a unique event that is often identified with the location where it is held, like Carnival in Rio de Janeiro or Oktoberfest in Munich. Hallmark events contribute significant economic benefits and even can create a competitive advantage for the host city or destination that attracts tourists.

A festival is a themed public celebration that conveys, through a kaleidoscope of activities, certain meaning to participants and spectators. Festivals are often celebrations of community or culture and feature music, dance, or dramatic performances. Examples include Lollapalooza, the Cannes Film Festival, and Junkanoo in the Bahamas.
Local Community Events
A local community event is generated by and for locals; although it may attract tourists, its main audience is the local community. The community may experience measurable economic impacts, as might happen at The Steppin’ Out Street Fair in Blacksburg (think hotel stays and eating out). Fundraisers and community picnics are also examples in this category.
Meetings and Conventions
The tourism industry also has a long history of creating, hosting, and promoting meetings and conventions that draw business travelers. In fact, Convention and Visitor Bureau’s (CVB’s) work hard to attract these meetings and conventions to their city to drive economic benefit for hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, etc.
There are several types of such events.
Conventions generally have very large attendance, and are held on a regular schedule but in different locations. They also often require a bidding process. Political conventions are one such example.
Association M eetings or C onferences are held regionally and nationally for hundreds of associations or events focused on specific themes. Examples would be the National Restaurant Association Annual Convention, ComicCon, or the National Auto Show.
Corporate M eetings will vary significantly in size and purpose and include regional or national sales meetings, shareholder meetings, training sessions, or celebrations. The location will vary depending on the nature of the meeting. They may be held at an airport property, a traditional corporate meeting facility or even an upscale resort.
Trade S hows and T rade F airs can be stand-alone events, or adjoin a convention or conference.
S eminars , W orkshops , and R etreats are examples of smaller-scale events.
As meeting planners have become more creative, meeting and convention delegates have been more demanding about meeting sites. No longer are hotel meeting rooms and convention centers the only type of location used; non-traditional venues have adapted and become competitive in offering services for meeting planners. These include architectural spaces such as airplane hangars, warehouses, or rooftops and experiential venues such as aquariums, museums, and galleries. 24
Transportation and travel services are another large element of the tourism industry. This area includes cruise ships, airlines, rail, car rentals, and even ride sharing such as Uber and Lyft. Each of these segments is impacted significantly by fuel costs, safety issues, load factors and government regulation.
If you’ve ever been on a cruise, you are in good company. According to CLIA (Cruise Lines International Association), 23 million passengers were expected to go on a cruise worldwide on 62 member lines in 2015. 25 The industry employs over 900,000 people. 26
Over 55% of the world’s cruise passengers are from North America, and the leading destinations (based on ship deployments), according to CLIA are: 27
- The Caribbean (36%)
- The Mediterranean (20%)
- Northern Europe (11%)
- Australia/New Zealand (6%)
- Alaska (6%)
- South America (3%)

The t ravel services sector is made up of a complex web of relationships between a variety of suppliers, tourism products, destination marketing organizations, tour operators, and travel agents, among many others. Under the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), the travel services industry group includes “establishments primarily engaged in travel arrangement and reservation services. Examples … are tourist and travel agencies; travel tour operators and wholesale operators; convention and visitors’ bureaus; airline, bus, railroad and steamship ticket offices; sports and theatrical ticket offices; and airline, hotel and restaurant reservation offices.” 28 Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveler (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travelers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveler and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies. 29 Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
Online travel agencies (OTAs)
Online travel agents (OTAs) are companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include Booking.com, Expedia.com, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs are gaining popularity with the travelling public; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion 30 and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013. 31 Over 40% of U.S. travelers booked flights online in 2014. 32
Tour operators
A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveler. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies. 33 Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveler could by purchasing individually.
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs)
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” 34 .
Country Clubs
Country c lubs are another part of the Hospitality industry with a very different service strategy focusing on serving members who will develop relationships with the staff compared to a more transactional service interaction in lodging, restaurants or airlines.
Country clubs do not focus as strongly on profit as they do on maximizing member satisfaction, retention and growth while maintaining an attractive fee structure. Country (or city) clubs, will typically have restaurant and bar operations, catered events and other amenities such as golf, tennis, pool, fitness facilities, etc. Depending on the type of club, family and youth events are important to maintain and grow membership.
Strong customer service, culinary, event management and general management skills are necessary to be successful in clubs.

Chapter Video
As in any other fast-moving industry, the landscape in Hospitality and Tourism is always changing. This video explores 10 of the more important current trends impacting the industry.
(Copyrighted material)
Key Takeaways
- The Tourism industry is the largest industry in the world with significant benefit and costs to a region. The global competition for the tourism dollar is significant within the US and between countries.
- Hotels vary significantly in size, quality, purpose, chain affiliation, and ownership. The complexity of the operation and leadership vary as well.
- Food and Beverage is made up of a wide variety of restaurant types from QSR, Fast Casual, Fine Dining and Ethnic. Institutional food service in business , hospitals, education, parks and concessions are a significant part of the Food and Beverage industry.
- The evolution of tastes and consumer expectations in food and beverage continue to provide opportunity and challenges in the industry for ethnic sustainable, organic, local, craft, and other unique experiences.
Chapter 16 References and Image Credits
Portions of this chapter were adapted from Westcott, Morgan (Ed) Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC. CC BY 4.0 https://opentextbc.ca/introtourism Available for free at: http://open.bccampus.ca
Image Credits: Chapter 16
Figure 16.1: JackMac34 (2015). “Untitled.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/italy-burano-postcards-971575/
Figure 16.2: “The Impact of Global Tourism.” (2016) Data retrieved from: http://www2.unwto.org/content/why-tourism
Figure 16.3: Yellowute (2007). “Shirley Plantation.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shirley_Plantation_2006.jpg
Figure 16.6 “Example of a Hotel Market segmentation by STR’s chain scale” Author’s own work. Licensed CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16.7: Christina Hsu (2009). “San Diego City and Bay at Night.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://flic.kr/p/6KZ5Cv
Figure 16.8: Anastasia Cortes (2016). “The Inn at Virginia Tech.” Public domain. Provided by author.
Figure 16.9: Dale Cruse (2014). “New Zealand langoustines at Troquet.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dalecruse/8551895022/
Figure 16.10: Imzadi1979 (2012). “An example of a typical American logo sign.” Public domain photograph. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logo_sign#/media/File:Logo_Sign.svg
Figure 16.11: J. Winters (2008) “A Red Robin Restaurant in Tukwila, Washington.” Public domain photograph. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Red_Robin_in_Tukwila,_Washington.jpg
Figure 16.12: “Le Procope.” © Michael Rys. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restaurant#/media/File%3AInside_Le_Procope.jpg
Figure 16.13 “The restaurant industry career path” Author’s own work. Licensed CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16 .15 : JohnSM (2013). “Rafting in Turkey.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/rafting-turkey-travel-1125213/
Figure 16 .16 : Graph data sources: Statista (2016). “ Number of commercial casinos in the United States from 2005 to 2013.” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/187972/number-of-us-commercial-casinos-since-2005/ and “ Global casino gaming revenue from 2006 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars).” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/271577/global-casino-gaming-market-revenue/ and “ U.S. casino gaming market revenue from 2004 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars) .” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/271583/casino-gaming-market-in-the-us/
Figure 16 .17 : Josh Hallett (2009). “ The ‘Big Bang’ at Wishes – Magic Kingdom – Walt Disney World .” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/hyku/3830182777
Figure 16.18: Peter23 (2011). “Beijing National Stadium.” CC BY- SA 3.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beijing_National_Stadium#/media/File:Beijing_national_stadium.jpg
Figure 16.19 : Skeeze (2014). “Mardi Gras in New Orleans.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/mardi-gras-new-orleans-festival-1176483/
Figure 16 . 20 : Roger W. (2012). “ Charlotte Amalie – Panorama (Postcard) ” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/24736216@N07/7170231567
Figure 16 . 21 : Dan Perry (2006). “Riviera Country Club in Pacific Palisades, California.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Country_club#/media/File:Riviera_Country_Club,_Golf_Course_in_Pacific_Palisades,_California_(168828797).jpg
Video Credits: Chapter 16
Sisyanti, Ling Ling, Wasim Amsal,Ella Qiu, and Rebecca Catherine Stephany. “10 trends in Hospitality and Tourism Industry.” February 6, 2015. Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SJ8Momwv7Qk
References: Chapter 16
Chapter 16 Hospitality & Tourism Copyright © 2018 by Richard Parsons; Stephen Skripak; Anastasia Cortes; Anita Walz; and Gary Walton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
If you build it, they will come: Why infrastructure is crucial to tourism growth and competitiveness

Tourism is expanding globally, but can infrastructure keep up?
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Maksim Soshkin

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, travel and tourism.
With international tourist arrivals reaching 1.4 billion in 2018— two years ahead of initial projections —the travel and tourism industry will continue to drive global connectivity. The World Economic Forum’s 2019 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report shows this growth is backed by improving global travel and tourism competitiveness, which stems, in part, from growing aviation capacity, increased international openness, and declining travel costs.
However, the report also shows the need for developing infrastructure, which may not be able to keep up with the additional 400 million arrivals forecasted by 2030 . While infrastructure challenges differ for various regions and levels of economic development, failure to address these challenges may reduce competitiveness, hurting the travel and tourism industry.
Infrastructure—including air, ground, port, and tourism services like hotel rooms and car rental services—plays a vital role in travel and tourism competitiveness, serving as the arteries of the industry. And from a global perspective, infrastructure continues to improve.

Since 2017 , air transport infrastructure is one of the most improved components in the index, with strong growth in scores across most regions, subregions and economic development levels. However, much of this performance has come from growing route capacity and the number of carriers operating. Perceptions of the quality of air transport infrastructure, while better since 2017, have grown more slowly, while most recent airport density figures indicate slightly reduced airport access than before. These results potentially indicate that travel demand and airline growth may eventually outstrip hard-infrastructure capacity. By 2037, the International Air Transport Association projects the number of air passengers could double to 8.2 billion.
The report also shows that global perspectives on the quality and efficiency of ground transport infrastructure and services have remained, on average, near stagnant. Given the projected growth in travel as well as the need for infrastructure to accommodate more tourism-related needs, significant work will be required to bridge multi-trillion dollar investment deficits for airports, ports, rail and roads.

The results could be used to assess the infrastructure readiness of economies by looking at their scores for infrastructure and tourist arrival trends. The figure above compares country subregion and income-level groupings against their growth in international tourist arrivals from 2013 to 2017. It is clear tourism is growing in most subregions and among all income groups, with many above the global rate of growth.
Most of the regions on the right side of the figure above are relatively advanced countries with well-developed infrastructure. As a result, they may have more capacity to handle tourism growth. Moreover, it is also apparent that, despite market maturity, such countries are still welcoming more and more tourists each year. As the figure shows, high-income economies had the largest increase in arrivals, growing faster than the global rate. But while these economies have strong infrastructure, their share of arrivals and growth rates reveals the pressure on their infrastructure.
High-income economies analysed accounted for nearly 65% of arrivals in 2017 and 74.3% of growth in arrivals between 2013 and 2017. Subregions like Southern Europe and Eastern Asia-Pacific have seen rapid growth in arrivals, putting pressure on their more developed infrastructure. Arrivals in Western European countries, which on average, have the best infrastructure in the ranking, might seem to be below the global rate of growth but accounted for nearly one-fifth of global arrivals in 2017, and nearly 14% of the increase globally since 2013.
Northern Europe has experienced some of the fastest growth in arrivals in recent years and had the third-largest improvement in scores for air transport infrastructure since 2017. But its well-developed infrastructure may still come under strain, with this year’s report showing the region’s growth in ground, port and tourist infrastructure was below the global average.
South-East Asia has also experienced strong growth in tourism in recent years, but its near-average infrastructure scores indicate it might lack the capacity to continue accepting tourists. Countries like Vietnam, Indonesia and the Philippines have recently seen a surge in tourism, but, despite improvement in scores, all rank below average for infrastructure.
The regions on the left side of the figure mostly consist of lower-income countries. While these economies do not account for the same volume of arrivals as the more developed regions and countries, they still face capacity issues because their infrastructure is less developed. Nevertheless, due to higher price competitiveness, economic growth and declining travel barriers, many of these countries have also seen some of the biggest percentage increases in arrivals.
Countries in subregions on the upper left-hand quadrant may be at greatest risk of strain due to rapid visitor growth and underdeveloped infrastructure. In particular, this is an issue for South Asia, Western Africa, South America and the Balkans and Eastern Europe. On the other hand, nations on the bottom left-hand quadrant have less tourism growth, though this might be due to their limited infrastructure capacity, among other factors.
How countries deal with their infrastructure will be a crucial factor in their long-term travel and tourism competitiveness. Even nations with developed airports and roads may face strain under growing utilization, which may lead to issues related to quality.
Have you read?
These islands are using tourists to help offset the effects of tourism, why china will soon be the world's top destination for tourists, in the age of the tourism backlash, we need 'destination stewards', tourism is damaging the ocean. here’s what we can do to protect it.
However, it is also important to note competitiveness relies on far more than just infrastructure. Emerging economies also have more work to do when it comes to improving business environments, addressing safety and security concerns and reducing travel barriers. Natural assets, which attract a significant number of visitors internationally, also need to be better protected. For example, South America and South-East Asia outscore the global average for natural resources by about 27% and 11%, respectively, but score below average for environmental sustainability. Consequently, many countries in these subregions may be at risk of damaging the very assets that make great travel destinations.
In some cases, improvements in one area of competitiveness without progress elsewhere can also lead to issues. For instance, Iceland’s improvement in air connectivity and surging visitor volumes was not matched by price competitiveness and overall tourism capacity, potentially explaining its recent slowdown .
Handling all these issues cannot be the purview of only travel and tourism stakeholders. Improving competitiveness, especially as it relates to travel and tourism, requires a holistic, multistakeholder approach.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Travel and Tourism .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

Turning tourism into development: Mitigating risks and leveraging heritage assets
Abeer Al Akel and Maimunah Mohd Sharif
February 15, 2024

Buses are key to fuelling Indian women's economic success. Here's why
Priya Singh
February 8, 2024

These are the world’s most powerful passports to have in 2024
Thea de Gallier
January 31, 2024

These are the world’s 9 most powerful passports in 2024

South Korea is launching a special visa for K-pop lovers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance. Understand the economic, social, and environmental benefits and costs of tourism. Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition. Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined. Examine the different categories of food service operations.
A tourism system can be defined as a framework that shows the interaction between: tourism supply at the destination, the bridging elements between supply and demand, and tourism demand (see Figure 4.1). The relationship between demand and supply, via the bridging elements, is a two-way link. In the tourism system, the supply at the destination ...
Components of tourism:Transport services . The relationship between transport and tourism is strong.. According to the most commonly accepted definitions of tourism, a person must travel away from their home environment for at least one night in order to be a tourist (although I would argue that this definition needs updating given that it doesn't account for novel forms of tourism such as a ...
Exploring the five major tourism and hospitality supply components. When it comes to understanding the tourism and hospitality industry, it's crucial to familiarize yourself with the five major supply components. These components play a vital role in shaping the overall experience for travelers and guests. Let's take a closer look at each ...
Figure 1.2 The tourism supply chain. [Long Description] Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it's important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date. Long Descriptions. Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the ...
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries. Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including ...
ABSTRACT. The tourism industry was seen as one of the main beneficiaries of globalisation prior to the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic. However, while tourism is a major driver of economic growth and social well-being, a transformation of the industry towards more sustainable practices along the tourism supply chain (TSC) is needed to ensure that sustainable development goals can be reached.
Tourism supply chains involve many components: accommodation, transport, excursions, bars and restaurants, handicrafts, food production, waste disposal, and the infrastructure that supports tourism within chosen destinations. The importance of one such component, transport, for the efficiency of the tourism supply chain is precisely the topic ...
These services are also included in the package holiday produced by the tour operator: the hospitality firms supply accommodation services of different variety and quality (see Sect. 9.2 ); transport firms supply different types of travel (see Sect. 9.3 ); and museums, amusement parks, and other firms supply leisure or cultural attractions (see ...
THE TRAVEL INDUSTRY. It is a tourism and hospitality network, which includes both the public and private sectors. The composite of organizations, both private and public, that are involved in the development, production, and marketing of products and services to serve the needs of the travelers." (Gee, Choy & Makens, 1997) In simpler terms ...
Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance. Understand the economic, social and environmental benefits and costs of tourism. Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition. Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined. Examine the different categories of food service operations.
4. Activities and Attractions. The fourth component of tourism and hospitality is activities and attractions. This includes museums, theme parks, tours, outdoor recreation, and more. Activities and attractions providers aim to provide visitors with unique experiences that they'll remember for years to come.
Natural resources Infrastructure Superstructure Hospitality Resources Transportation and Transportation equipment. Tourism Supply Components: Natural Resources. Land forms, climate. Infrastructure. underground and surface development, highways and roads (most of the time) Superstructure.
The Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply Components - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document discusses the macro perspective of tourism and hospitality. It identifies the direct and indirect components that make up the tourism and hospitality network, including public and private sector ...
Since 2017, air transport infrastructure is one of the most improved components in the index, with strong growth in scores across most regions, subregions and economic development levels.However, much of this performance has come from growing route capacity and the number of carriers operating. Perceptions of the quality of air transport infrastructure, while better since 2017, have grown more ...
4.6 Marketing plan. A marketing plan is a comprehensive plan for marketing activities to be undertaken to ensure the growth of the business. It is a combination of a review of the present, a vision for the future and defining the steps required to ensure that the vision is achieved.
Definition of tourism supply: The supply of all assets, services, and goods to be enjoyed or bought by visitors and occasioned by the journeys of visitors. Tourism supply consists of an ...
category deals with tourism development that is more complex and broader in scope compared to the production of daily travel services Tourism System can be defined as a framework that shows the interaction between tourism demand, the bridging components between supply and demand, and the tourism supply at a destination
W4 W5 the Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply Components - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
The document discusses the various components that make up the tourism and hospitality supply network. It identifies 5 major components: natural resources, infrastructure, superstructure, transportation and transportation equipment, and hospitality resources. It provides details on the types of facilities and services that fall under each component, such as accommodations options ...
MODULE 6 - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.