Get Vaccinated Before You Travel
It’s important to plan ahead to get the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit.

Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by:
- Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip
- Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines
- Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family’s travel plans
Avoid getting sick or coming back home and spreading the disease to others.

Vaccinate at least a month before you travel
See your doctor when you start to plan your trip abroad. It’s important to do this well in advance.
- Your body needs time to build up immunity.
- You may need several weeks to get all the doses of the vaccine.
- Your primary doctor may not stock travel vaccines. Visit a travel medical clinic .
- You’ll need time to prepare for your pre-travel appointment .
- If the country you visit requires a yellow fever vaccine , only a limited number of clinics have the vaccine and will probably be some distance from where you live. You must get it at least 10 days before travel.
Find out which vaccines are recommended or required for the countries you plan to visit .
TIP : Save time by getting routine vaccines during the same doctor visit. Use the Vaccine Self-Assessment Tool and discuss the results with your doctor. It tells you which U.S. recommended vaccines you (19 years and older) or your child (birth – 18 years) might need.
Last-minute travelers
When traveling to another country be aware your doctor may not carry a travel vaccine and you may have to visit a medical clinic.
Many travel vaccines require multiple shots or take time to become fully effective. But some multiple-dose vaccines (like hepatitis A) can still give you partial protection after just one dose. Some can also be given on an “accelerated schedule,” meaning doses are given in a shorter period of time.
- Discover and learn about specific diseases that can affect you while traveling
- What to do if you get sick after traveling
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
- Info Note For Passengers
INFO NOTE FOR TRAVELLERS
As part of the Government measures to prevent diseases that can potentially become epidemics, the Ministry of Health informs the general public and the international travelers visiting Rwanda of the following:
YELLOW FEVER
The following is the WHO list of Countries with risk of yellow fever transmission and countries requiring yellow fever vaccination. This list of countries is dynamic can change anytime depending on situation:
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela In a bid to prevent transmission of Yellow Fever in Rwanda,
1. All travelers traveling to Yellow Fever endemic countries should be vaccinated 10 days before traveling.
2. To enter Rwanda, a Yellow Fever vaccination certificate is not required to travelers (Residents / Non-Residents) coming from Yellow Fever non-endemic countries and without an active transmission outbreak of Yellow Fever.
3. To enter Rwanda, a Yellow Fever vaccination certificate is mandatory to travelers (Residents / Non-Residents) coming from Yellow Fever endemic countries and any country with an active Yellow Fever transmission outbreak
4. For travelers (Residents / Non-Residents) coming from an active Yellow Fever transmission outbreak country or have recently (within 24 days) visited an active Yellow Fever transmission outbreak country, the following instructions are applied:
i. An entry will bowed to a traveler (Residents / Non-Residents) who at arrival presents:
-A valid Yellow Fever vaccination certificate
-Without fever (less than 38.5oC)
-Consents to self-report for any symptoms for 6 days
iii. A traveler (Residents / Non-Residents) with an invalid Yellow Fever vaccination certificate (less than 10 days after vaccination) will be quarantined until the certificate becomes valid
iv. A traveler (Residents / Non-Residents) coming from a country with active Yellow Fever transmission or known Yellow Fever endemic country without a Yellow Fever vaccination certificate will be vaccinated upon entry.
v. No entry will be allowed to a traveler (Residents / Non-Residents) who does not consent for preventive measures described in points 1-4
vi. The cost related to quarantine and/or the vaccination upon entry will be covered by the traveler.
The following Covid-19 travel guidelines and procedures are in place for travelers, effective immediately. These guidelines will be regularly reviewed and revised in light of health conditions.
Before departure:
1. Covid-19 testing is no longer a requirement prior to boarding the flight to Rwanda. However, regular Covid-19 testing is encouraged.
2. The Passenger Locator Form is no longer a requirement before departure.
1. An additional Covid test is no longer required upon arrival at Kigali International Airport.
2. Face masks are no longer mandatory in Rwanda, but people are encouraged to wear a face mask in public indoors/closed spaces.
3. In addition, the public is urged to get frequently tested while continuing to observe preventive measures including social distancing and hand hygiene.
Test results:
Test results will be shared by SMS, and via the online portal accessible at www.rbc.gov.rw. In case of difficulty obtaining results, contact the RBC on 114 or [email protected].
1. A Covid test is no longer a requirement to depart Rwanda by air. However, Covid testing (at own cost) is available for all travellers whose final destination requires one at health centres and other designated sites.
2. All Rwandan travellers aged 12 years and above must show proof of full vaccination before departing Rwanda by air. Fully vaccinated for people aged 18 years and above means having two doses and a booster when eligible (administered 3 months after second dose.)
Emergency contact information
Call 114 or email [email protected]
- KAYAK for Business NEW
Rwanda Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Rwanda
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in enclosed environments and public transportation.
Rwanda entry details and exceptions
Ready to travel, find flights to rwanda, find stays in rwanda, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Rwanda from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Rwanda.
Can I travel to Rwanda if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Rwanda without restrictions.
Can I travel to Rwanda without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Rwanda without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Rwanda?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Rwanda.
Can I travel to Rwanda without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Rwanda?
Mask usage in Rwanda is not required in enclosed environments and public transportation.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Rwanda?
Restaurants in Rwanda are open. Bars in Rwanda are .
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Rwanda’s success in...
Rwanda’s success in rolling out its covid-19 vaccination campaign is a lesson to us all
- Related content
- Peer review
- Agnes Binagwaho 1 ,
- Kedest Mathewos 1
- 1 University of Global Health Equity
The discovery and approval of effective and safe covid-19 vaccines has provided a glimmer of hope during a seemingly intractable crisis. The vaccines were rapidly distributed across the globe, with priority given to the most at-risk populations in many rich countries. 1 While many have called for the equitable distribution of vaccines across the globe through COVAX, and continue to do so, this continues to be far from the reality. As of 1 April 2022, 64.5% of the world’s population has received at least one dose of the vaccine; yet, this proportion is only 14.5% in low-income countries. 2 It is in this context of vast vaccine inequity that we discuss Rwanda’s vaccination strategy and milestones over the past year.
Today, Rwanda has fully vaccinated over 60% of its population. 2 In a continent that is a covid-19 vaccine desert, this result is due to the hard work and early preparation of those in charge of the vaccine programme. Months before receiving covid-19 vaccines in the country, the Scientific Advisory Group and National Task Force for covid-19 vaccination met weekly to devise a vaccination strategy, identify gaps, and strengthen cold chain capacity. 3 Following these deliberations, Rwanda bought 437 new refrigerators, refrigerated vehicles, passive containers for transportation and 5 ultra-low temperature freezers to ensure readiness for the Pfizer vaccine which at that time needed be stored at −70°C. 3 4 By the time of arrival on 3 March 2021, the country was ready with the capacity to store over 5 million vaccines.
Following scientific advice aligned to the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) guidelines, Rwanda developed a vaccine priority list that included the most at-risk—medical professionals and community health workers, older populations, individuals with underlying conditions—including those in prisons and refugees—and all essential workers. 4 As more people were vaccinated in the country, the priority list was expanded to all individuals over 60 and over time, this age limit was reduced to 18 years old. 5 This national priority list was conceived rapidly and accurately using a nationwide demographic screening programme up to the community level and an up-to-date registry of non-communicable diseases at the facility level. This list is also currently being applied to the rollout of booster shots. 6
To make this equitable and effective distribution a reality, Rwanda adopted a coordinated and organised plan. Every single individual, both within the ministry of health and in implementing partner institutions, knew what to do. More than a month before vaccination started, at least two vaccination teams were appointed at each health facility across the country to ensure that healthcare workers had the capacity to vaccinate, manage, and electronically track the vaccinated. 3 Moreover, the location of vaccine delivery was adapted to reach communities that are most at-risk and hard-to-reach. For instance, door-to-door vaccination was adopted for those above 60 and those living with disabilities. 7 When the Ministry of Health expanded the eligibility list to include those above 18, the campaign was first focused in Kigali which is the most densely populated region and carries the highest covid-19 burden. 5 Afterwards, the delivery was done across the country following these criteria.
While many have claimed vaccine hesitancy to be the major hurdle to covid-19 vaccination in Africa, this is largely inaccurate. According to a 2018 Wellcome Trust study, the Rwandan population has the highest trust in the public health system, which explains the country’s high childhood vaccination rate. 8 9 This high level of trust was further reinforced by the government’s open communication. The Ministry of Health worked alongside various partners such as faith-based organizations, NGOs, local authorities, and the media to provide more information on the vaccines and dispel any misinformation. Examples of public engagement channels used include a one-page fact sheet and radio and TV channels. 10
One example of the vaccine rollout is on the night of 3 March 2021, 340 000 vaccines from COVAX – from Pfizer BioNTech and Oxford/AstraZeneca—arrived in Rwanda. 11 They were kept overnight at the central storage facility and recorded in an electronic registry. By noon of 4 March, the vaccines were distributed to all district hospitals that in turn distributed them to all health centers the same afternoon, using health sector trucks and other modes of safe transport available including military helicopters. The quantity of vaccines allocated to each district and health facility was based on a list created during the preparatory phase. 3 On the morning of 5 March, Rwanda had started vaccinating healthcare workers across the country and within three weeks, Rwanda had vaccinated 348 000 people, including doses donated by China at that time.
Rwanda has surpassed the 30% target it had set for the end of 2021 and is well on its way to achieving the 60% target for June 2022, having already vaccinated nearly 60% of its population. It is because of this efficiency and success that Rwanda Biomedical Center was named one of the covid-19 Vaccination Centers of Excellence by Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 12
Competing interests: none declared.
Provenance and peer review: commissioned, not peer reviewed
- ↵ Our world in data. Coronavirus vaccinations. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
- ↵ Tony Blair Institute for Global Change. Vaccinating Africa: What Governments Can Learn From Rwanda’s Effective Rollout. https://institute.global/advisory/vaccinating-africa-what-governments-can-learn-rwandas-effective-rollout
- ↵ World Health Organization. Rolling out Covid-19 vaccines in Rwanda. https://www.afro.who.int/news/rolling-out-covid-19-vaccines-rwanda
- ↵ Rwanda expands COVID vaccinations to people over 18. https://www.aa.com.tr/en/africa/rwanda-expands-covid-vaccinations-to-people-over-18/2344100
- ↵ Ministry of Health Rwanda. Twitter: https://twitter.com/RwandaHealth/status/1465369294699696140
- ↵ Africa ramps up vaccine drive as COVID cases surge. https://www.dw.com/en/africa-ramps-up-vaccine-drive-as-covid-cases-surge/a-58853367
- ↵ Wellcome Global Monitor. 2018. 18 June 2019. https://wellcome.org/reports/wellcome-global-monitor/2018
- McAlister H ,
- ↵ Factsheet covid 19 vaccine Kinya. https://rbc.gov.rw/fileadmin/user_upload/annoucement/Factsheet%20covid%2019%20vaccine%20Kinya.pdf
- ↵ 340 000 doses of COVAX vaccines due in Rwanda today. https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/340000-doses-covax-vaccines-due-rwanda-today
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Call 112 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company promptly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccinations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest information on vaccination recommendations and health risks in TravelHealthPro’s Rwanda guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Rwanda. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in Rwanda
Only limited medical facilities are available in Rwanda. If you have a serious accident or illness, you may need to be evacuated by air ambulance to Kenya or South Africa.
FCDO has a list of medical providers in Rwanda where some staff speak English.
There is also guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Rwanda .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Rwanda Travel Advisory
Travel advisory march 29, 2024, rwanda - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with updates to add area of Level 3.
Exercise normal precautions in Rwanda. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Exercise Increased Caution in:
- The Rwanda-Burundi border due to armed violence.
Reconsider Travel to:
- The Rwanda-Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) border due to armed violence.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Rwanda.
If you decide to travel to Rwanda:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Rwanda.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Rwanda- Burundi Border—Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution The Nyungwe Forest National Park abuts the border with Burundi. Borders may not be clearly marked. It is required to obtain permits from the Rwanda Development Board prior to entry. Relations between Burundi and Rwanda are tense and there have been cross-border incursions and armed violence.
Rwanda- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) Border – Level 3: Reconsider Travel Armed groups operate in DRC’s North and South Kivu provinces and Virunga Park which is adjacent to Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda. The area has experienced escalating levels of armed conflict which could spill across poorly marked borders. Permits are required from the Rwanda Development Board prior to entry to Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
How Rwanda is managing its COVID-19 vaccination rollout plans
Vice Chancellor, University of Global Health Equity
Disclosure statement
Agnes Binagwaho does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
View all partners
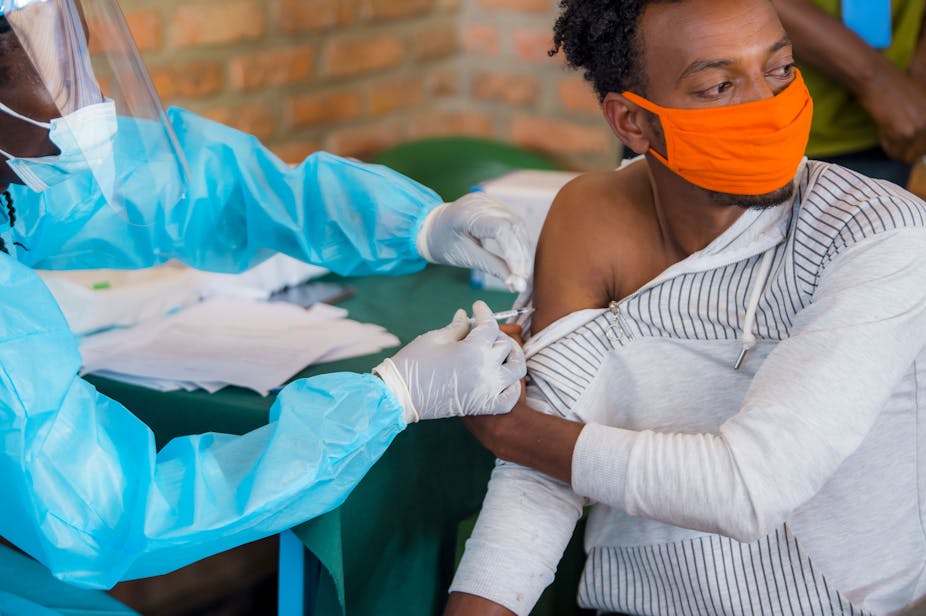
It’s been over a year since COVID-19 was declared a pandemic. In an amazing feat of science and technology, a number of safe and effective vaccine candidates have been developed. Most developed countries are well-advanced in rolling out vaccinations. The process is much slower in developing countries. In Rwanda, the government set a target of vaccinating 60% of the population – of nearly 13 million – by the end of 2022. To unpack Rwanda’s rollout strategy Ina Skosana from The Conversation Africa spoke to public health expert Professor Agnes Binagwaho.
What is the country’s COVID-19 vaccination strategy?
Rwanda’s strategy was developed based on scientific evidence and was rooted in the ideals of equity. This is much like Rwanda’s overall COVID-19 preparedness and response efforts .
The Ministry of Health defined a clear vaccination plan as soon as an agreement was finalised with COVAX , a global initiative aimed at equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines, and well before the vaccines from COVAX were delivered.
The plan had a priority list to ensure that essential workers and people most at risk of infection and COVID-19-related death would receive the vaccine first. The list of 3 million included frontline healthcare workers, the elderly, individuals with underlying conditions, and people living in crowded settings such as refugees and prison populations. Other essential workers such as teachers and women and men in uniform were also included.
Individuals were vaccinated across the country starting with healthcare workers, including the nearly 60,000 community health workers.
Weeks before the vaccines arrived in the country, the Ministry of Health prepared its storage and distribution capacity. In addition to preparing regular refrigerators used for other vaccines, Rwanda purchased five ultra-low refrigerators to store the Pfizer vaccine at -70 degrees Celsius.
This early logistical planning meant that Rwanda had the capacity to store 5 million doses before the vaccines arrived. The country also purchased refrigerated vehicles to ensure that all corners of the country could be reached.
Everyone in government and implementing partner institutions, such as UNICEF and the World Health Organisation (WHO), understood their role and were ready to start the campaign when the vaccines landed. To ensure equitable access to vaccines and remove any geographical barriers, Rwanda set up vaccination sites at health centres (one in each sector) and district hospitals. Healthcare workers in these sites were also trained before the arrival of the vaccines.
Rwanda put a lot of effort into fostering demand for the vaccines. The health ministry collaborated with civil society, faith-based organisations, local authorities and young volunteers to disseminate a one-page fact sheet with information on the vaccines. Radio and TV channels were also used to provide further information on the vaccines, with the Minister of Health and other health sector officials engaging with the public.
Lastly, to target vaccine hesitancy the government set up a toll free number so that people could report side, effects, or share positive stories.
What is the progress so far?
Rwanda received the first batch of vaccines in early March from the COVAX initiative: 342,960 Pfizer and AstraZeneca vaccines. Rwanda also received 50,000 donated doses from India on March 5th, 2021.
These were distributed within 48 hours to all district hospitals, which in turn distributed them to all health centres using trucks and military helicopters for hard-to-reach districts.
Within two days Rwanda had started its nationwide vaccination campaign. Vaccines were first administered to frontline healthcare workers as planned.
While both types of vaccines require two doses, Rwanda provided the first dose of AstraZeneca to as many people as possible, with the expectation of receiving more vaccines in time for the second dose. This allowed the country to maximise the number of people who were vaccinated. Rwanda is expecting to receive the second batch of COVID-19 vaccines before the end of April.
As of April 11th, 2021, 348,925 people in Rwanda had received their first dose of vaccines. This is nearly 9% of the 2021 target for vaccinated individuals.
What are the challenges?
Equitable distribution of vaccines continues to be a challenge across the world.
It is estimated the many people in low-income countries will have to wait until 2023 to be vaccinated.
Various factors contribute to this inequity. High-income countries are hoarding vaccines. Canada, for example, has secured more than 600% of the doses it needs to vaccinate its entire population. Moreover, these same countries are unwilling to share the vaccine technology.
These factors contribute to delays in getting vaccination programmes off the ground in developing countries. This is stalling the achievement of global herd immunity and preventing a quicker return to a state of normalcy.
In Rwanda, this delay can exacerbate an economy that has been pushed into recession during the pandemic, further affecting the economic well-being of individuals and businesses.
Unless high-income countries share the vaccine technology and decentralise the production of approved vaccines, we will all continue to face the repercussions of the COVID-19 pandemic.
What needs to happen next?
To meet its target of vaccinating 60% of the population of nearly 13 million by the end of 2022, Rwanda will need to procure more vaccines.
The country hopes to achieve this through international deals, through the African Vaccine Acquisition Task Team of the African Union as well as through the COVAX initiative.
Rwanda is closely following the evidence emerging about the safety of various vaccines and will continue to review the data regularly to ensure that the vaccines administered in the country are safe and effective.
The country will also continue to strictly enforce COVID-19 regulations such as mask wearing and social distancing given the limited supply of vaccines available in the country. These measures will also ensure the protection of the country in case of delays in vaccine delivery.
- Public health
- Coronavirus
- Community health workers
- COVID-19 vaccines
- Vaccine equity

Senior Enrolment Advisor

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

GRAINS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION CHAIRPERSON

Faculty of Law - Academic Appointment Opportunities

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Rwanda travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: April 10, 2024 08:12 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, rwanda - take normal security precautions.
Take normal security precautions in Rwanda.
Border with the Democratic Republic of Congo - Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid non-essential travel to areas within 10 km of the border with Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) due to the rebel groups in DRC near the border with Rwanda.
Back to top
Border with the Democratic Republic of Congo
The volatile situation in the eastern part of neighbouring Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) could lead to possible incursions into western Rwanda by DRC armed rebel groups.
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and bag snatching, occurs.
Theft is frequent in:
- hotel rooms
- crowded areas, such as markets
During your trip to Rwanda:
- ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and your other travel documents, are secure at all times
- avoid showing signs of affluence or wearing expensive jewellery
- avoid carrying large sums of cash or valuables
- keep your vehicle doors and windows locked at all times
Violent crime
Although rare, violent crime has occurred, namely:
- burglary, especially in Kigali
- armed robberies
Tourists are usually not targeted, however you could be at the wrong place at the wrong time.
During your trip:
- be aware of your surroundings at all times
- don’t venture out alone or travel outside major cities after dark
- avoid isolated areas
- if you're being robbed, hand over cash, electronic devices and valuables without resistance
Road safety
Road conditions.
The road system is generally good and well maintained in Kigali and on main roads throughout the country. Outside of these areas, most roads are not paved, and driving can be dangerous due to:
- insufficient lighting
- lack of traffic signs
- stray livestock
- poorly maintained vehicles
Driving habits
Drivers do not always respect traffic laws and sometimes drive at excessive speeds. However, speed cameras, present on all main roads, have reduced speeding frequency.
If you choose to drive in Rwanda:
- always drive defensively
- familiarize yourself with your itinerary before you leave
- avoid travelling after dark
- ask about insurance coverage options for roadside assistance when you rent a vehicle
Roadblocks are common throughout the country.
You may be asked for identification and your vehicle and luggage may be searched.
- Make sure your travel documents are up to date
- Do not go through a checkpoint without stopping, even if it appears unattended
- Follow the instructions of police officers
Cybersecurity
Cybercrime, malware attacks and online extortion occur in Rwanda.
Criminals can compromise public Wi-Fi networks to steal personal data or credit card information.
- Avoid online shopping on unencrypted websites
- Be cautious when posting information on social media
- Be especially cautious if you decide to meet someone you met online
- Be wary of unsolicited emails offering attractive business opportunities
- Don't click on suspicious links that ask for your banking information
Demonstrations
Demonstrations may occur, however a demonstration permit is required.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Adventure tourism
Outdoor activities, such as hiking, mountain biking, kayaking and other adventure activities can be dangerous if unprepared. Trails are not always marked, and weather conditions can change rapidly.
When visiting a national park:
- you must purchase a park permit from Rwanda’s Office of Tourism and National Parks
- consider hiring an experienced guide from a reputable company
- only use established trails
Rwanda’s Office of Tourism and National Parks
Water shortages
Water shortages may occur throughout the country during the long dry season from June to September.
- Plan accordingly
- Keep a supply of water on hand
Public transportation
Shared buses, motorbike taxis and minibuses are the most common forms of public transportation and can be dangerous due to reckless driving.
- Only use licensed public bus and auto taxi companies
- Confirm the fare with the driver before departing
- Don’t use public transportation at night
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Rwandan authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Rwanda.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required - a 30 day visa can be obtained upon arrival or in advance via the Irembo platform Work permit: required Business visa: required, valid for 90 days and may be extended once. You may obtain a 30-day visa upon arrival. Visa extension requests can be made via the Irembo platform.
- Irembo platform for visa applications – Government of Rwanda
- Rwanda Directorate General of Immigration and Emigration
East African Tourist Visa
The East African Tourist Visa (EATV) allows for multiple entries to Kenya, Uganda, and Rwanda. It is valid for 90 days and cannot be extended. You may obtain this visa:
- upon arrival
- at the nearest Rwandan embassy or consulate
If you get the EATV visa prior to your departure, your first entry point must be the country that issued the visa.
EATV application – Government of Rwanda.
Border closures
The border between Rwanda and Burundi has been closed since January 11, 2024. The border will remain closed until further notice.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.

Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is low potential for yellow fever exposure in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination may be recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
This destination is in the African Meningitis Belt, an area which has the highest rates of meningococcal disease in the world. Meningococcal disease is a serious and sometimes fatal infection.
Travellers who are at higher risk should discuss vaccination with a health care provider. High-risk travellers include those living or working with the local population (e.g., health care workers) or those travelling to crowded areas or taking part in large gatherings.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes.
Malaria is a risk to travellers to this destination. Antimalarial medication is recommended for most travellers to this destination and should be taken as recommended. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times:
- Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin.
- Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows.
- Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area.
- Wear permethrin-treated clothing.
If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Medical services and facilities
Public medical facilities in Kigali are adequate for routine procedures. Access to health care is limited outside of Kigali.
Private facilities are often better equipped but are more expensive.
Serious medical problems may require air evacuation to a neighboring country.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Prescription medication
Some prescription medications may not be available in Rwanda.
If you take prescription medications, make sure they’re legal before travelling to Rwanda.
- Bring sufficient quantities of your medication with you
- Always keep your medication in the original container
- Pack them in your carry-on luggage
- Carry a copy of your prescriptions
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can face heavy fines and imprisonment.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Non-biodegradable bags
Non-biodegradable bags are prohibited in Rwanda. If you arrive with such bags at the airport in Kigali, they will be confiscated.
Photography
Photography of sensitive installations is prohibited. This includes:
- military sites
- government buildings
- border crossing areas
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Rwanda.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Rwanda, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Rwanda.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Rwanda by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Rwanda to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Dress and behaviour
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
- seek permission from locals before photographing them
The recreational and commercial flying of drones is strictly regulated. You must seek the permission from Rwanda Civil Aviation Authority prior to operating a drone. If you don’t comply, you may be fined and your drone confiscated.
Drones – Visit Rwanda
You must carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
Third-party insurance is required to cover damages if you are involved in an accident resulting in injuries even if you are not found to be at fault. If you are suspected of causing an accident, your driver’s licence can be confiscated during the investigation. If the accident results in death, you may be subject to a jail sentence.
The currency of Rwanda is the Rwandan franc (RWF).
Rwanda is a cash-based economy. Electronic payments and online banking are becoming more available. Credit cards are usually accepted at:
- most hotels and lodges
- most businesses, restaurants and shops in Kigali
ATMs are available in large cities. Some ATMs may not accept foreign bank cards, but you can make withdrawals at the bank counter, using your passport as identification. Expect to handle other expenses in cash.
Most shops will not accept or exchange U.S. dollars printed before 2006.
Earthquakes
Rwanda is located in an active seismic zone. However, earthquakes are not common.
Earthquakes - What to Do?
There are several active and dormant volcanoes in and around Rwanda.
The Nyiragongo volcano, located near Goma DRC, is one of the world’s most active volcanoes. It may pose a threat in northwestern areas in Rwanda near the DRC border.
Past eruptions forced the evacuation of hundreds of thousands of people, caused significant damage to infrastructure, and resulted in many casualties.
If you are travelling near an active volcano:
- exercise caution
- take official warnings seriously and respect exclusion zones
- monitor local media to stay up to date on latest developments and volcanic activity levels
- follow the advice of local authorities
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from February to May and from September to December.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including those on road conditions
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Monitor weather reports
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
Local services
Emergency services exist but may be subject to certain limitations. In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 112
- medical assistance: 912
- gender- based violence: 3512
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the High Commission of Canada in Rwanda, in Kigali, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Travel Vaccines and Advice for Rwanda

Despite the 1994 genocide, Rwanda has a growing population and booming tourism trade.
The growing nation provides the opportunity to see mountain gorillas, bamboo forests and amazing volcanoes.
Rwanda is a must-visit for Africa-bound travellers.
Do I Need Vaccines for Rwanda?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Rwanda. The PHAC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Rwanda: hepatitis A , hepatitis B , typhoid , yellow fever , rabies , meningitis , polio , measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) , Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis) , chickenpox , shingles , pneumonia and influenza .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunizations:
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travellers
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Accelerated schedule available
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Shot lasts 2 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if travelling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-term travellers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Meningitis – Airborne & Direct Contact – Recommended for minors and those with additional risk factors.
- Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) – Various Vectors – Given to anyone unvaccinated and/or born after 1957. One time adult booster recommended.
- TDAP (Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis) – Wounds & Airborne – Only one adult booster of pertussis required.
- Chickenpox – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to those unvaccinated that did not have chickenpox.
- Shingles – Direct Contact – Vaccine can still be given if you have had shingles.
- Pneumonia – Airborne – Two vaccines given seperately. All 65+ or immunocompromised should receive both.
- Influenza – Airborne – Vaccine components change annually.
- Polio – Food & Water – May be recommended for some regions. Single adult booster recommended.
See the tables below for more information:
Malaria is endemic in Rwanda. Antimalarials are the best protection against infection. Be sure to use mosquito repellents as a second barrier against the disease.
Medical facilities are common throughout Rwanda, with the best services provided in Kigali. Some medicines and prescriptions may be hard to find here.
Visit our vaccinations page to learn more. Travel safely with Passport Health and schedule your appointment today by calling or book online now .
Customer Reviews
Passport health – travel vaccines for rwanda, do i need a visa or passport for rwanda.
A passport valid for at least 6 months beyond the expected departure date from the country. A visa is required for all business and tourism purposes. Tourist visas are valid for 30 days but if you plan on staying longer than that you must seek another class of visa before your visa expires. A business visa is valid for 90 days but may be extended once.
Sources: Embassy of Rwanda and Canadian Travel and Tourism
Proof of yellow fever vaccination is also required for entry.
Visit the Canadian Travel and Tourism website for more information on entry and exit requirements.
What is the Climate Like in Rwanda?
Rwanda’s weather is tropical and doesn’t change much throughout the year. The temperature is usually warm, but it can be cooler in some areas due to the high altitude. The weather in Rwanda’s most popular tourist destinations varies slightly. Kigali has a temperate climate with two rainy seasons, from March to May and October to December.
Volcanoes National Park has cooler weather due to its high altitude and rainy seasons in March to May and October to November. Nyungwe Forest National Park is a rainforest with temperatures ranging from 10 to 25 degrees and rainy seasons from September to May. Lake Kivu is a popular tourist destination with a tropical climate, and temperatures ranging from 20 to 30 degrees throughout the year.
It’s important to note that weather can be unpredictable, so it’s always good to check the forecast before going on a trip.
How Safe is Rwanda?
Travellers should be cautious around border areas. An armed militant group (The Democratic Forces of the Liberation of Rwanda) operate in the Democratic Republic of Congo and are near the border. Rape, pillaging and kidnapping can occur in the North and South Kivu provinces.
Also be cautious at Volcanoes National Park, for DRC militant groups also operate on the DRC border, though sometimes the borders are not marked.
The most common crimes that are reported are robbery. Don’t display cash, avoid walking at night, and drive with your doors and windows locked.
Genocide Memorial in Rwanda
In 1994, one million Tutsis and Hutus were murdered in the span of 100 days by the Interahamwe. A memorial to the victims of this genocide can is in the capital city of Kigali.
The memorial honors the 250,000 victims that were buried in a mass grave where the memorial is now placed. The memorial tells the history of colonization in Rwanda and the events that led up to the genocide. A particular section of the memorial is dedicated to the murdered children. The section showcases children’s stories using life-sized photographs and biographies of the children. The memorial also calls for justice through the court system.
This memorial not only remembers the genocide that occurred in Rwanda, but also takes a look at other genocides that have occurred throughout the world.
What Should I Pack for Rwanda?
Here are some essential items to consider for your trip to Rwanda:
- Bring light layers of clothing. It can be hot during the day, but it can get cooler at night.
- Sunscreen to protect your skin from the sun. Sunscreen is available here, but it may be quite expensive.
- Insect repellent and mosquito nets are important to have. Practice all precautions against mosquito bites to avoid malaria and zika.
- Comfortable walking shoes make exploring much easier. Roads can be muddy and uneven. Simple sandals won’t cut it.
Canadian Embassy in Rwanda
Canadian consular services can help travellers with many issues they may face including passport services. Once in Rwanda, the information for the Canadian consulate is:
Canadian Embassy Kigali 59, KN16 Ave, Kiyovu, Kigali, Rwanda Telephone: + 250 252 554 800
Stay safe abroad with Passport Health. Call or book online now and start travelling safely today!
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Rwanda? Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Rwanda? What is the Climate Like in Rwanda? How Safe is Rwanda? Genocide Memorial in Rwanda What Should I Pack To Rwanda? Canadian Embassy in Rwanda

- PIPEDA Policy and Consent Form
- Privacy Policy
- Automatic Data Collection Statement
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Ghana Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Ghana. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Global Measles March 22, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
There is no longer active cholera transmission and vaccine is not recommended.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Ghana.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Ghana.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to Ghana take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Ghana.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Meningitis (Meningococcal disease)
Recommended for travelers 2 months old or older traveling to areas of Ghana that are part of the meningitis belt during the dry season.
Meningococcal disease - CDC Yellow Book
Meningitis Belt Map
In Ghana poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Ghana are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Ghana who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Ghana. If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Ghana, there may be limited or no rabies treatment available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Ghana.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for all arriving travelers ≥9 months old.
Recommended for all travelers ≥9 months old.
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African tick-bite fever.
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Tick-bite fever
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Lassa Fever
- Breathe in air or eat food contaminated with the urine or droppings of infected rats
- Touch the body fluids of a person infected with Lassa virus or objects contaminated with infected body fluids
Lassa fever
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Ghana, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Ghana. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Ghana—such as dengue, leishmaniasis, and African sleeping sickness—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Ghana include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Ghana. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Ghana’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in Ghana. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Ghana may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Ghana, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Ghana, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Ghana .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Ghana, dial 193 for an ambulance, 192 for the fire department, and 191 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you during your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Ghana before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Ghana from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Ghana for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6-11 months, according to CDC's measles vaccination recommendations for international travel. Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book. Rabies: Rabid dogs are commonly found in Rwanda.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the CDC. While the CDC does not generally recommend the yellow fever vaccination for travel to Rwanda, the U.S. Embassy recommends travelers bring proof of yellow fever vaccination. The Rwandan government retains the right to turn travelers without the immunization away.
The U.S. Embassy in Kigali wishes to remind travelers to Rwanda that proof of yellow fever vaccination is required for entry. Due to a recent yellow fever outbreak in Angola, Rwandan immigration officials now require un-vaccinated air travelers over the age of one year to obtain a vaccine upon entry at the airport (cost $40 U.S. dollars).
The Rwanda-Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) border due to armed conflict. If you decide to travel to Rwanda: See the U.S. Embassy's webpage regarding COVID-19. Visit the CDC's webpage on Travel and COVID-19. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
Event : Effective December 16, 2021, all passengers arriving to Rwanda must quarantine for three (3) days at a designated quarantine hotel at their own cost. A COVID-19 PCR test will be taken upon arrival at the airport. A second test will be taken on day three (3), and a third test will be taken on day seven (7).
All Rwandan travellers aged 12 years and above must show proof of full vaccination before departing Rwanda by air. Fully vaccinated for people aged 18 years and above means having two doses and a booster when eligible (administered 3 months after second dose.) Emergency contact information. Call 114 or email [email protected].
Restaurants in Rwanda are open. Bars in Rwanda are . Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Rwanda such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Reconsider travel to Rwanda-Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) ... Vaccinations. The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Rwanda: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, typhoid, yellow fever, rabies, meningitis, polio, measles, mumps and rubella (MMR), ...
Rwanda. Specific. Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhoea. Prevention. Despite the 1994 genocide, Rwanda has a growing population and booming tourism trade. The growing nation provides the opportunity to see mountain gorillas, bamboo forests and amazing volcanoes. Rwanda is a must-visit for Africa-bound travellers.
Rwanda has surpassed the 30% target it had set for the end of 2021 and is well on its way to achieving the 60% target for June 2022, having already vaccinated nearly 60% of its population. It is because of this efficiency and success that Rwanda Biomedical Center was named one of the covid-19 Vaccination Centers of Excellence by Africa Centers ...
At least 8 weeks before your trip check: the latest information on vaccination recommendations and health risks in TravelHealthPro's Rwanda guide. where to get vaccines and whether you have to ...
Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel. Rwanda-Burundi Border—Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution The Nyungwe Forest National Park abuts the border with Burundi. Borders may not be clearly marked. It is required to obtain permits from the Rwanda Development Board prior to entry. Relations between ...
Published: April 19, 2021 11:56am EDT. A refugee receives his first dose of coronavirus vaccine in Kigali, Rwanda. Habimana Thierry/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images. Due to early logistical ...
Pre-travel vaccines and medications. You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary. Hepatitis A. There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver.
Specific. Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Despite the 1994 genocide, Rwanda has a growing population and booming tourism trade. The growing nation provides the opportunity to see mountain gorillas, bamboo forests and amazing volcanoes. Rwanda is a must-visit for Africa-bound travellers.
Malaria. CDC recommends that travelers going to Ghana take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.