
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets

Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Fact Sheet: Biden Administration Releases Additional Detail for Implementing a Safer, More Stringent International Air Travel System
As we continue to work to protect people from COVID-19, today, the Biden Administration is releasing additional detail around implementation of the new international air travel policy requiring foreign national travelers to the United States to be fully vaccinated. This updated policy puts in place an international travel system that is stringent, consistent across the globe, and guided by public health. Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of COVID-19 vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane to fly to the U.S., with only limited exceptions. The updated travel guidelines also include new protocols around testing. To further strengthen protections, unvaccinated travelers – whether U.S. Citizens, lawful permanent residents (LPRs), or the small number of excepted unvaccinated foreign nationals – will now need to test within one day of departure. Today, the Administration is releasing the following documents to implement these requirements: 1) a Presidential Proclamation to Advance the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic; 2) three Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Orders on vaccination, testing, and contact tracing; and 3) technical instructions to provide implementation details to the airlines and their passengers. With science and public health as our guide, the United States has developed a new international air travel system that both enhances the safety of Americans here at home and enhances the safety of international air travel. The additional detail released today provides airlines and international air travelers with time to prepare for this new policy ahead of the November 8 implementation date. As previously announced, fully vaccinated foreign nationals will also be able to travel across the Northern and Southwest land borders for non-essential reasons, such as tourism, starting on November 8. Additional detail on amendments to restrictions with respect to land borders will be available in the coming days. Travelers can find full details about today’s air travel announcement on the CDC and Department of State websites. A summary is below: Fully Vaccinated Status:
- Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane to fly to the U.S.
Proof of Vaccination:
- For foreign nationals, proof of vaccination will be required – with very limited exceptions – to board the plane.
- Match the name and date of birth to confirm the passenger is the same person reflected on the proof of vaccination;
- Determine that the record was issued by an official source (e.g., public health agency, government agency) in the country where the vaccine was given;
- Review the essential information for determining if the passenger meets CDC’s definition for fully vaccinated such as vaccine product, number of vaccine doses received, date(s) of administration, site (e.g., vaccination clinic, health care facility) of vaccination.
- The Biden Administration will work closely with the airlines to ensure that these new requirements are implemented successfully.
Accepted Vaccines:
- CDC has determined that for purposes of travel to the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and World Health Organization (WHO) emergency use listed (EUL) vaccines.
- Individuals can be considered fully vaccinated ≥2 weeks after receipt of the last dose if they have received any single dose of an FDA approved/authorized or WHO EUL approved single-dose series (i.e., Janssen), or any combination of two doses of an FDA approved/authorized or WHO emergency use listed COVID-19 two-dose series (i.e. mixing and matching).
- More details are available in the CDC Annex here .
Enhanced Testing:
- Previously, all travelers were required to produce a negative viral test result within three days of travel to the United States.
- Both nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), such as a PCR test, and antigen tests qualify.
- As announced in September, the new system tightens those requirements, so that unvaccinated U.S. Citizens and LPRs will need to provide a negative test taken within one day of traveling.
- That means that all fully vaccinated U.S. Citizens and LPRs traveling to the United States should be prepared to present documentation of their vaccination status alongside their negative test result.
- For those Americans who can show they are fully vaccinated, the same requirement currently in place will apply – they have to produce a negative test result within three days of travel.
- For anyone traveling to the United States who cannot demonstrate proof of full vaccination, they will have to produce documentation of a negative test within one day of departure.
Requirements for Children:
- Children under 18 are excepted from the vaccination requirement for foreign national travelers, given both the ineligibility of some younger children for vaccination, as well as the global variability in access to vaccination for older children who are eligible to be vaccinated.
- Children between the ages of 2 and 17 are required to take a pre-departure test.
- If traveling with a fully vaccinated adult, an unvaccinated child can test three days prior to departure (consistent with the timeline for fully vaccinated adults). If an unvaccinated child is traveling alone or with unvaccinated adults, they will have to test within one day of departure.
Limited Exceptions from the Vaccination Requirement:
- There are a very limited set of exceptions from the vaccination requirement for foreign nationals. These include exceptions for children under 18, certain COVID-19 vaccine clinical trial participants, those with medical contraindications to the vaccines, those who need to travel for emergency or humanitarian reasons (with a US government-issued letter affirming the urgent need to travel), those who are traveling on non-tourist visas from countries with low-vaccine availability (as determined by the CDC), and other very narrow categories.
- Those who receive an exception will generally be required to attest they will comply with applicable public health requirements, including, with very limited exceptions, a requirement that they be vaccinated in the U.S. if they intend to stay here for more than 60 days.
Contact Tracing:
- The CDC is also issuing a Contact Tracing Order that requires all airlines flying into the United States to keep on hand – and promptly turn over to the CDC, when needed – contact information that will allow public health officials to follow up with inbound air travelers who are potentially infected or have been exposed to someone who is infected.
- This is a critical public health measure both to prevent the introduction, transmission, and spread of new variants of COVID-19 as well as to add a critical prevention tool to address other public health threats.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
Situation in Haiti April 5, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update april 12, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Travel.State.Gov Newsroom
U.S. Passports News
International Travel News
U.S. Visas News
Intercountry Adoption News and Notices
Share this page:
Update on Change to U.S. Travel Policy Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for nonimmigrant travel
Worldwide Visa Operations: Update
Employment-Based Fourth Preference (EB-4) Announcement
Suspension of Visa Services in Sudan
Diversity Visa 2024 Update
Nonimmigrant Visa Fee Increases to Take Effect June 17, 2023
India EB-3 Retrogression
Expiration of Covid-Era Visa Application Fee Receipts
Digital Visa Authorization (DVA) Proof of Concept
Final Rule Governing Public Charge Grounds of Visa Ineligibility
Visa Waiver Travel for Israeli Citizens
Important Update on Waivers of the Interview Requirement for Certain Nonimmigrant Visa Applicants
Department of State to Process Domestic Visa Renewals in Limited Pilot Program
The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with an accepted COVID-19 vaccine to board a flight to the United States. CDC’s Amended Order Implementing Presidential Proclamation on Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic will no longer be in effect when the Presidential Proclamation Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic is revoked .
Please see: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/05/01/the-biden-administration-will-end-covid-19-vaccination-requirements-for-federal-employees-contractors-international-travelers-head-start-educators-and-cms-certified-facilities/
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Advertisement
Supported by
What to Know About the C.D.C. Guidelines on Vaccinated Travel
In updated recommendations, the federal health agency said both domestic and international travel was low risk for fully vaccinated Americans. But travel remains far from simple.
- Share full article

By Ceylan Yeginsu
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its guidance for fully vaccinated Americans in April, saying that traveling both domestically and internationally was low risk.
The long-awaited recommendations were issued by federal health officials after a series of studies found that vaccines administered in the United States were robustly effective in preventing infections in real-life conditions.
One is considered fully vaccinated two weeks after receiving the single dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, or two weeks after receiving the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna shots.
If you decide to travel, you might still have some questions. Here are the answers.
Will I still need to wear a mask and socially distance while traveling?
Yes. Under federal law, masks must be worn at airports in the United States, onboard domestic flights and in all transport hubs. The C.D.C. says that as long as coronavirus measures are taken in these scenarios, including mask wearing, fully vaccinated Americans can travel domestically without having to take a test or quarantine, although the agency warns that some states and territories may keep their local travel restrictions and recommendations in place.
For those wishing to travel internationally, a coronavirus test will not be required before departure from the United States unless mandated by the government of their destination. Vaccinated travelers are still required to get tested three days before travel by air into the United States, and are advised to take a test three to five days after their return, but will not need to self-quarantine.
Can I go abroad?
Yes, but only to countries that will have you.
More than half the world’s countries have reopened to tourists from the United States, including the countries of the European Union , which on June 18 added the United States to its “safe list” of countries, meaning that American travelers can now visit. While the European Union aims to take a coordinated approach to travel this summer, member states will be allowed to set their own requirements for travelers from individual countries based on their own epidemiological criteria, which means they may require testing or vaccination.
Some places like Turkey, Croatia and Montenegro had already been welcoming Americans with negative test results. Greece joined that growing list in May, ahead of most European countries, opening to fully vaccinated tourists and other foreigners with a negative test.
Many Caribbean nations have reopened to American tourists, but each has its own coronavirus protocols and entry requirements.
Here’s a full list of countries Americans can currently travel to.
What about domestic travel? Is it free and clear to cross state borders?
If you are fully vaccinated, the C.D.C. says you can travel freely within the United States and that you do not need to get tested, or self-quarantine, before or after traveling. But some states and local governments may choose to keep travel restrictions in place, including testing, quarantine and stay-at-home orders. Hawaii , for instance, still has travel restrictions in place.
Before you travel across state lines, check the current rules at your destination.
How are they going to check that I’m fully vaccinated?
Right now, the best way to prove that you have been vaccinated is to show your vaccine card .
Digital vaccine and health certificates showing that people have been vaccinated or tested are in various stages of development around the world and are expected, eventually, to be widely used to speed up travel.
The subject of “ vaccine passports ” is currently one of the most hotly debated topics within the travel industry, with questions over the equity of their use and concerns over health and data privacy.
In early April, Gov. Ron DeSantis of Florida issued an executive order that would ban local governments and state businesses from requiring proof of vaccination for services.
And in March, the European Union endorsed its own vaccine certificate , which some countries are already using, with more expected to adopt it by July 1.
But what about my kids? What’s the guidance on traveling with unvaccinated people?
The C.D.C. advises people against travel unless they have been vaccinated. If you must travel, the agency recommends testing one to three days before a trip and following all coronavirus guidance at your destination.
In May, the F.D.A. expanded its emergency use authorization of the Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vaccine to include adolescents between 12 and 15 years of age.
All air passengers aged two and older coming into the United States, including fully vaccinated people, are required to have a negative Covid-19 test result taken no more than three days before they board their flight.
What is my moral obligation to the places I visit where most people are not vaccinated?
The United States inoculation rollout has been among the fastest in the world, but there is a stark gap between its rapid rollout and the vaccination programs in different countries. Some nations have yet to report a single dose being administered.
Many countries are currently seeing a surge in new cases and are implementing strict coronavirus protocols, including mask mandates in public spaces, capacity limits at restaurants and tourist sites and other lockdown restrictions.
It is important to check coronavirus case rates, measures and medical infrastructure before traveling to your destination and not to let your guard down when you get there. Even though you are fully vaccinated, you may still be able to transmit the disease to local communities who have not yet been inoculated.
You can track coronavirus vaccination rollouts around the world here.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation.
Ceylan Yeginsu is a London-based reporter. She joined The Times in 2013, and was previously a correspondent in Turkey covering politics, the migrant crisis, the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

This page was published more than five years ago. Information on the page may be out of date.
- For U.S. Citizens/Lawful Permanent Residents
- Know Before You Go
- When You Return
What to Expect When You Return
Complete the cbp declaration form 6059b.
You have several entry options once you return from your trip. All travelers must complete a CBP Declaration Form 6059B itemizing all purchased merchandise and agricultural products.
Here are your options:
- Complete a paper form that may be obtained at the port of entry or on the flight or cruise.
- Complete the online form at a Global Entry kiosk. (Only preapproved Global Entry members are allowed to use these kiosks.)
- Complete the online form at an Automated Passport Control kiosk.
Keeping all your purchase receipts handy in an envelope in your carry-on bag will ease this process. If warranted, the CBP officer will calculate the duties to pay on your newly acquired goods.
Paying Duties
Personal exemptions that do not require the traveler to pay duty will be $200, $800 or $1600 depending on the countries you visited.
The duty-free exemptions ($200, $800, or $1600) apply if:
- The items are for your personal or household use or intended to be given as gifts.
- Merchandise is in your possession, that is, it accompanies you when you return to the United States. Items to be sent later may not be included in your duty-free exemption. (Exceptions apply for goods sent from Guam or the U.S. Virgin Islands.)
- Merchandise is declared to CBP. If you do not declare something that should have been declared, you risk forfeiting the item. If in doubt, declare it.
- You are returning from an overseas stay of at least 48 hours. This time limit does not apply if you are returning from Mexico or from the U.S. Virgin Islands.
- You have not used all of your exemption allowance, or used any part of it, in the past 30 days. For example, if you go to England and bring back $150 worth of items, you must wait another 30 days before you are allowed another exemption.
- The items are not prohibited or restricted as discussed in the section on Prohibited and Restricted Items. Before departing on your trip, check the latest information for the full list of prohibited and restricted items on the U.S. Department of the Treasury Cuba Sanctions website, as well as other related government resources.
Duty free exemption limits depend on the country or countries you visit and the length of stay. Learn which rates apply to the goods your purchase on your trip - call the CBP attaché at the country's U.S. embassy.
Your CBP Interview
To keep our borders secure and our nation safe, CBP must inspect everyone who arrives at a U.S. port of entry. The CBP officers are authorized to ask you questions about your trip and your personal background, including:
- Your citizenship
- The nature of your trip
- Anything you are bringing back to the United States that you did not have when you left.
Officers have legal authority to search you, your baggage or your vehicle. If asked to, place your opened baggage on the exam station. After the exam, you will be asked to repack and close your baggage.
CBP pledges to treat you courteously and professionally. If at any point you are unhappy with your treatment, ask to speak to a CBP supervisor. You may also call the CBP INFO Center at 877-227-5511. If calling within the United States, call 202-325-8000 or go to www.cbp.gov and click on Questions/Comments.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Rise in 'Extraordinarily Contagious' Measles Cases in the U.S.: 'It's Back' and 'Much More Serious Than the Chickenpox'
A sharp rise in cases since the start of 2024 could mean that the U.S. loses its measles elimination status
For more than two decades, the U.S. has considered measles to be “eliminated” — a status it has maintained in spite of a few isolated outbreaks.
However, a sharp rise in cases in the first three months of 2024 means that the U.S. may no longer be able to consider measles eliminated, the Center for Disease Control said Thursday.
"To be honest, I think we have lost our elimination status already," Dr. Bruce Farber, Chief of Public Health and Epidemiology for Northwell Health, told PEOPLE. "How can you say we're measles-free when we're seeing measles?"
Symptoms include a high fever, cough, runny nose and watery eyes — but the most notable symptom is the red rash, which often covers the entire body. Complications include pneumonia and encephalitis, which is when the brain swells.
"Measles is much more serious than the chickenpox," Farber tells PEOPLE. "A significant number will have a complication requiring hospitalization."
Since the beginning of 2020, the U.S. has recorded a total of 338 cases — but 29% of those cases have been reported since this year alone.
As the CDC says, “The rapid increase in the number of reported measles cases during the first quarter of 2024 represents a renewed threat to elimination.”
The cases were reported “almost all in persons who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown. As of the end of 2023, U.S. measles elimination status was maintained.”
The CDC noted that nearly in all the cases, those infected by measles had either traveled internationally, or spent time with someone who had.
In March, the Cincinnati Health Department warned that there was a potential for a measles exposure at a Disney on Ice performance.
Earlier, officials in Virginia flagged two airports — Dulles International Airport or Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport — as being the sites of potential measles exposures.
And in Philadelphia, there was a confirmed outbreak of measles, where one child may have been the source of infection for at least seven people at a daycare center and hospital.
Part of the issue, the CDC explains, is that measles is airborne.
Never miss a story — sign up for PEOPLE's free daily newsletter to stay up-to-date on the best of what PEOPLE has to offer, from celebrity news to compelling human interest stories.
“The virus is transmitted by direct contact with infectious droplets or by airborne spread when an infected person breathes, coughs, or sneezes,” the CDC says.
"If you take one person with measles. and you put them in a room with 10 others, and if they're not immune, then nine out of those 10 will get measles just from airborne spread," Farber tells PEOPLE. "It's extraordinarily contagious."
You don’t need to be in the same room as an infectious person either, as the CDC notes, “measles virus can remain infectious in the air for up to two hours after an infected person leaves an area.”
Measles is one of the vaccines included in the MMR shot, commonly given to children in the U.S. as part of their routine childhood vaccination schedule. It’s a two-dose shot, with the first being administered as early as 12 months, and a second dose administered at age four.
"There's no comparison to a cold. It's, it's nothing like a cold," Farber tells PEOPLE.
The agency ended its alert encouraging everyone to get vaccinated, adding that while the risk of transmission is low because of high population immunity, vaccination coverage remains below the amount “necessary to prevent sustained measles transmission.”
As for those who are hesitant to get the vaccine or give it to their child, Farber said, "there's no evidence, at all, that this MMR causes autism or any other serious problems. And measles does."
He continued: "It's very sad to see preventable diseases. We eliminated measles, from a practical basis, in the year 2000 and now it's back."
Related Articles
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
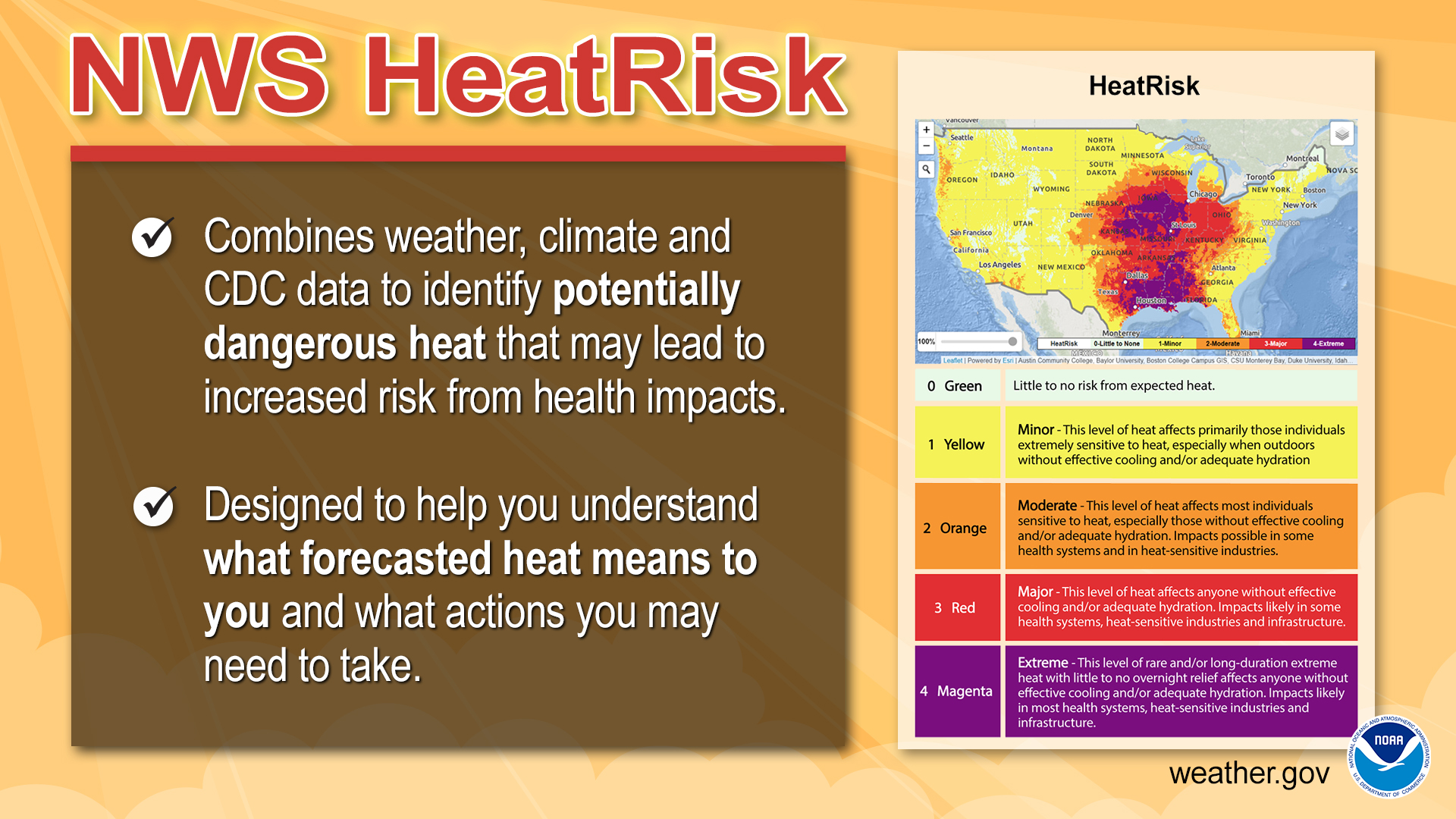
NOAA, CDC news conference to unveil a new heat forecast tool and health guidance
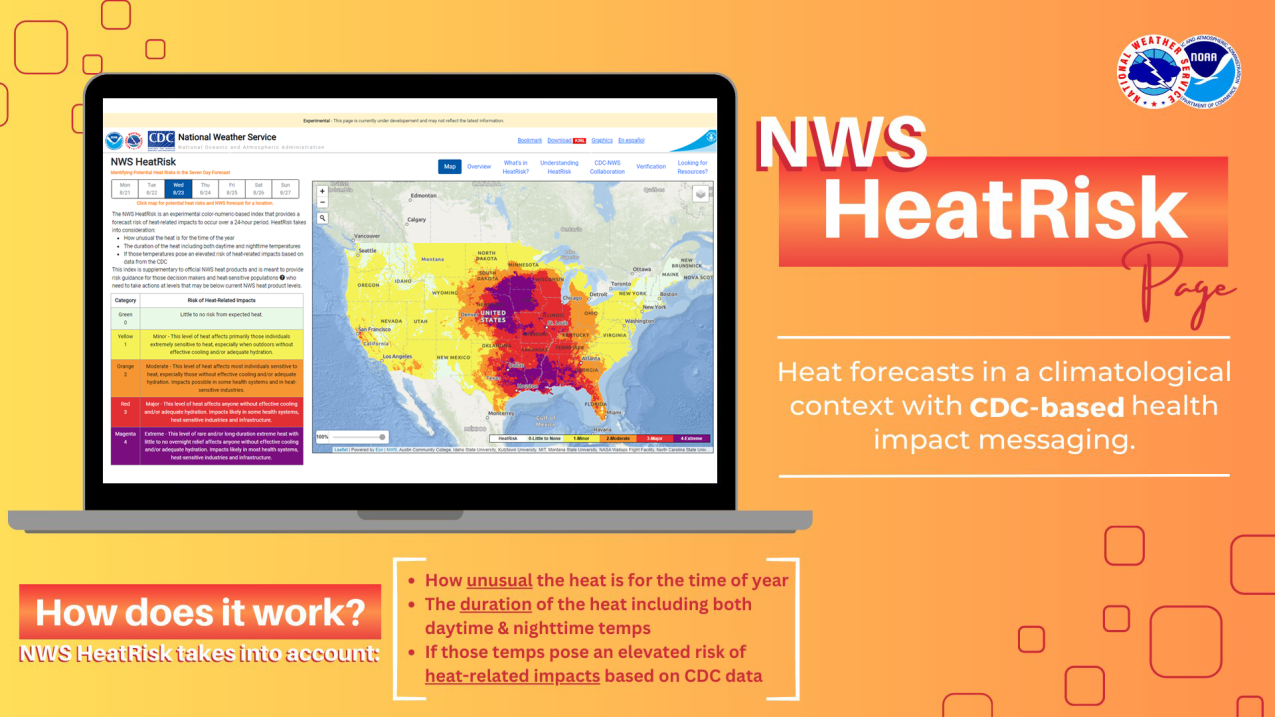
A glance at the new NOAA National Weather Service experimental HeatRisk tool and website for the contiguous U.S. The tool provides heat forecasts in a climatological context with CDC-based health impact messaging by taking into account how unusual the heat is for the time of year, the duration of the heat (including both daytime and nighttime temperatures) and if those temperatures pose an elevated risk of heat-related impacts based on CDC data. (Image credit: NOAA)
On Earth Day — ahead of the hot summer season — NOAA and CDC invite reporters to a news conference where new heat forecast tools supporting public health will be unveiled.
Heat is one of the deadliest forms of weather, and climate change is causing more frequent, intensive and longer heatwaves. Heat can exacerbate health problems for people, especially those who are pregnant, have cardiovascular disease or suffer from asthma.
NOAA, CDC news conference on new heat forecast tool and health guidance
Monday, April 22, 2024 at 11 a.m. EDT
Unity Health Care’s Brentwood Health Center 1251-B Saratoga Ave, NE, 2nd floor Washington, DC 20018
Note: This federally qualified health center serves patients who will benefit from the new heat guidance. Providers work with the unhoused and other high risk populations at this location.
- Don Graves , U.S. Deputy Secretary of Commerce
- Mandy Cohen , MD, MPH, Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Rick Spinrad, Ph.D. , NOAA Administrator
- Ken Graham , Director, NOAA’s National Weather Service
- Ari Bernstein , MD, MPH, Director, National Center for Environmental Health/Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Reporters interested in attending in-person must register by providing the names of the reporter/producer and camera crew to Michael Musher, [email protected] , by 4:00 p.m. EDT on April 19. For questions, please call 771-233-1304. Camera crews must arrive by 10:00 a.m. on the day of the event.
Parking: The lot entrance is on Saratoga Ave at the Israel Baptist Church. Once on the church’s property, take the driveway downhill to the health center parking lot. Staff will direct you to a free parking spot. [ Building Information offsite link ]
VIRTUAL REGISTRATION
Reporters who are unable to attend in person may participate via Zoom. Register to receive a link to the live stream of the event offsite link . Virtual participants will have the ability to ask questions during the Q&A portion of the event.
Media contact
Michael Musher, michael.musher@noaa.gov , (771) 233-1304

Related Features //


Measles outbreak puts elimination status at risk: CDC
The most recent outbreak of measles is threatening the United States' elimination status, according to a new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report published Thursday.
The first measles vaccine was introduced in 1963 and, thanks to a yearslong and highly effective vaccination campaign, measles was considered eliminated from the U.S. in 2000, meaning the disease is no longer constantly present.
Despite occasional outbreaks, the U.S. has been able to maintain its elimination status. Cases have popped up due to international travel and unvaccinated or undervaccinated communities.
However, the rapid increase in the number of measles cases during the first quarter of 2024 "represents a renewed threat to the U.S. elimination status," according to the CDC report.
As of April 4, 2024, there have been 113 cases of measles reported in the U.S. This is an at least a 17-fold higher figure than the average number of cases seen during the same period from 2020 to 2023.
"What was surprising about 2024 is that we've seen a significant increase," said Dr. John Brownstein, an epidemiologist and chief innovation officer at Boston Children's Hospital and an ABC News contributor. "It's an alarming number because it indicates a trend going in the wrong direction for us, a virus that we have successfully controlled, a virus that we successfully have an effective vaccine for."
"We're seeing a rise that is unfortunate, and actually preventable, and so this outbreak highlights the fact that we are not unfortunately done with measles," he added.
This year, the number of measles cases have soared in part due to several localized outbreak, including at a children's hospital and daycare center in Philadelphia , an elementary school in Florida and at a migrant center in Chicago . Measles is so infectious that a measles patient can infect up to 90% of close contacts who are not immune.
Dr. Paul Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, pointed out that almost all people in the U.S. who have had measles in recent years either traveled internationally to a country where measles has not been eliminated or were around someone who traveled internationally, and that immigrants are not responsible for the sporadic outbreaks.
He told ABC News that more than 20 years out since elimination status was declared, the U.S. should not be seeing as much of a renewed threat as it is.
"It's getting worse; I think it's fair to say that it is getting worse," Offit said. "Look, according to [the CDC's] definition. because there hasn't been 12 consecutive months of measles transmission, we're still considered to have eliminated measles ... but we're getting there."
This is not the first time that the measles elimination status has been at risk. In 2019, there were 1,274 reported cases due to outbreak in Washington state and in New York State and New York City.
The new report comes as there has been a dip in routine childhood vaccinations. A CDC report in November found that exemptions for routine childhood vaccination among U.S. kindergartners are at their highest levels ever.
The report found that about 93% of kindergarteners received select routine childhood vaccines, including the measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine for the 2022-23 school year. This is about the same as the previous school year but lower than the 94% seen in 2020-21 school year and the 95% seen in the 2019-20, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. The latter percentage had been the standard for about 10 years.
Offit said there is a critical percentage of parents choosing not to vaccinate their children with the MMR vaccine. There are various reasons, including vaccine hesitancy from the COVID-19 vaccine affecting the choice to receive other vaccines and not remembering how serious measles used to be prior to vaccines.
In the decade prior to the first measles vaccine in 1963, there were three to four million cases annually, which led to 48,000 hospitalizations and 400 to 500 deaths.
"Number one is to find out what it is that's causing them to choose not to vaccinate, what's the fear, because the fear can invariably be addressed with information," Offit said. "I think it's understandable how people can be hesitant to get a vaccine, but it is a dangerous game we play. I mean, it's a game of Russian roulette."
Despite the outbreak, the experts and the CDC say that anyone who has had a previous measles infection or who has received two doses of the MMR vaccine is essentially protected for life.
The CDC currently recommends receiving two doses of the MMR vaccine, with the first those at 12 to15 months old and the second dose between ages 4 and 6. One dose of the measles vaccine is 93% effective at preventing infection if exposed to the virus. Two doses are 97% effective, according to the CDC.
"We've had a vaccine that has been in use for a very long time and is shown to be incredibly effective in keeping our elimination status of measles going," Brownstein said. "But it's not about the vaccine itself. This is not a question of whether the vaccine works. This is a question of whether people work to get the vaccine."
Bringing a Dog into the United States
CDC is extending its temporary suspension of dog importation from high-risk dog rabies countries until July 31, 2024. This suspension includes dogs arriving from countries without high risk of rabies if the dogs have been in a high-risk country in the past 6 months. Learn about the current rules: What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States
CDC issues regulations to control the entry of dogs into the United States from other countries. These rules apply to all dogs, including puppies and service animals. They also apply whether you are a US citizen, legal US resident, or foreign national.
If you don’t follow CDC’s rules, your dog won’t be allowed to enter the United States. If denied entry, your dog will be sent back to the last country of departure at your expense. Country of departure is where the last trip originated—not where the dog was born or where it lives.
In addition, you must comply with US Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) and your US destination’s regulations . Regulations of US states or territories may be more strict than federal regulations. Please be aware that dogs imported for commercial (resale or adoption) purposes have additional requirements from USDA .
Determining If You Can Bring a Dog into the United States
Whether you can bring a dog into the United States depends on where the dog is coming from—especially if from a high-risk country for dog rabies.
To enter the United States, your dog will be required to meet specific criteria. Start by answering the questions below to determine if you can bring a dog into the United States.
YES : See Step 2 .
NO : Dog can enter at any port of entry with a 6-month travel history statement and healthy appearance.
Dogs that have NOT been in a high-risk country in the past 6 months are NOT required by CDC to present a rabies vaccination certificate . However, when you enter the United States, you must provide a written or verbal statement your dogs have NOT been in a country that is high risk for rabies within the last 6 months or since birth if under 6 months of age. While CDC doesn’t require proof of rabies vaccination, CDC recommends that all dogs be vaccinated against rabies, and your US destination may have additional requirements. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
YES: See Step 3 .
NO : Dog is not allowed to enter the United States.
All dogs that have been in a high-risk country in the past 6 months must be at least 6 months old to enter the United States. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
YES: See Step 4 .
NO: Dog is not allowed to enter the United States.
The microchip number must be listed on the dog’s rabies vaccination certificate. If you are unsure whether your dog has an ISO-compatible microchip , please contact your veterinarian for assistance. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
* The applicant is responsible for making sure the dog has an ISO-compatible microchip. If the dog does not have an ISO-compatible microchip, the applicant (or permit holder) can bring their own scanner that can read the microchip.
* Many US universal scanners have been unable to detect microchips that begin with the numbers 1 or 8. Please ensure your dog’s chip can be detected by a universal scanner if it begins with a number other than 9. If you are unsure, you should purchase your own scanner (available online) that can detect the microchip or have your dog re-microchipped.
*If the microchip cannot be scanned on arrival, your dog may be denied entry and returned to the country of departure at your expense.
YES: The dog may enter the United States under certain conditions.
See Option A at What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
NO: see Step 5
Note: expired US rabies vaccination certificates will not be accepted. If your dog’s US rabies vaccination certificate is expired, proceed to Step 5 .
YES : If you are importing 1 or 2 dogs, see Step 6 .
If you are importing 3 or more dogs , see Step 7 .
If you attempt to import your dog into the United States, the dog will be denied entry and returned to the country of departure at your expense. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
YES : The dog may enter with a CDC Dog Import Permit through one of 18 approved airports ( Option B ) OR without a permit through an airport with a CDC-approved animal care facility ( Option C ). See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States
NO : The dog must have a reservation to quarantine at an approved animal care facility in the United States upon arrival and enter through the airport where the facility is located. See Option C at What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States
YES : See Option C at What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States
NO : Go back to Step 6 for bringing 1-2 dogs .
Dogs that have NOT been in a high-risk country in the past 6 months are NOT required by CDC to present a rabies vaccination certificate . However, when you enter the United States, you must provide a written or verbal statement your dogs have NOT been in a country that is high risk for rabies within the last 6 months or since birth if under 6 months of age. While CDC doesn’t require proof of rabies vaccination, CDC recommends that all dogs be vaccinated against rabies, and your US destination may have additional requirements. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
NO: Dog is not allowed to enter the United States.
The microchip number must be listed on the dog’s rabies vaccination certificate. If you are unsure whether your dog has an ISO-compatible microchip , please contact your veterinarian for assistance. See What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States .
* Many US universal scanners have been unable to detect microchips that begin with the numbers 1 or 8. Please ensure your dog’s chip can be detected by a universal scanner if it begins with a number other than 9. If you are unsure, you should purchase your own scanner (available online) that can detect the microchip or have your dog re-microchipped.
YES: The dog may enter the United States under certain conditions.
If you are importing 3 or more dogs , see Step 7 .
NO: Dog is not allowed to enter the United States.
Why Entry of Dogs to the United States Is Controlled
Rabies is fatal: Rabies is over 99% fatal and is 100% preventable. The United States eliminated dog rabies in 2007, but dog rabies is not controlled in over 100 countries—creating a risk to the United States for imported dogs. Through regulations, CDC strives to protect America’s families, communities, and pets by preventing the reintroduction of dog rabies into the United States. Preventing infected dogs from entering the United States is a public health priority. Each rabid imported dog could infect people and other animals and could cost more than half a million dollars to contain.
Why it’s important now: Since 2015, four rabid dogs were imported into the United States. Historically, about 300 dogs annually have been denied entry to the United States due to inadequate paperwork. However, between January and December 2020 (during the COVID-19 pandemic), CDC documented an increase from previous years with more than 450 instances of incomplete, inadequate, or fraudulent rabies vaccination certificates for dogs arriving from high-risk countries .
The increase in the number of dogs inadequately vaccinated against rabies that importers were attempting to bring into the United States created a public health risk of importing dog rabies.
Protect dogs and people: CDC will use the extended suspension period to improve the importation process to better protect the health and safety of dogs being imported and their US families and communities.
- Travelers' Health
- Healthy Pets Healthy People
- Southern Border Health and Migration
- Port Health
- Division of Global Migration Health
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
'Expensive in every way': What travelers should expect this summer
Summer travel in 2024 will be "expensive in every way," said Katharine Nohr. And she should know.
She's planning a two-week adventure to Europe in June, which starts with a marathon flight from Honolulu to Zurich, where she'll speak at a conference. Then, she's hopscotching across Europe – to Vienna, then on to the Olympics. Nohr made plans to be in Nantes, France, to watch a soccer game, in Lille for basketball, and in Paris for gymnastics, boxing, and swimming.
Check out Elliott Confidential , the newsletter the travel industry doesn't want you to read. Each issue is filled with breaking news, deep insights, and exclusive strategies for becoming a better traveler. But don't tell anyone!
All told, it'll set her back five figures despite her best efforts, which include flying economy class and staying in the lowest-priced hotels.
"The trip is pricey, even with my efforts to economize," said Nohr, an attorney from Honolulu. "But it's a once-in-my-life adventure."
Flying cars are coming! Here's how they could change the way you travel.
'Flying feels different': Here's how air travel has changed recently
Summer travelers are pursuing exciting, expensive vacations
Nohr is part of a wave of travelers who are making big plans for this summer. The itineraries are exciting – and expensive.
Pretty much every barometer of travel intent is up for the summer travel season. Inflation and unemployment are low, and consumer sentiment and curiosity are high, fueling an unprecedented interest in travel during the summer of 2024.
"Bookings are rising," said Susan Sherren, who runs Couture Trips , a travel agency. "Unfortunately, hotel, tour, and air prices are not falling. So, if you plan on hitting the road this summer, make sure you are willing to splash some cash."
Travel companies say they're overwhelmed with summer reservations.
"The travel economy is booming," said Joe Ialacci, owner of Yacht Hampton Boating Club , a company that rents yachts in Sag Harbor, New York. He's seeing a 40% increase in rentals this summer compared to last year as Americans shift some of their vacation dollars to domestic destinations.
Prices aren't the only thing trending higher. People's expectations for their summer vacation are also higher than at any time since the pandemic, said Sangeeta Sadarangani, CEO of Crossing , a multinational travel agency headquartered in London.
"They're embracing the unknown," she said.
And one of the great unknowns is travel prices. How much higher will they be?
What will prices be like this summer?
It depends on where you're going. There's good news if you're traveling within the U.S.: flights and hotels are a little less expensive than last summer . But they're rising elsewhere. Here's the breakdown:
- Airfares are mixed. Domestic roundtrip airfares for summer will peak at $315 per ticket, according to the travel platform Hopper . Flights to Europe are cheaper, too. They've fallen 10% from last year to $882. But flights to South America are up 2% and flights to Canada have risen 7%. You'll pay an average of $708 to fly south of the border and $419 to head north.
- U.S. hotel rates are down. Domestically, they're about the same as last year at an average of $206 per night.
- Car rental prices are rising. Average domestic car rental rates are only up 3% this summer to $42 per day on a four-day rental, according to Hopper.
But you can avoid the high prices with a little strategic planning, experts say.
What to avoid this summer
American travelers are becoming more predictable in their summer vacation choices, said John Lovell, president of Travel Leaders Group . Immediately after the pandemic, they embarked on "revenge" vacations to far-flung locations. Now they're returning to more conventional vacations.
"We continue to see U.S. travelers heading back to the more traditional locations across Europe this year, like London, Rome, Athens and Munich," he said.
There are places that will be exceptionally busy – and exceptionally pricey – this summer.
- Paris during the Olympics. The Olympic Games are taking place in Paris this summer. Rooms are more than double the normal rates . which is typical of the Olympics. Paris is already crowded with tourists during the summer, so you can probably imagine what it will be like with the Olympics. Zut, alors!
- Taylor Swift is touring Europe this summer. Prices will be higher and the crowds will be denser. "If you aren't planning to attend one of her concerts, I recommend planning around those European cities when she's there," said Betsy Ball, co-founder of Euro Travel Coach . (Want to know if your schedules overlap? Here's Taylor Swift's concert schedule .)
- Other big summer events. Even if you steer clear of Taylor and the Olympics, you're still not out of the woods. There's the UEFA Euro 2024 football tournament in Germany in June. There's the Tour de France in July, which begins in Florence and finishes in Nice. France is also hosting the Paralympic Games in August and September, which will take place in Paris, Nice, Marseille and Bordeaux.
Air travel smells worse than ever. Here's how to fix it.
Pay less to fly: New strategies for finding cheap airfares now
When is the best time to book a 2024 summer vacation?
Since this is going to be a busy one, the sooner you book, the better. Hopper recommends buying your airfare two to three months before your departure for domestic flights, and for international – well, it's probably too late to get that rock-bottom fare. If you're reading this in April, you can still find something for late August or early September, according to its airfare experts.
As always, you can save money by booking a flight for midweek instead of on the weekend – and, of course, by keeping far, far away from the big travel holidays like Memorial Day, the Fourth of July and Labor Day.
Also, if you're going overseas, remember their holiday calendar is different. For example, half of Europe shuts down during August for summer vacation. It's worth a look-up, otherwise, you could face some real disappointments.
Strategies for traveling better during the summer
One tactic that consistently works is splitting your getaway into two sections. Take that required summer vacation with your family somewhere less expensive during the high season. Then, wait until shoulder season for the big trip.
That's what Ross Copas, a retired electrician from Tweed, Canada, is doing during the summer of 2024. It's a road trip across the northern U.S. by motorcycle – New York to Washington State, and then back east through Canada.
Then he's heading to Amsterdam in September for a 23-day European river cruise. He said the late summer getaway will be costly, but he doubts fares will fall anytime soon. "So price be damned," he added.
Actually, that's pretty smart. I took the same cruise he's planning on Viking River Cruises many years ago, and it was worth every penny.
With hotel rates rising in some places this summer, this is the right time to consider alternatives. Monica Fish, a writer from Glen Rock, N.J., is headed to Ireland to catch one of Taylor Swift's performances. She said hotel rooms in Dublin are overpriced if they're even available. But Fish found an affordable vacation rental.
"We just had to book it farther in advance than we normally would," she said.
Go ahead, follow the crowds this summer
I think it's fine to follow the crowds this summer. I'll be doing it. I'm planning to rent an apartment for a month in Switzerland with Blueground, a long-term apartment rental company. Then I'm crashing on a friend's sofa in Spain, then heading to Sweden to see other friends and visiting my brother in Finland. Yes, travel writers know people everywhere .
But don't follow the crowds off a cliff. There are places even I won't go. I might take the four-hour train trip from Zurich to Paris in June to check out my favorite patisseries, but I wouldn't go anywhere near the City of Lights during the summer games in July unless I made a reservation a long time ago.
And Taylor Swift? Puh-leeze. I'm more of a jazz guy.
Christopher Elliott is an author, consumer advocate, and journalist. He founded Elliott Advocacy , a nonprofit organization that helps solve consumer problems. He publishes Elliott Confidential , a travel newsletter, and the Elliott Report , a news site about customer service. If you need help with a consumer problem, you can reach him here or email him at [email protected] .
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Mexico Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Mexico. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Dengue in the Americas February 28, 2024 Dengue is a risk in many parts of Central and South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean. Some countries are reporting increased numbers of cases of the disease. Travelers to the Americas can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. Destination List: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, French Guiana (France), Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Haiti, Jamaica, Martinique (France), Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Saint Barthelemy, Saint Martin, Turks and Caicos Islands (U.K.)
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in Mexico December 11, 2023 There have been reports of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) in people traveling to the United States from Tecate, in the state of Baja California, Mexico.
- Salmonella Newport in Mexico September 08, 2022 Some travelers who have spent time in Mexico have been infected with multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella Newport.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Mexico.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Mexico. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Mexico.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Mexico take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Mexico.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Mexico. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Mexico, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Mexico.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites, chagas disease (american trypanosomiasis).
- Accidentally rub feces (poop) of the triatomine bug into the bug bite, other breaks in the skin, your eyes, or mouth
- From pregnant woman to her baby, contaminated blood products (transfusions), or contaminated food or drink.
- Avoid Bug Bites
Chagas disease
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Mexico, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Mexico. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Mexico—such as dengue, Zika, leishmaniasis, and Chagas disease—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Mexico include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Mexico. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Mexico’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Mexico. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Mexico may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Mexico, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Mexico, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Mexico .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Mexico, dial 066, 060, or 080. Write these numbers down to carry with you during your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Mexico before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Mexico from the US Department of State.
Americans in Mexico have been arrested for purchasing souvenirs that were, or looked like, antiques and that local customs authorities believed were national treasures. Familiarize yourself with any local regulations for antiques and follow these tips:
- When you are considering purchasing an authentic antique or a reproduction, ask if you are allowed to export these items before you purchase them.
- If you buy a reproduction, document on the customs form that it is a reproduction.
- If you buy an authentic antique, obtain the necessary export permit (often from the national museum).
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Mexico for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
US considers easing warnings for Americans traveling to China
- Medium Text

The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Reporting by Michael Martina, David Brunnstrom and Kanishka Singh; Editing by Sandra Maler and Sonali Paul
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

Haiti decrees long-awaited transition council, but questions remain
Haiti's government on Friday issued a decree formalizing the creation of a nine-member transitional presidential council, a long-delayed move intended as the first step in restoring security to the gang-ravaged Caribbean country.

Mexican public health officials are sounding an alarm after a study discovered the presence of animal tranquilizer Xylazine in opioids in cities on the country's northwest border with the United States.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Q. What are the requirements for travelers entering the United States through land POEs? A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following: Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website. During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued an Order on October 25, 2021 requiring airlines and other aircraft operators to collect contact information for passengers before their arrival into the United States from a foreign country, retain the information for 30 days, and transmit the information to CDC upon request.
Protect yourself and others from COVID-19: Get up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines before you travel.; Consider getting tested before travel.; Follow CDC's recommendations for wearing masks in travel and public transportation settings.; Get tested after arrival.; Countries may have their own entry and exit requirements.; ALL travelers 2 years and older: If you are flying to the U.S. from ...
The Do Not Board and Lookout lists have been used for people with suspected or confirmed infectious tuberculosis (TB), including multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and measles. During 2020-2022, CDC used these authorities to restrict travel of people with COVID-19 and close contacts who were recommended to quarantine.
0:00. 2:02. The U.S. is launching a new travel system on Nov. 8. Vaccinated foreign air travelers will need to show proof of full vaccination and test for COVID-19. The new travel system also adds ...
The U.S. Department of State and U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) remind all travelers that beginning tomorrow, January 26, all air passengers two years of age or older arriving to the United States must provide proof of a negative COVID-19 test or proof of recovery from COVID-19 before boarding.
CDC has determined that for purposes of travel to the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and World Health Organization (WHO) emergency use listed (EUL) vaccines.
The United States does not require that travelers test upon landing and entering the U.S. However, the CDC has expanded a program to offer free, voluntary tests to travelers upon arrival to help ...
In January 2021, when the C.D.C. first instituted the rule that all U.S.-bound travelers 2 years and older had to show a negative test or proof of recovery before boarding a flight, the United ...
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
What to Know About the C.D.C. Guidelines on Vaccinated Travel. In updated recommendations, the federal health agency said both domestic and international travel was low risk for fully vaccinated ...
Ned Price, Department Spokesperson. October 25, 2021. Today, the White House and CDC announced details of the new vaccination policy that will go into effect for international travelers on November 8. As of that date, foreign national air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination ...
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
The CDC's looser guidelines around quarantining after exposure to COVID-19 don't change much for international travelers. ... to the US. Air travel is pretty much back to normal now for U.S ...
Updated Requirements for Air Travelers to the U.S. due to COVID-19. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has announced a new Order for all air passengers traveling to the United States. Effective November 8, 2021, all non-immigrant, non-citizen air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination status prior to boarding ...
Yes, all inbound international travelers are now required to test within one day of departure for the United States. All flights departing after 12:01 a.m. ET December 6 had to abide by a new CDC ...
Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked. Page last reviewed: December 15, 2023. Content source: National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) Division of Global Migration Health (DGMH) Official U.S. government health recommendations for traveling. Provided by the U.S ...
CDC Announces Negative COVID-19 Test Requirement from Air Passengers Entering the United States from the People's Republic of China. Related Pages. Press Release. For Immediate Release: December 28, 2022 ... CDC is also expanding the Traveler-based Genomic Surveillance program (TGS), a voluntary program that serves as an early warning system ...
You may also call the CBP INFO Center at 877-227-5511. If calling within the United States, call 202-325-8000 or go to www.cbp.gov and click on Questions/Comments. Complete the CBP Declaration Form 6059BYou have several entry options once you return from your trip. All travelers must complete a CBP Declaration Form 6059B itemizing all purchased ...
Pet travel from the United States to North Macedonia; ... you'll need to meet specific CDC import requirements to bring your dog back into the United States. This extension is in effect until July 31, 2024. ... If you have questions about CDC requirements, contact CDC-INFO or call them at 404-718-3660. Find a USDA-Accredited Veterinarian.
A sharp rise in measles cases since the start of 2024 represents a "threat" the U.S.'s ability to declare it an eliminated disease, the CDC says.
A glance at the new NOAA National Weather Service experimental HeatRisk tool and website for the contiguous U.S. The tool provides heat forecasts in a climatological context with CDC-based health impact messaging by taking into account how unusual the heat is for the time of year, the duration of the heat (including both daytime and nighttime temperatures) and if those temperatures pose an ...
Pet Travel. Take a Pet From the United States to Another Country (Export) Bring a Pet From Another Country into the United States (Import) Take a Pet From One U.S. State or Territory to Another (Interstate) USDA-Accredited Veterinarians: Certifying Pets for International Travel; Pet Travel From the United States to Mauritius
The most recent outbreak of measles is threatening the United States' elimination status, according to a new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report published Thursday. The first ...
CDC is extending its temporary suspension of dog importation from high-risk dog rabies countries until July 31, 2024. This suspension includes dogs arriving from countries without high risk of rabies if the dogs have been in a high-risk country in the past 6 months. Learn about the current rules: What Your Dog Needs to Enter the United States.
American travelers are becoming more predictable in their summer vacation choices, said John Lovell, president of Travel Leaders Group. Immediately after the pandemic, they embarked on "revenge ...
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in Mexico December 11, 2023 There have been reports of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) in people traveling to the United States from Tecate, in the state of Baja California, Mexico. Salmonella Newport in Mexico September 08, 2022 Some travelers who have spent time in Mexico have been infected with multidrug ...
USDA does not allow travelers to bring back most poultry meat or poultry meat products from countries affected with certain serious poultry diseases:. Highly pathogenic avian influenza; Newcastle disease; To find out a country's status for these diseases, visit our animal disease status page.. Commercially-packaged and labelled, cooked, shelf-stable poultry items from affected countries that ...
The U.S. is considering easing advisories against its citizens traveling to China, Deputy Secretary of State Kurt Campbell said on Tuesday, acknowledging concerns that the warnings may have ...