- Site Search
- ENGINEERING.com
- Eng-Tips Forums
- Tek-Tips Forums


Join Eng-Tips ® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet's largest technical engineering professional community. It's easy to join and it's free.
Here's Why Members Love Eng-Tips Forums:
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More...
Register now while it's still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close


Electrically Safe Work Practices — NFPA 70E Basics

Workforce Development and its Role in Electrical Safety

EFCOG Best Practice #240 — Electrical Utility Risk Assessment

Protection from Electricity in Commercial Kitchen Installations
Nfpa code talk.
Since the release of the 2020 edition of NFPA 70®, National Electrical Code ® (NEC®), a lot of discussions have taken place around the many new or revised requirements that affect residential occupancies. Requirements like emergency disconnecting means, whole-house surge protection, and expanding GFCI requirements, to name just a few. However, I feel like while the lion’s share of attention gets placed on residential requirements, there is much more to know when it comes to commercial installations. After all, don’t commercial buildings share the same need for the safeguarding of persons and property from electrical hazards as dwelling units? According to fire report data, some of the leading causes of fire in a commercial setting involve cooking equipment, heating equipment, lighting, and other electrical equipment. All of which have a common denominator here, the use of electricity!
Let’s look at an area of a commercial building that has many of the components that cause a dangerous and potentially deadly event just lying in wait – a commercial kitchen. The NEC contains certain requirements aimed at protecting people and property from electrical dangers, but there are a few other documents that we will want to consult here as well. First, let us think about the direct danger of electrical hazards. Electrical shock remains the number one source of fatal workplace injuries due to electricity, and commercial kitchens have a host of reasons why protection from electricity must be a priority. Just about every surface in a commercial kitchen is conductive and bonded to the electrical system, either by direct contact to the equipment grounding conductor or by connection to another grounded surface such as the tile floor. Because of this, nearly any contact with an energized conductor has all the components needed for electrocution. To protect against this threat, the NEC relies on a time-tested approach that we know has a proven track record of saving lives from shock: the ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI).
Within a commercial kitchen, GFCI protection for personnel is going to be required on most receptacle outlets. This requirement applies to both single- and three-phase receptacles on branch circuits rated 150V to ground or less. On single-phase branch circuits, this applies to all receptacles up to 50A, and on three-phase circuits, the cut-off is 100A. There is also a requirement to protect certain appliances regardless of whether they are cord-and-plug connected. Dishwashers, vending machines, and drinking water coolers/bottle fill stations must all be GFCI protected when they are installed on branch circuits that are 150V to ground or less and that are 60A or less. New for the 2020 NEC is that they have also clarified that this protection is needed in areas that might only be used for food prep and don’t have the necessary cooking provisions to deem them a kitchen. Yet, they still have all of the same potential for electrical tragedy.
Another area of great concern in a commercial kitchen is the exhaust hood over major cooking appliances. It is this hood that keeps the smoke and fumes produced during the cooking process from entering the rest of the restaurant or whatever the building happens to be. There are also many other considerations that come along with this equipment that we must be aware of. Cooking equipment is a leading cause of fire in a commercial setting, so it stands to reason that there is a significant fire protection component to a commercial cooking hood. However, while the equipment needed to operate a kitchen hood might involve complex coordination, the premise is simple. The exhaust hood will pull a certain volume of air, smoke, and fumes out of the kitchen while running, and if the volume is large enough, this might require the use of a make-up air unit to pump fresh air back in. There will most likely be some form of automatic fire extinguishing system under the hood that is effective on grease fires. Lastly, any lighting within the hood must be able to withstand high heat and be easily wiped down to prevent a build-up of excess grease, which could potentially lead to grease fires if not kept in check.
The NEC contains many of the requirements to ensure that the electrical system does not contribute to kitchen fires when it comes to these exhaust hoods. However, we also need to look in NFPA 96, Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations , which deals with ventilation control and fire protection of commercial cooking operations. This standard covers exactly how this system is intended to operate, both to minimize the fire hazard and to maximize the effort to extinguish any fire that might occur. This includes requirements for how the hood system will function, but it also contains requirements that the electrical system installer needs to know about as well. Chapter 9 contains sections that discuss what type of electrical equipment is permitted to be installed within these systems. Items like luminaires, motors, and other electrical devices are generally not permitted to be installed within hoods or in the direct path of travel for exhaust products. However, if this equipment is listed for this purpose, then it is acceptable. This means that any light, motor, sensor, switch, or other pieces of the electrical system of a hood must be specifically designed to handle the environment to which it will be exposed. The main thing here is that we don’t want the electrical system to be the cause of a grease fire within a kitchen exhaust hood.
In addition to requiring special light fixtures and motors for hood systems, there is another major component to the functionality of the associated equipment that we must be aware of. In the event of a fire, one that would activate the extinguishing system (not the kind from the fancy chefs as they flambé your steak), a few things need to happen. First, a fire needs fuel and air to burn, so when the extinguishing system is activated, it must be set up to immediately turn off all sources of fuel and electrical power that produces heat to all the cooking equipment under the protection of the hood. This means, most likely, the use of shunt-trip devices supplying the affected circuits. After all, no need to continue pumping heat into the fire that the system is trying to put out. Also, if there is a make-up air system, upon activation of the extinguishing system, the supply air must also shut down, and the exhaust must automatically ramp up to maximum capacity. This robs the oxygen from the fire to help maximize the effectiveness of the extinguishing efforts. This is usually accomplished within the programming of the kitchen hood control system. However, as an electrical contractor, I was often called in to work on kitchen equipment that was modified or added by individuals who were unaware of these requirements. Unfortunately, these kitchens were disasters waiting to happen.
Next time you find yourself enjoying a good meal at your favorite restaurant with the ones you love, take a minute to appreciate all the components that go into protecting them from the dangers lurking behind those swinging doors. It takes a lot of effort, planning, and execution to ensure that our night out on the town stays safe. Coordination between all trades involved in a kitchen is paramount for safe installations and the key to working together to achieve a safe environment. It’s like the mantra of NFPA says, “It’s a big world. Let’s protect it together!”
Air-Conditioning Equipment Installations

Basic three-phase power measurements explained

Safety in Marinas

Find Us on Socials
Pre-Wired and Modular systems can save substantial time and money over traditional hard-wired methods.
A change in overall workforce development will occur when more states make programs like these a requirement of licensure within their state.
Electrical utility tasks involve high hazard activities where the risk is often undefined. This DOE best practice can be used as a guide for other type of projects.
404 Not found

- Electrical Repair
- Lighting Installation
- Hot Tub Wiring
- Emergency Electrical Service
- Ceiling Fan Installation
- Generator Installation
- Commercial Lighting Services
- Electrical Inspection
- What Is a Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work
What Is a Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work?
First things first: what is a shunt trip breaker? A shunt trip breaker is a specialized circuit breaker that is designed to remotely shut off power to a circuit in emergency situations, such as a fire or security breach. These breakers are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings, as well as other facilities where safety is a top priority. In this article, we'll explore this type of breaker in detail and explain why hiring an electrical services provider for a wiring shunt trip breaker is essential.
The Many Benefits of a Shunt Breaker
Let’s recap: a shunt trip breaker is an electrical component connected to a circuit breaker and allows for remote operation through a schematic and AMP connection. Now that you know what a shunt trip circuit breaker is, it's time to move to the next part of this article: the benefits of using a shunt breaker.
- Remote Shut-Off: One of the main benefits of shunt breakers is that they can be remotely shut off in the event of an emergency. This allows them to quickly and easily disconnect power in a fire or other emergency, which can help prevent damage to the building and protect the occupants.
- Increased Safety: Besides remote shut-off, shunt trip circuit breakers provide an added level of safety and security by automatically shutting off power to a circuit in the event of an emergency. This helps prevent electrical fires and other hazards, protecting both people and property.
- Easy Installation: Shunt breakers are relatively easy to install and can be integrated into existing electrical systems, making it possible to retrofit older buildings with these devices.
- Cost-Effective: A shunt breaker is a cost-effective solution for increasing safety and security in commercial and industrial buildings. They are relatively inexpensive to purchase and install and can help prevent costly damage to the building and its contents in case of any emergency.
- Compatibility: Shunt breakers are compatible with a wide range of electrical systems and devices, making them a versatile and practical solution for increasing safety in various settings.
How Does a Shunt Trip Breaker Work?
A shunt trip breaker works by tripping the breaker when it receives a signal from an external device, such as a fire alarm or security system. This helps to prevent dangerous electrical fires or other hazards. When an emergency occurs, the external device sends a signal to the breaker, which causes the breaker to trip and open the circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing power from reaching the circuit, allowing for a quick and easy power disconnection.
Types of Shunt Trip Breakers
Now that you know the answer to "How does a shunt trip breaker work", it's time to discover about the two main types of shunt trip breakers.
- Manual Shunt Trip Breaker: This type of trip breaker requires manual intervention to reset the breaker after it has been tripped, meaning someone must physically go to the breaker and reset it after an emergency situation. This breaker is typically used in smaller residential buildings or situations where a dedicated staff member is available to reset the breaker.
- Automatic Shunt Trip Breaker: This type of breaker can automatically reset itself after being tripped and is typically used in larger buildings or in situations where there is not always someone available to reset the breaker. These breakers are often connected to fire alarm systems or other emergency management systems for auto-reset.
When is a Shunt Trip Breaker Required?
If you're wondering when is a shunt trip breaker required, know that it is required in any electrical system where there is a need to quickly and easily shut off power in the event of an emergency, such as a fire or security breach. Continue reading as we describe the importance of using shunt trip breakers and how to figure out which one you need to use for your building or facility.
The Importance of Using a Shunt Trip Breaker
- Shunt trip breakers automatically shut off power in emergencies.
- They prevent dangerous electrical fires and other hazards.
- They allow for quick and easy power disconnection in emergencies.
- They are easy to install and cost-effective solutions for increasing safety.
- They can be connected to fire alarm and emergency management systems.
- They ensure that the electrical system is in compliance with safety regulations.
- They are a versatile and practical solution for increasing safety in various settings.
Which Type of Shunt Trip Breaker to Use?
A manual breaker may be appropriate for a smaller building or in situations with a dedicated staff member available to reset the breaker, while an automatic breaker may be more appropriate for a larger building or in situations where someone is not always available to reset the breaker. Another option to consider is the use of a shunt trip relay, which can be used to trigger a shunt trip breaker remotely. These relays are typically connected to fire alarm systems or other emergency management systems and can send a signal to the breaker to trip it when an emergency occurs.
Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram
If you're wondering how to wire a shunt trip breaker, know that wiring can seem like a daunting task, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can be done relatively easily. Follow the steps below:
- Obtain a "How to wire a shunt trip breaker wiring diagram." (Check above).
- Gather necessary tools and materials such as wire strippers, nuts, and a voltage tester.
- Disconnect the power and wire the shunt breaker according to the instructions provided.
- Reconnect power to the circuit and test the breaker to ensure it works properly.
It is important to pay close attention to the diagram and follow the instructions carefully. This will ensure that the breaker is wired correctly and functions. Once the wiring is complete, you can reconnect the power to the circuit and test the breaker to ensure that it is working properly. It is always better to consult with a professional if you aren't confident about the wiring process.
What Does a Shunt Trip Breaker Do?
We hope by now you know what does a shunt trip breaker do, but here's a recap: a shunt trip breaker is a specialized circuit breaker that protects your house electrical systems from damage or hazards in emergencies. It works by tripping the breaker when it receives a signal from an external device, such as a fire alarm or security system, preventing dangerous electrical fires or other regular hazards.
Nevertheless, it is important to understand what does shunt mean in electrical terms and the role of electrical shunt trip breakers in commercial and industrial settings. Finally, to determine the appropriate type of breaker for your specific needs, it is best to consult an electrical services provider. If you're based in Colorado or surrounding areas, McCarrick Electric has got you covered.
Superior Electrical Solutions in Colorado
At McCarrick Electric, we have 25+ years of experience providing top-quality electrical services in Colorado. We value all of our customers, and that's why we offer a 15% discount for first-time residential clients and veterans. We take pride in our integrity, attention to detail, and cost-effectiveness. For more information, connect with us via our contact form or give us a call.
Latest Blog Entries

What to Do If Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping?

Why Is Your Breaker Box Outside House? Here Are the Reasons

Why Won’t My GFCI Outlet Reset? How to Troubleshoot a GFCI Outlet


5 Ways to Prevent Short Circuits

Galvin Power is reader-supported. When you buy via our links, we may earn a commission at no cost to you. Learn more
What is a Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work?
Written by Edwin Jones / Fact checked by Andrew Wright

What is a shunt trip breaker? Does it add protection to your electrical system?
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of the shunt trip accessory and the main circuit breaker. This installs on the main breaker to add protection to your electrical system. This adds security to your electrical system as it manually or automatically cuts the electric supply in your circuit.
This accessory can help prevent short circuits and avoid electrical damage should a disaster occur in your home.
Let me tell you more about the shunt trip breaker to help you decide if you need additional protection for your electrical system.
Table of Contents
What is Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work
Where are shunt trip breakers most used, how to install a shunt trip accessory to the breaker.

You should know that shunt trip breakers are different from GFCI circuit breakers.
The GFCI circuit breaker contains one big white tail wire for neutral connections only. It cannot be connected to any control package because the GFCI circuit breaker is solely designed to detect a sudden electrical surge. It has no other purpose but to cut power in case of a short.
Meanwhile, the shunt trip breaker wiring comprises two wires. One connected to the ground, and another to a control system. The control system can be connected to a sensor or to a manual switch. When activated, the shunt trip accessory will cause the main breaker to trip.
For example, if you install a shunt trip with a smoke detector, it will activate and cut off the power should the smoke sensor trigger. It can also be installed with a remote switch , allowing you to trip your breaker manually.
It is crucial to know the difference between a regular circuit breaker and a circuit breaker installed with shunt trip accessories.

The shunt trip definition means that it is a way to cut off electrical power through other sensors, not just via thermal activation. Since this is an optional accessory for a circuit breaker, it is not required for a home electrical system.
However, it is recommended for added safety. This is especially true if you’re working with industrial machinery. Furthermore, you can use it as a manual emergency switch to shut down your main breaker.
Before installing a shunt trip, consider its cost and your existing system. You may need to change the breaker panel and circuit breakers, especially if it is not compatible with shunt trips. You may also need a new line to connect the remote emergency switch to your breaker box.
Generally, most commercial kitchens, elevators, and offices have this shunt trip breaker because it is required. Commercial kitchens use this device in compliance with ANSI/ASME CSD-1, while elevators and escalators comply with ASME A17.1. These codes refer to the controls and safety standards provided by ASME’s.
This question is a topic of discussion among Reddit members as well. Join the conversation here:
Found at a dominos by u/Guilty_Sympathy_496 in electricians
Mostly, installing a shunt trip relay requires that the breaker and the shunt be from the same maker. Also, not all breaker models are compatible with this accessory.
Once you’re sure that your system can take a shunt trip accessory, installation is pretty much straightforward. You can watch this video by Aaron CBIONE for some tutorials.
Note: Every circuit breaker comes with different instructions. It would depend on the brand and model of the breaker .
However, the critical part of every installation is that you need to connect the shunt to your sensor. You may need a shunt trip breaker diagram as a reference to ensure correct installation.
Also, check the brand and model of your breaker before proceeding with the installation. Some makers only allow a factory install of the shunt trip and other accessories. DIY installation may void the warranty of your breakers. It’s best to read up on the manual or consult an electrical professional before making any changes.
What is a shunt trip breaker? The shunt trip is an optional accessory for a circuit breaker for added protection to your system. It is designed to connect to a secondary sensor. It will trip the breaker automatically if the sensor is triggered. It can also be activated via a remote switch that you can install.
Do you think that a circuit breaker is enough to protect your investment? Or do you want an additional layer of protection for your electrical circuit? If you’re not decided yet, reach out to me in the comments section below, and I will be happy to help you.

I am Andrew Wright. With 8 years of experience designing, installing, and maintaining electrical power systems. I love my job, and I have always wanted to offer others the necessary help so they can take care of their houses.

Wire A Shunt Trip Breaker: Your Step-by-step Visual Guide
In the world of electrical engineering , dances with complex equipment are common. Few dances are as intricate as the one with the shunt trip breaker. As seasoned professionals, we guide you through this delicate ballet, ensuring your safety and the seamless operation of your electrical system.
Our comprehensive visual guide will demystify shunt trip breaker wiring, breaking down the process into manageable steps. By the end of this journey, you’ll possess the knowledge and skills to wire a shunt trip breaker with confidence.
First, let’s explore what a shunt trip breaker is and why it’s a crucial component in an electrical system.
Key Takeaways
- Shunt trip breakers are crucial in industrial settings and high-risk areas to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
- The wiring diagram of a shunt trip breaker allows it to receive a signal from a separate source for immediate shutdown.
- The key parts of a shunt trip breaker include the coil, breaker mechanism, and trip unit, which work together to cut off power in case of overloads or faults.
- Proper installation and regular maintenance of shunt trip breakers are essential for ensuring system safety and efficiency.
Understanding the Importance and Functionality of Shunt Trip Circuit Breakers
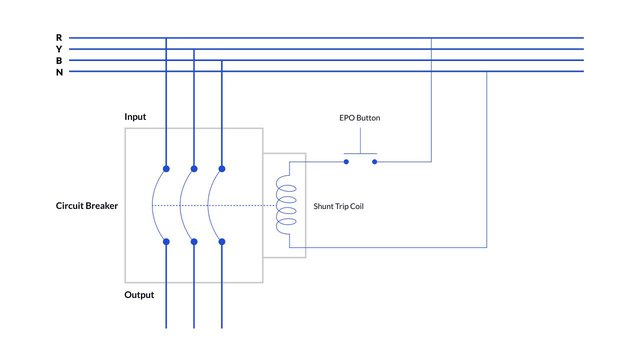
Diving into the heart of our discussion, it’s crucial to understand just what a Shunt Trip Circuit Breaker is. This innovative device shuts off an electrical circuit when it detects a problem, such as an overload or short circuit . This proactive functionality greatly reduces the risk of electrical fires and other potential hazards.
Its unique design allows the breaker to receive a signal from a separate source that triggers an immediate shutdown when necessary. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments where immediate circuit disconnection is paramount, like in industrial settings or high-risk areas.
Precision is key when installing a shunt trip breaker. A wrongly connected wire can compromise the breaker’s functionality, possibly leading to a dangerous situation. So, we strongly recommend professional installation to ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Learning the Basics: Diagrammatic Representation of a Shunt Trip Breaker
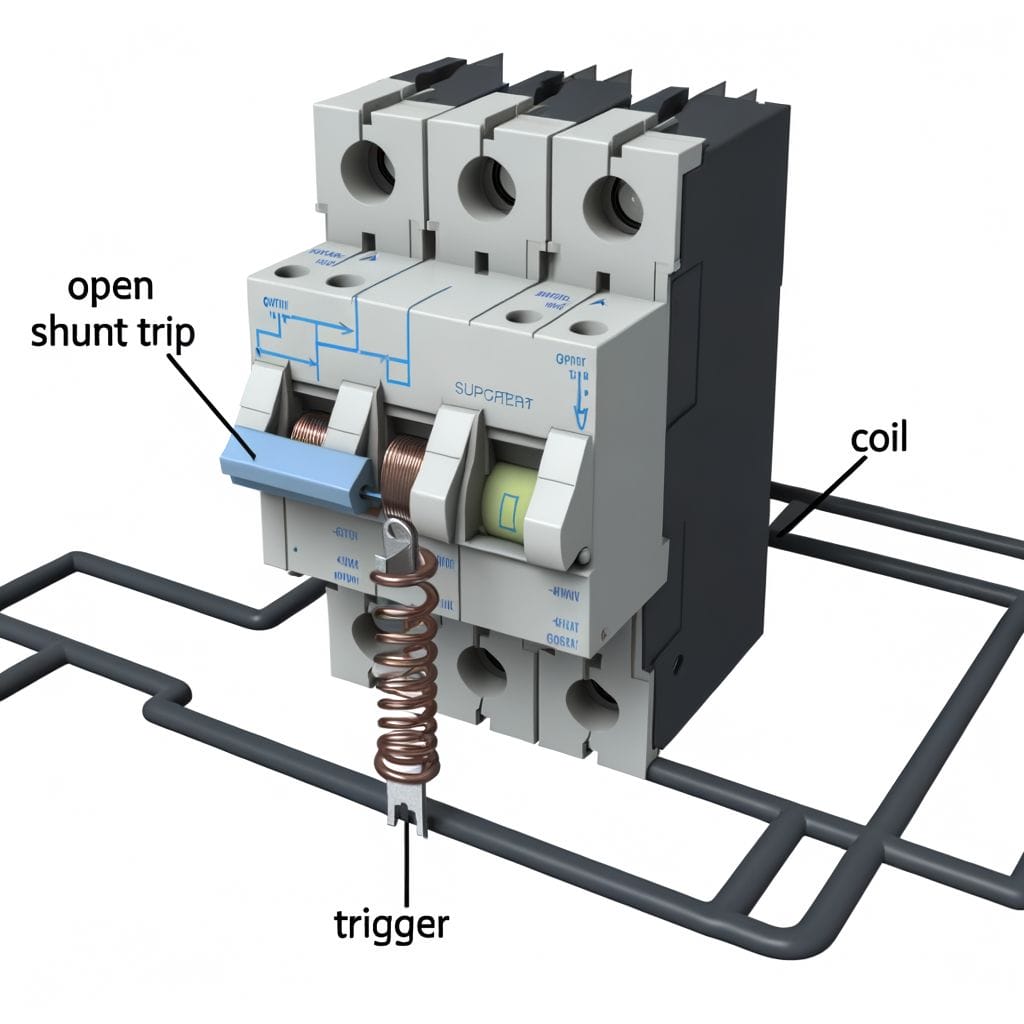
To grasp the workings of a shunt trip breaker, let’s delve into its diagrammatic representation. A shunt trip breaker is comprised of key parts like the coil, the breaker mechanism, and the trip unit. These parts work together to safely distribute electricity and prevent dangerous overloads.
The current first enters through the coil. When an electrical fault is detected, the coil becomes energized, triggering the trip unit. This in turn activates the breaker mechanism, causing the breaker to trip and cut off the power. It’s a simple and efficient system and serves as an innovative solution for electrical safety.
Detailed Steps to Wire a Shunt Trip Breaker Safely and Efficiently

Ready to wire a shunt trip breaker ? Start by preparing your workspace. Clear the area of any debris and make sure you have good lighting . Assemble your tools, which include a screwdriver, wire stripper, and multimeter.
Once your workspace is ready, follow the step-by-step process. Start by turning off the main power supply. After that, connect the shunt trip breaker to the circuit. Be sure to connect the wires correctly: the black wire to the breaker terminal, the white neutral wire to the neutral bus bar, and the green or bare ground wire to the ground bus bar.
Avoid common pitfalls like loose connections and incorrect wiring. Always double-check your work to ensure everything is wired correctly.
Connecting the Shunt Trip: An Essential Accessory for System Safety

A functioning shunt trip breaker represents an innovative approach to electrical safety. It automatically cuts power in the event of an electrical anomaly, shielding your system from damage. Hence, the importance of connecting the shunt trip can’t be overstated.
To wire a shunt trip breaker, we must employ a methodical approach. Connect the shunt trip coil to the breaker’s auxiliary terminal. Secure the connection using the recommended fasteners. Always test the shunt trip breaker to ensure it operates correctly and inspect the connection regularly for ongoing safety.
Troubleshooting Tips: Ensuring a Reliable Shunt Trip Breaker Connection
Even with careful installation, occasional challenges may arise in the wiring of a shunt trip breaker. To empower you further, let’s delve into troubleshooting tips for maintaining a reliable connection.
- Faulty Connections : If the shunt trip breaker isn’t functioning as expected, inspect the connections thoroughly. Ensure they are tight and secure. Reconnect any loose wires and tighten screws appropriately.
- Testing Procedures : Regularly test the shunt trip breaker using the recommended testing procedures. If the breaker fails to trip during a test, reassess the wiring and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting.
- Voltage Issues : Check the voltage supply to the shunt trip breaker. Ensure it aligns with the specified requirements. Any discrepancies may affect the breaker’s performance. Consult a professional if voltage-related concerns persist .
- Visual Inspection : Periodically inspect the breaker for signs of wear, damage, or overheating. Replace any damaged components promptly. Visual cues can provide early warnings of potential issues.
- Interference and Environmental Factors : Assess the surrounding environment for potential interferences, such as electromagnetic interference or extreme temperatures. Shield the breaker from external factors that could compromise its functionality.
By familiarizing yourself with these troubleshooting techniques, you can address issues promptly, ensuring a reliable and efficient shunt trip breaker connection. Remember, a well-maintained breaker contributes significantly to the overall safety and reliability of your electrical system.
Are the Wiring Steps for a Shunt Trip Breaker Similar to a Water Well Pressure Switch?
No, the wiring steps for a shunt trip breaker are not similar to a water well pressure switch. While both involve wiring, the purpose and functionality of each are different. In the case of a shunt trip breaker, the wiring process will be specific to its functionality and requirements, and would not be interchangeable with water well pressure switch wiring .
In wrapping up, we’ve guided you through the crucial steps of wiring a shunt trip breaker. We trust you now understand its importance and how it operates.
With safety as our primary concern, we’ve shown you the right way to connect the shunt trip. Remember, knowledge is power, and this guide arms you with the needed expertise.
Keep exploring our guides for more practical electrical tutorials. Your safety and satisfaction are our top priorities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a shunt trip breaker.
A shunt trip breaker is a type of circuit breaker that can be triggered remotely to trip the breaker. It is frequently used in commercial kitchens, elevators, and other applications where the breaker needs to be tripped manually or remotely in case of an emergency.
Can you explain the shunt trip breaker wiring diagram?
The shunt trip breaker wiring diagram shows the connections for the shunt trip terminals, control circuit, and external power source. It also illustrates how the breaker is typically wired to trip the circuit breaker remotely or automatically during a surge or in case of an emergency such as a smoke alarm.
What is the purpose of a shunt trip breaker?
The main purpose of a shunt trip breaker is to provide circuit protection and to trip the breaker remotely or automatically during a surge, alarm, or emergency situation. It can help minimize equipment damage and ensure the safety of the electrical system.
How does a shunt trip breaker work?
A shunt trip breaker works by using an electromagnet to trip the breaker when it receives a signal from the control circuit. This can be done manually, through a relay, or remotely depending on the particular shunt trip accessories and model of the breaker.
What are the components of a shunt trip breaker?
A shunt trip breaker includes the main circuit breaker, shunt trip terminals, external power source, control system, and the shunt trip accessories. These components work together to trip the breaker manually or remotely in case of an emergency.
Similar Posts

Solar Power Off the Grid Systems: The Best Energy Solutions
Looking to power your off-grid lifestyle with solar energy? Wondering about the best energy solutions available? Explore our…

5 Best Hallway Lights: Find the Perfect Illumination
Discover the perfect hallway lights to illuminate and enhance your home’s ambiance with our comprehensive guide. Featuring top…

Difference Between Floodlight and Spotlight: Choose Wisely
Setting the stage for your outdoor space involves more than just shedding light on a subject. The choice…

Home and Lighting Company: A Customer-Approved Review
Elevate your home with Home and Lighting Company‘s exquisite designs and functional lighting solutions. Customers love the seamless…

How Long Do Fluorescent Bulbs Last? Understanding Rated Life and Replacement Rates
Fluorescent bulbs are an increasingly popular choice for lighting. They use less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, last…

Cost of Solar Electricity per Kwh: Worthy of Investment?
Have you ever wondered if the cost of solar electricity per kWh truly makes it a worthy investment…

- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- General Electrical
- General Electrical Discussion
Commercial Kitchen Hood
- Add to quote
Ok so I got thrown into doing this kitchen hood. Not much info given. Basically I have a exhaust fan, make up air, and lights. Doing research on here I have figured basically everything needs to shut off except the exhaust...which could also depend on local requirements. Now my question is how exactly are the make up air and exhaust supposed to be controlled? Basically is it just a on/off PB on the wall that enables both units for normal operation? I can figure out the controlling to be inter connected with the fire suppression without much problems I am just actually unsure of the normal operation side of it.....never done one before. Also I have noticed you guys talk about using shunt trip breakers to kill power to make up air, lights etc, but could I just achieve the same results with contactors....or are the shunt trips needed?
I've seen it done with shunt trips as well as with contactors. Shunt trips are great for it. You would just run your shunt circuit through the contact in the fire suppression control box and if it triggered, it would trip all the breakers. Regarding the exhaust fan, typically (as I understand) the exhaust needs to stay on if it's already running, or it needs to turn on if it's NOT running. To achieve that you could put in a contactor controlled by a contact in the fire suppression box and just run a loop parallel to whatever switch turns the fan on normally.
The MAU should come with a control panel. You will have to install contactors for the exhaust fans. You will have control wiring from the fire suppression, to the control panel. And the control panel will operate the contactors. Don't use shunt trips.
Here you just need to kill the makeup air. Use a microswitch in the suppression box. Can't have positive pressure in a fire. It is also required to interlock the exhaust fan to the makeup air so it won't run without the exhaust fan.
farlsincharge said: It is also required to interlock the exhaust fan to the makeup air so it won't run without the exhaust fan. Click to expand...
Microswitch in the ansul panel operates no and nc contacts in the hood panel. Here we have to kill mau and all underhood electric including lights so I run mau and all underhood electrics on a small subpanel backfed with a two pole shunt trip breaker. Saves a buck that way.
Ok so this job is becoming more and more of a headache. The MAU is not in yet but they need the wiring run now to a JB by the location as the ducting is running through a separate tenant space and they can't have the other tenant shut down too long(don't ask). Is there any control wiring typically needed to go up to the MAU or is it just straight feeds and all the controls are done in the kitchen.
CanadianSparky said: Ok so this job is becoming more and more of a headache. The MAU is not in yet but they need the wiring run now to a JB by the location as the ducting is running through a separate tenant space and they can't have the other tenant shut down too long(don't ask). Is there any control wiring typically needed to go up to the MAU or is it just straight feeds and all the controls are done in the kitchen. Click to expand...
Most the new installs now just need a constant feed to the control panel, the on/off switch and temp sensor are wiref low voltage in parallel. Anything electric under hood and make up air shuts down during ansul op. What u can do is drag a feed from ex fan leg, make/break at ansul and feed contactor( s) feeding said items.
It is looking like All the controls will be done myself. They seem to have an ansul system with just a set of NO and NC contacts...None of the contacts will be able to handle the loads of any of the equipment. This is the equipment that was order....Don't ask me why but not my problem Exhaust fan(120v 20.8fla) :no: Make up air(specs are kinda up in the air because no one has answers but it is a 208 3ph) Hood lights Gas valve (no one has the answer if it is mechanical or electrical) Now I have never wired up a make-up air unit before and not sure what it comes with control wise as I can't get any specs or info on that either. Basically I have the feeds for exhaust and MAU ran up to where the units will be as we had to have this done because the ducting and wiring runs through another tenants space an they have basically been booted out until the ducting is done. Do the MAU typically have control wiring running up to the unit or is it all done in the kitchen. I plan on controlling the MAU, lights, valves, and exhaust all through a series or contractors which will be tied into the Ansul system.
Your in Canada so it may not apply but in the US an updraft hood exhaust has to be mounted with a hinge for NFPA. This means a whip with some slack so the fan can be tilted back for service. NFPA Fire Code #96: 7.8.2.1 “Rooftop terminations shall be arranged with or provided with the following: (8) A hinged upblast fan supplied with flexible weatherproof electrical cable and service hold-open retainer to permit inspection and cleaning that is listed for commercial cooking equipment..” NFPA Fire Code #96: 8.1.1.1 “Approved upblast fans with motors surrounded by the airstream shall be hinged, supplied with flexible weatherproof electrical cable and service hold-open retainers, and listed for this use. Hawkrod
- ?
- 93.6K members
Top Contributors this Month

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5) trip electrical power under the hood, typically shunt trip a main breaker feeding a subpanel for equipment under the hood. 6) the overload relays of the exhaust fan may be overridden, causing the fan to run to failure, if necessary (like a fire pump). 7) not turn off all lighting in kitchen; may rely on emergency lighting.
Equipment under kitchen hood anbm (Electrical) (OP) 9 Sep 08 18:50. Can anyone tell me which code and section requires all equipment under kitchen hood shall be protected by shunt trip breakers and those breakers shall be tripped via a signal from fire suppression system in case of fire? Thanks! anbm . RE: Equipment under kitchen hood ...
1.) The breaker supplying the power to the trips themselves might get turned off (even with a lockon) and go unnoticed. 2.) Breaker space is usually at a premium in kitchens, never seems to be enough. The shunt trip needs an extra pole space. 3.) Contactor = less $$, and easier to get.
Another area of great concern in a commercial kitchen is the exhaust hood over major cooking appliances. It is this hood that keeps the smoke and fumes produced during the cooking process from entering the rest of the restaurant or whatever the building happens to be. ... This means, most likely, the use of shunt-trip devices supplying the ...
3) if there are "HEAT PRODUCING" electical items under the hood I disconnect ones with a shunt go breaker activated via the ANSUL system. Like an electric fryer, electric grill, more. 4) EGO do NOT disconnect general purpose receptacles that supply refrigeration power, timer power, or other non-heat generating electrical items which exist in ...
CASService explains how to wire a shunt trip breaker or contactor to an exhaust hood control package. For questions, please contact CASService at 1-866-784-6...
Almost Retired. 8288 posts · Joined 2021. #4 · Feb 22, 2024. there is a simple relay option to a shunt trip breaker. much much less expensive. if the ahj will accept it. it is considered legal in my area. Sent from the keyboard of my 500k hard drive Compaq via a 10k dial up modem using ASCII code. brian john.
Shunt trip for all electrical under hood, including lights. Gas valves to shut off when hood is turned off. Mechanical gas valves shut off when suppression system activated. (Nothing for the electrician) ... and the kitchen hood is a separate permit, with stamped, approved drawings. Inspections by fire marshal, EI and plumbing inspector. ...
Overall, wiring a shunt trip breaker is quite simple and direct. Step 1: Get familiar with your shunt trip breaker's wiring schematic. It's crucial for a safe and correct installation. Step 2: Find the two screws on the shunt trip unit - these are where you'll connect your control circuit wires. Step 3: Attach the control circuit wires ...
A shunt trip breaker is a specialized circuit breaker that is designed to remotely shut off power to a circuit in emergency situations, such as a fire or security breach. These breakers are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings, as well as other facilities where safety is a top priority. In this article, we'll explore this type ...
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of the shunt trip accessory and the main circuit breaker. This installs on the main breaker to add protection to your electrical system. This adds security to your electrical system as it manually or automatically cuts the electric supply in your circuit. This accessory can help prevent short circuits and ...
Once your workspace is ready, follow the step-by-step process. Start by turning off the main power supply. After that, connect the shunt trip breaker to the circuit. Be sure to connect the wires correctly: the black wire to the breaker terminal, the white neutral wire to the neutral bus bar, and the green or bare ground wire to the ground bus bar.
NFPA Fire Code #96: 7.8.2.1. "Rooftop terminations shall be arranged with or provided with the following: (8) A hinged upblast fan supplied with flexible weatherproof electrical cable and service hold-open retainer to permit inspection and cleaning that is listed for commercial cooking equipment..". NFPA Fire Code #96: 8.1.1.1.
Welcome to our tutorial on wiring a Shunt Trip on QO™ Circuit Breakers. In this step-by-step guide, we'll walk you through the process of wiring a Shunt Trip...
This video shows Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram. A shunt trip device is an optional accessory in a circuit breaker (MCCB) that mechanically trips the brea...
http://www.electricalindustrynetwork.com Kitchen Hood Wiring Shut down using a non-shunt trip system. This video is a brief description of how it works. I do...
This video highlights how to wire elevator shunt trip using an addressable system sensor type relay, while also supervising for power loss with an MR-101 and...