
Propane / Heating Oil / HVAC Services
- My Account:
- Make Payment
- Why choose Petro overview
- Why choose Petro?
- Petro vs. other oil companies
- 24/7 customer service
- Other Services
- Video gallery
- Customer reviews
- Heating oil services overview
- Heating oil services
- Heating oil delivery services
- Propane services
- Propane equipment
- Bioheat Fuel
- Emergency weather services
- Pricing and payment plans
- Service and protection plans
- Special offers
- Heating oil FAQs
- Propane FAQs
- Seasonal offers
- Heating oil special offers
- Propane special offers
- Heating equipment special offers
- Featured articles
- Choosing a heating oil service provider: the hidden cost of a bargain
- Home heating oil: it is a great value
- How your oil home heating system works
- Why choose propane for your home
- Propane energy efficiency tips for your home
Get $100 free heating oil!

- Heating Systems overview
- Heating Systems
- Tank & Tankless Hot Water Heater Services
- Natural gas services
- Boiler and furnace repair
- Service plans
- Oil to gas conversions
- Emergency boiler and furnace services
- Heating FAQs
- Heating system special offers
- When should you repair or replace your furnace
- The heating equipment maintenance checklist every homeowner needs
- Tankless water heaters vs. storage tank water heaters
- 10 life hacks for saving on your heating bill this winter
- How to choose a tankless water heater
New energy-efficient heating systems!

- Air conditioning services overview
- Air conditioning services
- Ductless AC and mini-split
- AC tune-ups
- Stay Cool with Petro Air Conditioning Service Plans in Your Area
- Emergency AC repairs
- AC replacement
- AC special offers
- Cooling system tune up special offers
- Cooling system equipment offers
- Why you should switch to a new energy-efficient air conditioning system
- How often you should change the AC filters in your house and how to do it
- What is a ductless mini-split AC system
- What size of central air conditioner do you need
- Heat pumps vs. air conditioners: What's the difference and which should I get
- Time to replace your AC?
- Choosing the best home air conditioner
New energy-efficient AC systems!

- Generator Services overview
- Generator Services
- Tune-ups and service plans
- Generator FAQs
- Do you really need a backup generator?
- What type of generator do you need?
- The ultimate backup generator guide.
$150/mo and $0 down for a new generator!

- Contact us overview
- Request a quote
- Referral Rewards
- Sign up for My Account
- Careers Careers
Find your local office: See what services and offers are available in your area
- Connecticut
- East Hartford
- North Haven
- Capitol Heights
- Massachusetts
- South Plainfield
- Poughkeepsie
- Pennsylvania
- Southampton
- Rhode Island
- East Greenwich
- My Account overview
- Paying your bill
- Schedule an appointment
- Emergency services
- Customer FAQs
- Pay your bill online
- Automatic delivery facts you need to know
- Answers to most commonly asked questions
Control you want. Convenience you need.

My Account | Make Payment


Plumbing glossary: Plumbing terms you need to know as a homeowner.
Knowing all the parts that keep your house running can be challenging. As a new homeowner, or seasoned veteran, it’s essential to know a few terms and the accompanying items to keep your house running smoothly. This plumbing glossary will outline 54 essential plumbing terms you need to know to keep your plumbing running smoothly, as well as make you articulate about any future issues that may arise.
54 Plumbing terms you need to know.
Access panel.
An access panel is an opening in a wall or ceiling near a fixture. The access panel offers access to work on plumbing or electrical systems.

An angle stop is a shutoff valve between the water supply and plumbing fixture. It is used to shut off water flow while you repair the connected item.
An anode rod is located inside the water heater. The anode rod protects the water tank from corrosion due to magnesium or aluminum.

A backwater valve prevents disposed sewage from reentering the home.
A ball check valve is a type of backflow preventer. The ball check valve is placed on a water line to direct water flow in one direction.
The ballcock controls the flow of water in a gravity-operated toilet tank. When the toilet is flushed, the circular float will drop and open the ballcock. This results in water being distributed in the tank. As the water rises, the float rises to the level that shuts of the ballcock.

A branch is any secondary part of the drain system; also, referred to as the lateral line.
Branch vent
A branch vent connects vents with a vent stack.

The check valve is a type of backflow prevent. The check valve is installed on a pipe to allow water flow in one direction.
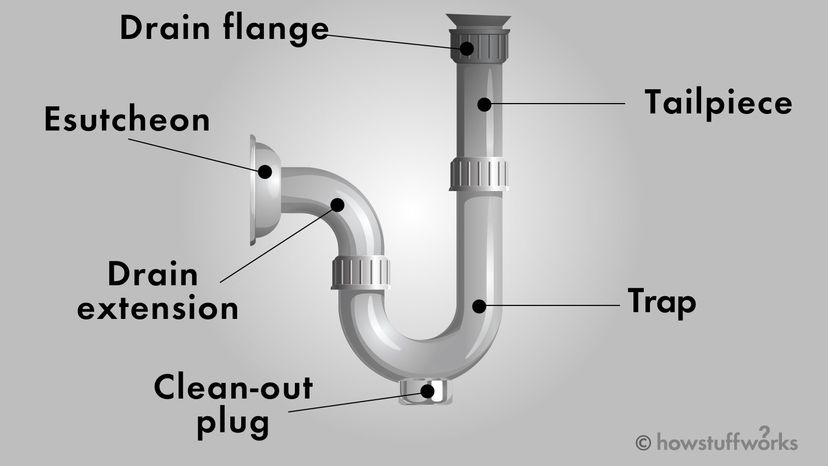
Cleanout plug
The cleanout plug is in a trap or drain pipe. The cleanout plug offers access to the drain line for clearing any blockage in the pipes.
Synonym for a toilet, also referred to as a “water closet”

Closet auger
A closet auger is a flexible rod that is used to access a toilet’s trap to remove any clogs.
Closet bend
The closet bend connects the closet flange to the toilets drain.

Closet flange
The closet flange is a ring that anchors the closet bend to the floor. The closet flange also includes closed bolts that secure the toilet in place.
The diaphragm is a flexible membrane that helps regulate water flow and build up within a valve.
The dip tube sends cold water to the bottom of the water heater tank.
The drip leg, also known as the “sediment trap”, is a pipe installed at the lower segment on a gas line. The capped off section collects condensation and debris.

The escutcheon is a protective cover under the faucet handle that masks the fixtures hole.
The fall, also known as flow or pitch, refers to the slope needed to create proper drainage in pipes.
A fixture refers to the plumbing device that provides water and/or disposal. Common fixtures in plumbing are toilets, sinks and showers.
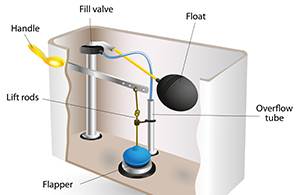
The flapper valve connects the water tank and toilet bowl. When the flapper valve opens, water flows from the tank into the bowl.
The float ball is the plastic ball attached to the ballcock. The rise and fall of water in the tank is determined by the float ball’s placement.
Floor flange
The floor flange, also known as a closet flange, connects a toilet to the sewer line.
The gas cock on a main gas line allows for the gas to be shut off.
The gate valve controls the flow of liquids in pipes.

Gravity operated toilet
A gravity operated toilet relies on downward pressure of water in a toilet tank to flush. Gravity operate toilets often have ballcocks in their tank.
Gray water is any waste water that comes from common fixtures, but not toilets.
Horizontal branch
The horizontal branch runs from plumbing fixtures to a waste stack.
Horizontal run
Horizontal run is the distance liquid travels from the entry point and exit of a pipe.

A hose bib is a common outdoor faucet.
The main line supplies water from the water company’s meter at street level to the branch pipes around your home.

A nipple is a short pipe that connects couplings and other fittings.
Power flush system
The power flush system compresses water to provide a pressurize flush. This system is often found in business and commercial settings.
PRV or pressure reducing valve
PRV, or pressure reducing valve, is a special valve that is installed directly on the main water line. The PRV constrains the amount of water entering from the water companies supply to normalize water pressure for home use.
PVC pipes are sturdy plastic pipes that are used for drainage, waste and vent systems.
Rim holes are a series of small holes around the toilet bowl. Water flowing from the rim holes washes over the surface of the bowl to refill the toilet bowl.

Saddle valve
The saddle valve is a mounted pipe run by a clamping device. The saddle valve is used to make quick connections between low-demand devices.
Septic tank
A septic tank is a small sewage treatment system for homes with no connection to local sewage pipes. Septic refers to the bacteria that decomposes the waste inside the tank.
Straight stop valve
A straight stop valve is a straight shutoff valve used to close off water supply during repairs.

A sump pump is used in basements that flood often. The sump pump sits in a pit that accumulates the water, where it pushes the water outside the home.
Supply line
A supply line is a metal or plastic line that carries water directly from the main line into a plumbing fixture.
T&P valve or temperature and pressure valve
The temperate and pressure relief valve is used to safely release excess heat or pressure in a water tank.
The tailpiece is a pipe that runs between a fixture and trap.
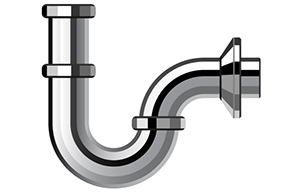
The trap is a curved section of drain line that prevents sewer odor from entering your home. All plumbing fixtures have a “P” trap, except for a toilet that has an “S” trap.
The trapway connects the toilet bowl to a waste outlet. The size of the trapway, also known as the passageway, influences clogging.
The trip lever is the flush handle and actuating arm on a toilet tank. The trip lever is attached to the flapper, which results in the toilet flushing. The trip lever can also refer to the drain in a tub.
The vent is a pipe that allows air into the drain system.
The vent stack, also known as a stink pipe, releases gas and odors outside the home.
Water hammer
The water hammer is a loud noise and vibration associated with pipes being turned on or off. The water hammer is caused by a sudden surge, or halt, of water in the pipes.
Now that you’ve reviewed the plumbing glossary, you can now effectively express any issues that may arise the next time you reach out to the professionals to fix your ballcock, sump pump or flapper valve. When you do finally reach out to the pros, make sure to reach out to Petro, the most trusted plumbing service provider.*
*plumbing services not available in all areas
Petro Home Services is proud to not only serve communities in DC , CT , MA , MD , NJ , NY , PA , and RI but we also proudly acknowledge the skills and experience of our expert team behind all resources. With insights on topics ranging from heating oil facts to common air conditioning questions , you can rely on Petro Home Services for facts and information to help you understand more about your heating, cooling and home comfort needs. This article and all articles on the Petro Home Services website have been approved by our team of home service experts.

Petro Articles By Category
- Heating Oil
- Heating Equipment
- Home Services
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
© 2023 Petro. All rights reserved
New message
This is modal body.
Your cart is empty.

Plumbing Terms and their Definitions
A list of plumbing terms and definitions

Safeplumbing.org is the website of Plumbing Manufacturers International. Learn More
Plumbing Industry
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is a not-for-profit, non-government organization that oversees the creation and use of voluntary health and safety standards for products and businesses across nearly all sectors of the U.S. economy.
An ancient alloy, composed primarily of copper and zinc, used in the manufacture of faucets and other plumbing fittings. Small amounts of other alloying materials are also added for various types of brass to address the requirements of specific applications. Brass is also the term for a faucet finish, also known as polished brass.
One of the basic elements (Cu), copper is used for plumbing piping, and is one of the alloys used to make brass, a key material in the manufacture of faucets and fittings.
A device designed to control and guide the flow of water. Examples include faucets, shower heads, shutoff valves, shower valves, and drinking fountain spouts. Some people call these "fixtures," but that term means something different to the plumbing industry. The differing usage of "fitting vs. fixtures" can lead to unintended consequences, such as when legislation calls for changes in fixtures, although the true intent involves changes in fittings. (See "Fixtures.")
A device for receiving water and/or waste matter that directs these substances into a sanitary drainage system. Examples include toilets, sinks, bathtubs, shower receptors, and water closet bowls. The term is used erroneously in common vernacular to describe fittings. (See "Fittings.")
Gallons per minute (GPM or gpm)
A measure of the rate at which water flows through a fixture or fitting at a certain pressure. It is measured by the number of gallons flowing from the device in one minute at a given water supply pressure.
Gallons per flush (GPF or gpf)
A measure of the total volume of water required to flush a water closet or urinal, measured in gallons.
While sometimes used by the general public to mean a bathroom or washroom, the plumbing industry uses lavatory to mean a bathroom washbowl or basin permanently installed with running water. The plumbing industry uses the term "sink" in reference to kitchen sinks.
Performance-based product standards
These standards define a desired outcome from products, related to what they do, rather than how they are made and what they are made of. These standards typically prescribe a means for determining whether the product delivers to the standard. For example, a performance-based product standard for fittings would specify the maximum amount of alloy materials, such as lead, that may be leached into the drinking water.
Porcelain enamel
A coating used on metal fixtures, such as cast iron sinks and bathtubs. Ceramic material is fired at high temperature to form a vitreous porcelain film that is fused to the base metal of the fixture or fused to a ground coat. Porcelain enamel gives metal plumbing fixtures their colors and desirable glossy surfaces.
Plumbing Manufacturers International (PMI)
A not-for-profit trade association of plumbing products manufacturers. PMI member companies produce most of the nation's plumbing products. Read more.
Product standards
Established by research and consensus, product standards define what products are made of, as well as how they perform. For plumbing products, product standards govern the characteristics, materials, performance and operability, as well as how products need to interact with other plumbing-system elements. For example, a product standard for fittings would define the alloys and the amounts that can be used in their manufacture.
Prescriptive product standards
These standards differ from performance-based product standards in that they attempt to achieve a desired outcome by specifying the characteristics, materials, performance and operability of products. For example, a prescriptive product standard for fittings would specify the maximum amount of alloy material, such as lead, that can come in direct contact with the drinking water.
PVD finishes
PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. This process, which occurs in a vacuum chamber, electrostatically applies extremely thin, but extremely dense coatings of exotic metal alloys onto fittings. The resulting finish is state-of-the-art in durability, scratch-resistance and lasting beauty for faucets. A wide range of finishes with PVD is possible, including chrome, nickel, brass and bronze.
A fitting with a movable part that opens or closes one or more passages and thereby allows a liquid flow to be started, stopped, and regulated. In plumbing, valves are used in faucets and showers, and can be called mixing valves because they control the mix of hot and cold water to achieve desired water temperatures.
Vitreous china
A type of pottery most commonly used for plumbing fixtures, such as toilets. It is a compound of ceramic materials fired at a high temperature to form a nonporous body. Exposed surfaces are coated with a ceramic glaze that fuses to the china when fired and gives vitreous china plumbing fixtures their colors and glossy appearance.
Clean Water
In the case of plumbing systems, leaching refers to the process of dissolving a soluble component out of a constituent material at a wetted surface. Materials commonly leached into drinking water from water distribution systems include copper, lead, and nickel.
One of the basic elements (Pb), lead is a soft metal that has been used in plumbing systems for thousands of years. The word "plumbing" derives from the Latin word for lead, plumbum. Lead has a unique ability to resist pinhole leaks, while being soft enough to form into shapes that deliver water most efficiently. Its softness and malleability were for a long time highly desirable properties for manufacturing everything from pipe to paint. Lead is a neurotoxin that can accumulate in the body in soft tissues, as well as bone.
Lead and Copper Rule (LCR)
A United States Environmental Protection Agency regulation dating back to 1991, LCR requires water systems to monitor drinking water that comes through faucets in homes and buildings. If lead concentrations exceed 15 parts per billion (ppb) or copper concentrations exceed 1.3 parts per million (ppm) in more than 10% of homes and businesses sampled in a regional plumbing system, the system must take actions to control corrosion and leaching. If the action level for lead is exceeded, the system must also inform the public about steps they should take to protect their health, including the possible replacement of plumbing system piping.
Under section 1417(d) of the Safe Drinking Water Act, "lead free" is defined as being no more than 0.2 percent of materials used in solders, and no more than 8 percent of materials used to manufacture pipe, fittings, and well pumps.
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWRs, or primary standards)
Legally enforceable federal standards that apply to public water systems. Primary standards limit the levels of contaminants in drinking water. A 1996 amendment to the Safe Water Drinking Act (SDWA) requires that the United States Environmental Protection Agency establish a list of contaminants every five years that are known or anticipated to occur in public water systems and may require future regulations under the SDWA.
Founded in 1944, NSF International is a not-for-profit, non-governmental organization that develops standards and product certifications in the area of public health and safety.
NSF/ANSI Standard 60
A standard related to chemicals used to treat drinking water. Developed by NSF and conforming to the ANSI voluntary standard, the standard was accepted by the NSF board in 1988 to evaluate products, such as softeners and oxidizers, to assure that usage amounts safeguard the public health and safety.
NSF/ANSI Standard 61
A standard related to products that come in contact with drinking water. Developed by NSF and conforming to the ANSI voluntary standard, the standard was accepted by the NSF board in 1988 to confirm that such products will not contribute excessive levels of contaminants into drinking water. Most U.S. states and many Canadian provinces require products used in municipal water distribution systems and building plumbing systems to comply with Standard 61.
Potable water
Water that is satisfactory for drinking, culinary and domestic purposes.
Proposition 65
Also known colloquially as Prop 65, California's Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986 requires companies to post notice of chemicals in products that can be released into the environment and have been determined by the state to be a cause of cancer. In early 2008, the list included 775 chemicals. Prop 65 impacts residents in other states when they receive such notices in purchased products, such as bathroom faucets. Companies will often post the notification on all products, rather than incur extra costs to isolate products sold only in California.
Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA)
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is a federal law originally passed by Congress in 1974 to protect public health by regulating the nation's public drinking water supply. Amendments were passed in 1986 and in 1996. The SDWA requires many actions to protect drinking water and its sources: rivers, lakes, reservoirs, springs, and ground water wells. SDWA authorizes the United States Environmental Protection Agency to set national health-based standards for drinking water to protect against both naturally occurring and man-made contaminants. Enforcement is accomplished through the National Primary Drinking Water Regulations.
Water Efficiency
A high-efficiency toilet that gives users the choice of flushing with the maximum amount of water allowed by law (1.6 gpf in the United States) or less water. The average amount of water used by the toilet cannot be more than 20 percent less than the maximum allowable, qualifying it to be considered high-efficiency and eligible for WaterSense labeling.
Energy Policy Act of 1992
Among the provisions of this federal legislation, the Energy Policy Act of 1992 (EPAct ’92) required that all residential toilets had to flush using no more than 1.6 gallons per flush.
The moveable part of a toilet flush valve that releases the water from the tank into the bowl when the toilet is flushed and seals the valve shut when the toilet is not being flushed. The most familiar version is a red replacement rubber ring that can deteriorate over time, leading to leaks and water waste. Newer flapper technologies are impervious to deterioration, increasing water efficiency and reducing operating costs.
Flush valve
Located at the bottom of a toilet tank, the flush valve discharges the water from the tank into the bowl when the toilet is flushed.
Gravity-fed toilets
The most common type of toilet in the United States, gravity-fed toilets rely on the force of gravity to flush the toilet effectively. The natural force of water dropping down from the tank scours the bowl clean and forces water and waste quickly into the trapway.
High efficiency toilet (HET)
A toilet with an average water consumption of 1.28 gallons per flush or 4.8 liters per flush, when tested in accordance with a standard or product specification, such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency's WaterSense program. HETs use 20 percent less water than mandated by the Energy Policy Act of 1992, which lowers utility bills and reduces the strain on septic systems. HETs are eligible for special rebates in many drought-prone areas. They are available as single flush gravity toilets, dual-flush gravity toilets or pressure-assisted toilets.
High efficiency urinal (HEU)
A urinal that uses a half gallon or less of water, half the amount allowed under the by the Energy Policy Act of 1992, Contributes to lower utility bills, while reducing the burden on septic systems. HEUs are sometimes thought to be waterless, which isn't true. Waterless urinals are one type of HEU, but there are also urinals that use water and still meet higher efficiency standards.
In the plumbing industry, low-flow fixtures and fittings refer to plumbing products that meet the water efficiency standard of the Energy Policy Act of 1992. The term is used interchangeably with the term "low consumption."
MaP Testing
A voluntary test protocol for toilets that measures the ability to remove solid waste, also referred to as "bulk." Cooperatively developed in 2003 by water utilities and water-efficiency specialists in the United States and Canada, it uses soybean paste (miso) as test media, in an effort to replicate "real world" waste. The test is conducted by successively increasing the amount of test media that is flushed until the toilet is no longer able to reliably or completely remove the media from the bowl. Results are reported as a MaP score , which is related to the number of grams of a test media that a toilet can adequately flush.
Metered toilets, or metered flush
A toilet with a mechanism that delivers a precise, non-variable amount of water with each flush.
Pressure-assisted toilets
A toilet that uses a compressed-air device to enhance the force of gravity used to clean the bowl when the toilet is flushed.
The channel in a toilet that connects the bowl to the waste outlet. The trapway is measured in terms of the largest diameter ball that can pass through it, called a ball-pass or ball-passage .
Ultra-low-flow
In the plumbing industry, ultra-low flow fixtures and fittings refer to plumbing products that exceed the water efficiency standard of the Energy Policy Act of 1992. The term is used interchangeably with the term "high efficiency"
WaterSense is a partnership program sponsored by United States Environmental Protection Agency, which works to promote water efficiency and enhance the market for water-efficient products, programs, and practices. Similar to the EnergyStar program that helps consumers choose energy-efficient appliances, WaterSense helps consumers to choose water-efficient products by specifying the maximum flow rates and minimum performance levels. Products certified as meeting current WaterSense product specifications are eligible to carry the WaterSense label.
Health & Safety
Accessible design.
An approach to designing buildings, homes and products that renders them easier to access and use by people with physical, sensory, or cognitive disabilities.
ADA-compliant device
A device which is fully compliant, when properly installed, with the current requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines (ADAAG), as legislated by the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
A federal law, passed in 1990, which prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities. The term "disability" means a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more of the major life activities of such individuals. Among the provisions in the law are requirements that impact plumbing products in the design of accessible bathrooms and facilities.
Automatic compensating valve
A valve that is supplied with hot and cold water, and provides a means of automatically maintaining the water temperature selected for an outlet. Automatic compensating valves are used to reduce the risk of scalding and thermal shock.
A flowing back or reversal of the normal direction of wastewater from homes and buildings, leading to the possible contamination of potable water systems.
Backflow prevention device
Any mechanical device designed to automatically prevent backflow.
Barrier-free
Products and buildings are considered "barrier-free" if they permit access by all users, including those in wheelchairs. In plumbing products, the term can refer to showers that do not have a lip preventing wheelchair access, as well as sinks and water fountains that are useable at different heights.
Pressure-balancing valve
Also known as a pressure-compensating valve, this device is designed to reduce the risk of thermal shock and scalding while showering. Required by code in most areas of the United States, a pressure-balance valve senses the hot and cold water pressures coming in from the supply line and compensates for variations to maintain the water temperature. Such variations can occur when a toilet is flushed or a washing machine started while someone is showering.
Proximity valves
An electronic valve for plumbing fixtures and fittings that enables them to be operated without being touched. Similar to auto-open doors and light sensors that are activated by movement, proximity valves deliver the benefits of being both barrier-free and sanitary to use. Proximity valves can operate toilets, urinals and faucets.
Thermostatic valves
Also known as a thermostatic compensating valve, this technology senses the temperature of the water to adjust the mix of hot and cold water. This maintains a safe, comfortable water temperature whether the fluctuation is due to a change in the pressure or the temperature of the incoming hot and cold water supplies.
Thermal shock
A large and rapid change in the water temperature. Thermal shock is a particular concern for showers where rapid changes in the temperature of the water can lead to scalding, as well as increased risk of injuries due to slips and falls. Technologies to prevent thermal shock include pressure-balance and thermostatic shower valves.
Universal design
Universal design should be accessibility that is not apparent and, at the same time, can accommodate a wide variety of people of all ages and statures. It allows access to a richer life by eliminating disability by design. This thoughtful approach to space and barriers allows the maximum number of people to use the widest variety of products in their homes for the greatest length of time.
Become a PMI Member
Work with fellow plumbing manufacturers and allied members to create profitable outcomes for your companies.
Look for the WaterSense® Label
WaterSense toilets, bathroom faucets, showerheads and other products have gained high consumer satisfaction while lowering water and energy expenses.
- (801) 661-8155
- Serving Salt Lake, Utah, & Davis Counties, and Surrounding Areas

Plumbing Terminology 101: A Guide To The Industry’s Lingo
The beehive plumbing team is here to help you better understand our industry’s professional language a little better.

There’s no doubt about it that the average homeowner in Northern Utah can have some difficulty in understanding all of the plumbing industry’s jargon, which is why we’ve developed this article that’s directly oriented plumbing terminology.
We understand how you may get confused when listening to some plumbers talk, which is why we’re more than happy to go over some of the basics when it comes to our industry’s lingo.
By going over the below terms, you can be more confident while letting us know the details of your next plumbing repairs !
Common Words Used Throughout The Plumbing Industry
The following words are what home and business owners will commonly hear from plumbing specialists:
- Blackwater: This plumbing term is another word for wastewater, and it particularly relates to sewage water that goes through our toilets. It can also mean wastewater that is stuck within your toilet during a clog or other types of toilet repairs .
- Greywater: This type of water refers to different types of wastewater that can be found throughout a property that isn’t connected to your toilets. This can include wastewater from your sinks, exterior hoses, water heater or other plumbing fixtures.
- Hard water: Northern Utah just so happens to have a really serious issue with hard water, because hard water flows through just about all of our homes. When a plumber refers to “hard water”, they’re describing an overabundance of mineral content within your property’s water supply. This type of mineral count can lead to serious issues like clogged fixtures and corrosion.
- Water softener: The Beehive Plumbing team specializes in water softeners , and these are plumbing devices that remove excess minerals from your water supply and provide better bathing experiences. Water softeners are also known to help people avoid damages to their bathroom and kitchen fixtures/appliances as well.
- Branch drain: This is the drain that’s connected to your shower floors, sinks, toilets, bathtubs, dishwashers, washing machines and a lot more. A branch pipe will flow directly towards your main drain pipe, which is connected to your municipal sewage line.
- Drain field: Your property’s drain field is a network of pipes that are underneath your yard and connected to your septic tank. The drain field is what helps clear contaminants out of the water within your septic tank.
- Fittings: A fitting is that small plumbing device that will effectively connect two different pipes together, and many plumbing issues will be rooted in loose or malfunctioning fittings.
- GPF: This stands for gallons per flush, and today’s modern toilets must have a 1.6 or lower GPF. Our team will help you better understand the GPF at your property and ensure that it’s up to current standards.
- Potable water: This is one of the oldest plumbing terms in the industry, and it refers to water that’s safe to drink and generally consume. We of course don’t keep our safe drinking water in pots anymore, but this term has remained popular in the plumbing, medical and legal fields.
- Trap seal: Every drain within your property that’s connected to your sewer line will entail a curved pipe that’s known as a trap seal, and this seal functions to prevent odors from emanating throughout your home or business. This device does wonders in terms of preventing any unwanted gases.
- Tee: This is a unique type of fitting that is T-shaped and connects three pipes together. Many plumbers will use a Tee fitting to develop drain line branches.
- Blow bag: Blow bags are common devices throughout the plumbing industry that will bust through clogged drains through the use of forced water. This is a part of the overall drain cleaning process called hydro jetting , and this is something that the Beehive team specializes within.
- Dope: This is a sealant that many plumbers will utilize to develop pressure-tight, leak-proof connections. Dope comes in a very thick, pasty consistency and it does a wonderful job as a more high-end type of plumber’s tape.
- Snake: Plumbing snakes are vital for countless drain cleaning jobs, and the actual tool is a metal cord that’s very flexible and wound into a tight spiral. Plumbers will utilize snakes to break up really tough clogs that are deep within a property’s pipes.
Reach Out To The Plumbing Experts At Beehive Plumbing To Schedule Your Next Appointment!
Beehive Plumbing has supported the Northern Utah community for over 20 years, and we’re proud to have created the very best team of plumbing experts in the entire region.
Our plumbing specialists will support you when it comes to any and all of your plumbing needs, so contact us online or call us at 801-661-8155 to speak with our team today and schedule your next appointment with us!
Call 24/7 Now:
We’re the solution to any and all plumbing or drain problems, 24/7 in utah, we're the solution to any and all plumbing or drain problems, 24/7 in utah, a few of our happy customers.

Why Beehive Plumbing

- [email protected]
- Privacy Policy
24/7 Services
- 24/7 Emergency Plumbing
- Sewer Repair
- Drain Cleaning
- Water Heaters
- Commercial Plumbing
- We're Hiring!
- Financing Available
Other Locations
- Bluffdale, Utah
- Bountiful, Utah
- Centerville, Utah
- Draper, Utah
- Davis County, Utah
- Kaysville, Utah
- Midvale, Utah
- Murray, Utah
- Park City, Utah
- Salt Lake City,Utah
- Sandy, Utah
- South Jordan, Utah
- Sugar House, Utah
- Utah County
- West Jordan, Utah
- West Valley City, Utah
Connect With Beehive Plumbing
Website designed and built by big fish local.
Copyright © 2022 Beehive Plumbing. All rights reserved.

- Plumber Login
- SEARCH BY NEED
- BROWSE BY ZIPCODE
- TESTIMONIALS
- Advertising For Plumbers
- Plumbering Events
- General Plumbing Articles
- Sewer Articles
- Faucet Articles
- Water Heater Articles
- HVAC Articles
- Leak Articles
- Kitchen Articles
- Plumbing Terms
- Remodeling Articles
- Drain Articles
- Winter Plumbing Article
- Locksmiths By ZIp
- Movers By Zip
- Electricians By Zip
Plumbing Glossary: A Comprehensive List of Plumbing Terms

Welcome to our plumbing glossary, a comprehensive collection of plumbing terms and definitions to help you better understand the world of plumbing. Whether you're a homeowner, DIY enthusiast, or simply looking to expand your plumbing knowledge, this glossary will serve as a handy reference for understanding common plumbing terminology.
Aerator: A device attached to the end of a faucet that mixes air with water, reducing splashing and conserving water.
Backflow: The reverse flow of water or other substances into the potable water supply system, often caused by a drop in pressure or back-siphonage.
Bleed Valve: A valve used to release excess air or pressure from a plumbing system, typically found on radiators or water heaters.
Check Valve: A valve that only allows fluid to flow in one direction, preventing backflow or reverse flow.
DWV: Abbreviation for Drain-Waste-Vent, referring to a plumbing system that carries wastewater from fixtures, drains, and vents it to the outside.
Flapper: A rubber or plastic component in a toilet tank that lifts when the flush lever is pressed, allowing water to flow from the tank into the bowl for flushing.
GPM: Abbreviation for Gallons Per Minute, a unit of measurement used to indicate the flow rate of water through a plumbing fixture or pipe.
Hose Bib: An outdoor faucet with a threaded spout for attaching hoses, commonly found on the exterior of homes.
Inlet Valve: A valve that controls the flow of water into a plumbing fixture, such as a toilet or sink.
J-Bend: A U-shaped pipe or fitting under a sink that traps water to prevent sewer gases from entering the living space.
Kitchen Sink Trap: A U-shaped pipe under the kitchen sink that traps debris and prevents odors from the sewer system.
Lateral Pipe: A horizontal pipe that connects a plumbing fixture to the main drain or sewer line.
Manifold: A plumbing fitting that distributes water or gas to multiple branches or outlets.
Nipple: A short piece of pipe with male threads on both ends used for connecting fittings or fixtures.
Overflow: An opening or pipe near the top of a fixture, such as a sink or bathtub, that allows excess water to drain away if the main drain is clogged or the fixture is overfilled.
P-Trap: A U-shaped pipe under a sink, shower, or bathtub that traps water to prevent sewer gases from entering the living space.
Rough-In: The initial installation of the plumbing system, including pipes, drains, and fixtures, before the final finishes are applied.
Sump Pump: A pump used to remove water from basements, crawl spaces, or low-lying areas to prevent flooding.
Tee: A plumbing fitting shaped like the letter "T" used to connect pipes at a 90-degree angle.
Union: A type of fitting that joins two pipes together and allows for their easy disconnection or repair.
Vent Pipe: A pipe that allows air to enter or exit a plumbing system, preventing siphoning and maintaining proper pressure.
Water Hammer: The loud banging or knocking noise in plumbing pipes caused by the sudden stoppage or change in flow of water.
Yoke Vent: A plumbing vent pipe that connects two or more vent stacks to allow for proper air circulation in the drainage system.
This glossary provides a glimpse into the wide range of plumbing terms and concepts you may encounter. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can better communicate with plumbers, understand plumbing diagrams, and tackle basic plumbing tasks with confidence. If you come across any unfamiliar terms, feel free to refer back to this glossary for clarification.
Leave Comment Below
Member login.
- Not a Registered User? Create Free User Account
- Are You a Local Business? List Your Company Now
Related Posts

- Our mission is to connect customers with trustworthy and skilled plumbers in their local area. We understand the frustrations that plumbing problems can bring, and our aim is to simplify and streamline the process of finding a reliable plumber.
- How It Works
- List Your Company
- Browse Categories
- Browse Locations
- Browse Zip Codes
- Plumbers - Get Listed Today
- Plumbers BY Zip
- All Rights Reserved
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy

Expert Advice On Improving Your Home
We recommend the best products through an independent review process, and advertisers do not influence our picks. We may receive compensation if you visit partners we recommend. Read our advertiser disclosure for more info.
Plumbing Terminology 101

Henry Parker
Henry Parker is a home improvement enthusiast who loves to share his passion and expertise with others. He writes on a variety of topics, such as painting, flooring, windows, and lawn care, to help homeowners make informed decisions and achieve their desired results. Henry strives to write high quality guides and reviews that are easy to understand and practical to follow. Whether you are looking for the best electric riding lawn mower, the easiest way to remove paint from flooring, or the signs of a bad tile job, Henry has you covered with his insightful and honest articles. Henry lives in Florida with his wife and two kids, and enjoys spending his free time on DIY projects around the house. You can find some of his work on Today’s Homeowner, where he is a regular contributor.
March 22, 2024
If you’ve ever consulted with a plumber or taken a trip to the hardware store for a bit of DIY plumbing you’ve probably encountered numerous confusing terms.
This problem becomes even more apparent when you consider that homes can have different types of septic systems, each with their own unique features. The following glossary contains both common an uncommon plumbing terms, alphabetized and broken down into categories for easier searching.

Common Plumbing Terms
- Bleed: to release excess air in a pipe by opening a valve at the end.
- Brass: generic slang term for any faucet or fixture.
- Branch Drain: fixture drain which leads to the main drain pipeline.
- Effluent: liquid waste in a septic system.
- Fitting: term used to describe any part that connects two sections of pipe.
- Flow Rate: how much water flows through a plumbing system; measured in either gallons per minute (GPM) or per hour (GPH).
- Gallons per Flush (GPF): measurement of water needed to flush; used to regulate toilets and flush valves; 1.6 GPF is the current legal maximum permitted for new toilets.
- Gray Water: water waste from non-toilet fixtures.
- KiloPascal (kPa): metric unit of pressure equaling 1/ 100th of an atmosphere.
- Maximum Containment Level (MCL): maximum amount of a contaminant permitted in a water supply by law.
- Non-Ferrous: contains no iron.
- Potable: water which is safe to consume.
- Pressure Head : unit of measure for pressure in a plumbing system describing the vertical force caused by water at a depth of one foot.
- Riser: vertical supply pipes which bring water from the branch to a fixture or to a higher floor.
- Sediment: debris that settles at the bottom of water tanks.
- Soil Pipe: pipe carrying waste from a toilet.
- Trap Seal: the water in a trap which serves as a liquid seal.
- Trap Weir: the highest point for water before it drains in both P-traps and S-traps.
- Water Hammer: a loud banging sound caused when the water supply is suddenly cut off from a fixture, causing hydraulic shock.
Plumbing Components and Fixtures
- Aerator: insert screwed onto a faucet nozzle that reduces splashing by mixing air into the flowing water.
- Ball Check Valve: valve which employs a ball which can seal against a seat to stop the flow in one direction.
- Closet Bend: curved fitting located under the toilet connecting it to the drain.
- Closet Flange: ring used to anchor a toilet and connects to the closet bend; sometimes called a floor flange.
- Flow Control Valve: device which can reduce costs and improve efficiency by reducing the water flow to a plumbing fixture.
- Gasket: flat rubber or fiber ring used to create a watertight seal between metal fixtures.
- Interceptor: device which separates oil and grease from drain systems.
- Main: the main pipeline in a supply or drain system to which all branches connect.
- Manifold: fitting that connects multiple branches to the main, acting as a distribution point.
- O-Ring: round rubber washer used to make valve stems watertight.
- Scald Guard: valve that maintains the balance between hot and cold water pressure in your shower by shifting back and forth behind the shower handle in response to sudden pressure drops.
- Shutoff Valve: valve under toilet or sink to stop water supply for repairs.
- Tee: T-shaped fitting used where three pipes intersect.
- Trap: a curved portion of plumbing designed to hold enough water to block, or seal, the section of pipe from gasses, odors, and pests.
- Valve Seat: the stationary section of a valve.
- Vent: sloped or vertical section of drainpipe designed to allow sewer gasses to escape and be replaced by outdoor air so pressure is not lost during the venting.
- Water Hammer Arrestor: device which prevents the banging sound known as water hammer by absorbing the hydraulic shock caused from suddenly cutting the water supply to a fixture.
- Wye Fitting: drain fitting which connects two sections of pipe at a 45 degree angle.
Plumbing Tools and Materials
- ABS: short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, this black plastic pipe is rigid and commonly found in drains, vents, and waste lines.
- Auger: flexible rod with a curved end used to pull clogs from a toilet trap.
- Blowbag : tool with a nozzle and rubber bladder attached to a hose and inserted into a clogged drain where it swells to fill the pipe and releases water in bursts to force a path through the obstruction.
- CPVC : chlorinated polyvinyl-chloride; black PVC pipe treated to withstand high temperatures; often used in water supply systems.
- Dope: plumbing lubricant used on pipe threads.
- Polybutylene (PB): bendable tubing used in some supply lines for bathroom fixtures.
- Polyethylene (PE): flexible pipes often used in supply lines.
- PEX: crossed-linked polyethylene; stronger than normal PE.
- Plumber’s Putty: putty with dough-like consistency used to seal the joints between fixture settings and metal pieces.
- Plunger: AKA “plumber’s helper”; six inch rubber suction cup with a wooden handle commonly used to unclog drains and toilets.
- PVC: rigid white pipe made of polyvinyl-chloride plastic; often used for drains and waste or vent pipes.
- Snake: thin, flexible cord of spiral-wound metal that fits down a drain and is rotated to dislodge clogs.
- Teflon Tape: fluorocarbon polymer tape with non-stick properties that is wrapped around the threads of a pipe to create a tighter joint seal.
Septic System-Specific Components
- Absorption Field: seeping field designed to filter and disperse the liquid waste from a septic tank; also referred to as a leach field.
- Leach Line: pipes which carry the liquid waste from the septic tank to an absorption/leach field.
- Septic Tank: large underground tank used mainly in rural settings where sewers are not available; temporarily stores waste as bacteria and gravity separates it into solids, liquids, and sludge before the liquids drain into an absorption field.

How to Safely Thaw and Prevent Frozen Pipes
April 12, 2024

4 Signs That Your Home Has Plumbing Leaks
April 5, 2024

Where to Position a Drain Vent Pipe
April 24, 2024

The Homeowner’s Guide to Repiping
April 10, 2024

5 Easy Ways To Repair PVC Pipe
April 6, 2024

How To Fix a Washing Machine Drain Overflow (In 6 Steps)

What Is the Best Sealant for Leaking Pipes?
April 16, 2024
ASK DANNY: Are Plastic Water Pipes Safe?
April 11, 2024

How to Find a Leak in Your Home’s Plumbing
April 9, 2024
Advertisement
Plumbing Basics
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
Plumbing follows the basic laws of nature — gravity , pressure and water seeking its own level. Knowing this, you can understand its "mysteries" and make dozens of fixes to your home's plumbing system. You can save yourself time , trouble and money !
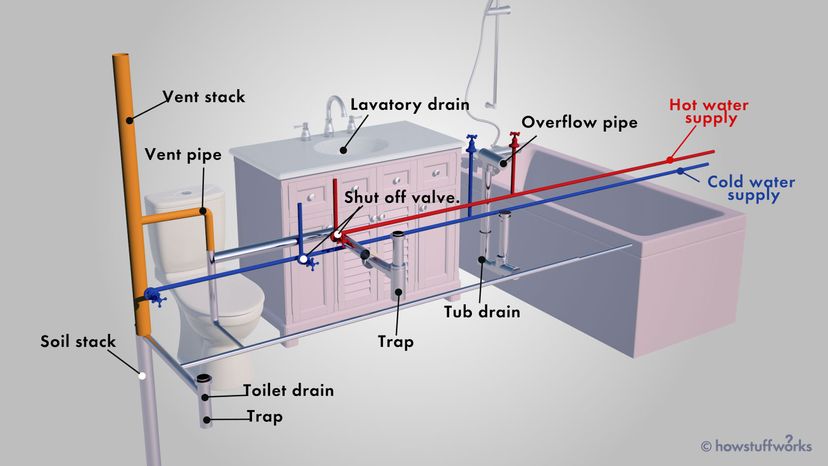
The plumbing system in your home is composed of two separate subsystems. One subsystem brings freshwater in, and the other takes wastewater out. The water that comes into your home is under pressure. It enters your home under enough pressure to allow it to travel upstairs, around corners or wherever else it's needed. As water comes into your home, it passes through a meter that registers the amount you use. The main water shut-off, or stop, valve is typically located close to the meter. In a plumbing emergency, it's vital that you quickly close the main shutoff valve . Otherwise, when a pipe bursts, it can flood your house in no time. If the emergency, like a leak, is confined to a sink, shower, or toilet , however, you may not want to turn off your entire water supply. Therefore, most fixtures should have individual stop valves.
Water from the main supply is immediately ready for your cold water needs. The hot water supply , however, requires another step. One pipe carries water from the cold water system to your water heater . From the heater, a hot water line carries the heated water to all the fixtures, out-lets, and appliances that require hot water. A thermostat on the heater maintains the temperature you select by turning the device's heating elements on and off as required. The normal temperature setting for a home water heater is between 140 degrees F and 160 degrees F (60 and 71 Celsius) but 120 degrees F (49 C) is usually adequate and is also more economical . Some automatic dishwashers require higher temperature water, though many of these have a water heater within them that boosts the temperature another 20 degrees F.
Drainage Systems
Whether your home is on a sewer or septic system , the systems within your home are essentially the same. Drainage systems do not depend on pressure, as supply systems do. Instead, waste matter leaves your house because the drainage pipes all pitch, or angle, downward towards the sewer . Gravity pulls the waste along. The sewer line continues this downward flow to a sewage treatment facility or a septic tank.
While the system sounds simple, there's more to it, including vents, traps and clean outs. The vents sticking up from the roof of your house allow air to enter the drainpipes. If there were no air supply coming from the vents , wastewater would not flow out properly and the water in the traps would need to be siphoned away.
Traps are vital components of the drainage system . You can see a trap under every sink. It is the curved or S-shape section of pipe under a drain. Water flows from the basin with enough force to go through the trap and out through the drainpipe, but enough water stays in the trap afterward to form a seal that prevents sewer gas from backing up into your home. Every fixture must have a trap. Toilets are self-trapped and don't require an additional trap at the drain. Older bathtubs frequently have drum traps, which not only form a seal against sewer gas but also collect hair and dirt in order to prevent clogged drains. However, drum traps aren't up to current code standards anymore . Some kitchen sinks have grease traps to collect grease that might otherwise cause clogging. Because grease and hair are generally the causes of drain clogs, traps often have clean-out plugs that give you easier access to remove or break up any blockage.
Since a drainage system involves all of these components, it is usually referred to as the DWV: the drain-waste-vent system . If water is to flow out freely and waste is to exit properly, all components of the DWV must be present and in good working order. Examine the pipes in the basement or crawl space under your house to help you understand the system better.
Supply and Drainage Subsystems
The supply and drainage subsystems are two distinct operations, with no overlapping between them. There are bridges between the two, however, and the bridges are what make the plumbing system worth having. In plumbing jargon, any bridge between the supply and drainage systems is a fixture.
Toilets, sinks, and tubs are fixtures . In addition, an outside faucet is a fixture and so is a washing machine. All devices that draw freshwater and discharge wastewater are fixtures, and all are designed to keep the supply and drainage systems strictly segregated.
Some fixtures have individual supply shutoff valves so you don't need to close the main shutoff to repair them. It's a good idea to make sure everyone in the family knows the location of the main shutoff valve in your house as well as how to use it. You may want to tag the main shutoff valve so anyone can easily find it.
Before you embark on any plumbing repairs, always turn off the water supply to the fixture or the main shutoff . In addition, check with your local plumbing code official before you add or change any pipe in your house. You will learn what is allowed and what is prohibited and whether or not a homeowner is allowed to do his or her own work. If you get the green light, you can save yourself a lot of money by doing your own repairs.
©Publications International, Ltd.
Plumbing Basics FAQ
What are the basics of plumbing, can a shower and toilet share a vent, what is the proper slope for plumbing, how do i find the water line in my house, how much does it cost to repair a pipe.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

PVCworkshop
Plumbing Glossary – Terms You Should Know
In this post, we’ll list some common plumbing terms and define what they mean. By studying these plumbing terms, you will be able to get a better understanding of what plumbers are talking about when they say certain things.
Plumbing Terms to Know
ABS – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a black plastic pipe used for drain, waste, and vent lines.
Air admittance valve – a device used to control the flow of air into plumbing systems. It eliminates the need for an additional vent pipe.
Air gap – the unobstructed vertical space between the outlet of a water supply fixture and the flood level rim of a receptor.
Anode rod – a sacrificial metal rod that is installed in a water heater to help prevent corrosion of the tank.
Aqueduct – a conduit used to convey water.

Baffle – a device installed in a grease interceptor or oil/water separator to disrupt the flow of incoming wastewater and promote the separation of FOG from sewage.
Backflow – any undesirable reversal of flow in a piping system.
Backflow preventer – a device that is used to prevent water or gas from flowing in the wrong direction and mixing with another substance.
Back siphonage – a problem that occurs when water or gas is siphoned through a plumbing system and ends up flowing backward. It can be caused by a combination of factors, including the use of too much water pressure or an open drain.
Backwater valve – a backwater valve is a device that is installed in the sewer line to prevent sewage and wastewater from backing up into the home.
Ball check valve – a type of valve that is used in plumbing systems to prevent the flow of gas or liquid back into a pipe. It uses a ball or other type of round object to seal the line.
Baseboard heater – a type of convection heater consisting of copper or aluminum tubing mounted on the wall near the floor, with fins attached to increase heat transfer.
Bidet – a plumbing fixture used for hygiene purposes, similar to a toilet.

Boiler – a closed vessel in which water is heated by combustion or other means and circulated, either as hot water or as steam, for heating or power.
Branch circuit – the wiring between the final overcurrent device protecting the circuit and the outlet(s).
British Thermal Unit (BTU) – the British thermal unit is a measurement of heat energy. It is often used to measure the efficiency of water heaters and other appliances.
Building drain – that part of the lowest piping of a drainage system that receives the discharge from soil, waste, and other drains inside the walls of the building and conveys it to the building sewer, beginning six inches (152 mm) outside the inner face of the wall.
Building sewer – the extension from the building drain to the public sewer or other points of disposal.
Cast iron pipe – a type of pipe that is made out of a durable material known as cast iron. It is used to carry drinking water and other liquid or gas supply lines.
Catch basin – a dry well that collects stormwater runoff and prevents flooding.
Check valve – a check valve is a device that allows fluid to flow in one direction only. It is often used in plumbing systems to prevent backflow.

CLF – Continuous Linear Feet (the total number of feet in a single unbroken run).
Closet bend – a part of a plumbing system that angles between two vertical sections. It is used to connect two types of pipes and protect them from being damaged by the bends.
Closet Flange – the closet flange is the part of the toilet that connects the bowl to the drain pipe. It also helps to seal the connection and keep sewer gases from escaping.
Concrete slab – a type of foundation consisting of a concrete slab poured directly on the ground.
Condensation – the change of water vapor to liquid water.

Conduit – a tube or duct used to protect and route electrical wiring.
Conway unit – a unit of measure for the discharge capacity of a drain, equal to 1 cubic foot per second (28.3 L/s).
CPVC – Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride, a type of plastic pipe used for hot and cold water lines.
Cross-connection – Any physical connection between a public water supply and a non-potable substance that could result in contamination of the public water supply.
DDCU – Drainage Double Check Valve Unit, a backflow preventer used to protect against back-siphonage and backpressure.
Dead end – the end of piping where no further flow can occur.
Demister – a device used to remove droplets of water from a gas stream.
Double-check valve – a type of backflow preventer that consists of two independently acting check valves.
Downspout – a vertical pipe used to convey rainwater from a gutter to the ground or storm sewer.

Drains – plumbing fixtures and appurtenances, including traps, for conveying wastes from building fixtures to the house sewer.
DWV – Drain-Waste-Vent, the piping system that removes sewage and wastewater from a home.
Effluent – sewage or other liquid waste that is discharged into the environment.
Elbow – a fitting used to change the direction of flow in piping, usually at an angle of 90° or 45°.
Escutcheon – a decorative plate installed around the point where a pipe enters a wall.
Excess air – air in a plumbing system that is not supposed to be there. It can cause problems with the flow of water, such as changes in temperature or pressure.
Faucet – a faucet is a plumbing fixture that controls the flow of water by turning a knob or lever. It is often used in kitchens and bathrooms to wash hands or dishes.
Faucet aerator – a faucet aerator is a small device that attaches to the end of a faucet. It helps to conserve water by mixing air with the water stream.
Fixture – a general term for any plumbing device that uses water, including lavatories, sinks, tubs and showers.
Flange – a flange is a ring-shaped device that connects pipes or other components to each other. It can also be used to connect various pipes together, such as the drain pipe and the vent pipe.
Flapper – the flapper is a solid rubber disk that can be found inside the toilet tank. It controls the level of water in the tank by either opening and closing or by lifting up or down, depending on its design.
Float ball – a round ball that is attached to a lever or rod and used in some types of plumbing fixtures, such as toilets. It is held in place by water and rises or falls as the water level changes.
Floor drain – a drain located on the floor of a room, used to remove water that has accumulated on the floor.
Flow control valve – a valve that is used to regulate the flow of water through a pipe or system. It can be adjusted by hand, but some types use multiple pressure settings.
Flush valve – a valve that is used to control the flow of water in some types of plumbing fixtures. It is usually found near the bowl of a toilet or the top of a urinal.
FOG – Fat, Oil and Grease, waste that can clog drains and cause sewage backups.
Gallons per flush – a term used to describe the amount of water that is used when a toilet or other type of plumbing device is flushed.
Gate valve – a gate valve is a type of valve that regulates the flow of water by opening and closing a gate, or flap, inside the pipe.
GPM – Gallons per Minute (the rate of flow of water).
Gravity-operated toilet – a type of toilet that relies on the natural downward flow of water. The flushing mechanism is entirely gravity-driven and does not use any mechanical or pressurized water.
Grease interceptor – a device used to trap FOG before it enters a sewer system.
Grit chamber – a tank used to separate grit from wastewater.
Grit – sand, gravel or other solid matter that can accumulate in a sewer system.
Header – a horizontal pipe used to connect multiple vertical pipes.
House drain – that part of the lowest piping of a drainage system that receives the discharge from soil, waste, and other drains inside the walls of the building and conveys it to the building sewer, beginning six inches (152 mm) outside the inner face of the wall.
House sewer – the extension from the house drain to the public sewer or another point of disposal.
Hydraulic shock – the sudden and dangerous release of energy that can be caused by excessive water pressure. It usually takes place in a burst pipe or other type of plumbing fixture.
I.D. – inside diameter that reflects the size of a pipe.
In-line heater- a type of water heater that is installed in the main water line to provide instantaneous hot water.
Knockout – an opening in the wall of a junction box or other enclosure, used to insert a conduit.
Lateral – a pipe that conveys wastewater from a building drain to a public sewer or another point of disposal.
Lead – a soft, malleable metal that is used for piping and solder.
Lip-type trap – a type of trap that uses a liquid seal to prevent sewage odors from entering the home.
Main – the principal supply pipe for water or gas in a building or structure.
Manhole – a vertical access shaft used to enter a sewer line for inspection or maintenance.

Marlex – a type of plastic used for sewer lines and other piping.
Meter pit – a chamber used to house a water meter.
Nipple – a short section of pipe with male threads on both ends, used to connect two threaded pipes.
No-hub coupling – a fitting used to connect two lengths of pipe that have different diameters or are made from different materials.
Nominal- the approximate size or inside diameters of a pipe that is used for identification.
O.D. – the outside diameter of a pipe reflecting the size of the pipe from its external end. It is usually slightly larger than the internal diameter.
Offset – a type of fitting used to connect two lengths of pipe that are not in alignment.
One-way trap – a type of trap that uses a liquid seal to prevent sewage odors from entering the home.
Pipe threads – special ridges that are used to join two pipes or other plumbing fittings together. They must be tightened enough to create a seal, but not so much that they cause stress fractures or leaks.
Plumbing codes – rules that are used to make sure that plumbing systems are installed according to safety standards.
Plumbing fittings – the pieces or joints that are used to connect one type of pipe to another, such as a thread or a union.
Potable water supply – water that is considered safe to drink and has been treated to remove any harmful contaminants. It is typically supplied by a public water system or other type of modern plumbing system.
Pressure regulator – a pressure regulator helps to control the water pressure in a home by adjusting the amount of water flowing through it.
P-trap – a type of trap that uses a liquid seal to prevent sewage odors from entering the home.
PVC – Polyvinyl chloride, a type of plastic used for sewer lines and other piping.
Rainwater leader – a pipe that conveys rainwater from a roof gutter to the ground or storm sewer.
Roof drain – a drain located at the low point of a sloped roof, used to remove water that has accumulated on the roof.
Saddle valve – a saddle valve is a type of valve that is installed on a water pipe to allow the user to easily control the flow of water.
Sanitary sewer – a system of pipes that conveys wastewater from building drains to a treatment plant or other point of disposal.
Sediment trap – a sediment trap is a device that traps the waste particles, sludge, and other sediments inside a plumbing system before it reaches the water heater or the faucets.
Septic tanks – a septic tank is a large underground container that holds sewage and wastewater. It is used in homes that are not connected to municipal sewer systems.
Sewage – wastewater that contains human waste.
Sewer – a system of pipes that conveys wastewater from building drains to a treatment plant or other point of disposal.
Sewer line – a pipe that conveys wastewater from a building drain to a public sewer or another point of disposal.
Shutoff valve – a shut-off valve is a device that stops the flow of water to a plumbing fixture or appliance. It is often used to prevent flooding in the event of a leak.
Siphon trap – a type of trap that uses a liquid seal to prevent sewage odors from entering the home.
Soil stack – a vertical pipe that conveys wastewater from toilets, sinks and other fixtures to the building sewer.
Stack – a vertical pipe that conveys wastewater from toilets, sinks and other fixtures to the building sewer.
Storm sewer – a system of pipes that conveys runoff from rain and melting snow to a natural waterway or treatment plant.
Sump – a pit used to collect water for pumping or discharge into a sewer system.
Sump pump – a device used to pump water from a sump to the sewer system or another point of disposal.
Tankless water heater – a type of water heater that heats water on demand, without the use of a storage tank.
Tee – a fitting used to connect three lengths of pipe, two of which are in alignment.
Trap – the trap is a section of pipe that curves back on itself to form a U-shape. It helps to prevent sewer odors from escaping into the home.
Vent – a pipe that conveys air into or out of a drain system, used to prevent odors and siphoning.
Vent stack – a pipe that is used to control the flow of air and gases through a plumbing system. It is usually attached to an opening on the roof or other high point of a building.
Vent systems – the piping or other components that control the flow of exhaust gases from a water heater, furnace, boiler, or other types of appliances.
Vertical stack – a vertical pipe that conveys wastewater from toilets, sinks and other fixtures to the building sewer.
Water hammer – water hammer occurs when the water flow is suddenly turned off, causing a buildup of pressure in the pipes. This can cause serious damage to plumbing fixtures and pipes if not properly addressed.
Water hammer arrestor – a device that is used to reduce the effects of water hammer, which causes pipes and fixtures to vibrate or make noise.
Water heater tank – a container that is used for holding hot water and heating it to a certain temperature. They are often made from cast iron or copper, but other materials can be used as well.
Water main – the primary water supply pipe that is located underground, typically in a street or even an alley or parking lot.
Watertight – describes a pipe or other type of container that has no leaks.
Water supply systems – water supply systems are a series of pipes that make it possible for water to be delivered from one point to another. They can include both the piping and the valves or pressure regulators that are used to control the flow of water through them.
Wye – a fitting used to connect three lengths of pipe, two of which are in alignment.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© 2023 PVCWorkshop

Member Login
- Plumbers Get Listed Today
- How It Works
- Plumbing Humor
- Plumbing Products
- Plumbing Blog
Plumbing Glossary

Plumbing Terms Every Homeowner Should Know
The plumbing system is the central nervous system in every home. Below, is a comprehensive plumbing glossary taht explains the common terms used by plumbers and plumbing professionals throughout the plumbing industry.
Knowing all the parts that keep your house running can be challenging. As a new homeowner, or seasoned veteran, it’s essential to know a few terms and the accompanying items to keep your house running smoothly. This plumbing glossary will outline 54 essential plumbing terms you need to know to keep your plumbing running smoothly, as well as make you articulate about any future issues that may arise.
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene , this black plastic pipe is rigid and commonly found in drains, vents, and waste lines.
Aerator
An aerator is an insert screwed onto a faucet nozzle that reduces splashing by mixing air into the flowing water.
Access Panel
An access panel is an opening in a wall or ceiling near a fixture. The access panel offers access to work on plumbing or electrical systems.
Air Admittance Valve
An air admittance valve is a mechanical one way valve used in place of traditional non mechanical (very reliable) vents. It is to allow air to enter waste piping and equalizing pressures. Vents are used to preserve the seal of trap in plumbing fixtures. Also known as auto trap vents.
An air gap is an air-filled space allowing contaminated water to discharge freely, preventing the contaminated water from ever siphoning back into the potable water supply.
An angle stop is a shutoff valve between the water supply and plumbing fixture. It is used to shut off water flow while you repair the connected item.
An anode rod is located inside the water heater. The anode rod protects the water tank from corrosion due to magnesium or aluminum.
An auger is a flexible rod with a curved end used to pull clogs from a toilet trap.
Automatic Compensating Valve
A valve that is supplied with hot and cold water, and provides a means of automatically maintaining the water temperature selected for an outlet. Automatic compensating valves are used to reduce the risk of scalding and thermal shock.
A flowing back or reversal of the normal direction of wastewater from homes and buildings, leading to the possible contamination of potable water systems.
Backflow Prevention Device
Any mechanical device designed to automatically prevent backflow.
A backwater valve prevents disposed sewage from reentering the home.
A ball check valve is a type of backflow preventer. The ball check valve is placed on a water line to direct water flow in one direction.
Ball Passage
The ball passage indicates the size of a ball that can pass through a toilet's trapway. It also refers to the size of the trapway of a toilet; the trap size is to be 1/8" larger than the ball that can pass through it.
The ballcock controls the flow of water in a gravity-operated toilet tank. When the toilet is flushed, the circular float will drop and open the ballcock. This results in water being distributed in the tank. As the water rises, the float rises to the level that shuts of the ballcock.
Barrier-Free
Products and buildings are considered "barrier-free" if they permit access by all users, including those in wheelchairs. In plumbing products, the term can refer to showers that do not have a lip preventing wheelchair access, as well as sinks and water fountains that are useable at different heights.
A basin is generally circular, vessel with slopping or curving sides for holding water for washing. Usually used to refer to a sink of some sort.
Best Plumbers
Best Plumbers is the leading plumbing directory that features and highlights the best local plumbers throughout the world. If you are in need of a really good plumber in your area, search https://BestPlumbers.com
A bib is often referred to as a bibcock or hose bibb. It is typically a faucet with nozzle bent downward. Also called: outside/outdoor faucet/spigot or garden faucet.
A bidet is pronounced as "B'Day", it is a plumbing fixture similar to a toilet bowl (but no solids are to be deposited in a bidet) used for washing genitals and posterior areas of the body. It is floor mounted, usually next to a toilet, and incorporates a washing basin, faucet and sprayer. Bidets are very popular in some countries such as France and have finally been "discovered" in the U.S.. A bidet is commonly equipped with a hot and cold mixing valve to provide warm water for washing.
A bisque refers to the finish on the unglazed areas of vitreous china fixtures.
Black Water
Black water is waste water from toilets.
A blowbag is a tool with a nozzle and rubber bladder attached to a hose and inserted into a clogged drain where it swells to fill the pipe and releases water in bursts to force a path through the obstruction.
A branch is any secondary part of the drain system; also, referred to as the lateral line.
Branch vent
A branch vent connects vents with a vent stack.
Bras is an ancient alloy, composed primarily of copper and zinc, used in the manufacture of faucets and other plumbing fittings. Small amounts of other alloying materials are also added for various types of brass to address the requirements of specific applications. Brass is also the term for a faucet finish, also known as polished brass.
BTU is an abbreviation for "British Thermal Unit"; a measurement of heat equal to the amount of heat necessary to raise one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit at sea level. (One BTU is equal to about 250 calories.)
Buchan Trap
A buchan trap is an obsolete way of venting a waste water drain. An in-line trap with a vent on the inlet side. Also known as a Bristol interceptor.
Cast iron was used for drainage, sewers, waste, and vent pipe and fittings. Very durable and heavy metal. Today, many top quality bath tubs are still made with cast iron. Pipes and fittings today are generally only used for commercial applications where fire ratings are involved.
A Centerset is a style of bathroom lavatory faucet having combined spout and handles. Handles are 4" from center of handle-to-handle. Also a single handle faucet installed on 4" center-to-center faucet holes.
The check valve is a type of backflow prevent. The check valve is installed on a pipe to allow water flow in one direction.
Circuit Vent
A circuit vent is where one common vent serves up to a maximum of eight fixtures connected to a horizontal branch drain. Circuit venting must be designed by a professional engineer. The vent must be installed between the two most upstream fixture drains and the vent cannot receive the discharge of any waste or soil.
Cleanout Plug
The cleanout plug is in a trap or drain pipe. The cleanout plug offers access to the drain line for clearing any blockage in the pipes.
Close-Coupled Toilet
A two-piece toilet. The toilet tank is separate from the toilet bowl. This is the most common type of toilet.
Synonym for a toilet, also referred to as a “water closet”.
A closet auger is a flexible rod that is used to access a toilet’s trap to remove any clogs.
Closet Bend
The closet bend connects the closet flange to the toilets drain.
The closet flange is a ring that anchors the closet bend to the floor. The closet flange also includes closed bolts that secure the toilet in place.
A commode is another term for toilet.
Console Lava
A console lava is a table-like fixture with an integral lavatory. The back is fixed to a wall and the front is supported by consoles (brackets) or legs.
Copper is one of the basic elements (Cu). Copper is used for plumbing piping, and is one of the alloys used to make brass, a key material in the manufacture of faucets and fittings.
A coupling is a fitting that joins two pieces of pipe (or other fittings) together.
CPVC stands for chlorinated polyvinyl-chloride. CPVC is black PVC pipe treated to withstand high temperatures; often used in water supply systems.
CW is the abbreviation for Cold Water.
CWP is the abbreviation for Cold Working Pressure.
CWT is the abbreviation for Copper Water Tube (refers to nominal pipe size).
Copper x copper, meaning the fitting is sized for copper pipe.
Cycle time refers to the amount of time it takes a toilet to complete it's flush cycle, from the instant it is flushed until the water supply shuts off.
A dam refers to the seal caused by water in a trapway.
The diaphragm is a flexible membrane that helps regulate water flow and build up within a valve.
The dip tube sends cold water to the bottom of the water heater tank.
A diverter is a valve which direct water to various outlets. They are used in showers, tub & shower combinations, bidets, Roman tub fillers and kitchen faucet sprayers.
The drip leg, also known as the “sediment trap”, is a pipe installed at the lower segment on a gas line. The capped off section collects condensation and debris.
Dope is plumbing lubricant used on pipe threads.
A high-efficiency toilet that gives users the choice of flushing with the maximum amount of water allowed by law (1.6 gpf in the United States) or less water. The average amount of water used by the toilet cannot be more than 20 percent less than the maximum allowable, qualifying it to be considered high-efficiency and eligible for WaterSense labeling.
DWV is the abbreviation for Drainage, Waste & Vent systems. Not for drinking water.
Dynamic Pressure
The pressure when the water is flowing.
Liquid waste, potentially hazardous, generally refers to liquid waste from septic tanks.
Elbow (aka ELL)
A fitting with two openings that changes the direction of the line. Also called an ell. It comes in a variety of angles, from 22 1/2° to 90°, though by far the most common is the 90°.
The shape of the front of a toilet bowl. Generally about 2" longer than the standard "round front" bowl.
An opaque vitreous composition applied by fusion to the surface of metal fixtures such as cast iron and pressed steel tubs, lavatories and sinks. Please do not confuse enameled steel with enameled cast iron. Cast iron with enameling is much more durable.
Energy Policy Act of 1992
Among the provisions of this federal legislation, the Energy Policy Act of 1992 (EPAct ’92) required that all residential toilets had to flush using no more than 1.6 gallons per flush.
(pronounced ih-skuhch-uhn) An ornamental or protective flange or shield beneath a faucet handle, This part covers the faucet stem and the hole in the fixture or wall. They are also found around shower arms, stop valves, and other piping that comes through the wall. Typically cosmetic, some escutcheons are gasketed to help with waterproofing, like escutcheons for body sprays.
The fall, also known as flow or pitch, refers to the slope needed to create proper drainage in pipes.
Abbreviation for female hose threads.
Abbreviation for female iron pipe size threaded fitting. Threads are inside the fitting.
A part used to join two sections of pipe or other fittings together. An example of a fitting is an elbow, bushing, or coupling.
A fixture refers to the plumbing device that provides water and/or disposal. Common fixtures in plumbing are toilets, sinks and showers.
The moveable part of a toilet flush valve that releases the water from the tank into the bowl when the toilet is flushed and seals the valve shut when the toilet is not being flushed. The most familiar version is a red replacement rubber ring that can deteriorate over time, leading to leaks and water waste. Newer flapper technologies are impervious to deterioration, increasing water efficiency and reducing operating costs.
The float ball is the plastic ball attached to the ballcock. The rise and fall of water in the tank is determined by the float ball’s placement.
Floor Flange
The floor flange, also known as a closet flange, connects a toilet to the sewer line.
Flow Control Valve
A flow control valve is a device which can reduce costs and improve efficiency by reducing the water flow to a plumbing fixture.
Flush Valve
The flush valve is located at the bottom of a toilet tank, the flush valve discharges the water from the tank into the bowl when the toilet is flushed.
The paste that is used in soldering metal joints. Flux aids the process by preventing oxidation of the joint.
Abbreviation for Female National Pipe Thread Taper.
Friction Loss
Pressure lost in a pipe due to turbulence created by water traveling through pipe.
Female sweat connection.
Flammable Vapor Ignition Resistant. Gas fired water heaters sold as of July 1, 2003, per the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), must include features to resist possible ignition of flammable vapors outside of the water heater combustion chamber.
Gallons per flush (GPF or gpf)
Gallons per flush is a measure of the total volume of water required to flush a water closet or urinal, measured in gallons.
Gallons Per Minute (GPM)
Gallons per minute (GPM) is a measure of the rate at which water flows through a fixture or fitting at a certain pressure. It is measured by the number of gallons flowing from the device in one minute at a given water supply pressure.
Gas Cock The gas cock on a main gas line allows for the gas to be shut off. Gasket A gasket is a flat rubber or fiber ring used to create a watertight seal between metal fixtures.
The gate valve controls the flow of liquids in pipes.
Gravity Operated Toilet
A gravity operated toilet relies on downward pressure of water in a toilet tank to flush. Gravity operate toilets often have ballcocks in their tank.
Gray water is any waste water that comes from common fixtures, but not toilets.
The water pressure exerted by gravity (2.31 feet of height means/delivers one pound of head).
High Efficiency Toilet (HET)
A toilet with an average water consumption of 1.28 gallons per flush or 4.8 liters per flush, when tested in accordance with a standard or product specification, such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency's WaterSense program. HETs use 20 percent less water than mandated by the Energy Policy Act of 1992, which lowers utility bills and reduces the strain on septic systems. HETs are eligible for special rebates in many drought-prone areas. They are available as single flush gravity toilets, dual-flush gravity toilets or pressure-assisted toilets.
High Efficiency Urinal (HEU)
A urinal that uses a half gallon or less of water, half the amount allowed under the by the Energy Policy Act of 1992, Contributes to lower utility bills, while reducing the burden on septic systems. HEUs are sometimes thought to be waterless, which isn't true. Waterless urinals are one type of HEU, but there are also urinals that use water and still meet higher efficiency standards.
Horizontal Branch
The horizontal branch runs from plumbing fixtures to a waste stack.
Horizontal Run
Horizontal run is the distance liquid travels from the entry point and exit of a pipe.
A hose bib is a common outdoor faucet.
Abbreviation for "hose threads." Garden hose threads are different than standard pipe threads. They are much more coarse and are 0.75 - 11.5 NH (normal hose). The 0.75 is the nominal diameter (3/4 inch) and the 11.5 is the number of threads per inch.
Abbreviation for "inside diameter." In plumbing, most pipes are sized by "nominal" (approx.) I.D. which means that when plumbers say 3/4" pipe, for example, it generally means that the outside diameter is wider than 3/4".
Interceptor
An interceptor is a device which separates oil and grease from drain systems.
Generally an abbreviation for "iron pipe size." Sometimes it means male pipe threads.
Generally an abbreviation for "iron pipe thread." Sometimes it means male pipe threads.
In the case of plumbing systems, leaching refers to the process of dissolving a soluble component out of a constituent material on a wet surface. Materials commonly leached into drinking water from water distribution systems include copper, lead, and nickel.
One of the basic elements (Pb), lead is a soft metal that has been used in plumbing systems for thousands of years. The word "plumbing" derives from the Latin word for lead, plumbum. Lead has a unique ability to resist pinhole leaks, while being soft enough to form into shapes that deliver water most efficiently. Its softness and malleability were for a long time highly desirable properties for manufacturing everything from pipe to paint. Lead is a neurotoxin that can accumulate in the body in soft tissues, as well as bone.
Lead and Copper Rule (LCR)
A United States Environmental Protection Agency regulation dating back to 1991, LCR requires water systems to monitor drinking water that comes through faucets in homes and buildings. If lead concentrations exceed 15 parts per billion (ppb) or copper concentrations exceed 1.3 parts per million (ppm) in more than 10% of homes and businesses sampled in a regional plumbing system, the system must take actions to control corrosion and leaching. If the action level for lead is exceeded, the system must also inform the public about steps they should take to protect their health, including the possible replacement of plumbing system piping.
Under section 1417(d) of the Safe Drinking Water Act, "lead free" is defined as being no more than 0.2 percent of materials used in solders, and no more than 8 percent of materials used to manufacture pipe, fittings, and well pumps.
In the plumbing industry, low-flow fixtures and fittings refer to plumbing products that meet the water efficiency standard of the Energy Policy Act of 1992. The term is used interchangeably with the term "low consumption."
Abbreviation for "Low Water Cut Off"
The main line supplies water from the water company’s meter at street level to the branch pipes around your home.
Male Threads
Male threads thread into female threads. Female fittings openings are larger than male fittings. Male fittings fit into/inside female fittings.
Manifold
A manifold is a fitting that connects multiple branches to the main, acting as a distribution point.
MaP Testing
A voluntary test protocol for toilets that measures the ability to remove solid waste, also referred to as "bulk." Cooperatively developed in 2003 by water utilities and water-efficiency specialists in the United States and Canada, it uses soybean paste (miso) as test media, in an effort to replicate "real world" waste. The test is conducted by successively increasing the amount of test media that is flushed until the toilet is no longer able to reliably or completely remove the media from the bowl. Results are reported as a MaP score , which is related to the number of grams of a test media that a toilet can adequately flush.
Metered Toilets, or Metered Flush
A toilet with a mechanism that delivers a precise, non-variable amount of water with each flush.
Abbreviation for male hose threads.
Mini-Widespread
A special style of bathroom lavatory faucet having separate spout and handles. But designed small enough that it will fit 4" center-to-center faucet holes.
Abbreviation for male pipe threads.
A nipple is a short pipe that connects couplings and other fittings.
Size used for identification only; not literal dimensions. Used to identify pipe and fitting sizes in plumbing. Refers to the inside diameter of the pipe which can vary by thickness of the pipe. The outside is a constant size. For copper pipe the outside diameter is always 1/8" larger than the nominal size. Example: 1/2" nominal is always 5/8" O.D.
Abbreviation for National Pipe Straight Threads Standard (IPS).
Abbreviation for National Pipe Straight Mechanical. Similar to garden hose threads NPSM fittings must be used with a washer between the male and female fittings to create a tight leak-proof seal. The threads themselves will not seal liquid from leaking at the fitting.
Abbreviation for National Pipe Tapered Threads Standard (FIP, MIP). NPT is the United States standard for tapered threaded fittings and pipe. Manufacturers are to follow this standard when fabricating or manufacturing pipes and fittings used for plumbing.
Founded in 1944, NSF International is a not-for-profit, non-governmental organization that develops standards and product certifications in the area of public health and safety.
NSF/ANSI Standard 60
A standard related to chemicals used to treat drinking water. Developed by NSF and conforming to the ANSI voluntary standard, the standard was accepted by the NSF board in 1988 to evaluate products, such as softeners and oxidizers, to assure that usage amounts safeguard the public health and safety.
NSF/ANSI Standard 61
A standard related to products that come in contact with drinking water. Developed by NSF and conforming to the ANSI voluntary standard, the standard was accepted by the NSF board in 1988 to confirm that such products will not contribute excessive levels of contaminants into drinking water. Most U.S. states and many Canadian provinces require products used in municipal water distribution systems and building plumbing systems to comply with Standard 61.
O-Ring
The o-ring is a round rubber washer used to make valve stems watertight.
Abbreviation for "outside diameter." The measurement of the diameter of the pipe as taken from the outside edge.
Abbreviation for "original equipment manufacturer."
One-Piece Toilet
On a one-piece toilet the toilet tank and bowl are not separate, but make one single fixture. Less common and usually more expensive, but generally a more stylish toilet.
The difference between the most wide OD and the most narrow OD on a pipe or tube. Found be subtracting the minimum outside diameter from the maximum outside diameter on a pipe.
Overflow Tube
If the ballcock malfunctions this vertical tube inside the toilet tank will direct water into the toilet bowl. This is the part that can sometimes make your toilet sound like it is constantly running, which is an indication that there is a problem with your ballcock.
Performance-Based Product Standards
Performance based product standards are standards that define a desired outcome from products, related to what they do, rather than how they are made and what they are made of. These standards typically prescribe a means for determining whether the product delivers to the standard. For example, a performance-based product standard for fittings would specify the maximum amount of alloy materials, such as lead, that may be leached into the drinking water.
PEX:
PEX is crossed-linked polyethylene; stronger than normal Polyethylene (PE).
Pipes (Measuring)
Unlike tubes, the measurement of a pipe (i.e. 2") roughly references the inside diameter (ID) of the pipe and not the outside diameter (OD). A 2" Sch 40 pipe actually has an OD of 2.375", a wall thickness of .154" and an ID of 2.067".
Plumber’s Putty
Plumber's putty is a putty with dough-like consistency used to seal the joints between fixture settings and metal pieces.
A plunger, often referred to as “the plumber’s helper”; is a six inch rubber suction cup with a wooden handle commonly used to unclog drains and toilets.
Point of connection
Polybutylene (PB)
Polybutylene is bendable tubing used in some supply lines for bathroom fixtures.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene are flexible pipes often used in plumbing supply lines.
Pop-Up Assembly
The drain mechanism of a faucet installed on a lavatory. The drain stopper "pops" up and down.
Porcelain Enamel
Porcelain enamel is a coating used on metal fixtures, such as cast iron sinks and bathtubs. Ceramic material is fired at high temperature to form a vitreous porcelain film that is fused to the base metal of the fixture or fused to a ground coat. Porcelain enamel gives metal plumbing fixtures their colors and desirable glossy surfaces.
Power Flush System
The power flush system compresses water to provide a pressurize flush. This system is often found in business and commercial settings.
Refers to mechanical venting in water heating. Generally (not always) water heaters that use power venting are more efficient than regular draft venting.
Abbreviation for "Pressure Regulator." Generally means water pressure regulator. Most codes require one if water pressures ever exceeds 80 pounds at any time on domestic potable water systems inside a structure.
Prescriptive Product Standards
Prescriptive product standards are standards that differ from performance-based product standards in that they attempt to achieve a desired outcome by specifying the characteristics, materials, performance and operation of products. For example, a prescriptive product standard for fittings would specify the maximum amount of alloy material, such as lead, that can come in direct contact with the drinking water.
Pressure-Assisted Toilets
A toilet that uses a compressed-air device to enhance the force of gravity used to clean the bowl when the toilet is flushed.
Pressure-Balancing Valve
Also known as a pressure-compensating valve, this device is designed to reduce the risk of thermal shock and scalding while showering. Required by code in most areas of the United States, a pressure-balance valve senses the hot and cold water pressures coming in from the supply line and compensates for variations to maintain the water temperature. Such variations can occur when a toilet is flushed or a washing machine started while someone is showering.
Priming Jet
The opening in the toilet bowl that allows the flow of water from the tank, designed to push waste through the trapway.

Product Standards
Product standards are established by research and consensus, product standards define what products are made of, as well as how they perform. For plumbing products, product standards govern the characteristics, materials, and performance, as well as how products need to interact with other plumbing-system elements. For example, a product standard for fittings would define the alloys and the amounts that can be used in their manufacture.
Proximity Valves
An electronic valve for plumbing fixtures and fittings that enables them to be operated without being touched. Similar to auto-open doors and light sensors that are activated by movement, proximity valves deliver the benefits of being both barrier-free and sanitary to use. Proximity valves can operate toilets, urinals and faucets.
PRV or Pressure Reducing Valve
PRV, or pressure reducing valve, is a special valve that is installed directly on the main water line. The PRV constrains the amount of water entering from the water companies supply to normalize water pressure for home use.
Pull Out Spray
When referring to a kitchen faucet this is a retractable hose/sprayhead. We'd like to mention that hoses used with a pull-out spray can turn out to be a high replaceable item. If you have a pull out sprayer be sure to pull it out straight each and every time. Do not kink the hose because if you do, no matter what brand, you could be ordering replacement hoses frequently.
PVC pipes are sturdy plastic pipes that are used for drainage, waste and vent systems.
PVD Finishes
PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. This process, which occurs in a vacuum chamber, electrostatically applies extremely thin, but extremely dense coatings of exotic metal alloys onto fittings. The resulting finish is state-of-the-art in durability, scratch-resistance and lasting beauty for faucets. A wide range of finishes with PVD is possible, including chrome, nickel, brass and bronze.
A fitting that connects pipes of different sizes together.
Refill Tube
Carries water from the ballcock to the overflow tube after the siphon break in order to refill the toilet bowl.
Relief Vent
Extra vent added to a vent line or drain line to keep the air pressure within the system in balance with the outside atmosphere. This will help keep the traps from air-locking or losing their trap seal. Required when a drainage stack extends 10 or more stories above the building drain. Such drainage stack shall be served by a parallel vent stack that connects to the drainage stack at each fifth floor. Relief vents of these types of drainage stacks shall not be less in diameter than either the drainage or vent stack, whichever is smaller. Also required when combination waste and vent systems are used for multiple floor or shower drains, floor sinks in markets, work tables in schools or similar applications where the fixtures are not close enough to walls to allow for conventional type venting. Relief vents for combination waste and vents shall not be less than one-half of the inside cross sectional area of the drain pipe it will serve.
Rim holes are a series of small holes around the toilet bowl. Water flowing from the rim holes washes over the surface of the bowl to refill the toilet bowl.
A vertical assembly of pipe and fittings that generally distributes water upward.
A rough-in is the portion of a plumbing installation that includes running the water supply lines and drain, waste & vent lines to the proposed location of each fixture.
Rough-In Dimensions
Rough-in dimensions give you the necessary information to install basic plumbing, electrical venting or other similar systems before installing the fixture. Many times a dimensional drawing is available that provides this information.
A complete or secondary section(s) of pipe that extend from supply to fixture or drain to stack.
Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA)
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is a federal law originally passed by Congress in 1974 to protect public health by regulating the nation's public drinking water supply. Amendments were passed in 1986 and in 1996. The SDWA requires many actions to protect drinking water and its sources: rivers, lakes, reservoirs, springs, and ground water wells. SDWA authorizes the United States Environmental Protection Agency to set national health-based standards for drinking water to protect against both naturally occurring and man-made contaminants. Enforcement is accomplished through the National Primary Drinking Water Regulations.
The saddle valve is a mounted pipe run by a clamping device. The saddle valve is used to make quick connections between low-demand devices.
Sanitary Fitting
A fitting that joins the assorted pipes in a drain, waste and vent system; designed to allow solid material to pass through without clogging.
Scald Guard
The scald guard is a valve that maintains the balance between hot and cold water pressure in your shower by shifting back and forth behind the shower handle in response to sudden pressure drops.
Schedule (SCH)
The "Schedule" designation tells you how thick the wall is for any size of pipe with the higher schedule numbers meaning a thicker wall. The most common schedules are Sch 40 and Sch 80, but the actual wall thickness varies depending on the size of the pipe.
Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR) used for determining the minimum wall thickness for pipe. SDR is found by dividing the outside diameter (OD) of the pipe by the wall thickness measurement. To find the minimum wall thickness of a pipe you simply divide the OD by the SDR.
Septic Tank
A septic tank is a small sewage treatment system for homes with no connection to local sewage pipes. Septic refers to the bacteria that decomposes the waste inside the tank.
Drainage outside of a building. Note that a "drain" is inside the building.
Shutoff Valve
The shutoff valve is valve under toilet, a sink or at the main line that stops the water supply for plumbing repairs.
Suction that takes place when water pressure drops which causes water or waste to be pulled through a descending outlet channel.
Siphon Break
Recognized by the gurgling sound that takes place at the end of a toilet flush, the siphon break is when air is re-introduced into the trapway, causing the siphoning action to cease.
A snake is a thin, flexible cord of spiral-wound metal that fits down a drain and is rotated to dislodge clogs.
Largest vertical drain line to which all branch waste lines connect; carries waste to the sewer line.
A metal alloy that is melted to join or mend metal surfaces; also, the act of melting solder into the joint.
A term used with PVC, CPVC and cast-iron fittings and pipe. For PVC or CPVC fittings and pipe; A male end of a fitting the same size as the pipe that is inserted and glued into the slip (hub) end of a fitting. For cast-iron pipe; The plain end of a cast-iron pipe. The spigot is inserted into the bell or hub (female) end of the next pipe to make a water tight joint.
An abbreviation normally used for PVC or CPVC fittings, to describe a non-threaded fitting with a spigot end (male) on one side and a slip (female) connector on the other side. The spigot end is the same size as the pipe and glues into a slip fitting. The slip fitting is a normal female hub end that fits over pipe.
Straight Stop Valve
A straight stop valve is a straight shutoff valve used to close off water supply during repairs.
Static Pressure
The pressure when NO water is flowing.
A valve that controls the flow of water to an individual fixture, allowing water supply to be stopped to one fixture without affecting the water supply to other fixtures.
Straight Stop
An "emergency" stop (valve) that is usually installed before the water supply line (below) to toilets and faucets. Angle stops are to be shut off in case of an emergency or repair and are generally not designed for daily on and off usage. The difference between a "straight stop" and an "angle stops" is that the "angle" stop changes direction by 90 degrees while a straight stop is like most valves and does not change direction.
Street Elbow
An elbow (90 degree bend) fitting that has a male end (same size as pipe) on one side and a female end (pipe fits inside this size) on the other side.
A sump pump is used in basements that flood often. The sump pump sits in a pit that accumulates the water, where it pushes the water outside the home.
Supply line
A supply line is a metal or plastic line that carries water directly from the main line into a plumbing fixture.
T&P Valve or Temperature and Pressure Valve
The temperate and pressure relief valve is used to safely release excess heat or pressure in a water tank.
The tailpiece is a pipe that runs between a fixture and trap.
Holds flush water for your fixture. On typical toilets the tank includes the ballcock, trip valve and flush lever.
The moving part of the flush valve that seals water in or allows water out of the tank during the flush cycle. Also known as the flapper, flush ball, stopper and seal disk.
Three bolts that hold together the tank, gasket and bowl of the toilet.
Tank Cover Lock
A device to prevent damage to and removal of the toilet tank cover and contents of the tank.
A tap is synonymous with faucet. Also tap refers to the divergence of water from one fitting to another.
A Tee is a T-shaped fitting used where three pipes intersect.
Teflon Tape
Teflon tape is fluorocarbon polymer tape with non-stick properties that is wrapped around the threads of a pipe to create a tighter joint seal.
A heat treatment technique to strengthen and harden glass for more safety. Also applies to water that has been mixed in order to avoid a temperature extreme.
Thermostatic Valves
Also known as a thermostatic compensating valve, this technology senses the temperature of the water to adjust the mix of hot and cold water. This maintains a safe, comfortable water temperature whether the fluctuation is due to a change in the pressure or the temperature of the incoming hot and cold water supplies.
Thermal Shock
A large and rapid change in the water temperature. Thermal shock is a particular concern for showers where rapid changes in the temperature of the water can lead to scalding, as well as increased risk of injuries due to slips and falls. Technologies to prevent thermal shock include pressure-balance and thermostatic shower valves.
Thread Sealant (Liquid)
Provides a water seal in threaded connections.
Thread Sealant (Tape)
Dry ribbons of sealant sold on spools. Unlike liquid sealant there is no chance of it getting into the supply lines and blocking water flow.
To ease installation and to prevent over-tightening this nut was designed to be tightened without tools.
Thumb Screw
To ease installation and to prevent over-tightening this screw was designed to be tightened without tools.
Installation where the sink is fit flush with the countertop.
Toilet Setting Compound
Provides a non-hardening watertight seal for the base of the toilet and the floor.
Torque Wrench
Tool for measuring the amount of force applied to a threaded connection.
Threads per inch.
Transfer Valve
A valve that changes the flow of water from one outlet to another
The trap is a curved section of drain line that prevents sewer odor from entering your home. All plumbing fixtures have a “P” trap, except for a toilet that has an “S” trap.
The seal caused by water in a trap preventing septic gasses from leaking back into the home. The trap seal is measured from the inlet of the trap to the top of the dam.
The trapway connects the toilet bowl to a waste outlet. The size of the trapway, also known as the passageway, influences clogging.
The trip lever on the outside of the toilet tank connects to the trip arm.
The chain that connects the toilet trip arm and the flapper on the flush valve.
The trip lever is the flush handle and actuating arm on a toilet tank. The trip lever is attached to the flapper, which results in the toilet flushing. The trip lever can also refer to the drain in a tub.
Tube (Measuring)
Unlike pipes, the measurement of a tube (i.e. 2") corresponds to it's outside diameter (OD). So the outside diameter of a 2" tube is truly 2".
Two-Piece Toilet
The toilet tank is separate from the toilet bowl. This is the most common type of toilet and is also called a close-coupled toilet.
Abbreviation for ultra low flush, which describes a toilet that deliver 1.6gpf or less.
UNC, UC, or NC
Abbreviation for Unified National Coarse Thread (National Coarse) - Use on fittings, nuts, & bolts - not for pipes.
UNF, UF, or NF
Abbreviation for Unified National Fine Thread (National Fine) - Use on fittings, nuts, & bolts - not for pipes.
Fitting that joins two sections of pipe, that allows them to be disconnected without cutting the pipe. Used primarily with steel pipes, but never in a DWV system.
Ultra-Low Flow
In the plumbing industry, ultra-low flow fixtures and fittings refer to plumbing products that exceed the water efficiency standard of the Energy Policy Act of 1992. The term is used interchangeably with the term "high efficiency"
Valve Seat
The valve seat is the stationary section of a valve.
A bathroom storage cabinet beneath the counter. Some plumbers also call a lavatory sink a vanity. Often a mirror is on the wall above.
The vent is a pipe that allows air into the drain system.
The vent stack, also known as a stink pipe, releases gas and odors outside the home.
Vitreous China
Vitreous China is a type of pottery most commonly used for plumbing fixtures, such as toilets. It is a compound of ceramic materials fired at a high temperature to form a nonporous body. Exposed surfaces are coated with a ceramic glaze that fuses to the china when fired and gives vitreous china plumbing fixtures their colors and glossy appearance.
Stands for: Vent Through the Roof.
Waste & Overflow
The drain assembly for a bathtub. The outlet at the top removes the "overflow" water during tub filling and the drain at the bottom removes "waste" water when the tub is drained.
Generally refers to a bathtub drain assembly.
Water Closet (WC)
Another term for toilet. Many in our industry will write WC on drawings or quotes which means water closet (aka: "toilet").
Water Hammer
The water hammer is a loud noise and vibration associated with pipes being turned on or off. The water hammer is caused by a sudden surge, or halt, of water in the pipes.
Water Hammer Arrestor
A water hammer arrestor is a device which prevents the banging sound known as water hammer by absorbing the hydraulic shock caused from suddenly cutting the water supply to a fixture.
WaterSense is a partnership program sponsored by United States Environmental Protection Agency, which works to promote water efficiency and enhance the market for water-efficient products, programs, and practices. Similar to the EnergyStar program that helps consumers choose energy-efficient appliances, WaterSense helps consumers to choose water-efficient products by specifying the maximum flow rates and minimum performance levels. Products certified as meeting current WaterSense product specifications are eligible to carry the WaterSense label.
When the drain discharge of one fixture is put into the vent stack of another fixture. Vertical wet venting is the most common and allows 4 fixtures of one or two fixture units each to discharge (drain) into a vent pipe serving another fixture. This can only be done if all of the fixtures involved are located on the same story as the wet vented fixture.
A style of bathroom lavatory faucet having separate spout and handles. Usually 8" from center of handle-to-handle. Some widespread faucets can be set with handles up to 12" apart.
Abbreviation for cold water, oil, gas pressure rating (water oil gas).
Working Pressure
Normal, maximum operating pressure design of a faucet, valve or plumbing product.
Wye Fitting
A wye fitting is a drain fitting which connects two sections of pipe at a 45 degree angle.
Now that you’ve reviewed the Best Plumbers plumbing glossary, you can now effectively express the plumbing issues that may arise the next time you reach out to a plumbing professional to fix your plumbing system.

- Finding Plumbers is easy by searching our trusted network of top-rated Plumbers.
- List Your Business
- Browse Categories
- Browse Locations
- Password Retrieval
- Plumbers - Join Our Website Today »
- Not a Registered User? Create Free User Account
- Are You a Local Business List Your Company Now
Join Our Newsletter
Glossary of Plumbing Terms and Definitions
Before hiring a plumbing company, it’s helpful to educate yourself on plumbing industry terms and processes..
Planning to hire a plumbing contractor in the near future? Learning key plumbing industry terms and definitions will help you navigate your way through your experience from beginning to end.
access panel An opening in the ceiling or wall near a plumbing fixture that allows plumbers to service the plumbing system or pipes.
Also known as: plumbing access panel, plumbing access
aerator A device added to the open end of a faucet that mixes air with water. Aerating the water creates a more even flow. Faucet aerators are inexpensive to install and can help conserve water and make shower and faucet spray seem more full.
Also known as: low-flow aerators, aerator shower heads, aerating faucets, faucet aerators
backflow preventer A device that stops wastewater and dangerous contaminants from flowing back into the drinkable water supply. Backflow preventers are often code requirements for sprinkler systems, hand-held showers, faucets with pullout spouts and kitchen sink sprayers.
Also known as: wastewater backflow preventer, backflow prevention valve
bathroom plumbing Fixtures, toilets, sinks, showers and piping that are found in the bathroom
Also known as: bathroom fixtures, bathroom plumbing repair, shower plumbing, toilet plumbing repairs
commercial plumbing Any plumbing repairs or installations that take place in a commercial building. Commercial plumbing is different than residential plumbing because it often deals with commercial-sized water heaters, boilers, larger piping and more involved plumbing systems. Some plumbing contractors specialize in commercial plumbing while others focus on residential plumbing.
Also known as: commercial building plumbing services, industrial plumbing, multi-tenant building plumbing, store plumbing, shopping center plumbing
coupling A fitting that connects two pieces of pipe. Common couplings for piping and plumbing include elbow fittings, tee fittings, cap couplings, plug fittings, nipple couplings, barb fittings and pipe reducer couplings. Plumbing system fittings can include closet flange couplings, trap primer couplings, clean-out fittings, combo-tee fittings, sanitary tee and double sanitary tee couplings, and wye fittings.
Also known as: pipe couplings, couplings, fittings, pipe valves, PVC couplings, CPVC couplings
drain cleaning A method of clearing organic debris and other materials from drains and pipes. Drain cleaning for residential structures and commercial buildings includes drain pressure washing, drain snaking, drain cleaning chemicals, clearing clogged drains, drain tree root clearing, and pipe degreasing.
Also known as: clog removal, degreasing, pipe cleaning, drain clearing, unclogging, clean drainage pipes
elbow A pipe fitting that has two openings and changes the direction of the plumbing line. Pipe elbows come in a variety of degrees to account for the various angles of piping.
Also known as: el fitting, ell coupling, pipe elbow, plumbing elbow, plumbing ell
fittings These usually refer to faucets, shower valves and tub fillers, but they may also refer to elbow fittings, tee fittings and flange fittings.
Also known as: plumbing fitting, fitting, pipe coupling
fixtures In plumbing, fixtures are the objects that water comes from. Plumbing fixtures include water spigots and faucets, shower, sinks, toilets, urinals, and external plumbing system fixtures.
Also known as: fixtures, faucets, kitchen fixtures, bathroom fixtures, plumbing fixtures
GPM “Gallons per minute” refers to the rate of water flow from faucets and shower heads. GPM flow is regulated by the federal government. New showerhead flow rates can’t exceed 2.5 GMP and new faucet flow rates can’t exceed 2.5 GPM or 2.2 GPM, depending on the pressure. Installing low-flow faucets and fixtures can result in water savings between 25 and 60 percent without a noticeable change in water pressure.
Also known as: gallons per minute, flow rate
GPF “Gallons per flush” is the amount of water a toilet uses per flush. The current law requires a maximum of 1.6 GPF (older styles were usually 3.5 GPF).
Also known as: gallons per flush, flush flow rate, flush capacity
ID Stands for “inside diameter,” which refers to the size of the diameter of a plumbing pipe when measured from the inside edges. All pipes are referred to according to their ID.
Also known as: inside diameter
kitchen plumbing Sinks, faucets, dishwashers, garbage disposals, drains, S-traps, slip joints and supply line water pipes that are found in the kitchen
Also known as: kitchen fixtures, kitchen pipes, kitchen plumbing repair, kitchen plumbing installation
new plumbing installation Refers to the installation of new plumbing lines , water pipes, drain lines, faucets and plumbing fixtures. New plumbing may be installed in new construction projects or in existing homes.
Also known as: plumbing installation, commercial plumbing installation, residential plumbing installation, industrial plumbing installation, plumbing replacement, plumbing reinstallation
OD “Outside diameter” refers to the dimension commonly used to size water pipes and tubing for plumbing.
Also known as: outside diameter
PVC pipes Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a hard white or cream-colored plastic that’s used to form plumbing pipes. PVC pipes are often used in venting and waste water systems that are not pressurized. PVC will melt if exposed to hot temperatures, so PVC pipes are used for cold water distribution.
Also known as: polyvinyl chloride, PVC piping
rooter service A drain cleaning service that unclogs pipes, cuts tree roots out of sewer lines and clears home piping to allow for better plumbing drainage.
Also known as: plumber’s snake, drain snaking, drain rootering, drain rooting, pipe rooter service, pipe snaking
rough-in The initial part of a plumbing installation that lays out all the basic plumbing lines without permanently connecting them. The rough-in generally includes water supply lines, water drains, water waste and vent lines that run to each fixture (toilet, sink, shower, etc.). It’s usually done before the plumbing inspection.
Also known as: roughing in, to rough in, roughing
toilet repair Some toilet repairs can be simple enough for homeowners to handle themselves, or they may require the assistance of a plumber. The most common toilet repairs include a toilet running continuously, a loose or sticking toilet handle, water on the floor around the toilet, leaking toilet tanks, poorly flushing toilets, clogged toilets, noisy toilets and toilet tank repairs.
Also known as: toilet problems, toilet problem repairs, toilet part replacement, toilet tank repairs, toilet unclogging, fixing the toilet
Use Diamond Certified Resource to find top rated companies.
Local, Top Rated Diamond Certified Companies Related to Your Topic Santa Clara County Plumbers Marin County Plumbers Contra Costa County Plumbers San Francisco Plumbers Sonoma County Plumbers
Related Articles The Homeowner's Guide to Plumbing Get Expert Advice From Owners of Top Rated Local Companies Become a Diamond Certified Preferred Member (Always Free)
Find Top Rated Companies in Your Area
Consumer resources, request and refer.
- We’ll Mail You a Free Diamond Certified Directory
- Become a Diamond Certified Preferred Consumer (ALWAYS FREE)
- Refer a Company to Try to Earn Diamond Certified
Connect with Diamond Certified
Plumbing and Pipe Fittings Glossary
Pipe fittings come in many types and sizes, which can make shopping for plumbing projects confusing. Knowing plumbing terms, like NPT, PEX, OD, or ID, can help you determine which size or type of fitting you need. Here are plumbing and pipe fitting terms we've defined to help you become a plumbing expert.
A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U W
Access panel.
A small door installed on a wall to provide access to a plumbing valve or connection.
A fitting to connect different types or sizes of fittings, piping or tubing that cannot be connected directly to a pipe or tubing.
Browse adapters .
Vertical air space that separates the potable water outlet of a plumbing fixture from a drain connection to prevent cross contamination. For example, a dedicated drinking water faucet with an integrated air-gap is commonly used with reverse osmosis systems. An air gap device, such as the Inline Gap-A-Flo AG150 , is used to connect the drain line from a water conditioner to the plumbing waste line.
Browse air gap devices .
Browse air gap faucets .
Learn why an air gap leaks and how to fix it .
A small 90-degree valve that transitions from household plumbing to supply lines to faucets or to toilet fixtures; can be quickly turned off in case of leaks.
Browse angle stops .
Valve that uses a lever to quarter-turn a pivoting ball inside to control fluid flow. The valve is OPEN when the lever is in-line (parallel) with the valve, thus allowing fluid to pass through the ball’s hole. The valve is CLOSED when the lever is turned 90-degrees (perpendicular) to the supply line valve.
Browse ball valves .
Barbed Fitting
A type of tubing connection that pushes into the inside of a tube, typically used with softer wall tubing. Barbs hold the tubing from coming off. Some installations require adding an outer clamp to keep the tubing from coming off under pressure.
Browse barbed fittings .

Any part of a plumbing distribution system that is not the main, riser or stack.
British Standard Parallel Pip (straight)
A specific standardized thread type used throughout Europe, Asia (not so much in China and Japan), Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. Straight thread version requires an O-ring or gasket to make the seal. Thread sealant not required.
British Standard Pipe Thread (tapered)
A thread type used primarily in China and Japan. Tapered with a 60-degree pitch thread (NPT has a 55 degree thread pitch) require tape or a sealing compound to ensure a good seal.
Bulkhead Fitting
A fitting that connects plumbing or tubing through the wall of a tank or vessel.
Browse bulkhead fittings .
A plumbing fitting used to reduce or enlarge to join different pipe sizes.
Browse bushings .
A measuring device used to determine inner and outer dimensions.

A fitting used on the end of a pipe or tube to seal.
Browse caps .
Check Valve
A fitting that only allows water or air flow in one direction.
Browse check valves .
A term used for a connecting a nipple fitting with no unthreaded area.
The inner ring that acts as the grabber when tubing is inserted. When used in regard to a quick-connect or push-to-connect fitting.
Browse collet covers and clips .
Compression Fitting
A type of threaded fitting used to c onnect copper, stainless steel, or plastic tubing by compressing a sleeve (ferrule) between a nut and the fitting body. Plastic tube also requires a tube insert (tube support) to prevent the pliable/flexible tube from collapsing when the compression nut and ferrule is tightened.

Browse compression fittings .
Learn how to use a compression fitting .
A common material used in plumbing pipe and fittings that comes in various wall thickness for various water, oil, and gas applications including potable water, waste pipe, and vent pipe. Most common is type L (underground and heavy duty) , M (available in both rigid and flexible forms used for inside wall home installations) , and K (rigid form used for residential water-supply lines).
A fitting that joins pipe or tubing together by gluing (PVC, CPVC), welding (steel), brazing or soldering (copper, brass etc.), or fusing (polypropylene, PVDF).
Browse couplers .
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride
A household pipe material, an alternative to copper or PEX.
A plumbing fitting that joins four tubes like an intersection.
Copper Tube Size
A plumbing size classification based on the nominal pipe size or inner diameter.
The process of cleaning and smoothing the end of the pipe after cutting prior to installing a fitting.
Degradation
In plumbing terms, can refer to the loss of material integrity such as corrosion.
A plumbing fitting that turns 90 degrees.
Browse elbows .
A fitting used at the end of a pipe to seal, also referred to as a cap .
Browse end-stops .
Female Thread
Threads on the inside diameter of a fitting or pipe.
The centerpiece of a compression fitting, also referred to as a sleeve .
Female Iron Pipe
A standardized thread type; female threads are on the inside diameter of the pipe.
Any plumbing part used to join or cap pipe or tubing.
Browse all fittings .
A plumbing term that refers to faucets, shower heads, toilets, and laundry outlets. Estimating peak flow rates for a household is accomplished by adding up all fixtures.
Browse faucets and fixtures .
A pipe connection fitting that bolts to another flange; typically used with large diameter pipe 3” and above.
Browse flanges .
Flare Fittings
A type of compression fitting used with metal tubing, usually soft steel, ductile (soft) copper and aluminum, though other materials are also used. Tube flaring is considered to be a type of forging operation and is usually a cold-working procedure. Thread Sealant is not typically used with flare fittings.
Float Valve
An automatic valve activated by a floating ball on the end of a rod. A toilet mechanism is an example.
Browse float valves .
Female Pipe Tapered
Standardized pipe thread type.
A sealing material used with certain fittings and plumbing fixtures. A garden hose connection uses a gasket.
Browse gaskets .
Garden Hose Thread
Standard Thread type used for garden hose.
High Density Polyethylene
Tubing made from polyethylene that is stiffer and less flexible than the more commonly used LLDPE.
Type of tubing connection that pushes into the inside of a tube to hold the tubing in place, typically used with softer wall tubing. Some installations require an additional outer clamp to keep the tubing from coming off under pressure.
Browse hose barbs .
Learn how to use a hose barb fitting .
Inner Diameter
Dimensional measurement used commonly with pipes. The inner diameter is also called the nominal pipe dimension to describe flow rate dimension. Copper Tube Size (CTS) is based on the inner diameter of a pipe.
A term used to describe a filter or filter housing placed in household plumbing.
Iron Pipe Thread
Standardized pipe thread type. Most commonly named by gender of the threads, MIP (male iron pipe) or FPT (female iron pipe).
Brand name for plastic material, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). See PVDF .
Linear Low Density Polyethylene
Most commonly used tubing material for connecting water filtration devices. It is a bit softer and more flexible than HDPE (high density polyethylene).
Locking Clip
A tool used with most quick-connect or push-to-connect fittings to hold tubing in place.
Browse locking clips .
Luer fittings are a standardized system of small-scale fluid fittings commonly used on medical and laboratory instruments; named after an early 20th-century instrument maker.
Browse luers .
Male Thread
Threaded fitting with threads on the outside. Common types include male NPT, male compression, male BSPP, male BSPT, male iron pipe (MIP), and male flare.
Male Flared Fitting
Male Iron Pipe

Needle Valve
A type of valve with a needle-shaped plunger that allows precise regulation of fluid flow.
Browse needle valves .
A straight pipe coupler with male threads on each end.
Browse nipples .
Nominal Pipe Size
Measurement of pipe based on the inner diameter (not actual diameter) . Fitting measurement is based on nominal pipe size, so they are actually larger in diameter than their labeled size.
National Pipe Tapered
National pipe thread is tapered with a 55-degree pitch and is the most common standardized thread type used in the U.S. The tapered design mashes together when male and female parts are tightened. Thread sealant is required. When using Teflon Tape, typically only 2 turns is needed. Pipe Dope (pipe-joint compound) may also be used on metal fittings and some plastic fittings.

National Pipe Straight
Standardized thread type. Straight threads are designed to bottom out on a gasket or O-ring to make the seal.
Outer Diameter
Outer diameter of tubing. Pipe is measured by the inner diameter, which is nominally sized (i.e. CTS).
Rubber type of gasket.
Browse O-rings .

Panel Mount
The term used when a product is designed to install on board or panel, such as a pressure gauge.
Polyethylene
A thermoplastic polymer used extensively as a tubing material for water distribution.
Refers to polyethylene tubing that has been cross-linked for additional structural strength to create pipe used mostly in household plumbing as an alternative to copper, PVC, and CPVC.
Pipe Cutter
A tool used to cut pipe.
Browse pipe cutters .
The term used for plumbing sealant to create a watertight seal on fitting threads.
Pipe Fitting
A widely used term that includes any fitting used to connect tubing or pipe.
Browse pipe fittings .
Pipe Thread
Each standardized thread type is designed for a specific application. Knowing the thread type of a pipe or fitting is important because fittings only mate with parts of the same thread type.
Learn how to determine pipe thread type and pipe size .

Determined by the pipe’s inner diameter (ID) to account for flow rate capacity.
A fitting used to close an open female fitting.
Browse plugs .
Pressure Regulator
A plumbing device used to reduce pressure, often from the city supply before it enters the house.
Browse pressure regulators .
Push-to-Connect Fitting
A category of fittings that connect tubing or pipe by pushing the fitting onto the tube.
Learn how to use a SharkBite push-connect fitting .

Material commonly used to make plastic pipes.
Material used for fittings when chemical compatibility is needed. PVDF has a higher chemical tolerance than polypropylene and acetal plastic, more commonly used in tube fittings.
Quick-Connect Fitting
A category of fittings that allows for easy installation onto a pipe or tube (aka push-to-connect or push-in fitting).
Browse quick-connect fittings .
Learn how to use a quick-connect fitting .

Quick-Disconnect Fitting
A category of tube fittings designed for frequent connections and disconnections with an optional built-in valve to stop the flow of fluid upon disconnecting (aka quick-couplings or interchange quick-coupling).
Browse quick-disconnect fittings .
Learn how to use a quick-disconnect fitting .
A plumbing fitting that connects tubing of different sizes.
Browse reducers .
The straight part of a plumbing tee. The 90-degree outlet is called the branch.
The ferrule in a compression fitting.
Slip/ Socket
The term used to describe glue and solvent pipe connections, such as PVC or CPVC.
When copper pipes are joined together by melting a soft metal alloy into the fittings.
Solenoid/ Shut-Off Valve
An electronically activated, automatic valve that controls water flow by opening or closing.
Browse shut-off valves .
Straight Thread
Non-tapered threads that retain the same diameter.
Street Elbow
An elbow fitting with male threads on one end and female on the other.
Tapered Thread
Threads that become narrow as they extend.

Common plumbing fitting that joins three tubes or pipes together. The straight part is called the run, and the 90-degree outlet is called the branch.
Browse tees .
Teflon Tape
PTFE tape (aka plumber's tape) is a type of pipe sealant wrapped in a clockwise direction on NPT and BSPT pipe threads. Compression fittings do not require a sealant. BSPP threaded fittings use a bonded seal ring gasket to make the positive seal. Low-density white Teflon tape is used on water lines. Yellow Teflon tape is used for gas lines.
Browse Teflon tape .
Thread Dimension
Measurements of thread per inch of a particular thread type.
Thread Size
Typically based on the nominal pipe size (which is approximate inner diameter) so they are always larger in diameter than their labelled size.
Learn more about pipe dimensions and thread sizes .
Measured by foot pounds ( a unit of energy equal to the amount required to raise one pound a distance of one foot), torque is the amount of force used to tighten a bolt or threaded part.
Torque Wrench
A wrench with a gauge to determine amount of torque used to tighten a bolt or threaded part.
A term used for smaller diameter plastic pipe.
Learn more about water pipes and plastic tubing .
A fitting that connects tubing in the shape of a U.
Browse U-Bend fittings .
Unified Fine Thread
A standardized thread type.
A fitting that connects two pipes of tubes.
Browse union fittings .
Unified National Special
A standardized thread type.
A plumbing fitting commonly used as an access point for drainage, featuring a 45° branch line to maintain a smooth flow.
Browse wye fittings .
- Its expected shipping date is:
- Use the chat feature or give us a call at 864-284-1801 for information about when it will be available for shipping.
- This does not qualify for free shipping.
Please note: This item is not available for same day shipping. Use the chat feature or give us a call at 864-284-1801 for further information.
The Plumbers Arms
- Live Sports Bali
- Famous Plumbers
- Plumbers Jokes
- Plumbers Cartoons
- Plumbers Gallery
- Plumbers Definitions
- Skip to content
The Plumbers Arms in Kerobokan is a popular destination for locals and tourists alike. The beautiful English Pub and the freshest food on the island makes it a great place for lunch, dinner and party nights.
Read More About Us
Testimonials
“The best English pub in Bali...”
Woohoo!! The pub is now a plastic bottle free! We can serve you our house water by the carafe or offer still and sparkling Balian water in glass bottles. Super proud to be reducing our waste and footprint at Bali's favourite local pub the # plumbersarms
The Plumbers Arms is fully air conditioned for lunch so get out of that heat and slip into something cool...
Read More About Plumbers Arms
Keep up to date on the latest from our network:
Social Bookmarks
Reservations! Call
+62 851 0044 9132

- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of plumbing
Examples of plumbing in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'plumbing.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
15th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Phrases Containing plumbing
- indoor plumbing
plumbing fixture
Dictionary Entries Near plumbing
Cite this entry.
“Plumbing.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/plumbing. Accessed 25 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of plumbing, more from merriam-webster on plumbing.
Thesaurus: All synonyms and antonyms for plumbing
Nglish: Translation of plumbing for Spanish Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about plumbing
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day, tendentious.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, 'gaslighting,' 'woke,' 'democracy,' and other top lookups, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of plumbing in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- sewage works
plumbing | American Dictionary
Plumbing | business english, translations of plumbing.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
of or relating to birds

Dead ringers and peas in pods (Talking about similarities, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Business Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add plumbing to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Introduction
As a first step, we want to tell you one Russian joke.
In Moscow, one man takes his smartphone and says, “Ok Google, I need to go to the toilet. Where I can find it?”. A voice of the smartphone answers, “Hey man, you are in trouble.”
The toilet problem is very strong in Moscow, and foreign tourists suffer more than Russians. You have almost no chances to find public WC, and no matter are you ready to pay or not. We will give you a few advices on this page. As locals, we know everything about this problem.
Many tourists try to find WC in subway stations. If you follow this idea, you will fail and will lose your time. There are toilets in the Moscow subway, but they are available only for personnel. We do not know any precedent when they let somebody in.
Every year we have a same comedy. The Moscow government declares their new plan of creation public WCs at every station. Every year nothing change. We the Russians usually say in such situation, “a cart is still standing on its place.”
Maps of Moscow WCs
The Google Maps knows a few of WCs, but it is not a decision of the problem.
WCs in trading centres
It is also a good idea. You should remember a few features.
Not every trading centre has own WC. The Sanitary Rules of Russia demand it from every trading centre larger than 10700 square feet (1000 square meters). We also do not know how some trading centres drive a coach and four through. No comments.
The Rules say every trading centre must have a WC, but the Rules do not say how many. So, you will probably get into a situation when there is only one toilet in a large trading centre. In this case, you will need to search for it.
We made a few photos of public WC in one of trading centres in Moscow. See our small gallery below.
WCs in restaurants
There is no any law in Russia that force a restaurant to let everybody using the WC. So, if you enter a restaurant and want to use a toilet, you will need to ask for a permission. Fortunately, Russia is a civilized country, and we never saw a precedent when somebody rejected.
Even if your request is rejected, you will order a cup of coffee, became a client and use the WC. We ask our readers to respect the law and act according to the law.
How to ask about WC in Russian
It is easy. The English word “toilet” sounds very close to the Russian word “tualet”. Even if you say in English, everybody will understand you. Do not hesitate to ask; Russians are usually ready to help.
We have only one advice for this situation. You should show that you a foreigner. If you will not do this, then people will be thinking you a local and will be explaining you something in Russian. Just say something in English to show you are a foreigner, and say the word “toilet”. You will receive an answer by a finger same as it shows the photo on the left.
Of course, it was a joke above. By the way, nowadays, you can find a few monuments to Vladimir Lenin in Moscow, but we do not recommend to follow in the direction he is showing. We the Russians walked in this direction for 74 years, and we still do not understand, where we were going and why.
You can think Russia is a wild country because of this toilet problem. This opinion is wrong. If you visit any private business centre, you will see a fine WC. If you visit a flat of ordinary Russian citizen, you will also find it is clean and in order.
But, if the government is in charge of something, then you will see a long list of problems that are not resolved from year to year. This is Russia.
We write this website to make your voyage to Russia perfect. Read other articles ( look for the list of links below and on the left from the text of every article )
2018 Primetime Emmy & James Beard Award Winner
R&K Insider
Join our newsletter to get exclusives on where our correspondents travel, what they eat, where they stay. Free to sign up.
A History of Moscow in 13 Dishes
Featured city guides.

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.
13 Facts About Brain Tumor Awareness Month US May
13 Facts About Community Garden Week Apr 1st To Apr 7th
40 facts about elektrostal.
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:



IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Plumbing Trap. A plumbing trap is formed by a pool of water collecting in a pipe with the shape of an inverted letter "P" or the letter "S" standing on its side. Per plumbing codes, every drain has to have a trap, and P-traps are the most common. The pool of water that collects in the inverted "P" seals the drain.
54 Plumbing terms you need to know. Access panel. An access panel is an opening in a wall or ceiling near a fixture. The access panel offers access to work on plumbing or electrical systems. Angle stop. An angle stop is a shutoff valve between the water supply and plumbing fixture. It is used to shut off water flow while you repair the ...
Save. A list of plumbing terms and definitions. Air Gap. A device mounted at the back of certain plumbing fixtures allowing discharge water to move freely into a drain pipe, but preventing contaminated water from back siphoning. Air Lock. The blockage of liquid flow of liquid due to an air bubble in the line. Anti-Siphon.
A device for receiving water and/or waste matter that directs these substances into a sanitary drainage system. Examples include toilets, sinks, bathtubs, shower receptors, and water closet bowls. The term is used erroneously in common vernacular to describe fittings. (See "Fittings.")
Snake: Plumbing snakes are vital for countless drain cleaning jobs, and the actual tool is a metal cord that's very flexible and wound into a tight spiral. Plumbers will utilize snakes to break up really tough clogs that are deep within a property's pipes. Reach Out To The Plumbing Experts At Beehive Plumbing To Schedule Your Next Appointment!
Sump Pump: A pump used to remove water from basements, crawl spaces, or low-lying areas to prevent flooding. Tee: A plumbing fitting shaped like the letter "T" used to connect pipes at a 90-degree angle. Union: A type of fitting that joins two pipes together and allows for their easy disconnection or repair. Vent Pipe: A pipe that allows air to ...
Plumbing Components and Fixtures. Aerator: insert screwed onto a faucet nozzle that reduces splashing by mixing air into the flowing water. Ball Check Valve: valve which employs a ball which can seal against a seat to stop the flow in one direction. Closet Bend: curved fitting located under the toilet connecting it to the drain. Closet Flange: ring used to anchor a toilet and connects to the ...
Plumbing follows the basic laws of nature — gravity, pressure and water seeking its own level.Knowing this, you can understand its "mysteries" and make dozens of fixes to your home's plumbing system. You can save yourself time, trouble and money!. The plumbing system in your home is composed of two separate subsystems. One subsystem brings freshwater in, and the other takes wastewater out.
Indoor Plumbing Terminology. From leaky pipes to clogged drains, countless issues can come up in any plumbing system. Taking care of them quickly can prevent damage to your home. Here are some terms to know when explaining your plumbing issue to a professional: Float valve: A valve that gauges the level of water in a tank and shuts off the flow ...
Drains - plumbing fixtures and appurtenances, including traps, for conveying wastes from building fixtures to the house sewer. DWV - Drain-Waste-Vent, the piping system that removes sewage and wastewater from a home. Effluent - sewage or other liquid waste that is discharged into the environment. Elbow - a fitting used to change the direction of flow in piping, usually at an angle of ...
The plumbing system is the central nervous system in every home. Below, is a comprehensive plumbing glossary taht explains the common terms used by plumbers and plumbing professionals throughout the plumbing industry. Knowing all the parts that keep your house running can be challenging.
Plumbing fixtures include water spigots and faucets, shower, sinks, toilets, urinals, and external plumbing system fixtures. Also known as: fixtures, faucets, kitchen fixtures, bathroom fixtures, plumbing fixtures. GPM. "Gallons per minute" refers to the rate of water flow from faucets and shower heads.
Below are some of the most commonly used definitions and explanations of plumbing, drain and sewer terms, tools, techniques and fixtures.. ABS: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene.A black plastic pipe used in plumbing for drains and vents. Absorption Field: A leeching or seeping field engineered to receive septic tank effluent. Adjustable Hot Limit Stop: Restricts hot water output in single ...
Teflon Tape. PTFE tape (aka plumber's tape) is a type of pipe sealant wrapped in a clockwise direction on NPT and BSPT pipe threads. Compression fittings do not require a sealant. BSPP threaded fittings use a bonded seal ring gasket to make the positive seal.Low-density white Teflon tape is used on water lines.
A fitting into which another fitting is inserted. Installation of plumbing fixtures to make the system usable. In plumbing, the devices that provide a supply of water and/or its disposal, e.g. sinks, tubs, toilets. The part on the bottom of the toilet tank that opens to allow water to flow from the tank into the bowl.
Travel distance, plumbing fixture access. Travel distance shall be measured from the most remote point of each room, area or space along the natural, unobstructed and accessible path of horizontal and vertical travel to the entrance to the nearest toilet room containing plumbing fixtures required to serve the room, area or space.
A vent connecting one or more individual vents with a vent stack or stack vent. [A] building sewer. 1. The area within a flood plain subject to a 1-percent or greater chance of flooding in any given year. 2. The area designated as a flood hazard area on a community's flood hazard map or as otherwise legally designated.
The meaning of PLUMBING is the act of using a plumb. How to use plumbing in a sentence.
PLUMBING definition: 1. the water pipes and similar systems in a building: 2. the work of connecting water and other…. Learn more.
Paid WCs in Moscow. They are usually located near train or subway stations. They are easy to notice; three or more cabins of a blue colour are usually different from surrounding objects. You can see the photos on the left. One cabin is used as a place for special worker who collect money and responsible for cleaning.
1: Off-kilter genius at Delicatessen: Brain pâté with kefir butter and young radishes served mezze-style, and the caviar and tartare pizza. Head for Food City. You might think that calling Food City (Фуд Сити), an agriculture depot on the outskirts of Moscow, a "city" would be some kind of hyperbole. It is not.
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
Welcome to the 628DirtRooster website where you can find video links to Randy McCaffrey's (AKA DirtRooster) YouTube videos, community support and other resources for the Hobby Beekeepers and the official 628DirtRooster online store where you can find 628DirtRooster hats and shirts, local Mississippi honey and whole lot more!