Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....


Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 May 2023
Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies
- Yunfeng Shang 1 ,
- Chunyu Bi 2 ,
- Xinyu Wei 2 ,
- Dayang Jiang 2 ,
- Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5446-7093 3 , 4 &
- Ehsan Rasoulinezhad ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7726-1757 5
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 275 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
7327 Accesses
7 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
Developing ecotourism services is a suitable solution to help developing countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. The primary purpose of this paper is to find out the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism for 40 developing economies from 2010 to 2021. The results confirmed a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. In comparison, with a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Ghost roads and the destruction of Asia-Pacific tropical forests
Jayden E. Engert, Mason J. Campbell, … William F. Laurance

Expert review of the science underlying nature-based climate solutions
B. Buma, D. R. Gordon, … S. P. Hamburg
Australian human-induced native forest regeneration carbon offset projects have limited impact on changes in woody vegetation cover and carbon removals
Andrew Macintosh, Don Butler, … Paul Summerfield
Introduction
The challenge of climate change has become a primary threat to living on the Earth in the last centuries (Rasoulinzhad and Taghizadeh-Hesary, 2022 ). Many meetings of the countries at the regional and international level are held on the topics of environment and climate change. Regardless of environmental issues, population growth, and the lack of control of greenhouse gas emissions, industrialization has been the most crucial cause of the climate change crisis. Chao and Feng ( 2018 ) address human activity as the leading cause of climate change and express that this challenge is a potential threat to living on Earth. Woodward ( 2019 ) argued that climate change threats include the rise in global temperature, the melting of polar ice caps, and unprecedented disease outbreaks. Therefore, urgent policies and solutions are essential to control and lower the risk of global change. One of the signs of climate change is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s surface. Figure 1 shows the temperature data from 1910 to 2021 for the four continents of Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America.
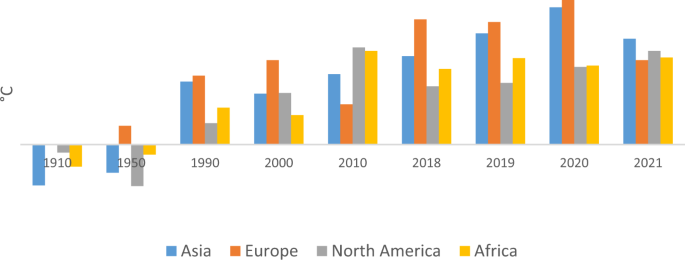
Source: Authors from NOAA ( https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series ).
The data in Fig. 1 shows that the air temperature has increased significantly over the past century, which has been more prominent in Asia and Europe. In 2021, we saw a decrease in temperature changes due to the spread of the Corona disease and a decrease in the rate of greenhouse gas emissions. However, the role of the Asian continent in increasing the global temperature has been more than other continents due to its large population and excessive consumption of fossil fuels.
During the past decades, the world’s countries have tried to formulate and implement various environmental policies collectively in the form of agreements or separately to fight environmental threats. Regarding international agreements, such things as the Paris Agreement of 2015, the Kyoto Protocol of 1997, the Montreal Protocol of 1987, and the Vienna Convention on the Protection of the Ozone Layer in 1985 can be addressed whose primary purpose is to integrate the goals and motivation of the international community to the world’s environmental threats. However, a group of earlier studies, such as Zheng et al. ( 2017 ), Takashima ( 2018 ), and Roelfsema et al. ( 2022 ), emphasized the inefficiency of these global agreements, especially after the left the USA from the Paris Agreement on 1 June 2017. The most important cause of this inefficiency has been the need for more motivation of countries to fulfill their international obligations towards environmental issues. However, many governments consider the threat of climate change only within their geographical boundaries and have tried to formulate and implement green policies to advance their environmental protection goals. These policies include green financial policies (green taxes, green subsidies), monetary policies (such as green loans and green financing), and cultural and social policies in line with sustainable development. The ultimate goal of these green policies is a green economy, an environmentally friendly economy, a zero carbon economy, or a sustainable economy. Lee et al. ( 2022 ) define the green economy as a broad concept comprising green industry, agriculture, and services. Centobelli et al. ( 2022 ) express that environmental sustainability should be more attention in the service sector owing to its penetration into social life and interactions.
Tourism and travel-related services are among countries’ main parts of the service sector. By creating the flow of tourists, tourism services can lead to capital transfer, job creation, cultural exchange (globalization), and increasing welfare in the country hosting the tours. According to the Yearbook of Tourism Statistics published by the World Tourism Organization, international tourism has increased from 522.2 billion US dollars in 1995 to nearly 1.86 trillion US dollars in 2019. This increase shows the importance of tourism services in generating income for countries, especially in the era of Corona and post-corona. Casado-Aranda et al. ( 2021 ) express that tourism services can be a central driver of economic growth recovery in post COVID era. Jeyacheya and Hampton ( 2022 ) argue that tourism can make high incomes for host countries leading to job creation and economic flourishing in destination cities for tourists.
An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relies on the post-corona era is the revitalizing of green economic growth. An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relying on the post-corona era is the revitalizing green economic growth (Bai et al., 2022 ; Werikhe, 2022 ), an opportunity that countries should pay more attention to in order to rebuild their economic activities. In other words, countries should plan their return to economic prosperity with environmental issues in mind. To this end, the issue of tourism finds a branch called Ecotourism or sustainable tourism which has environmental concerns and tries to help countries to improve environmental protection policies. Ecotourism is an approach based on environmental criteria, which is opposed to over-tourism (a type of tourism that disrupts the protection of the environment and destroys natural resources). The International Ecotourism Society defines Ecotourism as an efficient way to conserve the environment and improve local people’s well-being. It can be said that Ecotourism, along with various economic advantages (income generation, job creation, globalization, poverty alleviation), will bring environmental protection to the world’s countries, achieving the goals of green economic growth recovery and sustainable development. Xu et al. ( 2022 ) consider Ecotourism as one of the essential components of achieving sustainable development in the post-corona era.
Ecotourism in developing countries has more priorities compared to developed economies. Firstly, developing countries are often countries with financial problems of the government, and the governments in these countries need more capital to advance sustainable development goals. Therefore, developing ecotourism services can be a suitable solution to help these countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. Second, due to the spread of the Corona disease, developing countries have experienced numerous bankruptcy in the tourism services sector. Therefore, promoting ecotourism in these countries is of great importance in the post-corona era. Third, developing countries have a high share in the emission of greenhouse gases in the world due to their high dependence on fossil fuels and the lack of advanced green technologies. Fourth, due to bureaucratic processes, high cost, and lack of market transparency, greenwashing may happen in developing economies’ ecotourism industry, meaning that a company serving ecotourism services makes its activities seem more sustainable and ethical than they are. The term “greenwashing” can harshly impact the future development path of the ecotourism industry in developing economies. According to the reasons mentioned above, developing ecotourism in developing countries can be an essential factor in controlling and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in these countries.
This paper tries to contribute to the existing literature from the following aspects:
Calculating the ecotourism index for selected countries based on the criteria for measuring sustainable tourism stated by the World Tourism Organization in the United Nations. Considering that there is no specific index for ecotourism, the calculation of ecotourism in this article will be innovative.
Measuring the green governance index as a proxy for environmental policies for selected countries based on the Environment Social and Governance (ESG) data.
Selecting a sample of 40 developing countries from different geographical regions to calculate the interconnections between ecotourism, green governance, and climate change
Making a further discussion to address the role of uncertainty and the developing level of countries in the relationship between ecotourism and explanatory variables.
The main results confirm the existence of a uni-directional causal relationship running from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. A 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries accelerates ecotourism by 0.32%.
Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
The paper in continue is organized as follows: section “Literature review” provides a short literature review to determine the gaps this research seeks to fill. Section “Data and model specification” argues data and model specification. The following section represents empirical results. Section “Discussion” expresses discussion, whereas the last section provides conclusions, policy implications, research limitations, and recommendations to research further.
Literature review
This part of the article analyzes and classifies the previous literature on ecotourism and sustainable development in a rational and structured way. The importance of tourism in economic growth and development has been discussed in previous studies. However, the study of the effect of tourism on climate change has received little attention. Especially the relationship between sustainable tourism, climate change, and environmental policies is a problem that has yet to receive the attention of academic experts.
A group of previous studies has focused on the place of tourism in economic development and growth. Holzner ( 2011 ) focused on the consequences of tourism development on the economic performance of 134 countries from 1970 to 2007. They found out that excessive dependence on tourism income leads to Dutch disease in the economy, and other economic sectors need to develop to the extent of the tourism sector. In another study, Sokhanvar et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the causal link between tourism and economic growth in emerging economies from 1995 to 2014. The main results confirmed that the linkage is country-dependent. Brida et al. ( 2020 ) studied 80 economies from 1995 to 2016 to determine how tourism and economic development are related. The paper’s conclusions highlighted tourism’s-positive role in economic activities.
Another group of previous studies has linked tourism to sustainability targets. Sorensen and Grindsted ( 2021 ) expressed that nature tourism development has a positive and direct impact on achieving sustainable development goals of countries. In a new study, Li et al. ( 2022 ) studied the impacts of tourism development on life quality (as one of the sustainable development goals defined by the UN in 2015) in the case of Japan. They found that tourism development positively impacts the quality of life of age groups in the country. Ahmad et al. ( 2022 ) explored the role of tourism in the sustainability of G7 economies from 2000–2019. The primary findings revealed the positive impact of tourism arrivals on sustainable economic development. Zekan et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the impact of tourism on regional sustainability in Europe. They concluded that tourism development increases transport, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, tourism development causes environmental pollution.
Tourism that can pay attention to environmental issues is called “ecotourism.” Many new studies have studied different dimensions of ecotourism. Lu et al. ( 2021 ) expanded the concept of the ecotourism industry. The significant results expressed that smart tourist cities are essential for efficient ecotourism in countries. Thompson ( 2022 ) expressed the characteristics of ecotourism development through survey methodology. The results confirmed the importance of transparent regulations, government support, and social intention to promote ecotourism. In another study, Heshmati et al. ( 2022 ) employed the SWOT analysis method to explore the critical success factors of ecotourism development in Iran. They found that legal documentation and private participation are major influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran. In line with the previous research, Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) tried to explore the influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran by employing a SWOT analysis. They depicted that attracting investors is essential to enhance ecotourism projects in Iran. Hasana et al. ( 2022 ) reviewed research to analyze the earlier studies about ecotourism. The conclusions expressed that ecotourism is necessary for environmental protection. However, it is a challenging plan for the government, and they should carry out various policies toward ecotourism development. Kunjuraman et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of ecotourism on rural community development in Malaysia. The significant results confirmed that ecotourism could transfer-positive impacts.
Several earlier studies have concentrated on the characteristics of ecotourism in different developed and developing economies. For example, Ruhanen ( 2019 ) investigated the ecotourism status in Australia. The paper concluded that the country could potentially make a larger share of ecotourism to the entire local tourism industry. Jin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of local community power on green tourism in Japan. They concluded that the concept of agricultural village activity and regional support positively influences the development of green tourism in Japan as a developed economy. Choi et al. ( 2022 ) sought to find aspects of ecotourism development in South Korea. The preliminary results confirmed the importance of green governance and efficient regulation to promote a sustainable tourism industry. Baloch et al. ( 2022 ) explored the ecotourism specifications in the developing economy of Pakistan. They found that Pakistan’s ecotourism needs government support and the social well-being of the visited cities. Sun et al. ( 2022 ) studied ecotourism in China. They concluded that there is imbalanced development of ecotourism among Chinese provinces due to the need for more capital to invest in all ecotourism projects throughout the Chinese cities. Tajer and Demir ( 2022 ) analyzed the ecotourism strategy in Iran. They concluded that despite various potentials in the country, insufficient capital, lack of social awareness, and political tension are the major obstacles to promoting a sustainable tourism industry in Iran.
Another group of earlier studies has drawn attention to promoting eco-tourism in the post COVID era. They believe that the corona disease has created an excellent opportunity to pay more attention to environmental issues and that countries should move towards sustainable development concepts such as sustainable (eco) tourism in the post-corona era. Soliku et al. ( 2021 ) studied eco-tourism in Ghana during the pandemic. The findings depicted the vague impacts of a pandemic on eco-tourism. Despite the short-term negative consequence of the pandemic on eco-tourism, it provides various opportunities for developing this sector in Ghana. Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) employed the Fuzzy Dematel technique to find solutions for promoting eco-tourism during COVID-19. They found out that planning to increase the capacity of eco-tourism and incentive policies by governments can help promote the eco-tourism aspect under the pandemic’s consequences. Abedin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the consequence of COVID-19 on coastal eco-tourism development. The primary findings confirmed the negative impacts of a pandemic on the development of eco-tourism.
A review of previous studies shows that tourism can positively impact green growth and sustainable development. Sustainable tourism can be used as a policy to deal with the threat of climate change. This issue needs more attention in the corona and post-corona eras. Because in the post-corona era, many countries have sought to revive green economic growth, and ecotourism can be one of the tools to achieve it. As observed, a detailed study of the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policies has yet to be done. Therefore, this research will address and fill this literature gap.
Data and model specification
Data description.
The paper seeks to find the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policy for the panel of 40 developing economies from different regions from 2010 to 2021 (480 observations). The sample size could have been more extensive due to the lack of information on some variables. However, there are 480 observations in the data analysis of the data panel; therefore, the number of samples selected is acceptable.
To determine the proxies for main variables, CO2 emissions per capita are selected as the proxy for climate change. Many earlier studies (e.g., Espoir et al., 2022 ) have employed this variable as an appropriate variable representing the status of climate change. Regarding ecotourism, the World Tourism Organization proposed some measurements of sustainable tourism, and also following Yusef et al. ( 2014 ), the entropy weight method is employed to calculate a multi-dimensional ecotourism indicator comprising per capita green park area (square meters), gross domestic tourism revenue (US dollars), the ratio of good air quality (%), green transport, renewable water resources (km3) and deforestation rate (%). It is a novel ecotourism indicator that can show the ecotourism status in countries.
In addition, the green governance index is calculated as a proxy for environmental policy. Principally, the Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) data from World Bank are gathered to calculate this variable. With the improvement of the Green Governance Index, the quality of environmental policies will also increase, and vice versa. With the adverseness of the Green Governance Index, the efficiency of environmental policies will decrease.
Regarding control variables, the inflation rate as an influential factor in tourism flows is selected. The importance of this variable to promoting/declining tourism flows has been drawn to attention by some earlier studies, such as Liu et al. ( 2022 ). The inflation rate can raise the total cost of travel, causing a reduction in tourism flows, while any reduction in the inflation rate can increase the intention of tourists to travel. In addition, the KOF globalization index provided by the KOF Swiss Economic Institute is another control variable. A country with a higher degree of globalization means more readiness to accept tourists from countries with different cultures and religions.
Model specification
According to the variables mentioned above, 40 examined developing countries from 2010 to 2021, the panel co-integration model can be written as Eq. 1 :
ETOR indicates the ecotourism index, while CO2, GGI, INF, and GLOB denote Carbon dioxide emissions per capita, green governance index, inflation rate, and globalization index, respectively. i is 1,2,…,40 and shows examined developing economies, while t is time and contains 2010, 2011,..,2021.
Prior to the estimation of coefficients of Eq. 1 , the panel unit root tests are employed to find out whether the series is stationary. To this end, three tests of LLC (Levin et al., 2002 ), Breitung’s test ( 2000 ), and the PP-Fisher test (Philips and Perron, 1988 ). If all the variables are stationary at the first level of difference (I(1)), a panel co-integration test can be conducted to explore whether the model is spurious. To this end, Kao’s co-integration test ( 1999 ) and Pedroni’s residual co-integration test ( 2004 ) are conducted. If the co-integration relationship exists among variables, the panel causality test can be run to determine the causal linkages among variables. In this paper, the two steps of Engle and Granger (1987)‘s test, which is based on the error correction model (ECM) is used as Eqs. 2 – 6 :
In the above Equations, Δ is the first differences of variables, while θ and ECT represent the fixed country effect and error correction term.
The next step is the long-run panel co-integration estimations. To this end, Fully Modified OLS (FMOLS) and Dynamic OLS (DOLS) as robustness checks are conducted, which are two famous panel co-integration estimators (Rasoulinezhad, 2018 ). The FMOLS estimator has various advantages. It allows serial correlation, endogeneity, and cross-sectional heterogeneity (Erdal and Erdal, 2020 ).
Empirical results
In this section, we will implement the experimental research model. The purpose of implementing an econometric model based on panel data is to find the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism. As the first step, the panel unit root tests are conducted. The results are reported in Table 1 as follows:
According to Table 1 , all three-panel unit root tests depict that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. Next, the panel co-integration tests are conducted, and their results are represented in Tables 2 and 3 :
The two-panel co-integration tests’ findings confirm the presence of co-integration linkages among variables.
The panel causality test studies the short-term and long-term causal relationship among variables. Table 4 reports the results of the panel causality check as follows:
According to Table 4 , there is a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. At the same time, there is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback effect. In addition, there is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions. In contrast, ecotourism and the globalization index have a uni-directional causal linkage. In the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies. Regarding the long-term causality, it can be concluded that the ECT of ecotourism, green governance index, and globalization index are statistically significant. These three variables are major adjustment variables when the system departs from equilibrium.
In the last stage, the long-run estimations are done through FMOLS and DOLS estimators. Table 5 lists the results of the estimations by these two-panel co-integration estimators:
Based on FMOLS estimation, it can be concluded that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient in such a way that with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. By improving the state of green governance, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development. This finding aligns with Agrawal et al. ( 2022 ) and Debbarma and Choi ( 2022 ), who believe that green governance is essential to sustainable development. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. In other words, the variable of carbon dioxide emissions per capita has no significant effect on ecotourism in developing countries. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. With a 1% increase in the general prices of goods and services in developing countries, ecotourism will decrease by 0.34%. This finding aligns with Rahman ( 2022 ), who showed a negative relationship between inflation and sustainable development in their research. An increase in inflation means an increase in the total cost of a tourist’s trip to the destination country, inhibiting the growth of tourist services.
Regarding the globalization variable, this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. With a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in the country. This finding is consistent with the results of Akadiri et al. ( 2019 ), who confirmed that globalization is one of the crucial components in tourism development.
The DOLS estimator was also used to ensure the obtained findings’ validity. The results of this method are shown in Table 5 . The signs of the coefficients are consistent with the results obtained by the FMOLS method. Therefore, the validity and reliability of the obtained coefficients are confirmed.
In this section, we will briefly discuss the relationship between ecotourism and climate change and the environmental policy considering the uncertainty and the relationship between variables in developed and developing countries.
Consideration of uncertainty
Uncertainty as a primary reason for risk has become a research issue in recent decades. Uncertainty can make the future unpredictable and uncontrollable, affecting economic decision-making. Regarding tourism, the impacts of uncertainty have been drawn to attention by several earlier studies (e.g., Dutta et al., 2020 ; Das et al., 2020 ; and Balli et al., 2019 ; Balli et al., 2018 ). In general, uncertainty in the tourism industry reflects tourists’ concerns and consumption habits in the way that by increasing uncertainty, it is expected that tourists make sense of risks and postpone their tourism activities, and vice versa; in the sphere of certainties, the various risks are clear, and tourists can make rational decisions for their tourism plans and activities. In order to explore the impacts of uncertainties on eco-tourism of the examined developing economies, the geopolitical risk index (GPR) as a proxy for economic policy uncertainty index is gathered and added as a control variable to Eq. 1 . The estimations results by FMOLS are reported in Table 6 as follows.
According to Table 6 , the uncertainty (geopolitical risk) has a negative coefficient meaning that with a 1% increase in geopolitical risk, the eco-tourism industry in the examined developing countries decreases by approximately 0.69%. The signs of coefficients of other variables align with the earlier findings, represented in Table 5 . In addition, the magnitude of the impact of geopolitical risk is larger than the impacts of other variables highlighting the importance of lower geopolitical risk in these economies to reach sustainable tourism targets.
Difference in developed and developing economies
Considering the different structures and financial power of these two groups of countries, the relationship between the variables mentioned in these two groups is expected to be different. In the previous section, the results for the group of developing countries showed that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. Regarding the globalization variable, it can be mentioned that this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. In order to analyze the relationship between variables in the developed countries, the top 10 countries with the highest HDI in 2021 are selected (Switzerland (0.962), Norway (0.961), Iceland (0.959), Hong Kong (0.952), Australia (0.951), Denmark (0.948), Sweden (0.947) and Ireland (0.945)). The selected variables, explained in section “Data and model specification”, are collected from 2010 to 2021. The panel unit root tests confirmed that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. In addition, the presence of co-integration linkages among variables is revealed by the panel co-integration test. The panel co-integration estimator of FMOLS is employed to study the long-term relationship among variables. The findings are reported in Table 7 as follows:
According to the estimated coefficients, the green governance indicator positively and statistically significantly impacts ecotourism in the examined developed economies. However, the magnitude of the impact of this variable is more considerable for developing countries because these countries have more imbalances in markets and regulations. Therefore, the presence of good green tourism can have a more positive effect on advancing the goal of ecotourism. Contrary to the findings of developing countries, carbon dioxide emission in developed countries has a negative and significant effect, meaning that with an increase of 1% in carbon dioxide in developed countries, the level of ecotourism becomes more unfavorable by 0.034%. Moreover, inflation and globalization variables have significant negative and positive coefficients, respectively. However, the magnitudes of these two variables’ coefficients are also higher in developing countries. Ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to changes in macroeconomic variables such as green governance, globalization, and inflation.
Another difference between eco-tourism in developed and developing economies may be interpreted through the term “greenwashing,” introduced by Westerveld in 1986 (Maichum et al., 2016 ). In developing countries, due to the economic structure, limited knowledge, bureaucratic process, lack of legal eco-certification, and imperfect competition, a company involved in the eco-tourism industry makes an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into accepting the company’s services are in line with environmental protection policies. Hence, green governance in developing countries should have another role in regulating the eco-tourism market to lower the threat of greenwashing in eco-tourism services.
Conclusions and policy recommendations
Concluding remarks.
The findings of econometric modeling revealed the relationship between environmental policies, climate change, and ecotourism. Based on the findings of the econometric model, the following conclusions can be presented:
A uni-directional causal relationship runs from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator, which means that any changes in green governance and inflation rate cause changes in ecotourism, which is vital for developing economies where governance and inflation rate are two crucial issues.
There is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback hypothesis, expressing that in developing economies, any policies related to ecotourism cause changes in CO2 emissions and vice versa.
There is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions, whereas there is a uni-directional causal linkage from ecotourism to the globalization index. In other words, in the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies.
By improving green governance in developing economies, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development.
An increase in the inflation rate raises the total cost of a tourist’s trip to developing economies, inhibiting the growth of eco-tourist services.
Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in developing countries.
Policy implications
In order to achieve the promotion of ecotourism in developing countries, the implementation of integrated and effective strategic and practical policies is of great importance. According to the concluding remarks mentioned, practical policies are presented as follows for enhancing ecotourism in developed countries. The development of ecotourism requires the improvement of various infrastructures and mechanisms, which depends on the implementation of projects related to ecotourism in developing countries. Because most countries do not have enough financial power to invest in such projects, developing the green financing market can be one of the critical practical solutions. The green financing tool can increase the investment risk and return on investment in such projects, and as a result, the participation of the private sector in these projects will increase. With information and communication technology development, virtual tourism can solve many environmental issues related to human physical presence. Virtual tourism is one of the branches of tourism services that provide people with destinations, places of interest, and tourist attractions with full quality but in virtual form. Another practical policy is granting green loans to small and medium enterprises active in ecotourism. Despite the organizational agility, these companies do not have the significant financial power to develop different sectors of ecotourism; therefore, the cooperation of the banking industry of developing countries by providing green loans (with low-interest rates) can motivate small and medium-sized companies in the field of activities related to ecotourism. Government incentives to motivate businesses active in ecotourism and government deterrent policies (green tax) from businesses active in the field of tourism to lead them to increase the share of ecotourism in their activities can be a proper operational strategy. In developing countries, the role of government and green governance is vital in advancing the goals of ecotourism. By improving the level of its green governance, the government can create efficient policies, regulations, and social tools to create motivation and desire to accept ecotourism, an essential and undeniable issue in developing societies. Creating a guarantee fund for ecotourism companies in developing countries is another practical policy to support these companies financially. Guarantee funds can be established with the participation of the people of ecotourism destinations in order to strengthen the financial strength of ecotourism companies in these destinations.
Limitations and recommendations to further research
This research had a practical and innovative contribution to the literature on ecotourism in developing countries. The findings obtained from the econometric model analysis provided appropriate practical and strategic policies to the policymakers of countries interested in the development of ecotourism. However, access to data related to the ecotourism index and sustainable development of developing countries due to the lack of community in a specific database is considered one of the critical limitations of this research. This limitation caused many developing countries to be excluded from the research sample, which may have created a deviation in the research. Adding more countries to the test sample in future research is suggested to obtain complete and accurate results. Also, due to the outbreak of the Corona pandemic at the end of 2019 and the Russia-Ukraine war since the beginning of 2022, it is suggested that these two variables be included in the econometric model as an illusion in order to analyze their effects on the ecotourism of the countries of the world. Using other econometric methods, such as artificial neural networks, is suggested to model ecotourism in different countries. Complex modeling by taking into account trends and trends to predict the relationship between variables in the future will be an essential step in formulating effective programs in ecotourism.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abedin Z, Handayani W, Zaky E, Faturrahman A (2022) Perceived risk and attitude’s mediating role between tourism knowledge and visit intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: implementation for coastal-ecotourism management. Heliyon 8(10):e10724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10724
Article Google Scholar
Agrawal A, Brandhorst S, Jain M, Liao C, Pradhan N, Solomon D (2022) From environmental governance to governance for sustainability. One Earth 5(6):615–621
Article ADS Google Scholar
Ahmad N, Youjin L, Hdia M (2022) The role of innovation and tourism in sustainability: why is environment-friendly tourism necessary for entrepreneurship? J Clean Prod 379(Part 2):134799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134799
Akadiri S, Alola A, Akadiri A (2019) The role of globalization, real income, tourism in environmental sustainability target. Evidence from Turkey. Sci Total Environ 687:423–432
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bai X, Wang K, Tran T, Sadiq M, Trung L, Khudoykulov K (2022) Measuring China’s green economic recovery and energy environment sustainability: econometric analysis of sustainable development goals. Econ Anal Policy 75:768–779
Balli F, Shahzad SJH, Uddin GS (2018) A tale of two shocks: what do we learn from the impacts of economic policy uncertainties on tourism? Tour Manag68:470–475
Balli F, Uddin GS, Shahzad SJH (2019) Geopolitical risk and tourism demand in emerging economies. Tour Econ 25(6):997–1005
Baloch Q, Shah S, Iqbal N, Sheeraz M, Asadullah M, Mahar S, Khan A (2022) Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism. Environ Sci Pollut Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22496-w
Breitung J (2000) The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. In: Baltagi B (ed.). Nonstationary panels, panel cointegration, and dynamic panels, advances in econometrics. vol. 15. JAI Press, Amsterdam. pp. 161–178
Brida J, Gomez D, Segarra V (2020) On the empirical relationship between tourism and economic growth. Tour Manag 81:104131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104131
Casado-Aranda L, Fernandez J, Bastidas-Manzano A (2021) Tourism research after the COVID-19 outbreak: insights for more sustainable, local and smart cities. Sustain Cities Soc 73:103126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103126
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Centobelli P, Cerchione R, Esposito E (2022) Environmental sustainability in the service industry of transportation and logistics service providers: systematic literature review and research directions. Transp Res Part D Trans Environ 53:454–470
Chao Q, Feng A (2018) Scientific basis of climate change and its response. Glob Energy Interconnect 1(4):420–427
Google Scholar
Choi Y, Oh C, Chon J (2022) Applying the resilience principles for sustainable ecotourism development: a case study of the Nakdong Estuary, South Korea. Tour Manag 83:104237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104237
Das D, Dutta A, Bhadra A, Uddin GS (2020) Role of presidential uncertainties on the hotel industry. Ann Tour Res 81:102762
Debbarma J, Choi Y (2022) A taxonomy of green governance: a qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustain Cities Soc 79:103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103693
Dutta A, Mishra T, Uddin GS, Yang Y (2020) Brexit uncertainty and volatility persistence in tourism demand. Curr Issue Tour 24(16):2225–2232
Erdal H, Erdal G (2020) Panel FMOLS model analysis of the effects of livestock support policies on sustainable animal presence in Turkey. Sustainability 12:3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083444
Espoir D, Mudiangombe B, Bannor F, Sunge R, Tshitaka J (2022) CO2 emissions and economic growth: Assessing the heterogeneous effects across climate regimes in Africa. Sci Total Environ 804:150089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150089
Hasana U, Swain S, George B (2022) A bibliometric analysis of ecotourism: a safeguard strategy in protected areas. Region Sustain 3(1):27–40
Heshmati M, Gheitury M, Shadfar S (2022) Factors affecting possibility of ecotourism development and sustaining natural resources using SWOT approach in west Iran. Int J Geoheritage Parks 10(2):173–183
Holzner M (2011) Tourism and economic development: the beach disease. Tour Manag32(4):922–933
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Keshteli M (2021) Recovery solutions for ecotourism centers during the Covid-19 pandemic: utilizing Fuzzy DEMATEL and Fuzzy VIKOR methods. Exp Syst Appl 185:115594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115594
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Triki C (2021) Implementing sustainable ecotourism in Lafour region, Iran: applying a clustering method based on SWOT analysis. J Clean Prod 329:129716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129716
Jeyacheya J, Hampton M (2022) Pathway choice and post-Covid tourism: Inclusive growth or business as usual? World Dev Sustain 1:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wds.2022.100024
Jin C, Takao M, Yobuta M(2022) Impact of Japan’s local community power on green tourism. Asia Pacific J Region Sci 6:571–591
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Economet 90(1):1–44
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Kunjuraman V, Hussin R, Aziz R (2022) Community-based ecotourism as a social transformation tool for rural community: a victory or a quagmire. J Outdoor Recreat Tour 39:100524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jort.2022.100524
Lee C, Wang C, Ho S (2022) The dimension of green economy: Culture viewpoint. Econ Anal Policy 74:122–138
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CS (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Economet 108(1):1–24
Li J, Ridderstaat J, Yost E (2022) Tourism development and quality of life interdependence with evolving age-cohort-based population. Tour Manag 93:104621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104621
Liu A, Kim Y, Song H (2022) Toward an accurate assessment of tourism economic impact: a systematic literature review. Ann Tour Res Empirical Insight 3(2):100054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100054
Lu C, Huang J, Chen C, Shu M, Hsu C, Bapu T (2021) An energy-efficient smart city for sustainable green tourism industry. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 47:101494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101494
Maichum K, Parichatnon S, Peng KC (2016) Application of the extended theory of planned behavior model to investigate purchase intention of green products among Thai consumers. Sustainability 8:1077
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theory 20(3):597–625
Phillips PCB, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regressions. Biometrika. 75(2):335–346
Rahman M (2022) The effect of taxation on sustainable development goals: evidence from emerging countries. Heliyon 8(9):e10512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10512
Rasoulinezhad E (2018) A new evidence from the effects of Russia’s WTO accession on its foreign trade. Eur Econ Rev 8(1):73–92
Rasoulinezhad E, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022) Role of green finance in improving energy efficiency and renewable energy development. Energy Efficiency 15(2):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-022-10021-4
Roelfsema M, Soest H, Elzen M, Coninck HH, Kuramochi T, Harmsen M, Dagnomilis I, Hohne N, Vuuren D (2022) Developing scenarios in the context of the Paris Agreement and application in the integrated assessment model IMAGE: a framework for bridging the policy-modelling divide. Environ Sci Policy 135:104–116
Article CAS Google Scholar
Ruhanan L (2019) The prominence of eco in ecotourism experiences: an analysis of post-purchase online reviews. J Hosp Tour Manag 39:110–116
Sokhanvar A, Ciftcioglu S, Javid E (2018) Another look at tourism-economic development nexus. Tour Manag Perspect 26:97–106
Soliku O, Kyiire B, Mahama A, Kubio C (2021) Tourism amid COVID-19 pandemic: impacts and implications for building resilience in the eco-tourism sector in Ghana’s Savannah region. Heliyon 7(9):e07892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07892
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sorensen F, Grindsted T (2021) Sustainability approaches and nature tourism development. Ann Tour Res 91:103307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2021.103307
Sun Y, Ding W, Yang G (2022) Green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry from the perspective of shared inputs: Dynamic evolution and combination improvement paths. Ecol Indica 138:108824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108824
Tajer E, Demir S (2022) Ecotourism strategy of UNESCO city in Iran: applying a new quantitative method integrated with BWM. J Clean Prod 376:134284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134284
Takashima N (2018) International environmental agreements between asymmetric countries: a repeated game analysis. Jpn World Econ 48:38–44
Thompson B (2022) Ecotourism anywhere? The lure of ecotourism and the need to scrutinize the potential competitiveness of ecotourism developments. Tour Manag 92:104568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104568
Werikhe A (2022) Towards a green and sustainable recovery from COVID-19. Curr Res Environ Sustain 4:100124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crsust.2022.100124
Woodward A (2019) Climate change: disruption, risk and opportunity. Glob Trans 1:44–49
Xu L, Ao C, Liu B, Cai Z (2022) Cotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends. Environ Dev Sustain https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0
Yusef N, Rahman F, Jamil M, Iranmanesh M (2014) Measuring the quality of ecotourism services: case study–based model validation. Sage Open, https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014538270
Zekan B, Weismayer C, Gunter U, Schuh B, Sedlacek S (2022) Regional sustainability and tourism carrying capacities. J Clean Prod 339:130624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130624
Zheng H, Dai H, Lai H, Wang W (2017) U.S. withdrawal from the Paris agreement: reasons, impacts, and China’s response. Adv Clim Change Rese 8(4):220–225
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Administration, Zhejiang Yuexiu University, Zhejiang, China
- Yunfeng Shang
School of Economics, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China
Chunyu Bi, Xinyu Wei & Dayang Jiang
School of Global Studies, Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary
TOKAI Research Institute for Environment and Sustainability (TRIES), Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Faculty of World Studies, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Ehsan Rasoulinezhad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Yunfeng Shang , Dayang Jiang or Ehsan Rasoulinezhad .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shang, Y., Bi, C., Wei, X. et al. Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Download citation
Received : 11 November 2022
Accepted : 18 May 2023
Published : 31 May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Spatial effects of green finance development in chinese provinces under the context of high-quality energy development.
- Fangbin Qian
Economic Change and Restructuring (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Chapman University
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
Ecotourism Definition and Principles
Pros and cons.
- Examples of Ecotourism
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ecotourism is about more than simply visiting natural attractions or natural places; it’s about doing so in a responsible and sustainable manner. The term itself refers to traveling to natural areas with a focus on environmental conservation. The goal is to educate tourists about conservation efforts while offering them the chance to explore nature.
Ecotourism has benefited destinations like Madagascar, Ecuador, Kenya, and Costa Rica, and has helped provide economic growth in some of the world’s most impoverished communities. The global ecotourism market produced $92.2 billion in 2019 and is forecasted to generate $103.8 billion by 2027.
A conservationist by the name of Hector Ceballos-Lascurain is often credited with the first definition of ecotourism in 1987, that is, “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas.”
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education [both in its staff and its guests].”
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) looks at ecotourism as a significant tool for conservation, though it shouldn’t be seen as a fix-all when it comes to conservation challenges:
“There may be some areas that are just not appropriate for ecotourism development and some businesses that just won’t work in the larger tourism market. That is why it is so important to understand the basics of developing and running a successful business, to ensure that your business idea is viable and will be profitable, allowing it to most effectively benefit the surrounding environment and communities.”
Marketing an ecosystem, species, or landscape towards ecotourists helps create value, and that value can help raise funds to protect and conserve those natural resources.
Sustainable ecotourism should be guided by three core principles: conservation, communities, and education.
Conservation
Conservation is arguably the most important component of ecotourism because it should offer long-term, sustainable solutions to enhancing and protecting biodiversity and nature. This is typically achieved through economic incentives paid by tourists seeking a nature-based experience, but can also come from the tourism organizations themselves, research, or direct environmental conservation efforts.
Communities
Ecotourism should increase employment opportunities and empower local communities, helping in the fight against global social issues like poverty and achieving sustainable development.
Interpretation
One of the most overlooked aspects of ecotourism is the education component. Yes, we all want to see these beautiful, natural places, but it also pays to learn about them. Increasing awareness about environmental issues and promoting a greater understanding and appreciation for nature is arguably just as important as conservation.
As one of the fastest growing sectors of the tourism industry, there are bound to be some downsides to ecotourism. Whenever humans interact with animals or even with the environment, it risks the chance of human-wildlife conflict or other negative effects; if done so with respect and responsibility in mind, however, ecotourism can reap enormous benefits to protected areas.
As an industry that relies heavily on the presentation of eco-friendly components to attract customers, ecotourism has the inevitable potential as a vessel for greenwashing. Part of planning a trip rooted in ecotourism is doing research to ensure that an organization is truly providing substantial benefits to the environment rather than exploiting it.
Ecotourism Can Provide Sustainable Income for Local Communities
Sustainably managed ecotourism can support poverty alleviation by providing employment for local communities, which can offer them alternative means of livelihood outside of unsustainable ones (such as poaching).
Research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that communities in regions surrounding conservation areas in Costa Rica had poverty rates that were 16% lower than in areas that weren’t near protected parks. These protected areas didn’t just benefit from conservation funds due to ecotourism, but also helped to reduce poverty as well.
It Protects Natural Ecosystems
Ecotourism offers unique travel experiences focusing on nature and education, with an emphasis on sustainability and highlighting threatened or endangered species. It combines conservation with local communities and sustainable travel , highlighting principles (and operations) that minimize negative impacts and expose visitors to unique ecosystems and natural areas. When managed correctly, ecotourism can benefit both the traveler and the environment, since the money that goes into ecotourism often goes directly towards protecting the natural areas they visit.
Each year, researchers release findings on how tourist presence affects wildlife, sometimes with varying results. A study measuring levels of the stress hormone cortisol in wild habituated Malaysian orangutans found that the animals were not chronically stressed by the presence of ecotourists. The orangutans lived in the Lower Kinabatangan Wildlife Sanctuary, where a local community-managed organization operates while maintaining strict guidelines to protect them.
Ecotourism May Also Hurt Those Same Natural Ecosystems
Somewhat ironically, sometimes ecotourism can hurt ecosystems just as much as it can help. Another study in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution found that ecotourism can alter animal behaviors in ways that put them at risk. If the presence of humans changes the way animals behave, those changes may make them more vulnerable by influencing their reaction to predators or poachers.
It's not just the animals who are at risk. As ecotourism activities become too popular, it can lead to the construction of new infrastructure to accommodate more visitors. Similarly, more crowds mean more pressure on local resources, increased pollution, and a higher chance of damaging the soil and plant quality through erosion. On the social side, these activities may displace Indigenous groups or local communities from their native lands, preventing them from benefiting from the economic opportunities of tourism.
Ecotourism Offers the Opportunity to Experience Nature
Renown conservationist Jane Goodall has a famous quote: “Only if we understand, will we care. Only if we care, will we help. Only if we help, shall all be saved.” It can be difficult to understand something that we haven’t seen with our own eyes, and ecotourism gives travelers the opportunity to gain new experiences in natural areas while learning about the issues they face.
Ecotourism also educates children about nature, potentially creating new generations of nature lovers that could someday become conservationists themselves. Even adult visitors may learn new ways to improve their ecological footprints .
EXAMPLES OF ECOTOURISM
The East African country has some competitive advantages over its neighbors thanks to its rich natural resources, paired with the fact that it has allocated over 25% of its total area to wildlife national parks and protected areas. Because of this, an estimated 90% of tourists visit to Tanzania seeking out ecotourism activities. Ecotourism, in turn, supports 400,000 jobs and accounts for 17.2% of the national GDP, earning about $1 billion each year as its leading economic sector.
Some of Tanzania’s biggest highlights include the Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro , and Zanzibar, though the country still often goes overlooked by American tourists. Visitors can take a walking safari tour in the famous Ngorongoro Conservation area, for example, with fees going to support the local Maasai community.
The country is also known for its chimpanzees , and there are several ecotourism opportunities in Gombe National Park that go directly towards protecting chimpanzee habitats.
Galapagos Islands
It comes as no surprise that the place first made famous by legendary naturalist Charles Darwin would go on to become one of the most sought-after ecotourism destinations on Earth, the Galapagos Islands .
The Directorate of the Galapagos National Park and the Ecuadorian Ministry of Tourism require tour providers to conserve water and energy, recycle waste, source locally produced goods, hire local employees with a fair wage, and offer employees additional training. A total of 97% of the land area on the Galapagos is part of the official national park, and all of its 330 islands have been divided into zones that are either completely free of human impact, protected restoration areas, or reduced impact zones adjacent to tourist-friendly areas.
Local authorities still have to be on their toes, however, since UNESCO lists increased tourism as one of the main threats facing the Galapagos today. The bulk of funding for the conservation and management of the archipelago comes from a combination of governmental institutions and entry fees paid by tourists.
Costa Rica is well-known throughout the world for its emphasis on nature-based tourism, from its numerous animal sanctuaries to its plethora of national parks and reserves. Programs like its “Ecological Blue Flag” program help inform tourists of beaches that have maintained a strict set of eco-friendly criteria.
The country’s forest cover went from 26% in 1983 to over 52% in 2021 thanks to the government’s decision to create more protected areas and promote ecotourism in the country . Now, over a quarter of its total land area is zoned as protected territory.
Costa Rica welcomes 1.7 million travelers per year, and most of them come to experience the country’s vibrant wildlife and diverse ecosystems. Its numerous biological reserves and protected parks hold some of the most extraordinary biodiversity on Earth, so the country takes special care to keep environmental conservation high on its list of priorities.
New Zealand
In 2019, tourism generated $16.2 billion, or 5.8% of the GDP, in New Zealand. That same year, 8.4% of its citizens were employed in the tourism industry, and tourists generated $3.8 billion in tax revenue.
The country offers a vast number of ecotourism experiences, from animal sanctuaries to natural wildlife on land, sea, and even natural caves. New Zealand’s South Pacific environment, full of sights like glaciers and volcanic landscapes, is actually quite fragile, so the government puts a lot of effort into keeping it safe.
Tongariro National Park, for example, is the oldest national park in the country, and has been named by UNESCO as one of only 28 mixed cultural and natural World Heritage Sites. Its diverse volcanic landscapes and the cultural heritage of the indigenous Maori tribes within the create the perfect combination of community, education, and conservation.
How to Be a Responsible Ecotourist
- Ensure that the organizations you hire provide financial contributions to benefit conservation and find out where your money is going.
- Ask about specific steps the organization takes to protect the environment where they operate, such as recycling or promoting sustainable policies.
- Find out if they include the local community in their activities, such as hiring local guides, giving back, or through initiatives to empower the community.
- Make sure there are educational elements to the program. Does the organization take steps to respect the destination’s culture as well as its biodiversity?
- See if your organization is connected to a non-profit or charity like the International Ecotourism Society .
- Understand that wildlife interactions should be non-invasive and avoid negative impacts on the animals.
Ecotourism activities typically involve visiting and enjoying a natural place without disturbing the landscape or its inhabitants. This might involve going for a hike on a forest trail, mountain biking, surfing, bird watching, camping, or forest bathing .
Traveling in a way that minimizes carbon emissions, like taking a train or bike instead of flying, may also be part of an ecotourism trip. Because these modes of travel tend to be slower, they may be appreciated as enjoyable and relaxing ecotourism activities.
The Wolf Conservation Center ’s programing in New York State is an example of ecotourism. This non-profit organization is dedicated to the preservation of endangered wolf species. It hosts educational sessions that allow visitors to observe wolves from a safe distance. These programs help to fund the nonprofit organization’s conservation and wildlife rehabilitation efforts.
Stonehouse, Bernard. " Ecotourism ." Environmental Geology: Encyclopedia of Earth Science , 1999, doi:10.1007/1-4020-4494-1_101
" What is Ecotourism? " The International Ecotourism Society .
" Tourism ." International Union for Conservation of Nature .
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307712111
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033357
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010
https://doi.org/10.5897/JHMT2016.0207
" Galapagos Islands ." UNESCO .
" About Costa Rica ." Embassy of Costa Rica in Washington DC .
https://www.stats.govt.nz/information-releases/tourism-satellite-account-2019
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- Defeating Deforestation Through Rum, Chocolate, and Ecotourism
- Empowering Communities to Protect Their Ecosystems
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Why Bonobos Are Endangered and What We Can Do
- Why Are National Parks Important? Environmental, Social, and Economic Benefits
- IUCN President Tackles Biodiversity, Climate Change
- The World’s Smallest Tiger Is Inching Towards Extinction
- Ecuador Expands Protected Galapagos Marine Reserve by More Than 23,000 Square Miles
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- New Zealand Aims to Become World's Largest 'Dark Sky Nation'
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.
Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 17 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|162.248.224.4]
- 162.248.224.4
Character limit 500 /500
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Advances in Landscape Architecture
Role of Ecotourism in Sustainable Development
Submitted: 28 December 2012 Published: 01 July 2013
DOI: 10.5772/55749
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Advances in Landscape Architecture
Edited by Murat Özyavuz
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
32,468 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Overall attention for this chapters
Author Information
Tuğba kiper.
*Address all correspondence to:
1. Introduction
Ecotourism is a sub-component of the field of sustainable tourism. Ecotourism’s perceived potential as an effective tool for sustainable development is the main reason why developing countries are now embracing it and including it in their economic development and conservation strategies. Ecotourism, as an alternative tourism, involves visiting natural areas in order to learn, to study, or to carry out activities environmentally friendly, that is, a tourism based on the nature experience, which enables the economic and social development of local communities. It focuses primarily on experiencing and learning about nature, its landscape, flora, fauna and their habitats, as well as cultural artifacts from the locality. A symbiotic and complex relationship between the environment and tourist activities is possible when this philosophy can be translated into appropriate policy, careful planning and tactful practicum. Carefully planned and operated ecotourism sites, especially if it is village-based and includes local participation, is able to provide direct benefits that might offset pressure from other less sustainable activities that make use of natural and cultural resources. Eco tourism, natural resources, cultural heritage, rural lifestyle and an integrated tourism is a type of local economic activities. Therefore, ecotourism in naturel and culturel areas was carried out with a number of elements in their natural landscape and cultural landscape (water, vista, topography, vegetation, clean air), as well as in the variety of recreational activities suitable for all kinds of environments. Therefore, ecotourism and its natural assets and raw materials to create, as well as directing people to travel is an attractive force.
Ecotourism helps in community development by providing the alternate source of livelihood to local community which is more sustainable. Its aim is to conserve resources, especially biological diversity, and maintain sustainable use of resources, which an bring ecological experience to travelers, conserve the ecological environment and gain economic benefit. However, achieving the aims in ecotourism depends on whether they are environmentally and ecologically sustainable and economically applicable. Ecotourism helps in involving local community for the conservation of the ecology and biodiversity of the area that biodiversity in return provides the economic incentives to the local community. Eco-tourism contributes to conservation of biodiversity; sustains the well-being of local people; involves responsible action on the part of tourist and the tourism industry; promotes small and medium tourism enterprises; requires lowest possible consumption of natural resources; stresses local participation, ownership, and business opportunities, particularly for rural people; and above all includes the learning experiences.
In order for ecotourism to encourage patterns of sustainability, which can benefit local communities, protect the environment, and be economically viable, it must be comprehensive and account for the complexity of issues that have been mentioned in this paper.
This chapter has revealed that there is a need for sustainable development in tourism, and the connection between tourism and environment is much stronger than in other sectors. Ecotourism must account for social, economic and environmental implications, in order to succeed. The purpose of this study look at ways in which ecotourism and sustainable development can be evaluated; and suggest ways to improve current ecotourism practices. In parallel with this purpose, it was aimed at looking for an answer to questions of: What is Ecotourism? “What might be the effects of ecotourism?” What are the impacts and challenges of ecotourism? What are the possible benefits that ecotourism can bring? Within this scope, we focused on ecotourism’s definition, its objectives, the reasons of its emergence and development, its principles, its types, its environmental, social and economic impacts; ecotourism and sustainable development and on the examination of approaches to ecotourism in Turkey and Europe.
In this section, the subjects below will be discussed.
Introduction
What is ecotourism and its types?
What is sustainable development?
Ecotourism and environmental, social and economic impacts
Ecotourism and sustainable development relationship
Ecotourism – examples of implementation
2. What is ecotourism and its types?
Ecotourism, a unique subset of the tourism industry, is ‚focused on the enhancement or maintenance of natural systems through tourism. Ecotourism means different things to different people. To some, it is the general term that encompasses nature‐based, adventure, soft adventure, and cultural tourism. The term ecotourism was coined in 1983 by “Hctor Ceballos Lascurain” a Mexican environmentalist, and was initially used to describe nature-based travel to relatively undisturbed areas with an emphasis on education. Ecotourism guarantees the sustainable use of environmental resources, while generating economic opportunities for the local people ( Farrell & Runyan 2001 ; Bhattacharya, Chowdhury and Sarkar, 2011 ).
Ecotourism itself is meant to be a sustainable form of natural resource-based tourism. Even though ecotourism lacks a concrete definition, there are many wellrecognized definitions that have formed a clear picture of its core principles, which are shown in Table 1 .
Definitions of ecotourism
The (International) Ecotourism Society in 1990: Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people in 1996 by the World Conservation Union (IUCN) which describes ecotourism as: Environmentally responsible travel and visitation to natural areas, in order to enjoy and appreciate nature (and any accompanying cultural features, both past and present) that promote conservation, have a low visitor impact and provide for beneficially active socio-economic involvement of local peoples ( Joshi, 2011 )
Ecotourism tries to raise environmental consciousness by exploring ecology and ecosystems and by providing environmental type experiences. Taking part in ecology actively and getting first hand impressions of how ecosystems work influence peoples’ ways of thinking, which finally raises awareness of conservation and protection ( Ecotourism – Sustainable Tourism in National Parks and Protected Areas, 2005 ).
According to Patterson (2002 ), characteristics of an ecotourism business are that it:
Have a low impact upon a protected area’s natural resources and recreation techniques.
Involve stakeholders (individuals, communities, ecotourists, tour operators and government institutions) in the planning, development, implementation and monitoring phases
Limits visitation to areas, either by limiting group size and/or by the number of groups taken to an area in a season
Supports the work of conservation groups preserving the natural area on which the
experience is based.
Orients customers on the region to be visited.
Hires local people and buys supplies locally, where possible.
Recognizes that nature is a central element to the tourist experience.
Uses guides trained in interpretation of scientific or natural history.
Ensures that wildlife is not harassed.
Respects the privacy and culture of local people.
According to Chesworth (1995 ), Ecotourism has six characteristics. These are: a) ecotourism involves travel to relatively undisturbed natural areas and/or archeological sites, b) it focuses on learning and the quality of experience, c) it economically benefits the local communities, d) ecotourists seek to view rare species, spectacular landscapes and/or the unusual and exotic, e) ecotourists do not deplete resources but even sustain the environment or help undo damage to the environment, and f) ecotourists appreciate and respect local culture, traditions, etc.
It focuses primarily on experiencing and learning about nature, its landscape, flora, fauna and their habitats, as well as cultural artifacts from the locality. A symbiotic and complex relationship between the environment and tourist activities is possible when this philosophy can be translated into appropriate policy, careful planning and tactful practicum ( Rahman, 2010 ).
While the details vary, most definitions of eco-tourism boil down to a special form of tourism that meets three criteria:
it provides for environmental conservation;
it includes meaningful community participation;
it is profitable and can be self-sustained
As shown in Fig 1 , there is just a thin line of differentiation between sustainable tourism and ecotourism, which also shows that there is as such no absolute boundary between sustainable and unsustainable tourism ( Eriksson, 2003 ). According to Weaver (2001) ; Ecotourism exists within the broader classification of tourism types which, at an initial level, can be divided into ‘mass tourism’ and ‘alternative tourism’ ( Figure 1) . Mass tourism is seen as the more traditional form of tourism development where short-term, freemarket principles dominate and the maximization of income is paramount. The differences between mass tourism and ecotourism are shown in Table 2 .

Conceptual model of tourism ( Eriksson,2003 )
Ecotourism as a very specific form is part of the broad concept of nature-based tourism, or it can be said that ecotourism describes a nature-based operation in the field of tourism. “The most obvious characteristic of Ecotourism is that it is nature based” Figure 2 ( Weaver (2001 );
Distinct characteristics between mass tourism and ecotourism ( Dorobantu & Nıstoreanu, 2012 )

Relationship of ecotourism to other forms of tourism ( Hill & Gale, 2009 )
Adventure tourism is defined as: “an outdoor leisure activity that takes place in an unusual, exotic, remote or wilderness destination, involves some form of unconventional means of transportation, and tends to be associated with low or high levels of activity” ( Fennel & Dowling, 2003 ). According to this definition of adventure tourism and to that of ecotourism as previously stated, it seems that there are many overlapping concepts.
Ecotourism is a component of sustainable tourism. In many ways, sustainable tourism exemplifies the relationship between ecotourism and sustainable development ( Sâmbotın et al., 2011 ; Bansal & Kumar, 2011 );
Sustainable tourism will focus on three areas:
Quality – valuable experience for visitors and increased life quality for host communities through cultural identity, poverty reduction and environmental quality;
Continuity – exploitation is made at the optimum level that allows the preservation and regeneration of the natural resources;
Balance between the needs of tourism industry, environmental protection, and local communities by an equitable distribution of benefits among stakeholders
Standarts of ecotourism ( Weaver & Lawton, 2007 );
Protection of the Ecosystem
Maintenance of the ecosystem where the ecotourism attraction is located
Protection and maintenance of wildlife especially endangered species
Wildlife live harmoniously with people
Maintenance of the physico-chemical conditions of the area
Maintenance of the quality of fresh water and marine resources
No wastes overflow and contamination of the environment (water, soil and air)
Conservation of local culture and history
Culture of locality is maintained
Historical structures are maintained as part of cultural heritage
Infrastructures and signboards blend with the environment
Sustainability
Maintenance of Carrying Capacity of the environment;
Environmental education program is part of the ecotourism package;
Livelihood must benefit more the local community than outside entrepreneurs;
The local government supports the ecotourism project through ordinances and resolutions; and
The Management Board (community-based) and appropriate government agencies, e.g. DENR, support the project through strict enforcement of environmental laws
Experience and product management should follow principles and practices associated with ecological, socio-cultural and economic sustainability.
Many dimensions clearly emerge from these widely stated definitions including ( Matthews, 2002 )
Ecotourism occurs in natural areas (most often protected areas) and/or places of unique ecological or cultural interest
Ecotourism contributes to conservation or preservation of the natural resources and promotes stewardship of natural and cultural resources.
Ecotourism should create necessary funds to promote permanent protection of ecological and socio-cultural resources
The local residents accrue economic and social benefits thereby contributing to project’s long-term success.
Ecotourism incorporates environmental and cultural education.
Ecotourism should be effectively managed for the long-term through minimal negative impacts on the host environment.
Ecotourism should provide a quality tourism experience.
These principles and standards must be put in place by those who develop ecotourism products, as well as those who plan the development of an area-based ecotourism. In ecotourism branch a special place is given by the marketing concept. The importance of proper marketing is widely recognized throughout the tourism sector that today tourism market has become increasingly segmented over the methods of communication to reach consumers have multiplied and diversified ( Boghean & Boghean, 2006 ).
3. What is sustainable development?
The concept of sustainability first appeared in the public scene in the report put out by the World Commission on Environment and Development (Brundtland Commission) in 1987. The commission report advances the idea of sustainable development by noting that economic growth and environmental conservation are not only compatible but they are necessary partners. One cannot exist without the other ( Harris et al., 2002 ).Sustainable development is high potential for any community within economic, social, cultural, ecologic and physical constraints ( Bhuiyan et al., 2012 ). Sustainable development has been defined in many ways, but the most frequently quoted definition is from Our Common Future, also known as the Brundtland Report:
"Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It contains within it two key concepts ( IISD, 2012 ):
The concept of needs, in particular the essential needs of the world's poor, to which overriding priority should be given; and
The idea of limitations imposed by the state of technology and social organization on the environment's ability to meet present and future needs."
Van der Merwe & Van der Marwe (1999) add that Sustainable development is a program for changing the process of economic development so that it ensures a basic quality of life for all people and at the same time protects the ecosystems and community systems that make life possible and worthwhile.
This was the dominant dilemma addressed by the Brundtland Commission which indicated that sustainable development should, as a minimum, address the following elements ( Wall, 2007 );
Maintenance of ecological integrity and diversity;
Meet basic human needs;
Keep options open for future generations;
Reduce injustice; and
Increase self-determination.
It was further suggested that in order for this to occur, it would be necessary to:
Revive economic growth;
Change the quality of growth;
Meet essential needs such as for jobs, food, energy, water and sanitation;
Conserve and enhance the resource base;
Reorient technology and manage risk; and
Merge environment and economics in decision making.
Defined sustainable development as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It is often called intergenerational equality, the idea is that we should share natural resources not just with people who are alive on the planet today but also with future generations of the earth’s inhabitants. Sustainable development integrates economic, social with the aforementioned environmental goals. Sustainability highlights on the resource conservation ( Dixon & Pretorius, 2001 ; Mebratu, 1998 ; Jaini, Anuar & Daim, 2012 ). Dixon & Pretorius (2001 ) cite the International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives (ICLEI), which emphasizes environmental, social and economic concerns as three distinct but interrelated components of sustainable development.
According to Hall (2008 ) sustainable development and tourism present change which refers to the movement from one state or condition to another. Whether such a transition is positive or negative depends on the original criteria by which change is measured. Sustainable tourism requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving it requires monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective measures whenever necessary. Sustainable tourism should also maintain a high level of tourist satisfaction and ensure a meaningful experience to the tourists, raising their awareness about sustainability issues and promoting sustainable tourism practices amongst them ( World Tourism Organisation, 2001 ).
Sustainable development through ecotourism is a concerning issue in the world today. Many countries have ensured their regional development by this concept. In this concept, sustainable development may be occurred by the ecotourism and regional development ( Figure 3) simultaneously in an area. Dimensions of ecotourism development refer to the environmental, economic, and social aspects of tourism development, and a suitable balance between these dimensions must be established to maintain its long-term sustainability ( Bhuiyan et al, 2012 ).

Sustainable development throught ecotourism ( Bhuiyan et al., 2012 )
4. Ecotourism and environmental, social and economic impacts
Tourism can be sustainable if development meets the needs of tourists and local residents while protecting future opportunities. Ecotourism offers benefits for local residents, conservation, development and educationalexperiences. Ecotourism is a sustainable form of natural resource-based tourism. It focuses primarily on experiencing and learning about nature, its landscape, flora, fauna and their habitats, as well as cultural artefacts from the locality ( Dowling,1997 ; Fennell, 1999 ).
Ecotourism entails a combination of conservation and tourism (the economics related with it) to benefit local communities, especially focusing on sustainability ( Myburgh & Saayman, 2002 ).
Natural and cultural landscape values form a basis for ecotourism. These values are geographical position, microclimatic conditions, existence of water, natural beauties, existence of natural vegetation, existence of wildlife, surface features, geomorphologic structure, local food, festivals and pageants, traditional agricultural structure, local handicrafts, regional dress culture, historical events and people, heritage appeals, architectural variety, traditional music and folk dance, artistic activities and so on ( Gerry, 2001 ; Lane, 1993 , Lanquar, 1995 ; Soykan, 1999 ; Brıassoulis, 2002 , Catibog-Sinha & Wen, 2008 ; Mlynarczyk, 2002 ; Drzewiecki, 2001 ; Kiper, 2006 ).
Ecotourism operates for one or more of the eco-friendly alternatives for the economic use of natural resources compared with mining, hunting, farming and so on ( Li, 2006 ). Ecotourism promotes an enhanced appreciation of natural environments and environmental education by exposing visitors and locals to nature and conservation ( Bob et al., 2008 ).
Ecotourism is largely perceived to safeguard natural areas and thereby to contribute to the conservation of biodiversity. It focuses primarily on experiencing and learning about nature, its landscape, flora, fauna and their habitats, as well as cultural artefacts from the locality. In ecotourism planning the first issue that emerges is the environment and its conservation ( Munn, 1992 ; Ceballos-Lascurain, 1996 ; Gössling, 1999 ; Tisdell & Wilson, 2002 ; Lindsey et al., 2005 ; Lopez-Espinosa de los Monteros, 2002 ; Fung & Wong, 2007 )
An ecotourism destination must in no way be developed without planning in terms of environmental concern ( Rahman, 2010 ). Within the ecotourism implementation existence of water resources creates advantages in terms of both visuality and utilization. Climatic features of a region influence tourism directly and indirectly and play a crucial role in the development of tourism. Plants drawing interest thanks to their size, age or appearance are other appealing components of ecotourism. Flowering plants are important resources in ecoturism. Historical, natural and folkloric values are important sources for ecotourism. According to Soykan, traditional commercial products are one of the most significant appeals leading to development of ecotourism in a region. This is because whole production process from planting to harvest and processing bear cultural differences, and most of them are performed in traditional ways ( Kiper, 2011 ).
Ecotourism has the potential to seriously impact local communities, largely due to the tendency of ecotourists to have a greater interest in the culture and nature of the areas they visit, as compared to mass tourists ( McMinn, 1997 ).
Ecotourism destinations are always environmentally sensitive because ecotourism activities directly involve various environmental phenomena including bird watching, trekking, mountaineering, horse riding and elephant riding within the forest wilderness trail, staying in natural caves, studying about flora and fauna, simple bush walking, fishing, animal behavior study, ecological studies ( Rahman,2010 ). Ecotourism always incorporates various activities in nature (hiking, mountain climbing, observing the living beings in their natural habitat, etc.), but it may include cultural activities, too. Ecotourism is an important educational component, it is a chance to learn respect for nature, for the local culture, and for some it is a chance to self-reflection being inspired by the beauty of the surroundings.
5. Ecotourism and sustainable development relationship
Tourism is a highly complex activity and thus requires tools to assist in effective decision making to come to terms with the competing economic, social, and environmental demands of sustainable development ( Fadahunsi, 2011 ). Table 3 indicates some interesting examples of potential risks from tourism activities, which are especially crucial in naturel and culturel areas.
Potential Risks from Tourism (Ecotourism – Sustainable Tourism in National Parks and Protected Areas, 2005)
Ecotourism has been regarded as a panacea for solving many of the environmental and economic problems of lessdeveloped nations. Yet, regardless of how socially and environmentally responsible ecotourism may be in theory, in practice it remains rooted in the tourism industry ( Wall, 1997 ). Similarly, tourism activities generally can create various negative impacts on the surrounding environment. Increased human interference in ecologically fragile areas can cause irreversible change in the existing ecological processes. These problems can be reflected in degrading natural resources, vegetation structure and the size of the habitat patch, increasing deforestation and decreasing upstream water flow ( Tourism Queenland, 2002 ).
Ecotourism is rooted in the concept of sustainable development, as defined by the World Commission on Environment and Development’s Brundtland report (1987) ( Place, 1995 ; King & Stewart, 1992 ; McMinn, 1997 ; Stem et al., 2003 ). According to the emergence of sustainable tourism development it is proven that the milestone for its emergence was the Brundtland Report by the WCED in the year 1987. Previously, many ideas in this field had been developed at the IUCN -The World Conservation Union and referenced in the World Conservation Strategy published in 1980 ( Ritchie & Crouch, 2003 ). Ecotourism is often perceived as an tool for promoting sustainable development in developing countries. Ecotourism helps in community development by providing the alternate source of livelihood to local community which is more sustainable. Many view ecotourism as a viable way to protect the natural environment and create social and economic benefits for local communities. Ecotourism encompasses a spectrum of nature-based activities that foster visitor appreciation and understanding of natural and cultural heritage and are managed to be ecologically, economically and socially sustainable. Therefore, ecotourism is accepted as an alternative type of sustainable development. Ecotourism has attracted increasing attention in recentyears, not only as an alternative to mass tourism, but also as a means to promote a country’s economic development and environmental conservation. Its aim is to conserve resources, especially biological diversity, and maintain sustainable use of resources, which can bring ecological experience to travelers, conserve the ecological environment and gain ( Bansal & Kumar, 2011 ; Godratollah et al., 2011 ; Tewodros, 2010 ). Ecotourism is increasingly being lauded as a sustainable development option for rural communities, one that is able to spur economic development ( Vogt, 1997 ) and instill environmental protection at the same time ( Cater, 2002 ). If the environment has not at least achieved a net benefit toward its sustainability and ecological integrity, then the activity is not ecotourism.
Many groups have proposed sets of guidelines or principles for sustainable tourism and ecotourism. Ecotourism is a sustainable version of tourism in natural areas, including at the same time elements of rural and cultural tourism. Besides subscribing to the principles of sustainable tourism, ecotourism has specific principles: it contributes actively to the conservation of natural and cultural heritage, it includes local communities in planning, development and operation activities, and it contributes to their welfare, it involves complete and interesting explanations for visitors, regarding the natural and cultural resources, it is intended mainly to individual visitors and also to small organized groups ( Sâmbotın et al, 2011 ). According to Buchsbaum 2004 ; in many ways, sustainable tourism exemplifies the relationship between ecotourism and sustainable development. Many groups have proposed sets of guidelines or principles for sustainable tourism and ecotourism Tourism Concern and the World Wildlife Fund for Nature developed a wellknown list of principles and guidelines in 1991, which are presented in Table 4 .
Principles for Sustainable Tourism ( Blamey, 2001 ).
Medina (2005 ) explains that a criterion for sustainable tourism should include indicators of social and economic sustainability adding up to indicators of environmental sustainability. In addition, Wall (1997) has argued that for tourism to contribute to sustainable development it must be economically viable, environmentally sensitive and culturally appropriate, and the forms that this might take are likely to vary with location. The following table 5 . develops sustability goals of ecotourism. Achieving sustainable tourism—defined here as tourism that is ecologically benign, economically feasible and socially acceptable—is thus contingent on environmental protection and reconciling tourism activities with local socio-economic values ( Brown et al., 1997 ).
Three systems of sustainability in ecotourism development (According to Wall 1997; Alexander and Whitehouse 2004; ( Jiang 2008 ).
These criteria include quantification of environmental performance for most of the key environmental indicators. This allows recognition and encouragement of ecotourism product that makes measured environmental improvements which result in a more sustainable world (http://www.ecoroute.eu/brochures/Report_SW_Europe_draft30-04-2004.pdf. Review of criteria, procedures and legal framework for ecotourism in Europe).
According to Rome (1999 ); Ecotourism is one strategy for supporting conservation and providing income for communities in and around protected areas. It can contribute to economic development and conservation of protected areas by: a) generating revenues that can be used to sustainably manage protected areas, b) providing local employment and c) inculcating a sense of community ownership. However, without careful planning and management that balance ecological, social, and economic objectives, it may lead to environmental damage. Furthermore, envisioned as a positive approach towards sustainable development, unplanned or poorly planned and implemented tourism can have serious negative effects, offsetting the benefits it was designed to provide. Even the potential local benefits of ecotourism can lead to environmental damage to a protected area.
The core set of eight principles are that ecotourism product should: ( The Green Globe 21 International Ecotourism Standard , 2004 )
Focus on giving visitors the opportunity to personally and directly experience nature (Natural Area Focus);
Provide opportunities to experience nature in ways that lead to greater understanding, appreciation and enjoyment (Interpretation);
Represent best practice for environmentally sustainable tourism (Environmental Sustainability Practice);
Contribute directly to the conservation of natural areas (Contribution to Conservation);
Provide ongoing contributions to the local community (Benefiting Local Communities);
Be sensitive to, interpret and involve the culture/s existing in the area (Cultural Respect);
Consistently meets consumer expectations (Customer Satisfaction) ; and
Be marketed and promoted honestly and accurately so that realistic expectations are formed (Responsible Marketing).
One of the most influential ecotourism documents, the Quebec Declaration on Ecotourism (2002), produced after the World Ecotourism Summit during the International Year of Ecotourism, recognized that not only does ecotourism embrace the principles of sustainable tourism but it also embodies the following specific principles: (1) contributes actively to the conservation of natural and cultural heritage; (2) includes local and indigenous communities in its planning, development and operation, and contributes to their well-being; (3) interprets the natural and cultural heritage to visitors; (4) encourages independent travelers, as well as organized tours for small size groups. TIES’ (2010) asserts that those involved in ecotourism should follow six principles: (1) minimize impact; (2) build environmental and cultural awareness and respect; (3) provide positive experiences for visitors and hosts; (4) provide direct financial benefits for conservation; (5) provide financial benefits and empowerment for local people; and (6) raise sensitivity to hosts’ cultures political, and social climate)( McLaughlin, 2011 ).
The participants at the World Ecotourism Summit, held in Quebec in May 2002, have acknowledged that ecotourism respects the principles of sustainable tourism referring to the economic, social and environmental impact, with some further specific principles ( Sâmbotın et al, 2011 );
Ecotourism actively contribute to the conservation of natural and cultural heritage.
Ecotourism include local communities in the activities of planning, development and operation, and it contributes to
their welfare.
Ecotourism involves complete and interesting explanations for visitors, regarding the natural and cultural resources.
Ecotourism is intended mainly for individual visitors and small organized groups.
According to Ramwell and Henry (1996) point out four basic principles of sustainable development and sustainable ecotourism tourism development (Yogi, 2010).
Holistic and strategic planning
Conservation of essential ecological system
Conservation of both human (cultural) and natural heritage
Long term development and productivity for the future generation.
So both sustainable tourism and sustainable development focuses on the same key issues of ecology, society, and a systemic process of development that is guided by strategic planning ( Yogi, 2010 ).
6. Ecotourism – examples of implementation
More tranquil, natural and original spaces are preferred to ordinary tourism centers. Likewise, individuals have begun to prefer activities, which they can particularly perform in naturel and culturel areas and with which they can learn original cultural values and be within the nature, instead of sea-sand-sun tourism. Ecotourism has increased very quickly in recent years especially in developing countries. These are highlighted in Table 6 and pertain to economic aspects, impacts on culture, environmental concerns and development. In the Tourism Strategy of Turkey-2023 and the Ninth Development Plan (2007-2013), it is aimed to utilize natural, cultural, historical and geographical values of Turkey based on conservation-use balance, to increase the share of Turkey from tourism and to promote the attractiveness of regions via alternative tourism types like ecotourism ( Tourism Strategy of Turkey-2023 , 2007; Ninth Development Plan, 2006 ).
Ecotourism is implemented differently around the world, and the impacts on native cultures vary similarly. It is universal that tourism is a crucial industry to provide economic support to developing countries. An international pact in 1996 designated the tourism industry as the paramount economic growth strategy within Central America ( Moreno, 2005 ). At this point, “Ecotourism” activities have particularly recently become sectors which can create great changes both in socio-cultural and economic aspects.
Effects of eco-tourism in international countries ( Watkin, 2003 ; Kiper, Özdemir, Sağlam, 2011 )
Ecotourism activities have been sorted into the following categories: ( Economic Development Branch BC Ministry of Sustainable Resource Management, 2003 )
Marine Ecotourism
marine cruising including sailing, yacht and power cruising
sea kayaking tours
Land based Ecotourism
Bicycle Touring/Mountain Biking
Horseback Trail Riding
Hiking/Backpacking/Trekking
Freshwater River Rafting, Canoeing and Kayaking
Winter Tourism (Back Country /Tour Skiing, Dog Sledding, Snow Shoeing)
Walking, camping, boating, hunting, sight-seeing, swimming, cultural activities, observing wildlife and nature, skiing, visiting historical places, and horse riding among
The general trend in ecotourism is to increase experiences by encouraging activities such as long-distance walking, camping, boating, hunting, sight-seeing, swimming, cultural activities, bicycling, observing wildlife and nature, skiing, visiting historical places, and horse riding among others. Generally, instructive activities, for example, wildlife observation, participation in festivals, cultural activities and nature landscapes, attract most attention. Activities like hiking, outdoor sports, picnic, paragliding arranged according to different areas of interest influence the preferences of many visitors ( Kiper, 2011 ; Cengiz, 2007 ). According to Soykan, for Europeans rural roads are natural and cultural heritages. This is because they have natural, economic and cultural identities. Some give us opportunity to familiarize with local planting patterns by passing through agricultural lands, some lie among virgin natural areas with beautiful views (e.g. forests, rivers, lakes) and some connect the settlements which have unique cultural monuments. Therefore, in many countries in Europe (specifically Austria, Switzerland and France, which have mountainous areas) long distance trekking is well-organized ( Kiper, 2011 ).
In order for ecotourism to have a sustainable development, the analyses for determining land use suitabilities gain importance. It and other similar methods set standards or ranges of acceptable change and describe a methodology for determining these standards, measuring impacts and identifying management strategies for controlling negative impacts. They include ve includeIn recent years resources assessments have adopted oppottunity spectrum methods.
Opportunty spectrum this group includes ( Fagence, 2001 ; Rome, 1999 ) ;
ROS (Recreation Opportunty Spectrum)
TOS (Tourism Opportunty Spectrum)
LAC (Limits of Acceptable Change)
TA (Threshold Analysis, and more recently UET-ultimate environmental thresholds)
ECOS (Ecotourism Opportunty Spectrum)
Limits of Acceptable Change (LAC)
Visitor Impact Management (VIM)
Visitor Experience and Resource Protection (VERP)
Tourism Optimisation Management Model (TOMM)
The ECOS model ( Table 7) has been developed especially to cope with the peculiar needs of planning for ecotourism the capture of ecolpgical base-line data is the important first step.
Refinement to ECOS assesments could include
Landscape assesments (to differentiate geographical sectors according to their principal ecotourism resources, stages of “naturalness/change, levels of ecotourist interest)
Attractiveness indices ( to differentiate according to uniqueness, international drawing power, primacy-a measure of comparative attraction)
Resource status (to differentiate according to the degree of disturbance of the natural resource, and any circumstance which might impede its sustainability or cause its attractiveness to be forfeited –a form of carrying capacity assesment)
Conservation potential (including rehabilitation potential)
Marketing assesments (combining some of the other assessments according to an aggregation of attractiveness for particular consumer/tourist market segments –to interpet the feasibility of capturing and sustaining tourist interest)
This data is then assessed or measured in terms of the capacity to be used in ecotourism, with the assessment focusing on eight important factors:
ECOS models ( Fagence, 2001 )
Also, “Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods” are used widely in detecting land use suitabilities. The integration of ELECTRE, to give the order of precedence of uses, with GIS, a quite important means in spatial planning studies, will enable to reach successful results. Studies for determining the suitabilities for use of a land for ecotourism will also determine the development of the land in the following years and the sustainability of its resource values.
In the eco-tourism plans, diversifying economic and ecologic activities by starting and developing organized eco-tourism practice, enhancing the life quality of the locals with the economic gains provided by eco-tourism, increasing the participation of habitat conservation, improving environmental conscious, conserving natural, cultural and historical landscape values and passing them onto the next generation and popularizing ecotourism planning with the support and participation of responsible and related organizations should be aimed. Good planning of natural and cultural elements that create resources for eco-tourism activities and their management will make important contributions to the local public. ( Gültekin, 2010 ).
While envisioned as a positive approach towards sustainable development, unplanned or poorly planned and implemented tourism can have serious negative effects on the environment and on communities, offsetting the benefits it was designed to provide. In order to anticipate negative impacts and to prevent or mitigate them, ecotourism impacts monitoring is required. The sample of potential ecotourism monitoring ındicators are shown in Table 8 .
A sample of potential ecotourism monitoring ındicators ( Rome, 1999 )
7. Conclusion
Various tendencies also occur in the understanding of tourism upon changing living conditions. More tranquil, natural and original spaces are preferred to ordinary tourism centers. Likewise, individuals have begun to prefer activities, which they can particularly perform in naturel and culturel areas and with which they can learn original cultural values and be within the nature, instead of sea-sand-sun tourism. At this point, “Ecotourism” activities have particularly recently become sectors which can create great changes both in socio-cultural and economic aspects. Main purpose is not only ensuring the socio-economic development but also the protection of natural and cultural landscape values to ensure awareness of nature conservation on the other hand.
Ecotourism should be seen in direct relation to nature conservation (protected areas), with preservation of the authentic and involving local communities in all stages of the process. Development process is a lengthy process, which requires a sustained effort from all those involved but can bring major benefits in the long term, contribute directly to the creation of "sustainable existing 'target area ( Roxana, 2012 ).
Ecotourism is about ( Roxana, 2012 );
environmentally responsible travel to relatively undisturbed natural areas,
travel in order to enjoy, study and appreciate nature,
the promotion of conservation,
combining sustainable development with the natural environments,
the use of natural assets and resources in ecologically sensitive areas to create unique visitor experiences with minimal impact on the area.
After research we can draw the main conclusions of this work, as it follows: ( Sâmbotın, 2011 )
Ecotourism is a form of tourism developed in natural areas, whose goal is to acknowledge and to appreciate nature and local culture, which includes conservation measures and ensures an active involvement, generating benefits for the local population;
Ecotourism clothes the sustainable tourism principles, but differs from it by aspects related to local community issues, interpretation for visitors to a particular destination, the number of visitors;
Tourism has a complex impact on the environment, but it is also generating both cost and benefits;
The interest of tourists for travel in natural areas (land or water) has increased recently;
Ecotourism contributes to increased revenues from tourism, but also to the positive social effects;
Worldwide, there are a large number of natural areas associated with a specific cultural diversity, resulting in particular through the perpetuation of the long traditions and customs;
Tourists have a certain responsibility towards the destination visited and the environment by their choice itself, behavior and activities performed in that space, and therefore it is important to be informed about the quality and sensitivity of destinations.
These principles should be envisaged both for lovers of this form of tourism and service providers of such eco-touristic products.
Basic purposes of ecotourism are to preserve and utilize natural and cultural resources in a sustainable way and to enable economic development of local people. However, achieving the aims in ecotourism depends on whether they are environmentally and ecologically sustainable and economically applicable. In order to achieve these, a participative tourism planning is required ( Kiper, 2011 ). Figure 4 illustrates the multiple and diverse elements essential for ensuring that communities fulfil their role in ecotourism development ( Drumm & Moore, 2002 ).

Essential elements for ecotourism in community setting
Now that ecotourism has reached such stature, it is especially important to scrutinize its effectiveness as a strategy for sustainable development, and search for ways to improve policies and practices. Clearly ecotourism is not a universal remedy; but its potential to promote sustainable development deserves considerable attention.
In conclusion, According to Kiper, Özdemir and Sağlam (2011 ); ecotourism activities which are not performed according to the purpose, the principles and the characteristics cause the disturbance in environmental, economic and socio-cultural fields due to over-intensification to be occurred especially in sensitive ecosystems like naturel and culturel areas. Therefore, in order to provide sustainability in the ecotourism, it is necessary to know environmental, social and economical effects of ecotourism activities and to consider these effects during the planning. Tourism planning purposes this. relationship between rational resources requirements Ensuring the sustainable use of natural (water, vista, topography, clean air, natural vegetation structure, microclimatic features of climate, marine and coastal topographic structure and motion, etc.) and cultural resources (Archeological heritage, Religious structures, Conventional architecture, Traditional social activities) to the evaluation of the physical planning decisions in the field of ecological planning strategies ( Dinç and Kocan, 2012 ). Additionally, According to Bunruamkaew & Murayama (2012 ); ecotourism development must promote educational development and create awareness in people of the need to jointly maintain the ecosystem of the area. There is a need to implement development plans and manage natural resources in a way that ensures ecological and environmental integrity. Environmental education and interpretation is the key to creating an enjoyable and meaningful ecotourism experience, and is one of the key points of differentiation between ecotourism and other tourism products. Successful interpretive components of ecotourism products will foster appreciation and support for conservation efforts, local communities and culture.
- 23. Economic Development Branch BC Ministry of Sustainable Resource Management 2003 Land Based Ecotourısm Wınter Actıvıtıes (Backcountry Skııng, Snowshoeıng, Dogsleddıng. Stuart Gale & Associates Pierce Lefebvre Consulting, 9 Online [Available]: http://www.al. gov.bc.ca/clad/strategic_ land/blocks/cabinet/tour_rec_winter.pdf.
- 24. Ecotourism- Sustainable Tourism in National Parks and Protected Areas 2005 Banff National Park in Canada and Nationalpark Gesause in Austria-a Camparison, 170 Online [Available]: www.np-gesaeuse. at/.../Obenaus_oJ_Ecotourism.pdf.
- 40. http://www ecoroute.eu/brochures/Report_SW_Europe_draft30-04- 2004 pdf. Review of Criteria, Procedures And Legal Framework For Ecotourism in Europe. Labels of Tourism in Europe
- 41. IISD 2012 What is Sustainable Development?. International Institue for Sustainable Development, Online [Available]: www.iisd.org/sd.
- 64. Ninth Development Plan (2007-2013) 2006 Online [Available]: http:// ekutup.dpt.gov.tr/plan/plan9.pdf
- 67. QuickStart Guide to a Tourism Business 2006 Ecotourism vs Nature Based Tourism, Tourism Western Australia. http://www.tourism.wa.gov.au/Publications%20Library/Growing%20Your%20Business/Ecotourism%20vs%20Nature%20Based%20Tourism%20 3 final).pdf.
- 76. The Green Globe 21 International Ecotourism Standard 2004 Review of criteria, procedures and legal framework for ecotourism in Europe. http://www.ecoroute.eu/brochures/Report_SW_Europe_draft30-04-2004.pdf
- 78. Tourism Queenland 2002 Queensland Ecotourism Plan 2003 2008 Tourism Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2002. Online [Available]: http://www.tq.com.au/fms/tq_ corporate/ special interests /ecotourism2/Queensland %20).
- 79. Tourism Strategy of Turkey-2023 2007 Ministry of Culture and Tourism, Ankara, Turkey, 60 p.
- 85. Weaver D.B & Lawton, L.J. 2007 Twenty years on: The state of contemporary ecotourism research. Tourism Management, 28 1168 1179
- 88. World Tourism Organisation 2001 Indicators for Sustainable Development for Tourism Organisations: A Guidebook. Madrid, Spain.
© 2013 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Edited by Murat Ozyavuz
Published: 01 July 2013
By Gülhan Benli
4800 downloads
By Nazan Kuter
7758 downloads
By Murat Özyavuz, Aslı B. Korkut and Ayten Özyavuz
3306 downloads

What Is Ecotourism?
Conservation, offering market-linked long-term solutions, ecotourism provides effective economic incentives for conserving and enhancing bio-cultural diversity and helps protect the natural and cultural heritage of our beautiful planet., communities, by increasing local capacity building and employment opportunities, ecotourism is an effective vehicle for empowering local communities around the world to fight against poverty and to achieve sustainable development., interpretation, with an emphasis on enriching personal experiences and environmental awareness through interpretation, ecotourism promotes greater understanding and appreciation for nature, local society, and culture., the definition., ecotourism is now defined as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” (ties, 2015). education is meant to be inclusive of both staff and guests., principles of ecotourism, ecotourism is about uniting conservation, communities, and sustainable travel. this means that those who implement, participate in and market ecotourism activities should adopt the following ecotourism principles:.
- Minimize physical, social, behavioral, and psychological impacts.
- Build environmental and cultural awareness and respect.
- Provide positive experiences for both visitors and hosts.
- Provide direct financial benefits for conservation.
- Generate financial benefits for both local people and private industry.
- Deliver memorable interpretative experiences to visitors that help raise sensitivity to host countries’ political, environmental, and social climates.
- Design, construct and operate low-impact facilities.
- Recognize the rights and spiritual beliefs of the Indigenous People in your community and work in partnership with them to create empowerment.
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Green Global Travel
World's largest independently owned Ecotourism / Green Travel / Sustainable Travel / Animal & Wildlife Conservation site. We share transformative Responsible Travel, Sustainable Living & Going Green Tips that make a positive impact.
What Is Ecotourism? (The History & Principles of Responsible Travel)

Disclaimer: This post may contain affiliate links. All hosted affiliate links follow our editorial policies .
What is ecotourism? How does it work? Why does it matter? And how can we, as travelers, put the core principles of ecotourism into practice?
In recent years, the growth of interest in responsible travel has outpaced that of traditional sun/sand tourism by an increasingly wide margin.
With some experts estimating that ecotourism now represents 11.4% of all consumer spending, these sorts of questions have become more and more common.
And, as we continue to see more negative impacts of mass tourism on beloved destinations around the world, the answers to these questions will become increasingly vital.
Part of the confusion surrounding sustainable travel is the plethora of names being used for it within the industry.
E cotourism, a movement that began to take shape back in the 1980s, is the oldest and most commonly used word for it.
More recent industry buzzwords include sustainable tourism, green tourism, nature tourism, responsible tourism, ethical tourism, mindful travel, conscious travel, pro-poor tourism, and many others.
Regardless of what you call it, the central concepts that these philosophies share in common are that the travel industry as a whole should adopt more environmentally friendly practices, protect the natural and cultural heritage of a destination, and support local communities.
With the United Nations designating 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development , this seems like a great time to deepen the conversation about what ecotourism is and why it’s important for the future of travel.
Here we’ll explain the definition of ecotourism, examine its history and evolution, explore its core principles and benefits, and look at 10 ways that each of us as responsible travelers can ensure our adventures ultimately make a positive impact.
READ MORE: How Mass Tourism is Destroying Destinations

- The Definition of Ecotourism
- A Brief History of Ecotourism
- Ecotourism in the ’90s & Beyond
- The Principles of Ecotourism
- Ecotourism Principles in Action
The Benefits of Ecotourism
- Other Articles on Ecotourism

THE DEFINITION OF ECOTOURISM
According to The Oxford English Dictionary , the word “ecotour” was first recorded in 1973, followed by “ecotourism” in 1982.
There, the word is defined as, “Tourism to areas of ecological interest (typically exotic and often threatened natural environments), especially to support conservation efforts and observe wildlife; spec. access to an endangered environment controlled so as to have the least possible adverse effect.”
Ecotourism was perhaps best defined in 1990 by Megan Epler Wood, the co-founder of The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) and author of six influential books on the subject.
Her latest, Sustainable Tourism on a Finite Planet: Environmental, Business and Policy Solutions , was released in 2017.
Now the director of the International Sustainable Tourism Initiative at Harvard, Epler Wood’s original definition was more simple and to the point. She described ecotourism as, “Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people.”
In simple words, the meaning of ecotourism is travel that makes a positive impact on both the ECO logy and ECO nomy of a given destination.
One mistake many people make is assuming that ecotourism is all about conserving nature and wildlife by any means necessary. But if a destination or business’ tourism development strategy does not actively provide concrete financial benefits for the indigenous people, it’s not truly ecotourism.
Other NGOs, such as The Center for Responsible Travel (CREST, whose co-founder Dr. Martha Honey also served as the Executive Director of TIES for four years), have since expanded on Epler Wood’s concept to provide more in-depth definitions of ecotourism.
CREST currently defines ecotourism as, “Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, socially and economically sustains the well-being of local people, and creates knowledge and understanding through interpretation and education of all involved (including staff, travelers, and community residents).”
Other responsible travel organizations may have their own take on what ecotourism is, but these three are the most significant definitions.
READ MORE: Megan Epler Wood on the Evolution of Ecotourism

A BRIEF HISTORY OF ECOTOURISM
Ecotourism’s earliest origins arguably began with the Sierra Club’s Outing program. Launched in 1901, these annual expeditions took hikers into the Sierra Nevada’s backcountry in order to show members natural wonders, “so that those persons could become active workers for the preservation of the forests.”
The modern movement began to take root in the environmental activism of the 1970s. Some sources suggest that the term ecotourism was originally coined by Mexican architect-turned-environmentalist Héctor Ceballos-Lascuráin . He used the word to describe traveling to undisturbed areas in order to enjoy their natural beauty and culture.
In 1981 Ceballos-Lascuráin became the founding president of the Mexican Association for the Conservation of Nature, the most influential Mexican NGO in the conservation arena. In 1984 he founded the first Mexican ecotourism agency, ECOTOURS.
His 315-page book on Tourism, Ecotourism, and Protected Areas was published in 1996 by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). He served for many years as an Ecotourism Advisor to both the IUCN and United Nations World Tourism Organization.
Megan Epler Wood was another one of the ecotourism movement’s earliest adopters. She was a young wildlife biologist hired by World Wildlife Fund founder (and former EPA director) Russell Train right out of grad school in the early ’80s.
Their all-star team at the time also included Russell Mittermeier (now President of Conservation International) and Thomas Lovejoy , who’s known as the “godfather of biodiversity.”
“In the 1980s the idea of sustainable development was new,” Epler Wood recalls. “There was a big conversation about finding ways to benefit local people who wanted to conserve natural areas. A few years later my husband and I lived in Colombia on a joint Fulbright scholarship. [We realized that] people visiting the rainforest were bringing a majority of the benefits those locals were seeing.
READ MORE: Top Ecotourism Destinations According to Experts

ECOTOURISM IN THE ’90s & BEYOND
After she returned home in 1988, Epler Wood went on to produce The Environmental Tourist for PBS. She started pitching conservation NGOs a documentary on ecotourism that would be “the very first global investigation of how tourism could contribute to conservation of natural resources and local well-being.”
When that project lost its funding, she tapped into her contacts and started The International Ecotourism Society. The organization’s goal was to contribute to the development of ecotourism as a viable tool for conservation, protection of bio-cultural diversity, and sustainable community development.
Epler Wood left TIES in 2002 to start her own consulting firm. She was replaced by Dr. Martha Honey, the veteran journalist/historian who wrote the seminal book, Ecotourism and Sustainable Development: Who Owns Paradise? in 1999. She was Executive Director of the organization from 2003 to 2006, and eventually founded the Center for Responsible Travel in Washington, DC.
I had the pleasure of interviewing Dr. Honey during a keynote presentation at the TBEX Travel Blogging Conference in Cancun, Mexico in 2014. When I asked about the changes she’s seen in the ecotourism industry over the past 20 years, Dr. Honey insisted that they were positive for the most part.
“It hasn’t lost or changed its core values, which are essentially that tourism should be done in a way that’s beneficial to environmental conservation and local communities and respectful of local cultures…The Slow Food movement, organic agriculture, travel philanthropy, concern about human trafficking and child sexual abuse, fair trade , carbon offsets, and animal welfare are all branches on the original tree.
There have been countless other ecotourism icons over the past 30 years, from Jonathan Tourtellot (NatGeo’s Destination Stewardship Center) and Jeff Greenwald (founder of Ethical Traveler) to eco-design authority Hitesh Meta.
Now ecotourism is considered one of the fastest-growing sectors in the travel industry (about 5% annually), accounting for around 6% of the world’s gross domestic product. Even as the market for traditional tourism grew stagnant, the UNWTO’s global forecast projected rapid growth in the ecotourism industry over the next decade.
READ MORE: Q&A With Dr. Martha Honey on Ecotourism

THE PRINCIPLES OF ECOTOURISM
Ecotourism is essentially all about bringing nature/wildlife conservationists, local communities, and the responsible travel industry together to ensure development focused on long-term sustainability rather than short-term profits.
The goal is to develop tourist accommodations, activities, and attractions that benefit everyone involved– the local flora/fauna, the local people, travel industry stakeholders, and travelers alike.
With this mission in mind, the ecotourism industry has collectively developed a number of core guiding principles over the past few decades. Although international regulation and accreditation have remained elusive, these guidelines provide a general blueprint for responsible tourism development.
Many of these principles align with those of the Global Sustainable Tourism Council , which developed an extensive list of criteria for sustainable destinations, hotels, and tour operators.
1. Build Environmental & Cultural Awareness
Education is a key aspect of ecotourism initiatives, for locals and visitors alike. Most of these efforts are focused on improving awareness, sensitizing people to environmental issues, and encouraging them to be conscious of their impact on the places they visit.
Some tour operators create conservation education programs for local schools. Many offer interpretative guides, naturalists, and guest lecturers to help deepen travelers’ understanding of their experiences.
Immersive interactions with local cultures are also becoming increasingly common. These experiences often emphasize interaction rather than a typical performer-audience relationship with visitors.
2. Design & Operate Low-Impact Eco Tours/Facilities
Remember the old environmental adage, “Take only pictures, leave only footprints”? Today’s ecotourism industry strives to take it one step further.
The focus is all about sustainability, minimizing the negative carbon footprint travel often leaves on the environment. But these days the big picture goal is to create positive, rather than merely neutral impact.
From using alternative energy sources and ensuring all building materials are locally sourced to limiting eco tour group sizes, conscious consideration should be made to ensure low impact at every stage, from development to implementation.
3. Provide Financial Benefits for Conservation
The idea of using the revenue generated by ecotourism to help fund the conservation of nature and wildlife is not a new idea. In fact, it dates back more than 100 years, to the creation of the US National Parks Service .
Referred to by documentarian Ken Burns as “America’s Best Idea,” this concept has since been applied to more than 6,000 national parks in nearly 100 different countries around the world.
When managed properly, ecotourism can help provide a revenue-generating alternative to urbanization, deforestation, unsustainable agriculture, and poaching. And though critics claim ecotourism often fails to deliver on its promise, recent scientific studies continue to illustrate its conservation benefits.
4. Provide Financial Benefits for Local People
Critics have similarly pointed out that some ecotourism initiatives have created more problems for local people than they solve. Poorly managed programs can lead to conflicts over land and resources, unfair profit distribution, and cultural exploitation.
This is what happens when the phenomenon known as greenwashing – the disinformation disseminated by an organization so as to present an environmentally responsible public image– rears its ugly head.
True ecotourism MUST provide financial benefits to local people, whether through direct (tours, admission fees, and donations) or indirect means (such as taxes on travel or accommodation). It generally works best when there is smaller scale, slower growth, and greater involvement by local communities in all steps of the tourism development process.
5. Support Human Rights
Ecotourism initiatives should always strive to support human rights, economic empowerment, and democratic movements in a given destination.
In addition to increasing awareness about sociopolitical and environmental issues facing a given destination, ecotourism initiatives should support local businesses and the rights of indigenous inhabitants to control their land and assets.
This principle is arguably the most problematic and contentious. Should tour companies or travelers boycott a given destination due to human rights abuses or unfair treatment of its indigenous population? In many cases, such boycotts don’t punish the powers-that-be nearly as harshly as the locals who rely heavily on tourism revenue to survive.
READ MORE: Why Responsible Travel Matters
ECOTOURISM PRINCIPLES IN ACTION
Becoming a more responsible traveler is the best way to ensure your adventures are positive for the local people and the planet.
Whe n the core principles of ecotourism are applied, it can stimulate financial growth in developing nations, strengthening the global economy.
Individually, one person taking these baby steps to going green might not seem to make much of an impact. But if we all take simple strides towards being more conscious of our choices, collectively we can m ake a world of difference. Here’s how!
Lightening up your load saves money on baggage fees and increases plane fuel-efficiency.
Pack items that can be washed in the sink and are quick drying so they can be worn multiple times during your trip.
We recommend (but do not receive compensation from) the ExOfficio brand, and wear it everywhere we travel.
Take shorter showers, turn off the faucet while shaving and brushing your teeth, and re-use towels for multiple days.
And NEVER use the hotel laundry, as they typically wash each guest’s clothes separately, even if there are only a few items.
READ MORE: The Best Travel Clothing For 7 Travel Styles (An Epic Guide)

SAVE ENERGY
When you leave your hotel room, turn off the lights, heat/AC and TV.
Consider leaving the “Do Not Disturb” sign on the door so that the housekeeping staff won’t clean your room every day.
This will save on harsh chemical cleaning supplies and the electricity of vacuuming and washing bed linens.
REDUCE/REUSE/RECYCLE
Take a BPA-free water bottle you can refill, use just one bar of soap for both sink and shower.
Return brochures and maps once you’re finished using them, and hold on to your trash until you find a place to recycle it.
Seek out indigenous artisans and learn about their craft.
When we were in the Riviera Maya near Coba, we saw tons of assembly line art.
But instead we wound up buying from a man who taught local children and tourists the ancient craft of Mayan pottery and distributed profits equally among families in his village.
READ MORE: What Is An Eco Lodge? A Guide to Eco-Friendly Accommodations

LEAVE ONLY FOOTPRINTS
Stick to marked trails to avoid harming native flora, and consider taking a bag to pick up trash along your journey.
Not only is it a great way to help keep the outdoors beautiful, but it also protects wildlife that might eat or get tangled in the garbage.
BE A TRAVELER, NOT A TOURIST
Take time to immerse yourself in the local music, art and cuisine. Embrace the cultural differences that make it unique.
Get to know the locals and how they view life. You might be surprised at the things you learn when you open your mind to new ideas!
HONOR LOCAL TRADITIONS
Some cultures have very different traditions from yours.
Women are forbidden to show skin in some Muslim countries. For some, being photographed in like having your soul stolen.
Understand and respect these traditions, or risk offending the people whose culture you’re there to experience.
READ MORE: Embracing the Culture of the Maasai People of Tanzania

Developing nations are badly in need of basic necessities most people take for granted.
Traveling gives you a unique experience that stays with you for the rest of your life.
In return, consider giving something back, such as bringing school supplies on tours in which you know you’ll interact with locals.
SHOP SMARTER
Read labels, and ask questions like “What is this item made from?”
All over the planet people sell items made from non-sustainable hardwoods, endangered species, and ancient artifacts.
It may be alright in their country to sell them, but you can still vote with your wallet by refusing to buy them.
READ MORE: The Problem with Animal Selfies

THE BENEFITS OF ECOTOURISM
To quote CREST founder Dr. Martha Honey during our Keynote session at TBEX Cancun in 2014, we earnestly believe that ecotourism is “ simply a better way to travel . ” Here’s a look at how this transformational approach to travel benefits conservation, increases cross-cultural understanding, and ultimately turns travelers into environmental advocates:
Benefits to Wildlife
To see how ecotourism benefits nature and wildlife, let’s look at endangered species such as African Elephants . Ivory from Elephant tusks is worth $1500 a pound on the black market, which has led to a dramatic increase in poaching.
But Elephants are worth 76 times more alive than dead . When you consider the revenue from wildlife photography tours , luxury safari camps, and other ecotourism offerings, a single Elephant is worth $1.3 million over the course of its lifetime!
Other heavily poached species, such as Lions and Rhinos , have shown to be similarly valuable alive. Ecotourism offers a long-term alternative to exploitation, generating sustainable revenue and ensuring better overall health of the ecosystem.
Benefits to the Environment
Nature reserves and national parks help prevent deforestation and pollution, while also protecting the habitat of endemic species.
The revenue that ecotourism provides can help replace profits from exploitative practices such as mining or slash ‘n’ burn agriculture. It can also help ensure the long-term financial viability of the area.
Naturalist guides also help travelers understand the value of a pristine ecosystem, and teach them about the importance of conservation. This ultimately help to create a more mindful and conscious legion of travelers.
Benefits to Local People
When managed properly, ecotourism can offer locals alternative revenue streams. In wildlife-rich countries such as Rwanda , former poachers are often employed as guides or trackers, capitalizing on their knowledge of the animals and their habitat.
In Costa Rica , unemployment has fallen to less than 10% since the country started building its ecotourism infrastructure in the 1970s. The country now enjoys the highest standard of living in Central America .
Involving local communities in tourism management empowers them by ensuring that more revenue is reinvested locally. Ecotourism also offers indigenous peoples an opportunity to remain on ancestral land, conserve it, and preserve traditional culture.
Benefits to Travelers
In the words of United Nations Secretary General Talib Rifai, the Year of Sustainable Tourism provided “a unique opportunity to advance the contribution of the tourism sector to the three pillars of sustainability– economic, social and environmental– while raising awareness of the true dimensions of a sector which is often undervalued.”
Sure, being a responsible traveler takes a greater level of commitment to being conscious and mindful of the impact we have on the destinations we visit. But ecotourism also offers us incredible, transformative experiences, allowing us to develop closer personal relationships to the nature, wildlife, and local people we encounter during our adventures.
Learning about ecotourism during my life-changing experience in South Africa in 2000 permanently changed my understanding of mankind’s role in our planetary ecosystem. And I firmly believe that, once you’ve had that sort of travel experience, you’ll never want to travel the traditional way again. –Bret Love; photos by Bret Love & Mary Gabbett unless otherwise noted

OTHER ARTICLES ON ECOTOURISM
How Mass Tourism is Destroying Destinations Travelers Love
Why Responsible Tourism is Better
7 Harmful Practices Tourists Should Never Support
Why Slow Travel is Better
Why Community Based Tourism is Vital to Responsible Travel
What Is An Eco Lodge? A Guide to Eco-Friendly Accommodations
What Is Glamping? An Intro to Luxury Camping
10 Steps to Becoming a More Responsible Traveler
Green Travel Tips: The Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Travel
How to Choose a Green Hotel
How to Choose a Responsible Scuba Diving Tour Operator
How to Eat Ethically When You Travel
Top 10 Latin American Ecotourism Adventures
Top 10 Off the Beaten Path Ecotourism Destinations
Ecotourism in Costa Rica
Ecotourism in Jordan
Ecotourism in Antarctica
Ecotourism in Australia
Ecotourism in Cancun
Ecotourism in Egypt
Ecotourism in Ireland
Ecotourism in Jamaica
Ecotourism in New Zealand
Ecotourism in Northern Italy
Ecotourism in Sabah, Borneo
Ecotourism in Spain
Ecotourism in Taipei
Ecotourism in Tonga

About the Author
Green Global Travel is the world's #1 independently owned ecotourism website encouraging others to embrace sustainable travel, wildlife conservation, cultural preservation, and going green tips for more sustainable living.
We've been spotlighted in major media outlets such as the BBC, Chicago Tribune, Forbes, The Guardian, Lonely Planet, National Geographic, Travel Channel, Washington Post and others.
Owned by Bret Love (a veteran journalist/photographer) and Mary Gabbett (business manager/videographer), USA Today named us one of the world's Top 5 Travel Blogging Couples. We were also featured in the 2017 National Geographic book, Ultimate Journeys for Two, for which we contributed a chapter on our adventures in Rwanda. Other awards we've won include Best Feature from both the Caribbean Tourism Organization and the Magazine Association of the Southeast.
As Seen On…

Join the 300,000+ people who follow Green Global Travel’s Blog and Social Media
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends
1 Department of Management Science and Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030 China
2 Faculty of Economic and Management, Mudanjiang Normal University, Mudanjiang, 157011 China
Changlin Ao
3 College of Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030 China
Associated Data
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Web of Science.
With the increasing attention and awareness of the ecological environment, ecotourism is becoming ever more popular, but it still brings problems and challenges to the sustainable development of the environment. To solve such challenges, it is necessary to review literature in the field of ecotourism and determine the key research issues and future research directions. This paper uses scientometrics implemented by CiteSpace to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. Two bibliographic datasets were obtained from the Web of Science, including a core dataset and an expanded dataset, containing articles published between 2003 and 2021. Our research shows that ecotourism has been developing rapidly in recent years. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. According to the research results, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three phases: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. It could be concluded that it has entered the third stage of Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontier formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0.
Introduction
Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996 ; Higgins, 1996 ; Orams, 1995 ). With years of research and development, ecotourism has risen to be a subject of investigation in the field of tourism research (Weaver & Lawton, 2007 ). In 2002, the United Nations declared it the International Year of Ecotourism (IYE), and the professional Journal of Ecotourism was established in the same year.
With the progress and maturity of ecotourism as an academic research field, countless scholars have put forward standards and definitions for ecotourism (Sirakaya et al., 1999 ; Wight, 1993 ). The main objectives of ecotourism emphasize long-term sustainable development (Whitelaw et al., 2014 ), including the conservation of natural resources, the generation of economic income, education, local participation and the promotion of social benefits such as local economic development and infrastructure (Ardoin et al., 2015 ; Coria & Calfucura, 2012 ; Krüger, 2005 ; Oladeji et al., 2021 ; Ross & Wall, 1999 ; Valdivieso et al., 2015 ). It can also boost rural economies and alleviate poverty in developing countries (Snyman, 2017 ; Zhong & Liu, 2017 ).
With unrestricted increasing attention to the ecological environment and the improvement of environmental awareness, ecotourism is becoming ever more prevalent, and the demand for tourism is increasing year by year (CREST, 2019 ). This increase, however, leads to a number of environmental, social and economic challenges in the development of ecotourism. For example, due to the low public awareness of ecotourism, the increase in tourists has brought a series of negative impacts on the local ecological environment, culture and economy, including disrespect for local culture and environmental protection, as well as more infrastructure construction and economic burden to meet the needs of tourists (Ahmad et al., 2018 ; Chiu et al., 2014 ; Shasha et al., 2020 ; Xu et al., 2020 ). Such challenges and contradictions are urgent problems to be tackled by the sustainable development of ecotourism. Especially against the backdrop of the current pandemic, tourism has experienced a severe blow, but climate change and other environmental issues have not been improved (CREST, 2020 ). In this context, facing these challenges and difficulties, it is essential to re-examine the future development path of ecotourism, to explore how government agencies can formulate appropriate management policies while preserving the environment and natural resources to support sustainable tourism development. Accordingly, it is necessary to consult literature in the field of ecotourism to understand the research progress and fundamental research issues, to identify challenges, suitable methods and future research direction of ecotourism.
Some previous reviews of ecotourism offer a preview of research trends in this rapidly developing area. Weaver and Lawton ( 2007 ) provide a comprehensive assessment of the current state and future progress of contemporary ecotourism research, starting with the supply and demand dichotomy of ecotourism, as well as fundamental areas such as quality control, industry, external environment and institutions. Ardoin et al. ( 2015 ) conducted a literature review, analyzing the influence of nature tourism on ecological knowledge, attitudes, behavior and potential research into the future. Niñerola et al. ( 2019 ) used the bibliometric method and VOSviewer to study the papers on sustainable development of tourism in Scopus from 1987 to 2018, including literature landscape and development trends. Shasha et al. ( 2020 ) used bibliometrics and social network analysis to review the research progress of ecotourism from 2001 to 2018 based on the Web of Science database using BibExcel and Gephi and explored the current hot spots and methods of ecotourism research. These reviews have provided useful information for ecotourism research at that time, but cannot reflect the latest research trends and emerging development of ecotourism either of timeliness, data integrity, research themes or methods.
This study aims to reveal the theme pattern, landmark articles and emerging trends in ecotourism knowledge landscape research from macro- to micro-perspectives. Unlike previous literature surveys, from timeliness, our dataset contains articles published between 2003 and 2021, and it will reveal more of the trends that have emerged over the last 3 years. Updating the rapidly developing literature is important as recent discoveries from different areas can fundamentally change collective knowledge (Chen et al., 2012 , 2014a ). To ensure data integrity, two bibliographic datasets were generated from Web of Science, including a core dataset using the topic search and an expanded dataset using the citation expansion method, which is more robust than defining rapidly growing fields using only keyword lists (Chen et al., 2014b ). And from the research theme and method, our review focuses on the area of ecotourism and is instructed by a scientometric method conducted by CiteSpace, an analysis system for visualizing newly developing trends and key changes in scientific literature (Chen et al., 2012 ). Emerging trends are detected based on metrics calculated by CiteSpace, without human intervention or working knowledge of the subject matter (Chen et al., 2012 ). Choosing this approach can cover a more extensive and diverse range of related topics and ensure repeatability of analysis with updated data (Chen et al., 2014b ).
In addition, Shneider’s four-stage theory will be used to interpret the results in this review. According to Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), the development of a scientific discipline is divided into four stages. Stage I is the conceptualization stage, in which the objects and phenomena of a new discipline or research are established. Stage II is characterized by the development of research techniques and methods that allow researchers to investigate potential phenomena. As a result of methodological advances, there is a further understanding of objects and phenomena in the field of new subjects at this stage. Once the techniques and methods for specific purposes are available, the research enters Stage III, where the investigation is based primarily on the application of the new research method. This stage is productive, in which the research results have considerably enhanced the researchers’ understanding of the research issues and disclosed some unknown phenomena, leading to interdisciplinary convergence or the emergence of new research directions or specialties. The last stage is Stage IV, whose particularity is to transform tacit knowledge into conditional knowledge and generalized knowledge, so as to maintain and transfer the scientific knowledge generated in the first three stages.
The structure of this paper is construed as follows. The second part describes the research methods employed, the scientometric approach and CiteSpace, as well as the data collection. In the third part, the bibliographic landscape of the core dataset is expounded from the macroscopic to the microscopic angle. The fourth part explores the developments and emerging trends in the field of ecotourism based on the expanded dataset and discusses the evolution phase of ecotourism. The final part is the conclusion of this study. Future research of ecotourism is prospected, and the limitations of this study are discussed.

Methods and data collection
Scientometric analyses and citespace.
Scientometrics is a branch of informatics that involves quantitative analysis of scientific literature in order to capture emerging trends and knowledge structures in a particular area of study (Chen et al., 2012 ). Science mapping tools generate interactive visual representations of complex structures by feeding a set of scientific literature through scientometrics and visual analysis tools to highlight potentially important patterns and trends for statistical analysis and visualization exploration (Chen, 2017 ). At present, scientometrics is widely used in many fields of research, and there are also many kinds of scientific mapping software widely used by researchers and analysts, such as VosViewer, SCI2, HistCite, SciMAT, Gephi, Pajek and CiteSpace (Chen, 2011 , 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ).
Among these tools, CiteSpace is known for its powerful literature co-citation analysis, and its algorithms and features are constantly being refined as it continues to evolve. CiteSpace is a citation visual analysis software developed under the background of scientometrics and data visualization to analyze the basics that are included in scientific analysis (Chen, 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ). It is specialized designed to satisfy the need for systematic review in rapidly changing complicated areas, particularly with the ability to identify and explain emerging trends and transition patterns (Chen et al., 2014a ). It supports multiple types of bibliometric research, such as collaborative network analysis, co-word analysis, author co-citation analysis, document co-citation analysis, and temporal and spatial visualization (Chen, 2017 ). Currently, CiteSpace has been extensively used in more than 60 fields, including computer science, information science, management and medicine (Abad-Segura et al., 2019 ; Chen, 2017 ).
In this paper, we utilize CiteSpace (5.8.R1) to analyze acquired bibliographies of ecotourism to study emerging trends and developments in this field. From macro to micro, from intuitive to complex, from whole to part and from general to special, the writing ideas are adopted. Figure 1 presented the specific research framework of this study.

The research framework of this study
Data collection
Typical sources of scientific literature are Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar. Considering the quantity and quality of data, the Web of Science database was expected to provide the original data in this research. In order to comprehend the research status and development trends of ecotourism, this study systematically reviewed the ecotourism literature collected on the Web of Science Core Collection. The Web of Science Core Collection facilitates access to the world’s leading scholarly journals, books and proceedings of conferences in the sciences, social sciences, art, and humanities, as well as access to their entire citation network. It mainly includes Science Citation Index Expanded from 2003 to current and Social Sciences Citation Index from 2004 to present. Therefore, the data obtained in this study are from 2003 and were consulted on June 3, 2021.
In the process of data retrieval, it is frequently confronted with the choice between recall rate and precision rate. To address the problem of low recall rate in keyword or topic retrieval, Chen et al. ( 2014a , b ) expanded the retrieval results through ‘citation expansion’ and ‘comprehensive topic search’ strategies. However, when the recall rate is high, the accuracy rate will decrease correspondingly. In practical standpoint, instead of refining and cleaning up the original search results, a simpler and more efficient way is to cluster or skip these unrelated branches. Priority should be placed on ensuring recall rate, and data integrity is more important than data for accuracy. Therefore, two ecotourism documentation datasets, the core dataset and the expanded dataset, were obtained from the Web of Science by using comprehensive topic search and citation expansion method. The latter approach has been proved more robust than using keyword lists only to define fast-growing areas (Chen et al., 2014b ). A key bibliographic landscape is generated based on the core dataset, followed by more thorough research of the expanded dataset.
The core dataset
The core dataset was derived through comprehensive subject retrieval in Web of Science Core Collection. The literature type was selected as an article or review, and the language was English. The period spans 2003 to 2021. The topic search query is composed of three phrases of ecotourism: ‘ ecotour* ’ OR ‘ eco-tour* ’ OR ‘ ecological NEAR/5 tour* ’. The wildcard * is used to capture related variants of words, for example, ecotour, ecotourism, ecotourist and ecotourists. The related records that are requested include finding these terms in the title, abstract or keywords. The query yielded 2991 original unique records.
The expanded dataset
The expanded dataset includes the core dataset and additional records obtained by reference link association founded on the core dataset. The principle of citation expansion is that if an article cites at least one article in the core dataset, we can infer that it is related to the topic (Garfield, 1955 ). The expanded dataset is comprised of 27,172 unique records, including the core dataset and the articles that cited them. Both datasets were used for the following scientometrics analysis.
Bibliographic landscape based on the core dataset
The core dataset consists of a total of 2991 literature from 2003 to 2021. This study utilized the core dataset to conduct an overall understanding of the bibliographic landscape in the field of ecotourism.
Landscape views of core dataset
The distribution of the yearly publication of bibliographic records in the core and expanded datasets is presented in Fig. 2 . It can be observed that the overall number of ecotourism-related publications is on the rise, indicating that the scholarly community is increasingly interested in ecotourism. After 2018, the growth rate increased substantially. And in 2020, the number of publications in the expanded dataset is close to 5000, almost double that of 2017 and 5 times that of 2011. This displays the rapid development of research in the field of ecotourism in recent years, particularly after 2018, more and more researchers began to pay attention to this field, which also echoes the trend of global tourism development and environmental protection. With the increase in personal income, tourism has grown very rapidly, and with it, tourism revenue and tourist numbers, especially in developing states. For instance, the number of domestic tourists in China increased from 2.641 billion in 2011 to 6.06 billion in 2019, and tourism revenue increased from 1930.5 billion RMB in 2011 to 5725.1 billion RMB in 2019 (MCT, 2021 ). However, due to the lack of effective management and frequent human activities, the rapid development of tourism has led to various ecological and environmental problems, which require corresponding solutions (Shasha et al., 2020 ). This has played an active role in promoting the development of ecotourism and triggered a lot of related research. In addition, since 2005, the expanded dataset has contained numerous times as many references as the core dataset, demonstrating the importance of using citation expansion for literature retrieval in scientometric review studies.The data were consulted on June 3, 2021

The distribution of bibliographic records in core and expanded dataset. Note The data were consulted on June 3, 2021
The dual-map overlay of scientific map literature as Fig. 3 shows, against the background of global scientific map from more than 10,000 journals covered by Web of Science, represents the distribution and connections on research bases and application fields across the entire dataset of the research topics (Chen & Leydesdorff, 2014 ). Colored lines are citation links, and numbered headings are cluster labels. On the left side is the journal distribution which cites literature, regarding the field application of ecotourism, mainly covers multiple disciplines such as 3. Ecology, Earth, Marine, 6. Psychology, Education, Health, 7. Veterinary, Animal Science and 10. Economics, Economic and Political. On the right side is the distribution of journals of cited literature, representing the research basis of ecotourism. As can be observed from the figure, ecotourism research is based on at least five disciplines on the right, including 2. Environmental, Toxicology, Nutrition, 7. Psychology, Education, Social, 8. Molecular, Biology, Genetics, 10. Plant, Ecology, Zoology and 12. Economics, Economic, Political. It can be viewed that the research field of ecotourism spans multiple disciplines and is a comprehensive and complex subject. The dual-map overlay provides a global visualization of literature growth of the discipline level.

A dual-map overlay of ecotourism literature
The total number of papers issued by a country or an institution reflects its academic focus and overall strength, while centrality indicates the degree of academic cooperation with others and the influence of published papers. The top 15 countries and institutions for the number of ecotourism papers published from 2003 to 2021 are provided in Table Table1. 1 . Similar to the study of Shasha et al. ( 2020 ), the ranking of the top six countries by the number of publications remains unchanged. As can be seen from the table, the USA ranks first in the world, far ahead in both the number of publications and the centrality. China ranks second in global ecotourism publications, followed by Australia, England, South Africa and Canada. While the latest data show that Taiwan (China), Turkey and South Korea appear on the list. Overall, the top 15 countries with the most publications cover five continents, containing a number of developed and developing, which shows that ecotourism research is receiving global attention. In terms of international academic cooperation and impact of ecotourism, Australia and England share second place, Italy and France share fourth place, followed by South Africa and Spain. China’s centrality is relatively low compared to the number of publications, ranking eighth. Academic cooperation between countries is of great significance. Usually, countries with high academic publishing level cooperate closely due to similar research interests. International academic cooperation has enhanced each other’s research capacity and promoted the development of ecotourism research. Therefore, although some countries have entered this list with the publication number, they should attach importance to increase academic cooperation with other countries and improving the international influence of published papers.
The top 15 most productive countries and institutions on ecotourism
The Chinese Academy of Sciences and its university are the most prolific when it draws to institutions’ performance. It is the most important and influential research institute in China, especially in the field of sustainable development science. Australia has four universities on the list, with Griffith University and James Cook University in second and third place. USA also includes four universities, with the University of Florida in fourth place. South Africa, a developing country, gets three universities, with the University of Cape Town and the University of Johannesburg fifth and sixth, respectively. In comparison with previous studies (Shasha et al., 2020 ), Iran and Mexico each have one university in the ranking, replacing two universities in Greece, which means that the importance and influence of developing countries in the field of ecotourism is gradually rising. Based on the above results, it can be summarized that the USA, China, Australia and South Africa are relatively active countries in the field of ecotourism, and their development is also in a relatively leading position.
Most active topics
The foam tree map and the pie chart of the focal topics of ecotourism based on the core dataset generated by Carrot2 through the title of each article is illustrated in Fig. 4 . Developing and developed, case study, protected areas, sustainable tourism, tourism development and developing ecotourism are leading topics in the field of ecotourism research, as well as specific articles under the main topics. The lightweight view generated by Carrot2 provides a reference for the research, and then, co-word analysis is employed to more specifically reflect the topics in the research field.

Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics on ecotourism
The topics covered by ecotourism could be exposed by the keywords of the articles in the core dataset. Figure 5 displays the keywords analysis results generated based on the core dataset. From the visualization results in the figure, it can infer that ecotourism, conservation, tourism, management, protected area, impact, biodiversity, sustainability, national park and community are the ten most concerned topics. Distinct colors set out at the time of co-citation keywords first appear, and yellow is generated earlier than red. In addition, Fig. 5 can also reflect the development and emerging topics in the research field, such as China, Mexico, South Africa and other hot countries for ecotourism research; ecosystem service, economic value, climate change, wildlife tourism, rural tourism, forest, marine protected area and other specific research directions; valuation, contingent valuation, choice experiment and other research methods; willingness to pay, preference, benefit, perception, attitude, satisfaction, experience, behavior, motivation, risk, recreation and other specific research issues.

A landscape view of keywords based on the core dataset
Emerging trends and developments based on the expanded dataset
The expanded dataset, consisting of 27,172 records, is approximately nine times larger than the core dataset. This research applies the expanded dataset to profoundly explore the emerging trends and developments of ecotourism.
Keywords with citation bursts
Detection of citation bursts can indicate both the scientific community’s interest in published articles and burst keywords as an indicator of emerging tendencies. Figure 6 displays the top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts in the expanded dataset. Since 2003, a large number of keywords have exploded. Among them, the strongest bursts include ecotourism, bird, disturbance, reserve, Africa, challenge, sustainable development and strategy. Keywords with citation burst after 2017 are experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction, which have continued to this day. The results indicate dynamic development and emerging trends in research hotspots in the field of ecotourism.

Top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts
References with citation bursts
Figure 7 sets out the top 30 references in the expanded dataset with citation bursts. The articles with the fastest growing citations can also contribute to describe the dynamics of a field. References with high values in strength column are important milestones of ecotourism research. The two articles with strong citation bursts prior to 2010 focused on the human impact on the environment and animals. West et al. ( 2006 ) discussed the relationship between parks and human beings and the social impact of protected areas, and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) studied the decline of endangered great apes caused by a human pandemic virus. The paper with the strongest citation burst in the entire expanded dataset was released by Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), which looked at ‘green grabbing,’ the appropriation of land and resources for environmental purposes. Milcu et al. ( 2013 ) conducted a semi-quantitative review of publications dealing with cultural ecosystem services with the second strongest citation burst, which concluded that the improvement of the evaluation method of cultural ecosystem service value, the research on the value of cultural ecosystem service under the background of ecosystem service and the clarification of policy significance were the new themes of cultural ecosystem service research. In addition, many articles with citation burst discussed the evaluation method of ecosystem services value (Costanza et al., 2014 ; Groot et al., 2010 ), the evaluation of cultural ecosystem service value (Plieninger et al., 2013 ) and its role in ecosystem service evaluation (Chan et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Daniel et al., 2012 ). The most fresh literature with strong citation burst is the article of D’Amato et al. ( 2017 ) published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, which compared and analyzed sustainable development avenues such as green, circular and bio economy. In addition, it is worthwhile noting the use of R in ecotourism, with the persuasive citation burst continuing from 2012 to the present, as indicated by the orange arrow in Fig. 7 .

Top 30 references with the strongest citation bursts
Landscape view of co-citation analysis
The landscape view of co-citation analysis of Fig. 8 is generated based on the expanded dataset. Using g -index ( k = 25) selection criteria in the latest edition of CiteSpace, an annual citation network was constructed. The final merged network contained 3294 links, 2122 nodes and 262 co-citation clusters. The three largest linked components cover 1748 connected nodes, representing 82% of the entire network. The modularization degree of the synthetic network is 0.8485, which means that co-citation clustering can clearly define each sub-field of ecotourism. Another weighted mean silhouette value of the clustering validity evaluation is 0.9377, indicating that the clustering degree of the network is also very superior. The harmonic mean value amounts to 0.8909.

A landscape view of the co-citation network based on the expanded dataset
In the co-citation network view, the location of clusters and the correlation between clusters can show the intellectual structure in the field of ecotourism, so that readers can obtain an overall understanding of this field. The network falls into 25 co-citation clusters. The tags for each cluster are generated founded on the title, keywords and abstract of the cited article. Color-coded areas represent the time of first appeared co-citation links, with gray indicating earlier and red later. The nodes in the figure with red tree rings are references to citation bursts.
Timeline view
In order to further understand the time horizon and study process of developing evolution on clusters, after the generation of co-citation cluster map, the Y -axis is cluster number and the year of citation publication is X -axis, so as to obtain the timeline view of the co-citation network, shown as Fig. 9 . Clusters are organized vertically from largest to smallest. The color curve represents co-citation link coupled with corresponding color year, with gray representing earlier and red representing newer. Larger nodes and nodes with red tree rings indicate high citation or citation burst. The three most cited references of the year demonstrate below each node, in vertical order from least to most.

A timeline visualization of the largest clusters
The timeline view provides a reasonably instinctual and insightful reference to understand the evolutionary path of every subdomain. Figure 9 shows 19 clusters ranging from #0 to #18, with #0 being the largest cluster. As can be seen from the figure, the sustainability and activeness of each cluster are contrasting. For example, the largest cluster has been active since 2006, while the gray and purple clusters are no longer active.
Major clusters
Taking clustering as a unit and analyzing at the level of clustering, specifically selecting large or new type clustering, is the foothold of co-citation analysis, which can help to understand the principal and latest research fields related to ecotourism. Table Table2 2 displays a summary of the foremost 19 clusters, the first nine of which are all over 100 in size. The silhouette score of all clusters is greater than 0.8, indicating that the homogeneity of each cluster is high. The mean year is the average of the publication dates of references in the cluster. By combining the results in Table Table2, 2 , Figs. 8 and and9, 9 , it can be observed that the five largest clusters are #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #2 human disturbance, #3 whale shark and #4 ecosystem service. A recent topic is cluster #16 COVID-19 pandemic. #11 Ecological footprint and #14 social media are two relatively youthful fields.
Summary of major clusters
* LLR refers to Log-Likelihood Ratio
The research status of a research field can be demonstrated by its knowledge base and research frontier. The knowledge base consists of a series of scholarly writing cited by the corresponding article, i.e., cited references, while the research frontier is the writing inspired by the knowledge base, i.e., citing articles. Distinct research frontiers may come from the same knowledge base. Consequently, each cluster is analyzed based on cited references and citing articles. The cited references and citing articles of the five largest clusters are shown in Online Appendix A. Fig a) lists the 15 top cited references with the highest Σ (sigma) value in the cluster, where Σ value indicates that the citation is optimal in terms of the comprehensive performance of structural centrality and citation bursts. Fig b) shows the major citing articles of cluster. The citation behavior of these articles determines the grouping of cited literature and thus forms the cluster. The coverage is the proportion of member citations cited by citing articles.
Phase evolution research
Through the above analysis of the core dataset and the expanded dataset of ecotourism, we can see the development and evolution of the research field of ecotourism. The research process of ecotourism has gone through several stages, and each stage has its strategic research issues. Research starts with thinking about the relationship between humans and nature, moves to study it as a whole ecosystem, and then explores sustainable development. Hence, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly parted into three phases.
Phase I: Human disturbance research stage (2003–2010)
This phase of research concentrates on the influence of human activities such as ecotourism on the environment and animals. Representative keywords of this period include ecotourism, human disturbance, response, coral reef, bird, disturbance, recreation, reserve, park, South Africa and people. Representative articles are those published by West et al. ( 2006 ) and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) of human impact on the environment and animals. The representative clustering is #2 human disturbance, which is the third largest one, consisting of 130 cited references from 1998 to 2012 with the average year of 2004. This cluster has citation bursts between 2002 and 2010 and has been inactive since then. As showed in Fig S3 a) and b), the research base and frontier are mainly around the impact of human disturbances such as ecotourism on biology and the environment (McClung et al., 2004 ). And as showed in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9 , clusters closely related to #2 belong to this phase and are also no longer active, such as #5 off-road vehicle, #6 protected area, #10 poverty reduction and #12 sustainable lifestyle.
Phase II: Ecosystem services research stage (2011–2015)
In this stage, the content of ecotourism research is diversified and exploded. The research is not confined to the relationship between humans and nature, but begins to investigate it as an entire ecosystem. In addition, some specific or extended areas began to receive attention. Typical keywords are abundance, resource, Africa, risk, predation, consequence and science. The most illustrative papers in this stage are Fairhead et al. ( 2012 )’s discussion on green grabbing and Milcu et al. ( 2013 )’s review on cultural ecosystem services. Other representative papers in this period focused on the evaluation methods of ecosystem service value and the role of cultural ecosystem service in the evaluation of ecosystem service value. Most of the larger clusters in the survey erupted at this stage, including #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #3 whale shark, #4 ecosystem services. Some related clusters also belong to this stage, such as #7 neoliberal conservation, #8 responsible behavior, #9 tourism development, #13 mangrove forest, #15 volunteer tourism, #17 circular economy and #18 telecoupling framework.
Cluster #0 cultural ecosystem services are the largest cluster in ecotourism research field, containing 157 cited references from 2006 to 2019, with the mean year being 2012. It commenced to have the citation burst in 2009, with high cited continuing until 2019. Cultural ecosystem services are an essential component of ecosystem services, including spiritual, entertainment and cultural benefits. Thus, in Fig. 8 , the overlap with #4 ecosystem services can obviously be seen. In Cluster #0, many highly cited references have discussed the trade-offs between natural and cultural ecosystem services in ecosystem services (Nelson et al., 2009 ; Raudsepp-Hearne et al., 2010 ) and the important role of cultural ecosystem services in the evaluation of ecosystem services value (Burkhard et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Fisher et al., 2009 ; Groot et al., 2010 ). As non-market value, how to evaluate and quantify cultural ecosystem services is also an important issue (Hernández-Morcillo et al., 2012 ; Milcu et al., 2013 ; Plieninger et al., 2013 ). Besides, the exploration of the relationship among biodiversity, human beings and ecosystem services is also the focus of this cluster research (Bennett et al., 2015 ; Cardinale et al., 2012 ; Díaz et al., 2015 ; Mace et al., 2012 ). The citing articles of #0 indicate the continued exploration of the connotation of cultural ecosystem services and their value evaluation methods (Dickinson & Hobbs, 2017 ). It is noteworthy that some articles have introduced spatial geographic models (Havinga et al., 2020 ; Hirons et al., 2016 ) and social media methods (Calcagni et al., 2019 ) as novel methods to examine cultural ecosystem services. In addition, the link and overlap between #0 cultural ecosystem service and #17 circular economy cannot be overlooked.
Ecosystem services relate to all the benefits that humans receive from ecosystems, including supply services, regulatory services, cultural services and support services. Research on cultural ecosystem services is based on the research of ecosystem services. It can be viewed in Fig. 9 that the research and citation burst in #4 was all slightly earlier than #0. Cluster #4 includes 118 references from 2005 to 2019, with an average year of 2011. In its research and development, how to integrate ecosystem services into the market and the payment scheme to protect the natural environment is a significant research topic (Gómez-Baggethun et al., 2010 ). In Cluster #4, the most influential literature provides an overview of the payment of ecosystem services (PES) from theory to practice by Engel et al. ( 2008 ). Many highly cited references have discussed PES (Kosoy & Corbera, 2010 ; Muradian et al., 2010 ), including the effectiveness of evaluation (Naeem et al., 2015 ), social equity matters (Pascual et al., 2014 ), the suitability and challenge (Muradian et al., 2013 ), and how to contribute to saving nature (Redford & Adams, 2009 ). The cluster also includes studies on impact assessment of protected areas (Oldekop et al., 2016 ), protected areas and poverty (Brockington & Wilkie, 2015 ; Ferraro & Hanauer, 2014 ), public perceptions (Bennett, 2016 ; Bennett & Dearden, 2014 ) and forest ecosystem services (Hansen et al., 2013 ). The foremost citing articles confirm the dominant theme of ecosystem services, especially the in-depth study and discussion of PES (Muniz & Cruz, 2015 ). In addition, #4 is highly correlated with #7 neoliberal protection, and Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), a representative article of this stage, belongs to this cluster.
As the second largest cluster, Cluster #1 contains 131 references from 2008 to 2019, with the median year of 2014. As Fig S2 a) shows, the highly cited literature has mainly studied the status and protection of large carnivores (Mace, 2014 ; Ripple et al., 2014 ), including the situation of reduction (Craigie et al., 2010 ), downgrade (Estes et al., 2011 ) and even extinction (Dirzo et al., 2014 ; Pimm et al., 2014 ), and the reasons for such results, such as tourist visits (Balmford et al., 2015 ; Geffroy et al., 2015 ) and the increase in population at the edge of the protected areas (Wittemyer et al., 2008 ). The conservation effects of protected areas on wildlife biodiversity (Watson et al., 2014 ) and the implications of tourist preference heterogeneity for conservation and management (Minin et al., 2013 ) have also received attention. It is worth noting that the high citation rate of a paper using R to estimate the linear mixed-effects model (Bates et al., 2015 ) and the use of R in this cluster. The relationship between biodiversity and ecotourism is highlighted by the representative citing articles in research frontier of this cluster (Chung et al., 2018 ).
Cluster #3 refers to marine predator, and as shown in Fig. 8 , which has a strong correlation with #1. A total of 125 references were cited from 2002 to 2018, with an average year of 2011. References with high citation in #3 mainly studied the extinction and protection of marine life such as sharks (Dulvy et al., 2014 ), as well as the economic value and ecological impact of shark ecotourism (Clua et al., 2010 ; Gallagher & Hammerschlag, 2011 ; Gallagher et al., 2015 ). The paper published by Gallagher et al. ( 2015 ) is both the highly cited reference and main citing article, mainly focusing on the impact of shark ecotourism. It is also noteworthy that #6 protected area, #13 mangrove forest and #29 Mediterranean areas are highly correlated with these two clusters (Fig. 8 ).
Moreover, some clusters are not highly correlated with other clusters, but cannot be neglected at this stage of research. Cluster #8 responsible behavior includes 107 citations with the average year 2013, and mainly studied environmentally responsible behaviors in ecotourism (Chiu et al., 2014 ). Cluster #9 tourism development contains 97 cited references with mean year of 2015, focusing on the impact of such factors as residents’ perception on tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Cluster #15 volunteer tourism consists of 52 citations, with an average year of 2011, which mainly considers the role of volunteer tourism in tourism development and sustainable tourism (Wearing & McGehee, 2013 ). Cluster #18 telecoupling framework has 26 cited references with the mean year being 2015, and the application of the new integrated framework of telecoupling 1 in ecotourism can be seen (Liu et al., 2015 ).
At this stage, it can be seen that the research field of ecotourism begins to develop in the direction of diversification, including the value evaluation and related research of ecosystem services and cultural ecosystem services, as well as the exploration of wild animals and plants, marine animals and plants and biodiversity. Neoliberal conservation, tourists’ responsible behavior, tourism development, volunteer tourism and circular economy are all explored. Some new research methods have also brought fresh air to this field, such as the introduction of spatial geographic models and social media methods, the discussion of economic value evaluation methods, the widespread use of R and the exploration of telecoupling framework. Therefore, from this stage, research in the field of ecotourism has entered the second stage of scientific discipline development (Shneider, 2009 ), featured by the use and evolution of research tools that can be used to investigate potential phenomena.
Phase III: Sustainable development research stage (2016 to present)
This stage of research continues to explore a series of topics of the preceding phase and further extends the research field on this basis. The keywords at this stage are politics, marine protected area and valuation. Some other keywords are still very active today, such as experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction. The representative article is about sustainable development published by D'Amato et al. ( 2017 ), as shown in Fig. 8 belonging to #17 circular economy. The emerging clusters in this period are #11 ecological footprint, #14 social media and #16 COVID-19 pandemic. Cluster #11 contains 70 cited references from 2013 to 2020 with the mean year 2017. This clustering study mainly used the ecological footprint as an environmental indicator and socioeconomic indicators such as tourism to investigate the hypothesis of environmental Kuznets curve (Ozturk et al., 2016 ; Ulucak & Bilgili, 2018 ). Cluster #14 includes 52 cited references, with an average year of 2016. It can be seen that the introduction of social media data has added new color to research in the field of ecotourism, such as using social media data to quantify landscape value (Zanten et al., 2016 ) and to understand tourists’ preferences for the experience of protected areas (Hausmann et al., 2018 ), as well as from a spatial perspective using social media geo-tagged photos as indicators for evaluating cultural ecosystem services (Richards & Friess, 2015 ). As the latest and most concerned topic, cluster #16 contains 48 cited references, with mean year of 2018. This cluster mainly cites research on over-tourism (Seraphin et al., 2018 ) and sustainable tourism (Higgins-Desbiolles, 2018 ) and explores the impact of pandemics such as COVID-19 on global tourism (Gössling et al., 2021 ).
These emerging clusters at this phase bring fresh thinking to the research of ecotourism. First of all, the analysis of ecological footprint provides a tool for measuring the degree of sustainability and helps to monitor the effectiveness of sustainable programs (Kharrazi et al., 2014 ). Research and exploration of ecological footprint in ecotourism expresses the idea of sustainable development and puts forward reasonable planning and suggestions by comparing the demand of ecological footprint with the carrying capacity of natural ecosystem. Secondly, the use of social media data brings a new perspective of data acquisition to ecotourism research. Such large-scale data acquisition can make up for the limitations of sample size and data sampling bias faced by survey data users and provide a new way to understand and explore tourist behavior and market (Li et al., 2018 ). Finally, the sudden impact of COVID-19 in 2020 and its long-term sustainability has dealt a huge blow to the tourism industry. COVID-19 has highlighted the great need and value of tourism, while fundamentally changing the way destinations, business and visitors plan, manage and experience tourism (CREST, 2020 ). However, the stagnation of tourism caused by the pandemic is not enough to meet the challenges posed by the environment and the climate crisis. Therefore, how to sustain the development of tourism in this context to meet the challenges of the environment and climate change remains an important issue in the coming period of time. These emerging clusters are pushing the boundaries of ecotourism research and the exploration of sustainable development in terms of research methods, data collection and emerging topics.
Despite the fact that the research topics in this stage are richer and more diversified, the core goal of research is still committed to the sustainable development of ecotourism. The introduction of new technologies and the productive results have led to a much-improved understanding of research issues. All this commemorates the entrance of research into the third stage of the development of scientific disciplines (Shneider, 2009 ). In addition to continuing the current research topics, the future development of the field of ecotourism will continue to focus on the goal of sustainable development and will be more diversified and interdisciplinary.
This paper uses scientometrics to make a comprehensive visual domain analysis of ecotourism. The aim is to take advantage of this method to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. We have enriched the process of systematic reviews of knowledge domains with features from the latest CiteSpace software. Compared with previous studies, this study not only updated the database, but also extended the dataset with citation expansion, so as to more comprehensively identify the rapidly developing research field. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontiers formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images. Through this study, readers can swiftly understand the progress of ecotourism, and on the basis of this study, they can use this method to conduct in-depth analysis of the field they are interested in.
Our research shows that ecotourism has developed rapidly in recent years, with the number of published articles increasing year by year, and this trend has become more pronounced after 2018. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. Ecotourism also attracts the attention of numerous developed and developing countries and institutions. The USA, China, Australia and South Africa are in a relatively leading position in the research and development of ecotourism. Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics, and the landscape view of keywords provide the hotspot issues of the research field. The development trend of ecotourism is preliminarily understood by detecting the citation bursts of the keywords and published articles. Co-citation analysis generates the main clusters of ecotourism research, and the timeline visualization of these clusters provides a clearer view for understanding the development dynamics of the research field. Building on all the above results, the research and development of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three stages: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. Through the study of keywords, representative literature and main clusters in each stage, the development characteristics and context of each stage are clarified. From the current research results, we can catch sight that the application of methods and software in ecotourism research and the development of cross-field. Supported by the Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), it can be thought that ecotourism is in the third stage. Research tools and methods have become more potent and convenient, and research perspectives have become more diverse.
Based on the overall situation, research hotspots and development tendency of ecotourism research, it can be seen that the sustainable development of ecotourism is the core issue of current ecotourism research and also an important goal for future development. In the context of the current pandemic, the tourism industry is in crisis, but crisis often breeds innovation, and we must take time to reconsider the way forward. As we look forward to the future of tourism, we must adopt the rigor and dedication required to adapt to the pandemic, adhering to the principles of sustainable development while emphasizing economic reliability, environmental suitability and cultural acceptance. Post-COVID, the competitive landscape of travel and tourism will change profoundly, with preventive and effective risk management, adaptation and resilience, and decarbonization laying the foundation for future competitiveness and relevance (CREST, 2020 ).
In addition, as can be seen from the research and development of ecotourism, the exploration of sustainable development increasingly needs to absorb research methods from diverse fields to guide the formulation of policy. First of all, how to evaluate and quantify ecotourism reasonably and scientifically is an essential problem to be solved in the development of ecotourism. Some scholars choose contingent valuation method (CVM) and choice experiment (CE) in environmental economics to evaluate the economic value of ecotourism, especially non-market value. In addition, the introduction of spatial econometrics and the use of geographic information system (GIS) provide spatial scale analysis methods and results presentation for the sustainable development of ecotourism. The use of social media data implies the application of big data technology in the field of ecotourism, where machine learning methods such as artificial neural networks (ANN) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) are increasingly being applied (Talebi et al., 2021 ). The measurement of ecological footprint and the use of telecoupling framework provide a reliable way to measure sustainable development and the interaction between multiple systems. These approaches all have expanded the methodological boundaries of ecotourism research. It is worth noting that R, as an open source and powerful software, is favored by scholars in the field of ecotourism. This programming language for statistical computation is now widely used in statistical analysis, data mining, data processing and mapping of ecotourism research.
The scientometrics method used in this study is mainly guided by the citation model in the literature retrieval dataset. The range of data retrieval exercises restraint by the source of retrieval and the query method utilized. While current methods can meet the requirements, iterative query optimization can also serve to advance in the quality of the data. To achieve higher data accuracy, the concept tree function in the new version of CiteSpace can also serve to clarify the research content of each clustering (Chen, 2017 ). In addition, the structural variation analysis in the new edition is also an interesting study, which can show the citation footprints of typical high-yielding authors and judge the influence of the author on the variability of network structure through the analysis of the citation footprints (Chen, 2017 ).
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (1451MSYYB013) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.71874026 and No.71171044).
Authors’ contributions
In this study, LX proposed the research topic, designed the research methodology and framework, and made the data analysis. She was the major contributor in writing the manuscript. CA contributed to the design of the whole paper, including the research topic and methodology, and also participated in the writing and revision of the manuscript. BL and ZC were involved in data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Not applicable.
Liu, J., Hull, V., Batistella, M., DeFries, R., Dietz, T., Fu, F.,... Zhu, C. (2013). Framing Sustainability in a Telecoupled World. Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 26. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05873-180226
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Lishan Xu, Email: nc.ude.unjdm@0104102 .
Changlin Ao, Email: nc.ude.uaen@nilgnahcoa .
Baoqi Liu, Email: moc.qq@457115825 .
Zhenyu Cai, Email: moc.qq@697833194 .
- Abad-Segura E, Cortés-García FJ, Belmonte-Ureña LJ. The sustainable approach to corporate social responsibility: A global analysis and future trends. Sustainability. 2019; 11 (19):5382. doi: 10.3390/su11195382. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmad F, Draz MU, Su L, Ozturk I, Rauf A. Tourism and environmental pollution: Evidence from the one belt one road (OBOR) provinces of Western China. Sustainability. 2018; 10 (10):3520. doi: 10.3390/su10103520. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ardoin NM, Wheaton M, Bowers AW, Hunt CA, Durham WH. Nature-based tourism's impact on environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behavior: A review and analysis of the literature and potential future research. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2015; 23 (6):838–858. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2015.1024258. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balmford A, Green JMH, Anderson M, Beresford J, Huang C, Naidoo R, Walpole M, Manica A. Walk on the wild side: Estimating the global magnitude of visits to protected areas. PLoS Biology. 2015; 13 (2):e1002074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002074. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015; 67 (1):132904. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett NJ. Using perceptions as evidence to improve conservation and environmental management. Conservation Biology. 2016; 30 (3):582–592. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12681. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett EM, Cramer W, Begossi A, Cundill G, Díaz S, Egoh BN, Geijzendorffer IR, Krug CB, Lavorel S, Lazos E, Lebel L, Martín-López B, Meyfroidt P, Mooney HA, Nel JL, Pascual U, Payet K, Harguindeguy NP, Peterson GD, Prieur-Richard A-H, Reyers B, Roebeling P, Seppelt R, Solan M, Tschakert P, Teja Tscharntke BL, Turner PH, Verburg EF, Viglizzo PCL, White GW. Linking biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human well-being: Three challenges for designing research for sustainability. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability. 2015; 14 :76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2015.03.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett NJ, Dearden P. Why local people do not support conservation: Community perceptions of marine protected area livelihood impacts, governance and management in Thailand. Marine Policy. 2014; 44 :107–116. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2013.08.017. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brockington D, Wilkie D. Protected areas and poverty. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2015; 370 (1681):20140271. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0271. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burkhard B, Kroll F, Nedkov S, Müller F. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecological Indicators. 2012; 21 :17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.06.019. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calcagni F, Maia ATA, Connolly JJT, Langemeyer J. Digital co-construction of relational values: Understanding the role of social media for sustainability. Sustainability Science. 2019; 14 :1309–1321. doi: 10.1007/s11625-019-00672-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cardinale BJ, Emmett Duffy J, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava DS, Naeem S. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature. 2012; 486 :59–67. doi: 10.1038/nature11148. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. C. (1996). Tourism, ecotourism, and protected areas: The state of nature-based tourism around the world and guidelines for its development. World Congress on National Parks and Protected Areas, 4th, Caracas.
- Chan KMA, Guerry AD, Balvanera P, Klain Sarah, Satterfield T, Basurto X, Bostrom A, Chuenpagdee R, Gould R, Halpern BS, Hannahs N, Levine J, Norton B, Ruckelshaus M, Russell R, Tam J, Woodside U. Where are cultural and social in ecosystem services? A framework for constructive engagement. BioScience. 2012; 62 (8):744–756. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan KMA, Satterfield T, Goldstein J. Rethinking ecosystem services to better address and navigate cultural values. Ecological Economics. 2012; 74 :8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.11.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. Predictive effects of structural variation on citation counts. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology. 2011; 63 (3):431–449. doi: 10.1002/asi.21694. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Data and Information Science. 2017; 2 (2):1–40. doi: 10.1515/jdis-2017-0006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC. Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine a scientometric update (2000–2014) Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2014; 14 (9):1295–1317. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.920813. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC. Orphan drugs and rare diseases: A scientometric review (2000–2014) Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2014; 2 (7):709–724. doi: 10.1517/21678707.2014.920251. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, Tseng H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2012; 12 (5):593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Leydesdorff L. Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. Journal of the Association for Information Science. 2014; 65 (2):334–351. doi: 10.1002/asi.22968. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chiu Y-TH, Lee W-I, Chen T-H. Environmentally responsible behavior in ecotourism: Antecedents and implications. Tourism Management. 2014; 40 :321–329. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chung MG, Dietz T, Liu J. Global relationships between biodiversity and nature-based tourism in protected areas. Ecosystem Services. 2018; 34 :11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.09.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clua E, Buray N, Legendre P, Mourier J, Planes S. Behavioural response of sicklefin lemon sharks Negaprion acutidens to underwater feeding for ecotourism purposes. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 2010; 414 :257–266. doi: 10.3354/meps08746. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coria J, Calfucura E. Ecotourism and the development of indigenous communities: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Ecological Economics. 2012; 73 :47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.10.024. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costanza R, de Groot R, Sutton P, van der Ploeg S, Anderson SJ, Kubiszewski I, Stephen Farber R, Turner K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global Environmental Change. 2014; 26 :152–158. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Craigie ID, Baillie JEM, Balmford A, Carbone C, Collen B, Greena RE, Hutton JM. Large mammal population declines in Africa’s protected areas. Biological Conservation. 2010; 143 (9):2221–2228. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2010.06.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- CREST. (2019). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2019 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/213/2021/03/trends-and-statistics-2019.pdf
- CREST. (2020). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2020 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/docs/trendsStats2020.pdf
- D’Amato D, Droste N, Allen B, Kettunen M, Lähtinen K, Korhonen J, Leskinen P, Matthies BD, Toppinen A. Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2017; 168 :716–734. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.053. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daniel TC, Muhar A, Arnberger A, Aznar O, Boyd JW, Chan KMA, Costanza R, Elmqvist T, Flint CG, Gobster PH, Gret-Regamey A, Lave R, Muhar S, Penker M, Ribe RG, Schauppenlehner T, Sikor T, Soloviy I, Spierenburg M, Taczanowska K, Tam J, von der Dunk A. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. PNAS. 2012; 109 (23):8812–8819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114773109. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Díaz S, Demissew S, Carabias J, Joly C, Lonsdale Mark, Ash N, Larigauderie A, Adhikari JR, Arico S, Báldi A, Bartuska A, Baste IA, Bilgin A, Brondizio E, Chan KMA, Figueroa VE, Duraiappah A, Fischer M, Hill R, Koetz T, Leadley P, Lyver P, Mace GM, Martin-Lopez B, Okumura M, Pacheco D, Pascual U, Pérez ES, Reyers B, Roth E, Saito O, Scholes RJ, Sharma N, Tallis H, Thaman R, Watson R, Yahara T, Hamid ZA, Akosim C, Al-Hafedh Y, Allahverdiyev R, Amankwah E, Asah ST, Asfaw Z, Gabor Bartus L, Brooks A, Caillaux J, Dalle G, Darnaedi D, Driver A, Erpul G, Escobar-Eyzaguirre P, Failler P, Fouda AMM, Bojie Fu, Gundimeda H, Hashimoto S, Homer F, Lavorel S, Lichtenstein G, Mala WA, Mandivenyi W, Matczak P, Mbizvo C, Mehrdadi M, Metzger JP, Mikissa JB, Moller H, Mooney HA, Mumby P, Nagendra H, Nesshover C, Oteng-Yeboah AA, Pataki G, Roué M, Rubis J, Schultz M, Smith P, Sumaila R, Takeuchi K, Thomas S, Verma M, Yeo-Chang Y, Zlatanova D. The IPBES conceptual framework-connecting nature and people. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability. 2015; 14 :1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2014.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dickinson DC, Hobbs RJ. Cultural ecosystem services: Characteristics, challenges and lessons for urban green space research. Ecosystem Services. 2017; 25 :179–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.04.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dirzo R, Young HS, Galetti M, Ceballos G, Isaac NJB, Collen B. Defaunation in the anthropocene. Science. 2014; 345 (6159):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1251817. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dulvy NK, Fowler SL, Musick JA, Cavanagh RD, Kyne PM, Harrison LR, Carlson JK, Davidson LN, Fordham SV, Francis MP, Pollock CM, Simpfendorfer CA, Burgess GH, Carpenter KE, Compagno LJ, Ebert DA, Gibson C, Heupel MR, Livingstone SR, Sanciangco JC, Stevens JD, Valenti S, White WT. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. Life. 2014; 3 :e00590. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00590.001. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Engel S, Pagiola S, Wunder S. Designing payments for environmental services in theory and practice: An overview of the issues. Ecological Economics. 2008; 65 (4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.03.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Estes JA, Terborgh J, Brashares JS, Power ME, Berger J, Bond WJ, Carpenter SR, Essington TE, Holt RD, Jackson JBC, Marquis RJ, Oksanen L, Oksanen T, Paine RT, Pikitch EK, Ripple WJ, Sandin SA, Scheffer M, Schoener TW, Shurin JB, Sinclair ARE, Soulé ME, Virtanen R, Wardle DA. Trophic downgrading of planet earth. Science. 2011; 333 (6064):301–306. doi: 10.1126/science.1205106. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fairhead J, Leach M, Scoones I. Green Grabbing: A new appropriation of nature? The Journal of Peasant Studies. 2012; 39 (2):237–261. doi: 10.1080/03066150.2012.671770. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferraro PJ, Hanauer MM. Quantifying causal mechanisms to determine how protected areas affect poverty through changes in ecosystem services and infrastructure. PNAS. 2014; 111 (11):4332–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307712111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher B, Turner RK, Morling P. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecological Economics. 2009; 68 (3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.09.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallagher AJ, Hammerschlag N. Global shark currency: The distribution, frequency, and economic value of shark ecotourism. Current Issues in Tourism. 2011; 14 (8):797–812. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2011.585227. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallagher AJ, Vianna GMS, Papastamatiou YP, Macdonald C, Guttridgeg TL, Hammerschlag N. Biological effects, conservation potential, and research priorities of shark diving tourism. Biological Conservation. 2015; 184 :365–379. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2015.02.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garfield E. Citation indexes for science: A new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science. 1955; 122 (3159):108–111. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3159.108. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geffroy B, Samia DSM, Bessa E, Blumstein DT. How nature-based tourism might increase prey vulnerability to predators. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2015; 30 (12):755–765. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gómez-Baggethun E, de Groot R, Lomas PL, Montes C. The history of ecosystem services in economic theory and practice: From early notions to markets and payment schemes. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1209–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2021; 29 (1):1–20. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de Groot RS, Alkemade R, Braat L, Hein L, Willemen L. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecological Complexity. 2010; 7 (3):260–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2009.10.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen MC, Potapov PV, Moore R, Hancher M, Turubanova SA, Tyukavina A, Thau D, Stehman SV, Goetz SJ, Loveland TR, Kommareddy A, Egorov A, Chini L, Justice CO, Townshend JRG. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science. 2013; 342 (6160):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1244693. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hausmann A, Toivonen T, Slotow R, Tenkanen H, Moilanen A, Heikinheimo V, Minin ED. Social media data can be used to understand tourists’ preferences for nature-based experiences in protected areas. Conservation Letters. 2018; 11 (1):e12343. doi: 10.1111/conl.12343. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Havinga I, Bogaart PW, Hein L, Tuia D. Defining and spatially modelling cultural ecosystem services using crowdsourced data. Ecosystem Services. 2020; 43 :101091. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2020.101091. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hernández-Morcillo M, Plieninger T, Bieling C. An empirical review of cultural ecosystem service indicators. Ecological Indicators. 2012; 29 :434–444. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins BR. The Global structure of the nature tourism industry: Ecotourists, tour operators, and local businesses. Journal of Travel Research. 1996; 35 (2):11–18. doi: 10.1177/004728759603500203. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins-Desbiolles F. Sustainable tourism: Sustaining tourism or something more? Tourism Management Perspectives. 2018; 25 :157–160. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2017.11.017. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirons M, Comberti C, Dunford R. Valuing cultural ecosystem services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 2016; 41 :545–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-110615-085831. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kharrazi A, Kraines S, Hoang L, Yarime M. Advancing quantification methods of sustainability: A critical examination emergy, exergy, ecological footprint, and ecological information-based approaches [Review] Ecological Indicators. 2014; 37 :81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.10.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Köndgen S, Kühl H, N'Goran PK, Walsh PD, Schenk S, Ernst N, Biek R, Formenty P, Mätz-Rensing K, Schweiger B, Junglen S, Ellerbrok H, Nitsche A, Thomas Briese W, Lipkin I, Pauli G, Boesch C, Leendertz FH. Pandemic human viruses cause decline of endangered great apes. Current Biology. 2008; 18 (4):260–264. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.01.012. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kosoy N, Corbera E. Payments for ecosystem services as commodity fetishism. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1228–1236. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krüger O. The role of ecotourism in conservation: Panacea or Pandora’s box? Biodiversity & Conservation. 2005; 14 :579–600. doi: 10.1007/s10531-004-3917-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li J, Xu L, Tang L, Wang S, Li L. Big data in tourism research: A literature review. Tourism Management. 2018; 68 :301–323. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.03.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu J, Hull V, Batistella M, DeFries R, Dietz T, Fu F, Zhu C. Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world. Ecology and Society. 2013; 18 (2):26. doi: 10.5751/ES-05873-180226. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu J, Hull V, Junyan Luo W, Yang WL, Viña A, Vogt C, Zhenci Xu, Yang H, Zhang J, An Li, Chen X, Li S, Ouyang Z, Weihua X, Zhang H. Multiple telecouplings and their complex interrelationships. Ecology and Society. 2015; 20 (3):44. doi: 10.5751/ES-07868-200344. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mace GM. Whose conservation? Science. 2014; 345 (6204):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.1254704. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mace GM, Norris K, Fitter AH. Biodiversity and ecosystem services: A multilayered relationship. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2012; 27 (1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.08.006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McClung MR, Seddon PJ, Massaro M, Setiawan AN. Nature-based tourism impacts on yellow-eyed penguins Megadyptes antipodes: Does unregulated visitor access affect fledging weight and juvenile survival? Biological Conservation. 2004; 119 (2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2003.11.012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- MCT. (2021). Statistical Bulletin on Culture and Tourism Development 2020 . Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-07/05/content_5622568.htm
- Milcu AI, Hanspach J, Abson D, Fischer J. Cultural ecosystem services: A literature review and prospects for future research. Ecology and Society. 2013; 18 (3):44. doi: 10.5751/ES-05790-180344. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Minin ED, Fraser I, Slotow R, MacMillan DC. Understanding heterogeneous preference of tourists for big game species: Implications for conservation and management. Animal Conservation. 2013; 16 (3):249–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2012.00595.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muniz R, Cruz MJ. Making nature valuable, not profitable: Are payments for ecosystem services suitable for degrowth? Sustainability. 2015; 7 (8):10895–10921. doi: 10.3390/su70810895. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muradian R, Arsel M, Pellegrini L, Adaman F, Aguilar B, Agarwal B, Corbera E, Ezzine de Blas D, Farley J, Froger G, Garcia-Frapolli E, Gómez-Baggethun E, Gowdy J, Kosoy N, Le Coq JF, Leroy P, May P, Méral P, Mibielli P, Norgaard R, Ozkaynak B, Pascual U, Pengue W, Perez M, Pesche D, Pirard R, Ramos-Martin J, Rival L, Saenz F, Van Hecken G, Vatn A, Vira B, Urama K. Payments for ecosystem services and the fatal attraction of win-win solutions. Conservation Letters. 2013; 6 (4):274–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-263X.2012.00309.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muradian R, Corbera E, Pascual U, Kosoy N, May PH. Reconciling theory and practice: An alternative conceptual framework for understanding payments for environmental services. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1202–1208. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naeem S, Ingram JC, Varga A, Agardy T, Barten P, Bennett G, Bloomgarden E, Bremer LL, Burkill P, Cattau M, Ching C, Colby M, Cook DC, Costanza R, DeClerck F, Freund C, Gartner T, Goldman-Benner R, Gunderson J, Jarrett D, Kinzig AP, Kiss A, Koontz A, Kumar P, Lasky JR, Masozera M, Meyers D, Milano F, Naughton-Treves L, Nichols E, Olander L, Olmsted P, Perge E, Perrings C, Polasky S, Potent J, Prager C, Quétier F, Redford K, Saterson K, Thoumi G, Vargas MT, Vickerman S, Weisser W, Wilkie D, Wunder S. Get the science right when paying for nature's services. Science. 2015; 347 (6227):1206–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1403. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nelson E, Mendoza G, Regetz J, Polasky S, Tallis H, Cameron D, Chan KMA, Daily GC, Goldstein J, Kareiva PM, Lonsdorf E, Naidoo R, Ricketts TH, Shaw M. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 2009; 7 (1):4–11. doi: 10.1890/080023. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niñerola A, Sánchez-Rebull M-V, Hernández-Lara A-B. Tourism research on sustainability: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability. 2019; 11 (5):1377. doi: 10.3390/su11051377. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oladeji SO, Awolala DO, Alabi OI. Evaluation of sustainable ecotourism practices in Oke-Idanre Hills, Ondo-State, Nigeria [Article; Early Access] Environment Development and Sustainability. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01550-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oldekop JA, Holmes G, Harris WE, Evans KL. A global assessment of the social and conservation outcomes of protected areas. Conservation Biology. 2016; 30 (1):133–141. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12568. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orams MB. Towards a more desirable form of ecotourism. Tourism Management. 1995; 16 (1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0261-5177(94)00001-Q. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U, Saboori B. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2016; 23 :1916–1928. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5447-x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pascual U, Phelps J, Garmendia E, Brown K, Corbera E, Martin A, Gomez-Baggethun E, Muradian R. Social equity matters in payments for ecosystem services. BioScience. 2014; 64 (11):1027–1036. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biu146. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science. 2014; 344 (6187):1246752. doi: 10.1126/science.1246752. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plieninger T, Dijks S, Oteros-Rozas E, Bieling C. Assessing, mapping, and quantifying cultural ecosystem services at community level. Land Use Policy. 2013; 33 :118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.12.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raudsepp-Hearne C, Peterson GD, Bennett EM. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. PNAS. 2010; 107 (11):5242–5247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907284107. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Redford KH, Adams WM. Payment for ecosystem services and the challenge of saving nature. Conservation Biology. 2009; 23 (4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01271.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richards DR, Friess DA. A rapid indicator of cultural ecosystem service usage at a fine spatial scale: Content analysis of social media photographs. Ecological Indicators. 2015; 53 :187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.034. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG, Hebblewhite M, Berger J, Elmhagen B, Letnic M, Nelson MP, Schmitz OJ, Smith DW, Wallach AD, Wirsing AJ. Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science. 2014; 343 (6167):1241484. doi: 10.1126/science.1241484. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ross S, Wall G. Ecotourism: Towards congruence between theory and practice. Tourism Management. 1999; 20 (1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(98)00098-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seraphin H, Sheeran P, Pilato M. Over-tourism and the fall of Venice as a destination. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management. 2018; 9 :374–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2018.01.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharpley R. Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management. 2014; 42 :37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.10.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shasha ZT, Geng Y, Sun H-P, Musakwa W, Sun L. Past, current, and future perspectives on eco-tourism: A bibliometric review between 2001 and 2018. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2020; 27 :23514–23528. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08584-9. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shneider AM. Four stages of a scientific discipline; four types of scientist. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2009; 34 (5):217–223. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.002. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirakaya E, Sasidharan V, Sönmez S. Redefining ecotourism: The need for a supply-side view. Journal of Travel Research. 1999; 38 (2):168–172. doi: 10.1177/004728759903800210. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyman S. The role of private sector ecotourism in local socio-economic development in southern Africa. Journal of Ecotourism. 2017; 16 (3):247–268. doi: 10.1080/14724049.2016.1226318. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Talebi M, Majnounian B, Makhdoum M, Abdi E, Omid M. Predicting areas with ecotourism capability using artificial neural networks and linear discriminant analysis (case study: Arasbaran Protected Area, Iran) Environment, Development and Sustainability. 2021; 23 :8272–8287. doi: 10.1007/s10668-020-00964-y. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ulucak R, Bilgili F. A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018; 188 :144–157. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.191. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valdivieso JC, Eagles PFJ, Gil JC. Efficient management capacity evaluation of tourism in protected areas. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management. 2015; 58 (9):1544–1561. doi: 10.1080/09640568.2014.937479. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson JEM, Dudley N, Segan DB, Hockings M. The performance and potential of protected areas. Nature. 2014; 515 :67–73. doi: 10.1038/nature13947. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wearing S, McGehee NG. Volunteer tourism: A review. Tourism Management. 2013; 38 :120–130. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.03.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weaver DB, Lawton LJ. Twenty years on: The state of contemporary ecotourism research. Tourism Management. 2007; 28 (5):1168–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2007.03.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- West P, Igoe J, Brockington D. Parks and peoples: The social impact of protected areas. Annual Review of Anthropology. 2006; 35 :251–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.anthro.35.081705.123308. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitelaw PA, King BEM, Tolkach D. Protected areas, conservation and tourism-financing the sustainable dream. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2014; 22 (4):584–603. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2013.873445. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wight P. Ecotourism: Ethics or eco-sell. Journal of Travel Research. 1993; 31 (3):3–9. doi: 10.1177/004728759303100301. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wittemyer G, Elsen P, Bean WT, Burton ACO, Brashares JS. Accelerated human population growth at protected area edges. Science. 2008; 321 (5885):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.1158900. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu L, Ao C, Mao B, Cheng Y, Sun B, Wang J, Liu B, Ma J. Which is more important, ecological conservation or recreational service? Evidence from a choice experiment in wetland nature reserve management. Wetlands. 2020; 40 :2381–2396. doi: 10.1007/s13157-020-01348-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zanten BTV, Berkel DBV, Meentemeyer RK, Smith JW, Tieskens KF, Verburg PH. Continental-scale quantification of landscape values using social media data. PNAS. 2016; 113 (46):12974–12979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614158113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhong L, Liu L. Ecotourism development in China: Achievements, problems and strategies. Journal of Resources and Ecology. 2017; 8 (5):441–448. doi: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.05.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
The future of tourism is sustainable and regenerative

To make tourism sustainable and even regenerative, travellers themselves must undergo a mindset shift — but that's not easy in a cost-of-living squeeze. Image: Reuters/Jonathan Ernst
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Naoko Tochibayashi
Naoko kutty.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, davos agenda.
Listen to the article
- Japanese domestic tourism is recovering from the shock of the pandemic but international travel is lagging.
- Travellers increasingly demand sustainable and affordable options — but those are hard to come by in a cost-of-living squeeze.
- To make sustainable and regenerative tourism a reality, travellers themselves must undergo a mindset shift.
Since the significant easing of its pandemic border control measures last October, Japan has seen a steady return of foreign tourists.
According to the Japan National Tourism Organization (JNTO), the number of visitors to Japan in July reached 2.32 million, recovering to about 80% of 2019 levels.
And Japanese people are travelling their own country more, too. According to the travel trend survey by Japan Travel Bureau(JTB), 72.5 million people in Japan traveled within their country during the summer vacation season in July and August — almost returning to pre-pandemic levels. International travel, meanwhile, was low: 1.2 million people , which is 40% of the 2019 figures.
Many people wished to travel abroad but were unable or unwilling to do so cited concerns about safety and health, the lengthy immigration procedures involved in international travel and the unfavourable exchange rates and high costs.
For the outbound recovery to gain momentum, a safe and economically enabling environment is essential.
Have you read?
3 ways hotels and tourists can work together to decarbonize travel, japan airlines' clothing rental service aims for sustainable tourism, overtourism: a challenge to sustainability.
As the influx of tourists revitalizes local economies, a growing concern is emerging: the resurgence of overtourism, where popular destinations are flooded with an excessive number of visitors. In response, Prime Minister Kishida Fumio has announced plans to develop solutions this coming autumn to combat overtourism, addressing its negative impacts on local life, including congestion, traffic jams and litter.
Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, overtourism had started to plague certain Japanese tourist spots. As Japan's tourism industry and tourist destinations hit hard by the pandemic make strides toward recovery, it essential to view these challenges as opportunities for positive change and transform tourism into something more sustainable.
Hotels across Japan are accelerating their sustainability efforts. One noteworthy example is the Tokyo Station Hotel, located within the Tokyo Station building, which is designated as a National Important Cultural Property, is implementing the " CO₂ Zero STAY " programme to virtually eliminate CO₂ emissions generated during a stay by all rooms booked through the official website.
The World Economic Forum’s Platform for Shaping the Future of Mobility works across four industries: aerospace and drones; automotive and new mobility; aviation travel and tourism; and supply chain and transport. It aims to ensure that the future of mobility is safe, clean, and inclusive.
- Through the Clean Skies for Tomorrow Coalition , more than 100 companies are working together to power global aviation with 10% sustainable aviation fuel by 2030.
- In collaboration with UNICEF, the Forum developed a charter with leading shipping, airlines and logistics to support COVAX in delivering more than 1 billion COVID-19 vaccines to vulnerable communities worldwide.
- The Road Freight Zero Project and P4G-Getting to Zero Coalition have led to outcomes demonstrating the rationale, costs and opportunities for accelerating the transition to zero emission freight.
- The Medicine from the Sky initiative is using drones to deliver vaccines and medicine to remote areas in India, completing over 300 successful trials.
- The Forum’s Target True Zero initiative is working to accelerate the deployment and scaling of zero emission aviation, leveraging electric and hydrogen flight technologies.
- In collaboration with the City of Los Angeles, Federal Aviation Administration, and NASA, the Forum developed the Principles of the Urban Sky to help adopt Urban Air Mobility in cities worldwide.
- The Forum led the development of the Space Sustainability Rating to incentivize and promote a more safe and sustainable approach to space mission management and debris mitigation in orbit.
- The Circular Cars Initiative is informing the automotive circularity policy agenda, following the endorsement from European Commission and Zero Emission Vehicle Transition Council countries, and is now invited to support China’s policy roadmap.
- The Moving India network is working with policymakers to advance electric vehicle manufacturing policies, ignite adoption of zero emission road freight vehicles, and finance the transition.
- The Urban Mobility Scorecards initiative – led by the Forum’s Global New Mobility Coalition – is bringing together mobility operators and cities to benchmark the transition to sustainable urban mobility systems.
Contact us for more information on how to get involved.
This initiative, which uses the carbon offset system, calculates and visualizes the amount of CO₂ emissions generated by guest stays and invests the equivalent amount in emissions reduction activities, thereby reducing the emissions to virtually zero. All costs are covered by the hotel itself, meaning that guests contribute to expanding forest conservation efforts and supporting renewable energy simply by staying at the hotel.
Another player in the sustainable hospitality scene is Mori Trust Hotels & Resorts. They are taking steps to preserve tourism resources by introducing eco-friendly amenities like wooden and bamboo toothbrushes and hairbrushes, as well as razors and shower caps with reduced plastic content. They are also eliminating individual packaging for soaps and amenities while charging for these items. The company is currently reassessing the amenities used in their 18 hotels nationwide, which collectively use around 16 tons of plastic each year, and aims to cut down the plastic used in amenities by over 90% by 2024.
Traveller behaviour and tourism
As hotels and other players in the tourism industry move towards a more sustainable future, it is equally crucial that travellers, who are the main drivers of tourism, follow suit and change their attitudes and behaviours.
According to the Sustainable Travel Report 2023 , which gathered insights from over 33,000 travellers across 35 countries and territories, 76% of global travellers — and 56% of Japanese travellers — express a desire to embrace more sustainable travel over the coming 12 months. On the other hand, 76% of global travellers and 75% of Japanese travellers say that the global energy crisis and rising costs are impacting their spending plans. This has led to travellers being more budget-conscious, with only 43% of global travellers and 22% of Japanese travellers willing to pay extra for certified sustainable travel experiences.
In light of this trend, offering discounts and financial incentives by tourism providers may motivate travellers to opt for sustainable travel options. Furthermore, providing more information and choices can also promote sustainable travel, since almost half of both global and Japanese travellers feel there are not enough sustainable travel options available to them.
Regenerative tourism: the future of tourism
"There's one thing we can do: actively choose sustainable hotels and resorts, and contribute to their economic impact. Guests are the key to creating a sustainable environment," says travel journalist Naoko Terada, highlighting a crucial step that we all must take.
To achieve sustainable tourism that considers environmental, social and economic impacts, it is essential to change the mindset of travellers, who must act responsibly in terms of their impact on local communities and the natural environment. The realization of a future in which regenerative tourism, a further evolution of sustainable tourism, becomes mainstream depends on changing the behaviour of both hosts and travellers.
In the World Economic Forum's Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021: Rebuilding for a Sustainable and Resilient Future , Japan took the top spot in the development index ranking.
Japan, a highly regarded tourist destination, is leading the way in the future of regenerative tourism — where the more tourists visit, the more the place changes for the better — which will have a significant impact on the transformation of the global tourism industry.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Davos Agenda .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Davos 2024 Opening Film

Building trust amid uncertainty – 3 risk experts on the state of the world in 2024
Andrea Willige
March 27, 2024

Why obesity is rising and how we can live healthy lives
Shyam Bishen
March 20, 2024

Global cooperation is stalling – but new trade pacts show collaboration is still possible. Here are 6 to know about
Simon Torkington
March 15, 2024

How messages of hope, diversity and representation are being used to inspire changemakers to act
Miranda Barker
March 7, 2024

AI, leadership, and the art of persuasion – Forum podcasts you should hear this month
Robin Pomeroy
March 1, 2024

Ecotourism: Strategies for Sustainable Travel in 2024 and Beyond
Dr. Nick Becker, a pioneering sustainability expert and serial entrepreneur, seamlessly blends green technology and business acumen. With a Ph.D. in Environmental Engineering, he has co-founded groundbreaking startups and been featured on Forbes' "30 Under 30". His TEDx talk catalyzes tech-driven sustainability. Dr. Becker's passion for a greener future drives global change.
Introduction
Dr. Nick Becker is a visionary sustainability expert and seasoned serial entrepreneur, adept at harmonizing the realms of green technology and astute business acumen.
With a distinguished Ph.D. in Environmental Engineering, Dr. Becker has embarked on an extraordinary journey, co-founding trailblazing startups that are catalysts for transformation. His achievements have garnered industry recognition, earning him a coveted spot on Forbes' prestigious "30 Under 30" list.
A captivating orator, Dr. Becker's TEDx talk serves as a powerful catalyst, igniting a wave of tech-driven sustainability. His fervent commitment to ushering in a greener future has a profound impact on global change.
Ecotourism blends the excitement of exploring natural wonders with the responsibility of preserving them. This article aims to clearly understand how ecotourism can protect the environment, benefit local communities, and offer an enjoyable travel experience.
It delves into practical ecotourism strategies, explores their impact on destinations, and highlights the significance of making responsible travel choices.
Key Takeaways
- Ecotourism aims to minimize ecological impact, promote sustainable development, and emphasize conservation, community support, and environmental education.
- Ecotourism’s success depends on balancing economic growth with environmental protection, creating sustainable employment opportunities for local communities, and conserving natural resources.
- Innovative ecotourism projects and community-based initiatives worldwide demonstrate successful models of sustainable tourism, highlighting the importance of responsible travel, local engagement, and international support from organizations.
Understanding Ecotourism: A Modern Approach to Travel
Ecotourism is not just a passing trend in the travel industry but a responsible form of tourism that promotes conservation efforts that benefit local communities and educate people about preserving the environment and cultural heritage.
It establishes a vital connection between the desire to explore nature and the urgent need to protect it. By emphasizing sustainable development and reducing environmental impact, this deliberate approach to travel has set itself apart from other forms of tourism.
Watch this video by Dr. Hayley Stainton to learn more:
Ecotourism, endorsed by organizations such as The International Ecotourism Society and The World Tourism Organization, is a concept that emphasizes eco-friendly exploration .
It involves a commitment by travelers to reduce their ecological footprint while actively participating in activities designed to increase awareness of environmental protection and cultural values.
Destinations that cater specifically to ecotourists offer opportunities to experience the Earth’s magnificent natural beauty while also promoting responsible maintenance practices.
From unspoiled regions like those found in Amazonia to breathtaking vistas like those offered by the Himalayan peaks, ecotourism destinations provide a sanctuary where travelers can appreciate the planet’s splendor while also helping to preserve it.
The Core of Ecotourism: Conservation, Community, and Education
Ecotourism is based on three fundamental principles: preserving natural resources, supporting local communities, and educating people about ecological matters.
The main objective of conservation efforts is to protect the natural environments within national parks and other natural areas so that they can be enjoyed by future generations.
Ecotourism plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance necessary for the health and well-being of our planet.

Sustainable tourism is the foundation of ecotourism as it acknowledges the crucial role played by local communities. It respects their cultural heritage and provides opportunities for their development by adopting practices that promote their environment’s sustainability and improve their quality of life.
Every genuine ecotourism experience involves an educational component that fosters environmental consciousness among tourists. This deepens their appreciation for nature beyond simply what they see or do at various destinations.
Eco-Friendly Practices in Action
Eco-tourism involves a range of environmentally friendly practices, which include:
- Opting for sustainable modes of transportation, such as electric vehicles or rail systems.
- Participating in eco-tourism activities that aim to have minimal impact on the environment.
- Traveling slowly , consciously choosing destinations to connect with instead of rushing through many cities.
- Choosing accommodations that utilize renewable energy sources, have efficient waste management systems in place, and offer locally sourced food options.
These strategies are more than words; they are actively implemented to support conservation efforts essential to preserving the natural landscapes we cherish. These measures help ensure that our accommodations have a minimal ecological impact and are in harmony with the surrounding environment.
Ecotourism involves activities that connect visitors with nature while promoting responsible traveling habits. These activities could include trekking through wilderness areas, observing local wildlife species, or exploring marine environments.
Additionally, ecotourism initiatives typically integrate indigenous culture and history, providing educational experiences for visitors. To maintain a balance between economic gains for local communities and environmental preservation, ecotourism sites carefully regulate tourist numbers and promote off-season visits.
The Impact of Ecotourism on Local Economies
Ecotourism not only helps with environmental conservation but also provides economic benefits to local communities. By creating job opportunities such as positions for park rangers and cultural performers, ecotourism brings a steady flow of revenue into the economies of these areas, often transforming them into hubs of economic development.
In countries like Costa Rica, nature-based tourism has a significant impact on the national GDP, demonstrating how eco-friendly travel can coexist with generating economic opportunities and preserving natural habitats.

When travelers choose to spend their money on locally sourced goods and cuisine, they play a vital role in reducing ecological footprints while also promoting community prosperity.
The support given to local communities grows when tourists explore off-the-beaten-path adventures or participate in grassroots tourist initiatives that are supported by the residents.
Such initiatives have a positive financial impact on local communities, ensuring that their attractiveness as ecotourism destinations brings real progress and benefits to those who live there.
Balancing Economic Benefits with Environmental Protection
Genuine sustainable development in ecotourism requires a delicate balance between generating economic benefits and preserving nature. This balance involves supporting local businesses by ensuring fair wages and working conditions, investing in community infrastructure, and preserving cultural heritage.
These measures not only benefit conservation efforts but also help to boost the local economy and improve the well-being of those who reside in ecotourism destinations.
Choosing tour operators that hire local guides and provide authentic experiences – such as homestays with local families – can help boost the economic growth of the community while preserving the cultural integrity of the destination.
For instance, Bhutan’s Sustainable Development Fee is an excellent example of a direct financial contribution that combines environmental protection with economic benefits, ensuring that the experiences of travelers benefit both conservation efforts and the local people in equal measure.
Global Leaders in Ecotourism
There are a few nations that have become leaders in ecotourism by implementing standards for wildlife protection and sustainable tourism practices. These countries, such as Costa Rica, Chile, and Norway, have shown a strong commitment to these principles and have integrated them into their national identity.
They not only conserve their environment but also prioritize the well-being of their people. For travelers seeking genuine and responsible experiences, these countries have become top destinations for ecotourism.
Iceland and the Galapagos Islands are known as the best examples of ecotourism, with Iceland’s unspoiled landscapes and the Galapagos Islands’ unparalleled biodiversity attracting visitors from around the world.
The success stories of these destinations, as well as Chile’s Huilo Huilo and Chiloé Island, demonstrate the importance of balancing economic benefits with environmental conservation. These places are ideal destinations for anyone looking to explore nature while also supporting conservation efforts.
Case Study: Costa Rica’s Transformation
Costa Rica is a great example of how environmental preservation and sustainable development can go hand-in-hand. The Osa Peninsula, known for its diverse wildlife, including jaguars and macaws, is at the heart of this transition toward sustainable ecotourism.
Visitors can stay in eco-conscious accommodations and experience the beauty of the natural surroundings. This not only attracts millions of visitors each year but also highlights Costa Rica’s dedication to living in harmony with the environment.

Source: Lonely Planet
Costa Rica has effectively increased its forest coverage, which is a testament to its successful strategies for environmental conservation. The country’s strong commitment to sustainable ecotourism is a significant part of its national identity and positions it as a leader in offering ecological tourism opportunities.
This success serves as proof that tourism models focused on nature conservation are feasible and have substantial advantages.
Galapagos Islands: A Unique Ecosystem Under Careful Management
The Galapagos Islands were the first-ever UNESCO World Heritage Site and are home to a unique ecosystem that is carefully protected. These islands played a key role in Darwin’s Theory of Evolution and are safeguarded by Ecuadorian law to preserve their distinct wildlife and habitats.
To maintain their pristine condition, the islands have several regulations in place, including zoning laws, limited visitor numbers, and specific routes for tourism vessels. Tour operators in the Galapagos Islands must prioritize eco-friendly practices, not as an option but as a necessity.
This includes strategies to conserve water and energy, recycling programs, and providing fair wages and training opportunities for local staff. Tourists are required to pay a conservation fee, which, along with government support, helps fund environmental preservation projects that protect the unique native species of the islands, such as giant tortoises and marine iguanas.
Challenges and Controversies in Ecotourism
Although ecotourism aims to promote sustainable travel and conservation, it has its own set of problems and controversies. The increasing popularity of this form of tourism may unintentionally cause the destruction of forests, the decline in habitat quality, and subtle behavioral changes among wildlife, which can degrade soil health and vegetation.
Such disturbances can force animals out of their habitats and disrupt complex natural systems, throwing them off balance. Local communities also face several adverse effects from ecotourism, including:
- Outsiders often benefit financially at the expense of locals, leading to economic sidelining and erosion of cultural heritage within these communities.
- An increase in human activity within wild areas poses health risks and escalates the chances for conflicts between humans and animals.
- Pollution entering delicate ecosystems is a serious threat that needs to be considered.
- Trading souvenirs derived from wildlife perpetuates harm on already vulnerable environmental zones.
Preventing the Pitfalls of Ecotourism
To ensure ecotourism is sustainable, it is crucial to follow a comprehensive approach that includes certification programs, community engagement, and enforcement measures. For ecotourism to be truly sustainable in terms of cultural and social aspects, it must respect local customs and people.
This can be achieved by ensuring that they are well-informed and actively involved as key players. Tour operators should focus on protecting at-risk communities while also providing equitable employment opportunities to the local populace to ensure their operations provide substantial benefits.

Tourists also have a significant role to play, especially in voluntourism. It is important that they ensure these initiatives ethically manage their affairs to protect children and other vulnerable groups from harm. In addition, reducing travel’s environmental footprint is a critical consideration.
Travelers are urged to follow basic sustainable travel tips and select fewer flights or direct journeys whenever possible in an effort to minimize carbon emissions and reflect responsible travel ethics.
Participating in Ecotourism: How You Can Make a Difference
As conscious travelers, we have the power to create a positive impact by choosing destinations and activities that align with ecotourism values. By staying at eco-friendly accommodations, using sustainable modes of transportation, and reducing our waste, we can help protect the environment while enjoying our travels.
Making donations to local environmental organizations or actively participating in conservation initiatives can also enrich our travel experiences.
By engaging thoughtfully with each place we visit, we can enjoy fulfilling journeys that align with ecotourism principles while contributing to the protection of our planet’s natural beauty and biodiversity for generations to come.
Selecting Responsible Tour Operators
When choosing to travel, opting for tour operators who prioritize sustainable tourism practices is crucial to ensure that our explorations are aligned with ethical and environmental standards.
A responsible tour operator will be transparent about their sustainability efforts and initiatives, such as the ones supported by Royal Galapagos, which includes reducing plastic consumption and supporting conservation projects.
They will also be committed to minimizing their ecological footprint through responsible practices, including carbon offset programs.
In addition, they will prioritize positively impacting the local environment and its inhabitants. A tour operator that values wildlife preservation will prioritize promoting the observation of animals in their natural habitats without direct interaction.
Opting for companies that prioritize these values not only helps protect ecotourism destinations but also supports environmental consciousness and protective measures for nature.
Volunteering and Supporting Local Initiatives
Participating in local initiatives as a volunteer can make travel experiences more exciting while promoting community and environmental health. Engaging with communities in this way has a positive influence on those involved and creates unforgettable moments.
Travelers who volunteer their time gain deep immersion into local traditions, which helps with personal growth and a better understanding of global challenges.
Contributing through international volunteer work equips participants with essential life skills such as flexibility, communication abilities, and cooperative working proficiency.
Successful collaborations, like the one between the Royal Galapagos and the Galapagos Conservation Trust, demonstrate that volunteering contributes to funding conservation efforts.
These partnerships support sustainable progress in development projects that benefit both nature preservation efforts and elevate living standards for inhabitants within these communities.
Innovative Ecotourism Projects Around the World
The ecotourism industry has brought about innovative projects that are transforming the landscape of sustainable travel.
These pioneering initiatives offer a glimpse into the different ways ecotourism can be manifested, from special charter expeditions in the Galapagos Islands that focus on conservation and education to Slovenia’s green labeling system for accommodations and tourism services.
By collaborating with conservation groups or NGOs, ecotourism projects gain legitimacy and sustainability, ensuring that they create not only unique travel experiences but also contribute positively to the environment and local communities.
One such initiative is the partnership between Steppes Travel and the Galapagos Conservation Trust. Travelers aboard the Natural Paradise yacht can contribute directly to the preservation of the ecosystem while engaging with local conservation projects and experts.
These innovative ecotourism projects are essential in promoting sustainable tourism, as they provide models of how tourism can coexist with and even benefit conservation efforts. They set an example for ecotourism destinations worldwide.
Wildlife Sanctuaries and Their Role in Conservation
Serving as beacons for preservation, wildlife sanctuaries safeguard natural ecosystems and the species within them while enabling environmentally considerate wildlife encounters. Locations such as:
- Kenya’s Maasai Mara National Reserve
- Borneo’s Rainforest provides opportunities for tourists to witness animals in their own environments while bolstering conservation work through eco-tourism pursuits. Sanctuaries include:
- Yellowstone National Park in the USA
- Raja Ampat in Indonesia demonstrates how ecotourism can aid in preserving various species and afford visitors remarkable experiences.

Source: Brittanica
In remote locations such as Antarctica or Rwanda’s Volcanoes National Park, tourism is strictly regulated to minimize the environmental impact and maximize the funds directed towards conservation efforts.
In destinations like Madagascar and Svalbard, Norway, eco-friendly accommodations allow visitors to have close encounters with local wildlife and contribute to the economic stability of the area.
These protected areas are crucial for preserving biodiversity by providing responsible ways to experience nature, which educates travelers on the importance of conserving our natural habitats.
Community-Based Ecotourism Success Stories
Narratives from successful community-driven ecotourism initiatives highlight the benefits in terms of economic growth, heritage conservation, and environmental protection. The following are some examples:
- In Lorestan province, Iran, local communities have collaborated with researchers and policymakers to create a model for sustainable tourism. This collaboration has resulted in an enhancement of local capacity and improvements such as available rental accommodations and establishments along roads.
- Kichwa Ecolodge in Ecuador is another noteworthy example where active participation by the local community ensures they both oversee and profit from the lodge, including its adjacent natural resources.
- Auroville in India represents another distinct example dedicated to advancing eco-friendly lifestyles while preserving culture and nature.
- Efforts undertaken within Chilean locales and Indonesia’s Gunung Leuser National Park also exemplify how communal involvement can effectively manage cultural heritage sites and natural areas.
These instances highlight the importance of engaging locals when aiming for ecotourism achievements. Adhering to the principles set out by the Global Sustainable Tourism Council standards ensures these ventures contribute positively towards socioeconomic stability, ongoing cultural vitality, and environmental integrity.
By championing development tied with empowerment among their ranks, the outcomes highlight transformations wherein indigenous populations, together with other residents, can utilize their own unique cultural elements coupled with naturally occurring spaces to foster leading destinations focused on ecology.
These destinations simultaneously yield financial gains without compromising their ancestral legacy or ecosystems.
The Role of International Organizations in Promoting Ecotourism
International organizations, particularly the United Nations World Tourism Organization, play a crucial role in promoting ecotourism around the world by taking actions such as:
- Developing tourism-related policies
- Implementing standards similar to Costa Rica’s Certification for Sustainable Tourism (CST)
- Guiding countries and businesses towards adopting sustainable practices and standards
- Supporting the creation of destinations dedicated to ecotourism
- Integrating conservation principles into broader global tourism agendas
- Sharing successful approaches with the global ecotourism community
Their role is essential in encouraging and maintaining eco-friendly tourism practices worldwide.
Similarly, Ecotourism Kenya plays a significant role in advocating for eco-responsible travel behaviors that can be replicated in various areas.
Through its efforts to provide guidance, support initiatives, and accredit ecological tourism ventures, Ecotourism Kenya promotes environmental preservation while improving the quality of life of local communities. This enhances the regional significance and global impact of ecological tourism benefits.
As we watch the sunset on our ecotourism exploration, we are reminded of the tremendous impact that sustainable travel can have on our planet and its inhabitants.
Ecotourism offers a way for us to be more conscious and responsible as we experience the world. We can become stewards of the Earth’s future by preserving natural habitats and wildlife, empowering local communities economically, and educating travelers.
Let this journey through ecotourism’s principles, practices, and possibilities inspire you to consider how your travel choices can contribute to the greater good. Each trip can be a step toward a more sustainable and equitable world with the right approach.
Tourism can be a force for positive change, and we can cherish and preserve the beauty and diversity of our planet for generations to come.
References and Useful Resources
- https://ecotourism.org/what-is-ecotourism/
- https://www.webmd.com/balance/what-to-know-about-ecotourism
- https://www.unwto.org/tourism-statistics/measuring-sustainability-tourism
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecotourism
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ecotourism good or bad.
Participating in ecotourism is advantageous as it helps to reduce waste and pollution, promotes the sustainable use of natural resources, and aids in protecting ecosystems from further harm. It supports conservation efforts by minimizing energy consumption, utilizing renewable energies like solar power, and avoiding disposable plastics.
What is the main purpose of ecotourism?
Ecotourism aims to protect the environment while supporting local communities and preserving their culture.
What is ecotourism an example of?
Ecotourism is a form of sustainable travel that focuses on visiting natural areas to appreciate wildlife and support conservation efforts. The aim of this approach is to reduce environmental footprints and create positive impacts on both the environment and local communities. This stands in contrast to the broader impact of mass tourism.
What is the meaning of ecotourism?
Ecotourism, as defined by the International Ecotourism Society, is a form of travel that preserves natural areas while also promoting the well-being of local communities. The goal of ecotourism is to educate visitors about the environment and encourage sustainable practices that protect it. It also involves providing support for local communities. Essentially, ecotourism is a responsible and sustainable form of travel that benefits both the environment and the people who live in it.
What exactly defines ecotourism?
Ecotourism, which involves responsible travel to natural areas, is focused on supporting conservation efforts and benefiting local communities. This type of tourism aims to promote education about the preservation of nature and cultural appreciation. The goal is to have a positive impact on both the environment and the residents in the area.
Popular Related Posts

12 Leading Plastic Recycling Companies and Startups In 2024 [Full Review]

Eco-Friendly Parks: 7 Best Practices and 6 Great Examples Worldwide

Eco-Friendly Lifestyle Blog: The Simple Guide to Launch Yours in 2024

Solar Powered Greenhouse: The Ultimate Guide to Solar Charge your Greenhouse in 2024

12 Leading Green Concrete Companies In 2024
Get cutting-edge climate solutions delivered to your inbox.
The climate tech essentials. Bite-sized monthly updates for busy changemakers.
Pin It on Pinterest
- StumbleUpon
Let us take a walk to the sustainable tourism practices: a qualitative study through the lens of tourism experts
- Research Article
- Published: 04 January 2024
- Volume 31 , pages 12892–12915, ( 2024 )
Cite this article
- Vikas Arya 1 ,
- Vilte Auruskeviciene ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1563-4052 2 ,
- Srishti Agarwal 3 ,
- Priyanka Kokatnur 3 ,
- Harish Kumar 4 &
- Rajeev Verma 5
357 Accesses
Explore all metrics
The rising opportunities of sustainable tourism have brought many policies to control the exploitation of the environment and increase the reach of luxurious, safe, and authentic experiences to the different segments of tourists. This study seeks to prioritize the variables influencing the development of sustainable tourism and pinpoint key success factors that align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It adopts a tri-dimensional framework encompassing economic, social, and environmental aspects, further delineated into eleven sub-dimensions, to provide a quantitative evaluation of sustainable tourism. We conducted interviews with 26 tourism industry experts hailing from eight countries, analyzing their responses using interval type-2 fuzzy sets. The results underscore the critical role of specific components in advancing sustainable tourism. In the economic dimension, “financial resources and tourism costs” emerge as vital factors. In the social dimension, “health and safety” takes center stage, while “green infrastructure” plays a pivotal role in the environmental dimension. These findings underscore the significance of these aspects in promoting sustainable tourism. Furthermore, this study explores the strategic importance of sustainable tourism equity in shaping tourism planning and development for emerging markets.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Source: Authors
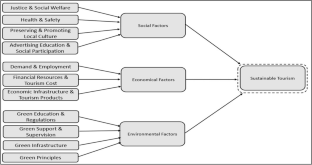
Similar content being viewed by others
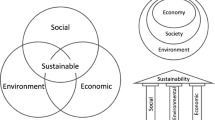
Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins
Ben Purvis, Yong Mao & Darren Robinson
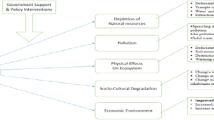
Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism
Qadar Bakhsh Baloch, Syed Naseeb Shah, … Asia Umar Khan

Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends
Lishan Xu, Changlin Ao, … Zhenyu Cai
Data availability
Data will be available on request.
Agarwal SA, Kasliwal N (2019) Indian consumer’s environmental consciousness and decision towards green services of hospitality industry. J Hosp Appl Res 14(2):22–40
Google Scholar
Ahmad N, Youjin L, Hdia M (2022) The role of innovation and tourism in sustainability: why is environment-friendly tourism necessary for entrepreneurship? J Clean Prod 379:134799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134799
Article Google Scholar
Alfaro Navarro JL, Andrés Martínez ME, Mondéjar Jiménez JA (2020) An approach to measuring sustainable tourism at the local level in Europe. Curr Issue Tour 23(4):423–437. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2019.1579174
Andereck KL, Valentine KM, Knopf RC, Vogt CA, Knollenberg W (2021) Tourists’ willingness to conserve resources and reduce their carbon footprint in national parks. J Sustain Tour 29(4):499–516
Andria J, di Tollo G, Pesenti R (2019) A fuzzy evaluation of tourism sustainability. In Business and consumer analytics: New ideas pp 911–932. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06222-4_24
Apak ÖC, Gürbüz A (2023) The effect of local food consumption of domestic tourists on sustainable tourism. J Retail Consum Serv 71:103192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103192
Arya V, Sethi D, Paul J (2019) Does digital footprint act as a digital asset? — enhancing brand experience through remarketing. Int J Inf Manage 49:142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.03.013
Arya V, Sharma S, Sethi D, Verma H, Shiva A (2018) Ties that bind tourists: embedding destination motivators to destination attachment: a study in the context of Kumbh Fair India. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 23(12):1160–1172. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2018.1528992
Arya V, Sambyal R, Sharma A, Dwivedi YK (2023) Brands are calling your AVATAR in Metaverse—a study to explore XR‐based gamification marketing activities and consumer‐based brand equity in virtual world. Journal of Consumer Behaviour. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.2214
Athari SA, Alola UV, Ghasemi M, Alola AA (2021) The (Un) sticky role of exchange and inflation rate in tourism development: insight from the low and high political risk destinations. Curr Issue Tour 24(12):1670–1685. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2020.1798893
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Abbas J, He C, Pilař L, Shah SAR (2023a) Tourism, urbanization and natural resources rents matter for environmental sustainability: the leading role of AI and ICT on sustainable development goals in the digital era. Resour Policy 82:103445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103445
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Luzon LI, Usman M, Jahanger A (2023) The relevance of international tourism and natural resource rents in economic growth: fresh evidence from MINT countries in the digital era. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25022-0
Barbieri C, Sotomayor S, Gil Arroyo C (2020) Sustainable tourism practices in indigenous communities: the case of the Peruvian Andes. Tour Plann Dev 17(2):207–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2019.1597760
Beames S, Mackenzie SH, Raymond E (2022) How can we adventure sustainably? A systematized review of sustainability guidance for adventure tourism operators. J Hosp Tour Manag 50:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2022.01.002
Becken S, Loehr J (2022) Tourism governance and enabling drivers for intensifying climate action. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2022.2032099
Becken S, Stantic B, Chen JS (2020) Climate change and tourism: impacts and challenges. Tourism Review 75(1):46–60
Berno T, Rajalingam G, Miranda AI, Ximenes J (2022) Promoting sustainable tourism futures in Timor-Leste by creating synergies between food, place and people. J Sustain Tour 30(2–3):500–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1895819
Bodhanwala S, Bodhanwala R (2022) Exploring relationship between sustainability and firm performance in travel and tourism industry: a global evidence. Social Respons J 18(7):1251–1269. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-09-2020-0360
Bramwell B, Lane B (2019) Critical research on the governance and management of tourism in protected areas. Curr Issue Tour 22(5):547–579
Briassoulis H (2002) Sustainable tourism and the question of the commons. Ann Tour Res 29(4):1065–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-7383(02)00021-X
Bricker KS, Schultz J (2011) Sustainable tourism in the USA: a comparative look at the Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria. Tour Recreat Res 36(3):215–229
Bramwell B, Lane B (2011) Critical research on the governance of tourism and sustainability. J Sustain Tour 19(4–5):411–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2011.11081668
Budeanu A, Miller G, Moscardo G, Ooi CS (2016) Sustainable tourism, progress, challenges and opportunities: an introduction. J Clean Prod 111:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.10.027
Buckley R (2012) Sustainable tourism: research and reality. Ann Tour Res 39(2):528–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2012.02.003
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Carlson J, Rahman MM, Rosenberger PJ III, Holzmüller HH (2016) Understanding communal and individual customer experiences in group-oriented event tourism: an activity theory perspective. J Mark Manag 32(9–10):900–925. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257X.2016.1181099
Chandra P, Kumar J (2021) Strategies for developing sustainable tourism business in the Indian Himalayan Region: insights from Uttarakhand, the Northern Himalayan State of India. J Destin Mark Manag 19:100546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2020.100546
Choe J, O’Regan M, Kimbu A, Lund NF, Ladkin A (2021) Quality of life perspectives for different social groups in a World Centre of Tourism and Leisure. Tour Stud 21(4):615–637. https://doi.org/10.1177/14687976211038758
Choi HSC, Sirakaya E (2005) Measuring residents’ attitude toward sustainable tourism: development of sustainable tourism attitude scale. J Travel Res 43(4):380–394. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287505274651
Chong K, Balasingam AS (2019) Tourism sustainability: economic benefits and strategies for preservation and conservation of heritage sites in Southeast Asia. Tourism Review 74(2):268–279. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-11-2017-0182
Darcy S, Cameron B, Pegg S (2010) Accessible tourism and sustainability: a discussion and case study. J Sustain Tour 18(4):515–537. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669581003690668
Da Silva J, Fernandes V, Limont M, Rauen WB (2020) Sustainable development assessment from a capitals perspective: analytical structure and indicator selection criteria. J Environ Manage 260:110147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110147
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sausmarez De (2007) Crisis management, tourism and sustainability: the role of indicators. J Sustain Tour 15(6):700–714
Dolnicar S, Crouch GI, Long P (2008) Environment-friendly tourists: what do we really know about them? J Sustain Tour 16(2):197–210. https://doi.org/10.2167/jost653.0
Dong XD, Nguyen TQT (2022) Power, community involvement, and sustainability of tourism destinations. Tour Stud 23(1):62–79. https://doi.org/10.1177/14687976221144335
Dredge D, Scott N, Lechner AM, Dominey-Howes D (2020) Spatial and coastal tourism. In Tourism and Water (pp. 109–126). Channel View Publications
Durband R (2021) Establishing sustainability standards in tourism. Handbook for sustainable tourism practitioners: the essential toolbox, 233
El Atiek S, Goutte S (2023) Impacts, sustainability, and resilience on the Egyptian tourism and hospitality industry after the Russian airplane crash in 2015. Res Int Bus Financ 64:101866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ribaf.2022.101866
El-Masry EA, El-Sayed MK, Awad MA, El-Sammak AA, Sabarouti MAE (2022) Vulnerability of tourism to climate change on the Mediterranean coastal area of El Hammam–EL Alamein Egypt. Environ Dev Sustain 24(1):1145–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01488-9
Eslami S, Khalifa Z, Mardani A, Streimikiene D, Han H (2019) Community attachment, tourism impacts, quality of life and residents’ support for sustainable tourism development. J Travel Tour Mark 36(9):1061–1079. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2019.1689224
Falatoonitoosi E, Schaffer V, Kerr D (2022) Does sustainable tourism development enhance destination prosperity? J Hosp Tourism Res 46(5):1056–1082. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348020988328
Farrell B, Twining-Ward L (2005) Seven steps towards sustainability: tourism in the context of new knowledge. J Sustain Tour 13(2):109–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580508668481
Firman A, Moslehpour M, Qiu R, Lin PK, Ismail T, Rahman FF (2023) The impact of eco-innovation, ecotourism policy and social media on sustainable tourism development: evidence from the tourism sector of Indonesia. Econ Res - Ekonomska Istraživanja 36(2):2143847. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2022.2143847
Fong SF, Lo MC, Songan P et al (2017) Self-efficacy and sustainable rural tourism development: Local communities’ perspectives from Kuching, Sarawak. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 22(2):147–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2016.1208668
Font X, Torres-Delgado A, Crabolu G, Palomo Martinez J, Kantenbacher J, Miller G (2023) The impact of sustainable tourism indicators on destination competitiveness: The European Tourism Indicator System. J Sustain Tour 31(7):1608–1630. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1910281
Garau G, Carboni D, Karim El Meligi A (2022) Economic and environmental impact of the tourism carrying capacity: a local-based approach. J Hosp Tour Res 46(7):1257–1273. https://doi.org/10.1177/10963480211031426
Geoffrey Deladem T, Xiao Z, Siueia TT, Doku S, Tettey I (2021) Developing sustainable tourism through public-private partnership to alleviate poverty in Ghana. Tour Stud 21(2):317–343. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797620955250
Ghoochani O, Ghanian M, Khosravipour B, Crotts JC (2020) Sustainable tourism development performance in the wetland areas: a proposed composite index. Tourism Review. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-02-2019-0061
Garrig’os-Sim’on FJ, Gald’on-Salvador JL and Gil-Pechu’an I (2015) The economic sustainability of tourism growth through leakage calculation. Tourism Econ 21(4):721–739. https://doi.org/10.5367/te.2014.0372
Ghahramani L, Khalilzadeh J, Kc B (2018) Tour guides’ communication ecosystems: an inferential social network analysis approach. Inform Technol Tour 20(1):103–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40558-018-0114-y
Go H, Kang M (2023) Metaverse tourism for sustainable tourism development: Tourism agenda 2030. Tourism Review 78(2):381–394. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-02-2022-0102
Gössling S (2021) Tourism, technology and ICT: a critical review of affordances and concessions. J Sustain Tour 29(5):733–750. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1873353
Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM (2020) Tourism and water: interactions, impacts, and challenges. Annu Rev Environ Resour 45:269–294
Gossling S, Scott D, Hall CM (2018) Tourism and Water (Vol. 13). Channel View Publications
Graci S, Maher PT, Peterson B, Hardy A, Vaugeois N (2021) Thoughts from the think tank: lessons learned from the sustainable Indigenous tourism symposium. J Ecotour 20(2):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/14724049.2019.1583754
Grilli G, Tyllianakis E, Luisetti T, Ferrini S, Turner RK (2021) Prospective tourist preferences for sustainable tourism development in Small Island Developing States. Tour Manage 82:104178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104178
GSTC (2021) Who We Are. Global Sustainable Tourism Council. Accessed during October 2023, https://www.gstcouncil.org/who-we-are/
GSTC (2022) The GSTC criteria: the global baseline standards for sustainability in travel and tourism. Global Sustainable Tourism Council. Accessed during October 2023, https://www.gstcouncil.org/the-gstc-criteria/
GSTC (2023) Certification. Global Sustainable Tourism Council. Accessed during October 2023, https://www.gstcouncil.org/certification/
Hall CM (2019) Constructing sustainable tourism development: the 2030 agenda and the managerial ecology of sustainable tourism. J Sustain Tour 27(7):1044–1060. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2018.1560456
Hall CM, Gossling S, Scott D (Eds.) (2015) The Routledge handbook of tourism and sustainability. Routledge
Hardy A, Beeton RJ, Pearson L (2002) Sustainable tourism: an overview of the concept and its position in relation to conceptualisations of tourism. J Sustain Tour 10(6):475–496. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580208667183
Hamid MA, Isa SM, Kiumarsi S (2021) Sustainable tourism practices and business performance from the tour operators’ perspectives. Anatolia 32(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2020.1830135
Han H (2021) Consumer behavior and environmental sustainability in tourism and hospitality: a review of theories, concepts, and latest research. J Sustain Tour 29(7):1021–1042. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1903019
He LY, Li H, Bi JW, Yang JJ, Zhou Q (2022) The impact of public health emergencies on hotel demand—estimation from a new foresight perspective on the COVID-19. Annals of Tourism Research, 94, May 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2022.103402
Hamid MA, Isa SM, Kiumarsi S (2020) Sustainable tourism practices and business performance from the tour operators’ perspectives. Anatolia 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2020.1830135
Higgins-Desbiolles F, Carnicelli S, Krolikowski C, Wijesinghe G, Boluk K (2019) Degrowing tourism: rethinking tourism. J Sustain Tour 27(12):1926–1944. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1601732
Higgins-Desbiolles F (2018) Sustainable tourism: sustaining tourism or something more? Tour Manage Perspect 25:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.11.017
Higuchi Y, Yamanaka Y (2019) The potential value of research-based evidence in destination management: the case of Kamikawa. Japan Tour Rev 74(2):166–178. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-11-2017-0188
Iorio M, Corsale A (2013) Diaspora and tourism: Transylvanian Saxons visiting the homeland. Tour Geogr 15(2):198–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2012.647327
Iqbal A, Ramachandran S, Siow ML, Subramaniam T, Afandi SHM (2022) Meaningful community participation for effective development of sustainable tourism: bibliometric analysis towards a quintuple helix model. J Outdoor Recreat Tour 39:100523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jort.2022.100523
Ivanov S, Gavrilina M, Webster C, Ralko V (2017) Impacts of political instability on the tourism industry in Ukraine. J Policy Res Tourism Leisure Events 9(1):100–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/19407963.2016.1209677
Ivars-Baidal JA, Vera-Rebollo JF, Perles-Ribes J, Femenia-Serra F, Celdrán-Bernabeu MA (2023) Sustainable tourism indicators: what’s new within the smart city/destination approach? J Sustain Tour 31(7):1556–1582
Iversen R (2022). Cultural exchange in sustainable tourism: a literature review. Current Issues in Tourism, 1–16
Jabbour CJC, Fiorini PDC, Wong CW, Jugend D, Jabbour ABLDS, Seles BMRP, ... et al (2020) First-mover firms in the transition towards the sharing economy in metallic natural resource-intensive industries: implications for the circular economy and emerging industry 4.0 technologies. Resources Policy 66:101596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101596
Kahraman C (Ed.) (2008) Fuzzy multi-criteria decision making: theory and applications with recent developments (Vol. 16). Springer Science and Business Media
Kahraman C, Öztayşi B, Sarı İU, Turanoğlu E (2014) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process with interval type-2 fuzzy sets. knowledge-Based Systems 59:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.02.001
Karnik NN, Mendel JM, Liang Q (1999) Type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 7(6):643–658. https://doi.org/10.1109/91.811231
Kaefer F (2022) Linda Veråsdal on ethical travel and responsible tourism in the Gambia. In Sustainability leadership in tourism: interviews, insights, and knowledge from practice pp 405–409. Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05314-6_64
Kamata H (2022) Tourist destination residents’ attitudes towards tourism during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Issue Tour 25(1):134–149
Katemliadis I, Kolongou ES, Drousiotis P (2021) Rising sustainability standards: the Cyprus sustainable tourism initiative. Worldwide Hosp Tour Themes 13(6):754–762. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1881452
Kerdpitak C (2022) The effects of innovative management, digital marketing, service quality and supply chain management on performance in cultural tourism business. Uncertain Supply Chain Manage 10(3):771–778. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2022.4.005
Ketter E (2020) Millennial travel: tourism micro-trends of European Generation Y. J Tour Futures 7(2):192–196. https://doi.org/10.1108/JTF-10-2019-0106
Komppula R (2014) The role of individual entrepreneurs in the development of competitiveness for a rural tourism destination—a case study. Tour Manage 40:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.07.007
Kim YJ, Palakurthi R, Hancer M (2012) The environmentally friendly programs in hotels and customers’ intention to stay: an online survey approach. Int J Hosp Tour Adm 13(3):195–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/15256480.2012.698169
Kilic M, Kaya I (2015) Investment project evaluation by a decision making methodology based on type-2 fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 27:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.028
Klintman M (2012) Issues of scale in the global accreditation of sustainable tourism schemes: toward harmonized re-embeddedness?. Sustainability: Science, Practice and Policy 8(1):59–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/15487733.2012.11908085
Kularatne T, Wilson C, Månsson J, Hoang V, Lee (2019) Do environmentally sustainable practices make hotels more efficient? A study of major hotels in Sri Lanka. Tourism Management 71:213-225 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.009
Kumar A, Misra SC, Chan FT (2022) Leveraging AI for advanced analytics to forecast altered tourism industry parameters: a COVID-19 motivated study. Expert Syst Appl 210:118628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118628
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kuo FI, Fang WT, LePage BA (2022) Proactive environmental strategies in the hotel industry: eco-innovation, green competitive advantage, and green core competence. J Sustain Tour 30(6):1240–1261. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1931254
Lasso A, Dahles H (2018) Are tourism livelihoods sustainable? Tourism development and economic transformation on Komodo Island, Indonesia. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 23(5):473–485. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2018.1467939
Lee CK, Olya H, Ahmad MS, Kim KH, Oh MJ (2021) Sustainable intelligence, destination social responsibility, and pro-environmental behaviour of visitors: evidence from an eco-tourism site. J Hosp Tour Manag 47:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2021.04.010
Lee SW, Xue K (2020) A model of destination loyalty: Integrating destination image and sustainable tourism. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 25(4):393–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2020.1713185
Liburd JJ, Edwards D (eds) (2010) Understanding the sustainable development of tourism. Goodfellow, Oxford, pp 19–44
Liu CH, Jiang JF, Gan B (2021) The antecedent and consequence behaviour of sustainable tourism: integrating the concepts of marketing strategy and destination image. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 26(8):829–848. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2021.1908384
Liu CR, Lin WR, Wang YC, Chen SP (2019) Sustainability indicators for festival tourism: a multi-stakeholder perspective. J Qual Assur Hosp Tour 20(3):296–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/1528008X.2018.1530165
Liu-Lastres B, Wen H, Huang WJ (2023) A reflection on the Great Resignation in the hospitality and tourism industry. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 35(1):235–249. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-05-2022-0551
Liu T, Juvan E, Qiu H, Dolnicar S (2022) Context-and culture-dependent behaviors for the greater good: a comparative analysis of plate waste generation. J Sustain Tour 30(6):1200–1218. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1918132
Liu Z (2003) Sustainable tourism development: a critique. J Sustain Tour 11(6):459–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580308667216
Lopes HS, Remoaldo PC, Ribeiro V, Martin-Vide J (2022) Pathways for adapting tourism to climate change in an urban destination—evidences based on thermal conditions for the Porto Metropolitan Area (Portugal). J Environ Manage 315:115161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115161
Lu J, Nepal SK (2009) Sustainable tourism research: an analysis of papers published in the Journal of Sustainable Tourism. J Sustain Tour 17(1):5–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580802582480
Mamirkulova G, Mi J, Abbas J, Mahmood S, Mubeen R, Ziapour A (2020) New Silk Road infrastructure opportunities in developing tourism environment for residents better quality of life. Global Ecol Conserv 24:e01194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01194
Mathew PV (2022) Sustainable tourism development: discerning the impact of responsible tourism on community well-being. J Hosp Tour Insights 5(5):987–1001. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHTI-02-2021-0052
Millar M, Baloglu S (2009) A green room experience: a comparison of business and leisure travelers’ preferences. Hospitality Management 1–12
MacKenzie N, Gannon MJ (2019) Exploring the antecedents of sustainable tourism development. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 31(6):2411–2427. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-05-2018-0384
Moayerian N, McGehee NG, Stephenson MO Jr (2022) Community cultural development: exploring the connections between collective art making, capacity building and sustainable community-based tourism. Ann Tour Res 93:103355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2022.103355
Molden O, Abrams J, Davis EJ, Moseley C (2017) Beyond localism: the micropolitics of local legitimacy in a community-based organization. J Rural Stud 50:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2017.01.001
Monaco S (2018) Tourism and the new generations: emerging trends and social implications in Italy. J Tour Futures 4(1):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1108/JTF-12-2017-0053
Mowforth M, Munt I (2019) Tourism and sustainability: development, globalisation, and new tourism in the third world. Routledge
Moyle BD, Weaver DB, Gössling S, McLennan CL, Hadinejad A (2022) Are water-centric themes in sustainable tourism research congruent with the UN Sustainable Development Goals? J Sustain Tour 30(8):1821–1836. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2022.2083903
Nash D, Butler R (1990) Towards sustainable tourism. Tour Manage 11(3):263–264
Nguyen TQT, Young T, Johnson P, Wearing S (2019) Conceptualising networks in sustainable tourism development. Tour Manage Perspect 32:100575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100575
Nok LC, Suntikul W, Agyeiwaah E, Tolkach D (2017) Backpackers in Hong Kong–motivations, preferences and contribution to sustainable tourism. J Travel Tour Mark 34(8):1058–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2016.1276008
Nunkoo R, Sharma A, Rana NP, Dwivedi YK, Sunnassee VA (2021) Advancing sustainable development goals through interdisciplinarity in sustainable tourism research. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.2004416
O’Hare D, Pegoraro A, Scarles C (2020) “Instagrammability”: an exploration of social media engagement and destination image in organic contexts. Curr Issue Tour 23(1):1–18
Pan SY, Gao M, Kim H, Shah KJ, Pei SL, Chiang PC (2018) Advances and challenges in sustainable tourism toward a green economy. Sci Total Environ 635:452–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.134
Article CAS PubMed ADS Google Scholar
Partanen M, Sarkki S (2021) Social innovations and sustainability of tourism: Insights from public sector in Kemi Finland. Tourist Studies 21(4):550–571. https://doi.org/10.1177/14687976211040246
Poudel S, Nyaupane GP, Budruk M (2016) Stakeholders’ perspectives of sustainable tourism development: a new approach to measuring outcomes. J Travel Res 55(4):465–480. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287514563166
Rahmadian E, Feitosa D, Zwitter A (2022) A systematic literature review on the use of big data for sustainable tourism. Curr Issue Tour 25(11):1711–1730. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1974358
Rasoolimanesh SM, Ramakrishna S, Hall CM, Esfandiar K, Seyfi S (2023) A systematic scoping review of sustainable tourism indicators in relation to the sustainable development goals. J Sustain Tour 31(7):1497–1517. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1775621
Rastegar R, Ruhanen L (2021) A safe space for local knowledge sharing in sustainable tourism: an organisational justice perspective. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1929261
Rodríguez-Díaz B, Pulido-Fernández JI (2020) Sustainability as a key factor in tourism competitiveness: a global analysis. Sustainability 12(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010051
Roxas FMY, Rivera JPR, Gutierrez ELM (2020-a) Framework for creating sustainable tourism using systems thinking. Current Issues in Tourism 23(3):280–296. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2018.1534805
Roxas FMY, Rivera JPR, Gutierrez ELM (2020b) Mapping stakeholders’ roles in governing sustainable tourism destinations. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management 45:387–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.09.005
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resources allocation. McGraw-Hill, London
Šagovnović I, Stamenković I (2022) Investigating values of green marketing tools in predicting tourists’ eco-friendly attitudes and behavior. Journal of Ecotourism 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/14724049.2022.2075003
Sahoo BK, Nayak R, Mahalik MK (2022) Factors affecting domestic tourism spending in India. Ann Tour Res Empirical Insights 3(2):100050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100050
Santos M, Veiga C, Santos JAC, Águas P (2022) Sustainability as a success factor for tourism destinations: a systematic literature review. Worldwide Hosp Tour Themes 14(1):20–37. https://doi.org/10.1108/WHATT-10-2021-0139
Sarı IU, Öztayşi B, Kahraman C (2013) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process using type-2 fuzzy sets: an application to warehouse location selection. In Multicriteria decision aid and artificial intelligence pp285–308. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118522516.ch12
Schmude J, Zavareh S, Schwaiger KM, Karl M (2020) Micro-level assessment of regional and local disaster impacts in tourist destinations. In Tourism in changing natural environments pp. 98–116. Routledge
Scott D, Gössling S (2022) A review of research into tourism and climate change—launching the annals of tourism research curated collection on tourism and climate change. Ann Tour Res 95:103409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2022.103409
Shafiee S, Ghatari AR, Hasanzadeh A, Jahanyan S (2019) Developing a model for sustainable smart tourism destinations: a systematic review. Tour Manage Perspect 31:287–300
Shafiee S, Jahanyan S, Ghatari AR, Hasanzadeh A (2023) Developing sustainable tourism destinations through smart technologies: a system dynamics approach. J Simul 17(4):477–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/17477778.2022.2030656
Shang Y, Lian Y, Chen H, Qian F (2023) The impacts of energy resource and tourism on green growth: evidence from Asian economies. Resour Policy 81:103359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103359
Sharif A, Afshan S, Nisha N (2017) Impact of tourism on CO 2 emission: evidence from Pakistan. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 22(4):408–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2016.1273960
Sharma K, Arya V, Mathur HP (2023) New higher education policy and strategic plan: commensurate India’s higher education in global perspective. FIIB Business Review 23197145221125351
Sharpley R (2023) Sustainable tourism governance: local or global? Tour Recreat Res 48(5):809–812. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2022.2040295
Sharpley R (2021) On the need for sustainable tourism consumption. Tour Stud 21(1):96–107. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797620986087
Sharpley R (2000) Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. J Sustain Tour 8(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580008667346
Shu H, Yu Q, Liu K, Wang A, Zha J (2022) Understanding wage differences across tourism-characteristic sectors: insights from an extended input-output analysis. J Hosp Tour Manag 51:88–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2022.02.030
Sisneros-Kidd AM, Monz C, Hausner V, Schmidt J, Clark D (2019) Nature-based tourism, resource dependence, and resilience of Arctic communities: framing complex issues in a changing environment. J Sustain Tour 27(8):1259–1276. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1612905
Sobaih AEE, Elshaer I, Hasanein AM, Abdelaziz AS (2021) Responses to COVID-19: The role of performance in the relationship between small hospitality enterprises’ resilience and sustainable tourism development. Int J Hosp Manag 94:102824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102824
Sørensen EB, Hjalager AM (2020) Conspicuous non-consumption in tourism: non-innovation or the innovation of nothing? Tour Stud 20(2):222–247. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797619894463
Streimikiene D, Svagzdiene B, Jasinskas E, Simanavicius A (2021) Sustainable tourism development and competitiveness: the systematic literature review. Sustain Dev 29(1):259–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2133
Strzelecka M, Dąbrowski JM, Uramowska M (2021) A review of environmental sustainability in tourism. J Clean Prod 279:123748
Sullivan K, Thomas S, Rosano M (2018) Using industrial ecology and strategic management concepts to pursue the Sustainable Development Goals. J Clean Prod 174:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.201
Sun L, Wang Y (2021) Global economic performance and natural resources commodity prices volatility: evidence from pre and post COVID-19 era. Resour Policy 74:102393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102393
Sun YY, Li M, Lenzen M, Malik A, Pomponi F (2022) Tourism, job vulnerability and income inequality during the COVID-19 pandemic: a global perspective. Ann Tour Res Empirical Insights 3(1):100046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100046
Terry Mok Connie Lam (1998) Hotel and tourism development in Vietnam. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing 7(1):85-91. https://doi.org/10.1300/J073v07n01_06
Thapa K, King D, Banhalmi-Zakar Z, Diedrich A (2022) Nature-based tourism in protected areas: a systematic review of socio-economic benefits and costs to local people. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 29(7):625–640 https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2022.2073616
Tolkach D, King B, Pearlman M (2013) An attribute-based approach to classifying community-based tourism networks. Tour Plann Dev 10(3):319–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2012.747985
Torres-Delgado A, Saarinen J (2017) Using indicators to assess sustainable tourism development: a review. New research paradigms in tourism geography, 31–47
Tuan VK, Rajagopal P (2019) Analyzing factors affecting tourism sustainable development towards Vietnam in the new era. Eur J Business Innov Res 7(1):30–42
Tzschentke N, Kirk D, Lynch PA (2004) Reasons for going green in serviced accommodation establishments. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 16(2):116–124. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596110410520007
UNWTO (2020) Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations World Tourism Organization. Accessed during October 2023, https://www.unwto.org/sustainable-development-goals
UNWTO (2018) Tourism and the SDGs: Journey to 2030. World Tourism Organization
Valenti WC, Kimpara JM, Preto BDL, Moraes-Valenti P (2018) Indicators of sustainability to assess aquaculture systems. Ecol Ind 88:402–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.12.068
Verma R, Arya V, Thomas A, Bolognesi E, Mueller J (2023) Does startup culture in the emerging country grow around societal sustainability? An empirical study through the lens of co-creational capital and green intellect. J Intellect Cap 24(4):1047–1074
Vespestad MK, Lindberg F, Mossberg L (2019) Value in tourist experiences: How nature-based experiential styles influence value in climbing. Tour Stud 19(4):453–474. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797619837966
Weaver DB, Moyle B, McLennan CLJ (2022) The citizen within: positioning local residents for sustainable tourism. J Sustain Tour 30(4):897–914. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1903017
Westoby R, Gardiner S, Carter RW, Scott N (2021) Sustainable livelihoods from tourism in the “10 New Balis” in Indonesia. Asia Pacific J Tour Res 26(6):702–716. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2021.1908386
World Tourism Organization (WTO) (2019), International tourism results 2018 and outlook 2019. http://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/pdf/unwto_barometer_jan19_presentation_en.pdf (accessed 24 August 2019)
World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) represents the Travel and Tourism Sector globally (2020), Accessed at https://wttc.org/ retrieved on 15 January 2020
Wu JS, Barbrook-Johnson P, Font X (2021) Participatory complexity in tourism policy: understanding sustainability programmes with participatory systems mapping. Ann Tour Res 90:103269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2021.103269
Zadeh L (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Prt I. Inform Sci 8(3):199–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255%2875%2990036-5
Zhang J (2016) Weighing and realizing the environmental, economic and social goals of tourism development using an analytic network process-goal programming approach. J Clean Prod 127:262–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.131
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Rabat Business School, International University of Rabat, Rabat, Morocco
ISM University of Management and Economics: ISM Vadybos Ir Ekonomikos Universitetas, Gedimino St. 7, 01103, Vilnius, Lithuania
Vilte Auruskeviciene
School of Management, MIT World Peace University, Pune, India
Srishti Agarwal & Priyanka Kokatnur
Great Lakes Institute of Management, Gurgaon Campus, Gurgaon, India
Harish Kumar
Indian Institute of Management, Ranchi, India
Rajeev Verma
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Vikas Arya conducted the analysis of data and provided an interpretation of the findings. Vilte Auruskeviciene wrote the manuscript draft and ensured consistency in referencing and citation formatting. Srishti Agarwal collected data, collaborated with Vikas Arya to analyze the data, and contributed to the discussion of the findings. Priyanka Kokatnur contributed to the research methodology development and data collection. Harish Kumar provided insights to the theoretical and managerial aspects of the study and contributed to the discussion section. Rajeev Verma conducted a literature review and collaborated with Vilte Auruskeviciene to integrate the literature review into the manuscript. All authors provided comments on previous versions of the manuscript, and they all read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Vilte Auruskeviciene .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Arya, V., Auruskeviciene, V., Agarwal, S. et al. Let us take a walk to the sustainable tourism practices: a qualitative study through the lens of tourism experts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31 , 12892–12915 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31503-7
Download citation
Received : 15 June 2023
Accepted : 08 December 2023
Published : 04 January 2024
Issue Date : February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31503-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sustainable tourism
- Eco-tourism
- AHP-type 2 fuzzy test
- Responsible consumers
- Tourism sustainable equity
- Tourism industry
- Green services
- SDGs in tourism
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
History of ecotourism
As long as people have stood on two feet, they have been traveling. Since the dawn of time, people have traveled for reasons relating to war, religion, trade, education, relaxation, leisure, entertainment and more. In the classical world, it was mainly the privileged elite that had the means to travel for amusement or entertainment. Indeed, the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all established infrastructure such as roads, seaside resorts, and maps to facilitate travel throughout the ancient world.
With the onset of the industrial revolution, however, traveling or touring became available to the masses. Railroads, improved roads, cars, domestic air travel, and other modes of transportation all made traveling accessible to large amounts of people, and with it the motivations for travel also began to change. As tourism became a formalized industry, people could choose from an assortment of travel options. You could take a day trip to the beach a few miles up the road; you could get in a bus to travel across state lines to take in a ball game or see a relative that had since moved away; or you could jump in an airplane to go on safari in the African jungle.
All these possibilities had not always been available to people living in the world of yesteryear. As people began to take advantage of these exciting and unique opportunities associated with the industrial revolution, the not-so-hidden cost of such opportunities began to become known. Air pollution, deforestation, mass extinction of species, global warming, and sea-level rise have all more-or-less been popularly attributed to the many after-effects of the industrial revolution.
Ecotourism was first conceptualized in the early 1980s as a type of travel for people who wanted to learn about different and exotic environments without causing the environmental harm or damage associated with other forms of tourism. It became an official term in 1982 when it was recorded in the Oxford English Dictionary, and read thusly:
“ ecotourism , n . ... Tourism to areas of ecological interest (typically exotic and often threatened natural environments), esp. to support conservation efforts and observe wildlife; spec. access to an endangered environment controlled so as to have the least possible adverse effect.”
Ecotourism gained momentum in the 1990s with environmental conservation and recognizing the planet an exhaustible resource becoming a mainstream consideration. Today, ecotourism continues to grow as more people travel with environmental consciousness. In 2002, the United Nations declared it the year of ecotourism, and in 2003 the Center for Responsible Travel is formed. Since that time, ecotourism has become a $263 billion industry, with a 65% growth rate from 2009 to 2013.
IOI’s passion is to empower isolated communities to grow in a sustainable way through educational travel. Therefor, they take the concept of Ecotourism one step further. Creating stewardship for the environment, they engage with their host communities through educational and social development projects.
Going on an educational adventure with IOI will guarantee you an unforgettable, immersive experience through homestay accommodations and service learning projects and civic engagement. Throughout, the academic component supplements the experience with background in culture, environmental and social aspects of the local community.
By Kevin Bulger, Intern and Guest Blogger

The end of development tourism: A new model for development cooperation
Subscribe to the sustainable development bulletin, patrick fine patrick fine nonresident senior fellow - global economy and development , center for sustainable development.
November 22, 2021
The time has come for international agencies, donors, and NGOs to adapt their business cultures and operating models to a new era of international development cooperation. The converging transformational forces of the COVID-19 pandemic and the movement to “decolonize development” have created new options for development partnerships to move away from the traditional use of expatriates in management and technical roles.
The first transformational force was the COVID-19 pandemic. By the middle of March 2020, international travel had shut down and organizations were scrambling to shift to remote work. While the capacity for virtual collaboration and remote work via video conferencing had been available for at least 10 years and there was some movement in this direction, the forced shift to a remote posture shattered cultural and perceived operational barriers to working remotely overnight. By May 2020, surprisingly few programs that had relied on external oversight and on-the-ground technical assistance had closed, and development organizations of all types (donors, multilateral development banks, NGOs) were expressing pride in how quickly they had adapted to collaborating and providing management and technical services virtually.
The converging transformational forces of the COVID-19 pandemic and the movement to “decolonize development” have created new options for development partnerships to move away from the traditional use of expatriates in management and technical roles.
The second transformational force that emerged in 2020 was the rise of a powerful movement around the need to “decolonize development.” While the decolonization critique is not new and echoes the 1970s outcry against “neo-colonialism,” the current manifestation has fired the passions of a new generation of development professionals caught up in the racial and social reckonings shaking the U.S. and Western Europe. In the context of international development, this translates into demands to address the power imbalances between donor nation and developing country organizations and professionals. In practical terms, it means greater transparency and local participation in how development assistance is programmed, greater local control over spending decisions, more use of local institutions and expertise, and achieving pay equity among international and national employees.
These two convergent forces have fundamentally changed the operating environment for international development organizations and cleared the path for more sustainable and cost-effective approaches to collaboration between international and local organizations, including the home office and country operations of large international organizations.
A new model for development cooperation
New approaches to project oversight and technical assistance are already embedding themselves in development organizations’ operations, but it would be useful for the development community to articulate these emerging practices as a preferred operating model guided by two simple principles:
First, whenever possible resident management and technical staff should be hired locally. The advantages here are well known: Local professionals possess the language and cultural skills and community networks essential to effective development work. Moreover, with the notable exception of most conflict-affected states, the excuse that local professionals are unavailable is no longer valid. A common and legitimate critique of international organizations is that the higher salaries and benefits they offer to expatriates are inherently inequitable, reinforce old colonial power imbalances, and can distort national labor markets. This first principle resolves these problems by eliminating differential treatment and employing all resident staff on a single set of terms and conditions of service that conform to the local labor market.
The second principle is that when external management and technical expertise are required, they should be provided virtually to the greatest extent possible. This recognizes that international collaboration is critical to addressing today’s development challenges, that complex endeavors frequently require highly specialized experience and skills, and that there is value in being part of larger international professional networks and initiatives.
Here it is worth digressing to address a weakness in the current decolonization narrative: the implication that donors need only provide the financing and leave recipient countries to handle the rest. This ignores the value of international collaboration in promoting innovation and technology transfer and in building capacity. All countries—rich and poor—are better off when they have economic, scientific, social, and institutional linkages to their neighbors and the larger international community. Going it alone is neither politically feasible nor practically desirable.
That said, the old argument that international organizations require expatriate on-the-ground presence to achieve results no longer holds water, thanks to the experience of working virtually over the last two years. However, embracing new practices does require changing organizational culture, as the allure of international travel and in-person collaboration are major motivators for many development professionals. While the approach proposed here does not eliminate all travel—certainly there is value in some in-person interaction (for example, to establish relationships, understand context, and conduct some types of research), the amount of international travel will greatly diminish. On the plus side, this will help international organizations reduce their carbon footprint, but as the new model takes hold, expect many U.S. and European development professionals to retire or change careers and many developing country counterparts to lament the reduction in opportunities to travel abroad.
So, what does this new model look like in practice?
It’s simple. All in-country positions are treated as local national positions with compensation and conditions of service geared to the local labor market. This doesn’t prevent an expatriate from competing for a position, but it removes the financial incentives to use expatriates.
Concurrently, short-term expatriate assignments, with rare exceptions, are virtual. This is far more economical, more environmentally friendly, and tilts power relations in favor of finding local employees while avoiding distortions to local labor markets.
Forty-five years ago, Ross Coggins’ satirical poem, “ The Development Set ,” summed up the contradictions and weaknesses inherent in the classic international development model. In 2020, the forced shift to remote work and a renewed and urgent concern about inequalities embedded in the development community’s traditional operating arrangements have created the conditions to replace “development tourism” with a new approach to development cooperation. Now, it is incumbent upon donors, multilateral institutions, and NGOs to take action.
Related Content
George Ingram
November 16, 2021
Justin Fugle
September 29, 2021
Global Economy and Development
Center for Sustainable Development
Janet Gornick, David Brady, Ive Marx, Zachary Parolin
April 17, 2024
Homi Kharas, Charlotte Rivard
April 16, 2024
Homi Kharas, Vera Songwe
April 15, 2024
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism and Croatia to Establish Research Centre for Sustainable Tourism
- 12 Apr 2024
UN Tourism is to work with the Government Croatia and the University of Zagreb to establish a research and development centre focused on sustainable tourism.
Croatia currently serves on UN Tourism’s Committee on Tourism and Sustainability, having chaired it between 2019 and 2023. Alongside the Government’s record of promoting responsible and sustainable tourism practices, this clear leadership and support for UN Tourism’s core values make it the ideal location to host a collaborative platform to drive innovation and catalyse positive change in the tourism sector.
Croatia leads by example in growing tourism in a sustainable manner
This landmark centre will engage stakeholders from the public and private sectors, academia, and civil society to will address some of the most critical challenges facing tourism, including:
- Reducing the Environmental Impact of Tourism: The centre will prioritize initiatives to minimize waste generation and plastic usage, thereby mitigating the environmental footprint of tourism activities.
- Increasing Usage of Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency: By promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources and implementing energy-efficient practices, the centre aims to reduce carbon emissions associated with tourism operations.
- Accelerating Adaptation to Climate Change: Recognizing the urgent need to address climate-related risks, the centre will support adaptation strategies to enhance the resilience of tourism destinations and communities.
- Preserving Social Sustainability and Local Communities: The centre will work to safeguard the cultural heritage and livelihoods of local communities by promoting responsible tourism practices and equitable distribution of benefits.
- Enhancing Evidence-Based Policy Making: Through rigorous research and data analysis, the centre will provide policymakers with the evidence needed to formulate effective policies that balance tourism development with environmental and social considerations.
- Providing Relevant and Updated Research: The centre will serve as a hub for cutting-edge research and knowledge exchange, delivering timely insights and best practices for the sustainable development of tourism.
In Zagreb, the Minister of Tourism and Sport of Croatia Nikolina Brnjac and UN Tourism Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili signed a Memorandum of Understanding to create the cutting-edge research institution.
Welcoming the collaboration, Secretary-General Pololikashvili said: “Croatia leads by example in growing tourism in a sustainable manner. The new research centre in Zagreb will contribute to UN Tourism’s commitment to data-driven policymaking at the regional, national and destination level, ensuring tourism grows responsibly and inclusively, for the benefit of communities everywhere.”
Minister of Tourism and Sport of Croatia Nikolina Brnjac adds: “I am proud that UN Tourism, the most relevant tourism organization globally, has recognized our efforts in Croatian tourism management reform and our strong commitment to sustainable tourism and put forward the initiative to create the first UN Tourism Centre for sustainable tourism in Croatia together with the Ministry of Tourism and Sport of the Republic of Croatia. With the University of Zagreb as a partner in the establishment of this Centre, I am convinced that this Centre will be successful and provide very relevant research for future sustainable development of tourism.”
Related Links:
- Download News Release on PDF
- UN Tourism: Regional Department for Europe
- Transforming Tourism for Climate Action
- Sustainable tourism development
Related Content

European Committee of the Regions and UN Tourism break ...

UN Tourism Launches Tourism Investment Guidelines for A...

UN Tourism Members Advance Agenda for Europe as Region ...

UN Tourism and Moldova Launch Joint Project for Female ...

Passing Thru Travel
Eco-Exploration: 12 Tips for Sustainable Travel in Developing Countries
Posted: March 1, 2024 | Last updated: March 1, 2024

Traveling to developing countries offers a unique opportunity to explore diverse cultures, landscapes, and traditions. However, it also comes with a responsibility to travel sustainably, ensuring that your journey positively impacts the local communities and environment. Sustainable travel in these regions involves choosing responsible travel practices and supporting local economies in a way that promotes conservation and cultural preservation. This guide provides insights into how to travel sustainably in developing countries, highlighting activities and destinations that facilitate responsible tourism and contribute to meaningful travel experiences.
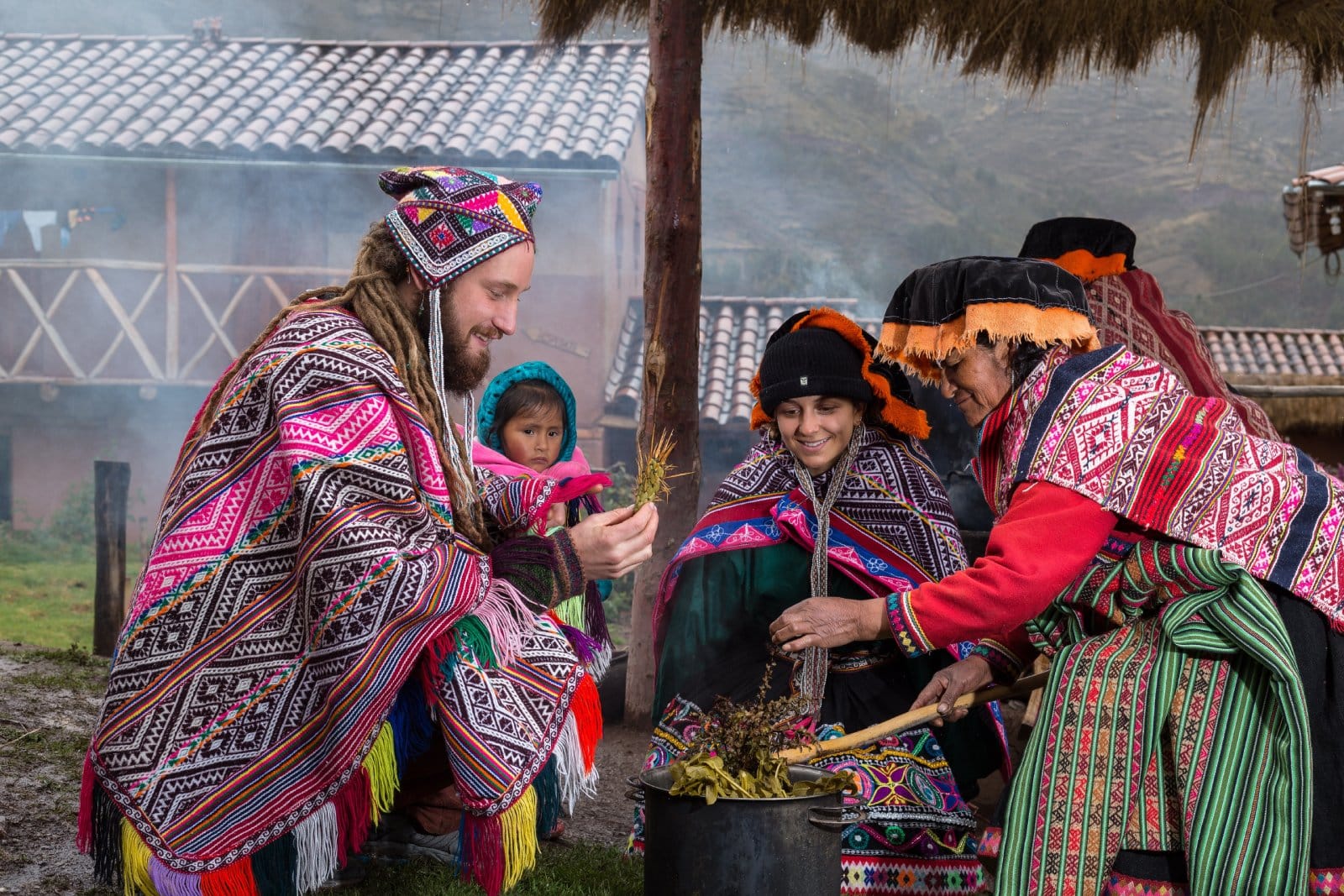

1. Community-Based Tourism Projects
Community-based tourism in developing countries offers a unique and immersive experience that directly benefits local communities. These projects allow travelers to engage with local cultures authentically and responsibly. They often include staying in homestays, participating in local festivals, and learning traditional crafts or cooking methods.
This form of tourism ensures that the economic benefits are shared within the community, fostering sustainable development. It also offers a deeper understanding of local lifestyles and traditions, creating a more meaningful and enriching travel experience. By choosing community-based tourism, travelers can play a vital role in preserving local cultures and contributing to the well-being of communities.
Insider’s Tip: Engage genuinely with the community members and be open to learning from their experiences and perspectives.

2. Eco-Lodges and Sustainable Accommodations
Eco-lodges and sustainable accommodations in developing countries are part of a commitment to environmental stewardship and community support. These lodgings are designed to have minimal environmental impact, often utilizing renewable energy sources, water-saving techniques, and sustainable building materials. Many eco-lodges are integrated into the natural surroundings, offering unique experiences like waking up to the sounds of the jungle or overlooking a serene landscape.
Staying at these places reduces your travel’s ecological footprint and supports local economies and conservation efforts. These accommodations often offer educational experiences about sustainability and conservation, adding an enlightening aspect to your stay.
Insider’s Tip: Choose locally owned and operated accommodations to ensure that your stay contributes to the local economy.

3. Voluntourism With Caution
Voluntourism in developing countries can be a rewarding experience if approached responsibly and ethically. It’s crucial to select projects that genuinely need volunteers and where your skills can make a meaningful contribution. Long-term projects in areas like environmental conservation, education, and community development are often more impactful.
Be wary of projects that may exploit vulnerable populations or create dependency. The key is to work with organizations that prioritize the needs of the local community and have transparent, ethical practices.
Insider’s Tip: Thoroughly research the organization and the project to ensure that your efforts will have a long-term positive impact.

4. Supporting Local Artisans and Crafts
Purchasing handicrafts from local artisans in developing countries directly supports the local economy and help preserve cultural heritage. These crafts are often made using traditional methods passed down through generations and reflect local culture and history.
When you buy these products, you’re not just taking home a souvenir; you’re contributing to the livelihood of artisans and helping keep traditional crafts alive. Markets, cooperatives, and artisan workshops are great places to find authentic, handcrafted items.
Insider’s Tip: Take time to learn about the craft and the story behind it, which often adds value to your purchase and enriches your understanding of the local culture.
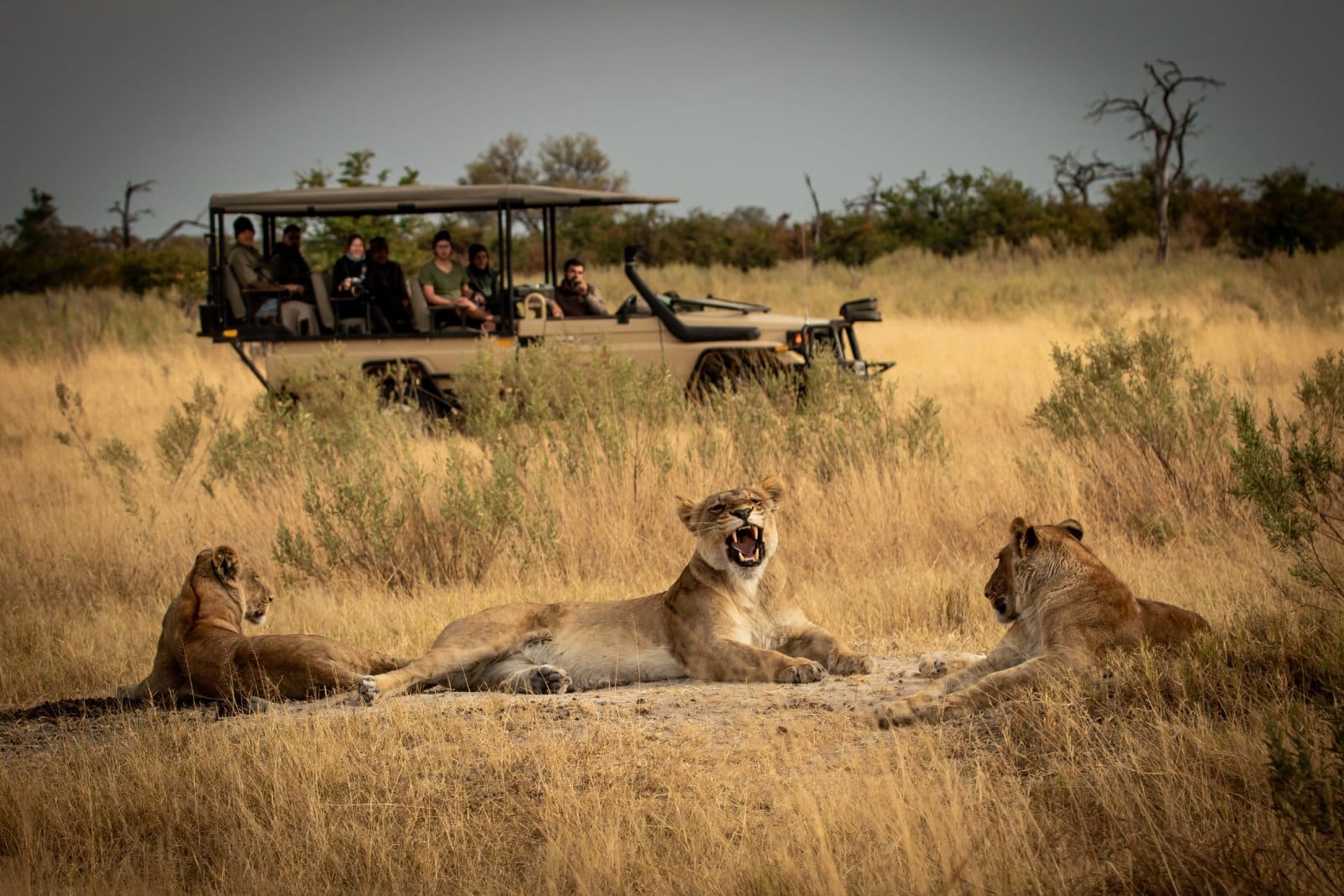

5. Responsible Wildlife Tours
Responsible wildlife tours in developing countries allow you to witness the majesty of wildlife in a way that respects their natural habitat and behavior. Choose tours and operators that adhere to ethical guidelines, such as maintaining a safe distance from animals, not interfering with their natural activities, and employing local guides with in-depth knowledge of the ecosystem.
These tours offer an incredible opportunity to see wildlife and contribute to conservation efforts, as many responsible tour operators support local wildlife protection initiatives.
Insider’s Tip: Opt for tours that contribute to conservation efforts or wildlife protection programs.

6. Participating in Cultural Exchange Programs
Cultural exchange programs in developing countries offer an immersive way to experience local cultures and traditions. These programs can range from homestays and language exchanges to participating in traditional ceremonies or festivals.
Through these exchanges, you gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of the local culture, which can be one of the most rewarding aspects of travel. These programs often support local initiatives and provide a more authentic and respectful way to experience different cultures.
Insider’s Tip: Be respectful and open-minded during these exchanges, as it is an opportunity to learn and share in a cross-cultural environment.

7. Eco-Friendly City Tours
Eco-friendly city tours in developing countries are a sustainable and enlightening way to explore urban environments. These tours often highlight green initiatives, historic sites, and local culture, offering insights into how cities adapt to and address sustainability challenges. Led by knowledgeable local guides, these tours can include walking, cycling, or using electric vehicles, minimizing environmental impact and providing an authentic perspective on the city.
Insider’s Tip: Choose tours led by local guides who can provide authentic insights and recommendations for further sustainable activities in the city.

8. Supporting Sustainable Agriculture and Local Food Projects
Engaging with sustainable agriculture and local food projects in developing countries is an enriching way to experience local cultures while supporting ethical and sustainable practices. These initiatives often focus on preserving traditional farming techniques, utilizing organic methods, and promoting biodiversity.
As a traveler, you can visit local farms to see sustainable agriculture, participate in farm-to-table experiences, or dine at restaurants that prioritize locally sourced and organic ingredients.
These activities offer a deeper understanding of the region’s culinary heritage and the challenges small-scale farmers face. By supporting these sustainable practices, you contribute to the local economy and encourage environmentally friendly farming methods.
Insider’s Tip: Engage with farmers or chefs to learn about local farming practices and their challenges, which can be eye-opening and educational.

9. Low-Impact Adventure Activities
Participating in low-impact adventure activities in developing countries is a way to explore and enjoy natural landscapes without leaving a harmful footprint. Activities like hiking, kayaking, cycling, bird watching, and responsible wildlife safaris offer immersive experiences in nature while maintaining environmental balance. These activities are designed to minimize impact on the natural environment, allowing wildlife and natural habitats to thrive undisturbed.
When participating in these activities, travelers can witness the beauty of untouched natural environments, contributing to their preservation. This responsible approach to adventure tourism ensures that the natural attractions remain pristine for future generations while offering the traveler an exhilarating experience.
Insider’s Tip: Always follow Leave No Trace principles to minimize environmental impact during these activities.

10. Sustainable Sea and Beach Experiences
Engaging in sustainable sea and beach experiences is crucial in preserving the delicate marine ecosystems of developing countries. Activities like eco-friendly snorkeling, sustainable diving practices, beach clean-ups, and educational coastal tours allow travelers to enjoy the marine world responsibly.
Operators of such activities often focus on protecting marine life, avoiding disruption to their natural habitats, and educating participants about marine conservation.
By choosing these experiences, travelers can enjoy the stunning beauty of the world’s oceans and beaches while actively contributing to their preservation. These responsible practices ensure that marine life is respected and that the oceans remain vibrant ecosystems full of life and beauty.
Insider’s Tip: Choose certified eco-friendly tour operators, especially for activities like snorkeling or diving, to ensure they follow environmentally responsible practices.

11. Participating in Local Environmental Initiatives
Involvement in local environmental initiatives is a powerful way for travelers to contribute to the sustainability of developing countries. These initiatives may include reforestation projects, wildlife conservation efforts, community-led recycling programs, and environmental awareness campaigns.
Participation in these initiatives helps address some of the pressing environmental challenges these countries face and offers a unique perspective on the local efforts being made to overcome them.
Travelers can learn about the local ecology, contribute to meaningful projects, and positively impact the environment. This kind of active participation fosters a deeper connection with the destination and its people, making travel more meaningful and impactful.
Insider’s Tip: Research initiatives that align with your interests and that have a proven track record of making a positive environmental impact.

12. Participating in Local Conservation Projects
Contributing to local conservation projects in developing countries offers an invaluable opportunity to support the preservation of biodiversity and natural habitats. These projects may involve habitat restoration, monitoring endangered species, and sustainable community development practices.
Participation not only aids in the vital work of conserving natural resources but also provides travelers with a profound understanding of the balance between human needs and environmental preservation. This engagement promotes a sense of global stewardship and offers a unique and enriching experience beyond traditional tourism.
Insider’s Tip: Research projects thoroughly to ensure they are ethical and have a proven track record of positive impact. Opt for projects that work closely with local communities and have transparent goals and methods.

The Bottom Line
Traveling sustainably in developing countries is an enriching and transformative experience beyond conventional tourism. It’s about forging meaningful connections with local communities, understanding and respecting different cultures, and contributing to positive change. As you embark on this journey, remember that your travel choices can profoundly impact you.
By being mindful and choosing responsibly, you enrich your travel experience and support the sustainable development of the destinations you visit. Embrace the beauty and diversity of these countries with respect and consideration, and let your journey leave a positive imprint on you and the places you explore. Safe travels, and may your adventures be as rewarding for the world as they are for you.
More Articles Like This…
Barcelona: Discover the Top 10 Beach Clubs
2024 Global City Travel Guide – Your Passport to the World’s Top Destination Cities
Exploring Khao Yai 2024 – A Hidden Gem of Thailand
The post Eco-Exploration – 12 Tips for Sustainable Travel in Developing Countries republished on Passing Thru with permission from The Green Voyage .
Featured Image Credit: Shutterstock / Joshua Resnick.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.
More for You
U.S. women’s track Olympians say photo was shocking but uniform isn’t
Popular Ice Cream Brand Files for Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
Therapists Say These 6 Common Habits Are Fueling Your Anxiety
I Lost White Friends When I Finally Spoke Out
Right-Wing 'Reacher' Fans Flip Out After Alan Ritchson Calls Trump A 'Rapist And A Con-Man'
Top 20 Saturday Night Live Sketches That Broke the Whole Cast
'Beetlejuice Beetlejuice' Trailer: Michael Keaton & Winona Ryder Meet Again, Jenna Ortega Joins Ghastly Family | THR News Video
Several Popular Fast Food Chains File Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
How to 'quiet quit,' from a former teacher who did it for 2 years so she could enjoy a better life while still getting a paycheck
12 safest places if World War 3 breaks out
Traumatic Disney Movies That Scarred a Generation of Children
16 Compliments You Didn’t Realize Are Actually Pretty Insulting
Panned M. Night Shyamalan Sequel Becomes Netflix Hit Five Years Later
Ex-PBS Producer Says He Was Fired From Al Roker Cartoon for Complaining Show Didn't Honor DEI Policy
Ketanji Brown Jackson's New Warning To Supreme Court
Kevin Durant Says He Stayed Healthy This Season By Staying Away From Floppers And Crash Dummies
Major Shoe Brand Files for Bankruptcy
People With Low Emotional Intelligence Are Known to Use These 4 Phrases
10 pairs of movies with strikingly similar plots that came out the same year
28 photos show what Iran looked like before the 1979 revolution turned the nation into an Islamic republic
Language selection
- Français fr
Minister of Tourism celebrates Canada’s tourism businesses during National Tourism Week 2024
From: Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
The Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec, made the following statement to mark National Tourism Week 2024
April 15, 2024 – Ottawa, Ontario
The Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec, made the following statement to mark National Tourism Week 2024:
“On behalf of the Government of Canada, I want to wish all Canadians a happy National Tourism Week!
“Canada is a tourism superpower. We have majestic mountains, dynamic downtowns, friendly folks and so much more. We have what the world wants!
“National Tourism Week is a chance to celebrate the faces and places that make our country so special, including the millions of Canadians who work in tourism.
“This year’s theme is Canada: Powered by Tourism , and it’s not hard to see why. Tourism is a pillar of our economy, helping employ nearly one in ten Canadians and generating billions of dollars every year!
“The people in our tourism sector are more than workers: they are ambassadors for Canada. They are often the first Canadians that a visitor meets when they arrive, and the last ones they see before heading home. The industry is a leader in hiring women, newcomers and young people—even the Prime Minister had one of his first jobs in tourism!
“Tourism is also about pride—the pride of sharing your home with the world.
“Our government is here for Canadian tourism. Guided by our Federal Tourism Growth Strategy , we want to help the industry reach its full potential, invest in Indigenous tourism and overcome challenges so tourism can thrive.
“Tourism has incredible potential, and we’re seizing it. Our goal is to increase the sector’s contribution to Canada’s GDP by 40% by 2030, to $61 billion. This means roughly 85,000 more jobs stemming directly from tourism.
“It’s about more than statistics, however. It’s about Canada taking its place as a tourism superstar. That’s why we’re supporting businesses through the Tourism Growth Program , a $108 million investment in tourism businesses across the country.
“Indigenous tourism has the power to advance reconciliation while creating opportunities across Canada. Through initiatives such as the Indigenous Tourism Fund , we’re partnering with communities and leaders to seize these opportunities.
“Of course, tourism is not without challenges, and we’re working with the industry to overcome them. We’re helping businesses attract and retain more staff. We’re improving transportation and housing. We’re also addressing climate change, an existential threat to Canadian tourism.
“This week, I’m inviting you to discover the attractions that make your community and country so special. Tourism is powerful because it creates connections, finds common ground and brings people together—and we need that now more than ever.
“Happy National Tourism Week!”
Marie-Justine Torres Press Secretary Office of the Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec 613-327-5918 [email protected]
Media Relations Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada [email protected]
Stay connected
Follow Canadian Tourism on social media. X (Twitter): @cdntourism
Follow Canada Business on social media. X (Twitter): @canadabusiness | Facebook: Canada Business
Page details

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit. The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21. For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
Developing ecotourism services is a suitable solution to help developing countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. The primary purpose of ...
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective ...
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as "responsible travel to natural areas that ...
Summary. Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world.
Ecotourism and Protected areas. According to the UN Tourism's definition, ecotourism refers to forms of tourism which have the following characteristics: All nature-based forms of tourism in which the main motivation of the tourists is the observation and appreciation of nature as well as the traditional cultures prevailing in natural areas.
Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996; Higgins, 1996; Orams, 1995).With years of research and development, ecotourism has risen to ...
So both sustainable tourism and sustainable development focuses on the same key issues of ecology, society, and a systemic process of development that is guided by strategic planning . Advertisement. 6. Ecotourism - examples of implementation. More tranquil, natural and original spaces are preferred to ordinary tourism centers. ...
Ecotourism plays a critical strategic role in regional development. In many remote communities, ecotourism is the main contributing factor in their economic growth. The role of ecotourism development in the sustainability of the local economy is widely known. However, the local communities' role in the development of the industry has been neglected. The presented study, therefore, examines ...
Ecotourism is a form of tourism marketed as "responsible" travel (using what proponents say is sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. The stated purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds for ecological conservation, to directly benefit the economic development and political empowerment of local ...
1. Introduction. Ecotourism initiatives encouraging development compatible with nature conservation are gaining ground across Europe (Nepal, Citation 2002).Given that the approach merges conservation with sustainable development, ecotourism fits well within the context of UNESCO Biosphere Reserves (BR), which, since their first introduction in the early '1970s, raised the debate on the ...
The Journal of Sustainable Tourism published nine papers related to the topic, followed by the Tourism Management Perspective and the Journal of Ecotourism, accounting for seven papers each (22.54% of 102). ... The fifth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) aims to achieve gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls by 2030 as a ...
Ecotourism is about uniting conservation, communities, and sustainable travel. This means that those who implement, participate in and market ecotourism activities should adopt the following ecotourism principles: Minimize physical, social, behavioral, and psychological impacts. Build environmental and cultural awareness and respect.
Although international regulation and accreditation have remained elusive, these guidelines provide a general blueprint for responsible tourism development. Many of these principles align with those of the Global Sustainable Tourism Council, which developed an extensive list of criteria for sustainable destinations, hotels, and tour operators. 1.
revenue for national development, and employ locals. Ecotourism, which primarily serves conserva tion interests, helps promote ecologically sound growth. 2.1. The economic role of Ecotourism in ...
Developing and developed, case study, protected areas, sustainable tourism, tourism development and developing ecotourism are leading topics in the field of ecotourism research, as well as specific articles under the main topics. The lightweight view generated by Carrot2 provides a reference for the research, and then, co-word analysis is ...
The realization of a future in which regenerative tourism, a further evolution of sustainable tourism, becomes mainstream depends on changing the behaviour of both hosts and travellers. In the World Economic Forum's Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021: Rebuilding for a Sustainable and Resilient Future , Japan took the top spot in the ...
an important sustainable development tool. With billions of dollars in annual sales, ecotourism is a real industry that seeks to take advantage of market trends. At the same time, it frequently operates quite differently than other segments of the tourism industry, because ecotourism is defined by its sustainable development results:
Sustainable tourism is the foundation of ecotourism as it acknowledges the crucial role played by local communities. It respects their cultural heritage and provides opportunities for their development by adopting practices that promote their environment's sustainability and improve their quality of life.
Tourism Revenue: Eco-tourism generates income for conservation initiatives, such as national parks and wildlife reserves. Community: Projects can support sustainable development, economic benefits, and social well-being by involving local communities in ecotourism activities. Positive Experiences
The rising opportunities of sustainable tourism have brought many policies to control the exploitation of the environment and increase the reach of luxurious, safe, and authentic experiences to the different segments of tourists. This study seeks to prioritize the variables influencing the development of sustainable tourism and pinpoint key success factors that align with the Sustainable ...
In 2002, the United Nations declared it the year of ecotourism, and in 2003 the Center for Responsible Travel is formed. Since that time, ecotourism has become a $263 billion industry, with a 65% growth rate from 2009 to 2013. IOI's passion is to empower isolated communities to grow in a sustainable way through educational travel.
These two convergent forces have fundamentally changed the operating environment for international development organizations and cleared the path for more sustainable and cost-effective approaches ...
12 Apr 2024. UN Tourism is to work with the Government Croatia and the University of Zagreb to establish a research and development centre focused on sustainable tourism. Croatia currently serves on UN Tourism's Committee on Tourism and Sustainability, having chaired it between 2019 and 2023. Alongside the Government's record of promoting ...
Residents' attitudes were determined by the transaction risk arising from the conflict between formal and informal institutions in the context of social transformation. The findings provide implications for tourism managers to achieve the sustainable development of tourist destinations in developing countries.
Sustainable development and the related challenges are the focus of the 2030 Agenda within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Albania is also a country that is part of these ambitious programmes and has continuously received funds from international organisations to achieve these objectives. Considerable progress has been made, and there is still much work to be done.
This form of tourism ensures that the economic benefits are shared within the community, fostering sustainable development. It also offers a deeper understanding of local lifestyles and traditions ...
The Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec, made the following statement to mark National Tourism Week 2024: "On behalf of the Government of Canada, I want to wish all Canadians a happy National Tourism Week!