Would you like to view this website in another language?

Travel allowance: A Comprehensive Guide for Employees
- Written by: Rinaily Bonifacio
- Last updated: 11 March 2024
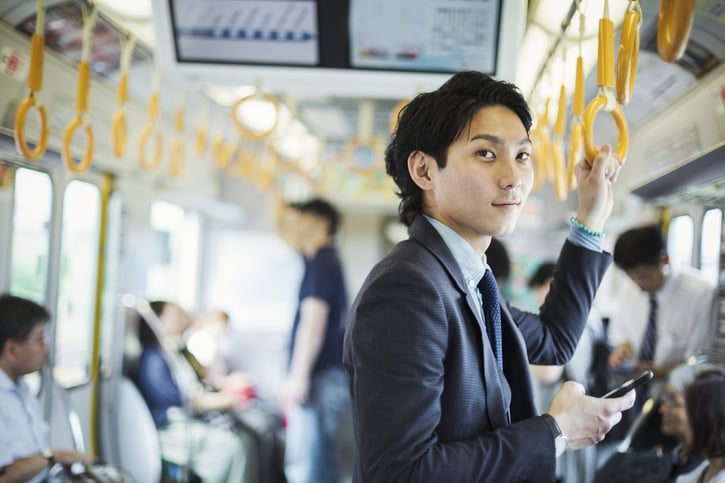

This article will explain travel allowance, when and how you can use it, and tips for getting the most out of your expenses.
Table of contents
What is travel allowance?
How does business travel allowance usually cover, what is a flat travel allowance, what is the daily allowance, easy ways on how companies manage their procedures for business travel allowances, effective communication, how to manage business travel allowances.
Travel allowance is a type of compensation employers provide to cover employee travel expenses incurred when traveling for business purposes. It helps with employee travel costs, such as transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidentals while on the job. Depending on the company policy, travel allowance may be given in cash or as reimbursed expenses.
For example, some companies provide a fixed daily amount for meals and lodging that employees can use during their travels. Other companies cover expenses incurred by employees when they submit receipts after their trip has ended. This is known as per diem allowance or transport allowance.
Business travel allowance typically covers the cost of airfare, hotel accommodations, and meals. It may also include per diem allowances such as ground transportation, parking, and incidentals. The exact coverage will vary depending on the company's policies and the type of business trip.
A flat travel allowance is a set amount of money an employee provides for travel costs. The employee is responsible for managing the funds and ensuring they are used for the intended purpose. This allowance is typically used for short trips or employees who travel infrequently.
.png?width=323&height=124&name=img-16%20(1).png)
Employee scheduling and Time-tracking software!
- Easy Employee scheduling
- Clear time-tracking
- Simple absence management
A daily allowance, also known as a per diem, is a set amount of money provided to employees for money incurred daily while traveling for business purposes. It typically covers things such as
- Transportation
- And incidentals.
The allowance amount is usually based on the location and duration of the business trip and is intended to cover living costs for that specific location.
Daily allowances are provided in addition to other travel compensation types, such as lodging or airfare reimbursement. The amount and coverage of a daily budget will vary depending on the company's policies and the nature of the business travel.
Companies can manage their procedures for business travel allowances by establishing clear guidelines and policies. This should include information on who is eligible for the assistance, what travel costs are covered, and how to submit expense reports. Additionally, companies can use travel management software to track and approve payments and ensure company policy compliance.
It is also essential for companies to communicate effectively with employees about travel allowance policies so that they are aware of their rights and obligations. This can include providing training and support and regular updates on any policy changes.
By managing their procedures for business travel allowances in a clear and organized manner, companies can ensure that their employees have the resources they need to complete their business trips while also managing the company's expenses.
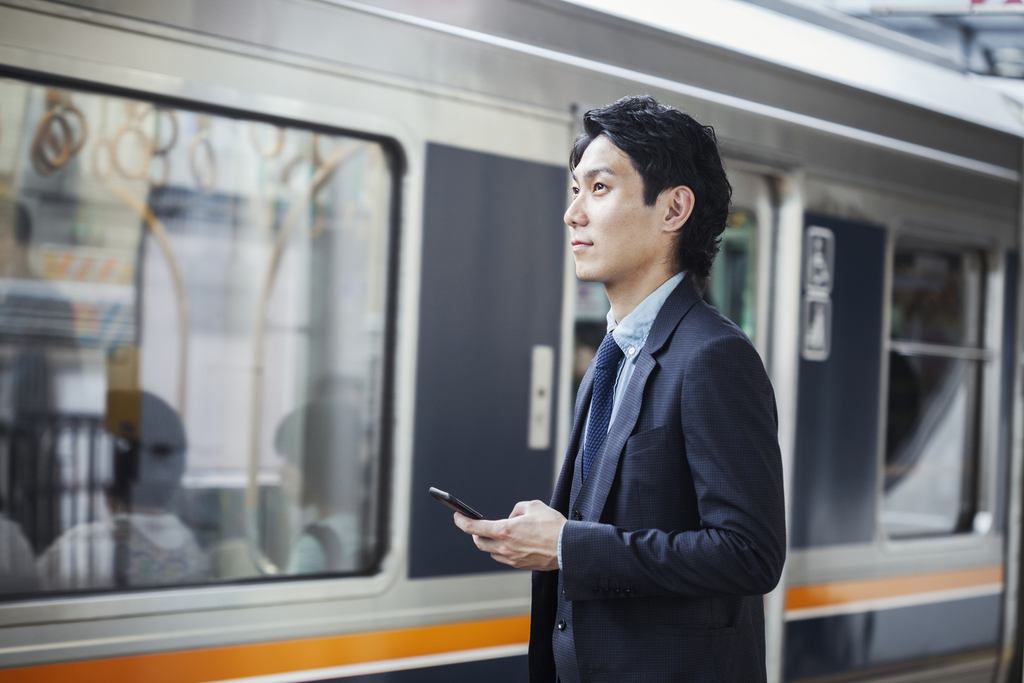

Another critical aspect of managing business travel allowances is to keep an eye on the per diem rates and lodging expenses. It is essential to ensure that these expenses are within the budget and are in line with the rates established by the General Services Administration (GSA). Companies should also consider implementing a system for meal allowance and car hire reimbursement, as well as for laundry services, parking fees, and other miscellaneous expenses.
To manage business travel allowances effectively, companies should establish clear guidelines for employees traveling within the continental United States and those traveling to foreign countries. This includes setting a budget for each travel and providing employees with the necessary forms for expense reporting and reimbursement.
In addition, companies can use data analysis to identify trends and patterns in travel expenses. This can help them make more informed decisions about travel policies and budgeting and potentially save money on future trips.
It's also important to consider the needs of business travelers and their families and to establish policies that support them. For example, companies may offer additional allowances for family members traveling with a business traveler or for international travel.
Overall, an efficient reimbursement system and clear travel policies can help ensure that employees are promptly reimbursed for their expenses and that the company's expenses are tracked and managed effectively. This can be a great way to manage business travel allowances and keep costs under control.
Written by:
Rinaily Bonifacio
Rinaily is a renowned expert in the field of human resources with years of industry experience. With a passion for writing high-quality HR content, Rinaily brings a unique perspective to the challenges and opportunities of the modern workplace. As an experienced HR professional and content writer, She has contributed to leading publications in the field of HR.
Please note that the information on our website is intended for general informational purposes and not as binding advice. The information on our website cannot be considered a substitute for legal and binding advice for any specific situation. While we strive to provide up-to-date and accurate information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information on our website for any purpose. We are not liable for any damage or loss arising from the use of the information on our website.
Ready to try Shiftbase for free?
- Whistleblowing Policy
- First Aid in the Workplace
- Cell Phone Policy at Work
- Inclement Weather Policy
- Employee Non-disclosure Agreement

Travel and Expense
What is a travel allowance definitions and insights.
A travel allowance can be an effective way to manage employee travel expenses and manage costs for the employee.
When employees travel for business, there are myriad expenses, from hotels to taxis or ride-sharing services. Using a travel allowance can help give travelers flexibility and control while increasing compliance with tax regulations.
What Is a Travel Allowance?
A travel allowance is compensation paid by an employer to employees to cover expenses incurred when traveling for business. In addition to lodging and transportation, travel allowances are typically used for airfare, meals, and other expenses related to business travel. It is business travel compensation, provided either before or after travel is completed.
Managing business travel compensation can be complex and hard to manage. The way businesses handle travel compensation is changing, as leaders look to implement tools that aid travelers and companies alike.
Technology is transforming how companies manage all aspects of employee travel , including the creation and coordination of travel allowances.
Types of Travel Allowance
There are many types of travel allowances, which can be given upfront or based on a reimbursement schedule. Here is a look at some of the most common.
Fixed Travel Allowance
A fixed travel allowance is a flat rate that is offered to an employee, irrespective of the level of expenses incurred. Employees are responsible for managing their travel expenses and determining how to use the money best to accommodate their needs. It is commonly used with employees for short trips or who travel infrequently.
Typically, with a fixed allowance, if the employee spends less than the allocated amount, the employee can keep the difference. If the employee spends more, they are responsible for making up the difference. Businesses using fixed travel allowance should work with their tax professional to understand the implications of this practice.
Daily Travel Allowance
Also called a per diem, a daily travel allowance is an amount used for each day of travel and can be used for lodging, transportation, meals, and other travel expenses. Typically, a traveler will reconcile the per diem by submitting an expense report and receipts. The traveler will be reimbursed for any expenses they spent in excess and will return money that was unspent.
Travel Reimbursement
This travel allowance requires the traveler to submit receipts for actual expenses incurred, which are then reimbursed. This process can be cumbersome and time-consuming for the traveler. If reimbursement is not done in a timely manner, it can be burdensome for the employee, who is essentially lending money to the company. Fortunately, there are technologies available today to simplify this work.
Mileage Allowance
This type of allowance pays the employee for miles traveled on business. It is typically used when employees use their own car for business-related travel. Technologies can tracking and reimbursing for mileage simpler and more accurate.
Methods for Calculating Travel Allowances
When using travel allowances as part of a corporate travel program, one key consideration is how the travel allowances are calculated.
The process often has to consider the distance traveled and the time spent traveling. Here is one way to calculate a travel allowance.
Location and Days of Travel
Start by determining the location of the traveler at midnight on each day of travel. A day of travel is defined as a 24-hour period an employee is conducting business while traveling.
The day of travel ends when the next day starts or they return home from a business trip to their home or office. For example, if an employee leaves for a trip at 4 p.m., the first day of travel is from 4 p.m. that day until 4 p.m. the next.
Lodging allowances are provided based on whether an employee spends the night in accommodations other than their own home. Typically, lodging allowances are based on the location and the current price rates for various hotel categories, based on company preferences for the level of hotels allowed.
Unlike with other categories, usually lodging is an either/or determination. Employees are either allowed the lodging allowance or not based on the circumstances of the trip.
Like with lodging, meal allowances are usually based on the prevailing costs of meals in each location. It assumes that a traveler will have three meals a day.
Typically, a meal allowance covers both meals and incidentals, such as snacks. Often it is prorated based on the time in any given day a traveler is on the road.
The meal allowance may also be reduced if there are meals provided as part of the work travel, such as part of a conference registration fee or transportation ticket.
Managing Travel Allowances
Managing travel allowances is a complex task. Here are some tips on how to effectively implement and manage a program:
- Develop a Clear Policy. Travelers need to understand the specifics in your travel program and how allowances are used. The policy needs to spell out, for example, what expenses are allowed and not allowed and the ways in which allowances are calculated. Transparency is essential to ensure all employees understand how travel expenses are covered
- Consider Incidentals. Business travelers face many complexities and challenges. You want a policy that makes it easy for travelers to navigate while on the road. Be sure your policy covers costs that may arise, including parking, fuel, tips, laundry services, printing, internet fees, and luggage check fees
- Analyze Data. You need a system in place that collects and reports on travel data to allow you to better understand trends, shifts and challenges. With visibility into your travel program, you can make timely, well-informed decisions
Developing Travel Allowance Policies and Guidelines
If your company wants to develop a travel allowance policy, where should you begin?
The policy should be rooted in a broader travel policy which should consider the following:
- Scope. What aspects of business travel will your policy cover?
- Coverage. Determine which elements of travel the policy will cover, such as air travel, lodging, meals, incidentals, and ground transportation
- Reimbursement Types. Will your company use travel allowances and, if so, which types?
- Participation. How will policies be determined? Be sure to include staff from human resources, finance, and departments that frequently travel, in determining the policy
- Safety. Be sure your policy provides protection for employees while they are traveling
- Expense Reporting. Develop tools or adopt that will be used for the reporting of travel expenses, with an emphasis on scalability, technology integration, and ease of use
Technological Advancements in Travel Allowance Management
Technology is changing the way companies manage business travel . There are powerful platforms available today that integrate travel policies, allow for the booking of travel and itinerary management and provide robust data collection and travel.
Employees need access to easy-to-use tools that allow for the recording of receipts and other transactions, let them reconcile expenses and generate expense reports, and simplify approvals and routing.
SAP Concur solutions can provide companies with integrated business travel, expense, and invoice solutions. With SAP Concur solutions, companies can book travel, manage expenses, integrate with business systems, manage invoices, and more.
Learn more about how SAP Concur solutions can simplify your travel management .
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Explore sell to government
- Ways you can sell to government
- How to access contract opportunities
- Conduct market research
- Register your business
- Certify as a small business
- Become a schedule holder
- Market your business
- Research active solicitations
- Respond to a solicitation
- What to expect during the award process
- Comply with contractual requirements
- Handle contract modifications
- Monitor past performance evaluations
- Explore real estate
- 3D-4D building information modeling
- Art in architecture | Fine arts
- Computer-aided design standards
- Commissioning
- Design excellence
- Engineering
- Project management information system
- Spatial data management
- Facilities operations
- Smart buildings
- Tenant services
- Utility services
- Water quality management
- Explore historic buildings
- Heritage tourism
- Historic preservation policy, tools and resources
- Historic building stewardship
- Videos, pictures, posters and more
- NEPA implementation
- Courthouse program
- Land ports of entry
- Prospectus library
- Regional buildings
- Renting property
- Visiting public buildings
- Real property disposal
- Reimbursable services (RWA)
- Rental policy and procedures
- Site selection and relocation
- For businesses seeking opportunities
- For federal customers
- For workers in federal buildings
- Explore policy and regulations
- Acquisition management policy
- Aviation management policy
- Information technology policy
- Real property management policy
- Relocation management policy
- Travel management policy
- Vehicle management policy
- Federal acquisition regulations
- Federal management regulations
- Federal travel regulations
- GSA acquisition manual
- Managing the federal rulemaking process
- Explore small business
- Explore business models
- Research the federal market
- Forecast of contracting opportunities
- Events and contacts
- Explore travel
- Per diem rates
- Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.)
- State tax exemption
- Travel charge card
- Conferences and meetings
- E-gov travel service (ETS)
- Travel category schedule
- Federal travel regulation
Travel policy
- Explore technology
- Cloud computing services
- Cybersecurity products and services
- Data center services
- Hardware products and services
- Professional IT services
- Software products and services
- Telecommunications and network services
- Work with small businesses
- Governmentwide acquisition contracts
- MAS information technology
- Software purchase agreements
- Cybersecurity
- Digital strategy
- Emerging citizen technology
- Federal identity, credentials, and access management
- Mobile government
- Technology modernization fund
- Explore about us
- Annual reports
- Mission and strategic goals
- Role in presidential transitions
- Get an internship
- Launch your career
- Elevate your professional career
- Discover special hiring paths
- Events and training
- Agency blog
- Congressional testimony
- GSA does that podcast
- News releases
- Leadership directory
- Staff directory
- Office of the administrator
- Federal Acquisition Service
- Public Buildings Service
- Staff offices
- Board of Contract Appeals
- Office of Inspector General
- Region 1 | New England
- Region 2 | Northeast and Caribbean
- Region 3 | Mid-Atlantic
- Region 4 | Southeast Sunbelt
- Region 5 | Great Lakes
- Region 6 | Heartland
- Region 7 | Greater Southwest
- Region 8 | Rocky Mountain
- Region 9 | Pacific Rim
- Region 10 | Northwest/Arctic
- Region 11 | National Capital Region
- Per Diem Lookup
Travel resources
Per diem look-up, 1 choose a location.
Error, The Per Diem API is not responding. Please try again later.
No results could be found for the location you've entered.
Rates for Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. Territories and Possessions are set by the Department of Defense .
Rates for foreign countries are set by the State Department .
2 Choose a date
Rates are available between 10/1/2021 and 09/30/2024.
The End Date of your trip can not occur before the Start Date.
Traveler reimbursement is based on the location of the work activities and not the accommodations, unless lodging is not available at the work activity, then the agency may authorize the rate where lodging is obtained.
Unless otherwise specified, the per diem locality is defined as "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city, including independent entities located within those boundaries."
Per diem localities with county definitions shall include "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city as well as the boundaries of the listed counties, including independent entities located within the boundaries of the key city and the listed counties (unless otherwise listed separately)."
When a military installation or Government - related facility(whether or not specifically named) is located partially within more than one city or county boundary, the applicable per diem rate for the entire installation or facility is the higher of the rates which apply to the cities and / or counties, even though part(s) of such activities may be located outside the defined per diem locality.
City Pair airfares
Visit City Pair Program to learn about its competitive, federally-negotiated airline rates for 7,500+ domestic and international cities, equating to over 13,000 city pairs.
- Search for contract fares
Note: All fares are listed one-way and are valid in either direction. Disclaimer - taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Your agency’s authorized travel management system will show the final price, excluding baggage fees. Commercial baggage fees can be found on the Airline information page.
Domestic fares include all existing Federal, State, and local taxes, as well as airport maintenance fees and other administrative fees. Domestic fares do not include fees such as passenger facility charges, segment fees, and passenger security service fees.
International
International fares do not include taxes and fees, but include fuel surcharge fees.
Note for international fares: City codes, such as Washington (WAS), are used for international routes.
Federal travelers should use their authorized travel management system when booking airfare.
- E-Gov Travel Service for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel System for the Department of Defense.
If these services are not fully implemented, travelers should use these links:
- Travel Management Center for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel Management Office for the Department of Defense.
GSA lodging programs
Shop for lodging at competitive, often below-market hotel rates negotiated by the federal government.
FedRooms provides federal travelers on official business with FTR compliant hotel rooms for transient and extended stays (up to 29 days). The program uses FEMA and ADA-compliant rooms with flexible booking terms at or below per diem rates. Federal employees should make reservations, including FedRooms reservations, via their travel management service.
Visit GSALodging for more details on FedRooms and for additional programs offering meeting space, long term lodging, and emergency lodging.
Privately owned vehicle (POV) mileage reimbursement rates
GSA has adjusted all POV mileage reimbursement rates effective January 1, 2024.
* Airplane nautical miles (NMs) should be converted into statute miles (SMs) or regular miles when submitting a voucher using the formula (1 NM equals 1.15077945 SMs).
For calculating the mileage difference between airports, please visit the U.S. Department of Transportation's Inter-Airport Distance website.

Plan a trip
Research and prepare for government travel.
Per diem, meals & incidental expenses (M&IE) Passenger transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.) Lodging Conferences/meetings Travel charge card State tax exemption

Services for government agencies
Programs providing commercial travel services.
Travel Category Schedule (Schedule L) E-Gov Travel Service (ETS) Emergency Lodging Services (ELS) Employee relocation

Travel reporting
Federal Travel Regulation Table of contents Chapter 300—General Chapter 301—Temporary Duty (TDY) Travel allowances Chapter 302 - Relocation allowances
- Business Travel
- Home Inspiration
- Sustainable Living
- Wellbeing & Wellness
- Area Guides
- Whitepapers

Business Travel Guide
A complete guide to corporate travel allowance.

Corporate travel is an essential part of doing business in today’s economy. Whether it’s attending meetings, conferences, or visiting clients, travel is necessary to keep businesses running. However, the cost of corporate travel can quickly add up, making it important for companies to have a clear policy on corporate travel allowance.
This allowance typically covers expenses such as transportation, accommodation, meals, and incidentals. The amount of the allowance can vary depending on the company’s credit policy , the employee’s position, and the destination of the trip.
In this guide, we will provide a complete overview of corporate travel allowance, including what it is, how it works, and best practices for implementing a corporate travel allowance policy.
What is a Corporate Travel Allowance?
Corporate Travel Allowance is a type of compensation that employers provide to cover employee travel expenses incurred when travelling for business purposes. It helps with employee travel costs, such as transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidentals while on the job. The purpose of the corporate travel allowance is to ensure that the employee is not out of pocket for business-related expenses.
This is also aspect of the employee benefits package, which can help attract and retain top talent. It is a way for employers to show their commitment to their employees and their well-being. The Corporate Travel Allowance is also a way for employers to ensure that their employees are comfortable and productive while travelling for business purposes.
Types of Travel Allowances
There are different types of company travel allowances that employers can provide to their employees. The most common types of travel allowances are:
- Mileage Allowance: This type of allowance reimburses employees for the cost of using their personal vehicle for business purposes. The mileage allowance is usually calculated based on the number of miles driven and the current IRS mileage rate.
- Per Diem Allowance: This type of allowance provides employees with a daily allowance to cover meals, lodging, and other incidental expenses while travelling for business purposes. The per diem allowance is usually based on the location and the length of the trip.
- Travel Expense Reimbursement: This type of allowance reimburses employees for the actual expenses incurred while travelling for business purposes. The expenses that are reimbursed include transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidental expenses.
Policy Development
Here is how to develop a travel allowance policy by establishing guidelines, setting allowance limits, and incorporating compliance.
- Establishing Guidelines
When developing a corporate travel policy, it is important to establish clear guidelines for employees to follow. This may include guidelines for booking procedures, preferred travel vendors, and allowable expenses. By establishing clear guidelines, employees will have a better understanding of what is expected of them when travelling for business purposes.
- Setting Allowance Limits
One of the most important aspects of a corporate travel policy is setting allowance limits. This involves determining the maximum amount of money that employees can spend on travel-related expenses, such as airfare, lodging, and meals. It is important to set reasonable limits that are in line with the company’s budget and travel needs.
- Incorporating Compliance
Incorporating compliance into a corporate travel policy is essential for ensuring that employees follow company policies and procedures. This may involve requiring employees to submit travel requests in advance, providing receipts for all expenses, and adhering to specific travel vendors. By incorporating compliance into a travel policy, companies can reduce the risk of fraud and ensure that travel expenses are properly managed.
Allowance Management
When it comes to managing corporate travel allowances, several key procedures need to be followed to ensure that the process is efficient and effective. This section will cover the three main areas of allowance management: allocation procedures, expense tracking and reporting, and reimbursement processes.
- Allocation Procedures
Allocation procedures refer to the process of determining how much money each employee is entitled to for their business travel expenses. This can be done in several ways, such as providing a set daily allowance or reimbursing actual expenses incurred. It is important to establish clear guidelines for how these allocations are made, taking into account factors such as the employee’s role, the nature of the trip, and the destination.
- Expense Tracking and Reporting
Expense tracking and reporting is a critical aspect of corporate travel allowance management. This involves keeping accurate records of all expenses incurred during business travel, including receipts, invoices, and other documentation. There are a number of travel and expense management software solutions available to help with this process, such as expense tracking apps and online reporting systems. It is important to ensure that all expenses are properly recorded and reported on time to avoid delays in reimbursement.
- Reimbursement Processes
The final stage of allowance management is the reimbursement process. This involves reviewing and approving expense reports, verifying that all expenses are legitimate and in line with company policy, and issuing payments to employees. It is important to establish clear procedures for how reimbursement requests are made, how they are reviewed and approved, and how payments are made. This can help to ensure that the process is efficient, transparent, and fair to all employees.
Optimising Allowance Strategy
To make the most of the corporate travel allowance, companies need to optimise their allowance strategy. This means identifying cost-saving practices, leveraging technology, and negotiating with vendors.
- Cost-Saving Practices
To save costs, companies can encourage employees to book travel in advance, use public transportation, and stay in budget-friendly hotels. They can also set limits on expenses such as meals and entertainment. By providing clear guidelines, companies can help employees make informed decisions and avoid overspending.
- Leveraging Technology
Technology can help companies optimise their allowance strategy by automating expense reporting, tracking travel expenses, and providing real-time insights. For example, companies can use expense management software to track employee expenses, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. They can also use travel management tools to book travel, manage itineraries, and communicate with employees.
- Negotiating with Vendors
Negotiating with vendors can help companies get better rates on travel expenses such as airfare, hotels, and car rentals. By working with preferred vendors, companies can also streamline the booking process and ensure that employees have a consistent experience. To negotiate effectively, companies should research vendors, understand their needs, and be prepared to walk away if the terms are not favourable.
Employee Considerations
When creating a corporate travel allowance policy, it is essential to consider the employees who will be affected by it. This section will discuss some of the employee considerations that should be taken into account.
- Communicating Policies
It is crucial to communicate the corporate travel allowance policy clearly and effectively to all employees. The policy should be made available to employees in a format that is easy to access and understand, such as an employee handbook or an online portal.
To ensure that employees are aware of the policy, it may be helpful to provide training or information sessions. This will help to answer any questions that employees may have and ensure that they understand the policy’s rules and regulations.
- Handling Exceptions
In some cases, exceptions to the corporate travel allowance policy may be necessary. For example, an employee may need to travel to a location that is not covered by the policy or may need to stay in a more expensive hotel due to extenuating circumstances.
To handle these exceptions, it is important to have a clear process in place. This process should outline how exceptions can be requested, who is authorized to approve them, and what documentation is required.
Ensuring Employee Satisfaction
Finally, it is important to ensure that employees are satisfied with the corporate travel allowance policy. This can be achieved by soliciting feedback from employees and making changes to the policy based on their suggestions.
One way to gather feedback is through surveys or focus groups. This will help to identify any areas where employees are dissatisfied with the policy and allow for changes to be made to improve their experience.
Lastly, by considering these employee considerations, companies can create a corporate travel allowance policy that is clear, fair, and effective.
Legal and Tax Implications
When it comes to corporate travel allowances, certain legal and tax implications must be taken into consideration. Failing to comply with these laws and regulations can result in legal and financial consequences for the company.
Therefore, it is essential to understand the legal and tax implications of corporate travel allowances.
One of the primary legal considerations when it comes to corporate travel allowances is tax laws.
According to GOV.UK , as an employer, you have certain tax, National Insurance, and reporting obligations when paying your employees’ travel costs. These obligations include costs for providing travel, reimbursing travel, accommodation, meals, and other subsistence expenses while travelling.
Employees who stay away overnight while travelling on business or attending work-related training are entitled to tax relief for personal subsistence expenses. However, it is essential to keep accurate records of all expenses and receipts to claim tax relief.
Avoiding Legal Pitfalls
Apart from tax laws, there are other legal implications to consider when it comes to corporate travel allowances.
For instance, the company must ensure that the travel allowance complies with the terms of the employment contract and does not discriminate against any employee based on protected characteristics such as age, gender, race, or disability.
Additionally, the company must ensure that the travel allowance is reasonable and does not exceed the actual expenses incurred by the employee. Failure to comply with these legal requirements can result in legal action and financial penalties for the company.
To avoid legal pitfalls, it is advisable to seek legal advice from a qualified professional before implementing a corporate travel allowance policy. This will ensure that the policy complies with all legal requirements and protects the interests of the company and its employees.
In summary, understanding the legal and tax implications of corporate travel allowances is crucial for any company that provides travel allowances to its employees.
Analysing Travel Allowance Impact
When it comes to assessing the impact of travel allowance on a company, there are two main factors to consider: employee productivity and financial efficiency.
Measuring Employee Productivity
One way to measure employee productivity is to look at the amount of work completed during business trips. If employees are able to focus on their work and complete tasks efficiently while on the road, it can be a sign that the travel allowance is sufficient and well-managed.
Another factor to consider is employee satisfaction. If employees feel that they are being adequately compensated for their time and expenses, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged during business trips. This can lead to increased productivity and better overall performance.
Assessing Financial Efficiency
From a financial perspective, travel allowance can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line. It is important to ensure that the allowance is set at a level that is both fair to employees and financially sustainable for the company.
One way to assess financial efficiency is to track travel expenses and compare them to the travel allowance provided. This can help identify areas where expenses are consistently exceeding the allowance, and adjustments can be made accordingly.
Another factor to consider is the cost of lost productivity. If employees are spending excessive amounts of time dealing with travel-related expenses or are unable to focus on their work while on the road due to financial concerns, it can result in lost productivity and increased costs for the company.
By carefully analysing the impact of travel allowance on both employee productivity and financial efficiency, companies can ensure that their travel policies are well-designed and effectively managed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What expenses are typically covered under a corporate travel policy.
Under a corporate travel policy, expenses typically covered include transportation, lodging, meals, and incidentals. Incidentals can include expenses such as laundry, phone calls, and internet access. Companies may also choose to cover expenses such as conference fees or transportation to and from the airport.
How is the travel allowance calculated for employees on business trips?
The travel allowance for employees on business trips is typically calculated based on the destination, the duration of the trip, and the company’s policy. Companies may choose to provide a daily allowance for meals or provide a company card for purchasing meals. The travel allowance may also vary depending on the employee’s level within the company.
What are the best practices for implementing a corporate travel policy?
The best practices for implementing a corporate travel policy include involving employees in the policy development process, clearly communicating the policy to employees, and providing training on the policy. Companies should also regularly review and update the policy to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Can you provide an example of a company travel policy for employees?
An example of a company travel policy for employees may include guidelines for booking travel, the types of expenses covered, and the process for submitting expense reports. The policy may also include guidelines for international travel, such as obtaining necessary visas and vaccinations.
What guidelines should be included in a travel policy to ensure compliance and fairness?
Guidelines that should be included in a travel policy to ensure compliance and fairness include specifying the types of expenses that are covered and the maximum amounts that can be claimed. The policy should also outline the process for submitting expense reports and the consequences for non-compliance.
How should a company handle travel allowances for international versus domestic travel?
Companies should consider the differences in expenses and regulations when handling travel allowances for international versus domestic travel. For example, international travel may require additional expenses such as visas and vaccinations, while domestic travel may require additional expenses such as rental cars or tolls. Companies should also consider the exchange rate when providing travel allowances for international travel.
Read more Business Travel Guide articles

9 Corporate Credit Card Policy Best Practices

What is MICE Travel? Everything You Need to Know in 2024

9 Benefits of Organizing Company Trips for Employees

12 Different Types of Tourism You Need to Know
Travel allowance guide: how to support employee expenses
Feb 27, 2024

Employers offer their employees a travel allowance for accommodation, transport, and food during a business trip. But there’s more than one way for a company to cover these expenses.
In this article, you’ll discover your options for supporting the expenses your employees incur during business travel.
What are business travel allowances?
When your employees travel for business reasons, the company should provide a travel allowance to cover the costs of their travel expenses, including transport, accommodation, and food.
Each company’s approach to covering an employee’s travel expenses will vary, but these are the most common approaches:
- Provide a company card to charge everything straight to the company.
- Issue a daily business travel allowance (per diem) to cover costs.
- Agree to reimburse all incurred expenses following the trip.
The average company spends around 10% of their annual revenue on travel — so it’s essential to take the right approach when it comes to travel allowances. But that’s not simple when costs fluctuate, and there’s uncertainty around the global economy.

Business travel compensation
Business travel compensation is an alternative name for business travel allowances . Depending on your company’s travel policy, it can be used to cover:
- Air travel.
- Accommodation.
Two commonly used approaches for covering business trip allowances include: handing employees a flat travel allowance (per diem) or covering all incurred employee travel expenses .
Let’s look at each of these in more detail and reveal a third option for ground travel. 👇
Flat travel allowance : pros and cons
Companies that pay a flat travel allowance give employees a fixed amount of money to spend as needed. If an employee spends more than this, they’ll be expected to cover the costs themselves.
Pros of flat business travel allowances
Giving business travellers a fixed basic travel allowance is a straightforward approach that comes with several advantages:
- Maintain a consistent spend for every trip.
- Removes the need for employees to claim expenses.
- Employees have a clear understanding of how much they can spend.
Cons of using flat business travel allowances
The downsides of a fixed travel allowance far outweigh the advantages:
- Regular updates are essential to remain in line with inflation and other rising costs.
- Employees may have to cover some work-related expenses out of their own pocket.
- Employers may hand out more than is necessary.
- Some travellers may have enough money while others have too little.
- Some employees may opt for the cheapest possible option in order to save money — and could use unsafe travel or accommodation.
- Depending on the destination, purpose of the trip, and role of the individual, the amount needed may differ.

Expense reimbursement: pros and cons
In this case, employers cover all incurred costs during business trips.
Frequent business travellers may have a company card to use during their trip. But, most employees are expected to use their own money and submit expense reports.
As submitting expense reports uses up valuable working time, it’s worth exploring quicker ways to make a claim. Fortunately, several expense management tools can speed up claiming expenses.
Pros of reimbursing travel expenses
Expecting your employees to use their own money and claim back the expenses incurred is time-consuming and potentially puts financial pressure on your employees. But there are some possible upsides with this travel allowance approach:
- Businesses only pay for actual expenses.
- Give employers more visibility of employee expenses.
- Gives flexibility to each traveller no matter the destination, length, or purpose of the business trips.
Cons of reimbursing actual expenses incurred
While there are benefits to reimbursing all employee expenses, there are potentially more drawbacks for employees and employers:
- Employees need to submit expense reports.
- Employees are out of pocket until they’re reimbursed.
- Some incidental expenses may not be strictly related to business purposes.
- Adds to the workload for Accounting teams as they need to process expense claims.
- Employers must set up clear travel policies so employees know which expenses they can claim.

The importance of a transport allowance
A transport allowance is one of the most essential allowances during a work-related trip — after all, you will be on the move.
As with allowances that cover other expenses, you may be given a company card or a daily allowance (per diem). But these are now both outdated ways of paying for business travel. And this is where Bolt Business will support your corporate travel needs.
With Bolt Business , employers can give employees a company payment method to use when travelling for work with the Bolt app.
When a company creates a Bolt Business account, the employees can set the company as a payment method for work rides in their Bolt app. This allows them to charge rides straight to the company without manually reporting expenses.
Business travel meal allowance
To cover the costs of meals during a trip, employers may provide a business travel meal allowance . It can work in one of three ways:
- Provide a company card.
- Give each employee a daily allowance to cover meals.
- Tell employees to pay using their own month and claim back the expenses later.
The downside to the third option is that it leaves your employees out of pocket until they’ve submitted an expense report, waited for approval, and received reimbursement — which can take several days.
Another option is to use Bolt Food for Business .
When your company creates a Bolt Business account, you can give certain employees permission to order food and groceries in the Bolt Food app using a company payment method.

Finding the right approach for travel allowances
Travel allowances are an essential part of any business trip. And the approach you take towards allowances for employees could influence the success of those trips.
Flat travel allowances (per diem) and expense reimbursement (actual incurred costs) both have their pros and cons., so it is important to consider the specifics of each trip before deciding.
Additionally, a transport allowance is crucial for any business trip, and Bolt Business is a great solution to address this need. Remember, getting travel allowances right is essential for both employers and employees, and it can make all the difference in the success of a business trip.
Get a transport allowance with Bolt Business
The Bolt app gives you a convenient way to travel in 45+ countries and 500+ cities — and you can use it as a business travel app , too.
With a Bolt Business account , you can give your employees a travel allowance in the Bolt app. These spending limits can be daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, annually, or for one time only — and travellers can’t exceed the spending limit.
Implementing travel allowances in this way means that you’ll only ever cover each traveller’s actual transport expenses. And by getting dropped off at your destination, there are no unexpected parking fees.
Set your employees up for a successful business trip by giving them a business travel allowance with Bolt Business.

Travel allowance FAQs
Get answers to some frequently asked questions about travel allowances.
What is a personal travel allowance?
Employers give a personal travel allowance to employees when they’re travelling for work. The company should support employees with the costs of transport, accommodation, and meals during the trip.
How do I ask for a travel allowance?
Start by reading your company’s travel policy; they may already offer a travel allowance. If not, provide a detailed breakdown of the expected costs during your trip and explain why the trip benefits the company.
Following your trip, follow up with your employer and provide proof of all purchases for which you wish to claim expenses.
How do you use a travel allowance?
Some companies will provide you with a company card, allowing you to charge expenses straight to your employer. Other companies will expect you to submit expense reports to claim your outgoings. Remember to hold onto your proof of purchase if this is the case.

Recent posts

An open letter to the entire food delivery industry
Apr 8, 2024
Dear competitors, You must be wondering why we’ve gathered you here today. Before we answer, we’d like to draw your attention to this GIF of a chicken holding its head still […]

Bolt Business records a 70% year-on-year rise in new signups
Mar 7, 2024
The number of new companies that created a Bolt Business account in 2023 grew by 70% year-on-year! This growth puts Bolt Business on course to becoming a B2B unicorn within […]

Benefits of micromobility in suburban areas — findings from TH Wildau study
Feb 22, 2024
Shared micromobility has become increasingly popular in many European countries. While its usage in bigger cities and inner-city areas is well-examined, there’s still a lack of research on micromobility ridership […]
Get a ride in 500+ cities across the world
Download app
Earn extra money driving your car
Sign up to drive

Travel Allowance: Meaning, Rules & More
What is travel allowance.
An employee may receive a travel allowance from their employer to help cover the costs associated with work travel. This kind of allowance is usually given on top of an employee's base pay or salary and is intended to cover the costs of business travel. The amount of travel reimbursement may differ based on the employer's policies, the nature and length of the journey, and the destination.
What are the Types of Travel Allowances?
Depending on the nature of the job, travel frequency, budget constraints of the company, and more such factors, different types of travel allowances can be offered to an employee.
1. Fixed Travel Allowance
A fixed travel allowance in salary implies that this is a fixed amount offered to the employee irrespective of the actual expenses incurred.
2. Daily Travel Allowance
As the name suggests, a daily travel allowance is offered to employees on a per-day basis, which covers their travel, meals, accommodation, and other such expenses.
3. Mileage Allowance
Employers can also provide a miles-based travel allowance to their employees, which depends on the number of miles they travel for business.
4. Travel Reimbursement
A travel reimbursement depends on the actual expense proofs submitted by an employee, which can include travel by air, rail or road.
The type of travel allowance offered by an employer may depend on various factors such as the nature of the job, frequency of travel, and budget constraints.
What are the Rules Applicable for Travel Allowance?
In India, there are specific tax rules governing travel allowances. Some of the basic travel allowance rules applicable to employees are as follows:
Exemption Limit
The exemption limit for travel allowances is determined by the Indian government and is subject to change. The exemption limit for travel allowance in India is ₹1,600 per month or ₹19,200 per year, as per FY 2022-2023. Read about taxation related to business travel in this blog .
Proof of Travel
The employer needs to provide proof of travel to claim the travel allowance, such as travel tickets, boarding passes, etc.
Actual Expenses
According to the travel allowance rules, if the amount of travel allowance exceeds the actual expenses incurred by the employee during travel, the excess amount is liable for a tax deduction.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
If the amount of travel allowance in salary exceeds the exemption limit, the excess amount is subject to TDS, at a rate of 5%.
Clubbing with Salary
The travel allowance is considered a part of the employee's salary and is subject to taxation accordingly.
Both employers and employees need to understand tax-related travel allowance rules. Employees must keep proper records of travel expenses and provide valid proof to claim the exemption. Employers should also ensure that they deduct TDS at the correct rate and report the travel allowance as a part of the employee's salary in their tax returns.
In conclusion
In conclusion, travel allowances are provided by employers to cover the expenses associated with work travel. Different types of travel allowances, such as fixed allowances, daily allowances, mileage allowances, and travel reimbursements, may be offered based on various factors. It is important for both employers and employees to understand the tax rules and regulations governing travel allowances, including exemption limits, proof of travel, taxation on excess amounts, TDS deductions, and the inclusion of travel allowances in the employee's salary. Compliance with these rules ensures proper documentation and accurate reporting of travel allowances for taxation purposes.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. is travel allowance fully exempted.
If the tax allowance amount in an employee’s CTC structure is less than ₹1,600, then the entire allowance would be tax-free. Anything above that is applicable for a standard tax deduction.
2. How do you use travel allowance?
Employees can use travel allowance by opting for road, rail, or air travel within the country.
3. Is travel allowance part of the salary?
Yes, an employer pays a travel allowance in salary to cover the employee's travel expenses. Travel allowance is part of an employee’s cost-to-company and can be claimed annually.
4. Who can claim a travel allowance?
According to the travel allowance rules, employees can claim the allowance to meet travel-related expenses. The eligibility for claiming travel allowance depends on the company's policies, the nature of the employer’s job, and more such factors.
NEW : Run fairer and faster compensation reviews - learn how here
Say Hello To The Future of Filing
Organise your employee data.
Latest blog posts, travel allowance: how it works for employers.

A travel allowance is an optional perk offered by the employer and is discussed on a case-by-case basis between the employer and the employee. The goal of the travel allowance is to help commuters financially. This article will give you all the information you need about the travel allowance, covering the benefits and rules that come with it.
- 1 What is a travel allowance?
- 2 Using travel allowance to retain employees
- 3 Travel allowance: employer's tax responsibility
- 4 How to calculate travel allowance
What is a travel allowance?
In the UK, a travel allowance is a form of financial assistance provided by employers to employees to cover their commuting costs. This allowance helps employees offset the expenses incurred while traveling between their residence and their workplace.
Here's how a travel allowance typically works in the UK:
Employer decision: The provision of a travel allowance is at the discretion of the employer. It's not a mandatory benefit and is usually offered as an incentive to attract and retain employees.
Negotiation and agreement : If an employer offers a travel allowance, the terms are usually negotiated and agreed upon between the employer and the employee. This can include the amount of the allowance, the frequency of payment and any specific conditions.
Commute distance: The travel allowance may be influenced by the distance the employee has to travel to reach their workplace. Longer distances often result in higher allowance amounts.
Taxation : In the UK, travel allowances are subject to taxation. The amount of tax varies depending on various factors, including whether the allowance is considered a taxable benefit or not. Generally, travel allowances are subject to income tax and National Insurance contributions.
Claiming expenses: Alternatively, some employers may provide a travel expense reimbursement system instead of a fixed allowance. In this case, employees can claim expenses for their actual travel costs, such as public transport fares or mileage if they use their own vehicle for commuting.
Reporting and documentation : Employers and employees need to keep accurate records of travel expenses, such as receipts for public transport tickets or mileage logs. These records are important for tax purposes and may be requested by tax authorities.
Tax relief: Some employees may be eligible for tax relief on their travel expenses. This is typically applicable if an employee's travel is necessary for their job and the employer doesn't reimburse the full amount of expenses. The employee can claim tax relief through HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC).
Cycle to work scheme: In the UK, there's a specific scheme called the "Cycle to Work" scheme, which allows employees to obtain bicycles and cycling equipment through salary sacrifice, thereby saving on tax and National Insurance contributions.
Public transport schemes: Some employers may offer discounted or subsidised public transport schemes to their employees as part of their travel allowance benefits.
It's important to note that the specifics of how a travel allowance works can vary from one employer to another. Additionally, tax laws and regulations may change over time, so it's essential to stay informed about the latest guidelines.
Using travel allowance to retain employees
The rising rents in major cities will likely lead more employees to relocate to rural areas in the future. The scarcity of skilled professionals makes finding capable employees even tougher due to sometimes lengthy commutes.
Despite the high number of commuters, many employees prefer workplaces close to home to minimise travel time and expenses. Employers can use travel allowances as an extra tool for retaining employees, alongside other measures.
Centralise Your Employee Data
Stop relying on lists and spreadsheets. Organise and edit personnel files and documents with ease, all in one secure, legally compliant place.
Travel allowance: employer's tax responsibility
An employer's tax responsibility for a travel allowance in the UK involves ensuring proper taxation and reporting of the allowance according to the guidelines set by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). The tax treatment of a travel allowance depends on various factors, including the nature of the allowance and the method of payment.
Here's an overview of an employer's tax responsibilities for a travel allowance:
Classifying the allowance: Employers need to determine whether the travel allowance is a taxable benefit or an expense reimbursement. This classification affects how the allowance is treated for tax purposes.
Taxable benefit: If the travel allowance is considered a taxable benefit, it will be subject to income tax and National Insurance contributions. Employers are responsible for deducting the appropriate tax and National Insurance from the allowance before paying it to the employee. The value of the taxable benefit is usually calculated based on the amount of the allowance provided.
Expense reimbursement: If the travel allowance is purely a reimbursement of actual expenses incurred by the employee, it may not be subject to income tax and National Insurance. However, the reimbursement must be supported by valid receipts or documentation, and the expenses must be directly related to the employee's business travel.
Flat Rate Scheme: In some cases, employers may choose to use a flat rate scheme for travel allowances. This involves applying a fixed amount for tax purposes, regardless of the actual expenses incurred. The use of a flat rate scheme is subject to HMRC's rules and limitations.
Record keeping: Employers are responsible for maintaining accurate records of the travel allowances provided to each employee. Proper documentation should include details of the allowance, dates, amounts, and the purpose of the travel.
Reporting to HMRC : Employers are required to report taxable benefits and expenses provided to employees on the annual P11D form. This form outlines the value of benefits and expenses provided during the tax year. Employers must submit the P11D form to HMRC and provide a copy to the employee.
PAYE Settlement Agreement (PSA): In certain cases, employers may choose to include travel allowances within a PAYE Settlement Agreement (PSA). A PSA allows employers to settle the tax liability on behalf of the employee, simplifying the reporting process.
Compliance: Employers must ensure compliance with all relevant tax laws, regulations, and guidelines when providing travel allowances to employees. Failure to accurately report and deduct the appropriate taxes can lead to penalties.
It's important for employers to stay informed about any changes in tax laws and regulations related to travel allowances. Consulting with tax professionals or seeking guidance from HMRC can help ensure that an employer's tax responsibilities are met accurately and in line with the current regulations.
How to calculate travel allowance
Calculating a travel allowance in the UK involves considering various factors, including the distance of the commute, the method of transportation and whether the allowance is a flat rate or based on actual expenses.
Here's a general overview of how travel allowances can be calculated:
1. Determine the method of calculation: Some employers use a flat rate for travel allowances. In this case, a fixed amount is provided for each qualifying journey. Alternatively, employers may reimburse employees for the actual expenses incurred during their commute. This requires employees to provide valid receipts or documentation.
2. Calculate the commute distance: For a flat rate allowance, the commute distance may not be a direct factor in the calculation. For reimbursement based on actual expenses, calculate the distance between the employee's home and workplace. This can be done using tools like Google Maps or GPS devices.
3. Calculate the allowance amount: If using a flat rate, the employer decides on a fixed amount to be paid per qualifying journey. This amount could be based on typical travel costs, distance, or other relevant factors.
If reimbursing actual expenses, the allowance amount would be based on the expenses submitted by the employee. These expenses may include public transport fares, mileage for using a personal vehicle, parking fees, and tolls.
4. Take into account tax considerations: Determine whether the travel allowance is taxable or not. Taxable allowances are subject to income tax and National Insurance contributions, while non-taxable reimbursements are not.
5. Report and document everything: Keep accurate records of the allowance calculations, receipts and documentation for each employee. This is important for tax reporting and compliance.
6. Decide on frequency of payment: - Decide how frequently the travel allowance will be paid (e.g. weekly or monthly).
7. Notify employees: Communicate the details of the travel allowance calculation method, amount and payment schedule to employees.
8. Apply tax and national insurance deductions: If the travel allowance is taxable, deduct the appropriate income tax and National Insurance contributions before paying the allowance to the employee. The amount deducted depends on the employee's tax code and earnings.
It's important to note that travel allowance calculations can be complex, and employers should ensure compliance with HMRC guidelines and regulations. Employers may also consider consulting with tax professionals or payroll experts to ensure accurate calculations and reporting. Additionally, employees should be aware of the tax implications and any reporting requirements related to the travel allowance they receive.
We would like to inform you that the contents of our website (including any legal contributions) are for non-binding informational purposes only and does not in any way constitute legal advice. The content of this information cannot and is not intended to replace individual and binding legal advice from e.g. a lawyer that addresses your specific situation. In this respect, all information provided is without guarantee of correctness, completeness and up-to-dateness.
Keep Vital Data At Your Fingertips
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Expenses and employee benefits
Expenses and benefits: travel and subsistence
As an employer paying your employees’ travel costs, you have certain tax, National Insurance and reporting obligations.
This includes costs for:
- providing travel
- reimbursing travel
- accommodation (if your employee needs to stay away overnight)
- meals and other ‘subsistence’ while travelling
Subsistence includes meals and any other necessary costs of travelling, for example parking charges, tolls, congestion charges or business phone calls.
There are different rules for reporting expenses relating to public transport .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Topic no. 511, Business travel expenses
More in help.
- Interactive Tax Assistant
- Report Phishing
- Fraud/Scams
- Notices and Letters
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Accessibility
- Contact Your Local IRS Office
- Contact an International IRS Office
- Other Languages
Travel expenses are the ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job. You can't deduct expenses that are lavish or extravagant, or that are for personal purposes.
You're traveling away from home if your duties require you to be away from the general area of your tax home for a period substantially longer than an ordinary day's work, and you need to get sleep or rest to meet the demands of your work while away.
Generally, your tax home is the entire city or general area where your main place of business or work is located, regardless of where you maintain your family home. For example, you live with your family in Chicago but work in Milwaukee where you stay in a hotel and eat in restaurants. You return to Chicago every weekend. You may not deduct any of your travel, meals or lodging in Milwaukee because that's your tax home. Your travel on weekends to your family home in Chicago isn't for your work, so these expenses are also not deductible. If you regularly work in more than one place, your tax home is the general area where your main place of business or work is located.
In determining your main place of business, take into account the length of time you normally need to spend at each location for business purposes, the degree of business activity in each area, and the relative significance of the financial return from each area. However, the most important consideration is the length of time you spend at each location.
You can deduct travel expenses paid or incurred in connection with a temporary work assignment away from home. However, you can't deduct travel expenses paid in connection with an indefinite work assignment. Any work assignment in excess of one year is considered indefinite. Also, you may not deduct travel expenses at a work location if you realistically expect that you'll work there for more than one year, whether or not you actually work there that long. If you realistically expect to work at a temporary location for one year or less, and the expectation changes so that at some point you realistically expect to work there for more than one year, travel expenses become nondeductible when your expectation changes.
Travel expenses for conventions are deductible if you can show that your attendance benefits your trade or business. Special rules apply to conventions held outside the North American area.
Deductible travel expenses while away from home include, but aren't limited to, the costs of:
- Travel by airplane, train, bus or car between your home and your business destination. (If you're provided with a ticket or you're riding free as a result of a frequent traveler or similar program, your cost is zero.)
- The airport or train station and your hotel,
- The hotel and the work location of your customers or clients, your business meeting place, or your temporary work location.
- Shipping of baggage, and sample or display material between your regular and temporary work locations.
- Using your car while at your business destination. You can deduct actual expenses or the standard mileage rate, as well as business-related tolls and parking fees. If you rent a car, you can deduct only the business-use portion for the expenses.
- Lodging and non-entertainment-related meals.
- Dry cleaning and laundry.
- Business calls while on your business trip. (This includes business communications by fax machine or other communication devices.)
- Tips you pay for services related to any of these expenses.
- Other similar ordinary and necessary expenses related to your business travel. (These expenses might include transportation to and from a business meal, public stenographer's fees, computer rental fees, and operating and maintaining a house trailer.)
Instead of keeping records of your meal expenses and deducting the actual cost, you can generally use a standard meal allowance, which varies depending on where you travel. The deduction for business meals is generally limited to 50% of the unreimbursed cost.
If you're self-employed, you can deduct travel expenses on Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss From Business (Sole Proprietorship) , or if you're a farmer, on Schedule F (Form 1040), Profit or Loss From Farming .
If you're a member of the National Guard or military reserve, you may be able to claim a deduction for unreimbursed travel expenses paid in connection with the performance of services as a reservist that reduces your adjusted gross income. This travel must be overnight and more than 100 miles from your home. Expenses must be ordinary and necessary. This deduction is limited to the regular federal per diem rate (for lodging, meals, and incidental expenses) and the standard mileage rate (for car expenses) plus any parking fees, ferry fees, and tolls. Claim these expenses on Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses and report them on Form 1040 , Form 1040-SR , or Form 1040-NR as an adjustment to income.
Good records are essential. Refer to Topic no. 305 for information on recordkeeping. For more information on these and other travel expenses, refer to Publication 463, Travel, Entertainment, Gift, and Car Expenses .
- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)
Managing business travel expenses
Guide to hmrc subsistence allowance & expenses, what is a subsistence allowance, how do hmrc subsistence rates work.
- The cost of food or drink must be incurred after the business trip has started
- The trip must be beyond their usual commute and be done as part of official business.
- The journey must take the employee away from their normal place of work for 5 hours or more.
Is meal allowance taxable?
- a meal or beverage is not purchased
- the meal does not constitute additional expenditure
- the “staying with friends or relatives allowance” is claimed
- meals have been taken at home
- meals are provided during a training course, conference or similar activity
- meals are provided on the train or plane and included in the ticket cost
What are the HMRC domestic subsistence allowance rates?
- £5 for travel of 5 hours or more (£10 supplement if travel is ongoing at 8pm)
- £10 for travel of 10 hours or more (£10 supplement if travel is ongoing at 8pm)
- £25 for travel of 15 hours or more (and ongoing at 8pm)
Overnight accommodation rate UK
Meal allowance rates overseas, how does a business report subsistence allowance spend.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct
2024 Guide to HMRC Mileage Rates for Businesses
Dealing with HMRC mileage rates can be tricky, but it doesn't have to be a headache.
If you're looking for a simpler way to manage business travel expenses and stay on top of compliance , we've got some insights that can help.
We'll be covering:
- What are the HMRC Mileage Rates?
- What is the HMRC Mileage Allowance?
- When Can Employees Claim Business Mileage from Home?
- What is Travel Allowance in the UK?
- What are HMRC Fuel Advisory Rates?
- HMRC Mileage Rates for Electric Cars
- Taxation of HMRC Mileage Rates
- How to Apply the HMRC Business Mileage Rates: A Guide for Employers
- Keeping a Mileage Log for HMRC Compliance
Let's make managing travel expenses easier together.
What are the HMRC Mileage Rates?
The HMRC sets specific mileage rates for individuals using their personal vehicles for business purposes. These rates are designed to simplify calculating travel expenses for employers and employees, ensuring fair compensation for business use of a personal car.
Breakdown of HMRC Mileage Rates

Cars & vans : For the first 10,000 miles in a tax year, the rate is 45 pence per mile. Once you exceed this threshold, the rate drops to 25 pence for each additional mile.
Motorcycles : A consistent rate of 24 pence per mile applies, irrespective of the distance travelled within the tax year.
Bicycles : Cyclists can claim 20 pence per mile for business miles travelled.
The HMRC 10,000 Mile Threshold
The initial 10,000 miles are considered to bear a higher cost, accounting for the vehicle's depreciation, maintenance, and running costs.
The rate reduction beyond 10,000 miles acknowledges the supposed decrease in these costs as the vehicle ages and accumulates mileage.
What do HMRC Mileage Rates Cover?
The HMRC mileage rates are meticulously calculated to cover all expenses associated with using a personal vehicle for business purposes.
This includes, but is not limited to:
Maintenance
Insurance costs
The intention is to offer a straightforward, fair mechanism for employees to be reimbursed without having to detail every individual cost incurred.
What is the HMRC Mileage Allowance?
The HMRC mileage allowance is a rate set by HMRC that allows businesses in the UK to reimburse employees for the use of their personal vehicles for business purposes.
The primary goal of the mileage allowance is to provide a tax-free threshold for mileage reimbursement, ensuring that employees are compensated for the business use of their vehicles without incurring additional tax liabilities.
Tax Implications of Mileage Allowances for Employers & Employees
The HMRC mileage allowance is designed with tax efficiency in mind.
Reimbursements made at or below the HMRC-approved rates are not subject to tax or National Insurance contributions. This applies to both employers and employees, making it a tax-efficient way to handle business travel expenses .
For Employers:
Reimbursements within the HMRC rates do not incur additional tax liabilities.
Payments above the HMRC rates must be reported, and the excess is subject to tax and National Insurance contributions.
For Employees:
Receiving mileage allowance at or below the HMRC rates does not affect taxable income.
If reimbursements are below the HMRC rates, employees can claim Mileage Allowance Relief on their tax return for the difference.
When Can Employees Claim Business Mileage from Home?
The HMRC guidelines allow employees to claim mileage for travel from their home to a temporary workplace or for specific business journeys that aren't part of their regular commute.
The key criteria for these claims under the HMRC mileage rates include:
Temporary workplace visits : If you’re travelling to a location for a limited duration or for a temporary purpose, this can qualify as a claimable business journey.
Distinct business journeys : Travelling from home directly to meet clients, attend business meetings at different locations, or carry out site visits are examples of claimable business mileage.
Regular Commute vs Business Travel: The Difference

Regular commute : This is travel between your home and your permanent place of work. These journeys are not claimable under HMRC mileage rates because they’re considered as non-business travel.
Business travel : This encompasses any travel that is solely for business purposes, excluding your normal commute. It's these journeys that the HMRC mileage rates aim to cover, ensuring employees are reimbursed for the additional costs incurred.
Claiming Your Business Mileage
For employees looking to claim their business mileage , here's a simplified process:
Document your journeys. Keep a detailed log of your business journeys, including dates, destinations, and miles travelled. Documentation is key to substantiating your claims.
Calculate your mileage. Use the current HMRC mileage rates to calculate your total claim amount. Remember, the rates differ depending on the vehicle used and the number of business miles covered.
Submit your claim. Provide your documented journey log and calculated mileage to your employer. Employers typically have a process in place for these reimbursements.
For employers:
Ensure clarity around what constitutes claimable business mileage and communicate this effectively to your team to streamline the reimbursement process.
Offer support and guidance on how to log and claim business mileage. This will not only ensure compliance with HMRC guidelines but also foster a transparent and supportive work environment.
What is Travel Allowance in the UK?
Travel allowance encompasses a broader spectrum of work-related travel expenses than mileage allowance. While mileage allowance specifically covers the costs of using a personal vehicle for business purposes, travel allowance can include various other travel-related expenses.
Travel Allowance vs Mileage Allowance: The Difference

Mileage allowance : Directly related to the use of a personal vehicle for business journeys, calculated using the HMRC mileage rates. It's designed to cover vehicle-related costs such as fuel, maintenance, and depreciation.
Travel allowance : Encompasses a wider range of employee travel expenses incurred due to business activities. This can include public transport fares, accommodation costs, and meals during business travel, in addition to mileage costs when using public or alternative modes of transport.
Criteria for Claiming Travel Allowances
To claim travel allowances effectively, understanding the criteria set by HMRC is essential. Claims must be for expenses wholly, exclusively, and necessarily incurred in the performance of the duties of employment.
Key criteria include:
Temporary work locations : Travel expenses to and from temporary work locations can qualify for travel allowance claims.
Necessary overnight stays : Costs incurred during necessary overnight business trips, including accommodation and meals, are claimable.
Public transport usage : Expenses related to business travel via public transport, including trains, buses, and taxis, fall under travel allowance.
What is Included in the Travel Allowance UK?

Transport costs : Train tickets, bus fares, taxi receipts, and airline tickets for business-related travel.
Accommodation : Hotel or other lodging expenses when overnight stays are required for business purposes.
Meals and subsistence : Reasonable costs for meals during business travel, subject to HMRC guidelines.
Incidental expenses : Minor costs associated with business travel, such as internet charges at a hotel.
Both employers and employees need to keep detailed records and receipts for all travel expenses claimed under the travel allowance.
This not only ensures compliance with HMRC regulations but also facilitates a smooth reimbursement process.
What are HMRC Fuel Advisory Rates?
HMRC Fuel Advisory Rates are guidelines set for the reimbursement of fuel expenses incurred during business travel in company cars and vans. These rates are designed to:
Reimburse employees for business travel in their company vehicles.
Allow employees to repay the cost of fuel used for private travel in company vehicles.
It’s important to note that these rates should not be used in circumstances other than those specified above.
How are Fuel Advisory Rates Calculated?
The process of calculating these rates is both systematic and reflective of current market conditions.
Here’s how HMRC determines the advisory fuel rates:
Quarterly reviews : HMRC reviews the rates quarterly, considering the latest fuel prices and vehicle efficiency data.
Fuel prices : The latest prices for petrol, diesel, and LPG are obtained from reliable sources, including the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero and the Automobile Association.
Vehicle efficiency : Average miles per gallon (MPG) figures are derived from manufacturer data and adjusted for annual sales to businesses. For LPG vehicles, the MPG used is 20% lower than for petrol due to lower energy density.
Electric vehicles : The advisory rate for electric cars is calculated using electricity price data and car electrical consumption rates, ensuring a fair assessment of electric vehicle running costs.
Note : You can calculate employee car and fuel benefits using HMRC’s calculator .
Applying the HMRC Fuel Advisory Rates
Employers can apply these rates in two key scenarios:
Reimbursing employees : If the mileage rate paid to employees does not exceed the advisory fuel rates based on the engine size and fuel type of the company car, there’s no taxable profit or National Insurance contribution due.
Employees repaying for private travel : Correct recording and repayment of private travel mileage at these rates or higher ensure there’s no fuel benefit charge.
Key Points for Employers & Employees:
Employers have the flexibility to use their own rates if their vehicles are more fuel-efficient or if the cost of business travel is higher than the guideline rates, provided they can justify the higher cost per mile.
Employees must accurately record all private travel mileage and use the correct rate to calculate repayments for fuel used for private travel.
HMRC Mileage Rates for Electric Cars
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a unique set of advantages and challenges when it comes to business travel. Recognising this, HMRC provides specific mileage rates for electric cars, distinct from those for petrol, diesel, or hybrid vehicles.
These rates are designed to account for the cost of electricity used for business travel, rather than fuel consumption, offering a fair and equitable means of reimbursement for EV users.
Impact of Electric Cars on Business Travel Expenses & Reimbursements
The adoption of electric vehicles can significantly alter the landscape of corporate travel expenses :
Cost-effectiveness : Generally, electric cars are cheaper to "fuel" compared to traditional petrol or diesel vehicles, potentially reducing overall travel expenses.
Environmental benefits : Encouraging the use of EVs aligns with corporate sustainability goals , reducing the carbon footprint associated with business travel.
Tax incentives : Utilising HMRC’s mileage rates for electric cars can also offer tax benefits, aligning financial incentives with eco-friendly practices.
What is the HMRC Mileage Rate for Electric Cars?
As of 1 March 2024, the HMRC mileage rate for fully electric cars is set at 9 pence per mile .
This rate provides a simple way for businesses and employees to calculate reimbursements for business travel using electric vehicles, ensuring that drivers are compensated for the electricity cost of their journeys.
Note : This rate is subject to periodic reviews by HMRC, reflecting changes in electricity costs and the evolving efficiency of electric vehicles. Make sure to stay updated with the latest rates to ensure compliance and maximise the benefits of integrating electric vehicles into your fleets.
Taxation of HMRC Mileage Rates
The HMRC mileage rates are designed to simplify the reimbursement process for business travel, providing a tax-efficient framework for compensating employees. But, are HMRC mileage rates taxable?
The answer hinges on adherence to the prescribed rates and the purpose of the journeys:
Non-taxable allowances : Mileage allowances paid at or below the HMRC-approved rates for business travel are not considered taxable income. These rates are calculated to cover the vehicle's operating costs, and reimbursements within these limits do not require tax payments from the employee.
Excess payments : Should an employer choose to reimburse at a rate higher than the HMRC-specified mileage rates without justifying the increased expense, the excess amount could be subject to tax and National Insurance contributions as it is considered earnings.
Employer Reporting Obligations
Employers play a crucial role in ensuring the tax efficiency of mileage reimbursements:
P11D forms : When providing mileage allowances, employers must report any amounts that exceed the approved HMRC mileage rates on the employee's P11D form . This form details benefits and expenses that have not been subject to PAYE tax.
PAYE Settlement Agreements : In some cases, employers may opt to cover the tax on excess mileage payments through a PAYE Settlement Agreement (PSA) . This agreement allows the employer to make one annual payment to HMRC covering all taxes due on minor, irregular, or impracticable employee expenses or benefits, including mileage rate excesses.
Are HMRC Mileage Rates Taxable?
As long as mileage allowances do not exceed the prescribed rates for the actual business miles travelled, they remain tax-free.
This approach incentivises the accurate recording and reporting of business travel, aligning employee reimbursements with actual travel costs without additional tax burdens.
How to Apply the HMRC Business Mileage Rates: A Guide for Employers
Understanding how to apply HMRC mileage rates correctly not only aligns with legal requirements but also supports fair and transparent compensation for employees using their personal vehicles for work .

Step 1: Understand the Rates
Familiarise yourself with the current HMRC mileage rates for cars, vans, motorcycles, and bicycles.
These rates are designed to cover the cost of using personal vehicles for business purposes, including fuel, maintenance, and wear and tear.
Step 2: Establish a Policy
Develop a clear corporate expense policy on business mileage that includes how and when mileage can be claimed, the documentation required for claims, and how the HMRC mileage rates will be applied within your organisation.
Need help building your expense policy? Use our free expenses policy template .
Step 3: Educate Your Team
Ensure that all employees understand the policy, the importance of accurate mileage tracking, and how to submit mileage claims.
Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and promotes compliance.
Step 4: Implement Mileage Tracking
Encourage employees to keep detailed logs of their business mileage.
Whether through manual logs or digital tools, accurate records are crucial for compliance and reimbursement.
Step 5: Verify & Calculate Reimbursements
Review submitted mileage logs for accuracy and calculate reimbursements using the HMRC mileage rates.
Ensure that claims are justified and fall within the guidelines provided by HMRC.
Step 6: Process Reimbursements
Timely process mileage expense claims, providing reimbursements through payroll or as a separate payment, according to your business practices.
Keeping a Mileage Log for HMRC Compliance
Let's break down why keeping a detailed mileage log is crucial and how digital tools can make this task simpler and more reliable:
The Benefits of Keeping Detailed Mileage Logs
Ensuring tax compliance : Precise mileage logs are your safeguard against tax issues. They serve as solid evidence that supports your travel expense claims according to HMRC mileage rates, ensuring you stay on the right side of tax laws.
Guaranteeing correct reimbursements : For both individuals and businesses, accurate logs mean accurate reimbursements. No guesswork involved - every mile travelled for business is accounted for and compensated correctly.
Preparedness for audits : Should HMRC inquire further into your travel claims, a comprehensive mileage log provides a clear, detailed account of your business journeys, proving that your claims are justified and compliant.
How Technology Simplifies Mileage Tracking
Gone are the days of pen and paper logs - technology offers a streamlined, error-minimising approach to mileage tracking .
One standout solution is ExpenseIn , an expense management solution that embodies efficiency and compliance in mileage tracking.
Why Choose ExpenseIn for Your Mileage Tracking Needs?

Automated journey tracking : Utilise GPS technology to automatically record your trips' start and end points, ensuring every business mile is accurately captured without manual input.
HMRC-compliant mileage logs : Generate logs that meet HMRC's strict requirements, detailing every aspect of your business travel, from dates and distances to the purpose of each journey.
Ease of use and integration : With user-friendly interfaces and compatibility with various financial systems, tools like ExpenseIn make mileage logging accessible and straightforward, no matter where you are.
Moving to a digital mileage log system is not just about compliance; it's about embracing a solution that offers clarity, convenience, and confidence in every mile you log for business.
Ready to transform how you track mileage? Take the first step with ExpenseIn. Book a demo today and discover how our tool can simplify your mileage logging, ensure HMRC compliance, and save you time and money.
Explore our faster, simpler and smarter approach to expense management.
Related stories, are your mileage expense records hmrc compliant.

HMRC PAYE Explained: Tax Deductions, Deadlines & Requirements

HMRC Subsistence Rates: Everything You Need to Know

Claiming Back Travel Expenses from HMRC: A Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses

Sign up to stay in the know
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest ExpenseIn news and expense management insights straight to your inbox.
- ATO Community
- Legal Database
- What's New
Log in to ATO online services
Access secure services, view your details and lodge online.
Travel allowances
Explains the PAYG withholding implications on travel allowances.
Last updated 24 August 2021
Travel allowance is a payment made to an employee to cover accommodation, food, drink or incidental expenses they incur when they travel away from their home overnight in the course of their duties.
Allowances folded into your employee's salary or wages are taxed as salary and wages and tax has to be withheld, unless an exception applies.
You include the amount of the travel allowance in the allowance box on your employee's payment summary.
The exception applies if:
- you expect your employee to spend all of the travel allowance you pay them on accommodation, food, drink or incidental expenses
- you show the amount and nature of the travel allowance separately in your accounting records
- the travel allowance is not for overseas accommodation
- the amount of travel allowance you pay your employee is less than, or equal to the reasonable travel allowance rate.
If the exception applies, you:
- don't withhold tax from the travel allowance you pay your employee
- don't include the amount of the travel allowance in the allowance box on your employee's payment summary
- only include the allowance on their payslip.
If the first two exception conditions are met but you pay your employee a travel allowance over the reasonable travel allowance rate, you're required to withhold tax from the amount that exceeds the reasonable travel allowance rate. You also need to include the total amount of the travel allowance in the allowance box on your employee's payment summary.
You are always required to withhold tax from a travel allowance for overseas accommodation and include the amount of the travel allowance in the allowance box on your employee's payment summary.
Check the relevant Single Touch Payroll (STP) employer reporting guidelines to see how to report these payments through STP:
- STP Phase 1 employer reporting guidelines – allowances
- STP Phase 2 employer reporting guidelines – allowances
Reasonable travel allowance rate
Each year we publish the amounts we consider reasonable for claims for domestic and overseas travel allowance expenses.
- TD 2021/6 Income tax: what are the reasonable travel and overtime meal allowance expense amounts for the 2021–22 income year?
- TD 2020/5 Income tax: what are the reasonable travel and overtime meal allowance expense amounts for the 2020–21 income year?
- TR 2004/6 Income tax: substantiation exception for reasonable travel and overtime meal allowance expenses
- Keeping travel expense records
- Tax return – allowances
- Tax return – work-related travel expenses
Thank you for signing up!
AI Summary to Minimize your effort
Transport Allowance for Salaried Employees - Meaning, Exemption, Calculation, Rules
Updated on : Mar 19th, 2024
11 min read
Transport Allowance is an allowance a company or employer provides to employees to compensate for their travel from their residence to the workplace. It is a type of special allowance. Like other allowances, transport allowance is a part of CTC and has fixed pay.
As the employee’s income tax computation is done by their employers for tax deduction purposes, salaried taxpayers may or may not be very concerned about their salary structuring and details of various kinds of allowances and exemptions available to them even before arriving at gross total income. However, understanding allowances and exemptions provided on such allowances is also significant for tax planning. This helps them choose the right CTC structure and lawfully claim the tax benefit to which they are entitled. Additionally the availability of the exemption depends on the tax regime chosen by the taxpayer.
This article will discuss one such allowance, i.e., transport allowance and its tax provisions.
What is Transport Allowance?
Transport allowance could mean allowance provided for the purpose of transport from residence to the place of work . However, transport allowance under Section 10(14) of Income-tax Act,1961 read with rule 2BB of Income-tax rules can be either of the following:
- Allowance granted to an employee to meet his expenditure for the purpose of commuting between his place of residence and office/place of duty
- Allowance granted to an employee working in the transport business to meet his personal expenditure during his duty performed in the course of running such transport from one place to another place provided the employee is not in receipt of daily allowance
Transport allowance is taxable in the hands of the employee since it is added to their gross salaries. However, employees can claim tax exemption for transport allowance as per the exemption limit.
Quantum of Exemption
Section 10(14) read with Rule 2BB provides for transport allowance exemption. The amount of exemption is as follows:
Changes by Finance Act, 2018
From the financial year 2018-2019, the tax exemption for medical and transport allowances has been merged. The Income Tax Department introduced a standard deduction in place of transport and medical allowance. From the financial year 2019-2020, the standard deduction is Rs 50,000, which covers the transport and medical allowance.
Thus, employees can claim the deduction of Rs 50,000 while filing their ITR without producing any bills or documents. Employers will consider the standard deduction to compute the net taxable salary while calculating the TDS. This change shall take effect from the financial year 2018-19. Accordingly, no separate transport allowance of Rs 1,600 per month is available to employees other than physically challenged employees and employees of a transport business. The limit of Rs 40,000 has been increased to Rs 50,000 in the Interim Budget 2019. Know the highlights of the Interim Budget 2019 here.
Difference Between Transport Allowance and Conveyance Allowance
A transport allowance is an allowance given to meet commuting expenses between the place of residence and office or to meet the personal expenditure of an employee of a transport business.
A conveyance allowance is an allowance granted to meet the expenditure on conveyance in the performance of office duty.
Transport allowance is fully taxable for all employees in both regimes. However it is exempt under both tax regimes to the extent of 3,200 per month for the employees who are physically challenged such as blind/deaf/dumb or orthopedically handicapped with disability of lower extremities. C onveyance allowance is exempt from tax only to the extent of actual expenditure incurred.
Illustration
Let us derive the taxable income of an employee for the FY 2017-18, FY 2018-19, FY 2019-20 and onwards.
Let us look the same illustration for an employee who is specially abled.
Transport Allowance Under the New Tax Regime
From the FY 2020-21, the government introduced the new tax regime for individual and HUF taxpayers under section 115BAC. In the new tax regime, there are flat tax rates and no deductions or exemptions. For example, an individual opting for the new tax regime cannot claim exemptions for HRA and others. Also, the individual cannot claim deductions for any tax-saving investments. However, the new tax regime allows an individual to claim the following tax-exempt allowances:
- Allowance by the employer to meet the cost of travel on tour or transfer. It includes an allowance towards the cost of travel, such as airfare, rail fare and other transportation costs.
- Any allowance by the employer to meet the ordinary daily charges incurred by an employee on account of absence from the usual place of duty. The allowance should be in respect of the tour or for the period of the journey in connection with a transfer. The allowance includes expenses an employee incurs for food and other daily costs while travelling.
- Allowance to meet conveyance expense incurred while performing duties of an office or employment of profit. However, in this case, the employer should not provide a free conveyance to the employee. The allowance includes travelling expenses an employee incurs while performing official duties.
In the case of an employee who is blind, deaf and dumb, or orthopedically handicapped, with a disability of lower extremities can claim transport allowance to meet expenditure on commuting between residence and the place of duty. The benefit is up to Rs 3,200 per month. The same would be fully taxable in the case of an employee with no disabilities.
How to Claim Transport Allowance While Filing Income Tax Return for an employee who is specially abled ?
Usually, employers take care of the tax exemption on transport allowance while deducting TDS from the paycheck. In such cases, employees have to enter the amount mentioned in Form 16 part B in the ‘Income from Salary’ column of their ITR Form .
But when an employer has given a tax benefit on transport allowance or forgotten to give the tax benefit in Form 16 , you can claim tax exemption by following the below process:
- Check the CTC structure from the salary slip.
- Check whether the amount of transport allowance is part of the CTC.
- If the amount in the CTC structure is less than Rs 3,200 per month, the entire travel allowance would be tax-free.
- If the amount in the CTC structure is more than Rs 3,200 per month, the tax-free amount would only be Rs 3,200 per month.
Related Articles
Income tax allowances and deductions Special allowance taxation Allowances and deductions available to a salaried
Frequently Asked Questions
A normal employee (other than a handicapped employee) cannot claim transport allowance for commuting between residence and place of work or employment.
The standard deduction is a flat deduction available from the taxable salary or pension income. The deduction amount is Rs. 40,000 for FY 2018-19, whereas it is increased to Rs.50,000 from FY 2019-20 and onwards.
You can furnish the proof or invoices of relocation expenses to your employer and claim tax-free reimbursement.
The tax exemption for medical reimbursement is no longer applicable. From the FY 2018-19, the fixed medical reimbursement and transport allowance stand replaced by a standard deduction.
No, if there is a company-run transportation service facility, they will not pay you a conveyance allowance whether you use the service or not.
No, your employer can pay whatever amount they find appropriate. However, only specially abled employees can avail the exemption against such allowances.
An employee who is handicapped can get the exemption of transport allowance up to Rs. 3,200 per month.
Yes, a handicapped employee can get an exemption of up to 3,200 per month if he pays taxes in any of the regime.
No, transport allowance is fully taxable in the case of a normal employee if he pays taxes in any regime.
70% of such allowance up to a maximum of Rs.10,000 per month will be exempted if he has not received daily allowance. Suppose If he receives a daily allowance, then he would not be eligible for this exemption.
Quick Summary
Was this summary helpful.
Clear offers taxation & financial solutions to individuals, businesses, organizations & chartered accountants in India. Clear serves 1.5+ Million happy customers, 20000+ CAs & tax experts & 10000+ businesses across India.
Efiling Income Tax Returns(ITR) is made easy with Clear platform. Just upload your form 16, claim your deductions and get your acknowledgment number online. You can efile income tax return on your income from salary, house property, capital gains, business & profession and income from other sources. Further you can also file TDS returns, generate Form-16, use our Tax Calculator software, claim HRA, check refund status and generate rent receipts for Income Tax Filing.
CAs, experts and businesses can get GST ready with Clear GST software & certification course. Our GST Software helps CAs, tax experts & business to manage returns & invoices in an easy manner. Our Goods & Services Tax course includes tutorial videos, guides and expert assistance to help you in mastering Goods and Services Tax. Clear can also help you in getting your business registered for Goods & Services Tax Law.
Save taxes with Clear by investing in tax saving mutual funds (ELSS) online. Our experts suggest the best funds and you can get high returns by investing directly or through SIP. Download Black by ClearTax App to file returns from your mobile phone.
Cleartax is a product by Defmacro Software Pvt. Ltd.
Company Policy Terms of use
Data Center
SSL Certified Site
128-bit encryption
Queensland premier defends BPIC agreement that delivers union tradies pay rises of more than $10 per hour
Queensland's premier has defended a deal brokered with construction unions that includes pay rises of more than $10 an hour over the next four years and an extra $1,000 a week to work away from home.
Union workers will receive a 5 per cent pay rise on the first of July, which will continue every year until the end of the agreement in 2027.
Carpenters and other qualified tradespeople will be paid nearly $1,948 a week.
By 2027, the same carpenters will be paid $2,351 a week, jumping from $54.12 an hour to $65.78.
Skilled labourers will also see their wages increase by $10 an hour over the agreement, increasing from $47.63 to $57.89. By 2027, they'll be paid $2,084 a week.
The deal comes at a time when Queensland is looking at huge array of projects across the next decade, ranging from Olympic infrastructure to green energy projects.
"These are all prevailing conditions in the industry," Premier Steven Miles said.
"I think it's appropriate that on government jobs, workers aren't competing with each other on wages.
"These conditions have been in place for some time."
Travel allowances and leave loading
The living away from home allowance section of the BPIC states that a "distant construction sites allowance of $1,000 per week or $200 per day for part weeks" will be paid when an employee is directed to work on a project "located 50 kilometres or more from the address of the employer".
A travel allowance will be paid to workers on government projects worth more than $50 million, while all workers will receive a $50 dollar travel allowance each day.
Starting in July that will jump to $55, and workers who travel more than 50 kilometres will be paid up to $95 dollars a day.
This too will go up over the next four years, reaching $106 per day in 2027.
Workers conducting emergency work or pouring concrete will be paid double time to work in the rain.
A site allowance will be paid per hour to workers on large projects, starting at $1.70 for projects worth $50 million to $80 million, reaching $10 an hour on projects worth $900 million to $1 billion.
All workers will accrue a rostered day off (RDO) every 10 working days, with RDO's still accumulating while workers are on leave.
"The purpose of this calendar is to ensure workers and site management manage their fatigue levels, thereby encouraging safer and more productive projects," the contract says.
Workers on leave will receive 17.5 per cent leave loading on top of their usual pay packet.
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Construction and Real Estate Industry
- State and Territory Government
- Azerbaijani
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Haitian Creole
- Kinyarwanda
- Kurdish (Kurmanji)
- Kurdish (Soranî)
- Odia (Oriya)
- Scots Gaelic
Employer financial incentives and support
Free support and assistance, jobs & skills wa employer incentive, apprenticeship and traineeship re-engagement incentive , construction training fund apprentice completion grant , construction training fund employer grants, construction training fund apprentice accommodation allowance program , defence industry existing worker incentive , defence industry reskilling and upskilling grant program, group training organisation wage subsidy, wa group training program, jobs board — find an employee, skills recognition apprenticeship program, skilling solutions for workforce development, travel and accommodation allowance, commonwealth government incentives for employers, apprentices and trainees, related services and information.
The Department of Training and Workforce Development provides a number of financial incentive and support programs to support the development of your workforce*.
A summary of the key financial incentives available to employers is provided here. Further detailed information is available on our Jobs & Skills WA website.
Financial incentives information on the Jobs & Skills WA WA website
Whatever your requirements, Jobs and Skills Centres (JSCs) offer free support and assistance with planning and developing your workforce. Services include support with recruitment, identifying your training needs, establishing a workforce development plan, finding an apprentice or trainee, and accessing financial incentives.
JSCs are located throughout Perth and across regional WA. Call your local centre on 13 64 64, or visit the Jobs & Skills WA website to find out more.
Find out how a JSC can help you

The Jobs & Skills WA Employer Incentive (JSWAEI) provides financial assistance for WA businesses who employ an apprentice or new entrant trainee.
Eligible employers will receive a base payment amount of up to $8,500, and may also be eligible for additional loading payments.
Find out more about the JSWAEI here
This incentive provides financial assistance to WA businesses that employ an apprentice or trainee whose training contract was terminated or cancelled by a previous employer, leaving them unable to complete their apprenticeship or traineeship. This enables employers to employ a person who has existing skills and knowledge gained through their previous training and employment.
Eligible employers (including group training organisations) will receive a one-off payment of $6,000 for re-engaging an apprentice and $3,000 for re-engaging a trainee.
Find out more about the ATRI here
This grant is a one off payment of $2,000 plus a $500 reimbursement for tools and safety equipment for construction apprentices and trainees who complete their qualification between 1 July 2023 and 30 June 2024.
Find out more about the ACG here
The WA Construction Training Fund (CTF) supports employers to reduce the cost of employing an apprentice or trainee in a range of building and construction occupations in WA, through the provision of the following grant payments.
- Apprenticeship and Traineeship Grant for Employers – up to $24,800 over the nominal duration of the apprenticeship/traineeship
- Disaster Recovery Grant – up to $3,000 annually to June 2025, for employers of apprentices and trainees working in areas of WA affected by declared natural disasters
Find out more about CTF employer grants here
This program provides financial assistance for eligible apprentices and trainees living in regional WA, who need to travel to attend scheduled off the job training with a registered training organisation (RTO).
The allowance covers the difference between the Department of Training and Workforce Development’s Travel and Accommodation Allowance (TAA), and the apprentice or trainee’s out of pocket expenses for commercial accommodation.
Find out more about the AAAP here
This incentive provides financial assistance for WA businesses undertaking work in WA's defence industry, who employ an existing worker trainee in one of the following qualifications:
- Certificate IV in Cyber Security (two-year traineeship);
- Diploma of Advanced Technologies (three-year traineeship); and
- Diploma of Engineering – Technical (two-year traineeship).
Eligible employers receive up to $4,250 (two- year traineeship), or $6,375 (three-year traineeship).
Find out more about DIEWI here
This grant program is part of the $11 million white (professional) and grey (paraprofessional) collar workforce development package announced by the WA State Government in its 2023—23 State Budget , with funding totalling $2.5 million over three years.
The DIRU program allows eligible defence industry firms, consortia of firms and defence industry peak organisations to apply for funds to develop new credit bearing micro-credentials, accredited short courses and skill sets in partnership with a Team WA university and/or a WA-based training provider and have it delivered to new or existing workers as and when required.
Find out more about DIRU here
The GTO Wage Subsidy assists small to medium enterprises working in WA's building and construction sector, by providing access to 300 apprentices and trainees employed through group training organisations (GTOs).
Eligible GTOs receive wage subsidy payments in arrears, to the total value of $95,237 (three-year apprenticeship) or $134,625 (four-year apprenticeship). Subsidy payments cover the average estimated award wage paid to apprentices and trainees in the building and construction sector.
Find out more about the GTO Wage Subsidy here
This program provides financial assistance to group training organisations (GTOs) to employ and support apprentices and trainees in priority target groups, and support them through to completion.
Eligible GTOs receive up to $13,400 in incentive payments for employing apprentices or trainees in nominated target groups.
Find out more about the WAGTP here
The Jobs & Skills WA jobs board is supported by our network of 15 Jobs and Skills Centres (JSCs) across WA who work directly with jobseekers and employers. Your local JSC will work with you to put your vacancy together, then post it on our jobs board
Once posted to the jobs board, we can also promote your employment opportunity through our social media channels and to all WA JSCs. These services are all free.
Jobs & Skills WA jobs board
If you have an employment opportunity for an Aboriginal person, we have a dedicated Aboriginal services jobs board. Your local JSC can assist in posting your vacancy, and this is also a free service.
Aboriginal services jobs board
Are you an employer in the construction industry? Do you have employees with skills, experience and knowledge, but no formal qualification? Would you like to help them achieve a trade qualification through an accelerated apprenticeship program for a range of financial incentives and support?
The Skills Recognition Apprenticeship Program (SRAP) offers your employees the opportunity to have their construction industry skills, knowledge and experience assessed and counted towards completion of a nationally recognised trades qualification. Best of all, the assessment is 100% free for eligible applicants — no cost to you or your employee.
Find out more about the SRAP
The Department also offers a range of skilling solutions to help your workers learn, adapt and grow with your business; enabling you to overcome challenges and pursue new opportunities. These include:
- fee-free and reduced-fee vocational education and training courses;
- free short course skill sets for targeted skills development;
- apprenticeships and traineeships;
- an out-of-contract-register to help connect apprentices to new employers;
- free Job Ready programs that provide training pathways to employment and support industry attraction;
- group training organisations; and
- jobs and careers assistance.
Find out more on our Jobs & Skills WA website
The Department of Training and Workforce Development provides financial assistance to support apprentices and trainees to complete their training contracts.
This allowance aids in the cost of travel and accommodation where there is a requirement for long distance travel to attend off the job training.
Find out more about the TAA
Information about Commonwealth Government incentives available to employers of apprentices and trainees can be found at apprenticeships.gov.au.
Visit the Australian Apprenticeships website
Australian Apprenticeship Support Network (AASN) providers can also assist with information about accessing incentives.
Find an AASN
*for eligible employers
- Vocational education and training in Western Australia
- Developing Western Australia's workforce

Provided by
- Facebook share (Opens in a new tab/window)
- Twitter (Opens in a new tab/window)
- LinkedIn (Opens in a new tab/window)
Acknowledgement of Country
The Government of Western Australia acknowledges the traditional custodians throughout Western Australia and their continuing connection to the land, waters and community. We pay our respects to all members of the Aboriginal communities and their cultures; and to Elders both past and present.
- Business Today
- India Today
- India Today Gaming
- Cosmopolitan
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Aajtak Campus

- Magazine Cover Story Editor's Note Deep Dive Interview The Buzz
- BT TV Market Today Easynomics Drive Today BT Explainer
- Market Today Trending Stocks Indices Stocks List Stocks News Share Market News IPO Corner
- Tech Today Unbox Today Authen Tech Tech Deck Tech Shorts
- Money Today Tax Investment Insurance Tools & Calculator
- Mutual Funds
- Industry Banking IT Auto Energy Commodities Pharma Real Estate Telecom
- Visual Stories

INDICES ANALYSIS
Mutual funds.
- Cover Story
- Editor's Note
- Market Today
- Drive Today
- BT Explainer
- Trending Stocks
- Stocks List
- Stocks News
- Share Market News
- Unbox Today
- Authen Tech
- Tech Shorts
- Tools & Calculator
- Commodities
- Real Estate
- Economic Indicators
- BT-TR GCC Listing
Dearness allowance, other payments: Revised rates for central government employees
The da was hiked in march 2024. with the hike, all other related allowances such as house rent allowance, daily allowance, gratuity ceiling and hostel subsidy have been increased in line with the 7th pay commission recommendations..
- Updated Apr 09, 2024, 3:22 PM IST

The Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) has recently notified the revised allowances available to central government employees. In March 2024, the dearness allowance (DA) for central government employees has recently been increased by 4 per cent to 50 per cent. Besides this, the Union Cabinet also cleared additional dearness relief (DR) of 4 per cent from 46 per cent earlier.
Related Articles
- Dearness Allowance: Govt announces DA for these central government employees. Check the details here
- 10% DA hike for these UP government employees. Check details
All these allowances were reviewed under the 7th Pay Commission reviewed that were extended to central government employees. The allowances applicable to Central Government Employees that have been revised are as follows:
Dearness allowance
Dearness Allowance or DA is the cost-of-living adjustment allowance that the Central government offers its current and retired members of the public sector. Last month, dearness allowance (DA) for central government employees was hiked 4 per cent to 50 per cent. Dearness relief (DR) for central government pensioners has also seen a 4 per cent hike, reaching 50 per cent. These adjustments are effective from January 1, 2024. The increased dearness allowance is set to benefit nearly 49.18 lakh central government employees and 67.95 lakh pensioners.
Child education allowance
The allowance for central government employees has been revised upwards to 25 per cent of the original allowance which was previously set at 50 per cent. The Child Education Allowance or Hostel Subsidy, however, is restricted to a maximum of two children with an amount cap of Rs 6,750 per month as the subsidy rate. In situations where a central government employee has a child with disabilities, their Child Education Allowance receives special consideration and is adjusted to twice the standard rate.
"The reimbursement of CEA for Divyang Children of Government servant shall be payable at double the normal rate of CEA i.e. Rs. 4500/- per month. In a case where Divyang Child is not able to attend school, the reimbursement of CEA for availing education / special education at residence, shall be made at double the normal rates of CEA subject to production of payment receipted by teacher/instructor etc., and self-certification by the Central Government servant for availing education of their child at his/her residence," the notification said.
Risk Allowance
This allowance is provided to central government employees engaged in hazardous duties or whose work may negatively impact their health over time. Risk allowance is not considered as “pay” for any purpose, said DoPT to ensure clarity in categorisation within the compensation structure.
Night Duty Allowance
As per the 7th Pay Commission revised norms, an adjustment has been made to the Night Duty Allowance (NDA). It is pertinent to acknowledge that night duty is defined as the timeframe stretching from 10 pm to 6 am. An employee becomes eligible for NDA when they attain a basic monthly salary threshold of Rs 43,600.
The computation of the hourly NDA rate transpires through use of this formula: [(Basic Pay + Dearness Allowance)/200]. In this formula, both Basic Pay and Dearness Allowance are derived from their current rates per determination by the 7th Central Pay Commission. The calculation for each individual's NDA amount relies upon the specific Basic Pay earned by that employee on any given night duty performance day.
Overtime Allowance Departments and Ministries have been delegated the duty of assembling a register for personnel classified as 'Operational Staff'; this process should not involve any increase in Overtime Allowance rates. The incorporation of Overtime Allowance could be linked with biometric attendance monitoring systems, with an aim to streamline procedures while ensuring transparency in scheduling duties beyond standard working hours.
Special allowance
For providing extra benefits to female employees with disabilities, particularly those with young children and children who have disabilities, a decision has been made to provide a special allowance. Under this arrangement revised under the 7th Pay Commission, women with disabilities will receive Rs 3000 per month. This allowance will be disbursed from the birth of the child until the child reaches two years of age.
Special allowance for Parliament Assistants
Special allowance paid to individuals fully engaged in Parliament duties during its sessions has been increased by 50 per cent. The previous rates of Rs 1500 and Rs 1200 for Assistants and UDCs, respectively. It has now been raised to Rs 2,250 and Rs 1,800.
This allowance will be granted at full rates for each calendar month in which Parliament convenes for at least 15 days. However, for months with shorter sessions, the allowance will be half the prescribed rates. Further, No over time allowance (OTA) shall be paid to Parliament Assistants for the calendar months in which the Parliament is in session.
TOP STORIES

- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Press Releases
Copyright©2024 Living Media India Limited. For reprint rights: Syndications Today

Add Business Today to Home Screen

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Travel allowance is a type of compensation employers provide to cover employee travel expenses incurred when traveling for business purposes. It helps with employee travel costs, such as transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidentals while on the job. Depending on the company policy, travel allowance may be given in cash or as reimbursed ...
A travel allowance is compensation paid by an employer to employees to cover expenses incurred when traveling for business. In addition to lodging and transportation, travel allowances are typically used for airfare, meals, and other expenses related to business travel. It is business travel compensation, provided either before or after travel ...
Use of the standard meal allowance for other travel. ... will no longer be allowed to be claimed as an unreimbursed employee travel expense as a miscellaneous itemized deduction due to the suspension of miscellaneous itemized deductions that are subject to the 2% floor under section 67(a). The suspension applies to tax years beginning after ...
Business travel deductions are available when employees must travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. A taxpayer is traveling away from home if they are away for longer than an ordinary day's work and they need to sleep to meet the demands of their work while away. Travel expenses must be ordinary and necessary.
Per diem rates look-up Allowances for lodging, meal and incidental costs while on official government travel. Mileage reimbursement rates Reimbursement rates for the use of your own vehicle while on official government travel.
Your agency's authorized travel management system will show the final price, excluding baggage fees. ... Federal employees should make reservations, including FedRooms reservations, via their travel management service. ... Chapter 301—Temporary Duty (TDY) Travel allowances Chapter 302 - Relocation allowances. Print Page Email Page.
Payments received by U.S. Government civilian employees for working abroad, including pay differentials, are taxable. However, certain foreign areas allowances, cost of living allowances, and travel allowances are tax free. Pay Differentials Pay differentials you receive as financial incentives for employment abroad are taxable.
The travel allowance for employees on business trips is typically calculated based on the destination, the duration of the trip, and the company's policy. Companies may choose to provide a daily allowance for meals or provide a company card for purchasing meals. The travel allowance may also vary depending on the employee's level within the ...
The company travel policy outlines provisions for business-related travel, detailing reimbursable expenses and guidelines. It covers transportation, accommodation, legal/medical expenses, and daily allowances. Employees are advised to exercise judgment and submit expenses timely for reimbursement. This company travel policy template is ready to ...
Organizations establish business travel allowances to cover expenses incurred by staff during their corporate trips. Typically these reimbursements are made to cover the cost of hotel rooms, meals, and transportation. However, policies should extend to include anything required for the employee to conduct the official business outlined in their ...
A Complete Guide to Business Travel Allowance. team.itilite. September 2, 2022. Travel management. When employees go on business trips, they spend money on multiple things. They book flights and hotels, commute to the meeting destination, and pay for miscellaneous services like meals and dry cleaning. All these expenses have to be covered by ...
Business travel meal allowance. To cover the costs of meals during a trip, employers may provide a business travel meal allowance. It can work in one of three ways: Provide a company card. Give each employee a daily allowance to cover meals. Tell employees to pay using their own month and claim back the expenses later.
Leave Travel Allowance/Leave Travel Concession is a type of allowance given by an employer to their employee for travelling to any place in India: either on leave, after retirement or after the termination of his service. Though it sounds simple, many factors need to be kept in mind before you plan to claim an LTA exemption.
In the event of an audit, employees must be able to produce receipts substantiating the amount claimed. HR Manual section 2203 - Allowances and Travel Reimbursements provides additional information, including travel timeframes (fractional day of travel, trip of less than 24 hours, trip of more than 24 hours, etc.).
1. Fixed Travel Allowance. A fixed travel allowance in salary implies that this is a fixed amount offered to the employee irrespective of the actual expenses incurred. 2. Daily Travel Allowance. As the name suggests, a daily travel allowance is offered to employees on a per-day basis, which covers their travel, meals, accommodation, and other ...
A travel allowance is an optional perk offered by the employer and is discussed on a case-by-case basis between the employer and the employee. The goal of the travel allowance is to help commuters financially. This article will give you all the information you need about the travel allowance, covering the benefits and rules that come with it. 1.
This includes costs for: providing travel. reimbursing travel. accommodation (if your employee needs to stay away overnight) meals and other 'subsistence' while travelling. Subsistence ...
Travel expenses are the ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job. ... you can generally use a standard meal allowance, which varies depending on where you travel. ... (for car expenses) plus any parking fees, ferry fees, and tolls. Claim these expenses on Form 2106, Employee Business ...
the official HMRC meal allowance rates for UK business travel. are: £5 for travel of 5 hours or more (£10 supplement if travel is ongoing at 8pm) £10 for travel of 10 hours or more (£10 supplement if travel is ongoing at 8pm) £25 for travel of 15 hours or more (and ongoing at 8pm) Many companies will have higher per diem rates for C-level ...
The Defense Travel Management Office (DTMO) serves as the administrative staff for the PDTATAC by developing, administering, and maintaining JTR. MAP and CAP meet monthly and evaluate issues pertaining to travel and transportation allowances for Uniformed Service members and DoD civilian employees respectively. Learn more about governance.
Travel allowance: Encompasses a wider range of employee travel expenses incurred due to business activities. This can include public transport fares, accommodation costs, and meals during business travel, in addition to mileage costs when using public or alternative modes of transport. Criteria for Claiming Travel Allowances To claim travel ...
To be a travel allowance, the allowance must be a payment to cover travel allowance expenses. This means a travel allowance must cover: accommodation; meals (food or drink) incidental expenses. A travel allowance doesn't have to cover all those expenses. The allowance may still be a travel allowance if it is only paid to cover 1-2 of these ...
Travel allowance is a payment made to an employee to cover accommodation, food, drink or incidental expenses they incur when they travel away from their home overnight in the course of their duties. Allowances folded into your employee's salary or wages are taxed as salary and wages and tax has to be withheld, unless an exception applies. You ...
Transport Allowance is an allowance a company or employer provides to employees to compensate for their travel from their residence to the workplace. It is a type of special allowance. Like other allowances, transport allowance is a part of CTC and has fixed pay. As the employee's income tax computation is done by their employers for tax ...
Travel allowances and leave loading. The living away from home allowance section of the BPIC states that a "distant construction sites allowance of $1,000 per week or $200 per day for part weeks ...
Travel and Accommodation Allowance. The Department of Training and Workforce Development provides financial assistance to support apprentices and trainees to complete their training contracts. This allowance aids in the cost of travel and accommodation where there is a requirement for long distance travel to attend off the job training.
The allowance for central government employees has been revised upwards to 25 per cent of the original allowance which was previously set at 50 per cent. The Child Education Allowance or Hostel ...