- 0 Shopping Cart


What are tourist honeypots?
Honeypots are areas which attract many tourists. They usually contain attractive scenery or historic/culturally significant buildings. These areas are so called because tourists flock to these places like ‘bees around honey’.
Latest Blog Entries
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Please Support Internet Geography
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
GeographyCaseStudy.Com
Detailed resources for pre-university Geography students
Tourism hotspots
By Matt Burdett, 7 November 2017
On this page, we look at the human and physical factors explaining the growth of rural and urban tourism hotspots including the role of primary and secondary touristic resources.

- Venice, Italy: Piazza San Marco (St Mark’s Square) has been described as ‘the drawing room of Europe’ and is a favourite with the tens of thousands of daily visitors to the city.
What is a tourism hotspot?
Tourism hotspots are places that experience high levels of tourist arrivals. These places can also be called tourist honeypots. The term honeypot usually refers to a small area such as a village in a national park, while hotspots operate at a variety of scales from small villages to entire regions.
Hotspots exist in places such as:
- Areas of outstanding natural beauty
- Historic city centres
- Coastal areas with sandy beaches in hot countries
In addition, these places must be:
- Easy to access
- Secure (not susceptible to terrorist attack, for example)
- Safe (free from disease; not experiencing frequent natural hazards)
Tourism hotspots usually have a very large number of visits at the same time. This can lead to seasonal hotspots and diurnal hotspots.
Seasonal hotspots have high levels of tourism at specific times of year, such as the summer months when Spanish beaches become very busy. On the graph below, the level of tourism is very low outside the warm summer months but reaches a rapid peak as tourists arrive for summer holidays from other countries.

- Theoretical seasonal variation in visitors for a Spanish beach resort
Diurnal hotspots have high levels of visitors at certain times of day, such as day trippers who visit Venice. The city receives many tourists during the middle of the day and far fewer in the morning or late afternoon as people return to their cruise ships for the evening. The number of tourists peaks in the middle of the day as tourists arrive and gradually leave after lunch.

- Theoretical diurnal variation in visitors for a historic Mediterranean town centre
Reasons for hotspot growth
There are many factors that can encourage the growth of tourism in a specific area. These are in addition to the factors that increase tourism in general, such as increasing income, leisure time and infrastructure.
These growth factors are effectively different types of tourist resources. These can be split into primary and secondary tourist resources. Primary tourist resources were created for non-tourist reasons but are today used by tourists. Secondary tourist resources were created specifically for tourists as one of their main functions.
Aside from the tourist resources in the destination itself, there are several other reasons why tourism hotspots grow.
Government policy
Government policy can encourage the development of a tourist hotspot. Deliberately attracting tourists to one location can help keep other locations tourist free. This is very closely connected to the issue of ‘zoning’.
Local government plans often involve the ‘zoning’ of an area. This means that some areas are put aside for conservation, others for tourism, others for local use, and so on. Each zone has specific activities within it. Tourist hotspots may develop in areas such as parts of a city centre, village centres or specific mountains that are deliberately chosen to develop the infrastructure required for large numbers of visitors.
Gateway / entry points
Several tourism hotpots are not actually destinations in themselves, but places where people have to pass through in order to get to the place they are aiming for. Due to the number of people passing through, these places often develop secondary tourist attractions and become tourist centres. These places include Lukla in Nepal, which is the main town at the beginning of the trail to Everest Base Camp. Another example is towns on international borders where people can cross from one country to another, such as Calais in France which has a high number of visitors because it is the nearest continental port to the United Kingdom.
Advertising
Advertising and travel programmes often promote the same locations to the extent they become very popular. For example, the Grand Canyon is known across the world as a primary tourist attraction, resulting in around five million tourist visitors each year (GrandCanyon.Com, 2017).
Word-of-mouth and social media
Some places are less well known but still attract a large number of visitors as word of mouth travels. Social media, including sites like Instagram and Facebook, can ensure that travel trends spread quickly. This can sometimes result in the rapid development of a tourist hotspot to the extent that the local services cannot effectively cope. The Philippine island of Boracay was inundated by 1.56 million visitors in 2015, over the government’s target limit of 1.5 million (Burgos, 2016). The excessive tourism caused traffic jams, air and water pollution and lead many visitors to question the over-development of the island and its role in destroying the beach paradise promised on many social media posts.
Burgos, N. 2016. Record tourist arrivals in Boracay. http://newsinfo.inquirer.net/754567/record-tourist-arrivals-in-boracay Accessed 7th November 2017.
GrandCanyon.Com, 2017. How Many Visitor Come to See the Grand Canyon? https://grandcanyon.com/news/how-many-visitors-to-grand-canyon/ Accessed 7th November 2017.
Tourism hotspots: Learning activities
- Define ‘tourism hotspot’. [2]
- Give examples of tourism hotspots. [3]
- Describe the conditions necessary for tourism hotspots to develop. [4]
- Distinguish between a seasonal hotspot and a diurnal hotspot. [2]
- Suggest reasons why some locations experience tourism growth and become tourism hotspots. [4]
Other tasks
For a suitable area near you, suggest:
- The factors that might lead it to become a tourist hotspot. (Split these into primary tourist resources and secondary tourist resources. These resources may already be present, or you may need to build them.)
- The benefits that a hotspot might bring to the local community.
- The negative consequences of excessive tourism for the local environment
Identify a tourism hotspot of your choice. Create a poster advertising the hotspot in a tourist-trade magazine. Identify the primary and secondary tourist resources that enable the hotspot to be a growth area for tourism.
© Matthew Burdett, 2018. All rights reserved.
All secondary material on this site is clearly referenced and may be subject to copyright restrictions by the original authors. All original material on this page is subject to copyright.
Share this:
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Honeypot (tourism)
A honeypot site is a location attractive to tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people. [1] [2]
Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying less discerning tourists. One such example is the construction of local parks to prevent tourists from damaging more valuable ecosystems farther from their main destination. Honeypots have the added benefit of concentrating many income-generating visitors in one place, therefore developing that area, and in turn making the area more appealing to tourists. [3]
However, honeypots can suffer from problems of overcrowding , including litter, vandalism, and strain on facilities and transport networks. [1] Honeypots attract tourists because of parking spaces, shopping centres, parks and public toilets. The tourist shops are normally placed all over the shopping centre, which creates pressure on the whole centre to keep the place looking tidy. For example, Stratford-upon-Avon has shops that are aimed mostly at tourists. On a particular street, there were five shops that were aimed towards the locals and ten shops catering to tourists, reflecting the business opportunity that tourism presents for shopkeepers and other business people in the local economy.
The once sleepy medieval village has attracted an increasing number of visitors over recent years and is a classic example of a tourist 'honeypot' . . . Ste. Enimie is one of these 'designated' places that are designed to attract people to it and therefore reduce the impact on the surrounding area. [4] [ unreliable source? ]
Related Research Articles

Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments.

Ecotourism is a form of tourism marketed as "responsible" travel to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. The stated purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds for ecological conservation, to directly benefit the economic development and political empowerment of local communities, or to foster respect for different cultures and human rights.

A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or an exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.

Tourism in Italy is one of the economic sectors of the country. With 65 million tourists per year (2019) according to ISTAT, Italy is the fifth most visited country in international tourism arrivals. According to 2018 estimates by the Bank of Italy, the tourism sector directly generates more than five per cent of the national GDP and represents over six per cent of the employed.

Tourism in France directly contributed 79.8 billion euros to gross domestic product (GDP) in 2013, 30% of which comes from international visitors and 70% from domestic tourism spending. The total contribution of travel and tourism represents 9.7% of GDP and supports 2.9 million jobs in the country. Tourism contributes significantly to the balance of payments.

Tourism in Singapore is a major industry and contributor to the Singaporean economy.

Cultural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual, and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions.

Tourism in Indonesia is an important component of the Indonesian economy as well as a significant source of its foreign exchange revenues. Indonesia was ranked at 20th in the world tourist Industry in 2017, also ranked as the ninth-fastest growing tourist sector in the world, the third-fastest growing in Asia and fastest-growing in Southeast Asia. In 2018, Denpasar, Jakarta and Batam are among of 10 cities in the world with fastest growth in tourism, 32.7, 29.2 and 23.3 percent respectively. The tourism sector ranked as the 4th largest among goods and services export sectors.

A visitor center or centre , visitor information center or tourist information centre is a physical location that provides information to tourists.

Cultural heritage tourism is a form of non-business travel whereby tourists engage with the heritage, tangible and intangible, moveable and immovable, of a region through activities, experiences, and purchases which facilitate a connection to the people, objects, and places of the past associated with the locations being visited. As opposed to natural heritage tourism, which focuses on visitors' interaction with the unimproved environment of the area being visited, including outdoor sports and recreation, hiking, diving, fishing, and naturalism, and pleasure tourism without any heritage interest, such as indoor recreation, gastronomy, and hospitality without any significant precedent in the history and heritage of the region, cultural heritage tourism can include activities such as tours of immovable cultural sites, such as historic house museums, historic fortifications, human history museums, and library documentary heritage collections, opportunities for purchases of moveable cultural property, such as antiques, antiquarian books, and other works and ephemera associated with the locations being visited, and opportunities for admission to or purchase of intangible heritage experiences associated with the tourism region, including gastronomic heritage and admissions to performances such as theatre, opera, ballet, indigenous dances, and storytelling.

Tourism in Turkey is focused largely on a variety of historical sites, and on seaside resorts along its Aegean and Mediterranean Sea coasts. Turkey has also become a popular destination for culture, spa, and health care. Since 2021, Turkey is the fourth most visited country in the world.

Tourism is an important sector for the Philippine economy. The travel and tourism industry contributed 6.2% to the country's GDP in 2022; this was lower than the 12.7% recorded in 2019 prior to the COVID-19 lockdowns. Coastal tourism, encompassing beach and diving activities, constitutes 25% of the Philippines' tourism revenue, serving as its primary income source in the sector. Popular destinations among tourists include Boracay, Palawan, Cebu and Siargao. While the Philippines has encountered political and social challenges that have affected its tourism industry, the country has also taken steps to address these issues. Over the past years, there have been efforts to improve political stability, enhance security measures, and promote social inclusivity, all of which contribute to creating a more favorable environment for tourism, such as the Boracay rehabilitation.

Sustainable tourism is a concept that covers the complete tourism experience, including concern for economic, social, and environmental issues as well as attention to improving tourists' experiences and addressing the needs of host communities. Sustainable tourism should embrace concerns for environmental protection, social equity, and the quality of life, cultural diversity, and a dynamic, viable economy delivering jobs and prosperity for all. It has its roots in sustainable development and there can be some confusion as to what "sustainable tourism" means. There is now broad consensus that tourism should be sustainable. In fact, all forms of tourism have the potential to be sustainable if planned, developed and managed properly. Tourist development organizations are promoting sustainable tourism practices in order to mitigate negative effects caused by the growing impact of tourism, for example its environmental impacts.

Tourism in Wales makes up a significant portion of the Welsh economy and attracting millions of visitors each year. The tourism industry in Wales was worth around £5bn in 2017. The tourism industry also makes a significant contribution to the Welsh economy, supporting over 100,000 jobs and more than 8% of the Welsh workforce. Wales attracts visitors from overseas, particularly from the United States, Australia, Germany and the Republic of Ireland.

Tourism in Senegal is a vital part of the West African nation's economy.

Tourism in Paris is a major income source. Paris received 12.6 million visitors in 2020, measured by hotel stays, a drop of 73 percent from 2019, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The number of foreign visitors declined by 80.7 percent. Museums re-opened in 2021, with limitations on the number of visitors at a time and a requirement that visitors wear masks.
The London Tourist Board was established in 1963 and became the official regional tourist board for London under the Development of Tourism Act in 1969. It was responsible for the marketing and promotion of the capital, providing tourist information services, and recommending improvements to the infrastructure and facilities for the growth of tourism. In 2003, it was renamed VisitLondon. In 2011, it was put into administration by the Greater London Authority, and the tourism responsibility was transferred to a new company, London & Partners.

In Metro Manila, Philippines, tourism is a significant industry. In 2012, the city and the region welcomed 974,379 overnight visitors. Serving as the main gateway to the Philippines' numerous destinations, the city attracts mainly international tourists, with a total of 3,139,756 visitors in 2012. Global Blue ranks Manila as the eleventh 'Best Shopping Destination' in Asia. The city holds the tenth position in MasterCard's global top 20 fastest-growing cities for international visitors from 2009 to 2013.
Tourism impacts tourist destinations in both positive and negative ways, encompassing economic, political, socio-cultural, environmental, and psychological dimensions. The economic effects of tourism encompass improved tax revenue, personal income growth, enhanced living standards, and the creation of additional employment opportunities. Sociocultural impacts are associated with interactions between people with differing cultural backgrounds, attitudes and behaviors, and relationships to material goods. Tourism can also have significant political impacts by influencing government policies and promoting diplomatic relations between countries. Environmental impacts can be categorized as direct effects including environmental damage, wildlife destruction, deforestation, water pollution, and indirect effects, such as increased harvesting of natural resources to supply food, indirect air and water pollution. Tourism also has positive and negative health outcomes for local people. The short-term negative impacts of tourism on residents' health are related to the density of tourist's arrivals, the risk of disease transmission, road accidents, higher crime levels, as well as traffic congestion, crowding, and other stressful factors. In addition, residents can experience anxiety and depression related to their risk perceptions about mortality rates, food insecurity, contact with infected tourists, etc., which can result in negative mental health outcomes. At the same time, there are positive long-term impacts of tourism on residents' health and well-being outcomes through improving healthcare access positive emotions, novelty, and social interactions.
- ↑ "honeypot". Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged (10th ed.). HarperCollins . 2009 . Retrieved 3 September 2013 .
- ↑ Ryan, Chris (3 June 2003). Recreational Tourism . Aspects of Tourism (2nd ed.). Channel View. p. 116 . ISBN 978-041505424-9 .
- ↑ "Ste. Enimie: The Management of a Tourist Honeypot" (PDF) . Discover Ltd. 2009 . Retrieved 2 September 2013 .
About: Honeypot (tourism)
A honeypot site is a location attracting throngs of tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people. Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying less discerning tourists. One such example is the construction of local parks to prevent tourists from damaging more valuable ecosystems farther from their main destination. Honeypots have the added benefit of concentrating many income-generating visitors in one place, therefore developing that area, and in turn making the area more appealing to tourists.


The UK’s Honeypot Villages: Coping with Increasing Tourism
Once summer arrives and the sun starts shining, many of us pack up the car and head straight to idyllic honeypot villages and coastal towns to make the most of it. After all, what’s more enjoyable than a stroll in the glorious countryside, sipping a drink in a pub garden or sinking your toes in the sand with an ice cream in hand?
Not to mention that due to the uncertainty around Brexit and how it could affect our finances, many of us are doing some careful budgeting and opting for staycations. Perhaps unsurprisingly, this has led to many tourist hotspots being overwhelmed with people in the summer months. In fact, Cornwall is “struggling to cope” and the tourist board has stopped promoting two beaches due to summer overcrowding.
Although this is certainly troublesome for residents, many rely on tourism for their household income. So how do these picturesque towns strike the right balance between encouraging tourism but managing the impacts of overcrowding?
Improve parking
In a busy tourist hotspot, adequate parking is essential. Fail to get this right and tourists will just park wherever they can, such as residential streets and main roads. This creates traffic jams and in turn, misery for commuters, locals and tourists alike.
Disperse people
Towns can cope better with increased footfall by spreading it out. It may seem obvious, but if all tourists are heading to the same places within a town or city, it’s going to feel overcrowded. Instead of promoting one particular area or attraction, local tourist boards could encourage people to head to different sites to spread people across a wider area.
Alternative timings
Most tourists will flock to honeypot villages and coastal towns during the summer months, so why not encourage them to come at less busy times? This will certainly reduce the impact of those busy summer months. One way to do this is to have events during quieter times of year. Alternatively, significant price reductions on activities and accommodation may encourage people to visit at non-peak times.
Control accommodation
For towns that are struggling with overcrowding, controlling available accommodation is another way to reduce the impact of tourism. Amsterdam is one city that has taken such measures — stopping hotel developments altogether. Doing this will help to take control of tourist numbers rather than let it spiral out of control.
There are many effective and efficient ways that towns can better cope with growing tourism. Whether that’s introducing cost incentives for out-of-season tourists, dispersing people or stricter controlling of accommodation, it will help to reduce the negative impacts of overcrowding while still encouraging people to visit. Win, win!
Related Posts
Thailo on the rise of asian markets: connecting continents, taxi from the airport, inc & co’s thailo logsitics raise the headcount.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
General Enquiries
- [email protected]
Advertising
- FEAST Authors
- FEAST Magazine
- Advertise With Us
- Writers’ Guidelines for Feast Magazine
Subscribe to Updates
Get the latest foody news from Feast Magazine.
By signing up, you agree to the our terms and our Privacy Policy agreement.

- Privacy Policy
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Geography Photographs: Tourism: Honeypot site
- All Geography Photographs Topics - Home
- Return to Topic - Tourism
- More examples of - Honeypot sites
Feature: Honeypot site

Ben Nevis, Lochaber, Scotland

©2021 thegeographyphotographer. All Rights Reserved. All images are the sole copyright of thegeographyphotographer. If you have any queries please click here .
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of honeypot noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- The toy section of the store is a honeypot for children.
- It is possible to escape the tourist honeypots by heading north.
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
Nearby words

What Are Honeypots? Types, Benefits, Risks, and Best Practices
In today’s world, cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes. Cybercriminals continually develop new methods to breach security systems and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Bringing us to the question, “what are honeypots, and what is their importance in organizations? Honeypots are one approach that organizations can use to strengthen their cybersecurity defences. This article will explore the types, benefits, risks, and best practices related to honeypots.
What Are Honeypots?
A honeypot is a cybersecurity tool designed to detect, deflect, and counteract attempts at unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. A honeypot is a decoy system or resource designed to attract and deceive attackers, allowing security analysts to monitor and study their behaviour.
There are two primary types: research and production honeypots.
1. Production Systems
They are designed to be integrated into a live environment and mimic natural systems and services. They can detect and prevent security vulnerabilities on legitimate systems they are designed to protect.
2. Research Honeypots
They are designed to simulate various systems and services and can be used to study and analyze attackers’ behaviour.
How Can You Use Honeypots?
Honeypot systems can be used for several purposes, including:
- Detection : Honeypots can help security professionals manage vulnerability and see attacks targeting their systems. By analyzing the internal network and behaviour of attackers on a honeypot, they can gain insight into their methods and block malicious bots.
- Deception : Honeypots can lure attackers away from real systems or applications, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
- Research : Honeypots can provide valuable information about cybercriminals’ latest attack techniques and tools. You can use this information to improve security measures and develop new defence strategies.
- Training : Honeypots can be a training tool for security professionals to gain experience dealing with cyber-attacks and develop incident response skills.
Types of Honeypots
Several types of honeypots can be used in a cybersecurity strategy. Some of the most common types include:
1. High-Interaction Honeypots
A high-interaction honeypot is designed to mimic systems and services as closely as possible. They provide attackers with a high degree of interaction and can capture important information about the attacker’s tactics and techniques. High-interaction honeypots can be expensive and time-consuming to maintain, but they can provide insight into attacker behaviour.
2. Low-Interaction Honeypots
These honeypots are designed to be lightweight and easy to set up and maintain. They simulate only a small subset of the functionality of systems and services. However, they can still effectively detect and alert the security team to the presence of attackers. A low-interaction honeypot system is often used as an early warning system, providing security personnel with alerts that indicate potential attacks.
3. Virtual Honeypots
These honeypots are virtual machines that are isolated from systems and resources. They can simulate various systems and services and are often used for research and training.
4. Sticky Honeypots
These honeypots are designed to be difficult for attackers to detect and remove. They are typically integrated into systems and services and can provide insight into attacker behaviour. However, they can also be risky as they are connected to systems and resources.
5. Watering Hole Honeypots
These honeypots target specific types of attackers. They are typically set up on websites or other online resources known to be frequented by a particular group of attackers. Watering hole honeypots can effectively detect and prevent attacks from targeted groups, but they can also be time-consuming and expensive to set up and maintain.
6. Decoy Honeypots
These honeypots mimic specific types of systems or services that attackers commonly target. They can draw attackers away from systems and resources and provide security personnel valuable insights into attacker behaviour.
7. Pure Honeypots
A pure honeypot is a type of honeypot that is completely passive and does not generate any network traffic on its own. Pure honeypots are designed to be as unobtrusive and undetectable as possible, mimicking a real system without active use. They wait for an attacker to interact with them and log all of the attacker’s actions.
Because pure honeypots do not generate any traffic, they are less likely to be detected by attackers, making them more effective at capturing and analyzing attacker behaviour. However, they may be less effective at detecting attacks, especially those targeting the honeypot.
Pure honeypots can be useful for gathering intelligence on the tactics and techniques used by attackers, identifying new attacks, and improving overall cybersecurity defences. However, they can also be resource-intensive to maintain and may require specialized skills to configure and monitor properly. As with any honeypot, it is important to consider the potential risks and benefits before deploying a pure one.
Each type of honeypot has its strengths and weaknesses, and organizations should carefully consider their objectives and resources when selecting a honeypot strategy. You can use specialized honeypot network security to meet specific cybersecurity needs. Here are some examples:
Examples of specialized Honeypots
- Client honeypots : These are designed to simulate vulnerable client systems, such as web browsers or email clients. They are useful for endpoint detection and response .
- Mobile honeypots : These honeypots simulate mobile devices or applications to detect attacks targeting the rapidly growing mobile computing ecosystem.
- Malware honeypots : Malware honeypots copy software applications and APIs to draw malware attacks. You can develop anti-malware software and hire security teams to determine which API flaws need fixing.
- SCADA honeypots : These are designed to simulate industrial control systems and supervise control and data acquisition systems. They detect attacks that target critical infrastructure.
- Spider honeypots are malicious bots and ad-network crawlers that prowl the internet. Spider honeypots are designed to catch hackers using links and sites on the internet that are easily accessible.
- Cloud honeypots : These honeypots simulate cloud computing environments to detect attacks that target cloud infrastructure or services.
Benefits of Honeypots
There are several benefits to using honeypots as a part of a cybersecurity strategy:
1. Honeypots can provide early warning of attacks
Honeypots can detect and alert security personnel to the presence of attackers before they can cause significant damage. By identifying and analyzing attackers’ behaviour early on, organizations can take proactive steps to prevent further attacks.
2. Honeypots can help organizations understand attacker tactics
Organizations can gain insights into their methods and motivations by studying attackers’ behaviour. You can use this information to improve security measures and prevent future attacks.
3. Honeypots can help identify security vulnerabilities
Honeypots can help organizations identify network and system configuration vulnerabilities by simulating various systems and services. It is crucial for businesses such as the tourism sector, which receives a lot of clients in the peak seasons. Therefore, there has been a call for mass tourism to honeypot sites against cyber criminals.
4. Honeypots can be used for training and education
Security personnel can use honeypots to practice and improve their skills in identifying and responding to attacks.
Risks of Using Honeypots In Your Organization
While honeypots can be effective tools for improving cybersecurity, they also come with some risks:
1. Honeypots can be costly and time-consuming to implement
Setting up and maintaining honeypots can be expensive and require significant time and resources.
2. Honeypots can create additional attack surfaces
If not properly implemented and maintained, honeypots can provide a backdoor for attackers to access the systems and resources they are designed to protect.
3. Honeypots can generate false positives
Honeypots can generate alerts that do not necessarily indicate an actual attack. These false positives can waste valuable time and resources and distract security personnel from legitimate threats.

4. Honeypots can be ineffective against sophisticated attackers
Sophisticated attackers may be able to detect and avoid honeypots, rendering them ineffective.
Best Practices for Honeypots
It is crucial to follow the best practices to minimize the risks associated with honeypots:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before implementing a honeypot strategy, it is important to define clear objectives and determine how you will use the information collected from the honeypot.
2. Isolate The Honeypot
Honeypots should be isolated from systems and resources to prevent attackers from using them as a backdoor to access the systems.
3. Use Multiple Honeypots
Using multiple honeypots can help reduce the risk of false positives and provide a more comprehensive view of attacker behaviour.
4. Regularly Update and Maintain The Honeypot
Honeypots should be regularly updated and maintained to remain effective and secure.
Featured Image Source: unsplash.com
Similar Posts
Outsource cybersecurity: expectations vs reality.
Sapphire has designed its UK-based Security Operations Centre (SOC) to help organisations respond quickly to threats and receive the optimum cyber security protection available today. Organisations across the UK benefit from Sapphire’s twenty-five years of experience from network monitoring to vulnerability management and incident response. Sapphire security analysts have a wealth of knowledge.
What Is Authorization to Operate (ATO)?
Information Technology systems are always more central to the operation of both business and government. But as the reliance on these systems grows, so do the consequences of outages and security incidents. Therefore, it is…
Man-in-the-Middle Attack: Prevention Best Practices and Detection
Identity-based cyber-attacks come in many forms and pose numerous risks for any organisation. One of the most common facilitators of identity-based cyber attacks is a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM). Here, it is difficult to differentiate between…
Certificate Pinning – What it Is, its Benefits, and Drawbacks
A few years back, the largest search engine, Google, started using certificate pinning. Following that, chrome would only accept websites with pinned certificates when trying to connect to Google. This meant that Chrome would block…

Sapphire Launches Third-Party Risk Management Services Powered by Agnostic Intelligence
By Valentina Dal Mas Sapphire clients supported to minimise the cost while maximising their awareness of the risks associated with their supply chain Newcastle, UK – 26 March 2024 – Sapphire, the UK-based pure-play cyber…
Guide to Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is a vital element of cybersecurity for any organisation that wants to protect itself from attacks. Since cybercriminals are always improving their skills and looking for vulnerabilities to exploit in…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact About Insights NISC
Compliance and Risk Gap Analysis Security Improvement Plan (SIP) Testing & Vulnerability Analysis Breach Attack Simulation
Perimeter Security Email & Web Security Identity & Access Management Malware Protection
Detect & Respond
XDR for Microsoft Managed Detection & Response Threat Intelligence Vulnerability Management Security Awareness Training Cyber Incident Response
Security Consultancy Digital Forensics
Email: [email protected] Registered Office: The Cube, Barrack Road, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE4 6DB Phone: +448455827001

privacy & Legal
Gap Analysis Security Improvement Plan (SIP) Testing & Analysis Breach attack simulation
Perimeter security Email & Web Security Identity & Access management Malware protection
XDR for Microsoft Managed Detection & Response Threat Intelligence Vulnerability Management Security Awareness Training Cyber incident response
Security Consultancy Digital forensics
- Português, Brasil
A honeypot is a cybersecurity defense technology that detects, lures, tracks, and analyzes unauthorized access to a website, computer systems and networks, or applications.
The term honeypot originates from espionage and security contexts and has been adapted as a cybersecurity defense technique. The name "honeypot" is derived from the idea of attracting bees (a.k.a. adversaries) with honey (a.k.a. fake access and useless data). In espionage and intelligence operations, a honeypot is a trap or a deceptive operation designed to attract and capture spies or enemies. The idea is to create an appealing target that entices individuals to reveal their true intentions or engage in activities that could be monitored or controlled. That same principle is applied to a honeypot as part of a threat intelligence gathering operation.
What is a Honeypot?
The concept behind a honeypot is to create a tempting target that appears to be a legitimate and valuable resource, enticing potential attackers to interact with it. However, the honeypot contains no real information, and it is isolated from your actual production systems to ensure that any activity is closely monitored and doesn't pose a real threat to your critical assets.
The purpose of a cybersecurity honeypot is to attract malicious actors and gather information about their tactics, techniques, and procedures. By observing and analyzing the behavior of attackers within the controlled environment of the honeypot, you can gain insights into their methods and use that information to better defend against real-world threats. Security professionals call this threat intelligence.
Are There Different Types of Honeypots?
There are many types of honeypots, but the most common are categorized as either high or low interaction. A low-interaction honeypot is one that, once found by the hacker, will be of little use to them. In some cases, the attacker is presented with a login prompt they cannot get past. The honeypot then logs and stores these attempts by the attacker to log in. The honeypot provides information on the attacker's IP address of origin, which can sometimes be attributed to a location, and the username and password that were used in the login attempt.
On the other hand, a high-interaction honeypot allows the attacker to go further to gather additional information about their intentions. The honeypot is constructed to encourage the attacker to log in with a designated set of usernames and passwords and stores any command the attacker attempts to use. A high-interaction honeypot often simulates the Secure Shell (SSH) service, a program used for authentication and secure communication, and can measure all SSH login attempts.
Other types of honeypots include:
Production Honeypots : These are deployed within a network to gather information about attacks, methods, and potential vulnerabilities. They mimic the behavior of real systems and applications to lure attackers into revealing their techniques. Production honeypots are primarily used for research and analysis of threats and are not directly part of the organization's operational infrastructure.
Research Honeypots : These are often used by security professionals and researchers to gain insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures used by attackers. Research honeypots can be either low-interaction or high-interaction. Low-interaction honeypots simulate only a limited set of services and interactions, while high-interaction honeypots replicate a wider range of services and behaviors, providing a more accurate view of attacker behavior.
How Do Honeypots Work?
Honeypots act as traps to lure in potential attackers and gather information about their techniques, tools, and motives. There are several key steps to a successful honeypot defense strategy. They include:
Deployment : Honeypots are intentionally created to appear as vulnerable or enticing targets. They can be standalone systems or virtual machines within a network. These systems may mimic real services, applications, or devices to make them seem attractive to attackers.
Imitation of Vulnerabilities : Honeypots are often configured with security vulnerabilities or misconfigurations to make them seem like easy targets. This could involve using outdated software, weak passwords, or unpatched systems.
Isolation : Honeypots are typically isolated from critical production systems to prevent attackers from moving laterally within the network or causing real damage. They might be placed in a separate network segment or virtual environment.
Monitoring and Logging : Honeypots are closely monitored to record all activities and interactions. This includes network traffic, login attempts, commands executed, and any changes made by the attacker. These logs provide valuable insights into attack methods and patterns.
Alerts and Responses : When an unauthorized user accesses the honeypot, it triggers alerts to security administrators. This allows them to assess the situation, analyze the attacker's behavior, and respond accordingly.
Deception and Delay : Honeypots can be designed to delay attackers, keeping them engaged and wasting their time. This can provide security teams with more opportunities to gather information and potentially track the attacker's movements.
Data Collection and Analysis : The information collected from honeypots helps security professionals understand attack techniques, tools, and motivations. This data can be used to refine security measures, update intrusion detection systems, and develop countermeasures against new threats.
Forensics and Attribution : Honeypots can assist in attributing attacks to specific individuals, groups, or nations based on the methods and patterns they exhibit when interacting with the honeypot.
Active and Passive Honeypots : Active honeypots interact with attackers, allowing them to perform actions and gather more information about their tactics. Passive honeypots, on the other hand, simply observe and log activities without engaging with the attacker.
Overall, honeypots play a crucial role in understanding and mitigating cyber threats. They offer insights into attacker behavior, enhance incident response capabilities, and contribute to overall cybersecurity strategies.
What Are the Benefits of Using Honeypots?
The benefits of honeypots include:
- Threat Intelligence: Honeypots provide real-time and accurate information about emerging threats and attack methods.
- Early Detection: By attracting attackers, organizations can identify potential threats before they can reach critical systems. In a managed detection and response environment, security researchers often set up honeypots in a controlled manner and then study them as part of 24/7 threat and response services.
- Understanding Attacker Behaviors: Honeypots allow security professionals to study attacker behavior, tools, and tactics, which can inform defensive strategies.
- Diversion from Real Assets: Honeypots divert attackers' attention away from valuable assets, giving defenders more time to respond effectively.
Overall, honeypots can be valuable tools for understanding and defending against cyber threats, but they should be used with a clear strategy, proper planning, and a thorough understanding of the associated risks.
What’s an Example of a Successful Honeypot Operation?
SophosLabs first discovered the Chalubo bot family through an attack on one of our honeypots, which we use to collect and analyze data on malicious activity. The Chalubo botnet, which incorporates malware such as Xor.DDoS and Mirai, was first discovered by our SophosLabs researchers in early September 2018. Security researchers created a honeypot server that was designed to appear vulnerable to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and other threats to capture information about the botnet. They were able to learn that one of Chalubo’s key components was a downloader, a Lua command script and the main bot, which was optimized for hardware running Intel x86 processors.
Our cybersecurity researchers also learned that the bots attempted to leverage brute force login credentials against an SSH server. The SophosLabs honeypots presented the attacker with the appearance of a real shell that accepts a wide range of credentials.
Final Thoughts on Honeypots from Sophos
While honeypots themselves don't directly protect sensitive data, they can contribute to your overall cybersecurity strategy by diverting attackers, enabling early threat detection, and providing valuable insights into attack techniques.
At Sophos, our experts leverage honeypots in lab environments often. We monitor both behavior and network traffic generated by honeypots and share what we find with our customers and the security community at large.
In 2019, we set up and studied ten cloud-based server honeypots placed worldwide to understand more about how adversaries gain access to systems. The results of this global study revealed the need for visibility and security to protect what businesses put into hybrid and all-cloud platforms. To learn more, download a free copy of our report, “ Exposed: Cyberattacks on Cloud Honeypots .”
Download Report
Related Articles
Introducing Sophos Central Custom Dashboards

MSP Perspectives 2024 Report

The State of Ransomware in Manufacturing and Production 2024
Catch up on More Cybersecurity News
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
[ huhn -ee-pot ]
- a pot, as of glass or silver, for storing and serving honey.
The senator engaged in an extramarital relationship with a honeypot set up by his political rivals.
I thought my money was safe, but the other investors were all honeypots who were lying about their profits.
The unregulated dating app was a honeypot for catfishing and predatory behaviors.
The author’s childhood home became a tourism honeypot for the small town.
- a computer system, isolated from the rest of its network, established as bait to lure malicious hackers into engaging with it, thereby revealing the identity or technique of the perpetrator without endangering the network or its data.
- a web page or section of hidden code in a web page that lures spammers into an interaction that identifies their content as spam or reveals its point of origin.
- Slang: Vulgar. the vagina.
/ ˈhʌnɪˌpɒt /
- a container for honey
Cornwall is a honeypot for tourists
Discover More
Word history and origins.
Origin of honeypot 1
Example Sentences
Pro-Kremlin propagandists portrayed a seasoned professional journalist as a mere honeypot— a covert agent aiming to use sexual attraction to compromise an intended target.
On Friday, Kevin Beaumont, working in his capacity as an independent researcher, said in a blog post that he had detected attacks on the honeypot he uses to keep abreast of attacks hackers are using in the wild.
The issue in that case was that the databases were creating a honeypot and a real risk.
On Stair's Honeypot rode Patsy, ordering and ranging everything everywhere.
The surly ranter became softened for a time, and, though he spoke of her to others as "Honeypot," he ruled his tongue in public.
Her father was on one side, mounted on his big black horse, and Louis Raincy guarded the left flank on "Honeypot."
This was a negotiation which was better left to Honeypot and Derry Down.
Patsy dismounted from Honeypot and bade Stair Garland get on board.

- Tourism: honeypot surveys

fieldwork focus
Honeypot surveys
The tourist industry is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the British economy. Tourists spend money and bring employment to popular locations. However, too many tourists in a place can sometimes lead to environmental and social problems. This Fieldwork Focus explains how to carry out fieldwork into tourist impacts at a honeypot site.
- Volume 26, 2014/ 2015
- Coastal fieldwork
- Primary data
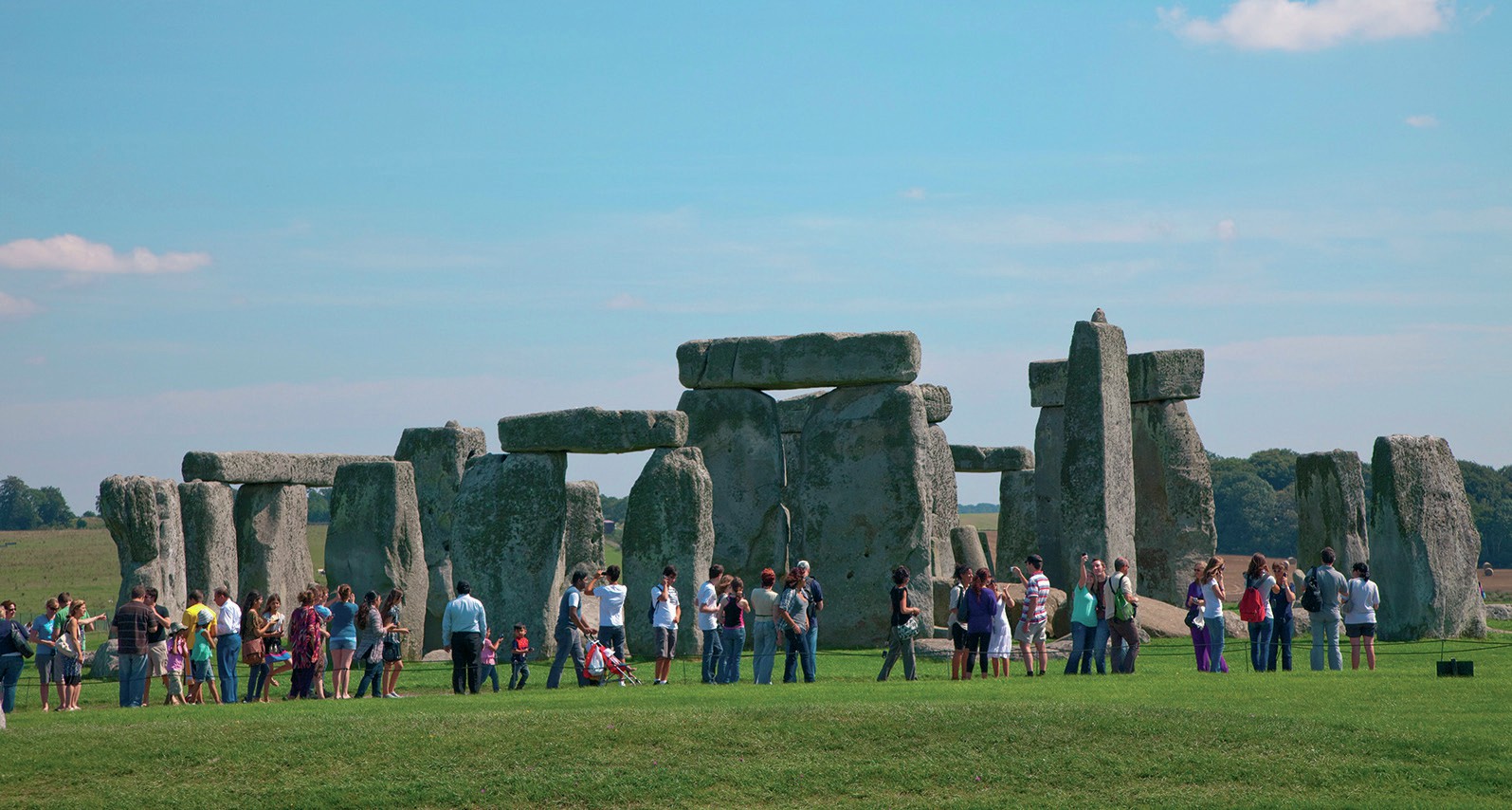

A n effective way to study the impact of tourism is to focus upon a specific location that attracts many tourists. Such places where people ‘swarm’ to are sometimes called ‘honeypots’.
Honeypots can be natural features (e.g. Cheddar Gorge, Lake Windermere), historical attractions (e.g. Stonehenge, Westminster Abbey), cultural locations (e.g. Stratford-upon-Avon) or coastal resorts (e.g. Newquay, Tenby). They are often compact in size and therefore can be prone to overcrowding at peak times, such as on bank holidays and during school summer holidays. However, their restricted size can make them convenient to study.
Your organisation does not have access to this article.
Sign up today to give your students the edge they need to achieve their best grades with subject expertise
Related articles:

The anatomy of a villain: the antagonist in The Lovely Bones
English Review

Stephen Greenblatt and new historicism: interpreting Othello

Truman Capote, 1924-84

The Bloody Chamber and Other Stories by Angela Carter
What is honeypot tourism?
A place that attracts high volumes of tourists
Add your answer:
How is the tourism around a honeypot site and it impacts important to geographers?
Tourism around a honeypot site can create both positive and negative impacts on the environment, culture, and economy of the area. Geographers study these impacts to understand how tourism can lead to issues like overdevelopment, strain on local resources, loss of cultural authenticity, and environmental degradation. By identifying and analyzing these impacts, geographers can propose sustainable tourism strategies to help manage and mitigate these effects.
What are the ratings and certificates for The Honeypot - 1920?
The Honeypot - 1920 is rated/received certificates of: UK:A
Is honeypot a malicious code?
No honeypot (in a nutshell) is used to lure and trap hackers from stealing information on the system
What special adaptation does the honeypot ant have?
The honeypot ant has the ability to steal honey from beehives. It is able to do this while going undetected.
Is Thorpe park a honeypot site?
What is a tourist honeypot.
A popular visitor attraction that attracts large numbers of tourist. It is a reference to bees buzzing around a hive or "honeypot"
Why is Lulworth Cove a tourist 'honeypot'?
it's a tourist honeypot because the Jurassic coast line and the world heritage site has attracted so many people to see lulworth that it's lijke a honeypot and they use this as a phrase geographically.
Is the Grand Canyon a honeypot site?
What are the honeypot sites in brecon beacons, what are the characteristics of a typical tourist honeypot.
maybe be busy
How long do honeypot ants live for?
about 3 years
How do banks test their new security systems?
HoneyPot Systems.
Top Categories


Honey Beast Locations Guide For Fallout 76
Quick links, what honey beast variants are there, where to find honey beasts, what events spawn honey beasts.
When you’re exploring the post-apocalyptic world of Fallout 76 , you are likely to come across many different types of enemies that you need to be on the lookout for. Honey Beasts are one such type to be wary of.
Fallout 76: The Best CAMP Locations
Killing Honey Beasts rewards you with different drop items, and gives you a decent amount of experience. Finding these beasts on the map is moderately difficult, although these large, terrifying monsters do have multiple possible spawn points. Follow this guide to find out all the Honey Beast locations in Fallout 76.
Updated April 24, 2024, by Andrew Scariati: With the Fallout show bringing dozens of new bloodthirsty Wastelanders to Fallout 76, you'll need to know the best Honey Beast locations in Fallout 76.
Finding a Honey Beast in Fallout 76 can be hard if the spawns are already poached, so here are updated Honey Beast locations, including the new spots introduced in the Once In A Blue Moon update.
In total, you may come across eleven types of Honey Beasts in the game. These variants are:
- Standard Honey Beast
- Putrified Honey Beast
- Raging Honey Beast
- Glowing Honey Beast
- Rabid Honey Beast
- Frenzied Honey Beast
- Poisonous Honey Beast
- Giant Honey Beast
- Deadly Honey Beast
- Scorched Honey Beast
- Prime Honey Beast
Despite differences in the nature and appearance of these variants, one thing they all have in common is the loot items they drop : Stimpak, Honey, Honeycomb, Gold Scrap, Excess Adhesive, and Royal Jelly.
One of the prime Honey Beasts locations in Fallout 76 is south of the Middle Mountains Pitstop in the Savage Divide region .
You can find three Honey Beast spawns in the area close to Solomon's Pond.
You could once encounter up to eight of these beasts here when the location was previously known as Middle Mountains Cabins.
The location was renamed with the Once In A Blue Moon update and is inhabited by the Blue Ridge Caravan Company, including two vendors: Vera and Clyde.
Likewise, in the same region, you should also investigate the Seneca Rocks Visitor Center. Honey Beasts tend to appear in this area along with Scorched Mobs .
These can kill the Honey Beast before you can get a hold of it, so make sure you get rid of the Mobs before they sabotage your hunt.
Head into the Treetops or a cave near Freddy Fear’s House of Scares areas in the Mire region to find an excellent Honey Beast location.
The chances of Honey Beasts appearing here are extremely high, so it's a good place to hunt .
Additionally, Honey Beasts appear in the garden area between the Whitespring Resort and Whitespring Golf Club.
Finally, you can also find a dead Honey Beast at the Freak Show , which is located east of Huntersville.
To recap, the best Honey Beast locations in Fallout 76 are:
- South of the Middle Mountains Pitstop near Solomon's Pond (Savage Divide)
- At the Seneca Rocks Visitor Center
- A cave near Freddy Fear's House of Scares (Mire Region)
- Between Whitespring Resort & Golf Club
- The Freak Show, east of Huntersville
- The Treetops
Fallout 76: Every Power Armor Set, Ranked
Besides these locations, you can find Honey Beasts when you take part in these events :
15 Must-Have Fallout 76 Weapons

TPA welcomes new canine to its K-9 bomb squad ahead of busy summer travel season
Meet the k9's keeping tpa safe.
Ariel Plasencia reports
TAMPA, Fla. - The Tampa International Airport Police Department welcomed a new canine to its K-9 bomb squad ahead of what is expected to be a busy summer travel season.
K-9 Hubert and his handler, officer Alex Cebotaru, just finished 11 weeks of training in Texas. The pair’s training will continue at the airport until July.
"Basically, our job is to find bombs. Well, his job is to find bombs," Cebotaru said of five-year-old Hubert.

Cebotaru met Hubert, who joins several other K-9s that sniff for bombs or drugs at the airport, for the first time while training in Texas.
The two were paired up based on their personalities.
"He's kind of laid back. But when it's time to work, we work very well," Cebotaru said.
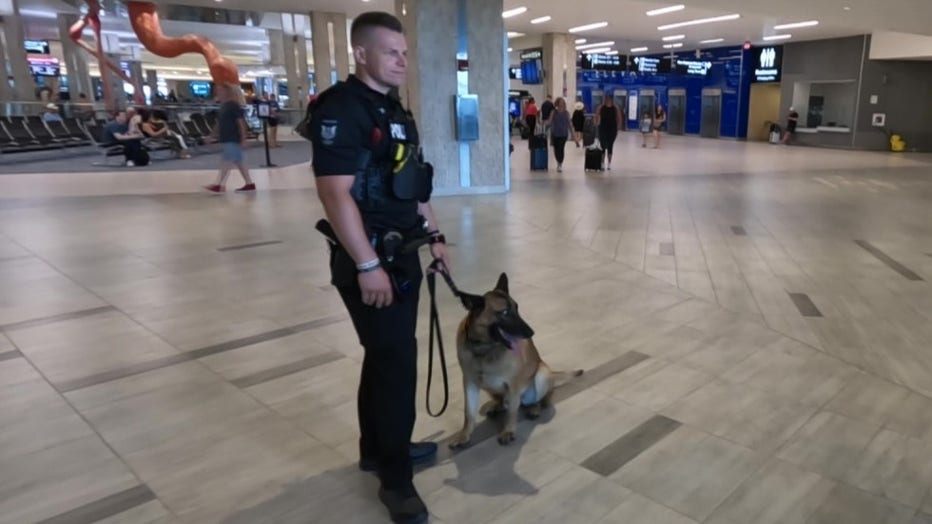

The officers work closely with their canines to scan ticket counters, security lines, and the baggage claim area, paying close attention to recognize when the dog has detected a suspicious odor.
READ: FAA: Travelers faced 2.1M hours of airport delays last year, prioritizes 'safety' and 'efficiency'
The airport is expecting to see 3.4 million passengers between Memorial Day and mid-August, which means more travelers, bags, and overall traffic compared to last summer.
"We have missions, and we have trainings that we have to do to prepare for an influx of more passengers, anything like that," Cebotaru said.
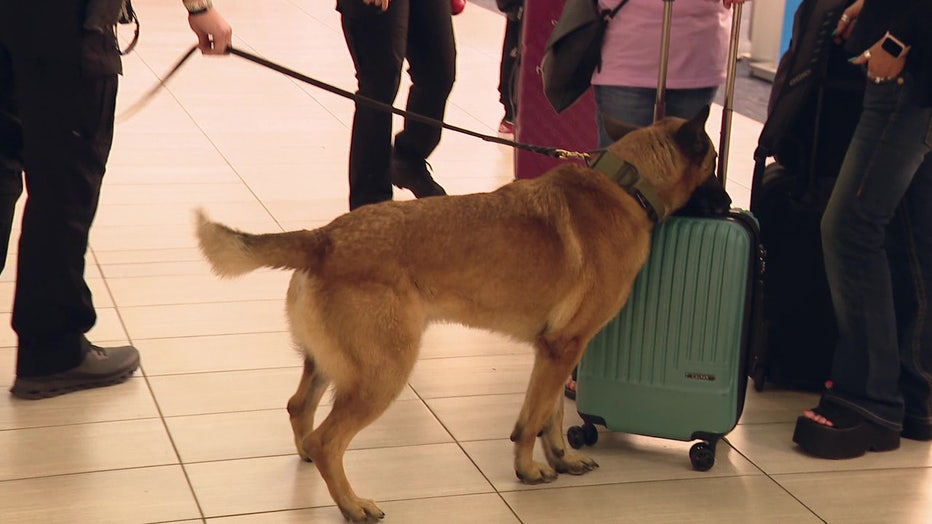

Hubert will officially complete his required training in July, which is when passengers will see the pair working around the airport.
"This was my dream, and I'm living my dream to be in this position," Cebotaru said. "It takes a lot of work, a lot of dedication, a lot of discipline."
Hubert and the other K-9s must be re-certified by TSA every year, which includes odor testing. K-9s must pass the test without errors to keep their certification.
WATCH FOX 13 NEWS:
SIGN UP: Click here to sign up for the FOX 13 daily newsletter
Every item on this page was chosen by a Veranda editor. We may earn commission on some of the items you choose to buy.

Step Aboard a Restored Presidential Yacht That Once Belonged to JFK and Jackie O.
Design veteran Jack Fhillips embarked on a three-year historic restoration to preserve this important piece of American history.
At the time, the nearly 100-year-old vessel needed an extensive architectural overhaul to save it from "certain demise," according to Fhillips. Charles Modica, a longtime client and local developer in Palm Beach County, had purchased the run-down ship and was seeking a historical interiors transformation that would replicate the decor of the Kennedy era as closely as possible.
Preceding Air Force One, presidential yachts (affectionately known as "Floating White Houses") were important destinations for escaping the "claustrophobic tension" of the Oval Office, Henry Kissinger wrote. They were used for everything from meetings with prominent world leaders to pleasure cruises down the Potomac after a tough day of running a country.
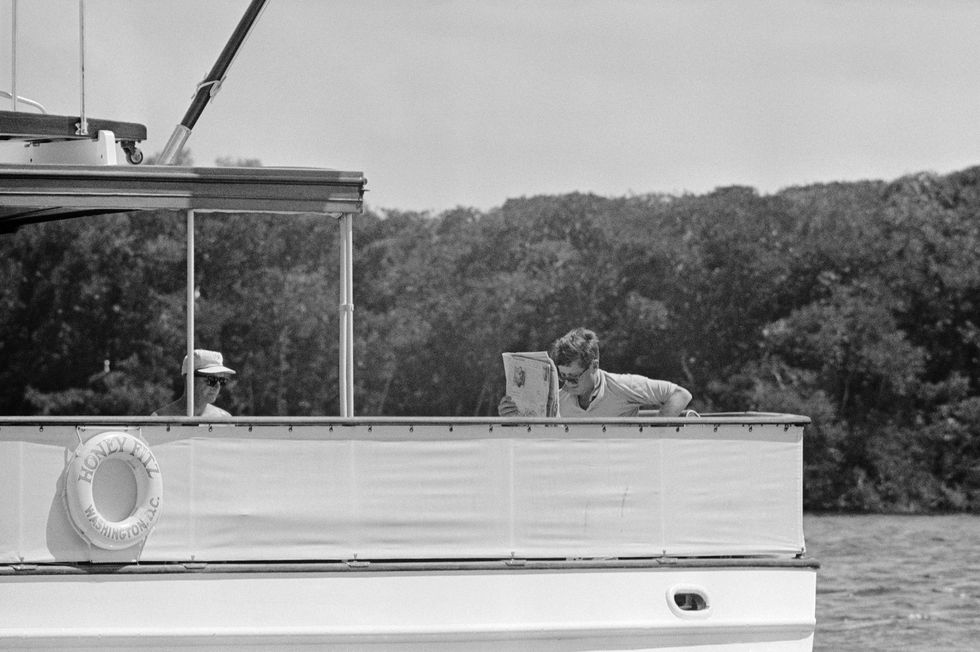
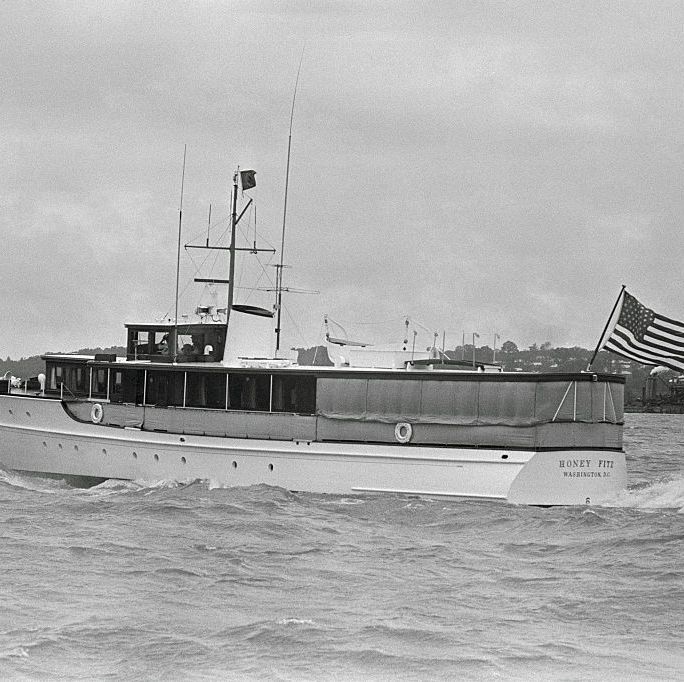
A revolutionary yacht in terms of speed upon its inaugural launch in 1931, the Honey Fitz served five consecutive U.S. presidents: Harry S. Truman, Dwight D. Eisenhower, John F. Kennedy, Lyndon B. Johnson, and Richard M. Nixon, after being originally commissioned for Sewell Avery of Montgomery Ward, one of the most prominent retail behemoths of the day. Though Nixon renamed the boat Patricia in honor of his wife, and it has since been renamed and repurposed by various private owners, the ship is best known as Honey Fitz in popular culture once JFK took the helm, and Modica sought to restore the vessel to its highest prominence.

"After 50 years of practicing, this project was a perfect and natural fit for my firm," says Fhillips, who has a background in historical preservation as well as interiors, and, as a resident of Palm Beach County, has worked on many private yachts.
The Honey Fitz first went through a three-year restoration process that required a complete overhaul of beams, subfloor, decks, and the superstructure of the yacht in line with experts in traditional shipwright methods, wooden yacht craftsmen, historical records, and U.S. Coast Guard regulations.
Fhillips finally got to take the reins with the interiors in January 2023 after combing through archived photographs, footage, and articles written about the ship, alongside the Honey Fitz 's captain and first mate. The team was able to piece together an immaculate interiors refitting and restoration that honors the ship's most historic (and glamorous) era during the Kennedy administration. Below, you can see a side-by-side view of the ship setting sail in 1961 and today.

"We serendipitously located the original company, Bielecky Brothers , in Queens, New York that Jackie Kennedy sourced for all the rattan furniture on the aft deck," Fhillips says.
To honor the yacht's storied past, Fhillips says, "We located copies of hand sketches of built-in sofas Jackie Kennedy drew on White House stationary that was recreated by a very talented man, Brad London, of Total Refit, Inc. "
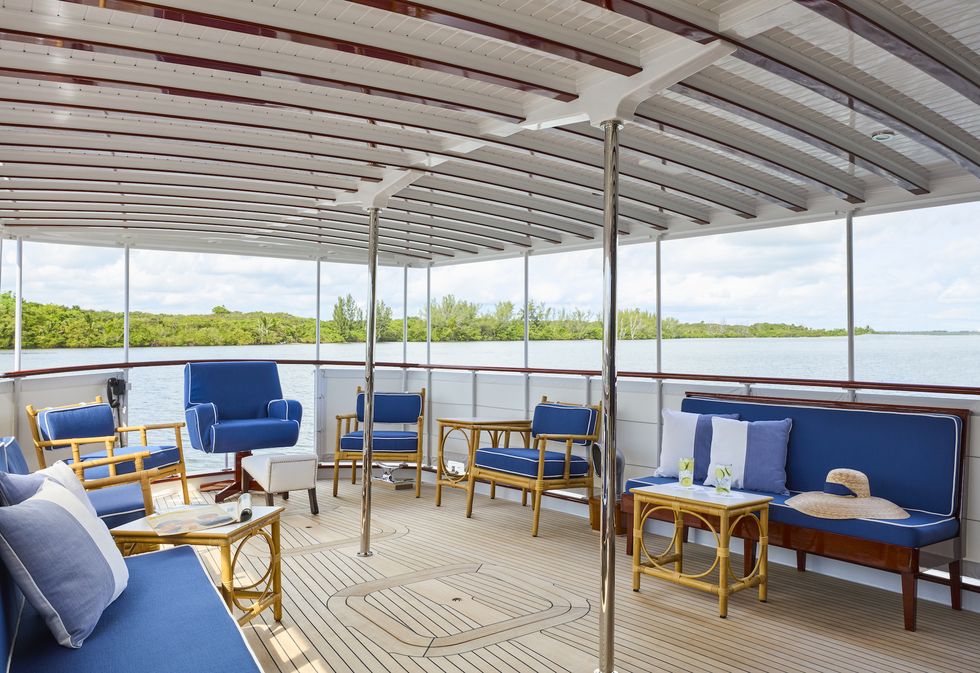

Those sofas are the focal point of the main salon, and the team also recreated the rattan oxbow club chairs, then styled the space with Kennedy family photos that would have been on the ship during the 1960s, as well as other memorabilia. Plenty more Kennedy mementos can be found in the stateroom in a vintage blue leather suitcase.
Modica had an English Regency-era antique dining set that was appropriate of the time that makes a perfect pairing with the LismoreWaterford crystal stemware reminiscent to the pattern gifted to JFK by the People of Ireland. The built-in buffet was rebuilt to its original integrity as well.
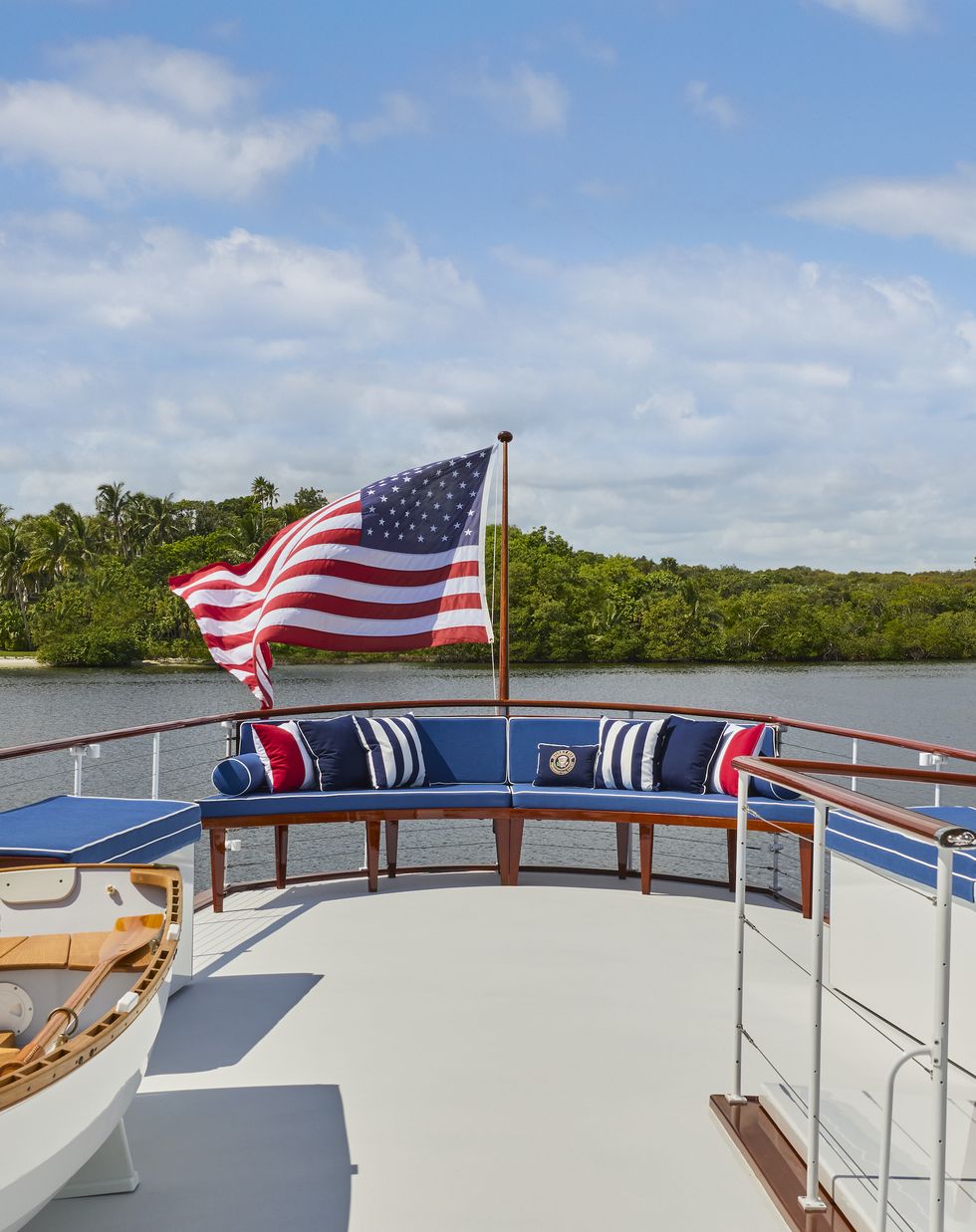

"My favorite spot on the boat would have to be the aft deck," Fhillips says. "It is so historically correct, from the iconic Kennedy captain's chair to the black telephone JFK used to the left of the chair. The rattan furniture was recreated, and we even located vintage gout stools that were seen in old photographs."
While the ship has completed its service to our country's presidents, it's certain to have a glamorous new era as it enters its next century. The Honey Fitz will now serve for use on limited charters and fundraising events, an ever-present reminder of the enduring legacy—and style—of both John F. Kennedy and Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis.

Fhillips and his team of experts spent three years restoring this iconic vessel to its former glory. First launched in 1931, Fhillips has prepared this yacht to look as good at 100 as it did on its first day at sea.

Fhillips had the iconic custom Jackie O-designed sofas recreated with help from Total Refit, LLC. ; they are covered in Perennials fabric. Vintage military campaign-style side tables, Chairish . Carpet, Pom Rugs .
Dining Area

The English Regency-era mahogany dining set is from the client's personal collection. Draperies, David's Workroom .

Fhillips brought in Waterford 's Lismore cut crystal that is reminiscent of the pattern gifted to JFK by the People of Ireland.

Even the yacht's bar space is based on the design during the JFK administration. The design team relied on archival photographs, footage, articles, and the knowledge of wooden yacht craftsmen.

The sleek galley kitchen may seem futuristic compared to its 1960s heyday, but its layout and design is in line with how it looked during the Kennedy administration.

The stateroom features custom embroidered Ralph Lauren pillows by Annapolis Pillow Company . Fhillips found the vintage Singer sewing stool on eBay .

The stateroom and bathroom are peppered with Kennedy memorabilia. The 19th century oil paintings are similar to the art selected by the Kennedys.
Fhillips commissioned replicas of the Bielecky Brothers furnishings Jackie Kennedy originally selected for the deck, while Canvas Designers Inc. recreated the iconic JFK custom captain's chair. Vintage gout stool, eBay .

All of the outdoor furnishings are covered in Perennials fabrics.
Lauren Wicks is a freelance writer and editor based in Birmingham, Alabama. Before going on her own, Lauren worked for brands such as VERANDA, EatingWell, and Cooking Light , and she covers all things lifestyle from interior design and luxury travel to wine and wellness.

The Ultimate House Tours Guide

Step Inside a Colorful and Historic English Estate

Step Inside a Garden-Inspired Home in Charlotte

A Palm Springs Villa Made for Desert Lounging

This California Home Is an Open-Air Masterpiece

Step Inside This Gatsby-esque Atlanta Estate

Tour a Greek Revival on the Kiawah River

Oscar de la Renta’s Home Is Pure Island Elegance

A Modernist Lakeside Playground

A Romantic and Coastal Block Island Retreat

Tour CeCe Barfield Thompson's NYC Apartment

Step Inside This Greek Revival Home Built in 1820

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What are tourist honeypots? Honeypots are areas which attract many tourists. They usually contain attractive scenery or historic/culturally significant buildings. These areas are so called because tourists flock to these places like 'bees around honey'.
Honeypot (tourism) A honeypot site is a location attractive to tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people. [1] [2] Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying tourists.
There are 3 main types of honeypot which are given below with case studies. Historical honeypot: A historical honeypot has an historical interest. It attracts historians and tourists. A good example of a historical honeypot is Stonehenge. The stones are as old as the pyramids in Egypt! Leisure honeypot: A leisure honeypot is a place where ...
Mass tourism involves tens of thousands of people going to the same resort, or honeypot site close honeypot site A popular visitor attraction or area, where large numbers of people visit., often ...
These places can also be called tourist honeypots. The term honeypot usually refers to a small area such as a village in a national park, while hotspots operate at a variety of scales from small villages to entire regions. Hotspots exist in places such as: Areas of outstanding natural beauty. Historic city centres.
Tourist honeypot sites attract visitors to an area which brings both benefits and costs to the area. Snowdon is the highest mountain in England and Wales (1085 m asl) and attracts 500,000 visitors each year, making it a tourist honeypot site. More than 10 million people visit Snowdonia each year bringing in £69 million to the local economy
What is honeypot tourism? GRASMERE is a village and tourist destination in Cumbria, England in the centre of the LAKE DISTRICT National Park. It is a HONEYP...
A honeypot site is a location attractive to tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people. [1] [2] Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying less discerning tourists.
A honeypot site is a location attractive to tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people.. Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying less discerning tourists.
A honeypot site is a location attracting throngs of tourists who, due to their numbers, place pressure on the environment and local people. Honeypots are often used by cities or countries to manage their tourism industry. The use of honeypots can protect fragile land away from major cities while satisfying less discerning tourists. One such example is the construction of local parks to prevent ...
Tourism management strategies: Councils build more homes for rent and developers erect more low-cost homes for sale to local people. Traffic calming measures on small roads and villages such as cattle grids and an overall speed limit. Fence off roadsides so people cannot damage verges. Speed limits (10 mph) for boats can limit the amount of ...
The first reason for Windsor's popularity is the number of tourist attractions. The main attraction is Windsor Castle, one of the official residences of the queen and the largest inhabited castle in the world. This grand estate is spread over 5 hectares and includes splendid state apartments containing treasures from the royal collection.
In a busy tourist hotspot, adequate parking is essential. Fail to get this right and tourists will just park wherever they can, such as residential streets and main roads. This creates traffic jams and in turn, misery for commuters, locals and tourists alike. Disperse people. Towns can cope better with increased footfall by spreading it out.
Honeypot site photograph: geography photo of a honeypot site with labels describing and explaining the main features of the honeypot site in the picture. Geography Photographs: Tourism: Honeypot site All Geography Photographs Topics - Home
Giant's Causeway. Address: 44 Causeway Rd, Bushmills BT57 8SU, UK. Official Website. 20 Best Mom Getaways in the U.S. Alyssa Ochs. Situated near the town of Bushmills at the edge of the wild North Atlantic in North Ireland, Giant's Causeway is a landscape of dramatic towering cliffs and a coastal area made up of about 40,000 basalt columns.
a place, thing or person that a lot of people are attracted to. The toy section of the store is a honeypot for children. It is possible to escape the tourist honeypots by heading north.
A honeypot is a cybersecurity tool designed to detect, deflect, and counteract attempts at unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. A honeypot is a decoy system or resource designed to attract and deceive attackers, allowing security analysts to monitor and study their behaviour. There are two primary types: research and production ...
Honeypots. A honeypot is a cybersecurity defense technology that detects, lures, tracks, and analyzes unauthorized access to a website, computer systems and networks, or applications. The term honeypot originates from espionage and security contexts and has been adapted as a cybersecurity defense technique. The name "honeypot" is derived from ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Honeypot definition: a pot, as of glass or silver, for storing and serving honey.. See examples of HONEYPOT used in a sentence.
Tourism Honeypot surveys. The tourist industry is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the British economy. Tourists spend money and bring employment to popular locations. However, too many tourists in a place can sometimes lead to environmental and social problems. This Fieldwork Focus explains how to carry out fieldwork into tourist impacts ...
A honeypot is a popular area visited by tourists. It may be of historical, leisure, or physical interest. It usually has one central attraction e.g. Stone Henge. Leisure and tourism.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is honeypot tourism, What is featured in honeypot tourism?, What are some examples of honeypot tourism? and more.
What is a tourist honeypot? A popular visitor attraction that attracts large numbers of tourist. It is a reference to bees buzzing around a hive or "honeypot"
Definition of Honeypot. A honeypot is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to deceive and monitor attackers or unauthorized users. Essentially, it's a trap set to detect, deflect, or study attempts at unauthorized use of information systems.
The listing broker's offer of compensation is made only to participants of the MLS where the listing is filed. 138 Petrelia Dr, Honey Brook, PA 19344 is pending. Zillow has 38 photos of this 4 beds, 3 baths, 2,982 Square Feet single family home with a list price of $609,990.
To recap, the. best Honey Beast locations in Fallout 76. are: South of the Middle Mountains Pitstop near Solomon's Pond (Savage Divide) At the Seneca Rocks Visitor Center. A cave near Freddy Fear ...
Meet the K9's keeping TPA safe. Ariel Plasencia reports. TAMPA, Fla. - The Tampa International Airport Police Department welcomed a new canine to its K-9 bomb squad ahead of what is expected to be a busy summer travel season. K-9 Hubert and his handler, officer Alex Cebotaru, just finished 11 weeks of training in Texas.
60047. 1221 Honey Lake Rd Unit 1201. Zillow has 17 photos of this $699,000 4 beds, 4 baths, 3,000 Square Feet single family home located at 1221 Honey Lake Rd #1201, Lake Zurich, IL 60047 built in 2024. MLS #12035001.
Amidst the turmoil and uncertainty of 2020, designer Jack Fhillips received the project of the lifetime: a complete restoration of the presidential Honey Fitz yacht that is most often associated with JFK and Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis.. At the time, the nearly 100-year-old vessel needed an extensive architectural overhaul to save it from "certain demise," according to Fhillips.