- Free Courses
- Trading Room
Save $228 on our Trade Together program, paid for by our partner.

How to Take Advantage of the Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
- 9 mins read ●
- Published: 31 August 2023
- Last Updated: 31 August 2023
In the financial markets, where every decision is a step towards profit or loss, having an edge over the market is invaluable. Now, imagine having the power to naturally spot trading opportunities others might miss, all while simplifying your strategy.
That’s where the Fair Value Gap trading strategy comes in. This strategy, used mainly by price action traders, is extremely simple yet incredibly powerful.
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools traders use to identify market imbalances and inefficiencies.
- FVGs occur when buying or selling pressure leads to significant price movements, leaving behind gaps on price charts.
- FVGs can be identified through technical analysis involving the analysis of candlestick patterns and price chart patterns.
- Traders can categorize FVGs into two types: Undervalued FVGs, where prices are lower than fair value, and Overrated FVGs, where prices are higher.
So, in this article, you will learn all you need to understand the basics of FVG and how to use it to build an effective price action trading strategy. Let’s dive right in.
What is the Fair Value Gap (FVG)?
How to identify a fair value gap on a price chart, how to trade using fvgs – the fair value gap trading strategy.
- Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
The concept of fair value gap goes by different terminologies among price action traders. Some call it imbalance, inefficiency, or liquidity void . But what exactly are these imbalances? They occur when buying and selling forces exert significant pressure, leading to substantial and rapid price movements. These movements, whether bullish or bearish, create gaps in the market, which are essentially the bread and butter of the FVG strategy.
The FVGs concept is rooted in the belief that the market naturally tends to correct itself . These price disparities or inefficiencies are not sustainable in the long term, and the market tends to gravitate back towards them before continuing in the same direction as the initial impulsive move.
Now, why are FVGs so crucial for price action traders? They provide a unique advantage by revealing entry and exit points in the market. Like many other types of price gaps, these FVG imbalances act as markers on the chart, guiding traders on when to get in and out of a position. However, the fair value gap differs from other price gaps.
Unlike other gaps where there’s no trading activity on a price chart, the FVG is based on a three-candlestick formation that creates an imbalance in the market’s price action. When this substantial move suddenly occurs, whether upward or downward, it leaves a gap between the first candle’s wick and the final candle’s wick; this is the FVG.
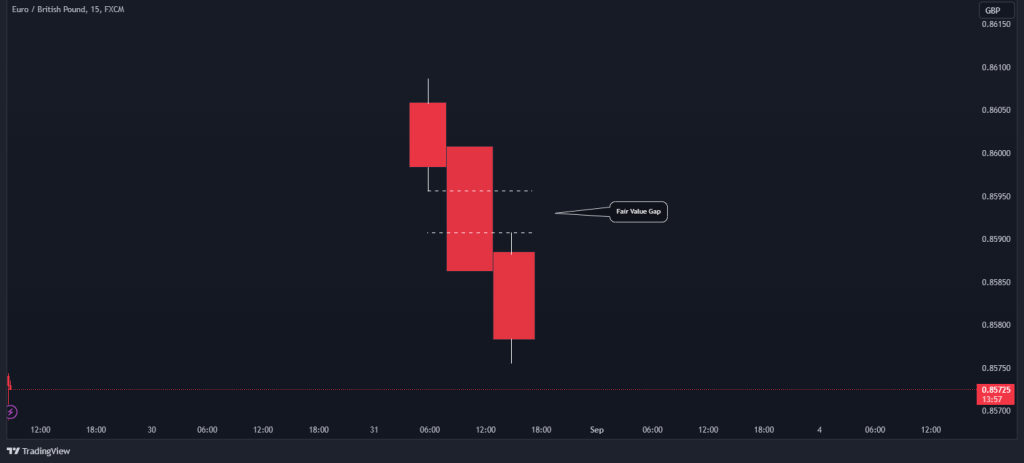
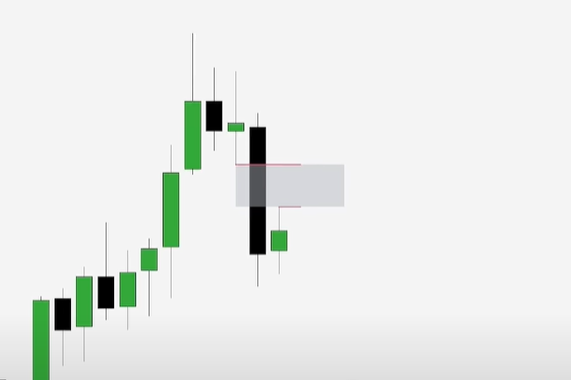
The gap in the above chart signifies an opportunity – a potential return to equilibrium. In this example, we can see the three-candle bearish formation where the lowest price of the first and the highest price of the third candle leave a hypothetical gap. Usually, following this formation, the markets tend to create a U shape and turn back to fill this gap.
It’s at this juncture where liquidity voids occur that traders can make informed decisions, leveraging the power of FVGs to capitalize on market corrections and profit from the realignment.
Like most chart patterns , the most tricky part of the fair value gap strategy is identifying this unique formation on a price chart. In the case of FVGs, a three-candle pattern must appear with specific rules. Then, when this happens, the space or gap between the wicks of the first and third candles is the fair value gap.
Here is how to identify an FVG on the chart:
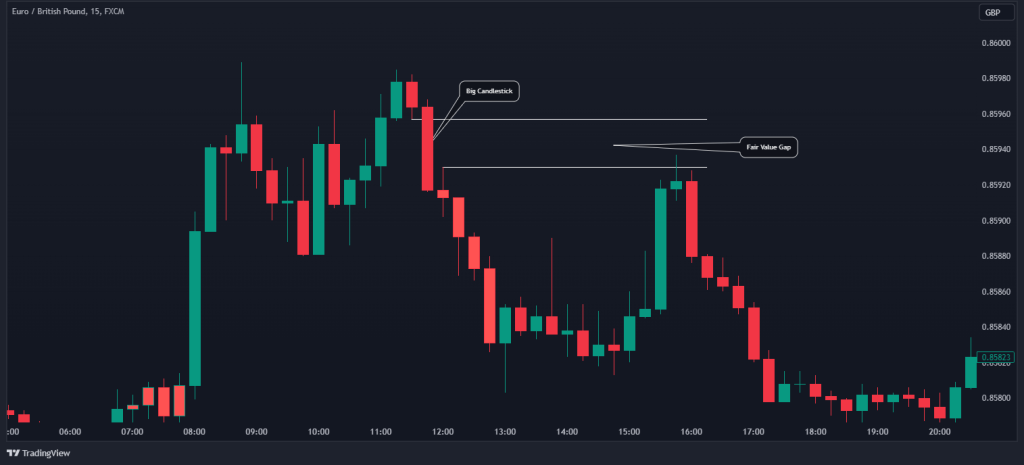
- Spotting the Big Candlestick: The first step in identifying a Fair Value Gap is to look for a substantial candlestick on your price chart. This candlestick should have a significant body-to-wick ratio, ideally around 70%.
- Analyzing Neighboring Candlesticks: Once you’ve identified the large candlestick, analyze the ones immediately preceding and following it. These neighboring candlesticks should not overlap the significant one entirely. Instead, minor overlaps may occur on the upper and lower sides of the substantial candlestick. Then, it is the gap between the wicks of neighboring candlesticks that create the fair value gap.
- Defining the Fair Value Gap: Finally, you must define the fair value gap and draw it on your price chart. In a bearish trend, the Fair Value Gap is the price area between the previous candlestick’s low and the following candlestick’s high. This is where the imbalance in the market becomes apparent, signifying a potential trading opportunity. The same applies to a bullish trend but with the opposite conditions.
In the EUR/GBP 15-Min chart below, you can see what the fair value gap candlestick pattern looks like on a price chart. Once you notice a big candlestick with a small candle prior to it and another small candle that appears after the big candlestick, you can search for the fair value gap entry level.
Additionally, Fair Value Gaps come in two distinct flavors, each carrying its own set of implications for traders:
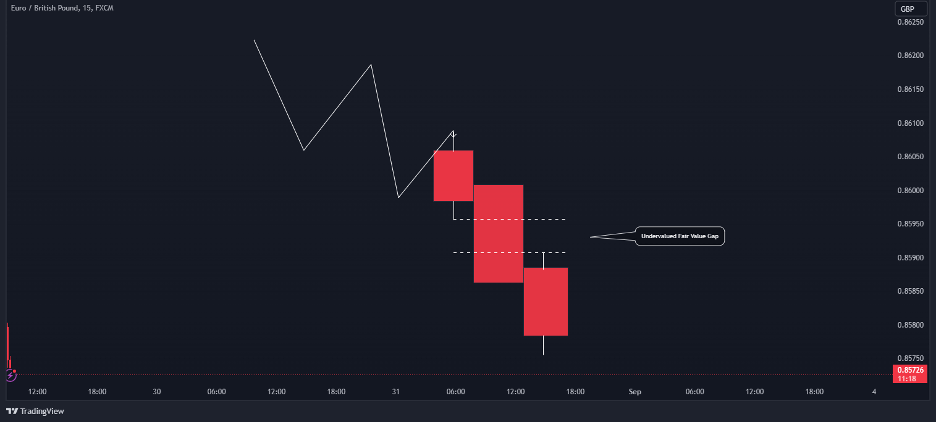
1. Undervalued Fair Value Gap (Bearish Fair Value Gap)
This type of FVG suggests that the price of a currency pair or any other financial asset is currently below its fair value. In simple terms, traders can anticipate that the market will retrace to correct this inefficiency. When you spot a significant bearish candlestick on your chart, it’s likely signaling the presence of an undervalued FVG.
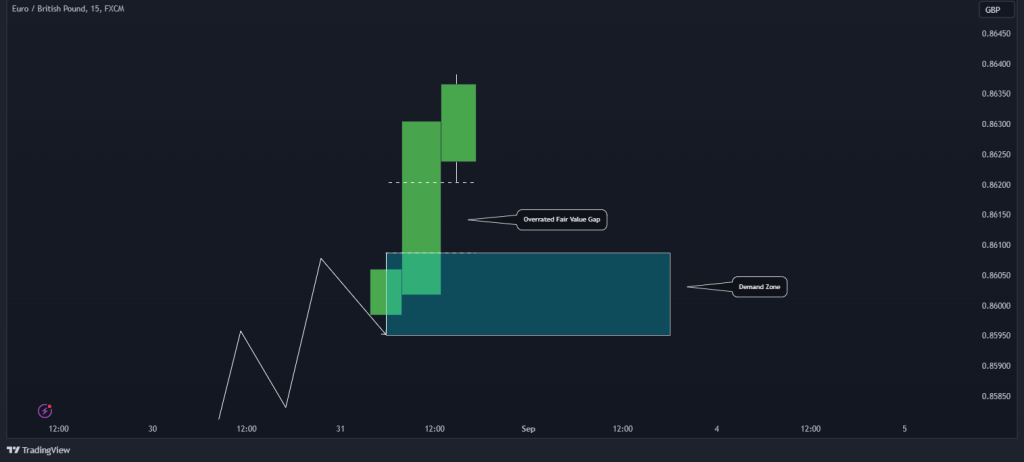
2. Overrated Fair Value Gap (Bullish Fair Value Gap)
Conversely, an Overrated FVG indicates that the price of a currency oaur or financial asset is currently trading above its fair value. Here, the market is overheated, and a correction is on the horizon. Traders can expect the price to retrace as the market balances itself before going up.
Ultimately, the most important part is to learn how to trade fair value gaps. The main reason why fair value gaps are usually connected to price action traders is that experienced traders can see it naturally. Once you learn how to identify a fair value gap on a price chart, then you’ll know when and where you should enter and exit a trade.
Also, keep in mind that there are several to trade the markets when FVG has been identified. For instance, some traders enter a trade expecting the markets to go back to fill the gap. Others wait for the gap to get filled and then enter a trade with the direction of the initial price movement.
Since the second method is considered more reliable, in this section we will show how to use this FVG trading strategy. So, here’s how to trade it:
1. Determine the Trend
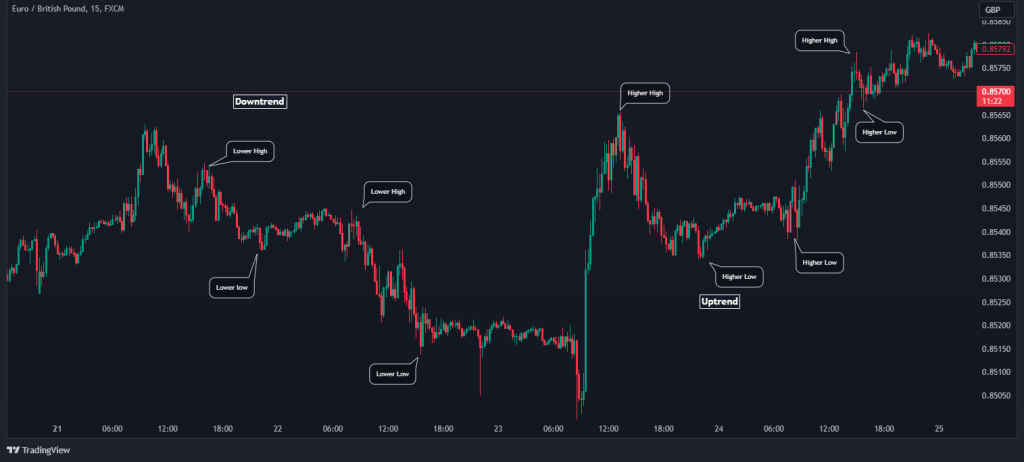
Trends play a pivotal role in this strategy. If the price is consistently forming higher highs and higher lows, you’re in an uptrend, and you should be looking to buy entries. Conversely, if the price is forming lower highs and lower lows, it indicates a bearish trend, and you should focus on selling entries.
Establishing the trend direction provides you with a fundamental framework for your trading decisions. If needed, switch to higher time frames, such as 1H, daily, and weekly. Also, to identify the market’s trend, you can trend lines and trend channels .
2. Identify Supply and Demand Zones
Once you’ve determined the trend, the next step is identifying supply and demand zones or order blocks that align with that trend. The simplest way to draw supply or demand zones is using the first candle that formed the FVG.
In the context of a bullish trend, pay particular attention to demand zones. These zones are areas where buying interest is strong and can potentially drive prices higher. Conversely, in a bearish trend, you’ll want to focus on supply zones, where selling pressure may dominate. The goal here is to pinpoint areas on the chart where significant price movements are likely to occur.
3. Use FVG to Determine the Entry Point
Next, you should identify the formation of the fair value gap. To do this, you can make use of the Fair Value Gap Indicator by Lux Algo on TradingView, which is a powerful tool to identify FVGs automatically. In the example below, you can see supply zones closest to an FVG during a bearish trend. When the price closes the gap, you should consider entering a short-sell position.
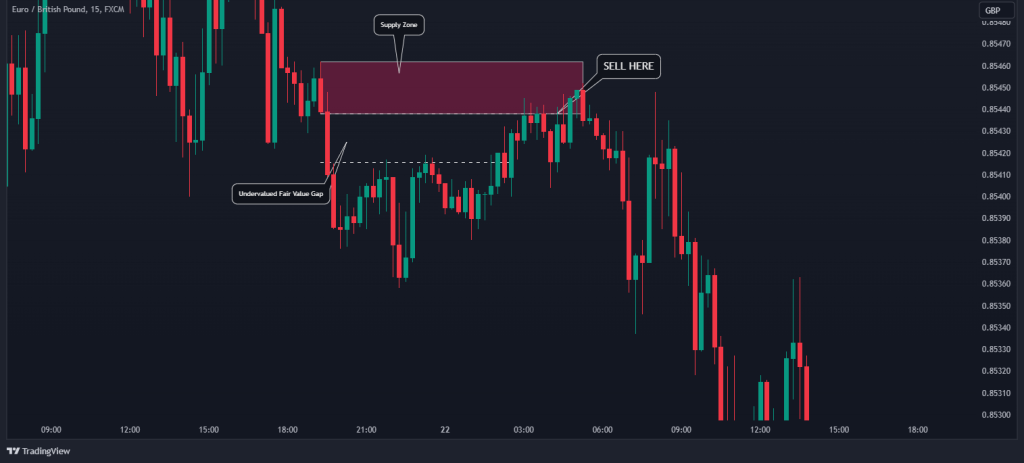
Remember, the presence of an FVG suggests a market imbalance that is likely to be corrected, potentially resulting in favorable price movements in your favor. Following the correction, the price is likely to move in the direction of the big candlestick or the initial price movement.
4. Set Stop Loss and Target Profit
As with any trading strategy, risk management is vital. When executing trades based on the FVG strategy, set appropriate stop loss and target profit levels. If you’re entering a trade from a supply zone, you should place your stop loss above that zone or, even better, above the first candle of the FVG three-candle formation. This helps protect your capital in case the market moves against your position.
Your take-profit target should be set just above the next demand zone in the direction of your trade. This zone represents a likely point where the market could reverse, allowing you to secure your profits. However, you can use this level to extend your earnings in case you notice a significant trend that is about to break the support level.

As you can see, the FVG trading strategy enables you to use a favorable risk-reward ratio. The main reason for that is the use of support and resistance levels as a protection tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the most popular questions on Fair Value Gaps:
What is the FVG level of trading?
The FVG level of trading refers to the point in the market where a Fair Value Gap (FVG) occurs . FVGs are discrepancies between the actual price of a financial asset and its perceived fair value, often caused by market inefficiencies. Identifying the FVG level involves recognizing these gaps on price charts, which traders can use to make informed decisions about potential price corrections and market opportunities.
What is the difference between imbalance and Fair Value Gaps?
Imbalance and Fair Value Gaps are closely related concepts in trading, but they have distinct implications. Imbalance refers to the disparity between buying and selling pressures in the market, leading to significant price moves. Fair Value Gaps, on the other hand, specifically pertain to the gaps formed on price charts due to these imbalances. While imbalance signifies the underlying forces at play, Fair Value Gaps are the visible outcomes of these imbalances, representing potential trading opportunities.
What is the smart money concept of FVG?
The smart money concept in relation to Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) suggests that well-informed and institutional investors (“smart money”) often exploit FVGs for profit. These savvy traders recognize the inefficiencies in the market and position themselves to benefit from the eventual price corrections that FVGs tend to prompt.
Do fair value gaps always get filled?
While the general principle is that Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) tend to get filled, it’s not an absolute rule. FVGs represent market imbalances that are expected to correct themselves over time, drawing prices back to the perceived fair value. However, external factors, sudden shifts in sentiment, or unexpected market developments can influence whether or not a specific FVG gets filled.
Risk Disclosure: The information provided in this article is not intended to give financial advice, recommend investments, guarantee profits, or shield you from losses. Our content is only for informational purposes and to help you understand the risks and complexity of these markets by providing objective analysis. Before trading, carefully consider your experience, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Trading involves significant potential for financial loss and isn't suitable for everyone.

Trade Like a Predator Hunt for Opportunities
Unlock FREE access to exclusive trading strategy videos. Then, join our Trade Together program for where we execute the strategy in live streams.
Here’s what you’ll get:
Sign up now for FREE access to our exclusive trading strategy videos. Want more? Explore our Trade Together program for live streams, expert coaching and much more.

Start learning how to trade today!
Or register using
Already have an account? Sign in
Great, you've been entered into our monthly prize draw. We'll notify you if you've won.
Thank you for downloading our trading plan!
Welcome back to HowToTrade
Don’t have an account? Register
Reset your password
Type your email and we'll send you a reset link
A password reset has been requested for . Check your email for your reset link.
*T&Cs apply. New customers only. Offer can be amended or revoked at any time.
© 2024 HowToTrade.com. All Rights Reserved.
Terms Privacy Policy Cookie Policy
Disclaimer: The information on the HowToTrade.com website and inside our Trading Academy platform is intended for educational purposes and is not to be construed as investment advice. Trading the financial markets carries a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Before trading, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, experience, and risk appetite. Only trade with money you are prepared to lose. Like any investment, there is a possibility that you could sustain losses of some or all of your investment whilst trading. You should seek independent advice before trading if you have any doubts. Past performance in the markets is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
HowToTrade.com takes no responsibility for loss incurred as a result of the content provided inside our Trading Academy. By signing up as a member you acknowledge that we are not providing financial advice and that you are making the decision on the trades you place in the markets. We have no knowledge of the level of money you are trading with or the level of risk you are taking with each trade.
The HowToTrade.com website uses cookies in order to provide you with the best experience. By visiting our website with your browser set to allow cookies, or by accepting our Cookie Policy notification you consent to our Privacy Policy, which details our Cookie Policy.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
"Join our Trade Together program and interact with us in real-time as we trade the markets together."

This website uses cookies
Complete Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, where every decision can lead to profit or loss, having a strategic edge is invaluable.
One such edge that price action traders often leverage is the concept of Fair Value Gaps (FVGs). In this blog post, we’ll explore what Fair Value Gaps are, why they matter, and how traders can harness them to build a powerful trading strategy.
What are Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) in Trading
Table of Contents
Fair value Gaps or FVG are the inner circle trader (ICT) trading concepts. According to him, Fair Value Gaps can be defined as an inefficiency in the delivery of price.
Learn more about ICT Fair Value Gap Interpretation .
Fair Value Gaps are anomalies in the market, signaling imbalances between buying and selling forces. These gaps manifest in a three-candle sequence on price charts, creating a distinctive pattern.
The psychology behind the fair value gap is that these gaps emerge due to inefficient price delivery.
The market returns to fill these gaps, presenting a valuable opportunity for Forex traders to execute their trades aligned with the movements of market makers or smart money.
Types of Fair Value Gaps
There are two types of fair value gap bullish and bearish FVG.
Bullish FVG
A bullish Fair Value Gap (FVG) forms when the market undergoes a dramatic shift from bearish to bullish, often with aggressive movements. This aggressive move breaks through previous key levels (lower highs) established during the bearish phase.
Without a change in market structure, the formation of a fair value gap is less reliable and not use FVG as a trading signal.
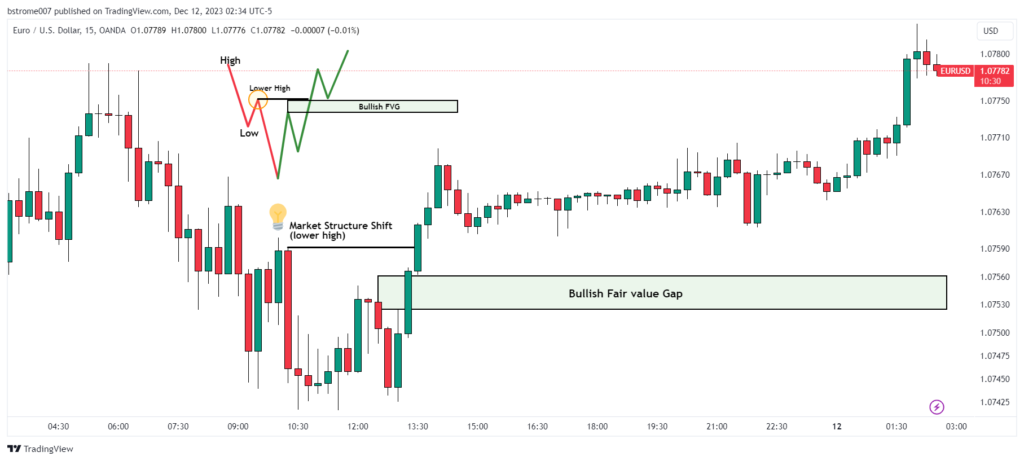
The EURUSD chart above illustrates the creation of a bullish fair value gap on December 12, 2023, at a 15-minute time frame. The chart indicates a shift in the market, marked by aggressive price movements transitioning from bearish to bullish, resulting in the formation of a bullish fair value gap or FVG.
Bearish Fair Value gap
In a similar vein, a bearish fair value gap (FVG) takes shape when the market experiences a significant shift from a bullish to a bearish state, typically accompanied by aggressive movements. This breaches prior crucial levels, such as higher lows established during the bullish phase.
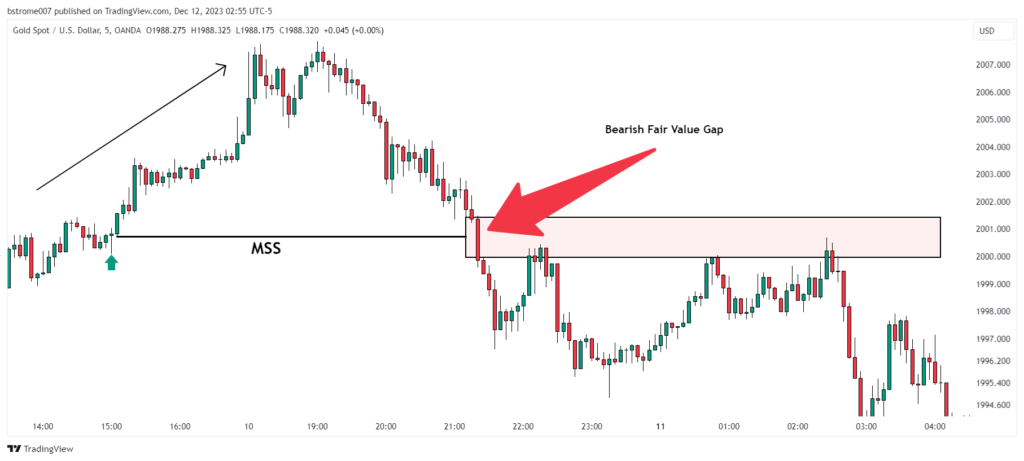
The XAUUSD (Gold/US Dollar) chart above reveals a bearish fair value gap on December 10, 2023, in a 5-minute time frame.
How to Find Fair Value Gap (FVG)
For finding a fair value gap or valid FVG find the steps explained below.
Market Structure Shif(MSS)
To identify a valid Fair Value Gap (FVG), the initial step is to detect a shift in market structure. This shift in market structure signifies a change in market sentiment, transitioning from bullish to bearish or vice versa.
Most of the time this market structure shift (MSS) is found near supply and demand zones .
. Big Candlestick with Large Body:
- Imagine a tall candle on your price chart, like a skyscraper compared to its neighbors. This is the first sign of a potential FVG.
2. Body vs. Wick Ratio:
- Look at the ratio of the candle’s body to its wicks (the thin lines above and below). Aim for a body size of around 70% or more compared to the wicks. A thick body indicates significant price movement.
3. Gap Above or Below Previous Candles:
- Now, check if the tall candle’s body creates a gap above or below the previous candles’ bodies. This gap represents a price range where no trading occurred, potentially hinting at a shift in market sentiment.
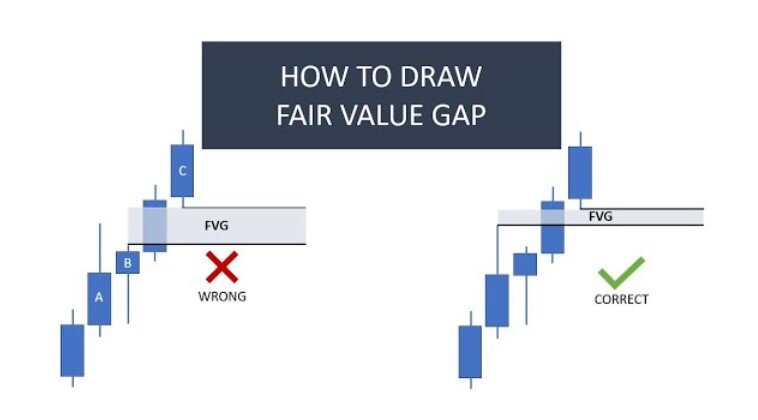
Checking Nearby Candlesticks:
Once you find the big candlestick, check the ones just before and after it. They shouldn’t fully cover the big one, but small overlaps are okay on the top and bottom. The fair value gap is the gap between the wicks of these nearby candlesticks.
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
Improving the text for clarity and coherence:
Trading a fair value gap involves more than simply identifying a three-candlestick pattern with a gap in the middle candle. It requires additional confluence factors for a comprehensive analysis. In the next section of this blog post, I will delve into the application of the ICT 2022 mentorship model to effectively navigate and trade fair value gaps.
ICT FVG Trading Strategy Component
ICT Kill Zones
Identifying Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) within specific time windows during major forex trading sessions, which ICT calls “kill zones,” is crucial. Pay attention to price action within the first 1-2 hours after the opening of both the London and New York sessions.
To delve deeper into these specific time windows, visit the official Inner Circle Trader website or refer to the detailed insights provided in this article.
Liquidity Sweep
Understanding market dynamics during ICT’s kill zones is crucial for informed trading decisions. Price action in these periods can be influenced by significant order flow, potentially impacting where liquidity resides.
By analyzing market context and observing price movements, traders can navigate these specific time intervals with greater awareness and manage their risk effectively.
Market Structure Shift (MSS)
The term “shift in market structure” denotes a change in market direction, transitioning either from a bullish to bearish sentiment or vice versa — essentially capturing the shift from an upward to a downward trend or from a downward to an upward trend.
If a fair value gap is formed after the Market Structure Shiftt (MSS) or a liquidity sweep within the ICT kill zones, it provides a high-probability trading setup that can significantly elevate your win rate.
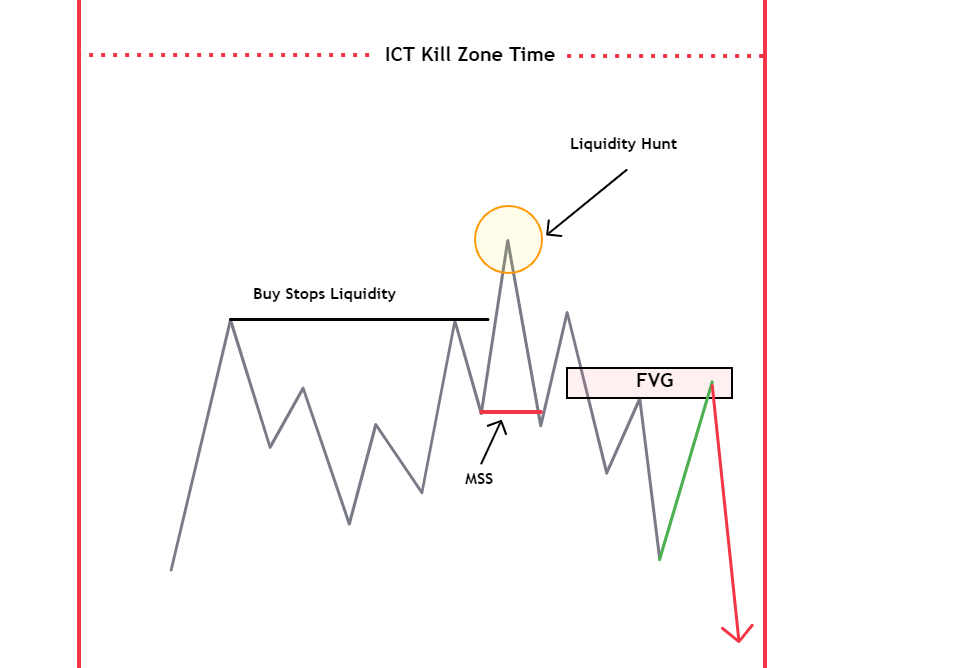
The diagram above illustrates the comprehensive model for trading Fair Value Gaps, combining all essential components, including time considerations, liquidity, stop-loss hunts, market structure shifts, and the Fair Value Gap itself.
This diagram is based on the ICT 2022 trading model.
- Recent Posts
- Dark Cloud Cover: A Guide to Trading This Bearish Candlestick Pattern - 26 December 2023
- Title: Piercing the Veil of Market Sentiment: The Piercing Pattern in Trading - 26 December 2023
- Bullish Marubozu: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading with Confidence - 26 December 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Powerful Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
Table of Contents
The fair value gap (FVG) trading strategy has become an increasingly popular approach among price action traders in recent years. This strategy aims to identify and capitalize on short-term inefficiencies or “gaps” in the market where buying and selling forces are imbalanced.
Download Free Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
What is a Fair Value Gap?
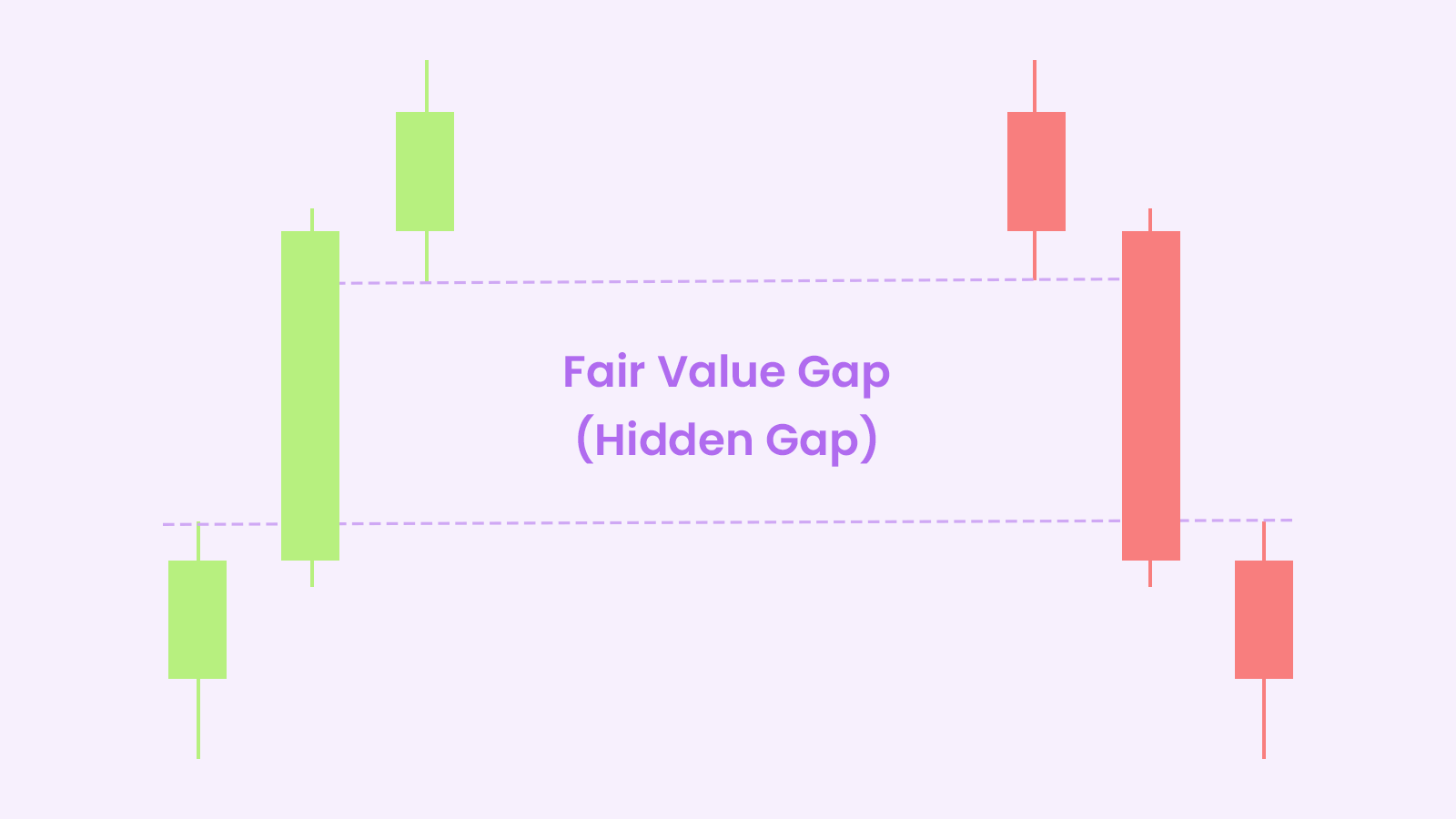
A fair value gap refers to a gap between the current market price and the estimated “fair” value of an asset based on its fundamentals. It typically occurs when there is a large, rapid price movement due to a market imbalance between buyers and sellers [1] .
Specifically, a FVG pattern consists of three candles on a price chart:
- Candle 1: A long bullish or bearish candle with a large range from high to low
- Candle 2: An even larger candle continuing the trend in the same direction
- Candle 3: A candle that does not share any common prices with Candle 1, leaving a “gap”
Fair value gap example
A FVG highlighted on a chart [2]
This gap between Candles 1 and 3 represents an imbalance between buying and selling pressure, creating a liquidity void. The assumption is that price will eventually return to “fill” this gap near the fair market value before continuing the overall trend.
FVGs can occur on any timeframe, from 1-minute charts up to daily or even weekly charts. They provide traders with high-probability short-term turning points to anticipate reversals or retracements.
Why Trade Using Fair Value Gaps?
There are several key benefits to using a FVG trading strategy :
- Identifies Imbalances : FVGs clearly highlight on a chart when buying/selling pressure causes short-term inefficiencies. This allows traders to easily spot market imbalances.
- High Probability : Statistics show price reversals tend to occur near FVGs around 70% of the time as the market moves to fill the liquidity void [1] .
- Precise Entries : FVGs indicate exact price levels for traders to target entries, creating very precise points of reference.
- Works on All Timeframes : The same principles apply to FVGs on 1-minute charts up to weekly charts, making this a versatile strategy.
- Simple Concept : Focusing just on the specific FVG pattern keeps analysis objective and simple compared to more complex indicators.
Overall, the FVG strategy provides a probabilistic approach that simplifies analysis. By using FVGs to anticipate short-term turning points, traders can precision-target entries and efficiently capitalize on price swings.
How to Trade Using Fair Value Gaps
Trading with fair value gaps follows three key steps:
1. Identify the FVG Pattern
The first step is visually identifying the characteristic FVG pattern on the chart of your chosen market and timeframe.
You’ll want to see a long bullish or bearish candle (Candle 1), followed by an even larger continuation candle (Candle 2), completed by a third candle (Candle 3) which leaves a gap from the first candle’s range.
If using charting software, you can apply a FVG indicator which will automatically highlight on your chart where these patterns occur, making them easier to spot.
2. Target Entries Near the Gap
Once you detect a FVG pattern, the gap level itself represents an ideal area to target entries for a high-probability reversal trade.
You’ll be looking to enter a short trade targeting a move back up to fill the gap after a down-move. Conversely, enter long trades aiming to fill FVG gaps created after upside moves.
Since you’ll be trading pullbacks/retraces, consider using other analysis like support/resistance or trendlines to fine-tune entries and stop losses.
3. Close at Opposing Levels
You can close FVG reversal trades as soon as price reaches the “fair value” gap level, taking quick profits.
However, more patient traders will aim for a risk/reward ratio of at least 1:2 by targeting opposing levels to close. For example, they may close short trades once price reaches former support zones or long trades at former resistance.
This allows capturing larger gains if the market continues reversing beyond just filling the liquidity void. Just be sure to trail stops to lock in profits.
Real Chart Examples
To see how it works in real market conditions, let’s analyze example FVG setups and trades:
Gold Futures 4hr Chart
Gold futures FVG example
Entering short on gold futures using the FVG strategy [2]
On this gold futures 4hr chart, a large bearish move created a FVG buy imbalance, highlighted by the shaded blue zone.
We can target short trades aiming for price to return to “fair value” near $1815. The initial 3:1 risk/reward is very favorable for this type of reversal setup.
EUR/USD Daily Chart
EUR/USD FVG
Here we see a bearish FVG pattern on the daily EUR/USD forex pair after a strong down move. This presents an area around 1.064 to target long bounce trades, with a stop under the low and target up near horizontal resistance.
These examples demonstrate how traders across different markets can apply the exact same FVG rules and concepts.
Optimizing the FVG Strategy
While the underlying concept is simple, there are several ways to further optimize trading with FVGs:
- Time FVGs with momentum – Enter trades shortly after price reverses near the gap rather than anticipating. This timing aligns entries with momentum.
- Focus on wider gaps – The bigger the buying/selling imbalance, the higher probability the gap gets filled after a reversal.
- Use multiple timeframes – Zoom into shorter timeframes to refine entry and stop loss levels near gaps identified on higher timeframes.
- Combine with other indicators – Corroborate trades using complementary indicators like RSI, MACD histogram, Stochastics, etc.
- Have a trading plan – Quantitatively define optimal risk/reward, win rate targets and use sound risk management per your trading plan rules.
A systematic, plan-based approach takes the FVG strategy to the next level.
Check our advanced Forex Scouts Gold V9 Robot
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy Risks and Challenges
Of course, like any trading method, the FVG strategy presents risks to be aware of.
- FVG gaps may not get filled – There’s still a chance price continues trending right through a gap without filling it. Use stop losses on every trade.
- Requires patience – Traders must wait for perfect FVG setups and resist overtrading.
- Not suited for all markets – Lower liquidity instruments with wider spreads pose challenges.
Additionally, markets don’t always move in clearly defined patterns. Traders may struggle to consistently and accurately identify precise FVG levels, reducing the strategy’s effectiveness.
Nonetheless, the high-probability nature of FVGs makes persisting through these challenges worthwhile for most short-term traders.
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy Conclusion
In summary, the fair value gap trading strategy offers a probabilistic tactic to spot and take advantage of short-term mispricings and liquidity voids in the market.
FVGs provide very clearly defined trade setups that occur across all markets and timeframes. By combining the simple FVG rules with savvy analysis and risk management, traders can gain an edge with this powerful approach.
While trading carries inherent risks, the odds typically favor those patient and skilled enough to effectively leverage gaps in market fairness.
Related Posts
I am a highly regarded trader, author & coach with over 16 years of experience trading financial markets. Today I am recognized by many as a forex strategy developer. After starting blogging in 2014, I became one of the world's most widely followed forex trading coaches, with a monthly readership of more than 40,000 traders! Make sure to follow me on social media: Instagram | Facebook | Linkedin | Youtube | Twitter | Pinterest | Medium | Quora | Reddit | Telegram Channel
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 66.30 % of retail investors lose their capital when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
- Pux.LanguageSelector.cs-cz
- Pux.LanguageSelector.it-IT
- Pux.LanguageSelector.pl-PL
What is Fair Value Gap and how to use it in trading?
Price action traders love them and smart money traders also can't get enough of them. In fact, there are few price pattern to that price reacts so strongly, offering a good risk/reward ration. So today, let's take a look at how fair value gaps are created, how to recognize them and most importantly - how to trade fair value gaps.
Price and candlestick formations are the building blocks of quality technical analysis and price action. They are relative easy to remember which makes them an ideal help for beginner traders to orient better in charts and plan their trades. The more advanced traders then use patterns to build their advanced trading strategies, such as Smart Money.
Today's article delves into one of the most popular price patterns: the fair value gap. We'll explore what this pattern entails and how to effectively trade it.
What is the Fair Value Gap?
Fair Value Gaps are price jumps caused by imbalanced buying and selling pressures. These gaps are sometimes called Price Value Gaps, or Singles, and you may also encounter the term imbalance . In this article, we will use the term Fair Value Gap (also referred to as FVG).
Fair Value Gap indicates a market situation where the supply of buyers is significantly higher or lower than the demand of sellers. This can cause the price of an instrument to move quickly towards higher supply or lower demand. The Fair Value Gap then shows the point in the chart where this rapid price movement occurred.
FVGs can be seen on charts as large candles that are not completely covered by the wicks of adjacent candles. The FVG formation consists of three candles and there are bullish and bearish FVGs. In simplified terms, we can illustrate them as follows:
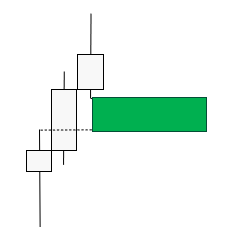
Fair Value Gaps represent a kind of anomaly, an imbalance in the market, a situation where the price has deviated from fair value. And since the market tends to return to fair value, it is possible to take advantage of this fact.
Price action traders rely on FVG to:
The likelihood that the market will bounce back to fill the FVG before continuing in the direction it was originally heading.
Once the FVG is filled, they are counting on the trend to continue in the direction of the covered gap.
Boost your trading knowledge with Purple Academy!

When does the Fair Value Gap form?
The situation where the market price deviates from the normal value, thus creating a Fair Value Gap, is not accidental. Therefore, below we describe the scenarios in which a FVG can be expected to form.
Important events
Major news that causes a sudden change in market sentiment can lead to a FVG. Such news is, for example, an unexpected increase in interest rates. This increase may then trigger a spike in the domestic currency, which will result in an FVG. There are many events that can cause significant market movement. These are not only macroeconomic data, but also political news, such as information about the outbreak of war, geographical events such as earthquakes, etc.
The publication of corporate economic results
If a company's results come as a significant surprise, there will be a rapid price movement. This may then be reflected in the price of the stock index of which the company is a part, which may then form the FVG.
Large institutional deals
Large institutional trades can also lead to FVGs. For example, if a large hedge fund buys a large number of shares, this can cause a gap in the market. Or if a central bank starts intervening in the market and buying (or selling) domestic currency, etc.
The publication of important news is often used by big traders to manipulate the market. This results in the creation of a gap, which is then quickly filled. How to read the moves of big traders is discussed in our article on Smart Money and trading using order blocks .
Don’t become a liquidity for someone else, use our Purple Strike indicator
Enter the market when the gap is filled. For precise entry, wait for trade confirmation on the lower timeframe. Again, the FVG can be used for confirmation. Or you can use our trend indicator Purple Strike .
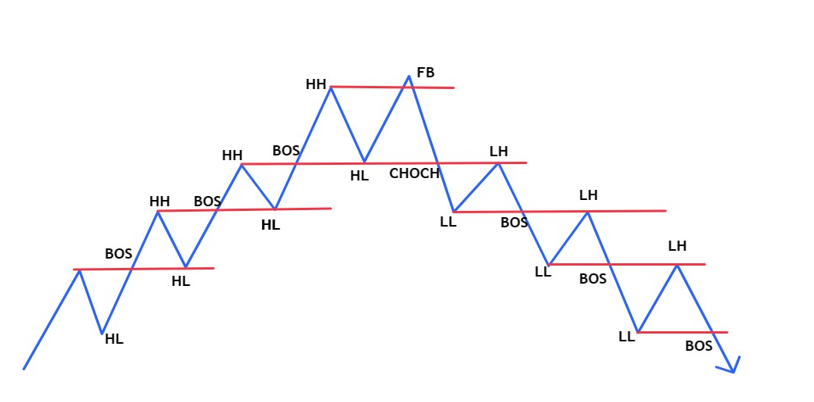
How to Trade the Fair Value Gap
Because these gaps represent an imbalance, Fair Value Gaps often fill up. We can use this knowledge to accurately determine the price level where we want to enter a trade.
Filling the gap
With this strategy, it is important to determine what the current trend is. This should be determined on a higher time frame, such as weekly, daily, or H4. A healthy uptrend produces a higher high (HH) and higher low (HL), while a downtrend produces a lower high (LH) and lower low (LL).
If the HH breaks in an uptrend or the LL breaks in a downtrend, a break of structure (BOS) is formed and the trend is likely to continue.
If a break of HL occurs in an uptrend to the downside, a change of character (CHOCH) occurs and the chance that the uptrend could reverse and start to decline increases. In a downtrend, the analogy is then reversed, i.e. when a break of the lower high (LH) to the upside increases the chance that the market decline could stop and the market could start to rise. An example is shown in Figure 2.
Sometimes, however, false breaks can also occur. These are then used to lure you into a trap in order to collect liquidity. Read the article about Smart Money and liquidity withdrawal .
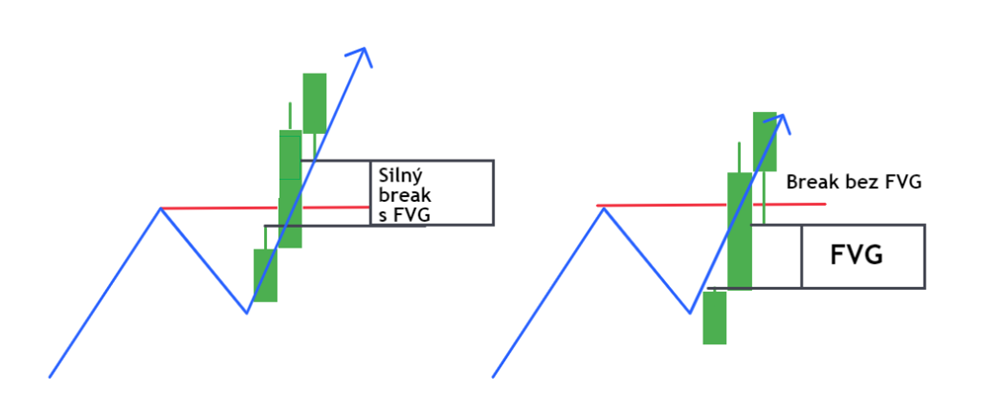
It is important to note the points where the BOS or CHOCH break occurs. If the break is accompanied by the formation of a FVG, then a strong impulsive move has occurred and the price is likely to continue in the direction of the FVG that formed the break. In such a case, a patient trader will wait for the moment when the broken line is returned (and therefore the gap that was formed on it is filled), and then consider entering in the direction of the filled gap.
If the break occurs such that the break line is not inside the gap, the situation is less reliable for the gap to act as support (uptrend) or resistance (downtrend). An example of a strong break with FVG and a less reliable break without FVG in a bullish trend is shown in the next figure.
In the case of a bearish trend, this is analogous:
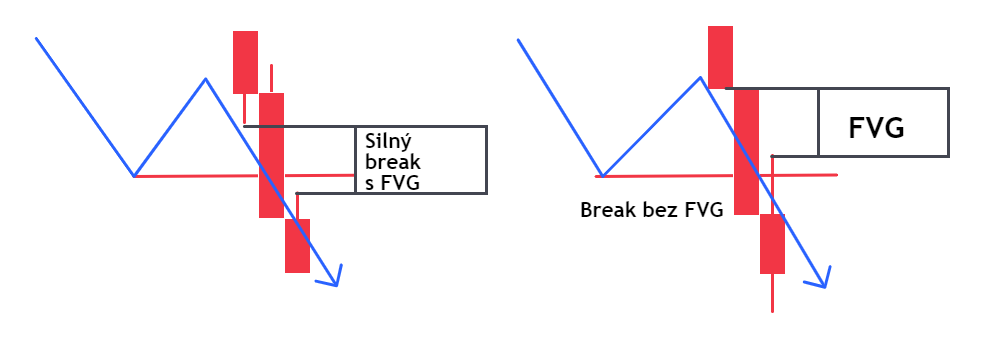
The idea is that the break of support or resistance should be inside the FVG , which has a visibly longer middle candle than the surrounding candles. These breaks indicate that they were made with impulsive force and tend to be more reliable. Therefore, it is preferable to focus on these situations.
We will show this practically in the following example, where we have the DJ30 instrument on the H4 chart.
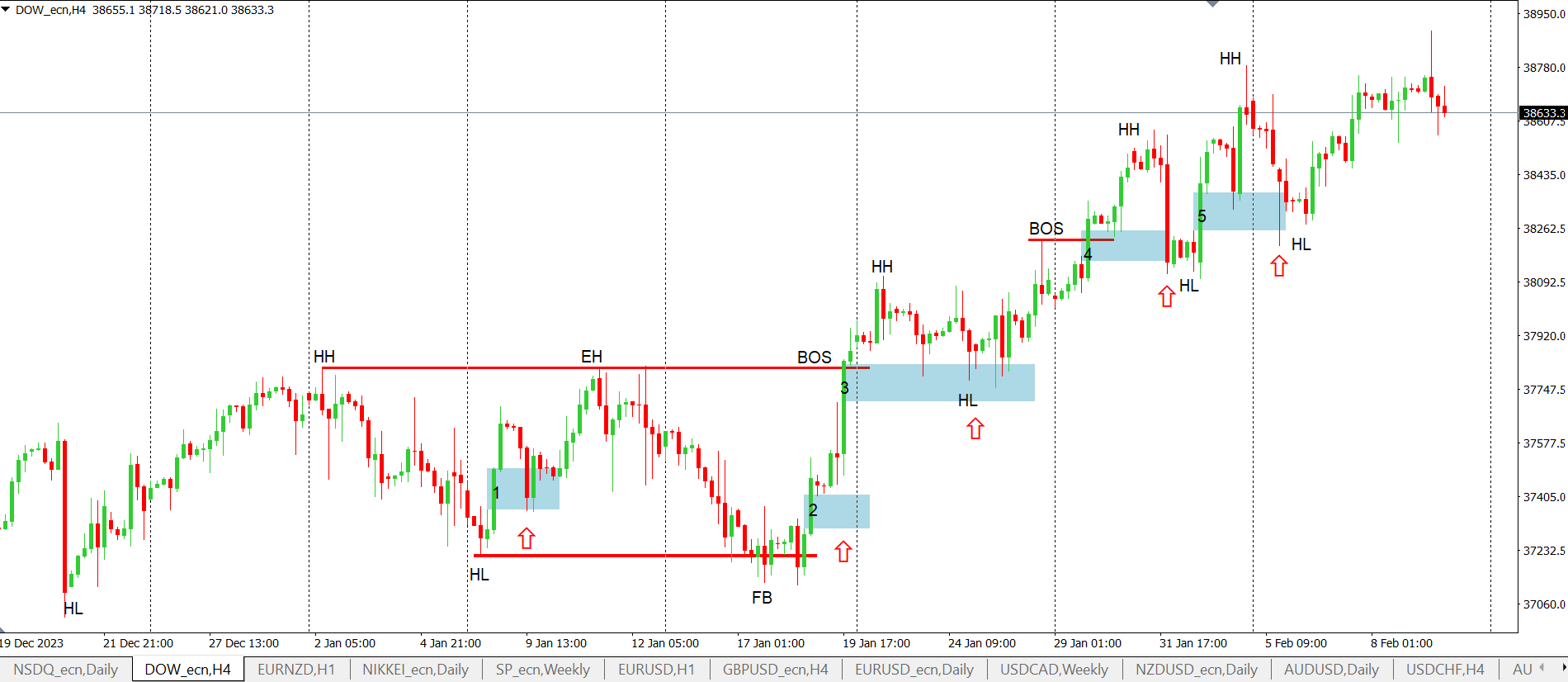
Dow Jones index on H4 chart
We have identified a growing trend in which several FVGs have been formed. In situation 3 and 4, an FVG has been formed with the formation of a BOS structure break in an uptrend. These are situations where it would be possible to enter a long trade in accordance with the previous theory. Then in situations 1, 2 and 5 the FVG was formed inside the uptrend structure.
We can also see that the gap was not always completely filled, so in this case the trade would not have occurred. Gaps 1, 4 and 5 were later filled (see arrow). Then in situation 3 there was a partial filling. In the case of the gap created in point 2, there was no gap filling at all.
You may also notice that when a gap is filled, it may also be 'overshot'. This is because gaps serve as indicators where liquidity is collected in the form of pending stop losses. Liquidity collection theory teaches that smart money will first collect this liquidity and only then will the market turn.
In the next chart we have examples with bullish and bearish FVG, a change in market character (CHOCH) and a BOS with a downtrend.
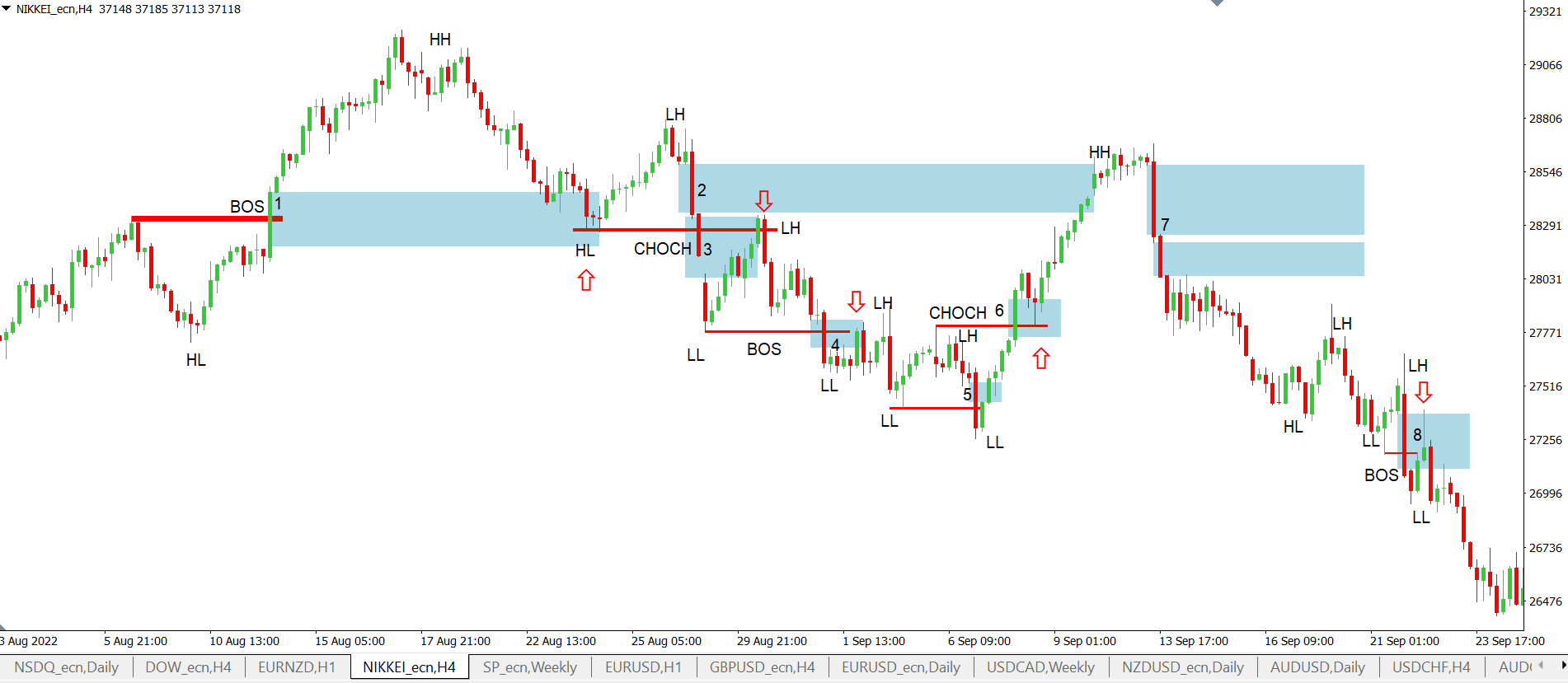
At FVG 1, the BOS is an uptrend, which was later tested and the price bounced up. At FVG 3, the previous higher low (HL) was broken, so there was a change in market character (CHOCH) which was confirmed by the bearish FVG, which is a strong confirmation. This was later filled and a short could be entered. Candle 4 offered a BOS (break of the lower low, LL) again with an FVG which was later retested and it would be possible to enter short again.
And what about candle 5? This candle did produce an FVG, but this FVG did not break the previous low. The low was indeed broken by a long candle, but the following candle closed above it. So, there was a breakout here, but no FVG (recall Figure 4). Thus, there was no BOS with a valid FVG, but a false break .
Then at point 6, there is again a breakout with a change in market character (CHOCH) as the previous lower high was broken to the upside. It would therefore be a possible long entry. Then the gap from candle 2 was filled and price then reversed down.
The gaps on candle 7 were not filled. Then at 8, the downtrend was confirmed by a lower high and lower low, and since there was a BOS of the lower low with the help of FVG, on retest, a short entry would be valid.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of FVG?
Advantages :
If a trader can trade FVG, he can achieve a good risk/reward ratio.
FVG can be easily identified in a chart.
This strategy can be used on a wide range of assets, including stocks, commodities and currencies.
It works on all time frames.
Disadvantages :
Sometimes gaps don't fill and sometimes can get "overshot”. This can cause uncertainty.
FVGs represent a form of liquidity collected by smart money. Therefore, sometimes the price can go far against the direction of the gap.
More tips for trading with FVG
- Use a combination of indicators: when trading FVG it can be useful to use a combination of indicators. For example, our Purple Gap indicator is an important tool.
- Use stop loses: When trading FVG, don't forget to use stop loses. This will help protect your profits and limit your losses.
- Wait for Confirmation: Before entering a trade, it is important to wait for confirmation that the market will indeed continue in the direction of the gap after the FVG is filled. This can be done by looking for a reversal bullish or bearish candle (such as engulf) on a lower timeframe after the gap is filled, or you can use our Purple Strike indicator.
- Liquidity Pick: If the gap is close to an area where liquidity could be picked (for example, FVG is near the previous day's high or low), wait for liquidity to be picked. Only then enter the trade.
A guide to candlestick formations and price patterns

Recommended articles

Newsletter subscription
What's new in Purple Trading, Market Shot, market analysis and articles...

CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 66.30 % of retail investors lose their capital when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Any opinions, news, research, analysis, prices, or other information contained on this website is provided as general market commentary, and does not constitute investment advice. L.F. Investment Limited. will not accept liability for any loss or damage, including without limitation to, any loss of profit, which may arise directly or indirectly from use of or reliance on such information.
The content on this website is subject to change at any time without notice, and is provided for the sole purpose of assisting traders to make independent investment decisions. L.F. Investment Limited has taken reasonable measures to ensure the accuracy of the information on the website, however, does not guarantee its accuracy, and will not accept liability for any loss or damage which may arise directly or indirectly from the content or your inability to access the website, for any delay in or failure of the transmission or the receipt of any instruction or notifications sent through this website.
At this time L.F. Investment Limited cannot and will not accept clients from outside European Economic Area and from Belgium, Switzerland and USA. You need to be 18 years old or legal age as determined by the laws of the country where you live in order to become our client.
Our payment providers are TrustPay, a.s. authorised and regulated by the National Bank of Slovakia and Emerchantpay Ltd. which is authorised and regulated by the Financial Services Authority (FCA) of the United Kingdom. Our Electronic money institution is Cardpay authorized by Central Bank of Cyprus.
Purple Trading is a Cypriot national trademark (no. 85981), National UK trade mark (no. UK00003696619) and European Union trade mark (no. 018332329) owned and operated by L.F. Investment Limited, 11, Louki Akrita, CY-4044 Limassol, Cyprus, a licensed Cyprus Investment Firm regulated by the CySEC lic. no. 271/15. The company is legally obligated to follow all laws of Cyprus and rules and conditions of its CySEC license. The subsidiary of L.F. Investment Ltd, LFA International Ltd., Aiolou & Panagioti Diomidous 9, Katholiki, 3020, Limassol, Cyprus, registration number: HE422638 is responsible for card processing.
CFDs with underlying asset a virtual currency pair are complex, extremely risky, and usually highly speculative and entail a high risk of losing all the invested capital and therefore are not appropriate for all investors. The values of virtual currencies values are subject to extreme price volatility and therefore may result in significant loss over a short period of time. Clients should not engage in trading in CFDs with underlying asset a virtual currency pair unless they have the necessary knowledge in this specific product; or if they can bear the loss of the entire invested amount. For more details please see the Risk Warnings and Disclosures .
- Terms and Conditions
- Terms of use for Strategies
- Client Complaints policy
- Conflicts of Interest Policy
- Client Classification policy
- Investor Compensation policy
- ETF Addendum Terms
- Order Execution policy
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Risk Warnings and Disclosures
- Collecting personal information
- Politically Exposed Person
- Investment risks categories

How to Trade Fair Value Gaps
- December 7, 2023
Optimus Futures
The article on Fair Value Gaps is the opinion of Optimus Futures, LLC.

- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are price jumps due to imbalanced buying and selling pressures, viewed by traders as opportunities amidst market uncertainty.
- FVGs can be spotted on charts as large candles not fully overlapped by the wicks of neighboring ones, differing from small gaps that don’t show significant buying/selling imbalances.
- Trading strategies for FVGs involve buying/shorting the gap, using FVGs as support/resistance levels, and implementing various indicators and stop losses.
What Are Fair Value Gaps?
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) as it’s often referred to, is basically a gap that forms when the buying and selling forces are wildly out of balance .
What causes this mismatch? Well, it could be a ton of things – a major news event, the release of certain economic data, or even hefty trades by big institutions. Does that make sense?
Let’s talk about how price action traders view Fair Value Gaps or FVGs. They often see these as chances to jump into the market, banking on the likelihood that the market will swing back to cover the gap before it carries on in the direction it was originally heading.
But here’s a word of caution – FVGs can sometimes act like pitfalls . There might be instances where the market doesn’t fill the gap and instead continues on its original path.
ALSO READ | How to Trade Price Gaps
But What Does “Fair Value” Even Mean? Good question. To really get how FVGs form, it helps to understand the idea of ‘fair value.’
Now, fair value is the price point where a security would be trading if the buying and selling forces were perfectly balanced. But when there’s an imbalance , that’s when the market price begins to drift away from this fair value.
In an FVG scenario, the market price will create a gap, either upward or downward, to a level that’s closer to the fair value.
Why does this happen? It’s because the imbalance in buying and selling pressures will eventually find a way to correct itself.
What Do FVGs Tell You?
FVGs indicate that there is a significant imbalance in buying and selling pressure . This imbalance can be caused by a number of factors, such as:
- News events: If there is a major news event that causes a sudden change in market sentiment, this can lead to an FVG. For example, if there is a surprise interest rate hike, this could cause the market to gap down.
- Economic data releases: Similarly, if there is a major economic data release that causes a sudden change in market sentiment, this could lead to an FVG. For example, if GDP growth is lower than expected, this could cause the market to gap down.
- Large institutional trades: Large institutional trades can also lead to FVGs. For example, if a large hedge fund is buying a large number of shares of a stock, this could cause the market to gap up.
This kind of uncertain environment can actually pave the way for opportunities for traders, particularly those who rely heavily on price action .
But like everything else in trading, it’s crucial to keep in mind the risks involved. You know what they say, right? “No risk, no reward”, but always be mindful of that risk part.
How To Identify Fair Value Gaps Gaps (and what are not FVGs)
FVGs can be identified on a chart by looking for a large candle whose neighboring candles’ upper and lower wicks do not fully overlap the large candle.
The space between the wicks of the neighboring candles is the FVG.
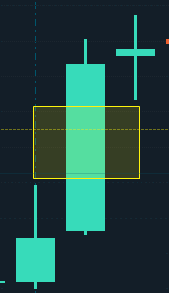
It is important to note that not all gaps are FVGs. For example, if there is a gap between two candles that are both very small, this is not an FVG.
This is because the imbalance in buying and selling pressure is not significant enough to create an FVG.
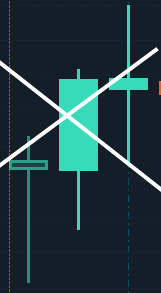
Here are some of the key characteristics of FVGs:
- They are created by a significant imbalance in buying and selling pressure.
- They are often large gaps, spanning multiple candles.
- They can be found on all time frames, but they are most commonly seen on daily and weekly charts.
- They can be filled or not filled.
Basically, you’re on the lookout for a large candle on a chart that’s not fully covered by the wicks of its neighboring candles – that space in between is your FVG.
Remember, not every gap is an FVG. For instance, a gap between two tiny candles isn’t one, because the buying and selling imbalance isn’t enough to make an FVG.
Key things to remember about FVGs:
- they’re formed by a significant buying and selling imbalance,
- they’re usually big spanning multiple candles, they’re found on any time frame (though mostly on daily and weekly charts), and
- they can either be filled or remain unfilled.
Strategies for Trading Fair Value Gaps
There are a number of different strategies that can be used to trade FVGs. Some common strategies include:
Buying the gap: This is the most common strategy for trading FVGs. The idea is to buy the market at the price level of the gap, and then sell it once the market retraces back to the gap.
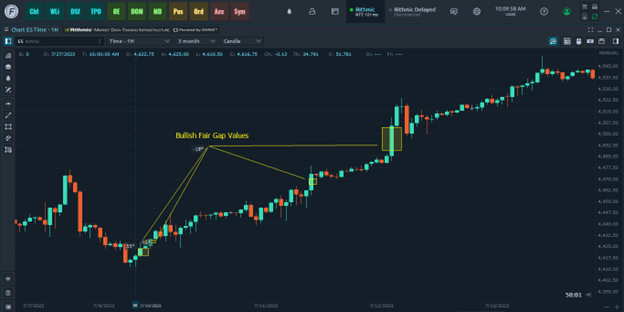
ES – 1-hour chart 7.7 to 7.13.23.
In this example, a trader could have used multiple exit strategies to take profits.
Shorter term traders might have taken a measured move approach, waiting for the position to reach a certain percentage of the amount risked (e.g. 2-to-1 reward/riask), Longer term traders might be aiming at the 4630.00 (March 2022) high.
Shorting the gap: This strategy is less common, but it can be profitable if done correctly.
The idea is to short the market at the price level of the gap, and then cover the short once the market retraces back to the gap.
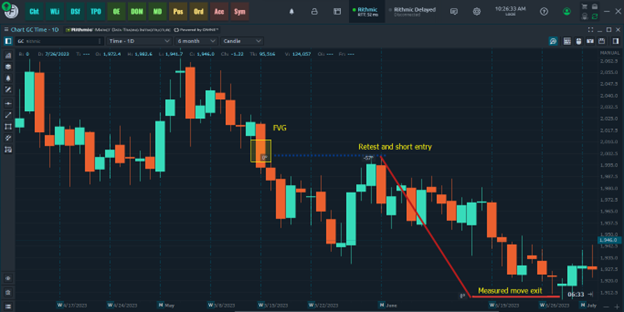
GC Daily Chart 4.11 to 7.4.23. Chart illustrates the FVG, retest, and profit target using the measured move method.
Using FVGs as support or resistance: FVGs can also be used as support or resistance levels.
For example, if a market gaps up and then retraces back to the gap level, this level can often act as support in the future.
Additional Tips for Trading FVGs
- Use a combination of indicators: It is often helpful to use a combination of indicators to trade Fair Value Gaps. This will help to confirm the trade and reduce the risk of false signals.
- Use stop losses: It is important to use stop losses when trading Fair Value Gaps. This will help to protect your profits and limit your losses.
- Wait for confirmation: Before entering a trade, it is important to wait for confirmation that the market is actually going to retrace back to the gap. This can be done by looking for a bullish or bearish reversal candle at the gap level.
- Be patient: Trading Fair Value Gaps can be a patient game. It is important to be patient and wait for the right trade before entering.
The Bottom Line
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are price jumps that happen when buying and selling pressures are not balanced, caused by things like big news, economic data releases, or large institutional trades.
Traders see these gaps as a sign of market uncertainty and potential opportunities.
However, they can also be risky, as the market might not always cover the gap. You can spot FVGs on a chart as large candles not fully overlapped by the wicks of their neighbors.
Not all gaps are FVGs; small gaps, for example, do not signal a significant buying and selling imbalance.
When trading FVGs, common strategies include buying or shorting the gap, and using FVGs as support or resistance levels.
It’s also advised to use a mix of indicators, stop losses, wait for confirmation, and be patient when trading FVGs. Understanding these can help you navigate the market better, but always consider the risks.
Trading in futures involves a significant risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results.
Subscribe to the Futures Trading Newsletter
- Trading Tips and Strategies
- Weekly Market Updates
- Platform Tutorials
- Free Trade Setups
Looking for content on something specific?
What Optimus Customers are Saying ...
Recent platform updates, recent blogs.
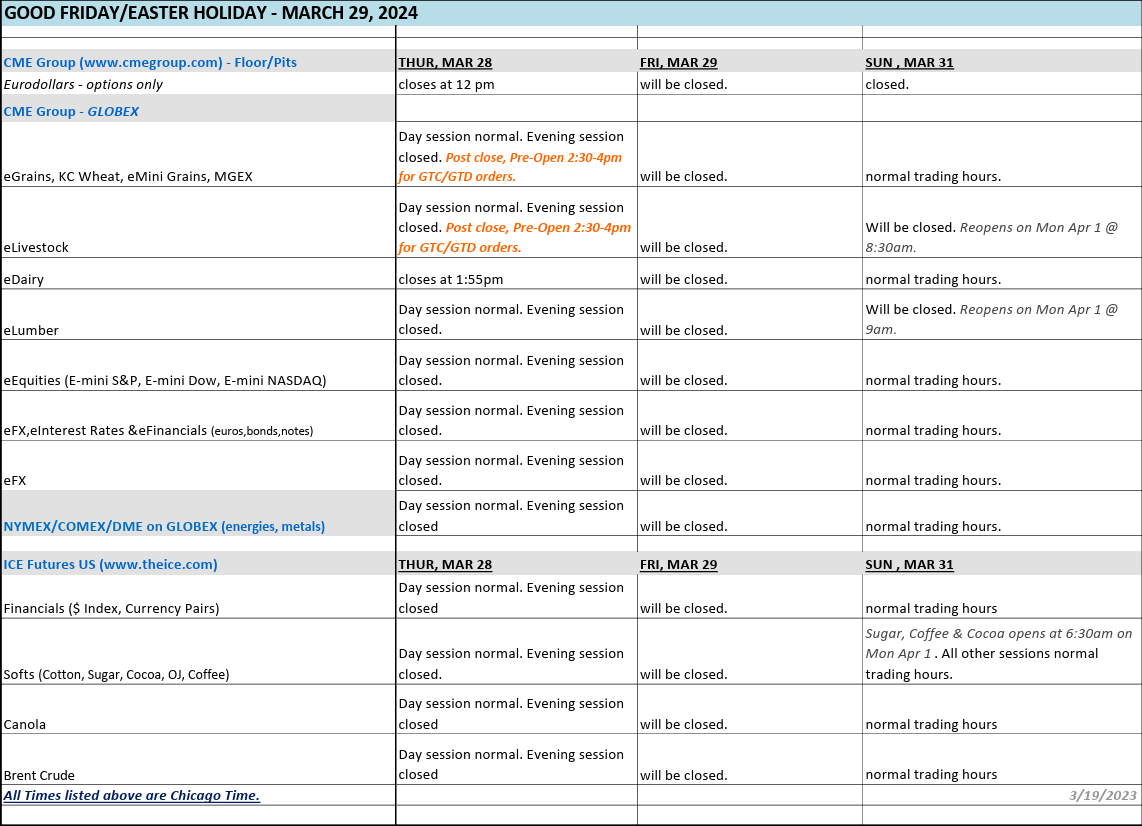
NOTICE: Good Friday & Easter Holiday Schedule – March 29, 2024
5 Best Volume Indicators on TradingView For Day Trading
How To Use The Anchored VWAP on TradingView
Related articles.

4160 NW 1st Avenue Suite 17 Boca Raton, FL 33431
Copyright © 2024 Optimus Futures – All Rights Reserved
This material should be viewed as a solicitation for entering into a derivatives transaction. Trading futures and options involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. The risk of loss in trading commodity interests can be substantial. You should therefore carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your financial condition.
The placement of contingent orders by you or broker, or trading advisor, such as a “stop-loss” or “stop-limit” order, will not necessarily limit your losses to the intended amounts, since market conditions may make it impossible to execute such orders. The high degree of leverage that is often obtainable in commodity interest trading can work against you as well as for you. The use of leverage can lead to large losses as well as gains. Optimus Futures, LLC is not affiliated with nor does it endorse any trading system, methodologies, newsletter or other similar service. We urge you to conduct your own due diligence.
If you are going to engage in any trading activity with Futures on Virtual Currencies including Bitcoin, please view NFA & CFTC advisories providing more information on these potentially significant risks.
- Full Risk Disclosure
- Terms and Conditions
- Micro Futures Contracts Risk Disclaimer
- Bitcoin and Virtual Currency Risk Disclosures
- Privacy Policy / Legal
What is Fair Value Gap (FVG) Trading Strategy | GUIDE
Unlock the secret to Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading. Explore market inefficiencies, discover profit potential, and master risk management. Whether you're new to trading or a seasoned pro, FVG can be your path to exciting opportunities!
Welcome to the world of Fair Value Gaps or FVGs as they're commonly referred to, a concept that can help you improvise your trading prowess. In this blog, we will simplify FVG, making it easy to understand and use in your trading strategy.
Why is this important?
Trading can be challenging, and traders are always on the lookout for strategies or concepts that can help them trade these markets. FVG is one such concept that has gained popularity in recent years. It's a concept that helps traders identify market inefficiencies or imbalances and make use of them.
Upon reading this blog, you'll have a clear grasp of what FVG is, how it works, and how you can use it to your advantage in trading through some uncertain market conditions. So, let's dive in and demystify the concept of Fair Value Gaps.
What is Fair Value Gap (FVG)?
At its core, FVGs could be thought of as a price magnet. It's a concept that helps traders identify moments when the market is a bit out of balance, creating opportunities for profit.
Think of FVG as a temporary imbalance in the market , where buying and selling are not equal. This imbalance often occurs after a significant price move.
Illustrating the Concept
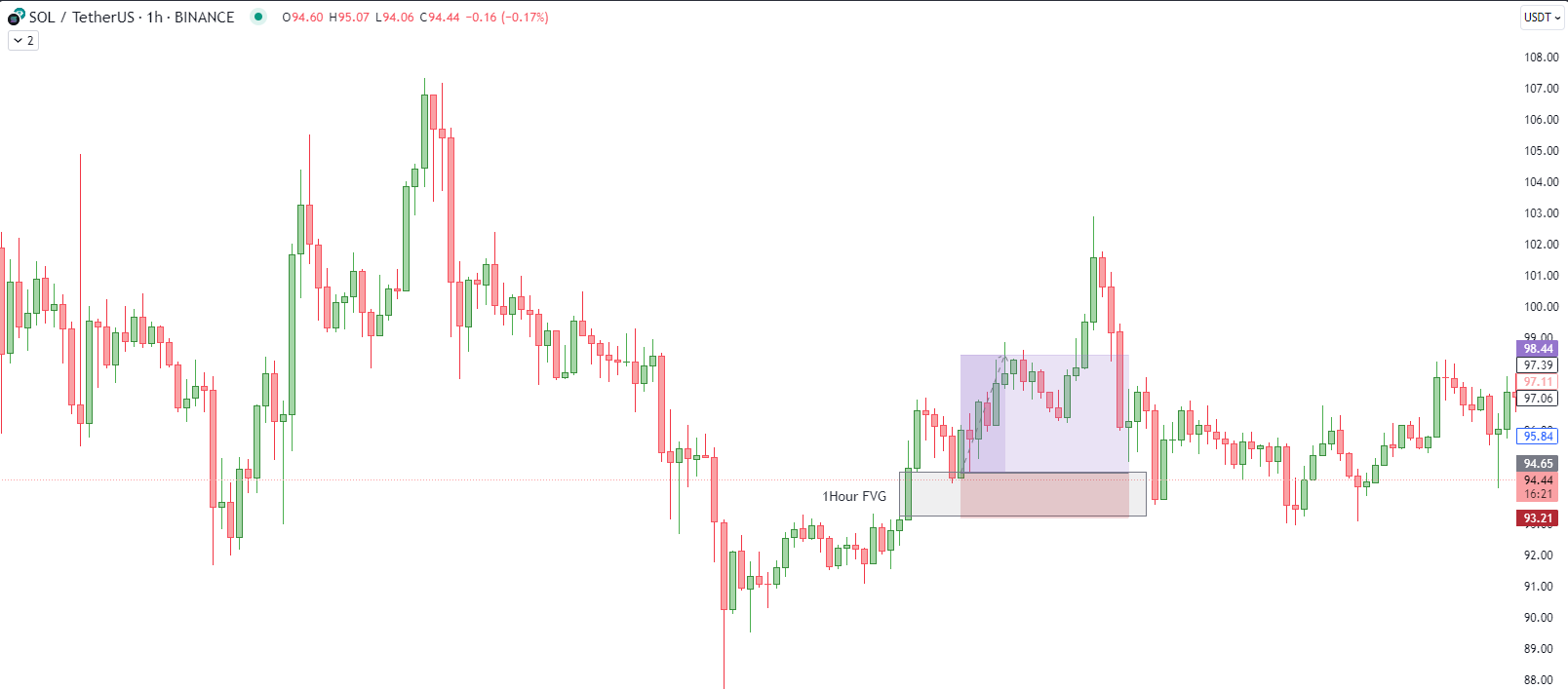
Let's visualize this with a simple diagram. Picture a candlestick chart representing a market's price movement. Suddenly, there's a big jump in price, creating a gap. This gap is the Fair Value Gap. It's the space between the candle prior to the impulse and the next candle after the said impulse .
Meet Alice and Bob To make it relatable, let's introduce Bob who's a passionate FVG trader. He opens his charts and sees a FVG on 1 Hour timeframe. He sets a long order at the end of the FVG and stops below the other end of the FVG as shown below.
He then waits patiently allowing price to retrace back to his pre-defined entry and he takes profits at some arbitrary region. Following a pre-defined entry and exits whether that's a Stop Loss or Take profit allows Bob to not seep any emotion into his trading ensuring proper risk management.
Be like Bob, anon. Risk management is much more important than where you enter - CryptoCred
How Does FVG Trading Work?
Now that we've grasped the basic idea of what FVG is, let's dive deeper into how FVG trading works.
- Market Inefficiencies and Imbalances The trading world, inefficiencies and imbalances occur when there's an unequal distribution of buying and selling pressure. This can happen for various reasons, such as unexpected news, large institutional trades, or simply due to market psychology.
Identifying Fair Value Gaps
Now that we understand the principles behind Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading, it's crucial to know how to identify these gaps in the real world of trading. This section will walk you through the methods of spotting FVG, including both manual and indicator-based approaches.
How to Identify FVG Identifying FVG is like having a treasure map and recognizing the "X marks the spot." Here's how traders can do it:
- Manual Method: Some traders prefer the hands-on approach. They scan through price charts, looking for a specific pattern called the " triple-candle pattern ." This pattern involves a large candle with the previous and subsequent candles' highs and lows not fully overlapping the large candle. The space between these wicks is the Fair Value Gap. It's like searching for hidden clues in a puzzle.
- Indicator-Based Method: For those who prefer a more automated approach, there are FVG indicators available. These indicators are like having a treasure detector. They highlight Fair Value Gaps automatically on the trading chart, making them easier to spot. It's a bit like having a guide to point you in the right direction.
To make things even clearer, let's look at some real trading charts with actual Fair Value Gaps highlighted.
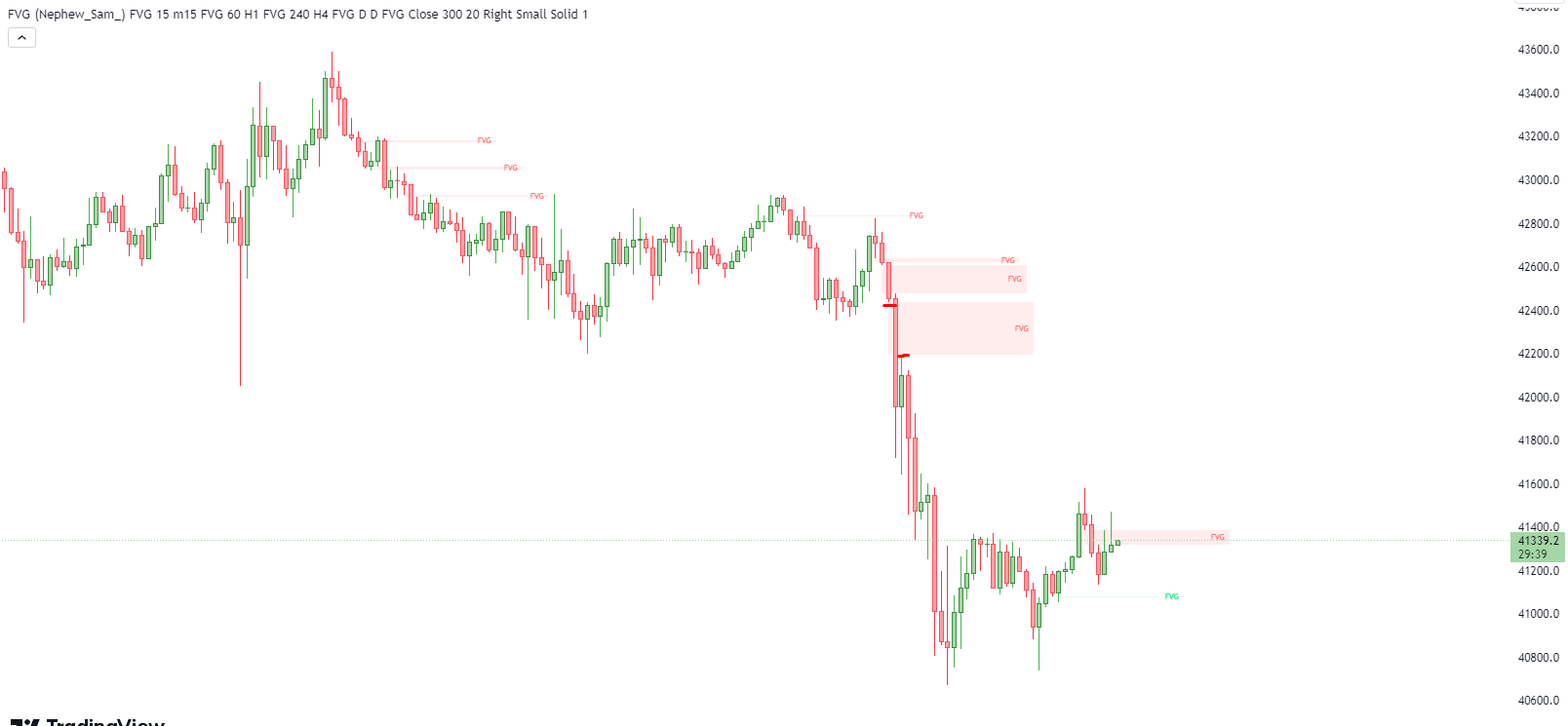
In this chart, we can see a Fair Value Gap highlighted between the wicks of the large candle via an FVG Indicator .
Identifying Fair Value Gaps is your first step in navigating the world of FVG trading. Once you've identified them, you can start planning your trading strategy to capitalize on these market imbalances.
FVG Trading Strategy
Now that we've learned how to identify FVGs, it's time to explore how to turn this knowledge into a successful trading strategy. In this section, we'll describe the basic steps involved in an effective FVG trading strategy, highlight the importance of discipline, and discuss essential risk management techniques.
Steps in FVG Trading Strategy
- Identification: Identify a Fair Value Gap on a trading chart, either manually or with the help of an FVG indicator.
- Observation: Once spotted, observe the market carefully. Pay attention to the direction of the prevailing trend.
- Wait Patiently: Wait for the price to revert back towards the Fair Value Gap, signaling the clearing of the imbalance.
- Entry: When the time is right, enter a trade. If the FVG is created during an upward move, consider a long position. If it forms during a downward move, think about a short position.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Exit: When the market moves in the desired direction and the imbalance is cleared, exit the trade and take your profits.
Risk Management Techniques
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Think of these as your safety nets. They automatically sell your position if the market moves against you beyond a certain point, limiting your losses.
- Position Sizing: Determine the size of your trade relative to your overall capital.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Assess the potential reward against the risk before entering a trade.
In the end, FVG trading is nothing without a proper risk management strategy and having an effective and sound exit plan. Having a well-defined strategy, the discipline to stick to it, and effective risk management techniques helps you to protect your capital.
Pros and Cons of FVG Trading
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading is crucial. Let's explore the pros and cons in a simple table format and discuss how these factors can influence traders' choices.
In summary, FVG trading offers both advantages and disadvantages. While it can be a profitable strategy when executed correctly, traders must be prepared for potential risks and challenges. Being informed about these pros and cons empowers traders to make well-informed decisions and adapt their strategies based on market conditions.
Scanning for Fair Value Gaps
In this section, we'll uncover the techniques traders can employ to scan for Fair Value Gaps (FVG) using price action criteria. We'll emphasize the significance of custom scans and provide a step-by-step guide or checklist to streamline your FVG scanning process.
How to Scan for FVG
- Price Action Criteria: Scanning for FVG begins with a keen eye for price action. Look for the telltale signs of a triple-candle pattern on your trading charts. Remember, this pattern consists of a large candle with the highs and lows of the preceding and succeeding candles failing to fully overlap the large candle. This is the first clue in your search.
- Custom Scans: To enhance your FVG scanning capabilities, consider employing custom scans or screeners. These tools can be like having a magnifying glass to pinpoint specific FVG setups in a vast sea of price data. Custom scans can be tailored to your preferred timeframes, asset classes, and trading strategies.
Step-by-Step Guide for Scanning FVG
Here's a simplified step-by-step guide or checklist to streamline your FVG scanning process:
- Select Your Assets: Determine the assets you want to trade and focus your scan on those markets. Whether it's stocks, crypto currencies, or commodities, clarity in your choices is key.
- Choose Timeframes: Decide on the timeframes you're comfortable with. Are you a day trader looking at shorter intervals, or do you prefer longer-term trends? Your choice will dictate your scan parameters.
- Identify the Triple-Candle Pattern: As you scan through price charts, keep an eye out for the triple-candle pattern. Remember, it's a large candle flanked by two smaller candles that don't fully overlap with it.
- Utilize Custom Scans: If available, use custom scans or screeners to narrow down your search. These tools can help you identify FVGs more efficiently.
- Verify FVGs: Once you've identified potential FVGs, verify them using additional technical analysis. Check for confirmation signals such as support and resistance levels, trend indicators , or other relevant chart patterns.
- Evaluate Risk-Reward: Before entering any trades based on FVGs, assess the risk-reward ratio. Ensure that the potential reward justifies the risk you're taking.
- Execute Your Strategy: If all criteria align, execute your FVG trading strategy. This may involve entering positions, setting stop-loss orders, and managing your trades according to your plan.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitor your positions and adapt as needed. FVGs may evolve over time, and market conditions can change, so staying vigilant is essential.
By following this step-by-step guide and incorporating custom scans into your trading routine, you can enhance your ability to spot FVGs efficiently and make well-informed trading decisions. Remember that practice and experience play a significant role in refining your scanning skills over time.
In conclusion, this journey through the world of Fair Value Gaps (FVG) trading has provided valuable insights into a strategy that can potentially unlock profitable opportunities in the financial markets. Let's recap the key takeaways and reiterate the importance of understanding FVG for trading success.
Key Takeaways
- Fair Value Gaps are market inefficiencies or imbalances that traders can identify on price charts, often appearing as a triple-candle pattern.
- FVG trading involves a step-by-step strategy, from identification and observation to entry and risk management.
- Traders can benefit from FVG trading's profit potential, reduced risk, and flexibility across various asset classes.
- However, it's essential to be aware of the risk of misjudgment, market volatility, and limited opportunities in some markets.
By understanding and mastering this strategy, you can uncover hidden opportunities, mitigate risks, and potentially achieve trading success. So, set sail on your FVG trading journey, and may your endeavors be as rewarding as a treasure hunt in uncharted waters.
Stay Tuned with #GooseAcademy
Website | Twitter | Telegram | Discord | Docs
Disclaimer: The statements, proposals, and details above are informational only, and subject to change. We are in early-stage development and may need to change dates, details, or the project as a whole based on the protocol, team, legal or regulatory needs, or due to developments of Solana/Serum. Nothing above should be construed as financial, legal, or investment advice.
Introduction to Liquid Staking
Wormhole airdrop what exactly is wormhole, learn about meteora | dynamic pools, vaults & amms.

Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Mastering Fair Value Gap Trading: Your Comprehensive Guide

Unlocking Fair Value Gaps: Your Gateway to New Trading Horizons
Imagine you’re a trader in pursuit of hidden treasures within the dynamic world of forex. Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are your compass, guiding you toward fresh trading opportunities. Let’s demystify FVGs and discover how they can be your ally in the trading journey, especially when paired with order blocks.
Step 1: Understanding Fair Value Gaps
FVGs emerge when price departs from a specific level where trading activity is sparse, embarking on a one-directional journey. It’s like a unique footprint left by price movement, signaling potential trading opportunities on the horizon.
Step 2: Unveiling the Power of FVGs
These gaps hold immense potential, especially when combined with order blocks. The synergy between FVGs and order blocks can be a game-changer in your trading strategy. It’s akin to aligning the stars in your favor.
Step 3: Chart Example Insights
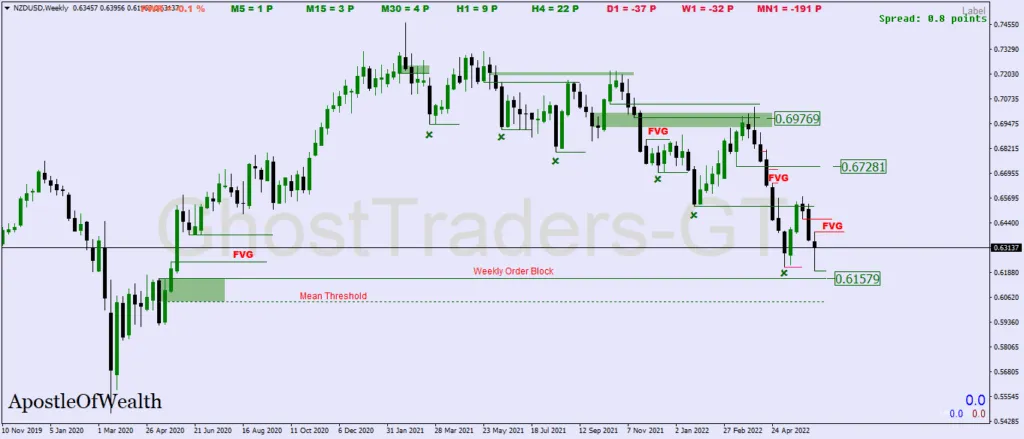
Let’s explore a real-life example from the charts. In the presence of a bearish order flow, we encounter a bearish fair value gap. The chart demonstrates how price plummeted significantly after closing this gap. It’s like reading the market’s intentions and riding the wave in the desired direction.
Step 4: The Magnetic Pull of FVGs
Price tends to gravitate toward areas where FVGs and liquidity voids are present. It’s as if these zones exert a magnetic pull on price. These are the regions where significant trading activity is expected.
Step 5: Crafting a Comprehensive Strategy
To fully harness the power of FVGs, it’s essential to combine them with your understanding of order flow trading. This holistic approach allows you to select the most strategic FVGs and liquidity voids that align with the market’s momentum.
In essence, FVGs are your hidden gems in the forex landscape. They offer a glimpse into the market’s past movements and future intentions. When coupled with order blocks and understood within the context of order flow trading, they become potent tools in your trading arsenal. So, embark on this journey with clarity, and let FVGs guide you toward new horizons in your trading endeavors.
Unlocking Consequent Encroachment in Forex: The Path to Precision
Imagine yourself as a trader, navigating the ever-changing tides of the forex market, seeking to understand the concept of consequent encroachment. It’s like deciphering a hidden code that can guide your trading decisions. Let’s delve into this term and uncover why it’s crucial for traders.
Step 1: Deciphering Consequent Encroachment
Consequent encroachment occurs when a fair value gap (FVG) is partially filled, specifically by 50%. This halfway point is known as the mean threshold of FVG. It’s like marking a milestone in the journey of price movement.
Step 2: Embracing Incomplete Fills
Traders should be aware that price might not always completely fill the FVG. This means that the price may not reach the opposite end of the gap. Consequently, targeting the mean threshold, or that 50% mark, is considered an ideal strategy to ensure you don’t miss out on potential trades.
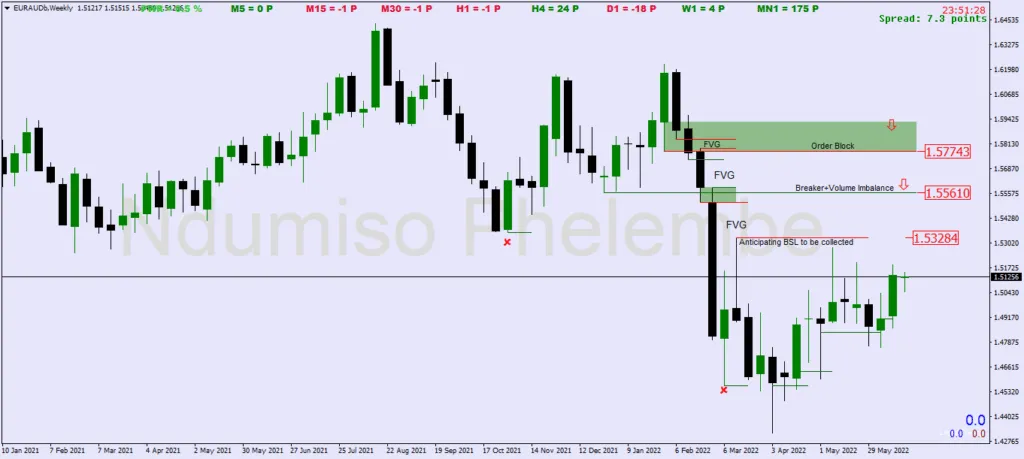
Step 3: Precision in Trading
Consequent encroachment is all about precision in trading. It’s about setting realistic expectations for how much of the gap price is likely to fill. By aiming for the mean threshold, you’re aligning your strategy with the market’s typical behavior.
In essence, consequent encroachment is a concept that allows traders to strike a balance between ambition and prudence. It acknowledges the possibility of incomplete FVG fills and provides a strategic approach to maximize trading opportunities without overreaching. So, as you embark on your trading journey, remember that precision can be your greatest ally, and consequent encroachment is a valuable tool in your arsenal.
Unlocking the Power of Institutional Order Flow Entry Drill (IOFED): Precision in Trading
Imagine yourself as a skilled trader, armed with a unique tool called Institutional Order Flow Entry Drill (IOFED). This concept allows you to navigate the intricacies of Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) with precision. Let’s delve into IOFED and why it’s a valuable addition to your trading knowledge.
Step 1: Defining IOFED
IOFED comes into play when price fills less than 50% of a Fair Value Gap (FVG). It’s like finding a specific key that unlocks the potential for profitable trades in the market. This is in contrast to consequent encroachment, where price fills exactly 50% of the FVG.
Step 2: Real-Life Chart Insights

Take a look at the chart example provided. Here, you can see how prices filled less than 50% of the fair value and then experienced a significant decline. This real-world scenario illustrates the power of IOFED in identifying trading opportunities.
Step 3: The Role of Institutional Order Flow
Understanding IOFED and consequent encroachment allows traders to grasp an essential market truth: prices may not always completely fill fair value gaps. This can happen due to the influence of heavy institutional order flow, which can rapidly push prices in one direction before the gap is fully filled.
Step 4: Precision in FVG Entry
Incorporating IOFED and consequent encroachment concepts into your trading strategy ensures that you’re not left on the sidelines when trading around FVGs. By considering these factors, you’re better equipped to make informed entry decisions and capture trading opportunities.
In essence, IOFED is your precision tool in the forex trading toolkit. It empowers you to make calculated decisions when dealing with FVGs. By recognizing that price may not fill gaps completely, especially in the face of strong order flow, you’re positioning yourself for success. So, as you embark on your trading journey, remember that precision matters and IOFED is your ally in achieving it.
Connecting the Dots: Fair Value Gaps and Order Blocks
Imagine yourself as a trader, peering into the intricate world of forex, where understanding the interplay between Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) and Order Blocks (OBs) is like uncovering a hidden treasure map. Let’s explore how these concepts are intertwined and why they hold the key to successful trading.
Step 1: Defining Order Blocks (OBs)
An Order Block in forex signifies a pivotal shift in the direction of price delivery. It’s like a signpost in the market, signaling that the landscape is about to change. This shift is confirmed and validated by the presence of a Fair Value Gap.
Step 2: The Essence of Fair Value Gaps (FVGs)
Fair Value Gaps are gaps in price movement that reveal underlying imbalances in the market. These gaps indicate buy-side inefficiency (a sell-side imbalance) or sell-side inefficiency (a buy-side imbalance). They’re like windows into the market’s psyche, showing moments of imbalance.
Step 3: The Symbiotic Relationship
The beauty of this connection lies in validation. When an Order Block is identified in the last close candle, it gains validation through the presence of a Fair Value Gap. It’s like a confirmation that the shift in price delivery is supported by underlying market dynamics.
Step 4: The Power of Validation
Validation is key in trading. It gives you the confidence that your analysis is on the right track. When an OB and FVG align, you’re not just observing price movements; you’re deciphering the market’s intentions.
In essence, Fair Value Gaps and Order Blocks are intrinsically linked. They’re your navigational tools in the forex landscape, helping you understand when and where shifts in market dynamics are occurring. By recognizing their connection, you’re positioning yourself for informed and validated trading decisions. So, as you venture further into the world of forex, remember that understanding the synergy between FVGs and OBs is your compass to trading success.
Decoding the Puzzle: Fair Value Gaps vs. Liquidity Voids
Imagine yourself as a detective in the world of trading, where you encounter two intriguing clues – Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) and Liquidity Voids. These concepts hold the key to understanding market imbalances, but what sets them apart? Let’s unravel the similarities and differences between these critical trading indicators.
Step 1: The Common Ground – Imbalances
Both FVGs and Liquidity Voids are like flags in the market, signaling the presence of imbalances – be it a sell-side or buy-side imbalance. They are your early warning system, highlighting moments when the market’s equilibrium is disrupted.
Step 2: Different Expressions
The key difference lies in how they manifest on the trading chart. Liquidity Voids materialize when price experiences sharp, one-directional movements, resulting in long-range candles. It’s like a sudden burst of energy in one direction, leaving its mark on the chart.
Step 3: Fair Value Gaps – The Gap in Price
On the other hand, Fair Value Gaps are literal gaps in price movement. These gaps indicate moments when price leaps from one level to another, leaving behind an empty space. It’s akin to a jump in the storyline of the market.
Step 4: The Chart’s Tale
If the trading chart were a storybook, Liquidity Voids would be the bold, action-packed chapters where price makes rapid strides, while FVGs would be the intriguing gaps in the narrative, hinting at untold secrets.
Step 5: Two Sides of the Same Coin
In essence, both FVGs and Liquidity Voids are your tools for detecting market imbalances. They represent different expressions of the same concept – a shift in the market’s equilibrium. By recognizing their similarities and differences, you’re better equipped to decipher the market’s story and make informed trading decisions.
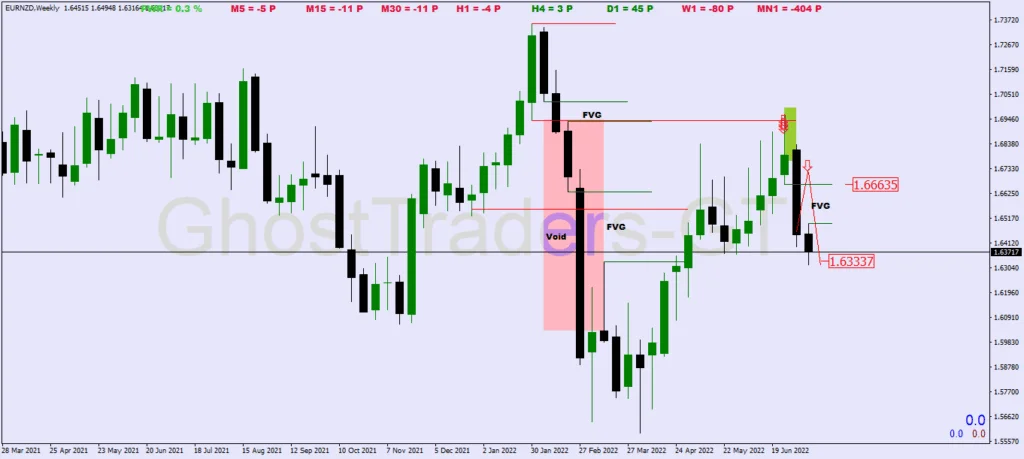
So, as you embark on your trading journey, remember that FVGs and Liquidity Voids are your allies in understanding market dynamics. They offer unique perspectives on imbalances, helping you navigate the trading landscape with clarity and insight.
Cracking the Code of Fair Value Gap Trading: A Strategy for Success
Imagine you’re embarking on a quest in the world of trading, armed with a powerful strategy called Fair Value Gap (FVG) Trading. It’s like having a secret weapon in your arsenal. Let’s explore how to trade FVGs and why they are your gateway to potentially lucrative opportunities.

Step 1: Anticipating Market Dynamics
In the ever-evolving world of trading, understanding market dynamics is like deciphering a puzzle. FVGs play a crucial role here. They signal moments when price collects either sell-side or buy-side liquidity. This information serves as a precursor to potential market shifts.
Step 2: The Three Scenarios
When price gathers sell-side or buy-side liquidity, it opens the door to three possible scenarios: reversal, retracement, or continuation. Think of these scenarios as pathways that price might follow.
Step 3: The Focus on Reversals
In Fair Value Gap trading, our primary focus is on trading reversals. Picture this as a pivot point in the market’s journey. When a Fair Value Gap forms, it becomes our entry point for trading reversals.
Step 4: Seizing Opportunities
Trading reversals is about capitalizing on moments when price shifts direction. It’s akin to catching a wave at just the right time. By using FVGs as your entry points, you position yourself strategically to seize these opportunities.
Step 5: Your Trading Edge
In essence, Fair Value Gap Trading is your edge in the market. It’s a strategy that enables you to anticipate and act upon market dynamics with precision. By focusing on reversals, you’re aligning your approach with the potential for significant price movements.
As you venture further into the world of trading, remember that Fair Value Gaps are not just gaps on the chart; they are windows of opportunity. By trading reversals with FVGs as your guide, you’re setting yourself on a path to navigate the market’s twists and turns with confidence and strategy.
Mastering Sell Setup Trading: Your Key to Anticipated Reversals
Imagine yourself as a trader, navigating the dynamic waves of the market with precision. Sell Setup Trading is your compass, guiding you toward anticipated reversals. Let’s dive into this strategy, dissect its essence, and uncover how it can be your ally in trading.
Step 1: The Art of Anticipation
In the world of trading, anticipation is everything. It’s like foreseeing the future of price movements. Sell Setup Trading revolves around anticipating a reversal in the market. This anticipation is fueled by a specific event – when price collects buy-side liquidity (BSL).
Step 2: Confirmation Through Market Structure
Anticipation alone isn’t enough; we seek confirmation. Imagine this as a detective waiting for that crucial piece of evidence. To confirm the anticipated reversal, we watch for a shift in market structure. It’s like a signpost that tells us the tide is turning.
Step 3: The Fair Value Gap Entry
Once the shift in market structure is confirmed, it’s time to pinpoint the entry point. Here, Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) step into the spotlight. These gaps become our gateway to initiating a sell short position. It’s like finding the perfect moment to take action.

Step 4: Seizing the Reversal Opportunity
Trading is all about seizing the right opportunities at the right time. In the context of Sell Setup Trading, it means capitalizing on anticipated reversals with precision. By using FVGs as our entry points, we position ourselves strategically.
Step 5: The Power of Strategy
In essence, Sell Setup Trading is a strategy that empowers you to make informed decisions in the market. It’s a combination of anticipation, confirmation, and strategic entry. It’s your tool for navigating the complex world of trading with confidence.
As you embark on your trading journey, remember that Sell Setup Trading is not just a strategy; it’s a mindset. It’s about understanding the market’s nuances and acting upon them with calculated precision. With this strategy as your ally, you’re poised to master the art of trading anticipated reversals.
Mastering Fair Value Gap Buy Setup Trading
Picture yourself as a trader, navigating the ever-shifting currents of the market with a purpose. Buy Setup Trading is your guiding star, leading you toward anticipated reversals. Let’s dissect this strategy, explore its core principles, and discover how it can empower your trading journey.
In the world of trading, anticipation is the name of the game. It’s like having a sixth sense for market moves. Buy Setup Trading revolves around anticipating a reversal – a shift in price direction. This anticipation is triggered when price collects Sell Side Liquidity (SSL).
Step 2: Confirmation Through Market Structure Shift
Anticipation is just the first step; confirmation is key. Think of this as gathering evidence to support your case. To confirm the anticipated reversal, we watch for a shift in market structure. It’s like waiting for the puzzle pieces to fall into place.
Step 3: The Fair Value Gap Trading Entry
Once the shift in market structure is confirmed, it’s time to pinpoint your entry point. This is where Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) come into play. These gaps serve as your gateway to initiating a buy or long position. It’s like finding the perfect moment to take action.
Trading is about seizing opportunities at the right time. In Buy Setup Trading, it means capitalizing on anticipated reversals with precision. By using FVGs as entry points, you position yourself strategically.
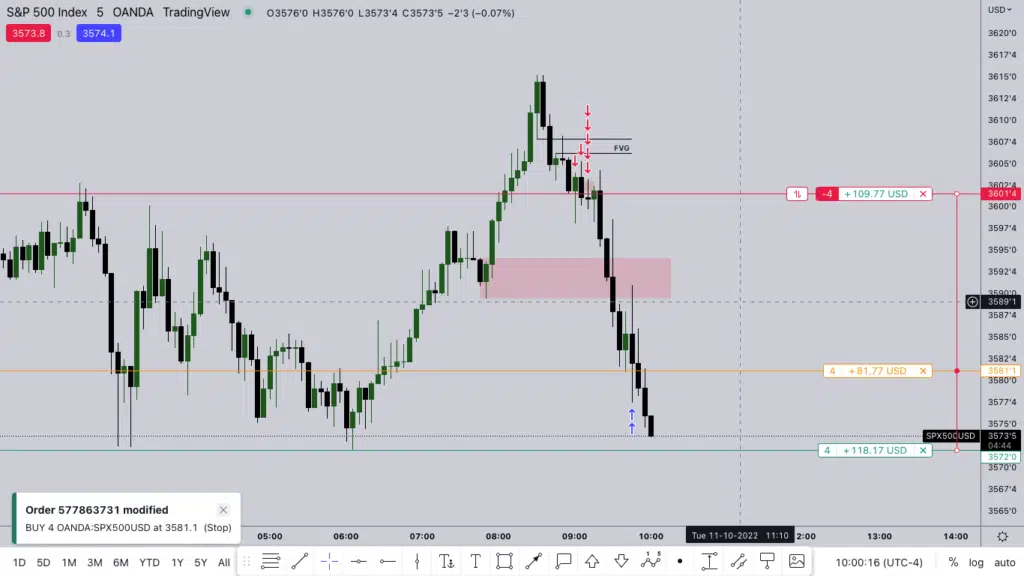
Related Posts

EURNZD and GBPUSD ANALYSIS
Dollar index trading analysis.

FVG Pattern
Introduction: unveiling the power of the fair value gap (fvg) trading pattern.
In the dynamic realm of financial markets, success often hinges on the ability to discern patterns that reveal hidden opportunities. One such pattern that has garnered increasing attention and acclaim is the Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading pattern. This strategic framework provides traders with a systematic approach to evaluating market discrepancies and making informed decisions.
A Glimpse into FVG Trading Pattern
The Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading pattern is a sophisticated methodology that revolves around the concept of assessing an asset’s market price in comparison to its intrinsic value. Essentially, it pinpoints the divergence between what an asset is currently valued at in the market and its true worth. This discrepancy serves as a beacon for traders, illuminating potential avenues for profitable trades.
The Imperative of FVG Understanding for Traders
Understanding the nuances of the FVG pattern is akin to wielding a powerful tool in the trader’s arsenal. It allows for the identification of undervalued or overvalued assets, providing a strategic advantage in the pursuit of profitable trades. The ability to navigate and leverage the FVG pattern empowers traders to make more informed decisions, potentially leading to enhanced returns on investments.
Patterns: The Cornerstone of Trading Strategies
Patterns form the very essence of successful trading strategies. They encapsulate the collective behavior of market participants, offering valuable insights into potential future movements. Recognizing and interpreting patterns is akin to deciphering the language of the market, allowing traders to anticipate shifts and position themselves strategically. The FVG pattern, in particular, provides a clear and actionable framework for identifying opportunities and managing risk.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading pattern, exploring its definition, historical context, and practical applications. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have gained a solid foundation in understanding and utilizing the Fair Value Gap trading pattern. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just embarking on your trading journey, the insights provided here will equip you with a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence and precision.
Understanding the Fair Value Gap (FVG) in Trading
Definition and technical explanation of fvg.
In the realm of trading, the Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a critical concept. It’s centered around evaluating an asset’s current market price in comparison to its intrinsic or fair value. This difference serves as a key indicator for traders, providing insights into potential trading opportunities.
From a technical standpoint, FVG is quantified by assessing the deviation between an asset’s market price and its calculated fair value. This calculation often involves advanced statistical models, incorporating factors like historical price trends, volatility, and market sentiment.
Historical Evolution of the FVG Pattern
The development of the Fair Value Gap pattern is rooted in the recognition of market inefficiencies. Traders and analysts observed that assets frequently traded at prices significantly different from their calculated fair values. This realization spurred the evolution of a systematic framework for identifying and capitalizing on these discrepancies.
Over time, this framework has become increasingly sophisticated, integrating advanced quantitative techniques and algorithmic models. Today, traders rely on cutting-edge tools and technologies to analyze vast datasets and pinpoint FVG opportunities with precision.
Relevance of the FVG Pattern in Contemporary Trading
In the fast-paced and highly competitive landscape of modern trading, the FVG pattern holds immense significance. Global markets are influenced by an array of dynamic factors, including algorithmic trading, high-frequency trading, and market sentiment algorithms. These factors can lead to rapid and significant price fluctuations.
The FVG pattern provides traders with a strategic advantage in navigating these complexities. Through rigorous quantitative analysis and advanced technical indicators, traders can identify precise entry and exit points based on FVG signals. This allows for more informed and timely trading decisions, minimizing exposure to market volatility.
Furthermore, with the advent of machine learning and artificial intelligence in trading, the FVG pattern has seen further refinement. Advanced algorithms can now process vast amounts of data in real-time, providing traders with unparalleled insights into FVG opportunities.
Components of the FVG Trading Pattern
Fair value determination: advanced techniques, precise calculation of fair value.
In the realm of trading, fair value determination transcends the surface-level assessment of financial statements. It delves into advanced quantitative techniques, employing statistical models, regression analyses, and proprietary algorithms. These methods draw on historical price data, trading volumes, volatility metrics, and other intricate indicators to pinpoint the precise fair value of an asset.
This meticulous approach allows traders to go beyond conventional valuation methods and harness the power of quantitative analysis for more accurate fair value estimations.
Dynamic Factors Influencing Fair Value
Different asset classes demand distinct considerations when calculating fair value. In equities, factors extend beyond earnings and financial ratios to include quantitative metrics like beta coefficients and volatility measures. In commodities, supply-demand models, futures pricing, and market sentiment algorithms come into play. For currencies, complex econometric models incorporating interest rate differentials, carry trades, and macroeconomic indicators offer deeper insights.
Mastering these quantitative models empowers traders to assess fair value dynamically, adapting to ever-changing market conditions.
Identifying Market Price Deviation: A Technical Perspective
Algorithmic differentiation of market price and fair value.
Distinguishing between market price and fair value requires advanced algorithmic models. These models integrate real-time data feeds, advanced statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms to calculate instantaneous fair values. By comparing these real-time fair values to actual market prices, traders can identify deviations and potential trading opportunities with high precision.
This algorithmic approach ensures traders are equipped to respond swiftly to market dynamics, leveraging the nuances of the Fair Value Gap.
Analyzing Deviation Causes through Technical Indicators
Understanding the reasons behind market price deviations demands a technical eye. Traders rely on intricate indicators like Supply and Demand , Supertrend or Currency Strength Meter to discern patterns and anomalies. These indicators serve as vital tools for identifying market sentiment shifts, sudden volume spikes, and other technical signals that may contribute to price deviations.
By interpreting these technical indicators, traders gain a deeper understanding of the underlying forces driving market price movements.
Implementing FVG Trading Strategies: A Technical and Risk Management Approach
1. technical analysis and fvg patterns, utilizing technical indicators for fvg opportunities.
Incorporating technical analysis is essential for confirming Fair Value Gap (FVG) opportunities. Traders rely on a diverse range of technical indicators, such as Supply and Demand , Supertrend or Currency Strength Meter that were mentioned above.
Here are several real-life examples of the indicators that might help to define the FVG patterns.

On the chart above the demand zones that are being formed in the direction of the movement confirm that price is moving towards the FVG area.

This GBPUSD chart shows the FVGs on the chart and the downtrend shown by Supertrend indicator allows to understand that only short direction patterns should be taken into account.

On the USDJPY chart above there are shown examples when the strength of the JPY currency dropped according to the Currency Strength Meter and these were ideal moments to open long positions on this pair.
By aligning these technical signals with FVG patterns, traders can enhance their confidence in identifying mispriced assets and making well-informed trading decisions.
Integrating Technical Analysis with FVG Trading Strategies
Technical analysis and the FVG pattern are not standalone tools; they complement each other in a symbiotic relationship. Traders leverage technical analysis to validate FVG signals and refine their entry and exit points. For instance, if a stock (or other asset) exhibits a significant deviation from its calculated fair value, traders may wait for additional confirmation from technical indicators before executing a trade.
This integration ensures that FVG trading strategies are grounded in robust technical analysis, enhancing the probability of successful trades.
2. Risk Management in FVG Trading
Mitigating risks in fvg trading.
Effectively managing risks is paramount in FVG trading. Traders employ a range of risk mitigation strategies to safeguard their capital. This includes setting predefined risk tolerance levels, carefully selecting trade sizes, and employing advanced techniques like options strategies for hedging.
Moreover, traders closely monitor external factors, such as market news and geopolitical events, that may influence the fair value of their assets. This vigilance allows for timely adjustments to trading positions, minimizing potential losses.
Implementing Stop-Loss Orders, Position-Sizing, and Diversification
Stop-loss orders are instrumental in limiting potential losses. Traders set predetermined price levels at which a position will be automatically closed to prevent further losses. Position-sizing is another critical component, ensuring that no single trade exposes a disproportionate amount of capital. By diversifying their portfolios across different asset classes, traders spread their risk and reduce the impact of adverse market movements.
The stop loss and take profit placements, as well as position size calculation as well as other useful trading routine can be automated with the Trade Panel .
In the context of FVG trading, these risk management and money management techniques serve as a safety net, allowing traders to navigate market volatility with confidence and discipline.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Staying Ahead in FVG Trading
Emphasizing the importance of staying updated on market trends.
In the fast-evolving world of financial markets, staying informed about the latest trends and developments is paramount. Traders who remain vigilant and adapt to changing market dynamics are better equipped to seize opportunities and mitigate risks. This entails keeping a close eye on economic indicators, geopolitical events, and emerging technologies that may impact asset valuations and FVG patterns.
Moreover, engaging with reputable financial news sources, participating in trading communities, and attending industry conferences can provide invaluable insights and keep traders at the forefront of market knowledge.
Strategies for Ongoing Education and Adaptation in FVG Trading
Continuous learning is the cornerstone of success in FVG trading. Traders should commit to expanding their knowledge base through a variety of strategies:
- Engage in Advanced Training : Enroll in specialized courses, webinars, and workshops focused on advanced trading techniques, quantitative analysis, and algorithmic modeling.
- Leverage Analytical Tools : Familiarize yourself with cutting-edge trading platforms and analytical software like indicators that can enhance your ability to identify and capitalize on FVG opportunities.
- Network and Collaborate : Connect with fellow traders, analysts, and experts in the field. Engaging in discussions and knowledge-sharing can lead to valuable insights and new perspectives.
- Stay Disciplined : Develop a structured approach to trading and adhere to a well-defined trading plan. Avoid impulsive decisions and base your actions on thorough analysis.
- Review and Adapt Strategies : Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your trading strategies . Identify areas for improvement and be open to refining your approach based on performance data.
By adopting a proactive stance towards learning and adaptation, traders can position themselves as agile and informed market participants, primed to navigate the complexities of FVG trading.
Conclusion: Mastering FVG Trading Patterns
In mastering FVG trading patterns, several key takeaways emerge:
- FVG as a Tactical Framework : The Fair Value Gap (FVG) pattern is not just a theoretical construct, but a dynamic framework that provides traders with a systematic approach to evaluating market discrepancies.
- Technical Expertise Matters : Incorporating advanced technical analysis and quantitative models is essential for confirming FVG opportunities and making precise trading decisions.
- Risk Management is Paramount : Implementing robust risk management strategies, including stop-loss orders, position-sizing , and diversification, is crucial in safeguarding capital and ensuring long-term success.
- Continuous Learning Drives Success : Staying updated on market trends, engaging in ongoing education, and adapting to changing market dynamics are key factors in achieving consistent success in FVG trading.
As you embark on your journey to apply FVG patterns in your trading strategies, remember that knowledge and discipline are your greatest assets. With a solid foundation and a commitment to continuous learning, you’re poised to navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence and precision.

Price Action 101: Fair Value Gap (FVG)

Drift is thrilled to introduce you to our new series, "Price Action Concepts 101". This series aims to equip aspiring price action traders with the latest concepts, allowing traders to start implementing these strategies on Drift. To kick off the series, we will delve into the world of Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), a widely-used concept in price action trading.
Lesson 1: Fair Value Gap (FVG)
The Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a widely utilized concept among price action traders today as it aids in the development of trading strategies and decision-making in the markets. Though its origin is uncertain, it is believed to have been popularized by the Inner Circle Trader .
What Is A Fair Value Gap?
Before diving into the practical use of the Fair Value Gap in trading, it's crucial to have a clear understanding of what it is and how to identify it on your charts. The Fair Value Gap, or FVG, is a widely utilized tool among price action traders to detect market inefficiencies or imbalances. Sometimes you will even see them labeled as inefficiencies by other traders. These imbalances arise when buying or selling pressure is significant, resulting in a large upward or downward move, leaving behind an imbalance in the market.
The idea behind FVGs is that the market will eventually come back to these inefficiencies in the market before continuing in the same direction as the initial impulsive move. FVGs are important since traders can achieve an edge in the market. Price action traders can also use these imbalances as entry or exit points in the market.
For a FVG to develop, there must be a set of three candles characterized by heavy buying or selling in the same direction. When there is a large move in either direction, a gap will be formed between the first candle's wick and the wick of the last candle, as illustrated in the figures below.

The illustration below does not depict a Fair Value Gap, as the previous candle's high level has counterbalanced the low level of the third candle. This price action is considered to be balanced.

How To Use FVGs To Trade Price Action?
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) can be found on all timeframes and there are numerous trading strategies that can be implemented using them. In this example, we will focus on utilizing FVGs for trend continuation after a significant impulsive move. As previously mentioned, we can anticipate the price to return to these FVGs before continuing in the same direction as the impulse move. Traders can take advantage of this by waiting for the price to reach the FVG area of interest and then entering a trade, targeting trend continuation.
For example, let's take a look at the Solana chart during its large run in January 2023. As seen on the left side of the chart, a FVG was formed and price consolidated over several days before it returned to test the FVG. Traders might have used this FVG as a key level of interest for entry into a long trade on SOL and rode it for further trend continuation.

How Can I Find FVGs On My Own?
Identifying Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) in the markets can be relatively straightforward due to their large impulse moves. However, if you need extra assistance, there are numerous free indicators available on TradingView that can aid in detecting these imbalances. Simply type in "FVG" or "Imbalance" in the search bar, and any of the top options should be able to assist you in identifying these imbalances in the market.
Trade On Drift
Deposit crypto as collateral on Drift and start trading, earning yield, and borrowing.
For more on Drift, head over to our Learn hub.
N othing in the text should constitute financial advice, Drift is not responsible for any losses that may occur by following the contents of this article. All content is provided here for educational purposes only.
You might also like

Drift Protocol, 2022. All rights reserved.

Understanding FVG in Trading: What is Fair Value Gap?

Uncover the pivotal concept that shapes trading strategies: the fair value gap. Intrigued by its significance and impact on trades? Let’s delve into the intricate world of fair value gaps, decoding their role and influence in the dynamic realm of trading.
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools traders use to identify market imbalances and inefficiencies. FVGs occur when buying or selling pressure leads to significant price movements, leaving behind gaps on price charts. Traders can categorise FVGs into two types: Undervalued FVGs, where prices are lower than fair value, and Overrated FVGs, where prices are higher.
The concept of fair value gap goes by different terminologies among price action traders and is rooted in the belief that the market naturally tends to correct itself. Fair Value Gaps provide a unique advantage by revealing entry and exit points in the market. Traders can use technical analysis involving candlestick patterns and price chart patterns to identify FVGs.
Key Takeaways:
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools used by traders to identify market imbalances and inefficiencies.
- FVGs occur when buying or selling pressure leads to significant price movements, leaving gaps on price charts.
- There are two types of FVGs: Undervalued FVGs and Overrated FVGs.
- Traders can use technical analysis to identify FVGs, including candlestick patterns and price chart patterns.
- FVGs provide entry and exit points in the market, giving traders an advantage in their trading strategies .
- What is FVG in Trading (Fair Value Gap)
Fair Value Gaps (FVG) in trading represent a powerful strategy, particularly embraced by price action traders in the dynamic world of financial markets. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of FVG, providing a thorough understanding of what it entails and its significance for traders.
Fair Value Gaps, often referred to as FVGs, are instrumental tools employed by traders to identify market imbalances and inefficiencies. These gaps manifest when there is a notable disparity between buying and selling pressures, leading to substantial price movements and leaving discernible gaps on price charts.
Traders meticulously analyse candlestick patterns and price chart formations to categorise FVGs into two distinct types: Undervalued FVGs, where prices dip below fair value, and Overrated FVGs, where prices surge above fair value.
The Essence of Fair Value Gaps
Termed as imbalances, inefficiencies, or liquidity voids, FVGs occur when significant buying or selling forces exert pressure, resulting in rapid and substantial price shifts. The fundamental belief underpinning FVGs is that the market inherently corrects itself, gravitating back towards these imbalances before continuing in the direction of the initial impulsive move.
Strategic Entry and Exit Points:
The crux of FVGs lies in their ability to act as strategic markers on the trading chart, guiding traders on opportune moments to enter or exit a position. Unlike other gaps, FVGs are rooted in a three-candlestick formation, creating an observable imbalance in the market’s price action.
Identifying Fair Value Gaps on Price Charts:
Spotting FVGs involves identifying a specific three-candle pattern on a price chart. The gap between the wicks of the first and third candles defines the Fair Value Gap, signifying a potential return to market equilibrium. For instance, in a bearish trend, the Fair Value Gap is the price area between the previous candlestick’s low and the following candlestick’s high.
Types of Fair Value Gaps:
Fair Value Gaps come in two distinct types – Undervalued and Overrated. Each type carries its own set of implications for traders. Undervalued FVGs signify prices lower than fair value, while Overrated FVGs indicate prices higher than fair value.
Utilising FVGs for Trend Continuation:
Traders can leverage FVGs for trend continuation after a significant impulsive move. By waiting for the price to reach the FVG area of interest and entering a trade, they position themselves for further trend continuation. A tangible example is observed in the Solana chart during its significant run in January 2023, where a FVG served as a key level of interest for entry into a long trade.
Tools for Identifying FVGs:
While identifying FVGs can be straightforward due to their distinct impulse moves, traders can utilise indicators on platforms like TradingView to assist in detecting these imbalances. Simply searching for “FVG” or “Imbalance” in the search bar can yield valuable tools for identifying FVGs.
Trading the FVG Strategy:
Mastering the FVG trading strategy involves understanding trends, identifying supply and demand zones, and utilizing indicators. Essential to this strategy is risk management, including setting appropriate stop-loss and target profit levels to safeguard capital and optimize returns.
- How to Identify and Trade using Fair Value Gaps
To effectively navigate the world of trading using Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), it is crucial to understand the process of identifying and utilizing these powerful market indicators. Traders can employ specific strategies to identify Fair Value Gaps on price charts, enabling them to find potential entry and exit points for their trades.
One effective approach to identifying Fair Value Gaps is to look for a three-candle pattern with specific rules. Firstly, it is important to spot a substantial candlestick with a significant body-to-wick ratio. Next, examine the neighboring candlesticks to ensure that they do not entirely overlap the significant candlestick. The gap between the wicks of the neighboring candlesticks represents the fair value gap .
To simplify this process, traders can utilize indicators such as the Fair Value Gap Indicator available on various trading platforms. This tool automates the identification process by highlighting potential Fair Value Gaps on price charts.
Once a Fair Value Gap has been identified, traders can incorporate it into their trading strategy. This involves determining the trend, identifying supply and demand zones, and utilizing the Fair Value Gap as an entry point. To manage risk effectively, traders should set appropriate stop loss and target profit levels. By following this approach, traders can potentially capitalize on market imbalances and inefficiencies revealed by Fair Value Gaps.
Example Trading Strategy:
- Determine the overall trend of the market.
- Identify key supply and demand zones.
- Locate a Fair Value Gap as an entry point within the identified zones.
- Set a stop loss to manage risk and a target profit level.
- Monitor the trade and adjust the stop loss or take profit levels as necessary.
The Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a powerful concept in trading that allows traders to identify market imbalances and capitalize on them. By understanding how to identify and trade using Fair Value Gaps, traders can gain a competitive edge in the financial markets.
Implementing Fair Value Gap analysis alongside other technical analysis tools can enhance trading decisions and improve profitability. Traders can utilize Fair Value Gaps in various trading strategies across different asset classes, including stocks, forex, and commodities.
It is essential for traders to continuously analyze market conditions and adapt their trading strategies accordingly. By staying informed about fair value calculations , market valuation , and stock market analysis , traders can make more informed investment decisions and maximize their returns.
In conclusion, the Fair Value Gap is a valuable tool for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets. By incorporating Fair Value Gap analysis into their trading strategies, traders can increase their chances of success and achieve their goals in the world of investment.
What is Fair Value Gap in trading?
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools traders use to identify market imbalances and inefficiencies. They occur when buying or selling pressure leads to significant price movements, leaving behind gaps on price charts.
How can I identify and trade using Fair Value Gaps?
To identify a Fair Value Gap on a price chart, traders need to look for a three-candle pattern with specific rules. Traders can use indicators like the Fair Value Gap Indicator on trading platforms to automate the identification process. Once a Fair Value Gap is identified, traders can use it as an entry point for their trades by determining the trend, identifying supply and demand zones, and setting stop loss and target profit levels.
What is the importance of Fair Value Gap in trading?
Fair Value Gaps provide a unique advantage by revealing entry and exit points in the market. By understanding how to identify and trade using Fair Value Gaps, traders can gain an edge in the financial markets and improve their profitability.

Income Strategies - How Much Can You Make Day Trading with $1,000

What is a Trading Desk – Know the Different Types
Table of content, top 5 best brokers.

How to Pay Taxes on Day Trading Guide – File with Ease

How Does Trading 212 Work Explained: Navigate Online Investing

How to Start Trading in South Africa: A Starter Guide

- Broker review
- Privacy policy
© 2022 PIP PENGUIN
Disclaimer Notices
The content on this site encompasses general news, our analyses, opinions, and material from third-party sources, all designed for educational and research aims. It is not meant as direct advice or a prompt to undertake any specific action, including investments or purchases. Before making financial decisions, we urge you to conduct thorough research, exercise personal judgment, and consult with professionals. The content is not tailored to individual financial circumstances or needs. Information on this website might not be in real-time or entirely accurate, with prices potentially sourced from market participants rather than exchanges. Any financial decisions you make are your sole responsibility, and reliance on any site information is at your own risk. PipPenguin makes no guarantees regarding the website’s information accuracy and will not be liable for any trading losses or other losses incurred from using this site. The site may contain ads and promotional content, for which PipPenguin could receive third-party compensation. However, this does not imply endorsement or recommendation of any third party’s services, and we are not responsible for your use of any external site or service. PipPenguin and its staff, executives, and affiliates disclaim liability for any loss or damage from using the site or its information.
Risk Disclaimers
This site provides information on cryptocurrencies, CFDs, and various financial instruments, along with details about brokers and trading platforms. These instruments are complex and carry a significant risk of loss. It’s important to fully understand how they work and assess if you can afford the associated risks before investing. We encourage doing extensive research before any investment and caution against investing in instruments that are not fully understood.
- Flux Charts
- Trading Concepts
Price Action
- Fair Value Gaps
- Break of Structures
- Change of Character
Technical Analysis
- Supply and Demand
Fair Value Gaps (FVG) Explained
In the trading of stocks and currencies, the use of fair value gaps in trading strategies has recently grown. Fair value gaps are a price action concept popularized by the ICT (Inner Circle Trader). They locate areas of imbalance on a chart where traders can enter positions to profit. In this article, we cover what FVGs are, how to locate them, the best strategies for using them, and the theory behind them.
What is a fair value gap (FVG)?
An FVG on a chart identifies an area where the fair price of an asset has recently changed. This change implies that when the price returns to where the FVG had just formed, it will either rise if it is a bullish FVG or fall if it is a bearish FVG. This concept is similar to that of supply and demand zones or support and resistance lines; however, FVG's form faster, giving those traders using them an advantage.
How to identify an FVG
FVG's are a three candle pattern. Identify a candle that is large relative to the candle on its left and right.

Find a bullish FVG
Identify a green candle that is large relative to the candles on its left and right.
The high value of the candle on the left of the large candle (1) should not overlap with the low value of the candle on the right (2) .
Draw a box, where the bottom is the left candle's high (4) and the top of is the right candle's low (3) . Extend the box out to the most recent candles. This box forms a bullish FVG.
When price falls and enters this zone, it is likely to reverse and rise again. If price falls past a bullish FVG zone's bottom, that FVG is invalid and should no longer be used.
Find a bearish FVG
Identify a red candle that is large relative to the candles on its right and left.
The low value of the candle left of the large candle should not overlap with the low of the candle on the right of the large candle.
Draw a box where the top of the box is the left candle's low and the bottom of the box is the right candle's high. Extend the box out to the most recent candles. This box forms a bullish FVG.
When the price rises and enters this zone, it is likely to reverse and fall. If the price rises past a bearish FVG zone's top, that FVG is invalid and should no longer be used.
What is the theory behind FVGs?
Typically, a large spike in price is a large buy order being executed. This large spike enables those people holding positions to exit for a profit at the higher price, which causes prices to fall after the spike. However, when large increases in price occur and price does not move down after, instead further increasing, we can assume that those people holding positions believe that this new price is safe for them to continue holding or even buy more.
Let us say that a stock is fluctuating between 9-10$. You purchase the stock at 9$ and are waiting for the stock to move back to 10$ to sell. News is released about the stock, and it shoots up to 11$. You and all the other people who were holding positions previous to the spike continue to hold, as you believe that the stock will now further increase. This means that the fair value of the stock has changed from 9-10$ to 10-11$. People now are willing to purchase the stock for around 10-11$, whereas before it was 9-10$. If the price rises and then moves back down to between 10-11$ people will start buying and driving it back up.
The first high of the candle to the left of the large spike candle represents the bottom of the new fair value, while the candle to the right of the large spike candle represents the high of the new fair value.
If the low of the last candle overlaps the high of the first, it means that enough people sold during the price shift to drive the price down to within the old fair value, meaning that there is insufficient confidence in the new increase for it to be considered a new fair value.
What time frames are best for fair value gaps (FVGs)?
Intraday time frames are best. Intraday means time frames less than one day, for example, 3 minute, 5 minute, and 15 minute time frames.
What stocks or securities are best for fair value gaps (FVGs)?
Fair value gaps can be used on any stocks, but stocks with a high trading volume, meaning a large number of people who are actively trading the stock, are best. This is also true for crypto currencies and futures.
How accurate are fair value gaps (FVGs)?
Fair value gaps are identified using a three candle pattern. This means that they form more quickly than other signals, but they can be less accurate.
- Break of Structures (BOS)
- (833) 587-3637
- Get started
TrendSpider’s Strategy Tester is the industry’s easiest, fastest, simplest, and most powerful way to create, test, and refine trading strategies – without taking any risk.
- Use 50 years of historical data to fine tune your approach for maximum profitability.
- Test any conditions, mix-and-match technicals, fundamentals and more.
- Generate robust charts, data and reports to help you optimize your strategies.
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy
In the world of finance, traders are always looking for an edge to help them generate profits. One strategy that has gained popularity in recent years is using fair value gaps in trading. In this article, we will explore what fair value gaps are, how they can be identified, and how traders can use them to develop a profitable trading strategy. We will also discuss the risks and challenges associated with fair value gap trading.
What Is a Fair Value Gap?
A fair value gap is especially popular among price action traders and occurs when there are inefficiencies or imbalances in the market, or when the buying and selling are not equal. Fair value gaps can become a magnet for the price before continuing in the same direction.
On a chart , a fair value gap appears in a triple- candle pattern when there is a large candle whose previous candle’s high and subsequent candle’s low do not fully overlap the large candle. The space between these wicks is known as the fair value gap.

Quick Tips:
- Download this fair value gap scanner
- Import this fair value gap example strategy
- Type ‘fair value gap’ into Assistant to add the fair value gap and fair value gap proximity indicators to your charts
The first step in this strategy is to identify fair value gaps. This can be done either manually by looking for the triple-candle pattern mentioned previously or by using a fair value gap indicator that highlights fair value gaps automatically on the chart.
Once a fair value gap is identified, traders wait for the price to revert back towards the fair value gap to clear out the imbalance before continuing to move in the direction of the prevailing trend.
TrendSpider’s Strategy Tester is the industry’s easiest, fastest, simplest, and most powerful way to create, test, and refine trading strategies.
For example, if a fair value gap is created in a move to the upside, traders would wait for the price to be pulled down toward the fair value gap and enter a long position with the goal of profiting from a continued move to the upside once the imbalance is cleared out.

Conversely, if a fair value gap is created in a move to the downside, traders would wait for the price to revert up toward the fair value gap and enter a short position with the goal of profiting from a continued move to the downside once the imbalance is cleared out.

The fair value gap trading strategy requires a disciplined approach to risk management, as traders need to be prepared for potential losses if the market does not move in the direction they anticipate. Traders can mitigate this risk by setting stop-loss orders to limit their losses and by using appropriate position sizing to manage their exposure to the market.
Pros and Cons of Fair Value Gaps
Like any trading strategy, there are both advantages and disadvantages to fair value gaps. Here are some of the pros and cons:
- Profit potential: If a trader can accurately identify a fair value gap and trade on it, they can potentially earn significant profits.
- Reduced risk: Because fair value gap trading is focused on identifying inefficiencies in the market, it can be less risky than other trading strategies that rely on making directional bets on the direction of an asset’s price movement.
- Flexibility: This strategy can be applied to a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies.
- Risk of misjudgment: The fair value gap trading strategy relies on the assumption that the asset’s price will reverse once a fair value gap is filled, but this is not always the case. The asset’s price could continue to move through and past it, resulting in losses for the trader.
- Market volatility: The market can be unpredictable, and even small movements in market prices can lead to significant losses for fair value gap traders.
- Limited opportunities: The opportunities for fair value gap trading may be limited in some markets, particularly in highly efficient markets.
In summary, fair value gaps can offer profitable opportunities for experienced traders who have the skills and knowledge to identify inefficiencies in financial markets. It is important for traders to carefully consider the pros and cons before implementing this strategy.
Example scanners to easily find Fair Value Gaps
Fair Value Gaps can be used in Scanning the market. To see how exactly it can be used in this way, we provide the following samples. Both scanners search the market for stocks using this indicator .

These fair value gap scanners utilize the price conditions that define a fair value gap to allow traders to instantly identify fair value gaps forming in real-time. Traders can import these scans directly into their accounts, save them as their own, and customize them via additional price, indicator, candlestick pattern, or other criteria.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, the fair value gap trading strategy can be a lucrative approach to the financial markets. By identifying inefficiencies with fair value gaps, traders can take advantage of the temporary imbalances that arise in the market. Overall, it is important for traders to carefully consider the risks and rewards of the fair value gap trading strategy and to develop a thorough understanding of the markets in which they operate. With the right approach and mindset, the fair value gap trading strategy can be a profitable and rewarding endeavor.
- Fair value gaps can sometimes lead to or be created by breaks in Market Structure
- Order Blocks are another powerful tool that fair value gap traders like to utilize
Preview some of TrendSpider’s Data and Analytics on select Stocks and ETFs

TrendSpider’s Strategy Tester is the industry’s most powerful backtesting solution. Best of all, it’s point-and-click easy-to-use. No coding required. If you can describe a strategy to a friend, you can backtest it in TrendSpider.
- Create, discover, tweak and test/re-test over and over until you find something that works for you
- Define your own entry and exit rules using any indicators, patterns, or data points you want
- Test with 50+ years of market historical data
- Launch strategies as automated trading bots that run with real-time market data
Technical Analysis Strategies
Moving average crossover strategies , sign up for the trendspider market update.
Nothing Found
- to navigate
Test Drive the All-in-One Super Platform for Active Investors and Traders
Better trading performance starts with using better trading tools. TrendSpider is the only institutional-grade market research and trading platform available to retail investors.
Try TrendSpider for 1 week with our Test Drive offer . Just pay $29 to cover the cost of market data and infrastructure. Free training included.

- Best Prop Firms
- Best Trading Journals
- Prop Trading Jobs
- Prop Firm Deals
- The 7 Best Prop Firms Today
- The 4 Best Proprietary Trading Firms For Beginners in 2024
- Top 4 Free Trading Journal Templates: Ramp Your Trading to the Next Level
- Apex Trader Funding Review 2024: The Inside Scoop
- Uprofit Review: The Prop Firm for You?
- Earn2Trade Review: The Inside Scoop to Help You Choose
- TopStep Review: The Inside Scoop
- Economic Calendar
- Earn2Trade vs TopStep: Discover Which Fits You Best
Fair Value Gaps & Liquidity Voids: Examples, Explanation, & How to Trade
Last updated October 18, 2023
What are Fair Value Gaps and Liquidity Voids?
Fair Value Gaps (FVG) and Liquidity Voids are price ranges you can exploit for better entries and exits on your trades. They're similar concepts, so let's look at them from the top and break it down.
Think of FVG and Liquidity voids as soft-spots in the market. They are paths of least resistance. That doesn't mean price will go through them, but price could go through them more easily.
You may have heard traders talk about the gap-fill phenomenon, the idea that " gaps want to be filled". This idea relates to that pattern, so we'll go through how and why.
Defining Fair Value Gaps (FGV)
Fair value gaps are ranges where you might seek an entry for a planned trade. It's a specific candle pattern based on the concept of liquidity voids.
Fair value gap patterns consist of three candles. The "gap" is the price range that is not shared by candles one and three. Candle two is generally a larger candle, providing a wide price range.
How to Spot Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gap candle pattern.
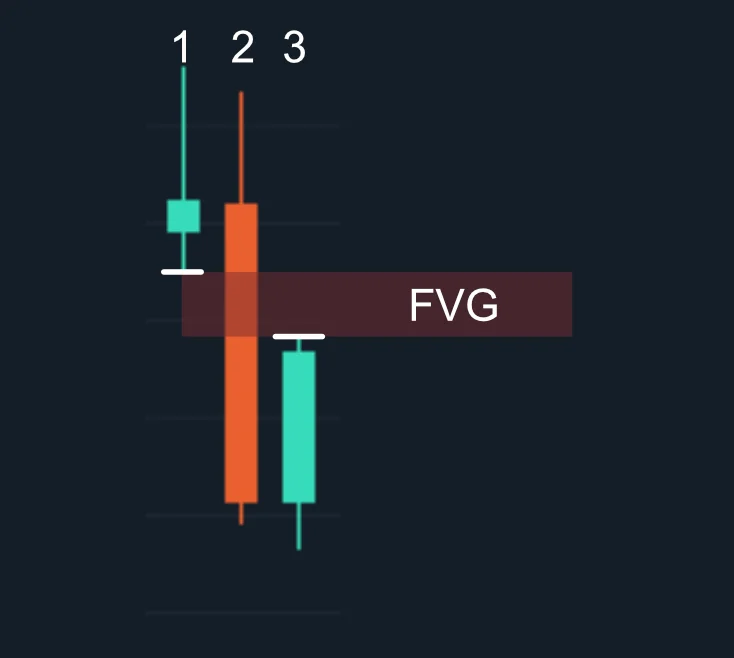
In this chart, the fair value gap exists between the low of candle 1, and the high of candle 3.
Candle 2 creates the range for this fair value gap, which forms when candle 3 fails to enter the range of candle 1.
The fair value gap in the image above is a buy-side fair value gap. Traders seeking a short entry might use this as their entry point. They'd have confidence in that entry because they expect buyers to push price into that FVG on a later candle.
As you can see, in candle 2, price has moved quickly down, leaving a liquidity void. Candle 3 has closed lower, not coming into the range of candle 1.
How do Fair Value Gaps Form
Fair value gaps form in three bars.
- Price moves outside the range of the first bar.
- The second bar passes quickly through the range outside the first bar.
- The second bar closes near the outside of its range.
- The third bar enters the range of the second bar but fails to enter the range of the first bar.
Fair value gaps can form on up moves or down moves, over any timeframe. The key ingredients are:
- Bar 2 is generally large, almost always larger than Bar 1.
- Bar 1 and Bar 3 do not share any common prices.
Fair value gaps create a small liquidity void, to which traders may expect price to return in later bars. For that reason, fair value gaps can be a desirable entry point.
How to Trade Fair Value Gaps
As with all patterns, how you trade FVGs is up to you. But, most traders look for FVGs as entry points. Personally, I use them as entry zones.
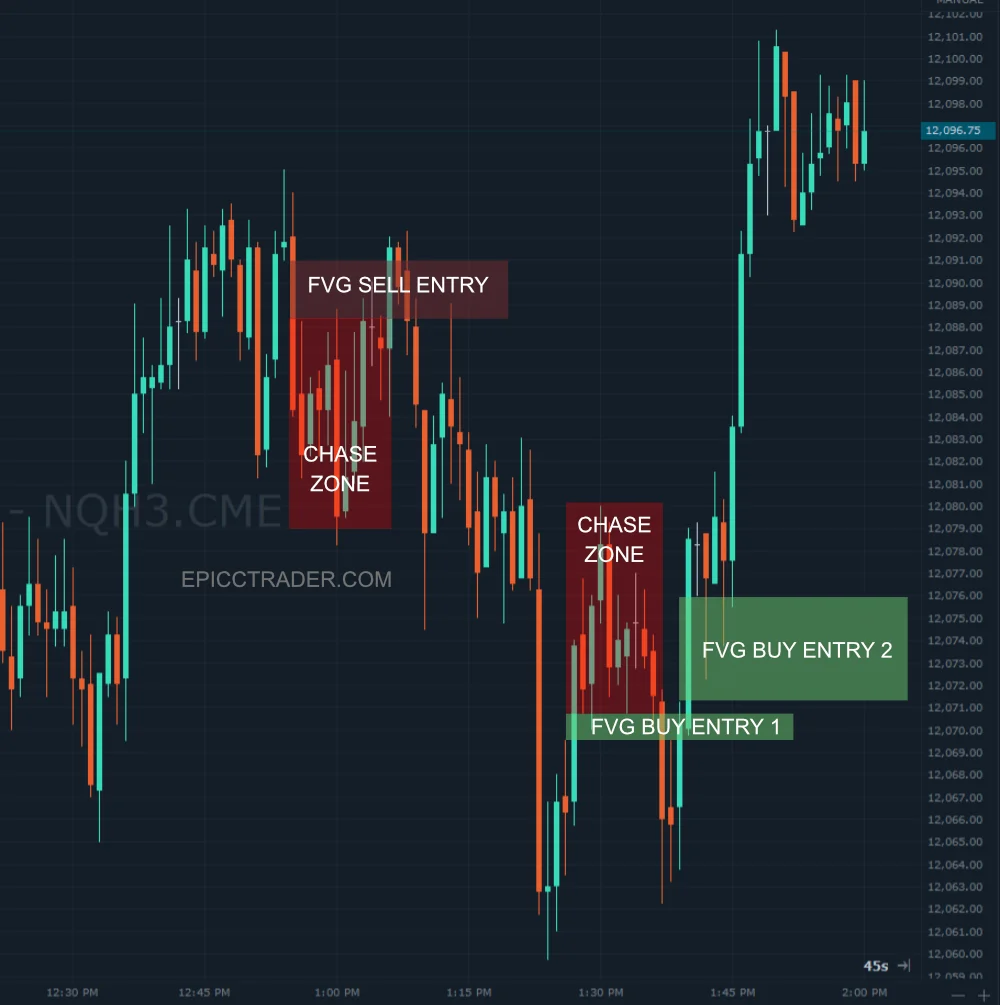
The fair value gap is a short-term liquidity void, and I expect price to trade into liquidity voids. So, if I have a setup, I will place an order there rather than chasing a move.
For short entries, candle 2 should be a down candle. It's helpful if candle 3 is an up candle, but that's not required, at least for me. But it does show that buyers are trying to push into that range.
For long entries, candle 2 should be an up candle. The same goes for candle 3 there, but in reverse.
As you can see in the image above, there were FVG sell entries and FVG buy entries in the span of just 30 minutes.
Short Entry
The "Sell Entry" on the chart is a short entry for the range below. If you were trading a short setup and looking for an FVG entry, you got one that worked. The max profit on that trade was 31 points, as of the time of this screenshot.
If you were working on a long setup and waiting for an FVG entry, you got two that worked. You would have had to take a little pain, but less than if you had chased. The max profit on that trade was 32 points as of the time of this screenshot.
You can see I labeled the area I call the "Chase Zone" on the chart above. You can also see there was no need to enter in that area, and doing so would have hurt all your trade stats.
You would have to take more pain, which we all hate. But the consequences are far greater. You have a worse entry, so you're starting out behind.
- Your max potential profit is less given any take profit price.
- Your max potential loss is greater given any stop price.
- Your win rate could be lower, depending on your stop price.
- Your Max Adverse Excursion (MAE) will be far greater. In other words, you would have taken more pain.
Key Takeaway
That highlights one of the main reasons to use fair value gaps as entries as opposed to chasing. You'll hear me say it like a broken record - waiting for price to come to you takes patience. But it pays.
It's important to note that the fair value gap itself is not a setup. It's a pattern traders look for when they have a setup and need an entry point. You must have some other reason to take the trade.
Liquidity Void Meaning
Liquidity voids are market soft-spots, and they're the simplest piece of this idea. For most of my career I've known them as order vacuums or vertical ranges .
Those vertical ranges typically consist of two or more expansion bars. Expansion bars get their name by expanding the range on the timeframe they occur. Expansion bars move outside the close of the prior bar and close well outside the recent range.
Because they explode outside the range quickly, they leave an order vacuum.
When that order vacuum forms as described above, you get a zone like a gap. Much like a gap, it can act as a "chute" for price.
Notice I didn't say "magnet". Magnets attract. Liquidity voids don't necessarily attract price, at least not immediately.
Think of liquidity voids more like a slick slide at a water park. Once price gets in the void, we can expect it to move through there more easily than it would through "thicker" areas.
You can use liquidity voids to determine what ranges you want to trade. They can help you decide potential entry and take-profit points. You can use them to avoid being too loose on a stop-loss. More on that below.
How to Spot a Liquidity Void
Now that you know what to look for, you can start spotting liquidity voids several times a day. Especially in this market (Feb 2023)!
- Start by watching for vertical ranges.
- Then look at the expansion bars. It's rare for there to be less than two. Exception: Big market data releases like FOMC
- If you intend to use liquidity voids in your trades, look for larger ones that give you plenty of range. Sometimes a partial retrace is more likely than a full retrace.
Liquidity Void Candle Pattern
The liquidity voids below formed by multiple expansion bars outside the prior ranges. You see them highlighted in red. We would expect these ranges to provide less than average support as price moves back down through them.
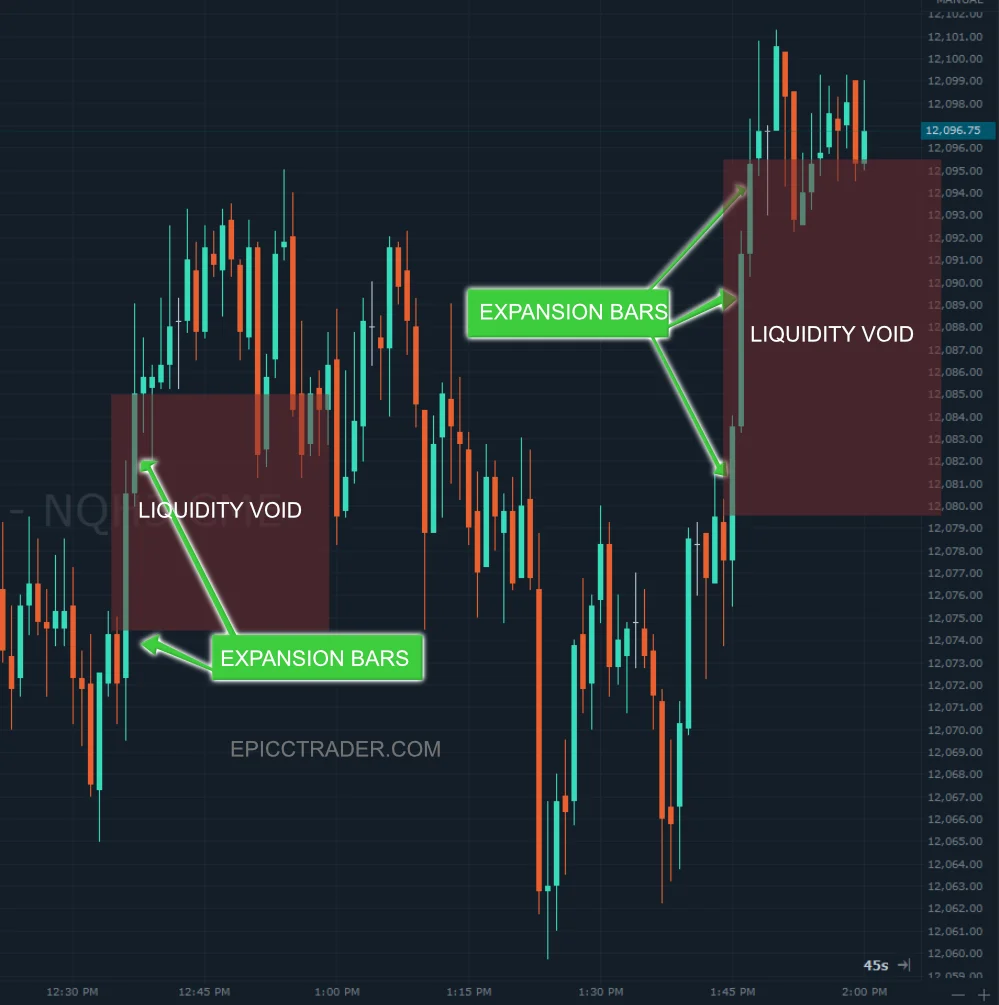
How do Liquidity Voids Form?
Liquidity voids form when price moves through a range quickly in one direction. It moves through that range or price zone without being tested or contested.
Think of it like a flash flood moving through what was a small creek. The flood waters rage through quickly, "washing out" the creek. This leaves behind a creek that is now wider, with less rock and dirt (structure) to slow the flow. Less resistance in any direction.
It will take time for normal waters (market participation) to bring back structure to that location (bids and offers). So, water (price) will move through that creek (range) more easily for some time.
When price moves quickly through a range uncontested, a few things happen:
- It clears out the order book. This creates the liquidity void, also called an order vacuum.
- Orders from participants trading in the direction opposite the move are still placing orders, at the edge of that range and into the range.
- Traders trading in the direction of the move haven't adjusted their prices, at least not yet.
- Traders trading in the direction of the move must now decide either to chase or keep their prices where they were. Institutional traders don't chase. So, new participants will have to step in to fill the vacuum, fill the liquidity void. And they'll likely be smaller participants.
- In securities regulated by Regulation NMS , the book may clear so quickly that NMS is suspended. This means that dealers can temporarily ignore the NBBO (National Best Bid/Offer), so traders placing market orders may get "bad fills". This makes these particular areas more prone to retracement.
This happens regardless of how much volume drove the move. It doesn't require high or low volume for a liquidity void to form.
How to Trade Liquidity Voids
You can trade liquidity voids in several ways. This all depends on your own trading style. But I'll cover some ways I use them. Most of these involve using liquidity voids to enhance trading setups.
1. Use Liquidity Voids to Determine Potential Targets
For a given setup, I will look for any liquidity voids in nearby ranges. When I spot a liquidity void in the path where I want price to move, I may plan my target based on that liquidity void.
I may expect price to trade at least halfway through the void, or all the way through the void. The larger the void, the more that expands my potential target.
I may use this to place multiple targets, taking partial size off at each layered target.
2. Use Liquidity Voids to Avoid Bad Entries
When I plan my entries, I look for liquidity voids and avoid placing my entries inside a void. I do this to avoid entering in an area where I can expect price to go easily past my entry.
I do this to lower my MAE (Max Adverse Excursion). This reduces potential pain, but also improves my win rate and R/R.
I would rather enter at the opposite edge of the void. For example, if getting long, I'd want to enter at the bottom of a liquidity void rather than the top or middle.
3. Use Liquidity Voids to Select Trades
Using liquidity voids to select trades helps me choose more prime setups. More A setups than B or C setups, as some may say.
Being selective is a large part of trading successfully. Choosing better setups allows for better profitability with less emotional toll.
Let's say I'm looking at two trades that are similar, both going in the same direction on the same day. But one has several liquidity voids in the path I "want" price to go, and the other doesn't have any. Which one do you think I'll prefer? Of course, the one with the liquidity voids!
This is not an exhaustive list. There are other ways to use liquidity voids. How might you use them for your setups?
Limitations of Liquidity Voids
Liquidity voids are a pattern with limitations, just like any other. They form based on real market dynamics, so they're more useful than many patterns. But you still need to know these limitations.
Naturally, a liquidity void may form more easily in areas where the order book is thin. But, and this is important:
- Don't form expectations about where a liquidity void may occur. That's not what this is about. Doing that is asking for trouble.
- Be careful about assuming the market is thin in a range just because of what is on the order book. There are plenty of tricks used to fool those who take the level II data seriously.
- Don't expect price to come back to the edge of a liquidity void just because there is one there. It may never come back to it, or it may take longer than you think.
- Price may go far away from a liquidity void before coming back to it.
- Not all liquidity voids get filled, just as not all gaps get filled.
It doesn't need to be more complicated than that. I see a lot of traders make it too complex. They factor in order flow, block orders, market profiles, and footprints. Before long, there's too much noise and too much room for second-guessing.
Fortunately for you, liquidity voids are simple and straightforward. They exist regardless of those factors. At the same time, liquidity voids are just one piece. You can choose not to use them, or to apply them to your strategy in whatever way works best for you.
Using Fair Value Gaps & Liquidity Voids Together
You can easily combine fair value gaps and liquidity voids to get more out of your trades. In the example below, assume you have some setup to get long. Let's see how using the FVG and liquidity void would help you get a favorable entry and improve your probabilities.
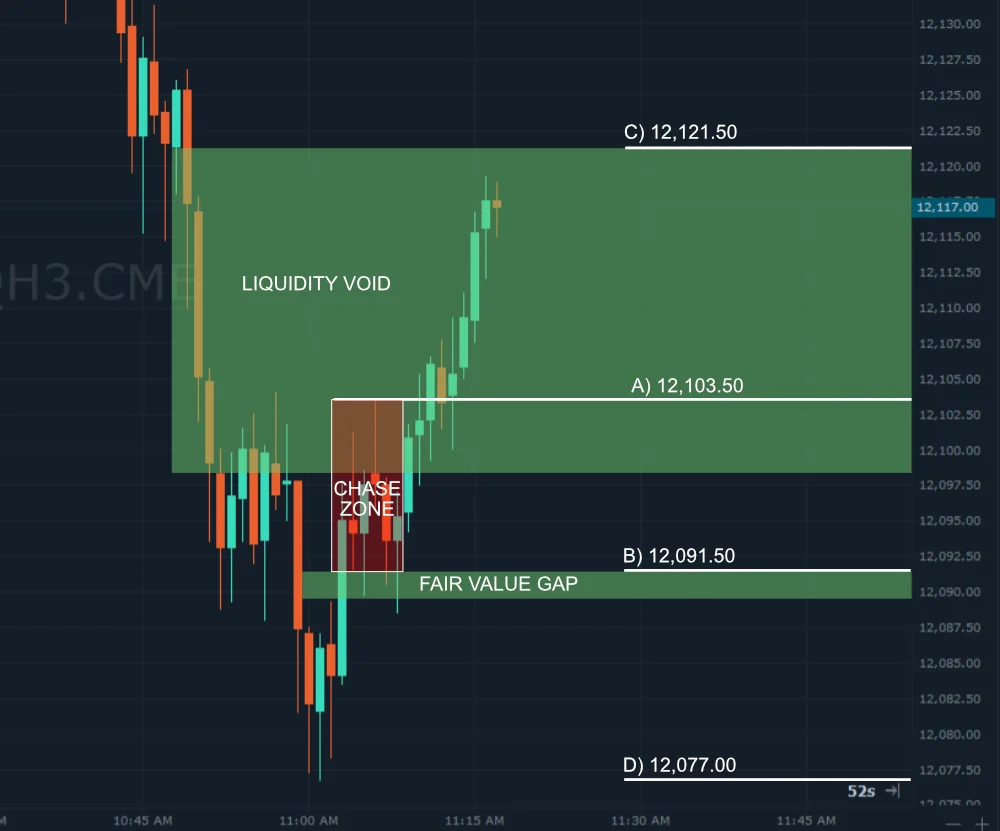
Let's assume in the example above your stop is at 12,077, and your target is 12,121.50
- You would have taken as much as 26.5 points of pain (12,103.50 to 12,077).
- Max potential profit would have been as little as 18 points.
- 13.5 of those 26.5 points could instead be part of your potential profit (12,090.50 to 12,103.5 = 13.5 pts) .
- If you made a short scalp, you got a max potential profit of 31.50 points out of it (12121.50 - 12,090 = 31.5).
- Your max pain was only 3 points.
- If price had pulled back to the local low again, MAE would have been 14.5 points (versus 26.5 for the chasers)
What Timeframe Should You Use For Liquidity Voids and Fair Value Gaps?
You can use liquidity voids over any timeframe. Liquidity voids occur across 5-second timeframes and 5-week timeframes. There difference in behavior between price vacuums over different timeframes, though.
Rules of Thumb for Liquidity Void and FVG Timeframes
- Shorter timeframes have shorter time windows for exploitation, and usually smaller ranges.
- Longer timeframes have larger time windows for exploitation, and usually larger ranges.
As with any other trade, you have to apply this concept to your strategy with R/R in mind. If you're trading a wider time range with wider ranges, you'll need to size well for the desired R/R, etc.
Constant Across Timeframes
- Just because you expect price to breeze through a liquidity void doesn't mean it will happen soon.
- Multiple liquidity voids can string together to create a bigger range. There may or may not be consolidation between each void.
- Not all liquidity voids will fill. You should track the fill frequency for liquidity voids over whichever timeframe you choose to trade .
- Only use the liquidity voids over the timeframe you're trading. In other words, don't use a liquidity void on the 4hr chart to trade a setup on the 5min chart.
Liquidity Void Variations Between Timeframes:
Very short timeframe (scalping) : Over the 1-10 second timeframe, you have one main difference. That is with how orders come back into the order vacuum.
- Market participants sending orders may not react quickly enough to change their prices.
- This means that you may have orders come into that void immediately but for a very short time.
- "slow-to-act" orders going with the direction of the move will still be at the 'beginning' prices of the move. This is because they haven't reacted yet to the change in price.
Short timeframes (day trading): Over 15-30min timeframes, liquidity voids can fill quickly or with delay. They may fill in one or two moves, or two sessions later.
- Liquidity voids may be filled fully, partially, or not at all.
- They may even fill multiple times in each direction within the same day.
- They may be partially filled and then filled fully later in the day by a secondary move.
- Or, don't forget, they may not be filled that day.
Longer timeframes (swing trading and investing) : On a daily and weekly timeframe, liquidity voids that get filled may take days or months. There may be significant price fluctuations before the void is filled.
What about volume, and order flow?
If you want to use volume and order flow in your trading, go for it. Don't abandon something where you have an established edge.
But I can remind you to verify that edge. Study your journal and the stats to see if adding those to this concept provides edge. In my experience, it does not.
A Note on Terminology
I've been trading these price-action concepts with various strategies over the last 20 years. Only recently has someone assigned them these terms and spread those terms through YouTube.
Fair Value Gaps in Forex, Stocks, Futures
Term: "Fair Value Gap" in forex belongs to a completely separate forex concept, so I'm not sure why they chose it.
Anyhow, Fair Value Gap in this article describes the price-action trading tactic, not an intrinsic value.
Liquidity Voids in Trading
Term: "Liquidity Void" also belonged to a different, broad concept in banking finance. We obviously weren't here to discuss that. We're focused on identifying and trading specific price action.
I've used "Fair Value Gap" and "Liquidity Void" because that's what newer traders are using. But, the price-action concepts precede these names by decades. They're as old as institutional trading - but very few knew about them until now.
So, I also use more basic terms like "order vacuum" and "vertical range," because that's how I've taught others.
Related Articles
Gap Fills: Statistics & How to Trade Them
Stock Gaps: Discover the 9 Main Types & How to Pounce on Them
Earnings Growth Rate: Meaning, Formula, & Importance
PEG Ratio: Calculator, Meaning, Formula & How it Can Help You
Daniel Larsen
Daniel created epicctrader.com to help new and experienced traders level up. He began trading in 2002, and has spent over a decade trading professionally, for prop firms and clients. When he's not at a computer, you can find him on the ocean, in a canyon, or in the mountains.
APEX TRADER FUNDING: 80% OFF FIRST MONTH THEN 80% LIFETIME DISCOUNT. CODE: RAGVSGRE. RESETS ARE 50% OFF WITH THIS SALE! PASS IN AS LITTLE AS 1 DAY! UPROFIT: 50% OFF ALL UPROFIT PROGRAMS & RESETS FOR LIFETIME OF SUBSCRIPTION WITH THIS LINK EARN2TRADE: 40% OFF TCP 50K EVALS THROUGH 04/30/24 11:59PM CT ! AUTOMATIC WITH THIS LINK. TOPSTEP: 70% OFF ALL EVALUATIONS - APPLIED AUTOMATICALLY WITH THIS LINK BLUSKY TRADING CO: UP TO 65% OFF ALL EVALUATIONS (EXCEPT STATIC) ! Code: 25K: APRIL25, 50K: APRIL50, 100K: APRIL100 | No Funded Setup Fee . . Ends TBD ELITE TRADER FUNDING: 0% OFF 1ST MONTH - 0% O FF LIFETIME - ALL TRADING EVALUATIONS EXCEPT FAST TRACK TAKEPROFIT TRADER: 50% OFF LIFETIME + A FREE EXTRA EVAL WHEN YOU PASS. NO FUNDED ACCOUNT SETUP FEES ! AUTOMATIC WITH THIS LINK TRADERSYNC: BLACK FRIDAY SALE IS ON - UP TO 65% OFF ANNUAL PLANS TRADESVIZ: BLACK FRIDAY - 55% OFF + FREE 1-YR SUB TO EZSTOCKSCREENER.COM ($60 VALUE) TRADINGVIEW:
Advertiser Disclosure
Most of the offers that appear on the website are from prop firms and software companies from which epicctrader.com receives compensation. This site does not include all prop firms or trading tools available. Some are excluded for good reason, some for no reason at all.
Opinions expressed here are mine alone, not those of any prop firm or software company. They have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any of those entities.
I am a trader, with many years of experience trading for prop firms. My content comes from my experiences and the experience of fellow traders. I am not a licensed financial advisor. The content on this site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.
Third party company-specific information, deals, and offers shown here may not reflect the most current updates, and you should always rely on what is on the third-party company's site. I make every effort to keep things as current as possible, but these changes don't happen instantaneously, and companies can change terms at any time day or night. I am not responsible for discrepancies, when in doubt, rely on the other company.

Home > Blog > Learn Price Action > FVG in Trading: A Complete Guide to Fair Value Gap
FVG in Trading: A Complete Guide to Fair Value Gap

FVG in trading means the fair value gap , which refers to the difference between the current value of an asset or currency and its fair value due to inefficiency or imbalance in the market.
Fair value gap is the most important term in price action trading that a trader should understand. There are many uses and benefits of fair value gaps in trading. It can also be used as a target or trade entry level.
I will explain the fair value gap in detail with a trading strategy in this article, so read the complete article.
How to identify the fair value gap?
There are two ways to identify the fair value gap in trading the financial market.
The first is by fundamental analysis, such as market inefficiencies, information asymmetry, or irrational behavior by market participants.
The second method is to determine the FVG by technical analysis, such as analyzing the candlesticks to determine the imbalance.
I will explain the second method as we focus only on price action and technical analysis.
To determine the FVG in technical analysis, follow the following criteria:
- Find a huge-size candlestick with a 70% body-to-wick ratio. You should compare the candlestick size with the last 20 to 40 candlesticks.
- Now analyze the neighboring candlesticks. Both neighboring candlesticks should not overlap the big candlestick. A minor overlap can happen on the upper and lower side of the big candlestick.
- The price area between the previous candlestick’s low and the next candlestick’s high will act as the fair value gap or FVG.
Types of fair value gaps
Based on fair value difference, the FVG is categorized into two types
- Undervalued FVG
- Overrated FVG
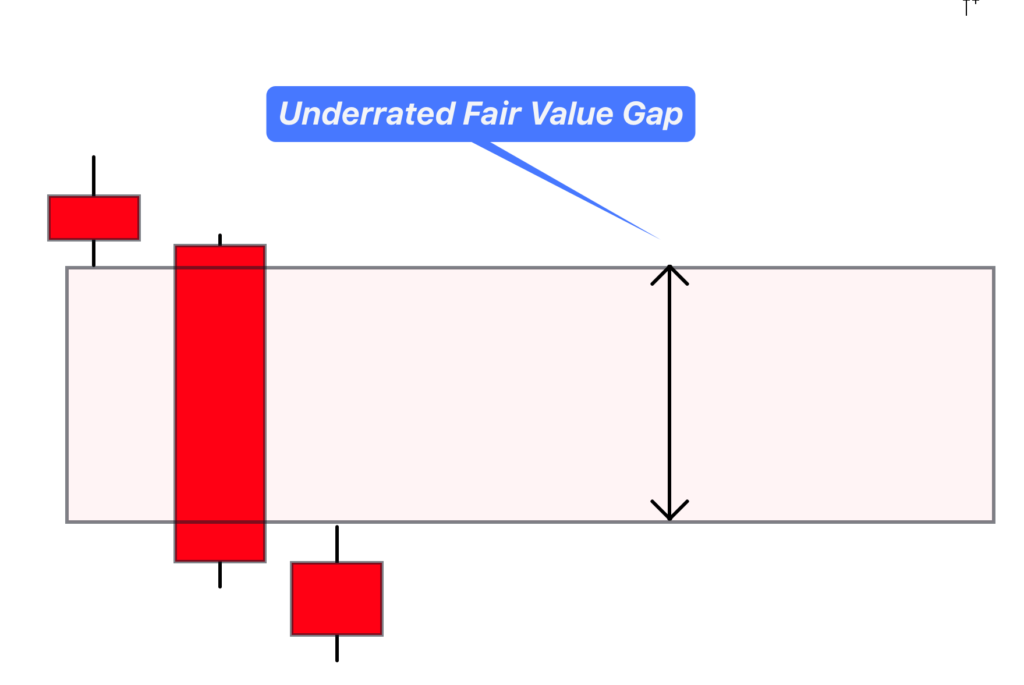
Undervalue FVG: it means that the price of a currency or financial asset is lower than its fair value. In this case, a price will increase in the future to balance this inefficiency. In technical analysis, a big bearish candlestick will show the FVG.
Overrated FVG: it means that the price of a currency or financial asset is higher than its fair value. In this case, the price will decrease to balance the inefficiency. In technical analysis, a big bullish candlestick will show the FVG.
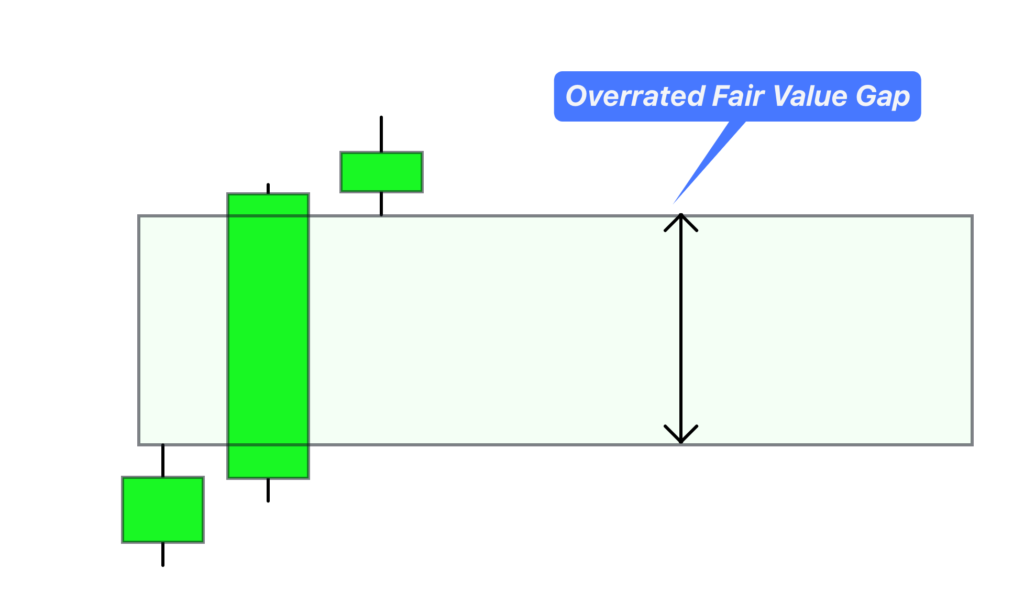
How to draw the fair value gap zone on a candlestick chart?
To draw the FVG gap on the candlestick chart, we will use neighboring candlesticks’ high and low prices.
- In the undervalued FVG, draw a rectangle using the previous candlestick’s low and the next candlestick’s high. Then extend the rectangle to the right until the price fills that zone.
- For overrated FVG, draw a rectangle using the previous candlestick’s high and the next candlestick’s low. Then extend it to the right until the price fills that zone.
Click Here Get Access to Fair Value Gap Indicator
What does the fair value gap tell traders?
The fair value gap acts as a magnet for the price. Because it is a rule of nature that everything wants to come to rest or be balanced. In the same way, the price also wants to remain in balance. So, when an imbalance is created, the price tries to balance it.
In technical analysis, the price will balance the FVG gap zone. It will remain imbalanced if the price does not overlap the FVG zone.
The trading market is purely natural and works on the laws of nature. In technical analysis, we use those laws of balance and imbalance to forecast the trading market.
In short, the FVG tells traders the possible future direction of price.
For example, if there is an undervalued FVG, we can say that price will increase to fill that FVG zone.
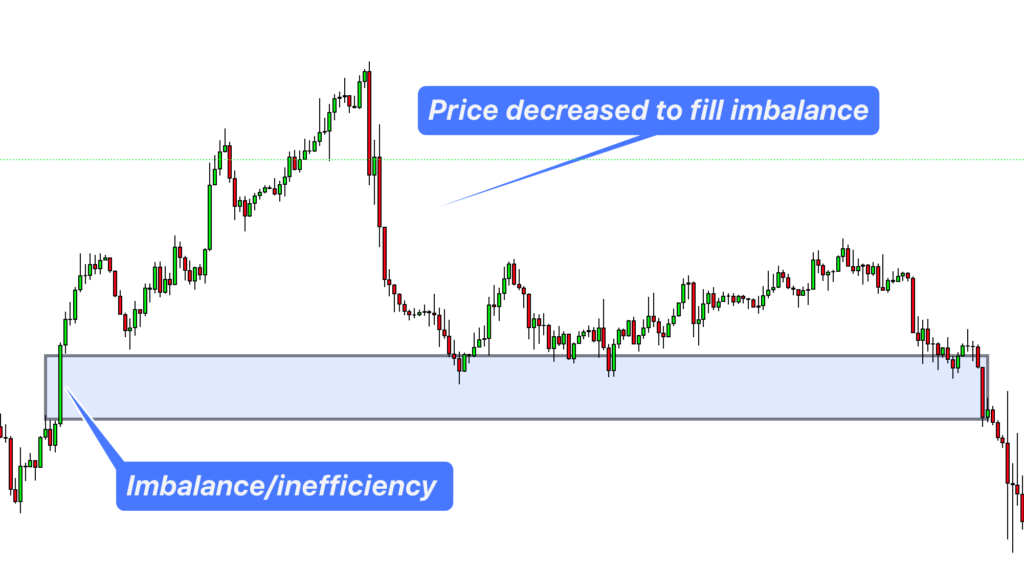
How to trade the fair value gap?
There are two ways to trade the fair value gap. One is by adding the confluence of other technical tools with the FVG, while the other uses the price bounce from the FVG zone.
I will explain both methods. However, I suggest the first method that contains the confluence of other technical tools because it is a high-probability method.
I will use this method’s supply and demand zones with the fair value gap. You can also use the order block zones instead of supply and demand . It depends on your strategy.
Here we will combine the undervalued FVG with the demand zone while the overrated FVG with the supply zone .
- Find an undervalued fair value gap on the candlestick chart that is unfilled. Then draw a rectangle on the chart to highlight it.
- Look for the demand zone on the chart. When a demand zone forms, buy from the demand zone with a stop-loss level below the zone.
- Close the trade once the price fills the FVG. Here FVG zone will act as take profit level.
Because the price must fill the imbalance zone, we know the future price direction. That’s why we used the demand zone to confirm the direction and also managed the risk with tight stop loss and high-risk reward ratio.
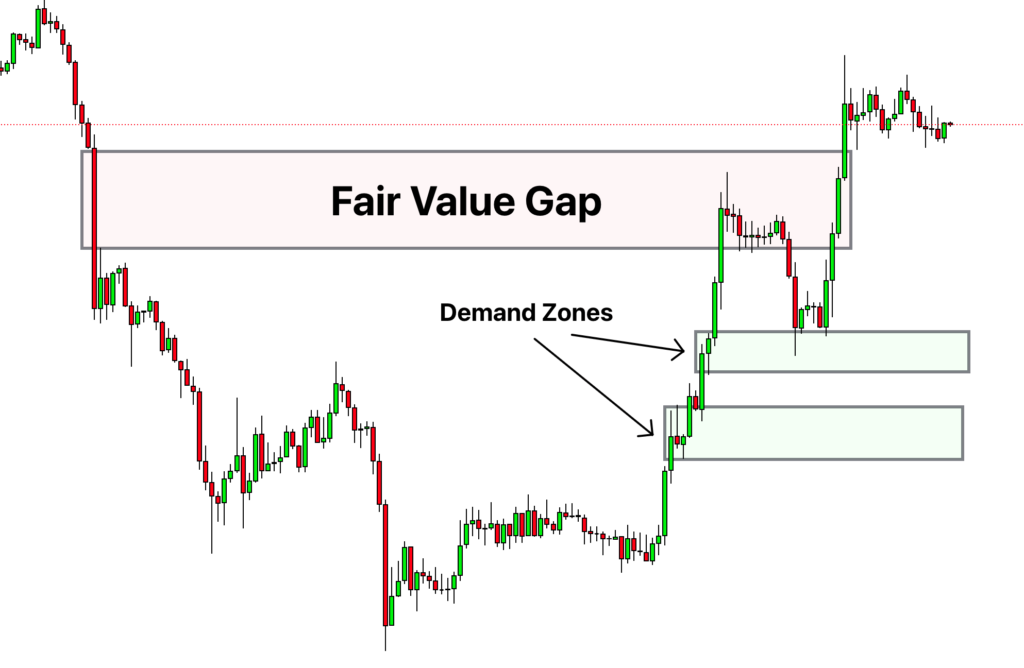
Sell signal
- Find an overrated fair value gap zone on the candlestick chart.
- Then look for a strong supply zone and sell from the supply zone keeping stop-loss above the zone.
- Close the trade once the price balances the inefficiency or fair value gap.
Most of the time, the price bounces from the FVG zone. For example, if the price is in a bullish trend and there is an overrated fair value gap. Then the price will retrace to the FVG zone, and after filling this gap, the price will bounce and will continue the bullish trend .
This method makes it hard to get exact entry and stop-loss prices. You should always add other technical tools, such as candlestick patterns. For example, when the price fills the zone, look for a bullish candlestick pattern and open a buy trade with a stop loss below the low of the candlestick pattern.
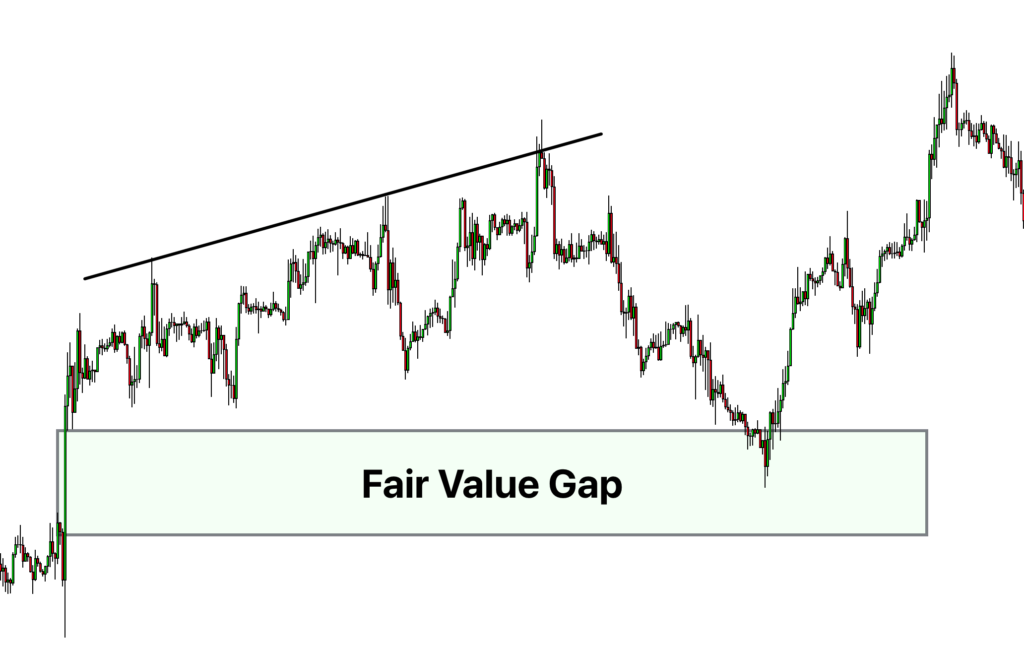
It would be best if you traded toward the trend in this method to get a higher winning ratio. For example, look for overrated FVG zones if the trend is bullish. While if the trend is bearish, then find the underrated FVG zones.
Believe me that the fair value gap is the advanced price action concept, and most technical analysis traders don’t know about this concept. it also works most of the time and can help get a high winning ratio with a high-risk-reward ratio.
I use the fair value gap and supply and demand in trading. Because these are the most advanced concept of technical analysis. I highly recommend learning the fair value gap to master the technical analysis.
How to find Order Blocks in Cryptocurrency?
March 10, 2023
A Complete Guide to Dead Cat Bounce Pattern
March 25, 2023
Do you want to get success in Trading?
Here's the roadmap:, related posts.
Open Range Breakout (ORB) Trading Strategy
Fair Value Gap Concept: A Beginner’s Guide
9 Smart Money Concepts that Every Trader Must Know
Supply and Demand Trendline Strategy
S&P 500 Trading Strategy using 5th Wave Pattern
What are Kill Zones in Forex?
Break of Structure (BOS) in Trading
6 thoughts on “FVG in Trading: A Complete Guide to Fair Value Gap”
I have been loosing for a long time and I believe FVG will help me to recover as I this is the advanced method
You switched the drawings for the undervalued and overrrated FVG
Just be aware that supply and demand zones dont work anymore, backtest it and see, institutional money will generally break through S&D zones to take out stops to fill their orders. Use FVG and watch the big money turn the tide, thats when you jump in.
I want to say thank you guys for the hard work making a lot of sense and more knowledge about the whole system and FVG and supply and demand and order block, they all works just like the way big banks Institutions uses In the financial market. I’ve learned a lot and put a lot of efforts to learn on my own with this training material and it makes a lot of sense to me because it help to make strong trading decision In this business. I really love learning to become a better trader.
thank you guys again
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

What Is A Fair Value Gap? ( FVG )
Harnessing FVGs for Price Action Trading:
The most simple trading strategy.

Trading Abbreviations
What are Trading Indicators?

What is market cap?

- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy


FVG Sessions [LuxAlgo]
In true TradingView spirit, the author of this script has published it open-source, so traders can understand and verify it. Cheers to the author! You may use it for free, but reuse of this code in a publication is governed by House Rules . You can favorite it to use it on a chart.
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The FVG level of trading refers to the point in the market where a Fair Value Gap (FVG) occurs. FVGs are discrepancies between the actual price of a financial asset and its perceived fair value, often caused by market inefficiencies. Identifying the FVG level involves recognizing these gaps on price charts, which traders can use to make ...
A bullish Fair Value Gap (FVG) forms when the market undergoes a dramatic shift from bearish to bullish, often with aggressive movements. This aggressive move breaks through previous key levels (lower highs) established during the bearish phase. Without a change in market structure, the formation of a fair value gap is less reliable and not use ...
A fair value gap (FVG) is a concept used primarily by price action traders to identify market inefficiencies or imbalances. These imbalances occur when buying and selling forces are not equal, leading to significant and rapid price movements. The fair value gap is visualized on a price chart as a gap formed within a three-candle sequence.
Trading with fair value gaps follows three key steps: 1. Identify the FVG Pattern. The first step is visually identifying the characteristic FVG pattern on the chart of your chosen market and timeframe. You'll want to see a long bullish or bearish candle (Candle 1), followed by an even larger continuation candle (Candle 2), completed by a ...
In this article, we will use the term Fair Value Gap (also referred to as FVG). Fair Value Gap indicates a market situation where the supply of buyers is significantly higher or lower than the demand of sellers. This can cause the price of an instrument to move quickly towards higher supply or lower demand.
GC Daily Chart 4.11 to 7.4.23. Chart illustrates the FVG, retest, and profit target using the measured move method. Using FVGs as support or resistance: FVGs can also be used as support or resistance levels. For example, if a market gaps up and then retraces back to the gap level, this level can often act as support in the future.
Key Takeaways. Fair Value Gaps are market inefficiencies or imbalances that traders can identify on price charts, often appearing as a triple-candle pattern. FVG trading involves a step-by-step strategy, from identification and observation to entry and risk management. Traders can benefit from FVG trading's profit potential, reduced risk, and ...
IOFED comes into play when price fills less than 50% of a Fair Value Gap (FVG). It's like finding a specific key that unlocks the potential for profitable trades in the market. This is in contrast to consequent encroachment, where price fills exactly 50% of the FVG. Step 2: Real-Life Chart Insights. Take a look at the chart example provided.
A Glimpse into FVG Trading Pattern. The Fair Value Gap (FVG) trading pattern is a sophisticated methodology that revolves around the concept of assessing an asset's market price in comparison to its intrinsic value. Essentially, it pinpoints the divergence between what an asset is currently valued at in the market and its true worth.
The Fair Value Gap, or FVG, is a widely utilized tool among price action traders to detect market inefficiencies or imbalances. Sometimes you will even see them labeled as inefficiencies by other traders. These imbalances arise when buying or selling pressure is significant, resulting in a large upward or downward move, leaving behind an ...
The Fair Value Gap, or FVG, is a term you'll often hear in trading, and it's actually pretty straightforward. In simple terms, FVG is all about identifying a gap or a difference in the value of an asset - like a stock or a currency - on a trading chart. To understand FVG, we first need to grasp what 'fair value' means in trading.
By waiting for the price to reach the FVG area of interest and entering a trade, they position themselves for further trend continuation. A tangible example is observed in the Solana chart during its significant run in January 2023, where a FVG served as a key level of interest for entry into a long trade. Tools for Identifying FVGs:
An FVG on a chart identifies an area where the fair price of an asset has recently changed. This change implies that when the price returns to where the FVG had just formed, it will either rise if it is a bullish FVG or fall if it is a bearish FVG. This concept is similar to that of supply and demand zones or support and resistance lines ...
Step 4: Find a Fair Value Gap. This next step is crucial. After price has made two lower lows, we will look for our short trade entry. We do this by finding a bearish fair value gap on the chart where price will likely return. Make sure to enable your fair value gap tool on the indicator so you can easily spot them.
For example, if a fair value gap is created in a move to the upside, traders would wait for the price to be pulled down toward the fair value gap and enter a long position with the goal of profiting from a continued move to the upside once the imbalance is cleared out.. Conversely, if a fair value gap is created in a move to the downside, traders would wait for the price to revert up toward ...
The Fair Value Gap Strategy (FVG) is a trading approach that relies on price action analysis and involves identifying market inefficiencies or imbalances. The strategy offers a variety of customizable settings to match your preferences and includes an entry and exit strategy to guide you through trades. The script operates in the following manner: It begins by searching for fair-value-gaps and ...
Had you waited and entered in the FVG: 13.5 of those 26.5 points could instead be part of your potential profit (12,090.50 to 12,103.5 = 13.5 pts). If you made a short scalp, you got a max potential profit of 31.50 points out of it (12121.50 - 12,090 = 31.5). From the worst (highest) entry price in the FVG: Your max pain was only 3 points.
FVG in trading means the fair value gap, which refers to the difference between the current value of an asset or currency and its fair value due to inefficiency or imbalance in the market.. Fair value gap is the most important term in price action trading that a trader should understand. There are many uses and benefits of fair value gaps in trading. It can also be used as a target or trade ...
On the left side of the chart, a FVG materialized, and the price consolidated over several days before revisiting the FVG. Savvy traders might have recognized this FVG as a pivotal level, strategically using it as an entry point for a long trade on SOL, riding the momentum for further trend continuation.
Fair value gaps (FVG) highlight imbalances areas between market participants and have become popular amongst technical analysts. The following script aims to display fair value gaps alongside the percentage of filled gaps and the average duration (in bars) before gaps are filled. Users can be alerted when an FVG is filled using the alerts built into this script.
The FVG Sessions indicator highlights the first fair value gap of the trading session as well as the session range. Detected fair value gaps extend to the end of the trading session. Alerts are included on the formation of a session fair value gap, price being within a session fair value gap, mitigations, and price crossing session fair value gaps average. 🔶 USAGE https://www.tradingview ...
359 views, 21 likes, 5 loves, 4 comments, 0 shares, Facebook Watch Videos from FVG Beach Club ASD: Fvg Beach Club - Ipplis FINALE Entry Level L3 AIBVC-ASI Tour
FVG MTB TOUR. 602 likes · 1 talking about this. Il circuito ufficiale granfondo/marathon MTB FCI del Friuli Venezia Giulia!
Your privacy. This website uses cookies to enhance and personalize your experience. For more information about our collection and use of your information, including our use of cookies, please check out our privacy policy.